Effects of Vitamin D on the Renin–Angiotensin System and Acute Childhood Pneumonia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Role of Vitamin D in the Skeletal and Immune Systems
3. Acute Childhood Pneumonia
3.1. Pathology
3.2. Antibiotics
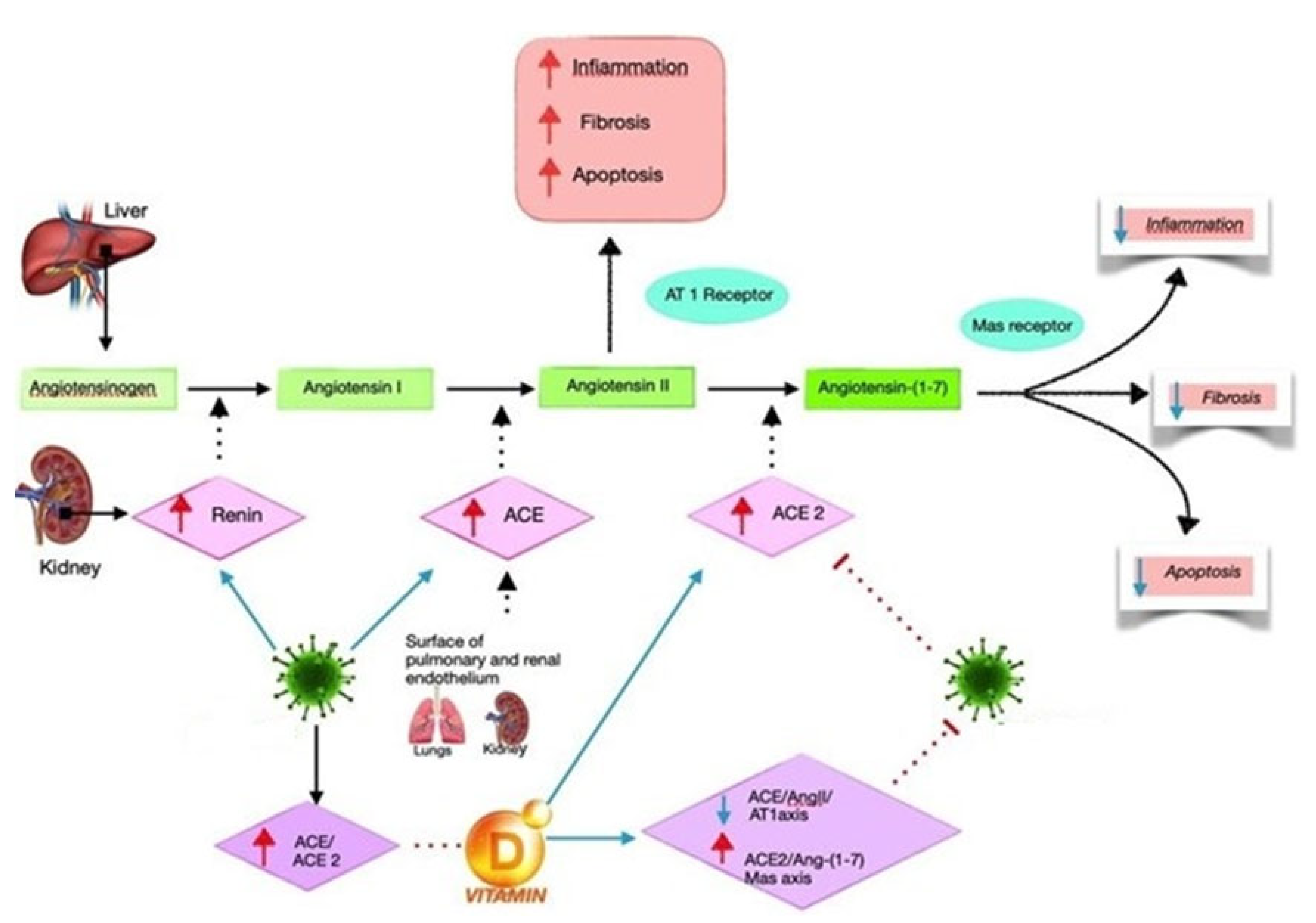
4. Renin–Angiotensin System and Infectious Disease
5. Vitamin D and RAS
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, P.H.; Turner, A.G.; Morris, H.A. Vitamin D actions to regulate calcium and skeletal homeostasis. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posa, F.; Di Benedetto, A.; Cavalcanti-Adam, E.; Colaianni, G.; Porro, C.; Trotta, T.; Brunetti, G.; Muzio, L.L.; Grano, M.; Mori, G. Vitamin D Promotes MSC Osteogenic Differentiation Stimulating Cell Adhesion and αVβ3 Expression. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 6958713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikle, D.D. Vitamin D and the skin: Physiology and pathophysiology. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2011, 13, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Atkins, G.J.; Anderson, P.H.; Findlay, D.M.; Welldon, K.J.; Vincent, C.; Zannettino, A.C.; O’Loughlin, P.D.; Morris, H.A. Metabolism of vitamin D3 in human osteoblasts: Evidence for autocrine and paracrine activities of 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Bone 2007, 40, 1517–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posa, F.; Di Benedetto, A.; Colaianni, G.; Cavalcanti-Adam, E.A.; Brunetti, G.; Porro, C.; Trotta, T.; Grano, M.; Mori, G. Vitamin D Effects on Osteoblastic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Dental Tissues. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 9150819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballini, A.; Gnoni, A.; De Vito, D.; Di Palma, G.; Cantore, S.; Isacco, C.G.; Saini, R.; Santacroce, L.; Topi, S.; Scarano, A.; et al. Effect of probiotics on the occurrence of nutrition absorption capacities in healthy children: A randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled pilot study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 8645–8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzolla, A.P.; Di Cosola, M.; Ballini, A.; Santacroce, L.; Lovero, R.; Testa, N.F.; Lacarbonara, V.; De Franco, A.; Troiano, G.; Cantore, S.; et al. The Association between Nutritional Alterations and Oral Lesions in a Pediatric Population: An Epidemiological Study. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 9992451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signorini, L.; Ballini, A.; Arrigoni, R.; De Leonardis, F.; Saini, R.; Cantore, S.; De Vito, D.; Coscia, M.F.; Dipalma, G.; Santacroce, L.; et al. Evaluation of a Nutraceutical Product with Probiotics, Vitamin D, Plus Banaba Leaf Extracts (Lagerstroemia speciosa) in Glycemic Control. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord.-Drug Targets 2021, 21, 1356–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieben, L.; Masuyama, R.; Torrekens, S.; van Looveren, R.; Schrooten, J.; Baatsen, P.; Lafage-Proust, M.H.; Dresselaers, T.; Feng, J.Q.; Bonewald, L.F.; et al. Normocalcemia is maintained in mice under conditions of calcium malabsorption by vitamin D-induced inhibition of bone mineralization. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 122, 1803–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzanelli, M.G.; Distratis, P.; Lazzaro, R.; Cefalo, A.; Catucci, O.; Aityan, S.K.; Dipalma, G.; Vimercati, L.; Inchingolo, A.D.; Maggiore, M.E.; et al. The Vitamin D, IL-6 and the eGFR Markers a Possible Way to Elucidate the Lung–Heart–Kidney Cross-Talk in COVID-19 Disease: A Foregone Conclusion. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeke, F.; Takiishi, T.; Korf, H.; Gysemans, C.; Mathieu, C. Vitamin D: Modulator of the immune system. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2010, 10, 482–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S. Oral paricalcitol for the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism in chronic kidney disease. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2006, 2, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- WHO. Revised WHO Classification and Treatment of Pneumonia in Children at Health Facilities: Evidence Summaries; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tazinya, A.A.; Halle-Ekane, G.E.; Mbuagbaw, L.T.; Abanda, M.; Atashili, J.; Obama, M.T. Risk factors for acute respiratory infections in children under five years attending the Bamenda Regional Hospital in Cameroon. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rudan, I.; Boschi-Pinto, C.; Biloglav, Z.; Mulholland, K.; Campbell, H. Epidemiology and etiology of childhood pneumonia. Bull. World Health Organ. 2008, 86, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- le Roux, D.M.; Zar, H.J. Community-acquired pneumonia in children—A changing spectrum of disease. Pediatr. Radiol. 2017, 47, 1392–1398, Erratum in Pediatr Radiol. 2017, 47, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rashmi, R.D.; Meenu, S.; Sushree, S.N. Vitamin D as an adjunct to antibiotics for the treatment of acute childhood pneumonia. In The Cochrane Collaboration; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Anthony, J.; Scott, G.; Wonodi, C.; Jennifer, C.; the Pneumonia Methods Working Groupa. The Definition of Pneumonia, the Assessment of Severity, and Clinical Standardization in the Pneumonia Etiology Research for Child Health Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, S109–S116. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, A.K.C.; Wong, A.H.C.; Hon, K.L. Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Children. Recent Pat. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Discov. 2018, 12, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, H.; Moore, D.; Andronikou, S.; Argent, A.C.; Avenant, T.; Cohen, C.; Green, R.J.; Itzikowitz, G.; Jeena, P.; Masekela, R.; et al. Diagnosis and management of community-acquired pneumonia in children: South African Thoracic Society guidelines. Afr. J. Thorac. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 26, 98–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassi, Z.S.; Padhani, Z.A.; Das, J.K.; Salam, R.A.; Bhutta, Z.A. Antibiotic therapy versus no antibiotic therapy for children aged 2 to 59 months with WHO-defined non-severe pneumonia and wheeze (Review). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 2021, CD009576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Reyes, M.X.; Rugeles, C.G. Oral antibiotics versus parenteral antibiotics for severe pneumonia in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 2006, CD004979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.S.; Byington, C.L.; Shah, S.S.; Alverson, B.; Carter, E.R.; Harrison, C.; Kaplan, S.L.; Mace, S.E.; McCracken, G.H., Jr.; Moore, M.R.; et al. The management of community-acquired pneumonia in infants and children older than 3 months of age: Clinical practice guidelines by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barson, W. Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Children: Inpatient Treatment; Post, T.W., Ed.; UpToDate: Waltham, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Boccellino, M.; Di Domenico, M.; Donniacuo, M.; Bitti, G.; Gritti, G.; Ambrosio, P.; Quagliuolo, L.; Rinaldi, B. AT1-receptor blockade: Protective effects of irbesartan in cardiomyocytes under hypoxic stress. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vitiello, A.; Ferrara, F. Correlation between renin-angiotensin system and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 infection: What do we know? Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 883, 173373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitiello, A.; Ferrara, F. Therapeutic Strategies for SARS-CoV-2 acting on ACE-2. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 156, 105579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitiello, A.; Pelliccia, C.; Ferrara, F. Drugs acting on the renin–angiotensin system and SARS-CoV-2. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, F.; Vitiello, A. Scientific Hypothesis for Treatment of COVID-19′s Lung Lesions by Adjusting ACE/ACE2 Imbalance. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2021, 21, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavishi, C.; Maddox, T.M.; Messerli, F.H. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Infection and Renin Angiotensin System Blockers. JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Recinos, A.; LeJeune, W.S.; Sun, H.; Lee, C.Y.; Tieu, B.C.; Lu, M.; Hou, T.; Boldogh, I.; Tilton, R.G.; Brasier, A.R. Angiotensin II induces IL-6 expression and the Jak-STAT3 pathway in aortic adventitia of LDL receptor-deficient mice. Atherosclerosis 2007, 194, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dellino, M.; Cascardi, E.; Vinciguerra, M.; Lamanna, B.; Malvasi, A.; Scacco, S.; Acquaviva, S.; Pinto, V.; Di Vagno, G.; Cormio, G.; et al. Nutrition as Personalized Medicine against SARS-CoV-2 Infections: Clinical and Oncological Options with a Specific Female Groups Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellino, M.; Lamanna, B.; Vinciguerra, M.; Tafuri, S.; Stefanizzi, P.; Malvasi, A.; Di Vagno, G.; Cormio, G.; Loizzi, V.; Cazzato, G. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines and Adverse Effects in Gynecology and Obstetrics: The First Italian Retrospective Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzato, G.; Cascardi, E.; Colagrande, A.; Foti, C.; Stellacci, A.; Marrone, M.; Ingravallo, G.; Arezzo, F.; Loizzi, V.; Solimando, A.G.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 and Skin: New Insights and Perspectives. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamma, R.; Rutigliano, M.; Lucarelli, G.; Annese, T.; Ruggieri, S.; Cascardi, E.; Napoli, A.; Battaglia, M.; Ribatti, D. Microvascular density, macrophages, and mast cells in human clear cell renal carcinoma with and without bevacizumab treatment. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 355.e311–355.e319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verginelli, F.; Pisacane, A.; Gambardella, G.; D’Ambrosio, A.; Candiello, E.; Ferrio, M.; Panero, M.; Casorzo, L.; Benvenuti, S.; Cascardi, E.; et al. Cancer of unknown primary stem-like cells model multi-organ metastasis and unveil liability to MEK inhibition. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamma, R.; Annese, T.; Ruggieri, S.; Brunetti, O.; Longo, V.; Cascardi, E.; Mastropasqua, M.G.; Maiorano, E.; Silvestris, N.; Ribatti, D. Inflammatory cells infiltrate and angiogenesis in locally advanced and metastatic cholangiocarcinoma. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 49, e13087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitiello, A.; Ferrara, F. Pharmacological agents modifying the renin angiotensin and natriuretic peptide systems in COVID-19 patients. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2021, 133, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, E.D.; Hawkins, R.G.; Watanabe, M. Interaction of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D and Plasma Renin Activity in High Renin Essential Hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 1990, 3, 903–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resnick, L.M.; Müller, F.B.; Laragh, J.H. Calcium-regulating hormones in essential hypertension: Relation to plasma renin activity and sodium metabolism. Ann. Intern. Med. 1986, 105, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaschitz, A.; Pilz, S.; Ritz, E.; Grammer, T.; Drechsler, C.; Boehm, B.O.; März, W. Independent association between 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D, 25-hydroxyvitamin D and the renin–angiotensin system: The Ludwigshafen Risk and Cardiovascular Health (LURIC) study. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, J.P.; Williams, J.; Fisher, N.D. Plasma 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Regulation of the Renin-Angiotensin System in Humans. Hypertension 2010, 55, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, C.W.; Oh, Y.S.; Shin, Y.S.; Kim, C.-M.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, E.J.; Chang, Y.S.; Bang, B.K. Intravenous calcitriol regresses myocardial hypertrophy in hemodialysis patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1999, 33, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Kong, J.; Wei, M.; Chen, Z.-F.; Liu, S.Q.; Cao, L.-P. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 is a negative endocrine regulator of the renin-angiotensin system. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, T.; Yao, L.; Xing, Y.; Zhao, X.; Fu, J.; Xue, X. Chronic vitamin D deficiency induces lung fibrosis through activation of the renin-angiotensin system. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, W.; Pan, W.; Kong, J.; Zheng, W.; Szeto, F.L.; Wong, K.E.; Cohen, R.; Klopot, A.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.C. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Suppresses Renin Gene Transcription by Blocking the Activity of the Cyclic AMP Response Element in the Renin Gene Promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 29821–29830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H. Vitamin D alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulation of the renin-angiotensin system. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 7432–7438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z. Effect of Vitamin D on ACE2 and Vitamin D Receptor Expression in Ratswith LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury. Chin. J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 12, 1284–1289. [Google Scholar]
- Cepeda, S.J.; Zenteno, A.D.; Fuentes, S.C.; Bustos, B.R. Vitamina D y enfermedades respiratorias pediátricas [Vitamin D and pediatrics respiratory diseases]. Rev. Chil. Pediatr. 2019, 90, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zovi, A.; Ferrara, F.; Pasquinucci, R.; Nava, L.; Vitiello, A.; Arrigoni, R.; Ballini, A.; Cantore, S.; Palmirotta, R.; Di Domenico, M.; et al. Effects of Vitamin D on the Renin–Angiotensin System and Acute Childhood Pneumonia. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111545
Zovi A, Ferrara F, Pasquinucci R, Nava L, Vitiello A, Arrigoni R, Ballini A, Cantore S, Palmirotta R, Di Domenico M, et al. Effects of Vitamin D on the Renin–Angiotensin System and Acute Childhood Pneumonia. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(11):1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111545
Chicago/Turabian StyleZovi, Andrea, Francesco Ferrara, Roberta Pasquinucci, Livia Nava, Antonio Vitiello, Roberto Arrigoni, Andrea Ballini, Stefania Cantore, Raffele Palmirotta, Marina Di Domenico, and et al. 2022. "Effects of Vitamin D on the Renin–Angiotensin System and Acute Childhood Pneumonia" Antibiotics 11, no. 11: 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111545
APA StyleZovi, A., Ferrara, F., Pasquinucci, R., Nava, L., Vitiello, A., Arrigoni, R., Ballini, A., Cantore, S., Palmirotta, R., Di Domenico, M., Santacroce, L., & Boccellino, M. (2022). Effects of Vitamin D on the Renin–Angiotensin System and Acute Childhood Pneumonia. Antibiotics, 11(11), 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111545










