Clonal Complexes 23, 10, 131 and 38 as Genetic Markers of the Environmental Spread of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL)-Producing E. coli
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
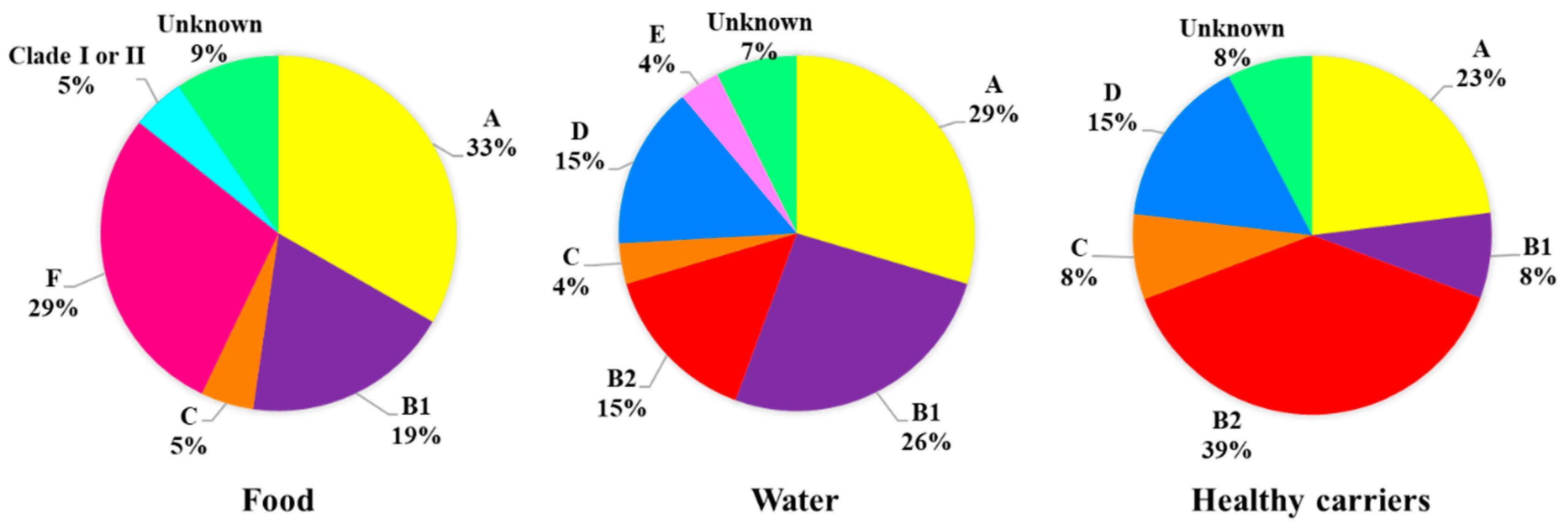
2.1. Classification of E. coli ESBL Strains According to Phylogenetic Groups
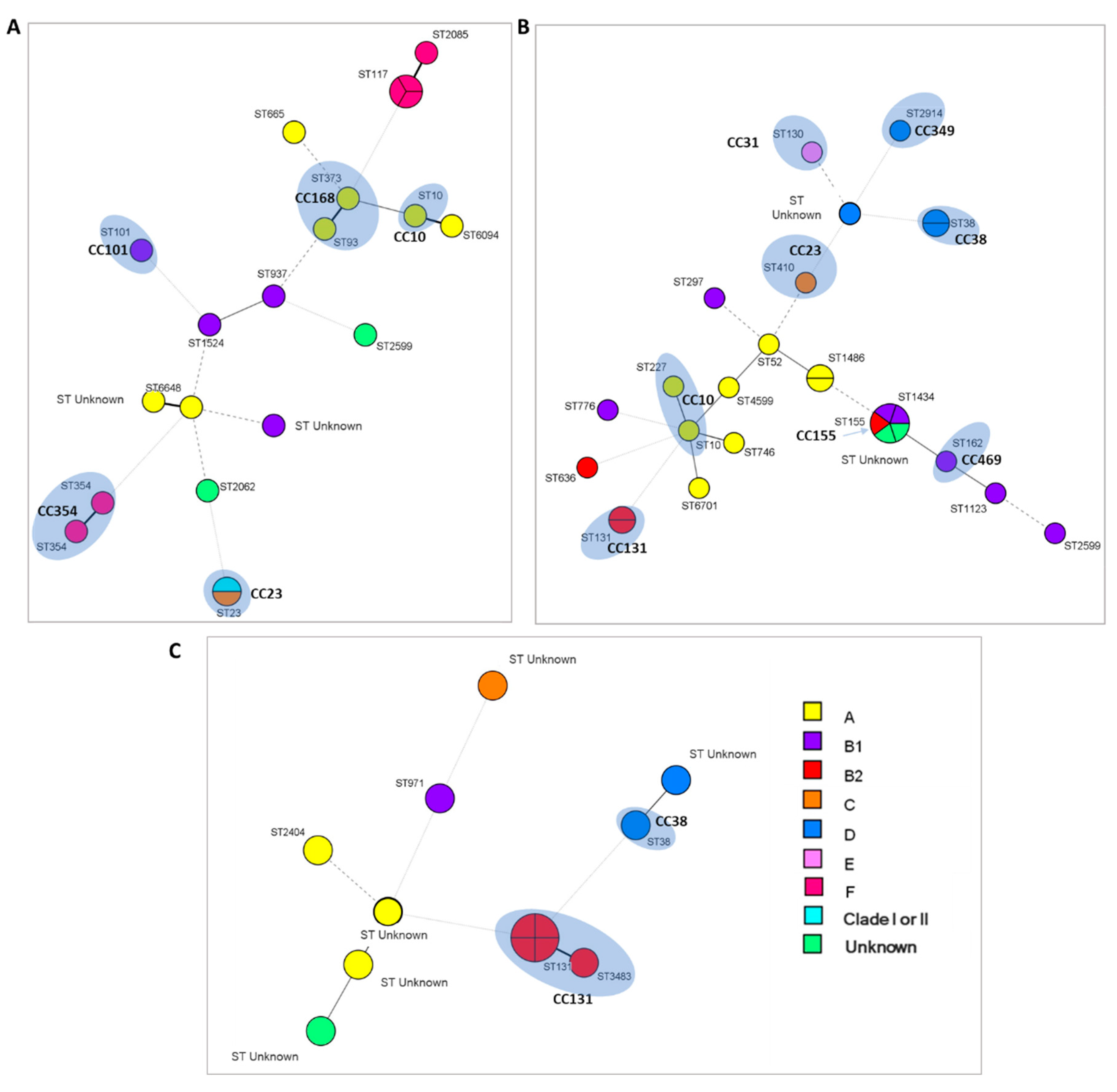
2.2. Analysis of CCs and STs by MLST
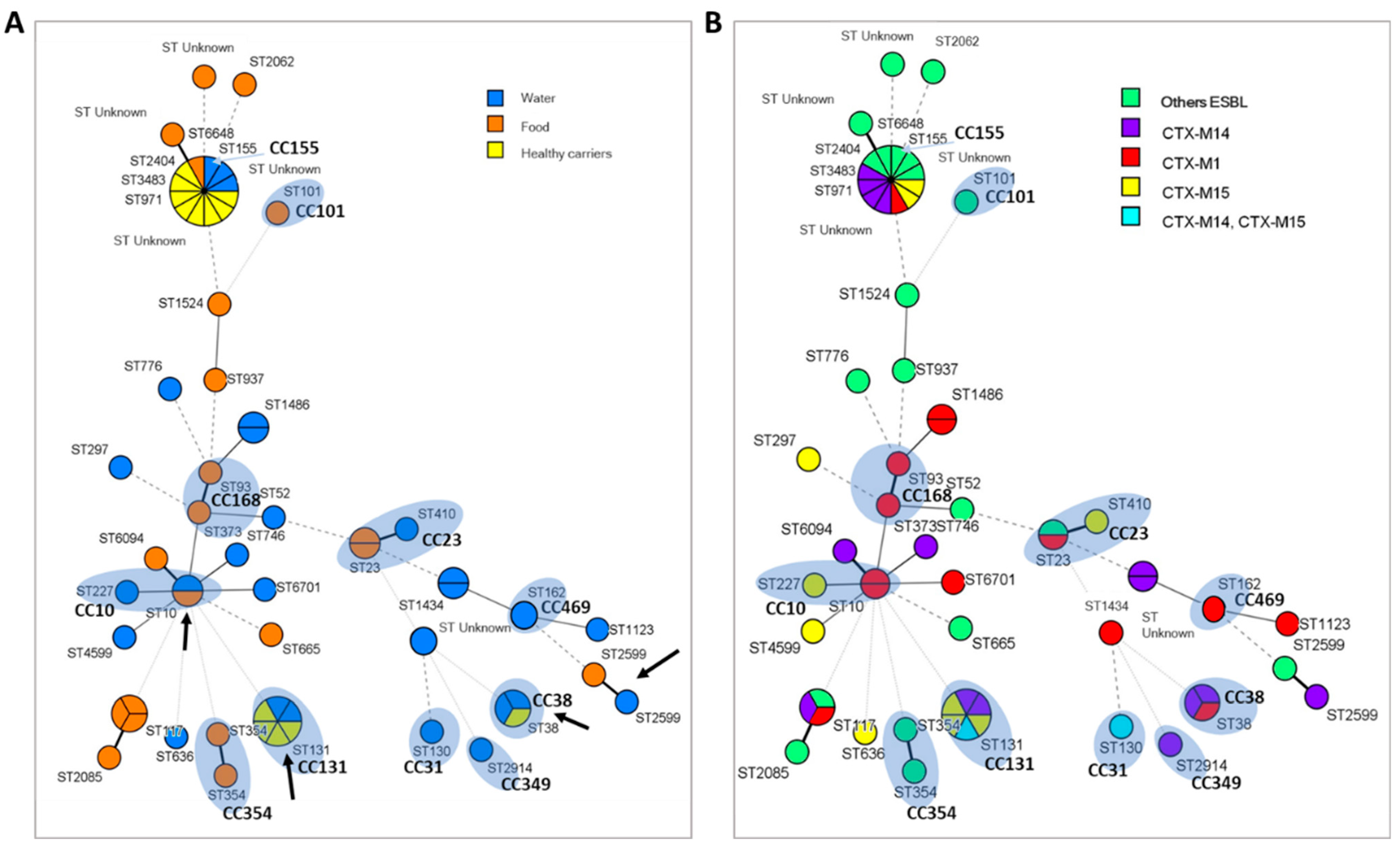
ST and CC Relationship of Strains Isolated from Different Environments
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Selection of E. coli Strains
4.2. Bacterial DNA Extraction
4.3. Determination of Phylogenetic Groups
4.4. Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST)
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria to Guide Research, Discovery, and Development of New Antibiotics; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- WHO Antimicrobial resistance. Global report on surveillance. World Heal. Organ. 2014, 61, 383–394. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas-Chanoine, M.H.; Bertrand, X.; Madec, J.Y. Escherichia coli ST131, an intriguing clonal group. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 543–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allocati, N.; Masulli, M.; Alexeyev, M.F.; Di Ilio, C. Escherichia coli in Europe: An overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 6235–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croxen, M.A.; Finlay, B.B. Molecular mechanisms of Escherichia coli pathogenicity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.R.; Russo, T.A. Extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli: “The other bad E. coli”. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2002, 139, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branger, C.; Zamfir, O.; Geoffroy, S.; Laurans, G.; Arlet, G.; Vu Thien, H.; Gouriou, S.; Picard, B.; Denamur, E. Genetic background of Escherichia coli and extended-spectrum β-lactamase type. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzer, P.J.; Inouye, S.; Inouye, M.; Whittam, T.S. Phylogenetic distribution of branched RNA-linked multicopy single-stranded DNA among natural isolates of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 6175–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.R.; Delavari, P.; Kuskowski, M.; Stell, A.L. Phylogenetic Distribution of Extraintestinal Virulence-Associated Traits in Escherichia coli. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.; Torres, C.; Silva, N.; Carneiro, C.; Radhouani, H.; Coelho, C.; Araújo, C.; Rodrigues, J.; Vinué, L.; Somalo, S.; et al. Genetic characterization of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases in Escherichia coli isolates of pigs from a portuguese intensive swine farm. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2010, 7, 1569–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, Y.; Hernández, E.; Millán, B.; Araque, M. Distribución de grupos filogenéticos y factores de virulencia en cepas de Escherichia coli uropatógena productora de β-lactamasa CTX-M-15 aisladas de pacientes de la comunidad en mérida, Venezuela. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2014, 46, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clermont, O.; Bonacorsi, S.; Bingen, E. Rapid and simple determination of the Escherichia coli phylogenetic group. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4555–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clermont, O.; Christenson, J.K.; Denamur, E.; Gordon, D.M. The Clermont Escherichia coli phylo-typing method revisited: Improvement of specificity and detection of new phylo-groups. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Walk, S.T.; Gordon, D.M.; Feldgarden, M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T. Genome sequencing of environmental Escherichia coli expands understanding of the ecology and speciation of the model bacterial species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7200–7205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clermont, O.; Gordon, D.M.; Brisse, S.; Walk, S.T.; Denamur, E. Characterization of the cryptic Escherichia lineages: Rapid identification and prevalence. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 2468–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, T.; Falush, D.; Lan, R.; Colles, F.; Mensa, P.; Wieler, L.H.; Karch, H.; Reeves, P.R.; Maiden, M.C.J.; Ochman, H.; et al. Sex and virulence in Escherichia coli: An evolutionary perspective. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 60, 1136–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathers, A.J.; Peirano, G.; Pitout, J.D.D. Escherichia coli ST131: The Quintessential Example of an International Multiresistant High-Risk Clone. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 90, 109–154. [Google Scholar]
- Merino, I.; Shaw, E.; Horcajada, J.P.; Cercenado, E.; Mirelis, B.; Pallarés, M.A.; Gómez, J.; Xercavins, M.; Martínez-Martínez, L.; De Cueto, M.; et al. CTX-M-15-H30Rx-ST131 subclone is one of the main causes of healthcare-associated ESBL-producing Escherichia coli bacteraemia of urinary origin in Spain. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 2125–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojer-Usoz, E.; González, D.; Vitas, A.I.; Leiva, J.; García-Jalón, I.; Febles-Casquero, A.; de la Soledad Escolano, M. Prevalence of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in meat products sold in Navarra, Spain. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitas, A.I.; Naik, D.; Pérez-Etayo, L.; González, D. Increased exposure to extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae through the consumption of chicken and sushi products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 269, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Etayo, L.; González, D.; Leiva, J.; Vitas, A.I. Multidrug-resistant bacteria isolated from different aquatic environments in the North of Spain and South of France. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, D.; Gallagher, E.; Zúñiga, T.; Leiva, J.; Vitas, A.I. Prevalence and characterization of β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in healthy human carriers. Int. Microbiol. 2019, 23, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar-Páramo, P.; Sabbagh, A.; Darlu, P.; Pradillon, O.; Vaury, C.; Denamur, E.; Lecointre, G. Decreasing the effects of horizontal gene transfer on bacterial phylogeny: The Escherichia coli case study. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2004, 30, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, C.; Pires, M.M.; Stoppe, N.C.; Hachich, E.M.; Sato, M.I.Z.; Gomes, T.A.T.; Amaral, L.A.; Ottoboni, L.M.M. Escherichia coli phylogenetic group determination and its application in the identification of the major animal source of fecal contamination. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 161, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massot, M.; Daubié, A.S.; Clermont, O.; Jauréguy, F.; Couffignal, C.; Dahbi, G.; Mora, A.; Blanco, J.; Branger, C.; Mentré, F.; et al. Phylogenetic, virulence and antibiotic resistance characteristics of commensal strain populations of Escherichia coli from community subjects in the paris area in 2010 and evolution over 30 years. Microbiology 2016, 162, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coura, F.M.; Diniz, S.D.A.; Silva, M.X.; Mussi, J.M.S.; Barbosa, S.M.; Lage, A.P.; Heinemann, M.B. Phylogenetic Group Determination of Escherichia coli Isolated from Animals Samples. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Tansawai, U.; Sanguansermsri, D.; Na-udom, A.; Walsh, T.R.; Niumsup, P.R. Occurrence of extended spectrum β-lactamase and AmpC genes among multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli and emergence of ST131 from poultry meat in Thailand. Food Control 2018, 84, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangchhia, B.; Abraham, S.; Bell, J.M.; Collignon, P.; Gibson, J.S.; Ingram, P.R.; Johnson, J.R.; Kennedy, K.; Trott, D.J.; Turnidge, J.D.; et al. Phylogenetic diversity, antimicrobial susceptibility and virulence characteristics of phylogroup F Escherichia coli in Australia. Microbiology 2016, 162, 1904–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.R.; Johnston, B.D.; Gordon, M. Rapid and Specific Detection of the Escherichia coli Sequence Type 648 Complex within Phylogroup F. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewers, C.; Bethe, A.; Stamm, I.; Grobbel, M.; Kopp, P.A.; Guerra, B.; Stubbe, M.; Doi, Y.; Zong, Z.; Kola, A.; et al. CTX-M-15-D-ST648 Escherichia coli from companion animals and horses: Another pandemic clone combining multiresistance and extraintestinal virulence? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 1224–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.Y.; Wakeham, D.; Brouwers, H.J.M.; Cobbold, R.N.; Abraham, S.; Mollinger, J.L.; Johnson, J.R.; Chapman, T.A.; Gordon, D.M.; Barrs, V.R.; et al. Human-associated fluoroquinolone-resistant Escherichia coli clonal lineages, including ST354, isolated from canine feces and extraintestinal infections in Australia. Microbes Infect. 2015, 17, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coque, T.M.; Novais, A.; Carattoli, A.; Poirel, L.; Pitout, J.; Peixe, L.; Baquero, F.; Canton, R.; Nordmann, P. Dissemination of clonally related E. coli strains expressing ESBL CTX-M-15. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Reyes, M.; Vicente, D.; Gomariz, M.; Esnal, O.; Landa, J.; Oñate, E.; Pérez-Trallero, E. High rate of fecal carriage of extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in healthy children in Gipuzkoa, northern Spain. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 1822–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojer-usoz, E.; Gonzalez, D.; Vitas, A.I. Caracterización de Enterobacterias Productoras de β-Lactamasas de Espectro Extendido Aisladas en Muestras Alimentarias, Ambientales y Clínicas. Doctoral Thesis, Universidad de Navarra, Pamplona, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mercat, M.; Clermont, O.; Massot, M.; Ruppe, E.; De Garine-Wichatitsky, M.; Miguel, E.; Fox, H.V.; Cornelis, D.; Andremont, A.; Denamur, E.; et al. Escherichia coli population structure and antibiotic resistance at a buffalo/cattle interface in southern Africa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walk, S.T.; Alm, E.W.; Gordon, D.M.; Ram, J.L.; Toranzos, G.A.; Tiedje, J.M.; Whittam, T.S. Cryptic lineages of the genus Escherichia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 6534–6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondratyeva, K.; Salmon-Divon, M.; Navon-Venezia, S. Meta-analysis of Pandemic Escherichia coli ST131 Plasmidome Proves Restricted Plasmid-clade Associations. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oteo, J.; Diestra, K.; Juan, C.; Bautista, V.; Novais, Â.; Pérez-Vázquez, M.; Moyá, B.; Miró, E.; Coque, T.M.; Oliver, A.; et al. Extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in Spain belong to a large variety of multilocus sequence typing types, including ST10 complex/A, ST23 complex/A and ST131/B2. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 34, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmar Campos, C.; Fenner, I.; Wiese, N.; Lensing, C.; Christner, M.; Rohde, H.; Aepfelbacher, M.; Fenner, T.; Hentschke, M. Prevalence and genotypes of extended spectrum beta-lactamases in Enterobacteriaceae isolated from human stool and chicken meat in Hamburg, Germany. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojer-Usoz, E.; González, D.; Vitas, A.I. Clonal diversity of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli isolated from environmental, human and food samples. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, P.M.; Manges, A.R.; Johnson, J.R. Food-borne origins of Escherichia coli causing extraintestinal infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 712–719. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Said, L.; Jouini, A.; Klibi, N.; Dziri, R.; Alonso, C.A.; Boudabous, A.; Ben Slama, K.; Torres, C. Detection of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Enterobacteriaceae in vegetables, soil and water of the farm environment in Tunisia. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 203, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manges, A.R.; Geum, H.M.; Guo, A.; Edens, T.J.; Fibke, C.D.; Pitout, J.D.D. Global extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli (Expec) lineages. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00135-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, P.; Singh, N.S.; Kanaujia, P.K.; Virdi, J.S. Distribution and molecular characterization of genes encoding CTX-M and AmpC β-lactamases in Escherichia coli isolated from an Indian urban aquatic environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, B.A.; Sidjabat, H.E.; Paterson, D.L. Escherichia coli O25b-ST131: A pandemic, multiresistant, community-associated strain. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorado-García, A.; Smid, J.H.; van Pelt, W.; Bonten, M.J.M.; Fluit, A.C.; van den Bunt, G.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Hordijk, J.; Dierikx, C.M.; Veldman, K.T.; et al. Molecular relatedness of ESBL/AmpC-producing Escherichia coli from humans, animals, food and the environment: A pooled analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedra-Carrasco, N.; Fàbrega, A.; Calero-Cáceres, W.; Cornejo-Sánchez, T.; Brown-Jaque, M.; Mir-Cros, A.; Muniesa, M.; González-López, J.J. Carbapenemase-producing enterobacteriaceae recovered from a Spanish river ecosystem. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lv, L.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Lu, J.; Liu, E.; Wan, M.; Xun, H.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Rapid increase in carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in retail meat driven by the spread of the blaNDM-5-carrying IncX3 plasmid in China from 2016 to 2018. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00573-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamborova, I.; Dolejska, M.; Vojtech, J.; Guenther, S.; Uricariu, R.; Drozdowska, J.; Papousek, I.; Pasekova, K.; Meissner, W.; Hordowski, J.; et al. Plasmid-mediated resistance to cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones in various Escherichia coli sequence types isolated from rooks wintering in Europe. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mora, A.; López, C.; Herrera, A.; Viso, S.; Mamani, R.; Dhabi, G.; Alonso, M.P.; Blanco, M.; Blanco, J.E.; Blanco, J. Emerging avian pathogenic Escherichia coli strains belonging to clonal groups O111: H4-D-ST2085 and O111: H4-D-ST117 with high virulence-gene content and zoonotic potential. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 156, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronco, T.; Stegger, M.; Olsen, R.H.; Sekse, C.; Nordstoga, A.B.; Pohjanvirta, T.; Lilje, B.; Lyhs, U.; Andersen, P.S.; Pedersen, K. Spread of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli ST117 O78: H4 in Nordic broiler production. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćwiek, K.; Woźniak-Biel, A.; Karwańska, M.; Siedlecka, M.; Lammens, C.; Rebelo, A.R.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Kuczkowski, M.; Chmielewska-Władyka, M.; Wieliczko, A. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of mcr-1-positive multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli ST93, ST117, ST156, ST10, and ST744 isolated from poultry in Poland. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 1597–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, F.; Jiang, M.; Wen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhuge, X.; Dai, J. Complete genomic analysis of ST117 lineage extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC) to reveal multiple genetic determinants to drive its global transmission: ST117 E. coli as an emerging multidrug-resistant foodborne ExPEC with zoonotic potential. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Savin, M.; Bierbaum, G.; Hammerl, J.A.; Heinemann, C.; Parcina, M.; Sib, E.; Voigt, A.; Kreyenschmidt, J. Isolation and characterization of ESKAPE-bacteria and ESBL-producing E. coli from waste- and process water of German poultry slaughterhouses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartof, S.Y.; Solberg, O.D.; Manges, A.R.; Riley, L.W. Analysis of a Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Clonal Group by Multilocus Sequence Typing. Society 2005, 43, 5860–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Etayo, L.; González, D.; Vitas, A.I. Clonal Complexes 23, 10, 131 and 38 as Genetic Markers of the Environmental Spread of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL)-Producing E. coli. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111465
Pérez-Etayo L, González D, Vitas AI. Clonal Complexes 23, 10, 131 and 38 as Genetic Markers of the Environmental Spread of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL)-Producing E. coli. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(11):1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111465
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Etayo, Lara, David González, and Ana Isabel Vitas. 2022. "Clonal Complexes 23, 10, 131 and 38 as Genetic Markers of the Environmental Spread of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL)-Producing E. coli" Antibiotics 11, no. 11: 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111465
APA StylePérez-Etayo, L., González, D., & Vitas, A. I. (2022). Clonal Complexes 23, 10, 131 and 38 as Genetic Markers of the Environmental Spread of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL)-Producing E. coli. Antibiotics, 11(11), 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111465





