Phomoxanthone A, Compound of Endophytic Fungi Paecilomyces sp. and Its Potential Antimicrobial and Antiparasitic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Identification of Chemical Constituents
2.2. Antimicrobial Activity
2.3. In Vitro Antiprotozoal
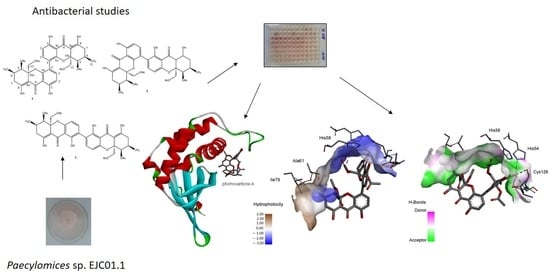
2.4. Computational Studies
2.4.1. Molecular Docking
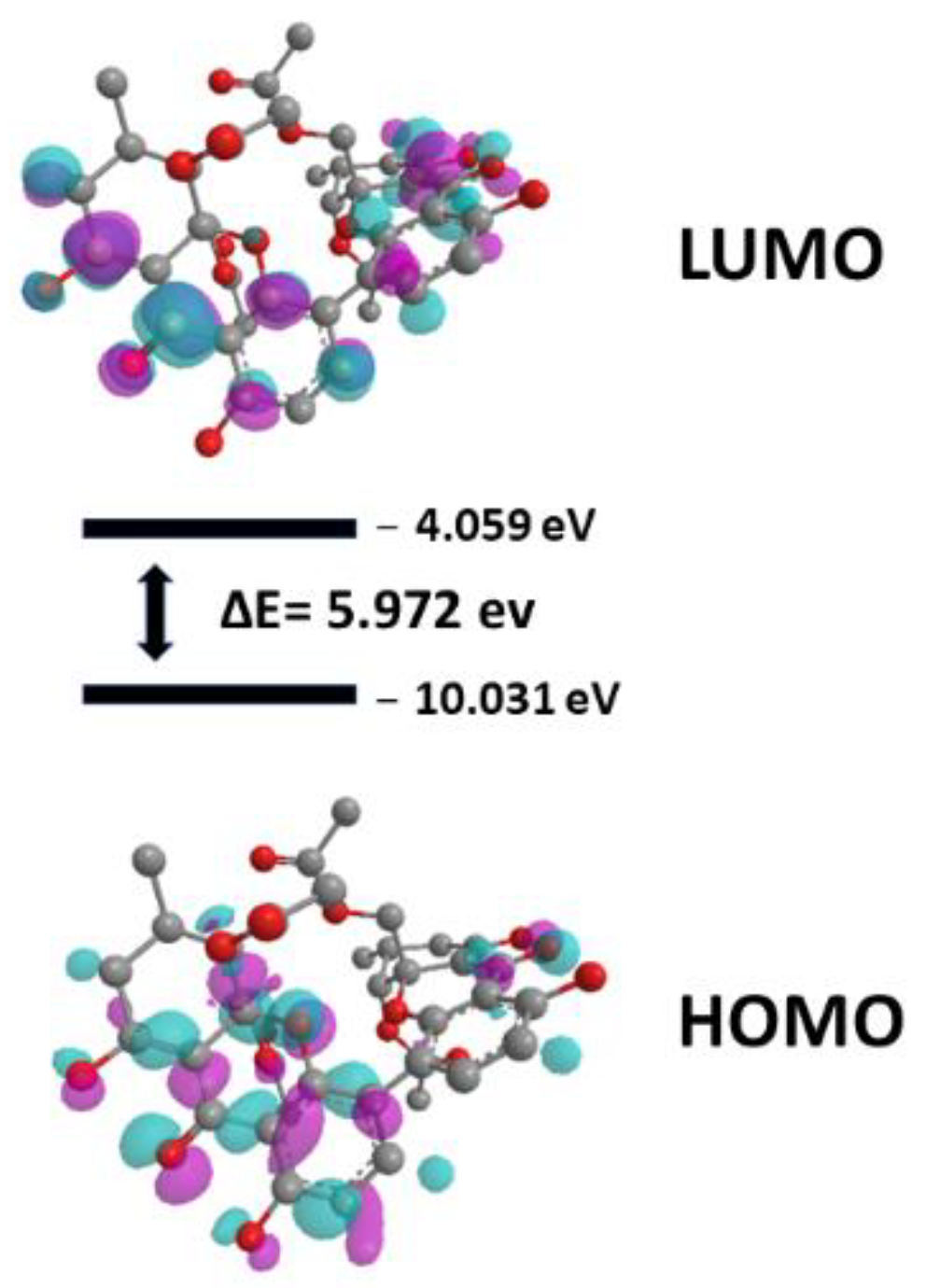
2.4.2. Quantum Studies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Fungus
4.2. Bacteria
4.3. Parasites
4.4. Animals and Ethical Statements
4.5. Peritoneal Macrophage Collection and Culture
4.6. Culture of Paecilomyces sp. in Rice and Chemical Constituents’ Isolation
4.7. General Procedures
4.8. Antimicrobial Assay
4.9. Antileishmanial and Antitrypanosomal Activity Assay
4.10. Cytotoxicity Assay and Selectivity Index
4.11. Molecular Docking
4.12. DFT Studies
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, Z.-B.; Wang, X.; Li, G.-H. Secondary Metabolites and Their Bioactivities Produced by Paecilomyces. Molecules 2020, 25, 5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Gavíra, A.; Huertas, V.; Diánez, F.; Sánchez-Montesinos, B.; Santos, M. Paecilomyces and Its Importance in the Biological Control of Agricultural Pests and Diseases. Plants 2020, 9, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-Q.; Xu, K.; Liu, X.-M.; Zhang, P. A Systematic Review on Secondary Metabolites of Paecilomyces Species: Chemical Diversity and Biological Activity. Planta Med. 2020, 86, 805–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.-Q.; Lin, S.-T.; Kumaravel, K.; Zhou, H.; Wang, S.-Y.; Liu, Y.-H. Polyketide-Derived Metabolites from the Sponge-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp. F40. Phytochem. Lett. 2018, 27, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veríssimo, A.C.S.; Pinto, D.C.G.A.; Silva, A.M.S. Marine-Derived Xanthone from 2010 to 2021: Isolation, Bioactivities and Total Synthesis. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pina, J.R.S.; Silva-Silva, J.V.; Carvalho, J.M.; Bitencourt, H.R.; Watanabe, L.A.; Fernandes, J.M.P.; de Souza, G.E.; Aguiar, A.C.C.; Guido, R.V.C.; Almeida-Souza, F.; et al. Antiprotozoal and Antibacterial Activity of Ravenelin, a Xanthone Isolated from the Endophytic Fungus Exserohilum Rostratum. Molecules 2021, 26, 3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Yuan, M.; Zheng, C.; Xu, H. Xanthone Glucosides: Isolation, Bioactivity and Synthesis. Molecules 2021, 26, 5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Das, P.C.; Joshi, P.C. Naturally Occurring Xanthones from Terrestrial Flora. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 1992, 69, 611–636. [Google Scholar]
- Shagufta; Ahmad, I. Recent Insight into the Biological Activities of Synthetic Xanthone Derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 116, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaka, M.; Jaturapat, A.; Rukseree, K.; Danwisetkanjana, K.; Tanticharoen, M.; Thebtaranonth, Y. Phomoxanthones A and B, Novel Xanthone Dimers from the Endophytic Fungus Phomopsis Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1015–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaka, M.; Palasarn, S.; Kocharin, K.; Saenboonrueng, J. A Cytotoxic Xanthone Dimer from the Entomopathogenic Fungus Aschersonia sp. BCC 8401. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 945–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wezeman, T.; Bräse, S.; Masters, K.-S. Xanthone Dimers: A Compound Family Which Is Both Common and Privileged. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 6–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masters, K.-S.; Bräse, S. Xanthones from Fungi, Lichens, and Bacteria: The Natural Products and Their Synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 3717–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagenaar, M.M.; Clardy, J. Dicerandrols, New Antibiotic and Cytotoxic Dimers Produced by the Fungus Phomopsis l Ongicolla Isolated from an Endangered Mint. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1006–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciegler, A.; Hayes, A.W.; Vesonder, R.F. Production and Biological Activity of Secalonic Acid D. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1980, 39, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, V.; Nagem, T.J.; de Oliveira, F.F. Tetraoxygenated Naturally Occurring Xanthones. Phytochemistry 2000, 55, 683–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andricopulo, A.; Salum, L.; Abraham, D. Structure-Based Drug Design Strategies in Medicinal Chemistry. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 771–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.N.; Ponnusamy, K.; Jeon, Y.; Kim, S.-U.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, C. Identification, Fermentation, and Bioactivity against Xanthomonas Oryzae of Antimicrobial Metabolites Isolated from Phomopsis Longicolla S1B4. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 20, 494–500. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, C.S.; Thompson, J.A.; Xavier, K.B. AI-2-Mediated Signalling in Bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 156–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Li, M. Recent Progresses on AI-2 Bacterial Quorum Sensing Inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, D.; Zhu, J. Mechanism of Action of S-Ribosylhomocysteinase (LuxS). Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2004, 8, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Banerjee, K.; Ervasti, M.M.; Kezilebieke, S.; Dvorak, M.; Rinke, P.; Harju, A.; Liljeroth, P. Electronic Characterization of a Charge-Transfer Complex Monolayer on Graphene. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 9945–9954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miar, M.; Shiroudi, A.; Pourshamsian, K.; Oliaey, A.R.; Hatamjafari, F. Theoretical Investigations on the HOMO–LUMO Gap and Global Reactivity Descriptor Studies, Natural Bond Orbital, and Nucleus-Independent Chemical Shifts Analyses of 3-Phenylbenzo[d]Thiazole-2(3H)-Imine and Its Para-Substituted Derivatives: Solvent and Substituent Effects. J. Chem. Res. 2021, 45, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaugg, K.; Velasco, J.; Robins, K.A.; Lee, D.-C. Understanding the Electronic Properties of Acceptor–Acceptor′–Acceptor Triads. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 5434–5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsässer, B.; Krohn, K.; Flörke, U.; Root, N.; Aust, H.J.; Draeger, S.; Schulz, B.; Antus, S.; Kurtán, T. X-Ray Structure Determination, Absolute Configuration and Biological Activity of Phomoxanthone A. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 2005, 4563–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; She, Z.; Shao, C.; Wen, L.; Liu, F.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, Y. 1H And13C NMR Signal Assignments of Paecilin A and B, Two New Chromone Derivatives from Mangrove Endophytic FungusPaecilomyces Sp. (Tree 1–7). Magn. Reson. Chem. 2007, 45, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radji, M.; Sumiati, A.; Rachmayani, R.; Elya, B. Isolation of Fungal Endophytes from Garcinia Mangostana and Their Antibacterial Activity. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, F.; Kim, E.L.; Li, J.L.; Hong, J.; Bae, K.S.; Chung, H.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, J.H. Antibacterial Polyketides from the Jellyfish-Derived Fungus Paecilomyces Variotii. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1826–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hong, J.; Yin, J.; Moon, H.R.; Liu, Y.; Wei, X.; Oh, D.-C.; Jung, J.H. Dimeric Octaketide Spiroketals from the Jellyfish-Derived Fungus Paecilomyces Variotii J08NF-1. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2832–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiono, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Shibuya, F.; Yasuda, Y.; Koseki, T.; Supratman, U. Isolation of a Phomoxanthone A Derivative, a New Metabolite of Tetrahydroxanthone, from a Phomopsis Sp. Isolated from the Mangrove, Rhizhopora Mucronata. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 1735–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhler, P.; Stuhldreier, F.; Anand, R.; Kondadi, A.K.; Schlütermann, D.; Berleth, N.; Deitersen, J.; Wallot-Hieke, N.; Wu, W.; Frank, M.; et al. The Mycotoxin Phomoxanthone A Disturbs the Form and Function of the Inner Mitochondrial Membrane. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marko Oblak; Miha Kotnik; Tom Solmajer Discovery and Development of ATPase Inhibitors of DNA Gyrase as Antibacterial Agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 2033–2047. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, T.; Sankhe, K.; Suvarna, V.; Sherje, A.; Patel, K.; Dravyakar, B. DNA Gyrase Inhibitors: Progress and Synthesis of Potent Compounds as Antibacterial Agents. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 923–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherer, B.A.; Hull, K.; Green, O.; Basarab, G.; Hauck, S.; Hill, P.; Loch, J.T.; Mullen, G.; Bist, S.; Bryant, J.; et al. Pyrrolamide DNA Gyrase Inhibitors: Optimization of Antibacterial Activity and Efficacy. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 7416–7420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepesheva, G.I.; Hargrove, T.Y.; Kleshchenko, Y.; Nes, W.D.; Villalta, F.; Waterman, M.R. CYP51: A Major Drug Target in the Cytochrome P450 Superfamily. Lipids 2008, 43, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Lv, Q.; Yan, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y. The Fungal CYP51s: Their Functions, Structures, Related Drug Resistance, and Inhibitors. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.; Yin, Y.; Yao, K. Quorum Sensing: A Prospective Therapeutic Target for Bacterial Diseases. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 2015978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Grenier, D.; Yi, L. The LuxS/AI-2 System of Streptococcus Suis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 7231–7238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezzonico, F.; Smits, T.H.M.; Duffy, B. Detection of AI-2 Receptors in Genomes of Enterobacteriaceae Suggests a Role of Type-2 Quorum Sensing in Closed Ecosystems. Sensors 2012, 12, 6645–6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleitas Martínez, O.; Rigueiras, P.O.; Pires, Á.D.S.; Porto, W.F.; Silva, O.N.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C.; Franco, O.L. Interference With Quorum-Sensing Signal Biosynthesis as a Promising Therapeutic Strategy Against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 8, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Grenier, D.; Yi, L. Regulatory Mechanisms of the LuxS/AI-2 System and Bacterial Resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01186-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumer, A.; Khan, M.W. The Effect of Alkyl Chain and Electronegative Atoms in Anion on Biological Activity of Anilinium Carboxylate Bioactive Ionic Liquids and Computational Approaches by DFT Functional and Molecular Docking. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, E.A.A.; Pina, J.R.S.; Feitosa, A.O.; Carvalho, J.M.; Borges, F.C.; Marinho, P.S.B.; Marinho, A.M.R. Bioprospecting of antimicrobial activity of extracts of endophytic fungi from Bauhinia guianensis. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2017, 49, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Methods for Diluition Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically: Approved Standard, 10th ed.; CLSI Document M07-A10; CLSI: Berwyn, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cellular Growth and Survival: Application to Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, A.S.; Valli, M.; Ferreira, L.L.; Souza, J.M.; Krogh, R.; Meier, L.; Abreu, H.R.; Voltolini, B.G.; Llanes, L.C.; Nunes, R.J.; et al. Novel Trypanocidal Thiophen-Chalcone Cruzain Inhibitors: Structure- and Ligand-Based Studies. Future Med. Chem. 2022, 14, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

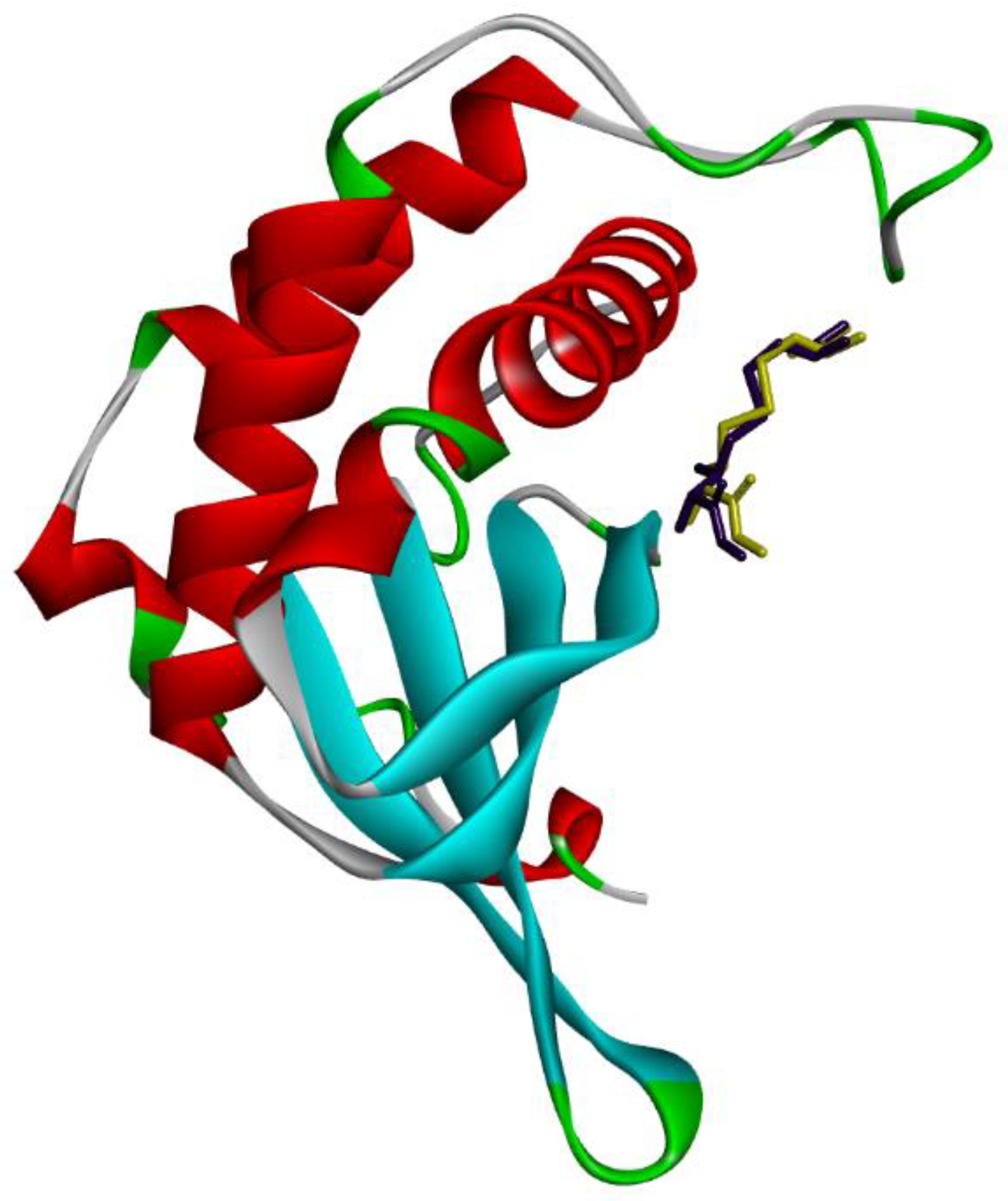
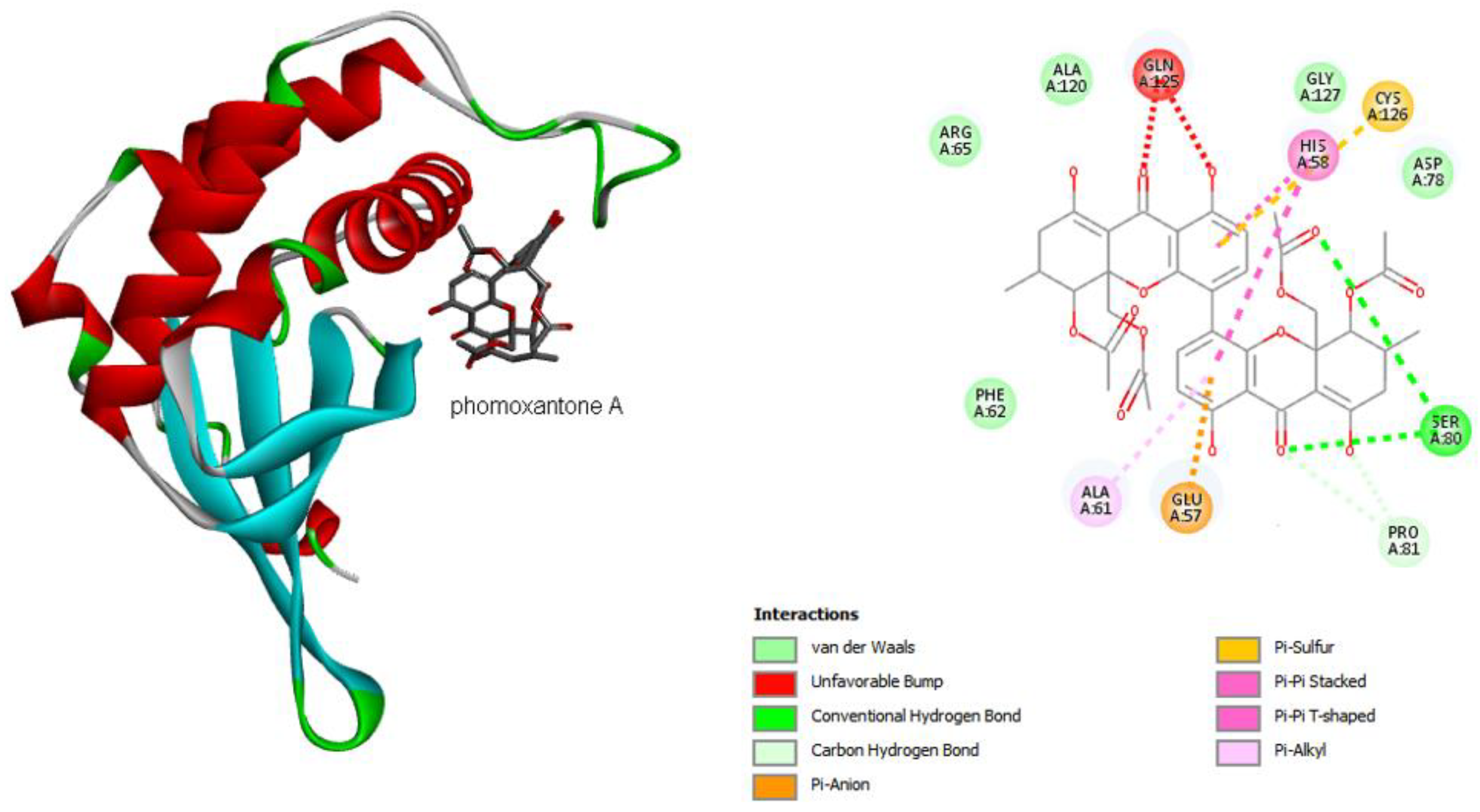
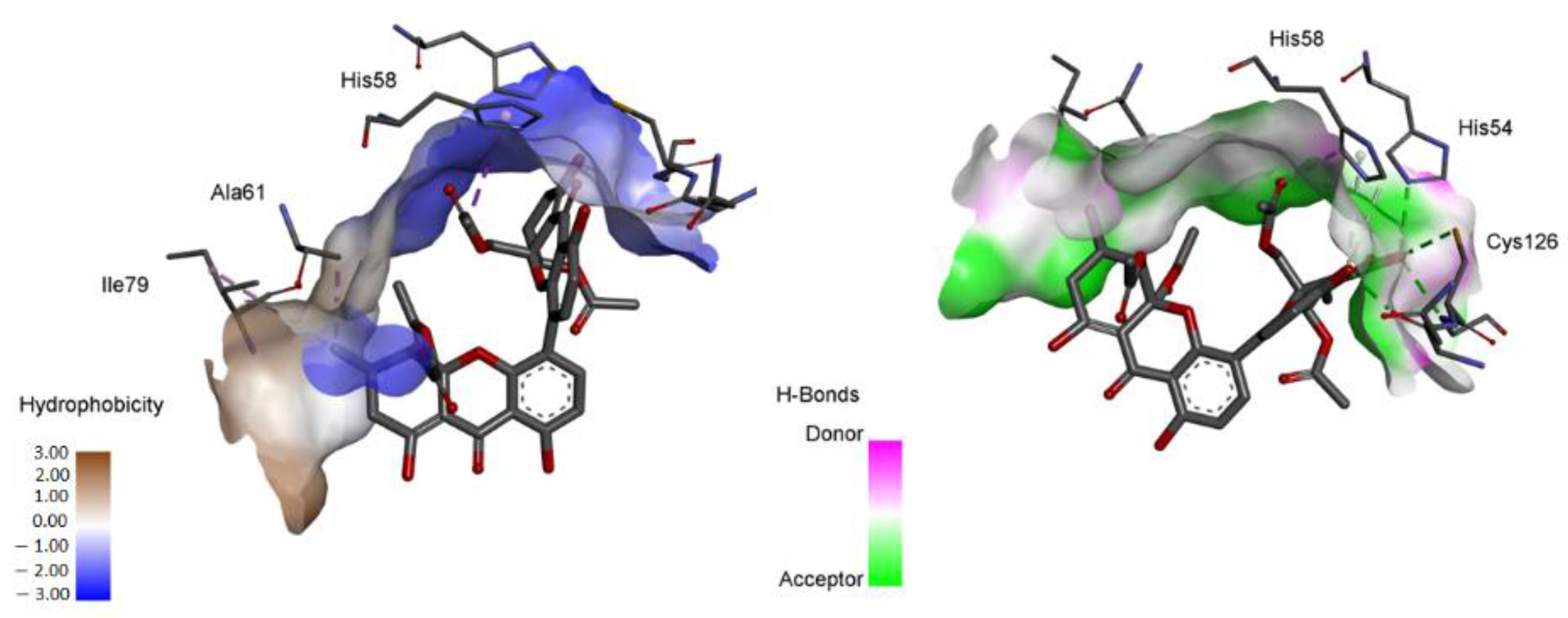
| Compound | MIC (µg mL−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram (+) Bacteria | Gram (−) Bacteria | ||||
| Bacillus subtilis (ATCC 6633) | Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 29213) | Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922) | Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 27853) | Salmonella typhimurium (ATCC 14028) | |
| Extract MeOH-1 | (=) 156.25; (−) 39.06 | NT | (=) 312.5; (−) 78.12 | (−) 78.12 | NT |
| Extract hexane | (−) 312.5 | NT | (−) 312.50 | (−) 625 | NT |
| Extract AcOEt | (=) 312.5; (−) 39.06 | NT | (=) 1250; (−) 39.06 | (−) 312.5 | NT |
| Extract MeOH-2 | (=) 625; (−) 78.12 | NT | (=) 1250; (−) 312.5 | (−) 625 | NT |
| Phomoxanthone A | (=) 7.81 | (−) 500 | (−) 125 | (+) | (+) |
| Penicillin | (=) 7.81 | (=) 7.81 | (=) 7.81 | (=) 7.81 | (=) 7.81 |
| Vancomycin | (=) 7.81 | (=) 7.81 | (=) 7.81 | (=) 7.81 | (=) 7.81 |
| Tetracycline | (=) 7.81 | (=) 7.81 | (=) 7.81 | (=) 7.81 | (=) 7.81 |
| Compound | Peritoneal Macrophages | L. amazonensis | T. cruzi | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC50 (µg mL−1) | IC50 (µg mL−1) | SI | IC50 (µg mL−1) | SI | |
| Phomoxanthone A | 28.79 ± 1.261 | 16.38 ± 1.079 | 1.76 | 28.61 ± 1.071 | 1.01 |
| Amphotericin B | 8.505 ± 1.082 | 0.02476 ± 1.137 | 343.5 | - | nd |
| Benznidazole | 172.0 ± 1.214 | - | Nd | 3.459 ± 1.103 | 49.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramos, G.d.C.; Silva-Silva, J.V.; Watanabe, L.A.; Siqueira, J.E.d.S.; Almeida-Souza, F.; Calabrese, K.S.; Marinho, A.M.d.R.; Marinho, P.S.B.; Oliveira, A.S.d. Phomoxanthone A, Compound of Endophytic Fungi Paecilomyces sp. and Its Potential Antimicrobial and Antiparasitic. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101332
Ramos GdC, Silva-Silva JV, Watanabe LA, Siqueira JEdS, Almeida-Souza F, Calabrese KS, Marinho AMdR, Marinho PSB, Oliveira ASd. Phomoxanthone A, Compound of Endophytic Fungi Paecilomyces sp. and Its Potential Antimicrobial and Antiparasitic. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(10):1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101332
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamos, Gisele da Costa, João Victor Silva-Silva, Luciano Almeida Watanabe, José Edson de Sousa Siqueira, Fernando Almeida-Souza, Kátia S. Calabrese, Andrey Moacir do Rosario Marinho, Patrícia Santana Barbosa Marinho, and Aldo Sena de Oliveira. 2022. "Phomoxanthone A, Compound of Endophytic Fungi Paecilomyces sp. and Its Potential Antimicrobial and Antiparasitic" Antibiotics 11, no. 10: 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101332
APA StyleRamos, G. d. C., Silva-Silva, J. V., Watanabe, L. A., Siqueira, J. E. d. S., Almeida-Souza, F., Calabrese, K. S., Marinho, A. M. d. R., Marinho, P. S. B., & Oliveira, A. S. d. (2022). Phomoxanthone A, Compound of Endophytic Fungi Paecilomyces sp. and Its Potential Antimicrobial and Antiparasitic. Antibiotics, 11(10), 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101332