Aerosol Inhalation Delivery of Ceftriaxone in Mice: Generation Procedure, Pharmacokinetics, and Therapeutic Outcome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
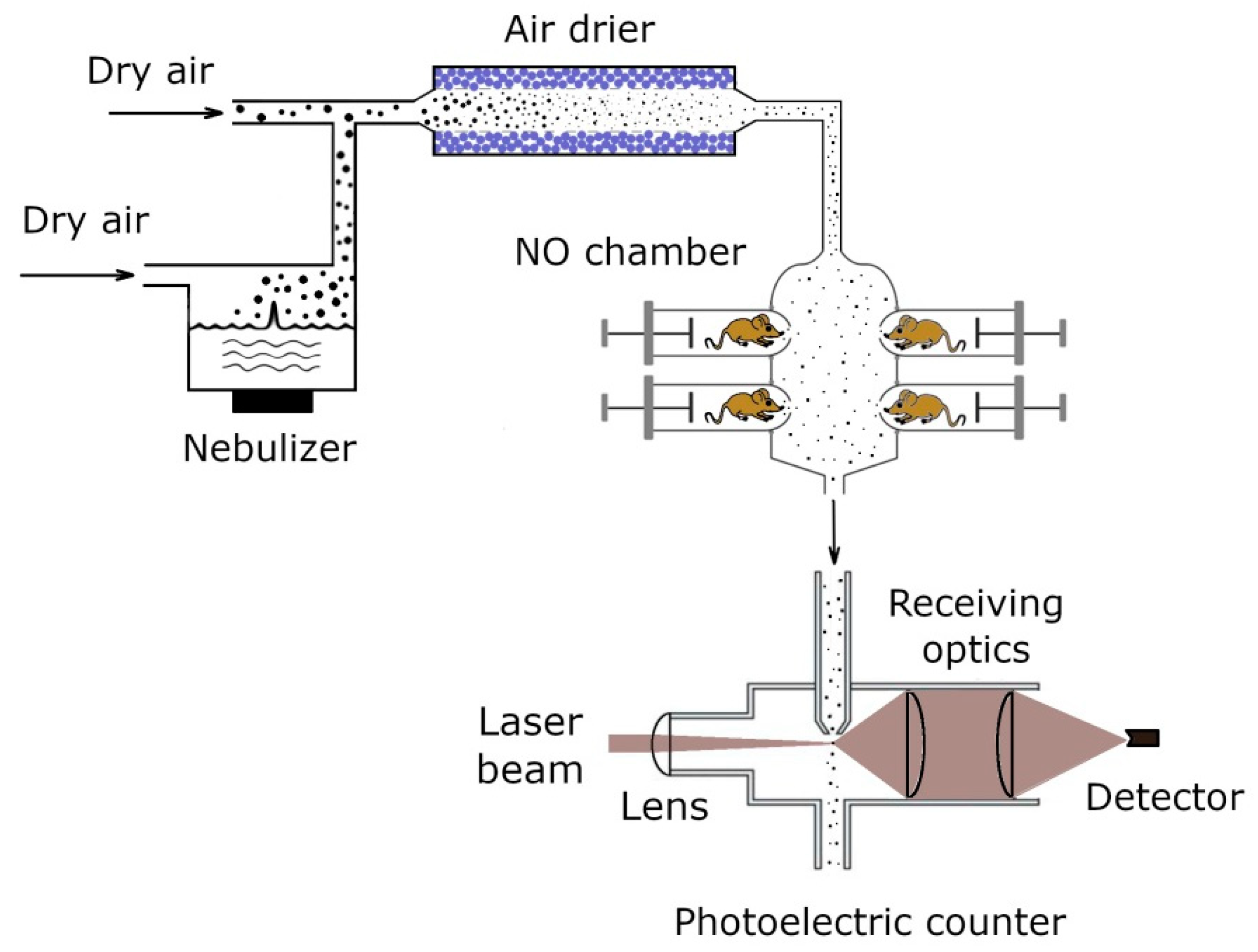
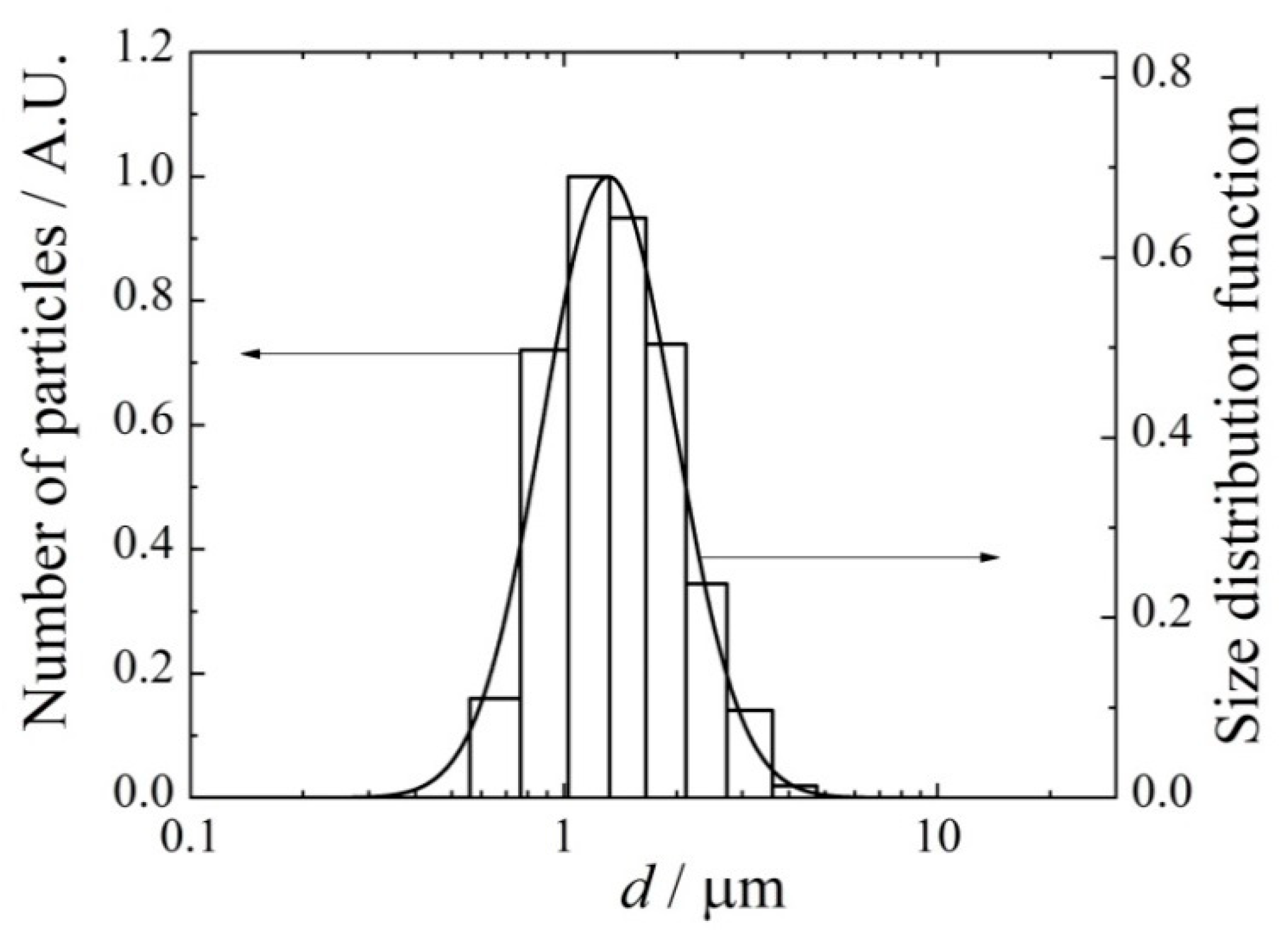
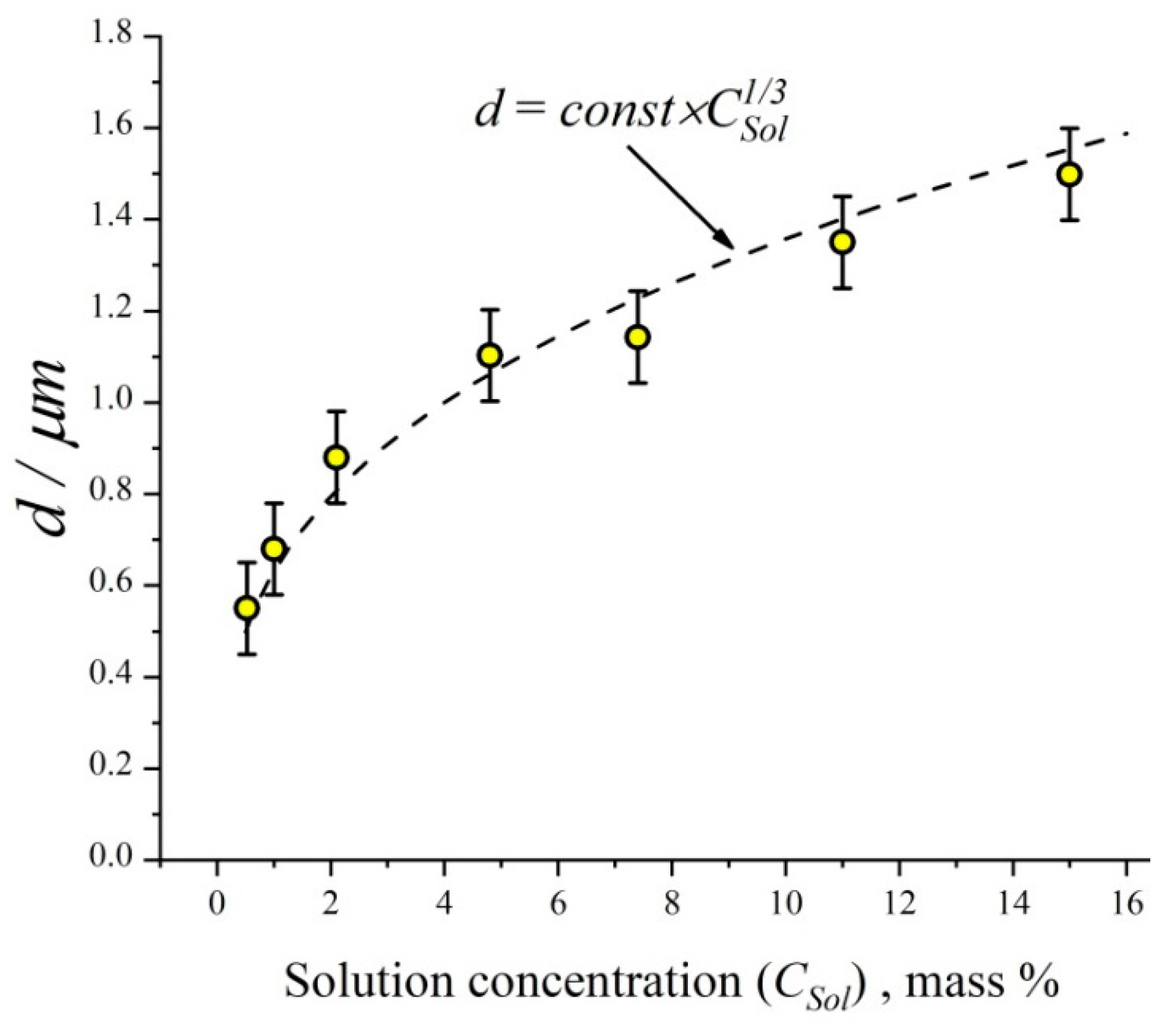
2.1. Aerosol Generation and Inhalation Equipment
2.2. Sample Preparation and Chromatographic Analysis in Pharmacokinetic Measurements
2.3. Histologic Analysis
2.4. Inhalation Dose
2.5. Antibacterial Effect Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
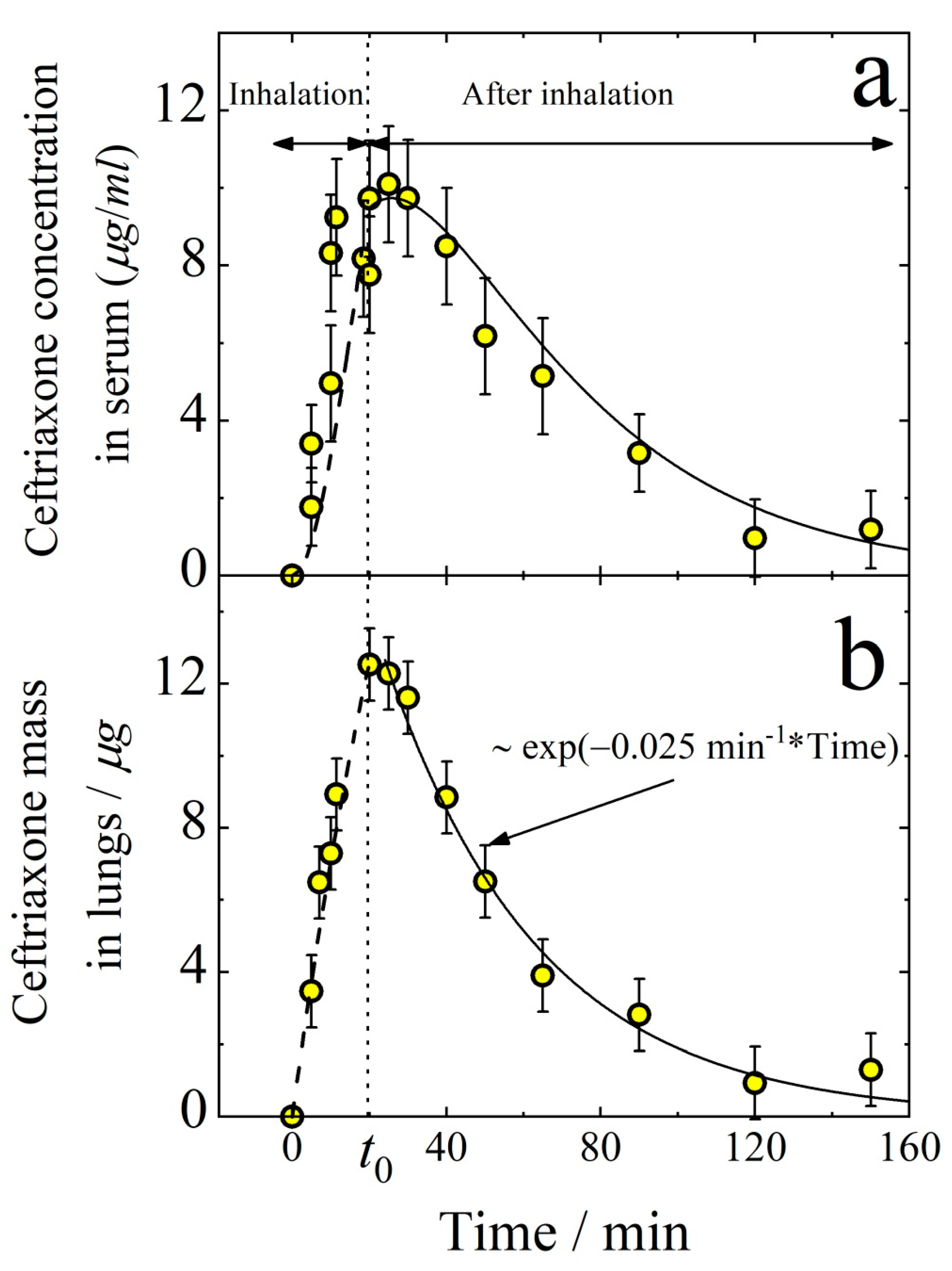
3.1. Pharmacokinetics of Aerosolized Ceftriaxone
3.2. Antibacterial Effect from Ceftriaxone Aerosol Delivery
3.2.1. Experiments with Klebsiella pneumoniae 82
3.2.2. Experiments with Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25 953
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chandel, A.; Goyal, A.K.; Ghosh, G.; Rath, G. Recent advances in aerosolised drug delivery. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douafer, H.; Andrieu, V.; Brunel, J.M. Scope and limitations on aerosol drug delivery for the treatment of infectious respiratory diseases. J. Control. Release 2020, 325, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlinski, A. Assessing New Technologies in Aerosol Medicine: Strengths and Limitations. Respir. Care 2015, 60, 833–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, J.S.; Sarasija, S. Pulmonary drug delivery strategies: A concise, systematic review. Lung India 2012, 29, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Wenzler, E.; Fraidenburg, D.R.; Scardina, T.; Danziger, L.H. Inhaled Antibiotics for Gram-Negative Respiratory Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 29, 581–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restrepo, M.I.; Keyt, H.; Reyes, L.F. Aerosolized Antibiotics. Respir. Care 2015, 60, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quon, B.S.; Goss, C.H.; Ramsey, B.W. Inhaled Antibiotics for Lower Airway Infections. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2014, 11, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabuj, M.Z.R.; Islam, N. Inhaled antibiotic-loaded polymeric nanoparticles for the management of lower respiratory tract infections. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 4005–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weers, J. Inhaled antimicrobial therapy—Barriers to effective treatment. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 85, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onischuk, A.A.; Vosel, S.V.; Borovkova, O.V.; Baklanov, A.M.; Karasev, V.V.; Di Stasio, S. Experimental study of homogeneous nucleation from the bismuth supersaturated vapor: Evaluation of the surface tension of critical nucleus. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 224506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onischuk, A.; Valiulin, S.; Vosel, S.; Karasev, V.; Zelik, V.; Baklanov, A. Surface tension of sulfur nanoparticles as determined from homogeneous nucleation experiments. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 97, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onischuk, A.A.; Tolstikova, T.G.; Sorokina, I.V.; Zhukova, N.A.; Baklanov, A.M.; Karasev, V.V.; Dultseva, G.G.; Boldyrev, V.V.; Fomin, V.M. Anti-inflammatory effect from indomethacin nanoparticles inhaled by male mice. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2008, 21, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onischuk, A.A.; Tolstikova, T.G.; Sorokina, I.V.; Zhukova, N.A.; Baklanov, A.M.; Karasev, V.V.; Borovkova, O.V.; Dultseva, G.G.; Boldyrev, V.V.; Fomin, V.M. Analgesic effect from ibuprofen nanoparticles inhaled by male mice. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2009, 22, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onischuk, A.; Tolstikova, T.; An’Kov, S.; Baklanov, A.; Valiulin, S.; Khvostov, M.; Sorokina, I.; Dultseva, G.; Zhukova, N. Ibuprofen, indomethacin and diclofenac sodium nanoaerosol: Generation, inhalation delivery and biological effects in mice and rats. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 100, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onischuk, A.A.; Tolstikova, T.G.; Baklanov, A.M.; Khvostov, M.V.; Sorokina, I.V.; Zhukov, N.A.; An’kov, S.V.; Borovkova, O.V.; Dultseva, G.G.; Boldyrev, V.V.; et al. Generation, inhalation delivery and anti-hypertensive effect of ni-soldipine nanoaerosol. J. Aerosol Sci. 2014, 78, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiulin, S.; Onischuk, A.; Baklanov, A.; Dubtsov, S.; An’Kov, S.; Tolstikova, T.; Plokhotnichenko, M.; Dultseva, G.; Mazunina, P. Excipient-free isoniazid aerosol administration in mice: Evaporation-nucleation particle generation, pulmonary delivery and body distribution. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 563, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiulin, S.V.; Onischuk, A.A.; Dubtsov, S.N.; Baklanov, A.M.; An’Kov, S.V.; Plokhotnichenko, M.E.; Tolstikova, T.G.; Dultseva, G.G.; Rusinov, V.L.; Charushin, V.N.; et al. Aerosol Inhalation Delivery of Triazavirin in Mice: Outlooks for Advanced Therapy Against Novel Viral Infections. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 110, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valiulin, S.; Onischuk, A.; Baklanov, A.; Dubtsov, S.; An’Kov, S.; Shkil, N.; Nefedova, E.; Plokhotnichenko, M.; Tolstikova, T.; Dolgov, A.; et al. Aerosol inhalation delivery of cefazolin in mice: Pharmacokinetic measurements and antibacterial effect. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 121013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elander, R.P. Industrial production of β-lactam antibiotics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 61, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 5479530, Ceftriaxone 2021. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nim.nih.gov/compound/Ceftriaxone (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- Gijsen, M.; Dreesen, E.; Van Daele, R.; Annaert, P.; Debaveye, Y.; Wauters, J.; Spriet, I. Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Target Attainment Based on Measured Versus Predicted Unbound Ceftriaxone Concentrations in Critically Ill Patients with Pneumonia: An Observational Cohort Study. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onischuk, A.A.; Baklanov, A.M.; Valiulin, S.; Moiseenko, P.P.; Mitrochenko, V.G. Aerosol diffusion battery: The retrieval of particle size distribution with the help of analytical formulas. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arms, A.D.; Travis, C.C. Reference Physiological Parameters in Pharmacokinetic Modeling; EPA Report No. EPA/600/6-88/004; Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Health and Environmental Assessment: Washington, DC, USA, 1988.
- Schleibinger, M.; Steinbach, C.L.; Töpper, C.; Kratzer, A.; Liebchen, U.; Kees, F.; Salzberger, B.; Kees, M.G. Protein binding char-acteristics and pharmacokinetics of ceftriaxone in intensive care unit patients. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 80, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
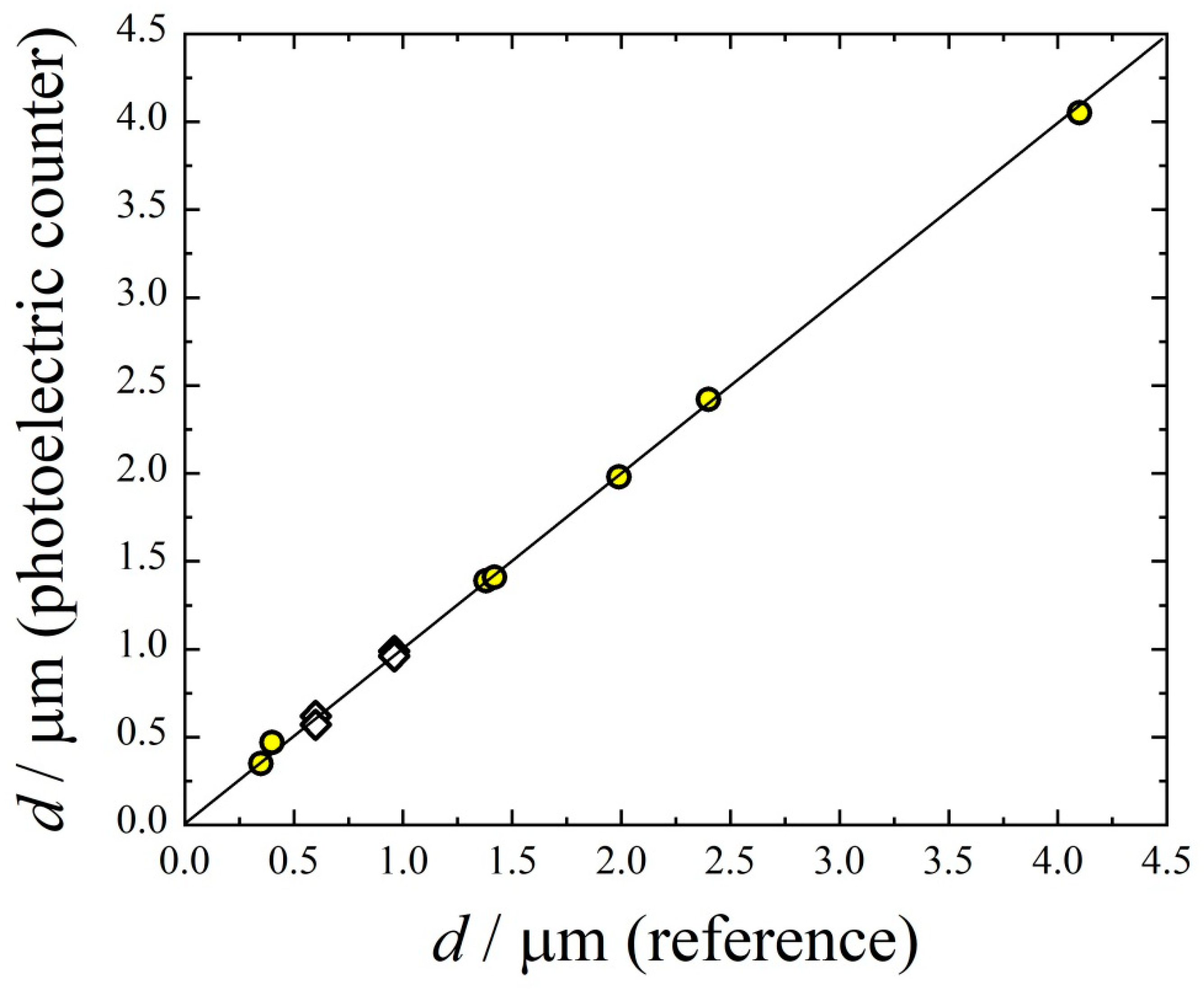
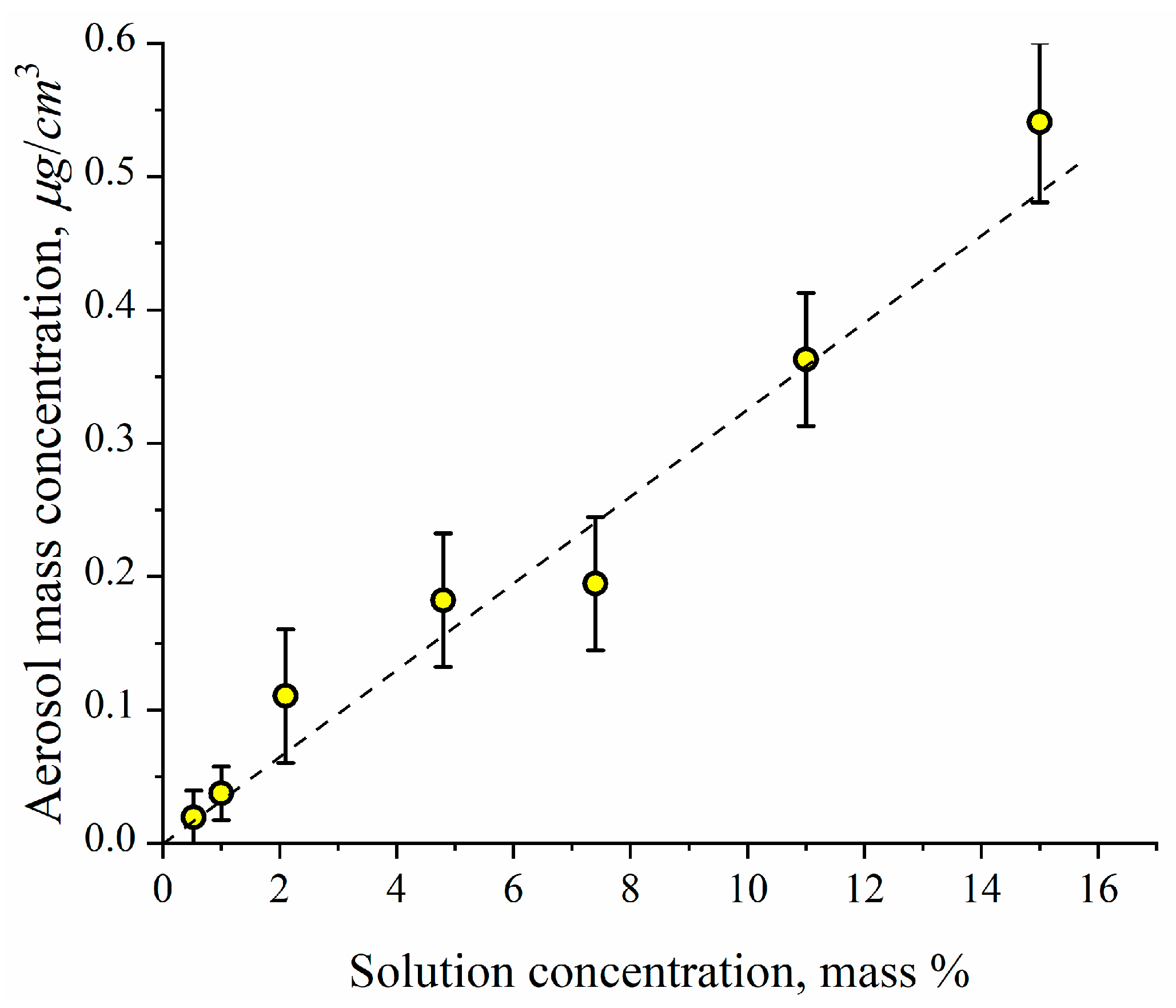
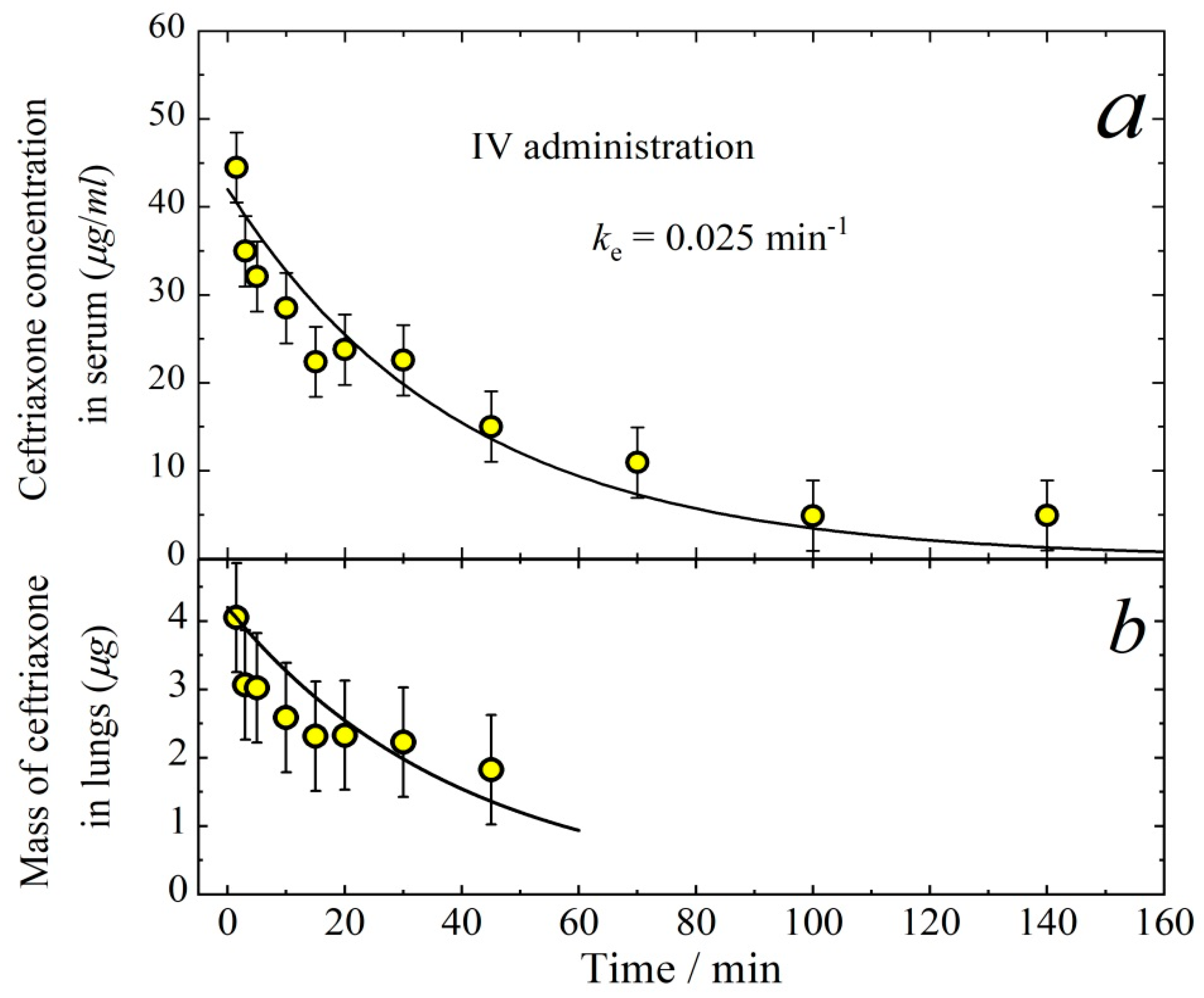
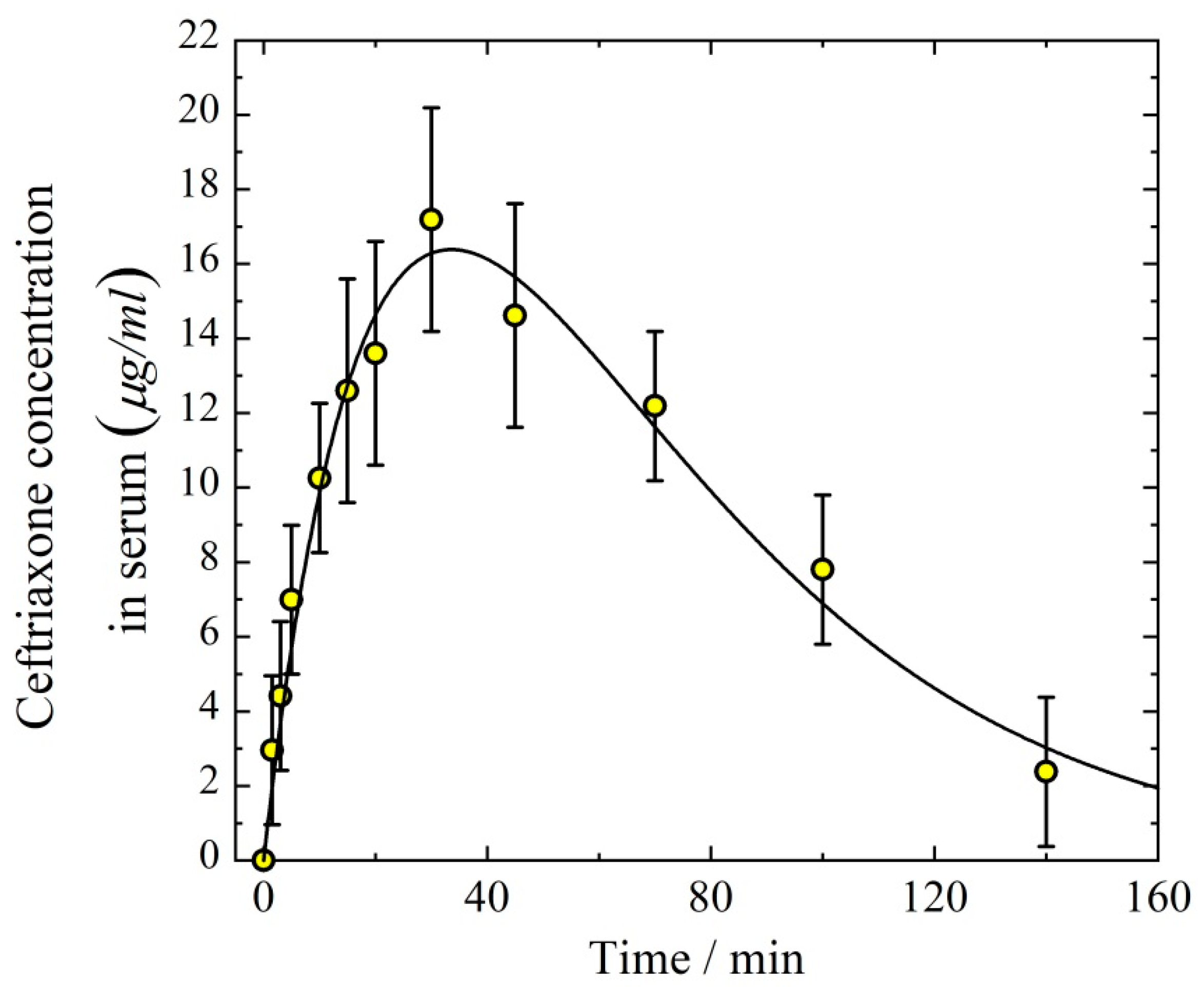
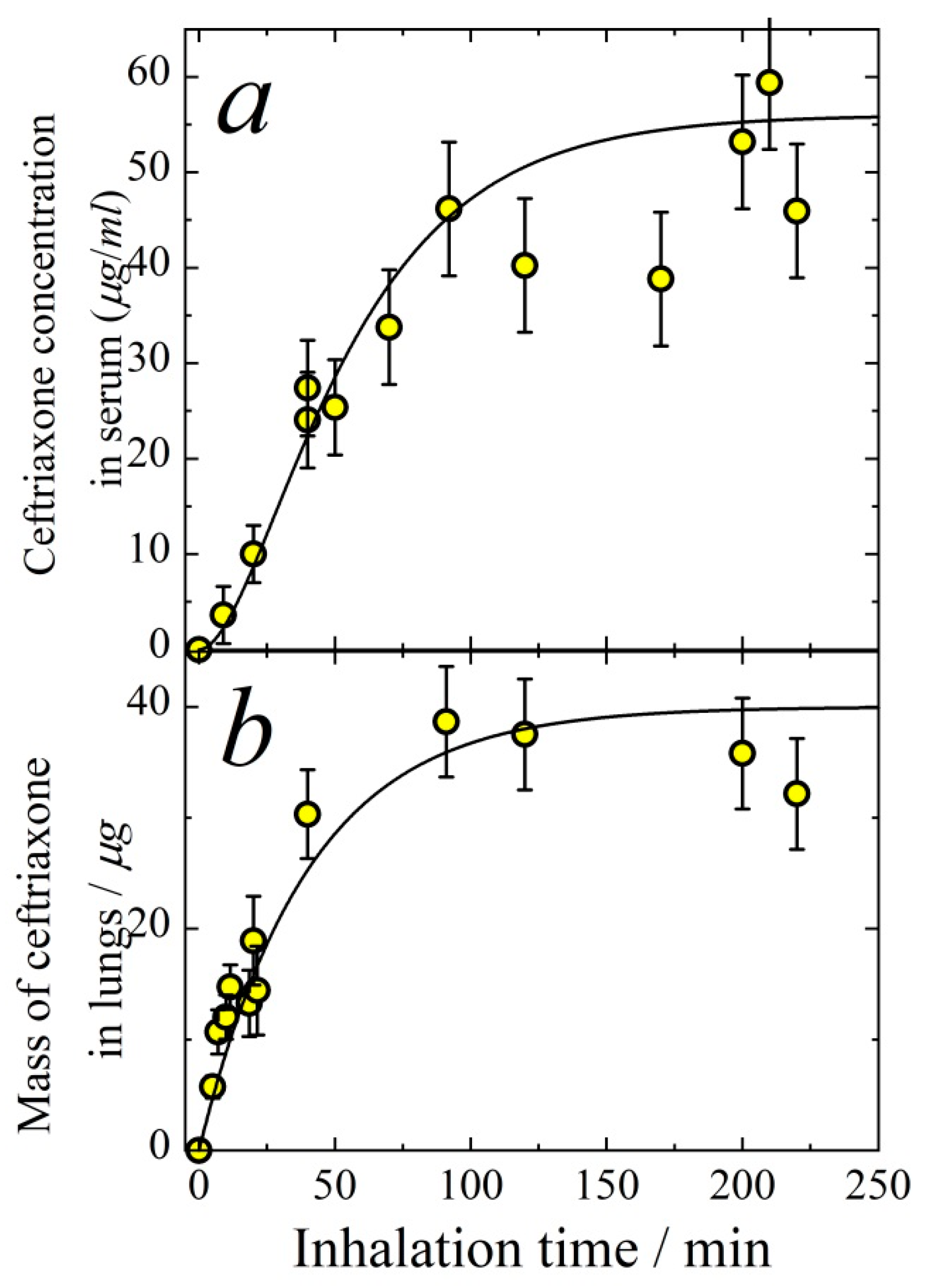
| d/μm | ITot μm/min | IET μm/min | Ilung μm/min | klung /min−1 | kresp /min−1 | ε | εlung | εET | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.26 ± 0.03 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 5.5 ± 0.5 | 4.5 ± 0.5 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 0.025 ± 0.005 | 0.050 ± 0.005 | 0.62 ± 0.05 | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 0.51 ± 0.04 |
| 0.16 ± 0.02 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 3.4 ± 0.3 | 2.8 ± 0.3 | 0.60 ± 0.05 | 0.025 ± 0.005 | 0.050 ± 0.005 | 0.62 ± 0.05 | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 0.51 ± 0.04 |
| Delivery Route | Body-Delivered Dose, mg/kg | Absorption Rate Constant, min−1 | Elimination Rate Constant ke, min−1 | AUC (Serum) μg·min/ cm3 | AUC (Lungs) μg·min | Volume of Distribution Vd, cm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aerosol inhalation | 3.1 ± 0.3 | 0.050 ± 0.005 | 0.025 ± 0.005 | 760 | 820 | 2.1 ± 0.5 |
| Intravenous | 5.0 ± 0.2 | - | 0.025 ± 0.005 | 1680 | - | 2.6 ± 0.5 |
| Intraperitoneal | 5.0 ± 0.2 | 0.03 ± 0.003 | 0.025 ± 0.005 | 1600 | - | 2.8 ± 0.5 |
| Time | Manipulation |
|---|---|
| 0 h 0 min | Infection |
| 0 h 10 min | 20 min aerosol administration |
| 2 h 20 min | 20 min aerosol administration |
| 4 h 40 min | 20 min aerosol administration |
| Time | Manipulation |
|---|---|
| 0 h 0 min | Infection |
| 0 h 10 min | Ceftriaxone administration |
| 2 h 0 min | Ceftriaxone administration |
| 4 h 0 min | Ceftriaxone administration |
| Mouse Number | Reference 2 | Aerosol | Intraperitoneal |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25,800 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 14,800 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 12,800 | 100 | 0 |
| Group | Number of Animals | 1st Day | 2nd Day | 3rd Day | 4th Day | 5–9th Days | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | D | A | D | A | D | A | D | A | D | ||
| Reference 1 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 0 |
| Reference 2 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 3 | 7 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 10 |
| Aerosol | 14 | 14 | 0 | 12 | 2 | 12 | 2 | 12 | 2 | 12 | 2 |
| IV | 14 | 14 | 0 | 12 | 2 | 11 | 3 | 11 | 3 | 11 | 3 |
| IP | 14 | 14 | 0 | 13 | 1 | 13 | 1 | 13 | 1 | 13 | 1 |
| Time | Manipulation |
|---|---|
| 0 h 0 min | Infection |
| 0 h 10 min | 20 min aerosol administration |
| 2 h 20 min | 20 min aerosol administration |
| 4 h 40 min | 20 min aerosol administration |
| Time | Manipulation |
|---|---|
| 0 h 0 min | Infection |
| 0 h 10 min | Ceftriaxone administration |
| 2 h 0 min | Ceftriaxone administration |
| 4 h 0 min | Ceftriaxone administration |
| Mouse Number | Reference 1 | Reference 2 | Aerosol | IP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 38,500 | 400 | 400 |
| 2 | 0 | 36,000 | 200 | 600 |
| 3 | 0 | 11,700 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 9600 | 0 | 0 |
| Group | Number of Animals | 1st Day | 2nd Day | 3rd Day | 4th Day | 5–9th Days | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | D | A | D | A | D | A | D | A | D | ||
| Reference 1 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| Reference 2 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 5 |
| Aerosol | 6 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| IP | 6 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| Mouse Number | Reference 2 | Aerosol | Intraperitoneal |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1100 | 100 | 0 |
| 2 | - | 200 | 0 |
| 3 | - | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | - | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valiulin, S.V.; Onischuk, A.A.; Baklanov, A.M.; An’kov, S.V.; Dubtsov, S.N.; Alekseev, A.A.; Shkil, N.N.; Nefedova, E.V.; Plokhotnichenko, M.E.; Tolstikova, T.G.; et al. Aerosol Inhalation Delivery of Ceftriaxone in Mice: Generation Procedure, Pharmacokinetics, and Therapeutic Outcome. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1305. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101305
Valiulin SV, Onischuk AA, Baklanov AM, An’kov SV, Dubtsov SN, Alekseev AA, Shkil NN, Nefedova EV, Plokhotnichenko ME, Tolstikova TG, et al. Aerosol Inhalation Delivery of Ceftriaxone in Mice: Generation Procedure, Pharmacokinetics, and Therapeutic Outcome. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(10):1305. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101305
Chicago/Turabian StyleValiulin, Sergey V., Andrei A. Onischuk, Anatoly M. Baklanov, Sergey V. An’kov, Sergey N. Dubtsov, Alexander A. Alekseev, Nikolay N. Shkil, Ekaterina V. Nefedova, Maria E. Plokhotnichenko, Tatyana G. Tolstikova, and et al. 2022. "Aerosol Inhalation Delivery of Ceftriaxone in Mice: Generation Procedure, Pharmacokinetics, and Therapeutic Outcome" Antibiotics 11, no. 10: 1305. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101305
APA StyleValiulin, S. V., Onischuk, A. A., Baklanov, A. M., An’kov, S. V., Dubtsov, S. N., Alekseev, A. A., Shkil, N. N., Nefedova, E. V., Plokhotnichenko, M. E., Tolstikova, T. G., Dolgov, A. M., & Dultseva, G. G. (2022). Aerosol Inhalation Delivery of Ceftriaxone in Mice: Generation Procedure, Pharmacokinetics, and Therapeutic Outcome. Antibiotics, 11(10), 1305. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101305





