Outpatient Antibiotic Use and Costs in Adults: A Nationwide Register-Based Study in Finland 2008–2019
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antibiotic Use
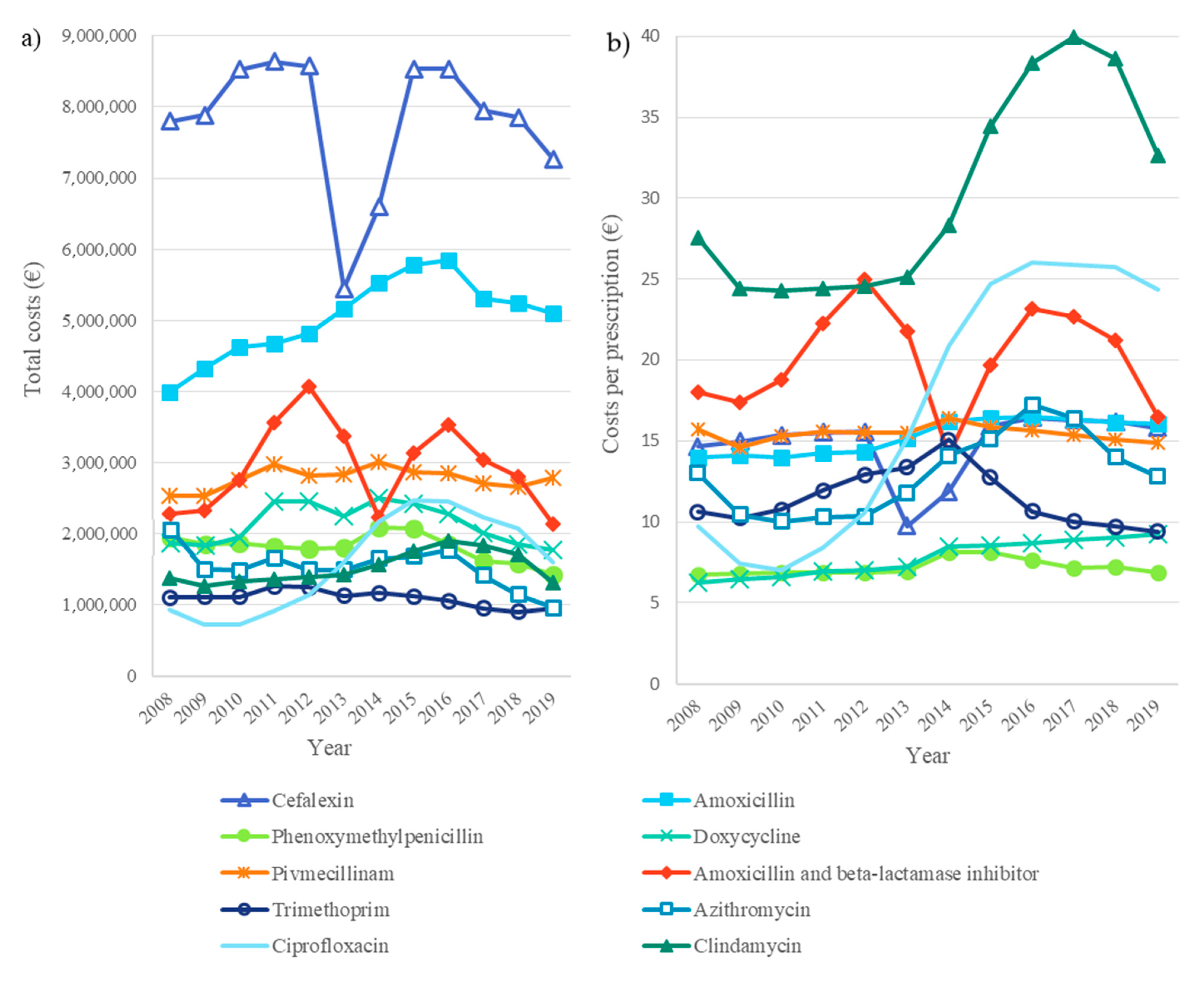
2.2. Antibiotic Costs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Setting
3.3. Data Source
3.4. Analysis
3.5. Ethics
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019, a systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/antimicrobial-resistance/global-action-plan/en/ (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- European Commission. A European One Health Action Plan against Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR). Available online: https://health.ec.europa.eu/system/files/2020-01/amr_2017_action-plan_0.pdf (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Hakanen, A.; Jalava, J.; Kaartinen, L. The National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance 2017–2021. 2017. Available online: https://stm.fi/documents/1271139/1359637/12_17_National_Action_Plan_on_Antimicrobial_Resistance_2017_2021_V1+(002).pdf/9ff43364-6cc2-4e39-b0cf-5664460a3d9e/12_17_National_Action_Plan_on_Antimicrobial_Resistance_2017_2021_V1+(002).pdf?t=1535980865000 (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- European Court of Auditors. Addressing Antimicrobial Resistance: Progress in the Animal Sector, but This Health Threat Remains a Challenge for the EU. Special Report Nro 21. 2019, pp. 1–58. Available online: https://www.eca.europa.eu/en/Pages/DocItem.aspx?did=51992 (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Forssten, S.D.; Kolho, E.; Lauhio, A.; Lehtola, L.; Mero, S.; Oksaharju, A.; Jalava, J.; Tarkka, E.; Vaara, M.; Vuopio-Varkila, J. Emergence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae during the years 2000 and 2004 in Helsinki, Finland. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 1158–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaakola, S.; Lyytikäinen, O.; Rimhanen-Finne, R.; Salmenlinna, S.; Savolainen-Kopra, C.; Liitsola, K.; Jalava, J.; Toropainen, M.; Nohynek, H.; Virtanen, M.; et al. Infectious Diseases in Finland 2016; National Institute for Health and Welfare (THL): Helsinki, Finland, 2017; Available online: https://www.julkari.fi/bitstream/handle/10024/135619/URN_ISBN_978-952-302-978-1.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Wuorela, M.; Jalava, J. Virtsatieinfektioiden aiheuttajien mikrobilääkeresistenssin lisääntyminen on haaste kliinikoille ja lääkevalvontajärjestelmille. Duodecim 2019, 135, 1221–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Parviainen, S.; Saastamoinen, L.; Lauhio, A.; Sepponen, K. Outpatient antibacterial use and costs in children and adolescents: A nationwide register-based study in Finland, 2008–2016. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 2426–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bell, B.G.; Schellevis, F.; Stobberingh, E.; Goossens, H.; Pringle, M. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of antibiotic consumption on antibiotic resistance. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blix, H.; Engeland, A.; Litleskare, I.; Rønning, M. Age- and gender-specific antibacterial prescribing in Norway. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 59, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kourlaba, G.; Gkrania-Klotsas, E.; Kourkouni, E.; Mavrogeorgos, G.; Zaoutis, T.E. Antibiotic prescribing and expenditures in outpatient adults in Greece, 2010 to 2013, evidence from real-world practice. Eurosurveillance 2016, 21, 30266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brauer, R.; Ruigómez, A.; Downey, G.; Bate, A.; Garcia Rodriguez, L.A.; Huerta, C.; Gil, M.; de Abajo, F.; Requena, G.; Alvarez, Y.; et al. Prevalence of antibiotic use: A comparison across various European health care data sources. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2016, 25, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleming-Dutra, K.E.; Hersh, A.L.; Shapiro, D.J.; Bartoces, M.; Enns, E.A.; File, T.M.; Finkelstein, J.A.; Gerber, J.S.; Hyun, D.Y.; Linder, J.A.; et al. Prevalence of Inappropriate Antibiotic Prescriptions Among US Ambulatory Care Visits, 2010–2011. JAMA 2016, 315, 1864–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mundkur, M.L.; Franklin, J.; Huybrechts, K.F.; Fischer, M.A.; Kesselheim, A.S.; Linder, J.A.; Landon, J.; Patorno, E. Changes in Outpatient Use of Antibiotics by Adults in the United States, 2006–2015. Drug Saf. 2018, 41, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, V.; Monetti, V.M.; Guerriero, F.; Trama, U.; Guida, A.; Menditto, E.; Orlando, V. Prevalence of antibiotic prescription in southern Italian outpatients: Real-world data analysis of socioeconomic and sociodemographic variables at a municipality level. Clinicoecon. Outcomes Res. 2018, 10, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, P.; Johnsen, S.; Thomsen, R. Decreasing trends, and geographical variation in outpatient antibiotic use: A population-based study in Central Denmark. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Gulliford, M.C. Reducing antibiotic prescribing in primary care in England from 2014 to 2017, Population-based cohort study. BMJ Open 2019, 7, 23989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo, J.A.; Moreiro, M.A.B.; Dezcallar, M.Z.; Amengual, J.R.; Casas, A.R.; Jäger, E.C.; Camps, A.B.; Cánaves, J.L. Evolution of the outpatient antibiotic prescription between 2012 and 2018. Characteristics of the ABPresclín platform created for the analysis of antibiotic prescription in the health service of the Balearic Islands. Rev. Esp. Salud. Publica 2020, 94, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, H.; Saito, M.; Sato, J.; Goda, K.; Mitsutake, N.; Kitsuregawa, M.; Nagai, R.; Hatakeyama, S. Indications and classes of outpatient antibiotic prescriptions in Japan: A descriptive study using the national database of electronic health insurance claims, 2012–2015. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, L.M.; Bartoces, M.; Fleming-Dutra, K.E.; Roberts, R.M.; Hicks, L.A. Changes in US outpatient antibiotic prescriptions from 2011–2016. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD.stat. Available online: https://stats.oecd.org/index.aspx?DataSetCode=HEALTH_PHMC (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Antimicrobial Consumption Database (ESAC-Net). Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/antimicrobial-consumption/surveillance-and-disease-data/database (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Finnish Medicines Agency Fimea, The Social Insurance Institution. Finnish Statistics on Medicines 2020; Finnish Medicines Agency Fimea, The Social Insurance Institution: Helsinki, Finland, 2021; Available online: https://www.julkari.fi/handle/10024/143552 (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Niemenoja, O.; Taalas, A.; Taimela, S.; Bono, P.; Huovinen, P.; Riihijärvi, S. Time series analysis of the incidence of acute upper respiratory tract infections, COVID-19 and the use of antibiotics in Finland during the COVID-19 epidemic: A cohort study of 833 444 patients. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e046490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Finland. Population. Available online: https://www.tilastokeskus.fi/tup/suoluk/suoluk_vaesto_en.html (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- The Social Insurance Institution of Finland. Statistical Database Kelasto. Available online: https://tietotarjotin.kela.fi/tilastodata/2051231/Tilastotietokanta%20Kelasto?q=kelasto (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- World Health Organization. Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) Classification. Available online: https://www.who.int/tools/atc-ddd-toolkit/atc-classification (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Browne, A.J.; Chipeta, M.G.; Haines-Woodhouse, G.; Kumaran, E.P.A.; Kashef Hamadani, B.H.; Zaraa, S.; Henry, N.J.; Deshpande, A.; Reiner, R.C., Jr.; Day, N.P.J.; et al. Global antibiotic consumption and usage in humans, 2000–2018, a spatial modelling study. Lancet Planet Health 2021, 5, e893–e904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmu, A.A.; Rinta-Kokko, H.; Nohynek, H.; Nuorti, J.P.; Jokinen, J. Impact of national ten-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine program on reducing antimicrobial use and tympanostomy tube placements in Finland. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkinen, T.; Block, S.L.; Toback, S.L.; Wu, X.; Ambrose, C.S. Effectiveness of intranasal live attenuated influenza vaccine against all-cause acute otitis media in children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2013, 32, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polkowska, A.; Harjunpää, A.; Toikkanen, S.; Lappalainen, M.; Vuento, R.; Vuorinen, T.; Kauppinen, J.; Flinck, H.; Lyytikäinen, O. Increased incidence of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in Finland, 2010–2011. Eurosurveillance 2012, 17, 20072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Working Group Set by the Finnish Medical Society Duodecim, the Finnish Society of Nephrology, the Society of Clinical Microbiologists, the Finnish Society of Infectious Diseases Physicians, the Finnish Medical Association of Clinical Chemistry, the Finnish Paediatric Society, the Finnish Society of Urology and the Finnish Society of General Medicine. Urinary Tract Infections. Current Care Guideline. Finnish Medical Society Duodecim, 2.3.2020. Available online: www.kaypahoito.fi (accessed on 21 October 2022). (In Finnish).
- SWEDRES|SVARM Sales of Antibiotics and Occurrence of Antibiotic Resistance in Sweden. 2020. Available online: https://www.sva.se/media/8d9678c390929e9/swedres_svarm_2020.pdf (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Smith, D.R.M.; Dolk, F.C.K.; Smieszek, T.; Robotham, J.V.; Pouwels, K.B. Understanding the gender gap in antibiotic prescribing: A cross-sectional analysis of English primary care. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e020203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pharmaceuticals Pricing Board. Reference price system. Available online: https://www.hila.fi/en/reference-price-system/ (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Kantele, A.; Lääveri, T.; Mero, S.; Vilkman, K.; Pakkanen, S.H.; Ollgren, J.; Antikainen, J.; Kirveskari, J. Antimicrobials increase travelers’ risk of colonization by extended-spectrum betalactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantele, A.; Kuenzli, E.; Dunn, S.J.; Dance, D.A.; Newton, P.N.; Davong, V.; Mero, S.; Pakkanen, S.H.; Neumayr, A.; Hatz, C.; et al. Dynamics of intestinal multidrug-resistant bacteria colonisation contracted by visitors to a high-endemic setting: A prospective, daily, real-time sampling study. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e151–e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauhio, A.; Hästbacka, J.; Pettilä, V.; Tervahartiala, T.; Karlsson, S.; Varpula, T.; Varpula, M.; Ruokonen, E.; Sorsa, T.; Kolho, E. Serum MMP-8,-9 and TIMP-1 in sepsis: High serum levels of MMP-8 and TIMP-1 are associated with fatal outcome in a multicentre, prospective cohort study. Hypothetical impact of tetracyclines. Pharmacol. Res. 2011, 64, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wess, R.A.; Schmidt, T.; Höger, S. Challenges of regulatory environmental risk assessment for human pharmaceuticals with focus on antibiotics. Chimia 2020, 74, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EMA, ECDC, OECD, EFSA Joint Report 7.3.2022 Antimicrobial Resistance in the EU/EEA—A One Health Response. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/antimicrobial-resistance-eueea-one-health-response (accessed on 21 October 2022).




| Prescription Rate (Number of Prescriptions/1000 Adults/Year) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotic Category | ATC Code | 2008 | 2019 | ∆ (%) |
| Tetracyclines | J01A | 85 | 52 | −39% |
| Beta-lactam antibacterials, penicillins | J01C | 207 | 195 | −6% |
| Other beta-lactam antibacterials | J01D | 133 | 104 | −22% |
| Sulfonamides and trimethoprim | J01E | 34 | 24 | −29% |
| Macrolides, lincosamides and streptogramins | J01F | 80 | 32 | −60% |
| Quinolone antibacterials | J01M | 43 | 22 | −49% |
| All antibacterials for systemic use * | J01 | 582 | 428 | −26% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pyörälä, E.; Sepponen, K.; Lauhio, A.; Saastamoinen, L. Outpatient Antibiotic Use and Costs in Adults: A Nationwide Register-Based Study in Finland 2008–2019. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111453
Pyörälä E, Sepponen K, Lauhio A, Saastamoinen L. Outpatient Antibiotic Use and Costs in Adults: A Nationwide Register-Based Study in Finland 2008–2019. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(11):1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111453
Chicago/Turabian StylePyörälä, Elisa, Kati Sepponen, Anneli Lauhio, and Leena Saastamoinen. 2022. "Outpatient Antibiotic Use and Costs in Adults: A Nationwide Register-Based Study in Finland 2008–2019" Antibiotics 11, no. 11: 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111453
APA StylePyörälä, E., Sepponen, K., Lauhio, A., & Saastamoinen, L. (2022). Outpatient Antibiotic Use and Costs in Adults: A Nationwide Register-Based Study in Finland 2008–2019. Antibiotics, 11(11), 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111453





