Gentamicin–Ascorbic Acid Encapsulated in Chitosan Nanoparticles Improved In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity and Minimized Cytotoxicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Loading Capacity and Encapsulation Efficiency
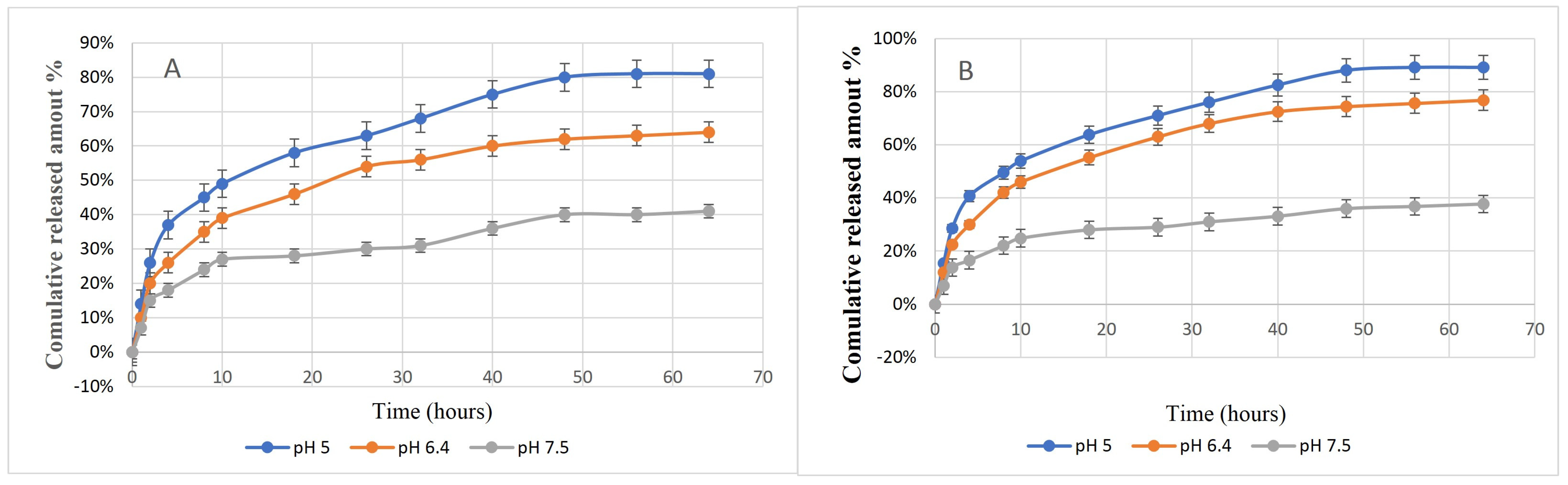
2.2. In Vitro Release Study
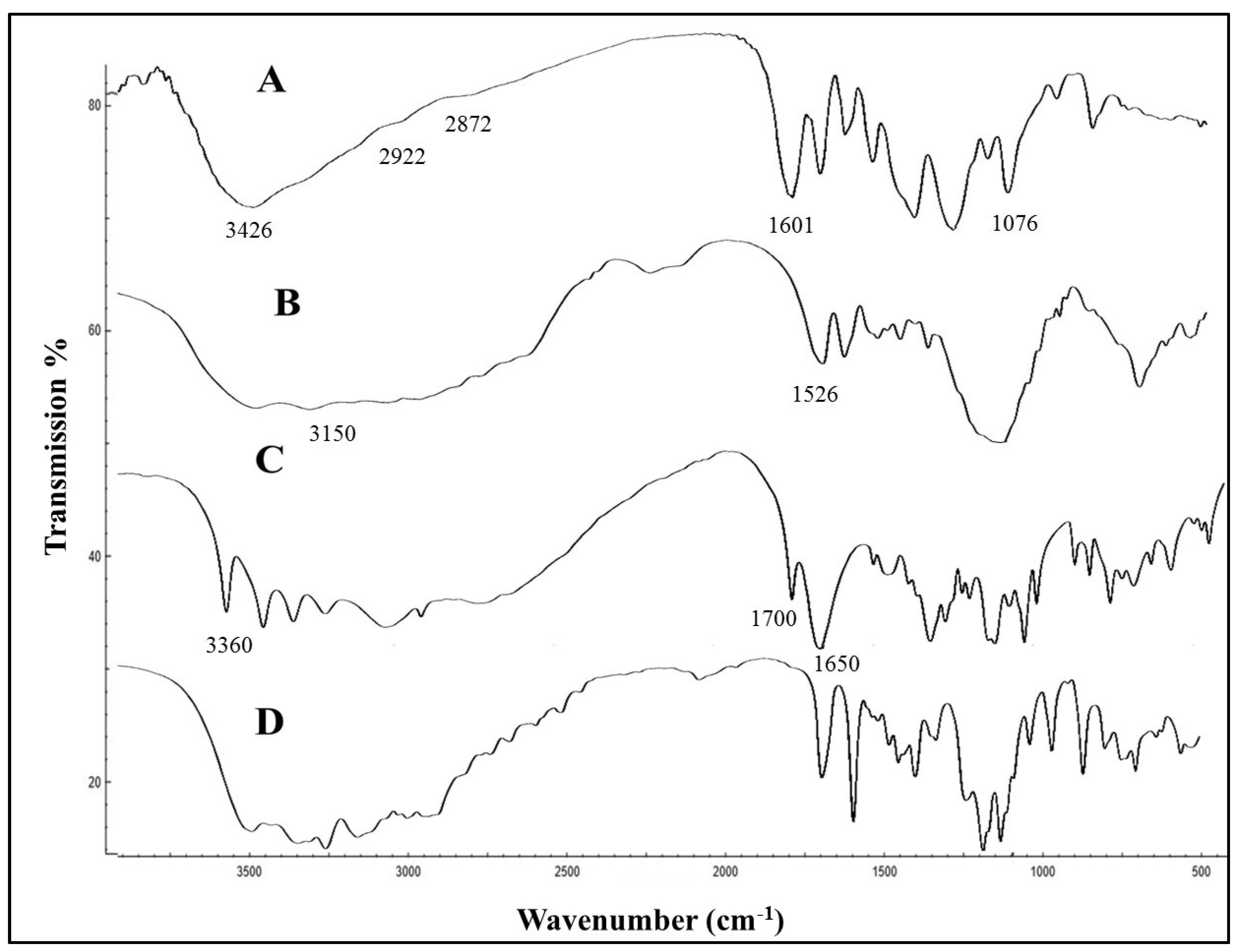
2.3. Characterization of GM–AA–CSNPs
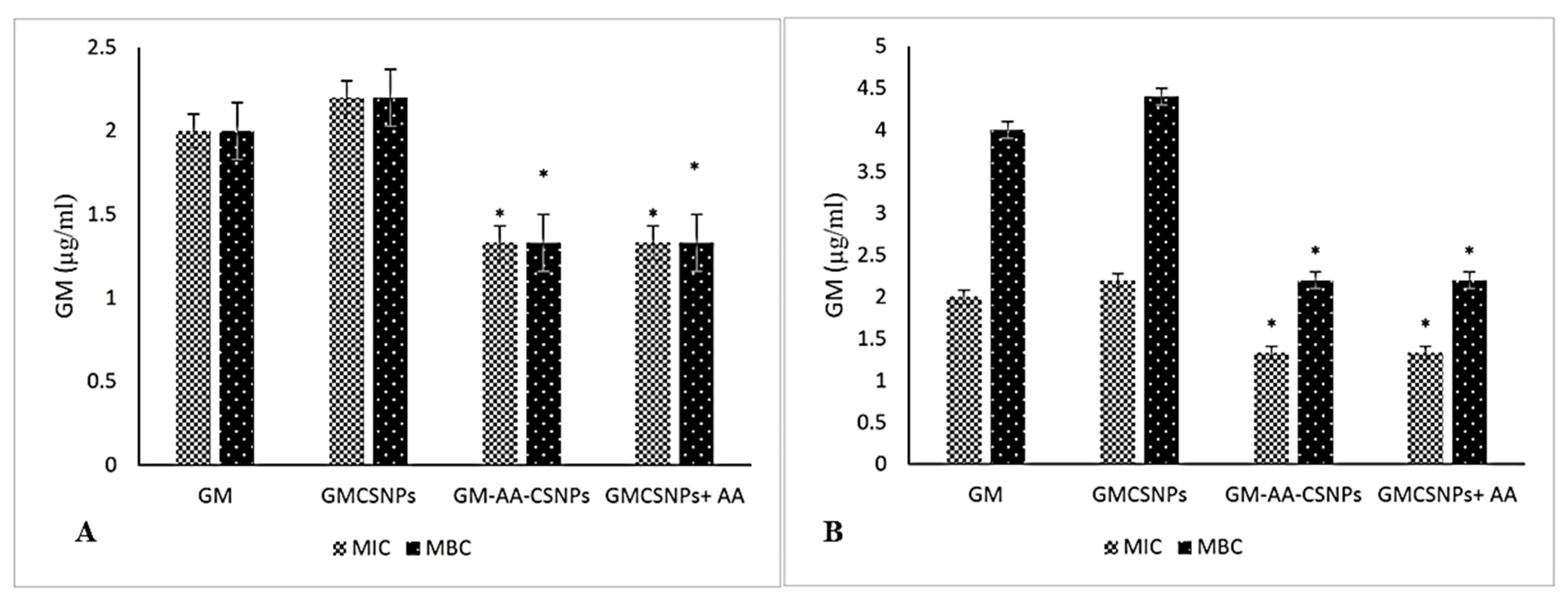
2.4. Antimicrobial Activity of Free and Loaded Gentamicin
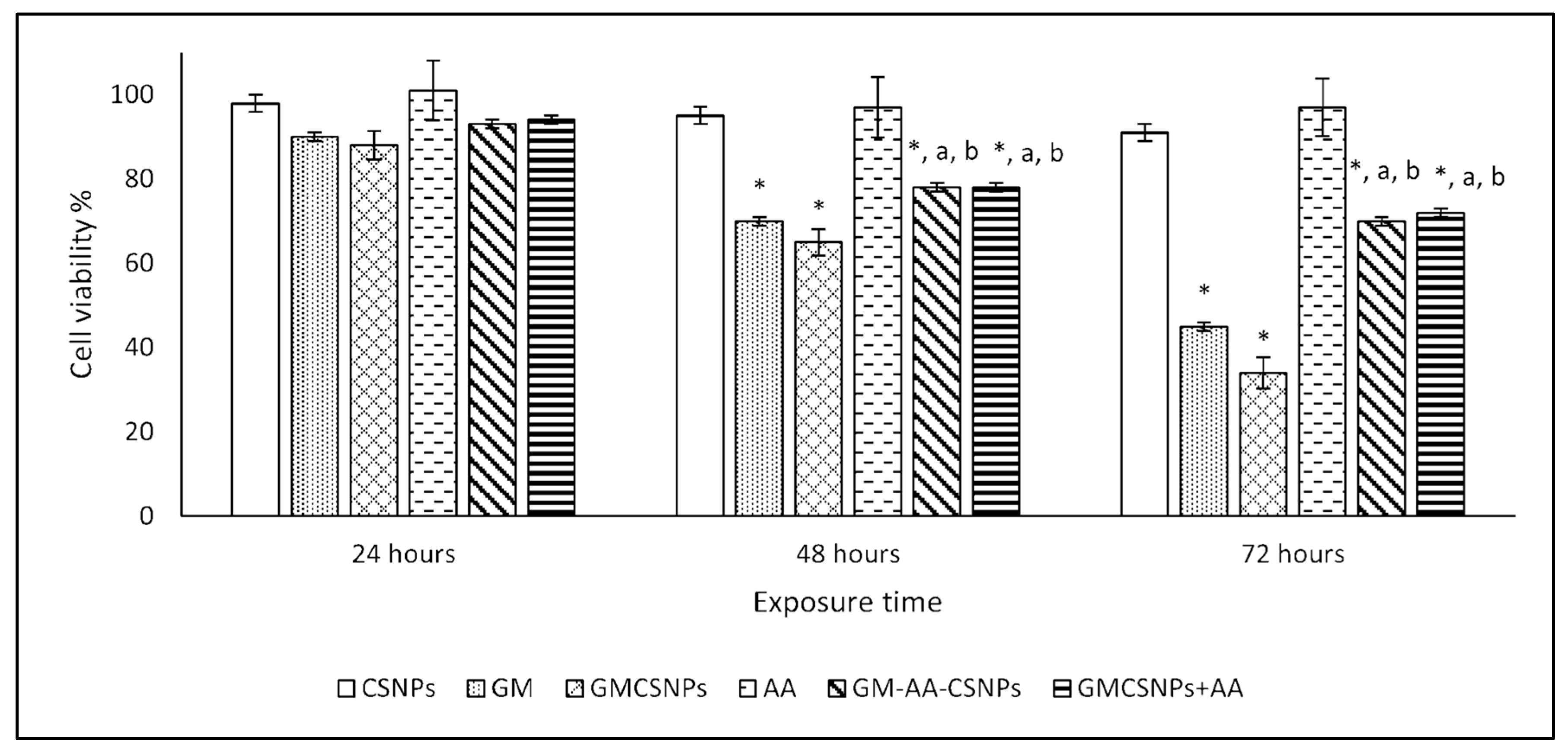
2.5. Cytotoxicity Assay
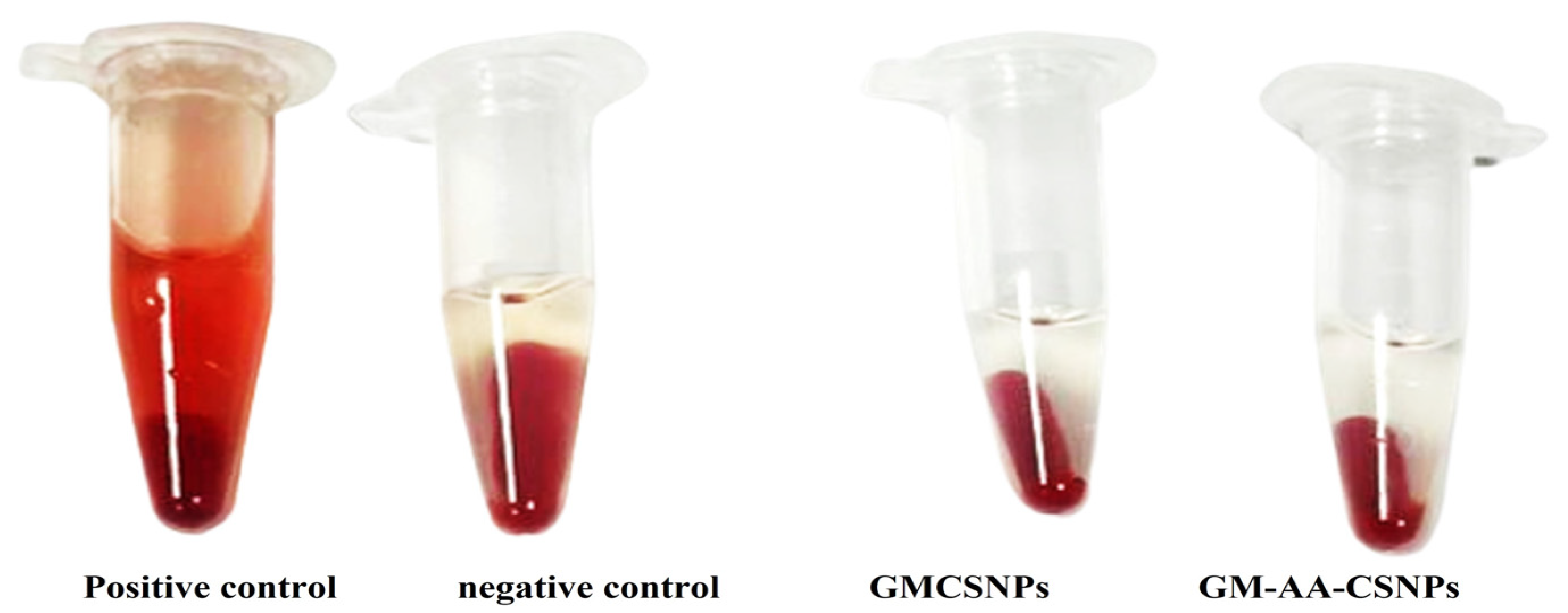
2.6. Hemolysis Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Chitosan-Loaded Gentamicin and Ascorbic Acid
4.2. Encapsulation Efficiency and Loading Capacity
4.3. In Vitro Release Studies
4.4. Characterization of GM–AA–CSNPs
4.5. Antibacterial Activity Test
4.6. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration and Minimum Bactericidal Concentration
4.7. Cytotoxicity
4.8. Biocompatibility Assay of GM–AA–CSNPs
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, N.; Joshi, A.; Toor, A.P.; Verma, G. Chapter 27—Drug Delivery: Advancements and Challenges. In Nanostructures for Drug Delivery; Andronescu, E., Grumezescu, A.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 865–886. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Gao, W.; Hu, H.; Zhou, S. Why 90% of clinical drug development fails and how to improve it? Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 3049–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, S.; Panghal, A.; Flora, S.J.S. Nanotechnology: A Promising Approach for Delivery of Neuroprotective Drugs. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khella, K.F.; El Maksoud, A.I.A.; Hassan, A.; Abdel-Ghany, S.E.; Elsanhoty, R.M.; Aladhadh, M.A.; Abdel-Hakeem, M.A. Carnosic Acid Encapsulated in Albumin Nanoparticles Induces Apoptosis in Breast and Colorectal Cancer Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabit, H.; Abdel-Hakeem, M.; Shoala, T.; Abdel-Ghany, S.; Abdel-Latif, M.M.; Almulhim, J.; Mansy, M. Nanocarriers: A Reliable Tool for the Delivery of Anticancer Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Li, C.; Ouyang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Zhong, Q.; Li, P.; Li, S.; Yang, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhao, Q. Synthesis of gentamicin-grafted-chitosan with improved solubility and antibacterial activity. React. Funct. Polym. 2019, 137, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.J.; Abdelghany, S.M.; Quinn, D.J.; Ingram, R.J.; Gilmore, B.F.; Donnelly, R.F.; Taggart, C.C. Gentamicin-loaded nanoparticles show improved antimicrobial effects towards Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 4053–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambial, S.; Dwivedi, S.; Shukla, K.K.; John, P.J.; Sharma, P. Vitamin C in Disease Prevention and Cure: An Overview. Indian, J. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 28, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.A.; Nascimento, M.A.; Bozzo, T.A.; Cintra, A.; da Silva, S.M.; Dalboni, M.A.; Mouro, M.G.; Higa, E.M. Ascorbic acid reduces gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats through the control of reactive oxygen species. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posadowska, U.; Brzychczy-Włoch, M.; Pamuła, E. Gentamicin loaded PLGA nanoparticles as local drug delivery system for the osteomyelitis treatment. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2015, 17, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Reynolds, M.; Li, Y.V. Synthesis and characterizations of gentamicin-loaded poly-lactic-co-glycolic (PLGA) nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2021, 23, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Chen, S.; Li, D.; Rao, W.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Guan, X.; Chen, Z. The Synergistic Antibacterial Mechanism of Gentamicin-Loaded CaCO3 Nanoparticles. Front. Chem. 2018, 5, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorati, R.; DeTrizio, A.; Spalla, M.; Migliavacca, R.; Pagani, L.; Pisani, S.; Chiesa, E.; Conti, B.; Modena, T.; Genta, I. Gentamicin Sulfate PEG-PLGA/PLGA-H Nanoparticles: Screening Design and Antimicrobial Effect Evaluation toward Clinic Bacterial Isolates. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razei, A.; Cheraghali, A.M.; Saadati, M.; Ramandi, M.F.; Panahi, Y.; Hajizadeh, A.; Siadat, S.D.; Behrouzi, A. Gentamicin-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles Improve Its Therapeutic Effects on Brucella-Infected J774A.1 Murine Cells. Galen Med. J. 2019, 8, e1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.-C.; Huang, T.-H.; Yang, S.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; Fang, J.-Y. Nano-Based Drug Delivery or Targeting to Eradicate Bacteria for Infection Mitigation: A Review of Recent Advances. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Joo, J.; Kang, J.; Kim, B.; Braun, G.B.; She, Z.-G.; Kim, D.; Mann, A.P.; Mölder, T.; Teesalu, T.; et al. Antibiotic-loaded nanoparticles targeted to the site of infection enhance antibacterial efficacy. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gemeinder, J.L.P.; de Barros, N.R.; Pegorin, G.S.; Singulani, J.D.L.; Borges, F.A.; Del Arco, M.C.G.; Giannini, M.J.S.M.; Almeida, A.M.F.; Salvador, S.L.D.S.; Herculano, R.D. Gentamicin encapsulated within a biopolymer for the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli infected skin ulcers. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 32, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodir, W.K.W.A.; Razak, A.H.A.; Ng, M.H.; Guarino, V.; Susanti, D. Encapsulation and Characterization of Gentamicin Sulfate in the Collagen Added Electrospun Nanofibers for Skin Regeneration. J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Hao, S.; Wu, D.; Huang, R.; Xu, Y. Preparation, characterization and in vitro release of chitosan nanoparticles loaded with gentamicin and salicylic acid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 85, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, N.H.; Le Thanh, T.; Sangpueak, R.; Treekoon, J.; Saengchan, C.; Thepbandit, W.; Papathoti, N.K.; Kamkaew, A.; Buensanteai, N. Chitosan Nanoparticles-Based Ionic Gelation Method: A Promising Candidate for Plant Disease Management. Polymers 2022, 14, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.W.; Song, I.H.; Um, S.H. Role of Physicochemical Properties in Nanoparticle Toxicity. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 1351–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donahue, N.D.; Acar, H.; Wilhelm, S. Concepts of nanoparticle cellular uptake, intracellular trafficking, and kinetics in nanomedicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 143, 68–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrini, L.; Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Pazos-Perez, N. Surface Modifications of Nanoparticles for Stability in Biological Fluids. Materials 2018, 11, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, S.; Gupta, S.; Narang, R.K.; Budhiraja, R.D. Amoxicillin Loaded Chitosan–Alginate Polyelectrolyte Complex Nanoparticles as Mucopenetrating Delivery System for H. Pylori. Sci. Pharm. 2011, 79, 673–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, A.; Katas, H.; Zin, N. Antibacterial effects of chitosan–tripolyphosphate nanoparticles: Impact of particle size molecular weight. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakha, M.; Saleem, M.; Mallick, B.C.; Jha, S. The effects of interfacial potential on antimicrobial propensity of ZnO nanoparticle. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hakeem, M.A.; Abdel-Haseb, O.M.; Abdel-Ghany, S.E.; Cevik, E.; Sabit, H. Doxorubicin loaded on chitosan-protamine nanoparticles triggers apoptosis via downregulating Bcl-2 in breast cancer cells. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 55, 101423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hakeem, M.A.; Mongy, S.; Hassan, B.; Tantawi, O.I.; Badawy, I. Curcumin Loaded Chitosan-Protamine Nanoparticles Revealed Antitumor Activity Via Suppression of NF-kappaB, Proinflammatory Cytokines and Bcl-2 Gene Expression in the Breast Cancer Cells. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 3298–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanović, M.; Đošić, M.; Janković, A.; Kojić, V.; Vukašinović-Sekulić, M.; Stojanović, J.; Odović, J.; Sakač, M.C.; Rhee, K.Y.; Mišković-Stanković, V. Gentamicin-Loaded Bioactive Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Composite Coating Electrodeposited on Titanium. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 3994–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, A.J.; Garcia, M.; Shepherd, J.; Rehman, I.; Sheila, M. Bacteria induced pH changes in tissue-engineered human skin detected non-invasively using Raman confocal spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2019, 55, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Song, G.; Sun, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Prevalence and Therapies of Antibiotic-Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diggle, S.P.; Whiteley, M. Microbe Profile: Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Opportunistic pathogen and lab rat. Microbiology 2020, 166, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, K.M.; Serio, A.W.; Kane, T.R.; Connolly, L.E. Aminoglycosides: An Overview. Cold Spring Harb Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a027029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beganovic, M.; Luther, M.K.; Rice, L.B.; Arias, C.A.; Rybak, M.J.; LaPlante, K.L. A Review of Combination Antimicrobial Therapy for Enterococcus faecalis Bloodstream Infections and Infective Endocarditis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Y.; Liao, B.; Cheng, L.; Ren, B. Reactive Oxygen Species in Pathogen Clearance: The Killing Mechanisms, the Adaption Response, and the Side Effects. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 622534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, S.; Ali, S.; Tahir, H.M.; Kazmi, S.A.R.; Mughal, T.A.; Younas, M. Evaluation of antibacterial activity of vitamin C against human bacterial pathogens. Braz. J. Biol. 2021, 83, e247165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiecińska-Piróg, J.; Skowron, K.; Bogiel, T.; Białucha, A.; Przekwas, J.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E. Vitamin C in the Presence of Sub-Inhibitory Concentration of Aminoglycosides and Fluoroquinolones Alters Proteus mirabilis Biofilm Inhibitory Rate. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zahrani, S.S.; Bora, R.S.; Al-Garni, S.M. Antimicrobial activity of chitosan nanoparticles. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2021, 35, 1874–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, F.; Ghotaslou, R.; Salehi, R.; Kafil, H.S.; Hasani, A.; Gholizadeh, P.; Nouri, R.; Rezaee, M.A. Effects of Gentamicin-Loaded Chitosan-ZnO Nanocomposite on Quorum-Sensing Regulation of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Mol. Biotechnol. 2021, 63, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, S.; Mondal, D. Antibacterial Efficacies of Nanostructured Aminoglycosides. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 4724–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabee, M.M.S.M.; Awang, M.S.; Bustami, Y.; Hamid, Z.A.A. Gentamicin loaded PLA microspheres susceptibility against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli by Kirby-Bauer and micro-dilution methods. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 2267, p. 020032. [Google Scholar]
- Boot, W.; Schmid, T.; D’Este, M.; Guillaume, O.; Foster, A.; Decosterd, L.; Richards, R.G.; Eglin, D.; Zeiter, S.; Moriarty, T.F. A Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Loaded with Gentamicin and Vancomycin Successfully Eradicates Chronic Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Orthopedic Infection in a Sheep Model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e01840-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Melcón, C.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; García-Fernández, C.; Carballo, J.; Capita, R. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) for Twelve Antimicrobials (Biocides and Antibiotics) in Eight Strains of Listeria monocytogenes. Biology 2021, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mal, P.; Dutta, S.; Bandyopadhyay, D.; Dutta, K.; Basu, A.; Bishayi, B. Gentamicin in Combination with Ascorbic Acid Regulates the severity of Staphylococcus aureus Infection-Induced Septic Arthritis in Mice. Scand. J. Immunol. 2012, 76, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abdelraheem, W.M.; Refaie, M.M.M.; Yousef, R.K.M.; El Fatah, A.S.A.; Mousa, Y.M.; Rashwan, R. Assessment of Antibacterial and Anti-biofilm Effects of Vitamin C Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1594. [Google Scholar]
- Song, R.; Murphy, M.; Li, C.; Ting, K.; Soo, C.; Zheng, Z. Current development of biodegradable polymeric materials for biomedical applications. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 3117–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asuzu, P.C.; Trompeter, N.S.; Cooper, C.R.; Besong, S.A.; Aryee, A.N.A. Cell Culture-Based Assessment of Toxicity and Therapeutics of Phytochemical Antioxidants. Molecules 2022, 27, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshay, O.N.; Ewees, M.G.; Abdel-Bakky, M.S.; Hafez, S.M.N.A.; Abdelrehim, A.B.; Bayoumi, A.M. Resveratrol reduces gentamicin-induced EMT in the kidney via inhibition of reactive oxygen species and involving TGF-β/Smad pathway. Life Sci. 2020, 258, 118178. [Google Scholar]
- Derakhshanfar, A.; Roshanzamir, M.; Bidadkosh, A. Dose-related protecting effects of vitamin C in gentamicin-induced rat nephrotoxicity: A histopathologic and biochemical study. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 22, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omotoso, D.; Olajumoke, J.M. Ameliorative Effects of Ascorbic Acid and Allium sativum (Garlic) Ethanol Extract on Renal Parenchyma of Gentamicin-induced Nephropathic Rats. J. Complement. Altern. Med Res. 2020, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Harpe, K.M.; Kondiah, P.P.; Choonara, Y.E.; Marimuthu, T.; du Toit, L.C.; Pillay, V. The Hemocompatibility of Nanoparticles: A Review of Cell–Nanoparticle Interactions and Hemostasis. Cells 2019, 8, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, R.; Aggarwal, T.; Thapliyal, N.; Kumar, A.; Priya; Yadav, P.; Kumari, V.; Reddy, B.S.C.; Chandra, P.; Maurya, P.K. Red blood cells as an efficient in vitro model for evaluating the efficacy of metallic nanoparticles. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvekar, P.; Palaskar, J.; Metgud, S.; Maria, R.; Dutta, S. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of silver nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus. Biomater. Investig. Dent. 2020, 7, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.; Vargas-Morales, O.; Zern, B.; Anselmo, A.C.; Gupta, V.; Zakrewsky, M.; Mitragotri, S.; Muzykantov, V. The Effect of Polymeric Nanoparticles on Biocompatibility of Carrier Red Blood Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152074. [Google Scholar]


| Drug (100 µg/mL) | Staphylococcus aureus Inhibition Zone (mm) after (24/48 h) | Pseudomonas aeruginosa Inhibition Zone (mm) after (24/48 h) |
|---|---|---|
| CSNPs | 8/8 | 9.5/9.7 |
| GM | 24.0/24.2 | 21.5/21.5 |
| GMCSNPs | 23.4/32.1 | 20.1/29.4 |
| GM–AA–CSNPs | 24.2/34.0 | 21.8/31.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdel-Hakeem, M.A.; Abdel Maksoud, A.I.; Aladhadh, M.A.; Almuryif, K.A.; Elsanhoty, R.M.; Elebeedy, D. Gentamicin–Ascorbic Acid Encapsulated in Chitosan Nanoparticles Improved In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity and Minimized Cytotoxicity. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111530
Abdel-Hakeem MA, Abdel Maksoud AI, Aladhadh MA, Almuryif KA, Elsanhoty RM, Elebeedy D. Gentamicin–Ascorbic Acid Encapsulated in Chitosan Nanoparticles Improved In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity and Minimized Cytotoxicity. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(11):1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111530
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdel-Hakeem, Mohamed A., Ahmed I. Abdel Maksoud, Mohammed Abdullah Aladhadh, Khalid Abdulrahman Almuryif, Rafaat M. Elsanhoty, and Dalia Elebeedy. 2022. "Gentamicin–Ascorbic Acid Encapsulated in Chitosan Nanoparticles Improved In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity and Minimized Cytotoxicity" Antibiotics 11, no. 11: 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111530
APA StyleAbdel-Hakeem, M. A., Abdel Maksoud, A. I., Aladhadh, M. A., Almuryif, K. A., Elsanhoty, R. M., & Elebeedy, D. (2022). Gentamicin–Ascorbic Acid Encapsulated in Chitosan Nanoparticles Improved In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity and Minimized Cytotoxicity. Antibiotics, 11(11), 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111530






