Exploring the Nature of the Antimicrobial Metabolites Produced by Paenibacillus ehimensis Soil Isolate MZ921932 Using a Metagenomic Nanopore Sequencing Coupled with LC-Mass Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Screening of the Antimicrobial Activities of the Recovered Bacterial Isolates
2.2. Molecular Identification
2.3. The Antimicrobial Activities of the Extracted Metabolite(s) of Paenibacillus ehimensis Isolate MZ921932
2.4. Metagenomics Analysis of the Soil Sample
2.5. Identification of Secondary Metabolite(s) Gene Clusters Paenibacillus ehimensis Isolate MZ921932
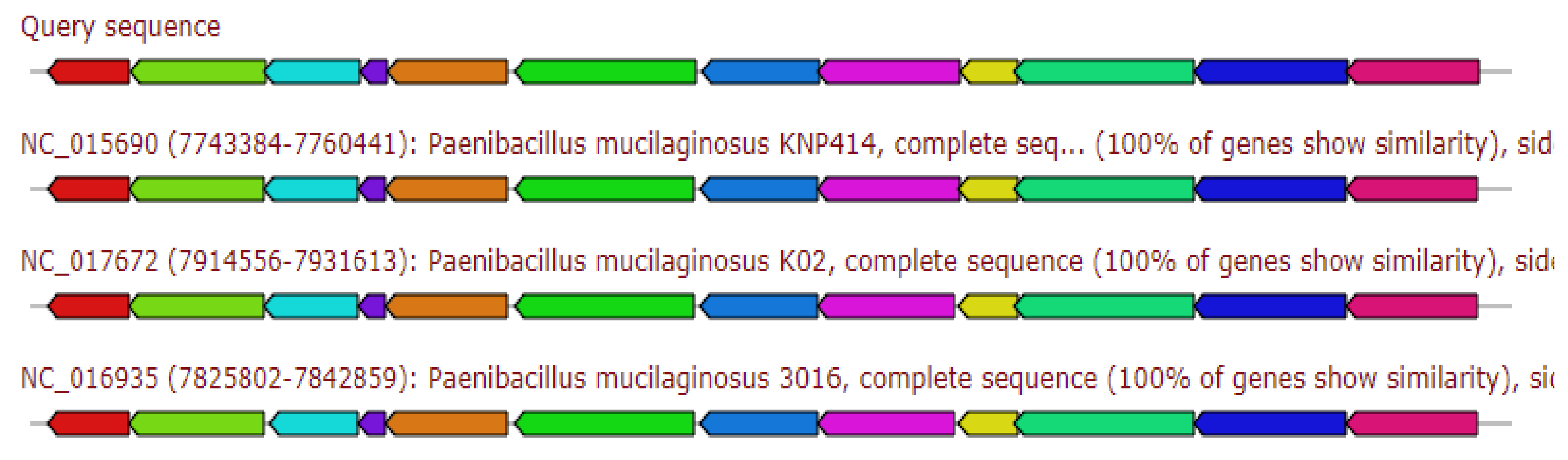
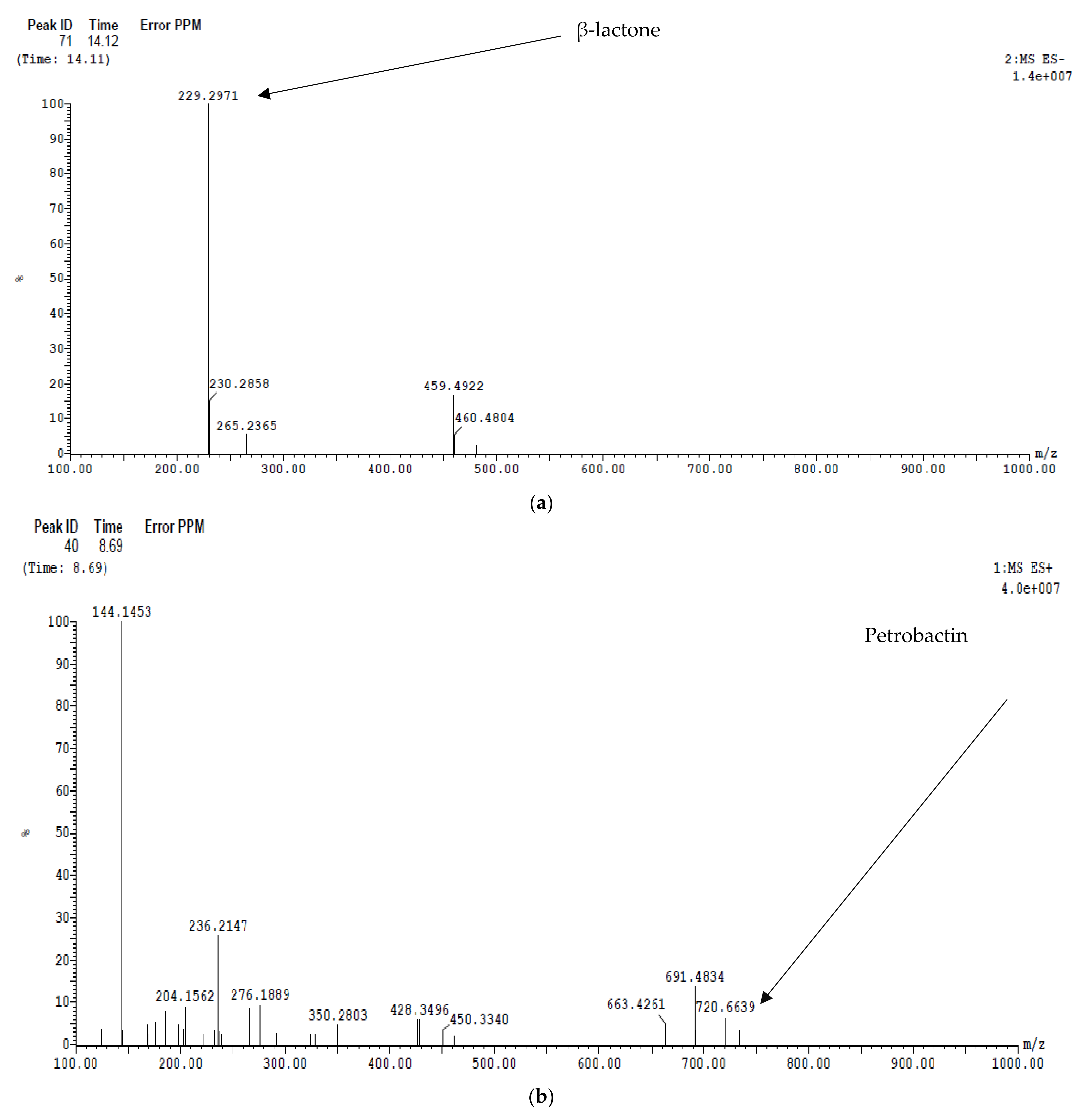
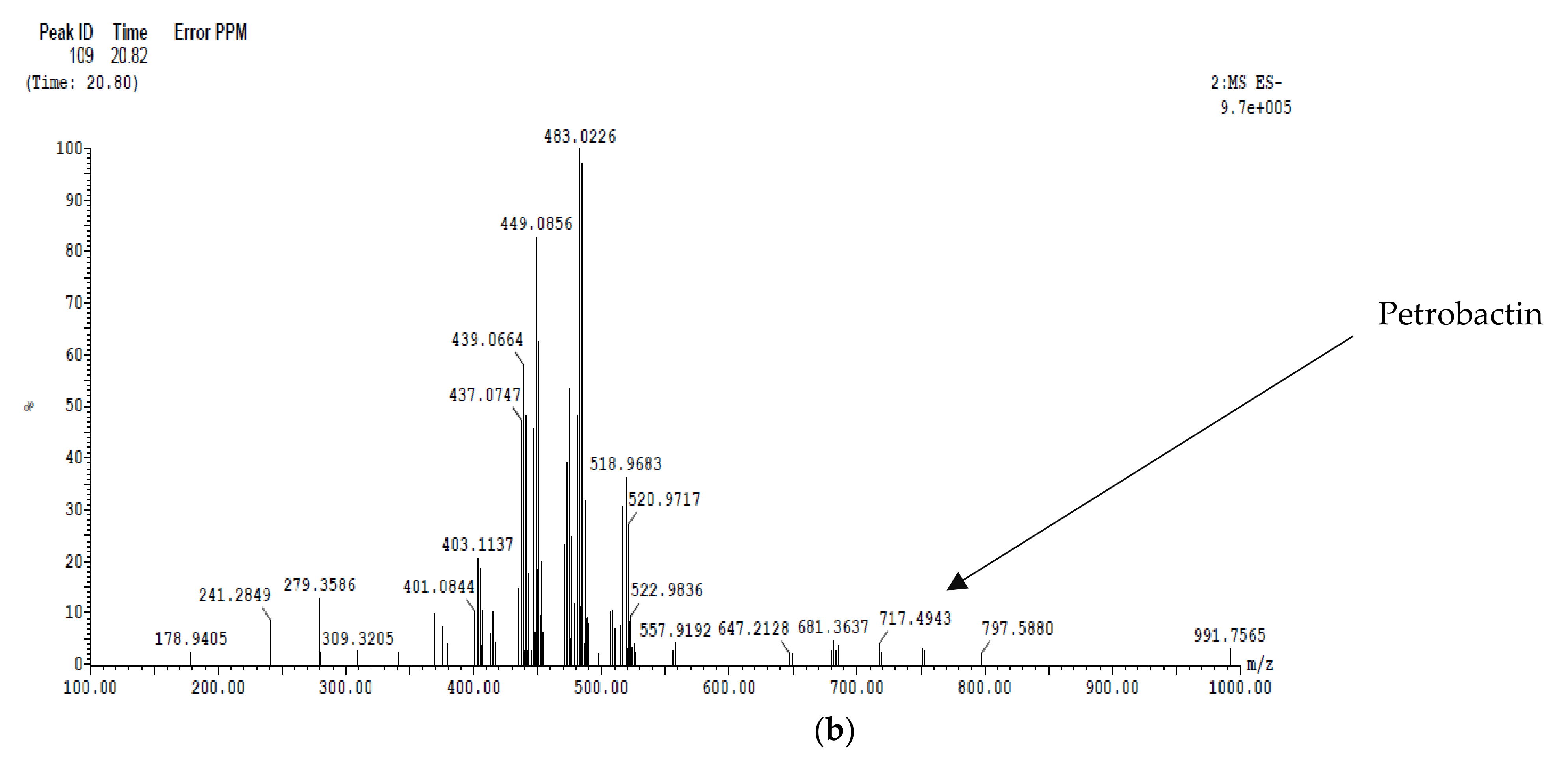
2.5.1. Siderophore Petrobactin
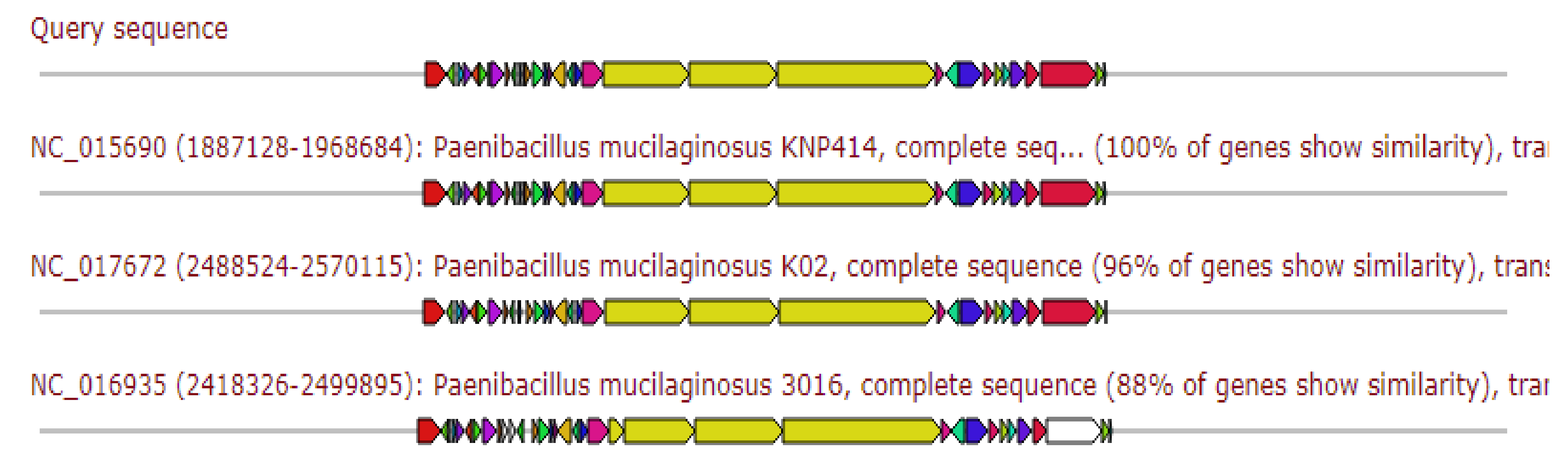
2.5.2. Traditional (Multi-)Modular Non-Ribosomal Peptide Synthases
2.5.3. Hybrid Region: Beta-Lactone Containing Protease Inhibitor and Non-Ribosomal Peptide Fragment
2.5.4. Traditional (Multi-)Modular Non-Ribosomal Peptide Synthases
2.5.5. Hybrid Region: Thioamide-Containing Non-Ribosomal Peptide and Traditional (Multi-)Modular Non-Ribosomal Peptide Synthases
2.5.6. Terpene
2.5.7. Trans-AT Polyketide
2.5.8. Hybrid Region: Thioamide-Containing Non-Ribosomal Peptide and Traditional (Multi-)Modular Non-Ribosomal Peptide Synthases
2.6. Characterization of the Antimicrobial Metabolite(s)
2.6.1. TLC Analysis
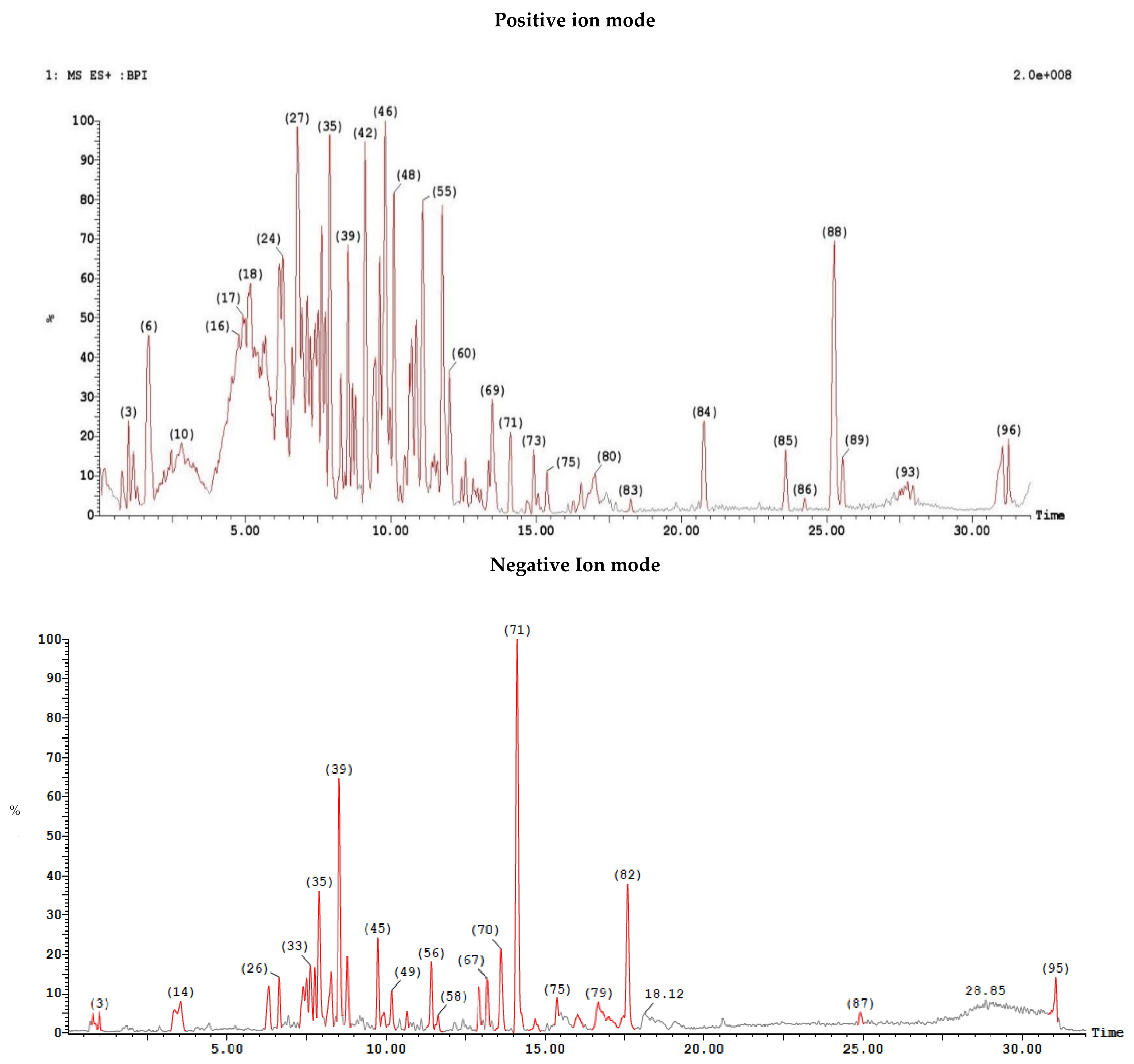
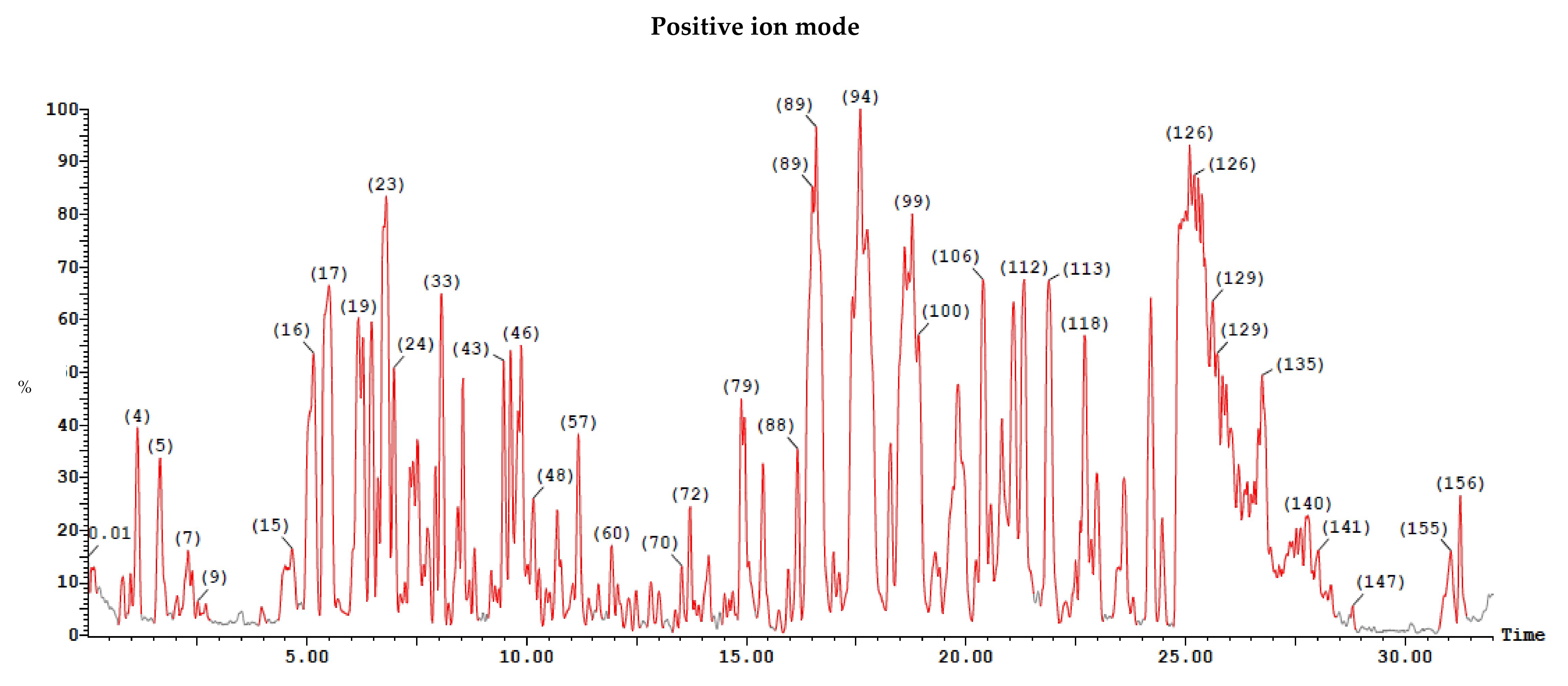
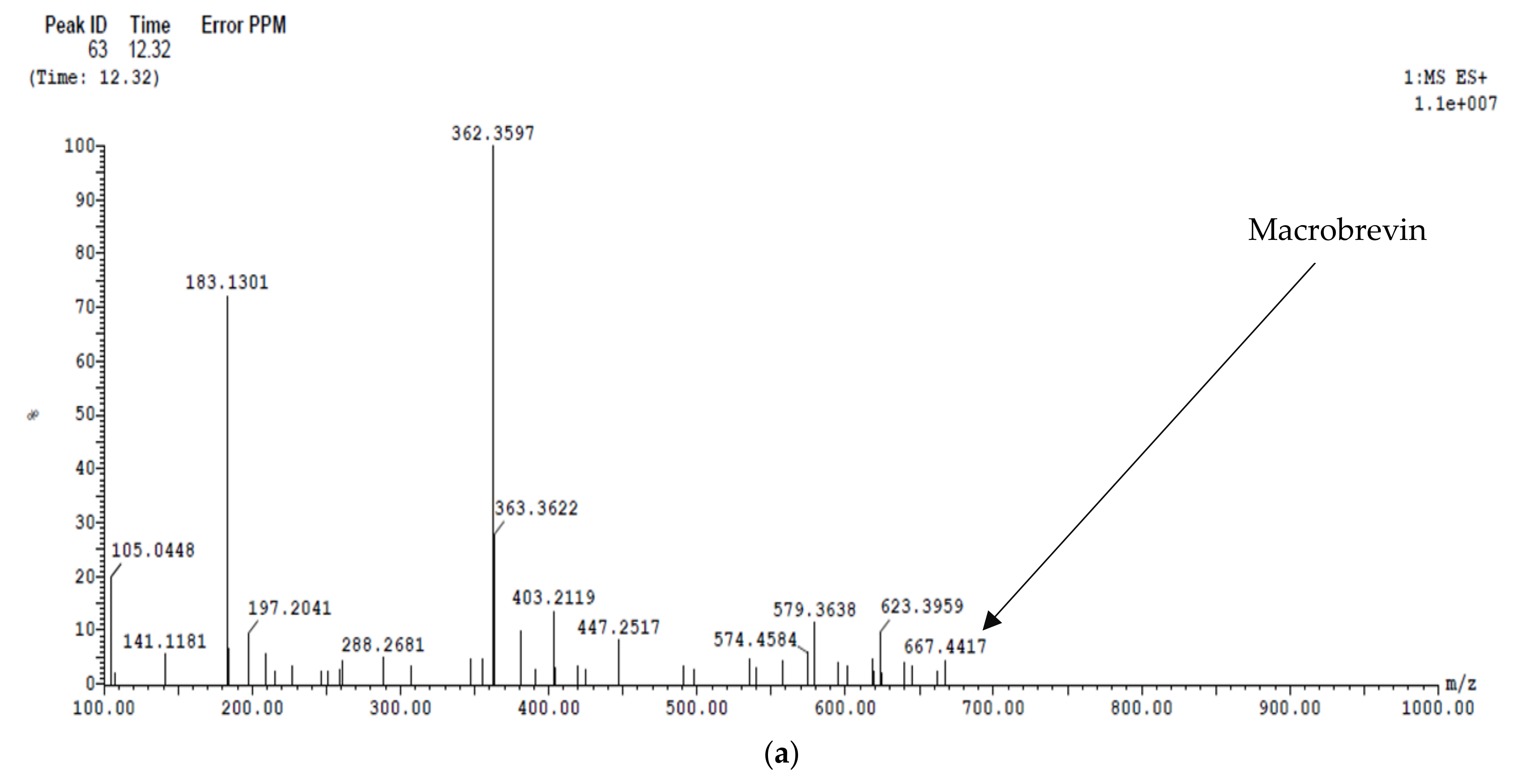
2.6.2. LC/MS Analysis
Ethyl Acetate Extract
Dichloromethane Extract
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation and Characterization
4.2. Preliminary Screening
4.3. 16 S Ribosomal RNA Gene
4.4. Production of the Antimicrobial Metabolite(s) in Shake Flasks
Seed Culture Preparation and Growth Conditions
4.5. Purification of the Antimicrobial Metabolite(s)
4.6. In Vitro Testing of the Antimicrobial Activities of the Extracted Metabolite(s)
4.7. Metagenomics Analysis of the Soil Samples
4.7.1. DNA Extraction and Quantification
4.7.2. Library Construction
4.7.3. Sequencing and Data Analysis
4.7.4. Genome Sequencing Aligning and Analysis
4.8. Characterization of the Antimicrobial Metabolite(s)
4.8.1. Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) Analysis
4.8.2. Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectroscopy (LC/MS) Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, T. Antibiotics from soil bacteria. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2000, 7, 189–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatz, A.; Bugle, E.; Waksman, S.A. Streptomycin, a Substance Exhibiting Antibiotic Activity Against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria. SEBM 1944, 55, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotchkiss, R.D.; Dubos, R.J. The isolation of bactericidal substances from cultures of Bacillus brevis. J. Biol. Chem. 1941, 141, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltz, R.H.J.M. Antimicrobials from Actinomycetas: Back to the future. Mecrobe 2007, 2, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, L.; Baltz, R.H. Natural product discovery: Past, present, and future. J. Ind. Microbiol. 2016, 43, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mülner, P.; Schwarz, E.; Dietel, K.; Herfort, S.; Jähne, J.; Lasch, P.; Cernava, T.; Berg, G.; Vater, J.J.P. Fusaricidins, Polymyxins and Volatiles Produced by Paenibacillus polymyxa Strains DSM 32871 and M1. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ash, C.; Priest, F.G.; Collins, M.D. Molecular identification of rRNA group 3 bacilli (Ash, Farrow, Wallbanks and Collins) using a PCR probe test. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1993, 64, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Shi, H.; Du, Z.; Wang, T.; Liu, X.; Chen, S. Comparative genomic and functional analysis reveal conservation of plant growth promoting traits in Paenibacillus polymyxa and its closely related species. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, E.N.; MacDonald, J.; Liu, L.; Richman, A.; Yuan, Z.-C.; Factories, M.C. Current knowledge and perspectives of Paenibacillus: A review. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naing, K.W.; Anees, M.; Kim, S.J.; Nam, Y.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, K.Y. Characterization of antifungal activity of Paenibacillus ehimensis KWN38 against soilborne phytopathogenic fungi belonging to various taxonomic groups. Ann. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Chhatpar, H.S. Purification and characterization of chitinase from Paenibacillus sp. D1. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 164, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piuri, M.; Sanchez-Rivas, C.; Ruzal, S. A novel antimicrobial activity of a Paenibacillus polymyxa strain isolated from regional fermented sausages. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 27, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Land, M.; Hauser, L.; Jun, S.-R.; Nookaew, I.; Leuze, M.R.; Ahn, T.-H.; Karpinets, T.; Lund, O.; Kora, G.; Wassenaar, T.; et al. Insights from 20 years of bacterial genome sequencing. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2015, 15, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hover, B.M.; Kim, S.-H.; Katz, M.; Charlop-Powers, Z.; Owen, J.G.; Ternei, M.A.; Maniko, J.; Estrela, A.B.; Molina, H.; Park, S.; et al. Culture-independent discovery of the malacidins as calcium-dependent antibiotics with activity against multidrug-resistant Gram-positive pathogens. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltokhy, M.A.; Saad, B.T.; Eltayeb, W.N.; El-Ansary, M.R.; Aboshanab, K.M.; Ashour, M.S.E. A Metagenomic Nanopore Sequence Analysis Combined with Conventional Screening and Spectroscopic Methods for Deciphering the Antimicrobial Metabolites Produced by Alcaligenes faecalis Soil Isolate MZ921504. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchings, M.I.; Truman, A.W.; Wilkinson, B. Antibiotics: Past, present and future. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2019, 51, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.C.; Mori, T.; Rückert, C.; Uria, A.R.; Helf, M.; Takada, K.; Gernert, C.; Steffens, U.A.E.; Heycke, N.; Schmitt, S.; et al. An environmental bacterial taxon with a large and distinct metabolic repertoire. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 506, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincke, T.; Behnken, S.; Ishida, K.; Roth, M.; Hertweck, C. Closthioamide: An unprecedented polythioamide antibiotic from the strictly anaerobic bacterium Clostridium cellulolyticum. Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 2055–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, A. Extraction and characterization of secondary metabolites produced by bacteria isolated from industrial wastewater. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 40, 101811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenupriya, J.; Thangaraj, M. Isolation and molecular characterization of bioactive secondary metabolites from Callyspongia spp. associated fungi. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2010, 3, 738–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procópio, R.E.; Silva, I.R.; Martins, M.K.; Azevedo, J.L.; Araújo, J.M. Antibiotics produced by Streptomyces. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 16, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, S.E.; Abdelaziz, N.A.; El-Housseiny, G.S.; Aboshanab, K.M. Octadecyl 3-(3, 5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) propanoate, an antifungal metabolite of Alcaligenes faecalis strain MT332429 optimized through response surface methodology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechol. 2020, 104, 10755–10768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, S.E.; El-Housseiny, G.S.; Abdelaziz, N.A.; El-Ansary, M.R.; Aboshanab, K.M. Optimized Production of the Allylamine Antifungal “Terbinafine” by Lysinibacillus Isolate MK212927 Using Response Surface Methodology. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, M.; Li, J.; Ross, A.C.; Vederas, J.C.; Jensen, S.E. Paenibacillus polymyxa PKB1 produces variants of polymyxin B-type antibiotics. Chem. Biol. 2011, 18, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aw, Y.-K.; Ong, K.-S.; Lee, L.-H.; Cheow, Y.-L.; Yule, C.M.; Lee, S. Newly isolated Paenibacillus tyrfis sp. nov., from Malaysian tropical peat swamp soil with broad spectrum antimicrobial activity. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.-C.; Shen, X.-B.; Ding, R.; Qian, C.-D.; Fang, H.-H.; Li, O. Isolation and partial characterization of antibiotics produced by Paenibacillus elgii B69. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 310, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Stern, N.J.; Svetoch, E.A.; Eruslanov, B.V.; Kovalev, Y.N.; Volodina, L.I.; Perelygin, V.V.; Mitsevich, E.V.; Mitsevich, I.P.; Levchuk, V.P. Paenibacillus polymyxa purified bacteriocin to control Campylobacter jejuni in chickens. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 1450–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetoch, E.A.; Stern, N.J.; Eruslanov, B.V.; Kovalev, Y.N.; Volodina, L.I.; Perelygin, V.V.; Mitsevich, E.V.; Mitsevich, I.P.; Pokhilenko, V.D.; Borzenkov, V.N. Isolation of Bacillus circulans and Paenibacillus polymyxa strains inhibitory to Campylobacter jejuni and characterization of associated bacteriocins. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Kisla, D.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, C.; Green-Church, K.B.; Yousef, A.E. Isolation and identification of a Paenibacillus polymyxa strain that coproduces a novel lantibiotic and polymyxin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baindara, P.; Chaudhry, V.; Mittal, G.; Liao, L.M.; Matos, C.O.; Khatri, N.; Franco, O.L.; Patil, P.B.; Korpole, S. Characterization of the antimicrobial peptide penisin, a class Ia novel lantibiotic from Paenibacillus sp. strain A3. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiddaman, P.; Rossall, S. Effect of substrate on the production of antifungal volatiles from Bacillus subtilis. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1994, 76, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouseoud, M.; Maachi, R.; Amrane, A.; Boudergua, S.; Nabi, A.J.D. Evaluation of different carbon and nitrogen sources in production of biosurfactant by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Desalination 2008, 223, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waschulin, V.; Borsetto, C.; James, R.; Newsham, K.K.; Donadio, S.; Corre, C.; Wellington, E. Biosynthetic potential of uncultured Antarctic soil bacteria revealed through long-read metagenomic sequencing. ISME J. 2021, 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priya, G.; Lau, N.-S.; Furusawa, G.; Dinesh, B.; Foong, S.Y.; Amirul, A.-A.A. Metagenomic insights into the phylogenetic and functional profiles of soil microbiome from a managed mangrove in Malaysia. Agri Gene 2018, 9, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swayambhu, G.; Bruno, M.; Gulick, A.M.; Pfeifer, B. Siderophore natural products as pharmaceutical agents. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 69, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillotson, G.S. Trojan Horse Antibiotics–A Novel Way to Circumvent Gram-Negative Bacterial Resistance? Infect. Dis. 2016, 9, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jangra, M.; Kaur, M.; Tambat, R.; Rana, R.; Maurya, S.K.; Khatri, N.; Ghafur, A.; Nandanwar, H. Tridecaptin M, a new variant discovered in mud bacterium, shows activity against colistin-and extremely drug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00338-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, S.; Findlay, B.; Bakhtiary, A.; Acedo, J.; Rodriguez-Lopez, E.M.; Mercier, P.; Vederas, J.C. Antimicrobial lipopeptide tridecaptin A1 selectively binds to Gram-negative lipid II. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11561–11566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.L.; Wackett, L.P. Rings of Power: Enzymatic Routes to β-Lactones. In Comprehensive Natural Products III: Chemistry and Biology, Enzymes and Enzyme Mechanisms; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 323–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Liu, X.; Zhou, X.; Guo, J.; Truong, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Chen, Z. Unusual biosynthesis and structure of locillomycins from Bacillus subtilis 916. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 6601–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezadi, F.; Ardebili, A.; Mirnejad, R. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing for polymyxins: Challenges, issues, and recommendations. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01390-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallucci, M.N.; Oliva, M.; Casero, C.; Dambolena, J.; Luna, A.; Zygadlo, J.; Demo, M.J.F. Antimicrobial combined action of terpenes against the food—Borne microorganisms Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus. Flavour Fragr. J. 2009, 24, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahizan, N.A.; Yang, S.-K.; Moo, C.-L.; Song, A.A.-L.; Chong, C.-M.; Chong, C.-W.; Abushelaibi, A.; Lim, S.-H.E.; Lai, K.-S. Terpene derivatives as a potential agent against antimicrobial resistance (AMR) pathogens. Molecules 2019, 24, 2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertsen, H.L.; Musiol-Kroll, E.M. Actinomycete-derived polyketides as a source of antibiotics and lead structures for the development of new antimicrobial drugs. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pranav, P.S.; Mahalakshmi, B.; Sivakumar, R.; Karthikeyan, R.; Rajendhran, J. Whole-Genome Sequence Analysis of Paenibacillus alvei JR949 Revealed Biosynthetic Gene Clusters Coding for Novel Antimicrobials. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 1168–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Song, C.; Li, Z.; Kuipers, O.P. Antimicrobial activity screening of rhizosphere soil bacteria from tomato and genome-based analysis of their antimicrobial biosynthetic potential. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.; Choi, S.-K.; Ryu, C.-M.; Park, S.-H. Chronicle of a soil bacterium: Paenibacillus polymyxa E681 as a tiny guardian of plant and human health. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.R.; Jadeja, V.J. Isolation of actinomycetes: A complete approach. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 606–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, L.S.H. Isolation, characterization and identification of actinomycetes from agriculture soils at Semongok, Sarawak. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 3697–3702. [Google Scholar]
- Agadagba, S.K.; Bash, E.; Chitte, R.; Deshmukh, S.; Kanekar, P.; Chutipongtanate, S. Isolation of Actinomycetes from soil. J. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 4, 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, E.I.; Yavuz, M.; Kizil, M. Molecular characterization of rhizospheric soil streptomycetes isolated from indigenous Turkish plants and their antimicrobial activity. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elston, H.R.; Baudo, J.A.; Stanek, J.P.; Schaab, M. Multi-biochemical test system for distinguishing enteric and other gram-negative bacilli. Appl. Microbiol. 1971, 22, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Elela, G.M.; Ibrahim, H.A.; Hassan, S.W.; Abd-Elnaby, H.; El-Toukhy, N. Alkaline protease production by alkaliphilic marine bacteria isolated from Marsa-Matrouh (Egypt) with special emphasis on Bacillus cereus purified protease. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 4631–4642. [Google Scholar]
- Arasu, M.V.; Duraipandiyan, V.; Agastian, P.; Ignacimuthu, S. In vitro antimicrobial activity of Streptomyces spp. ERI-3 isolated from Western Ghats rock soil (India). J. Mycol. Méd. 2009, 19, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Qasim, M.; Begum, F.; Begum, F.; Rahman, H. Isolation and molecular identification of Bacillus safensis (MK-12.1) exhibiting broad-spectrum antibacterial activity against multi-drug resistant isolates. J. Bacteriol. Mycol. Open Access 2021, 9, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, S.K.; Ahmad, P.; Keerthana, S.S.S.; Cressida, P.J.; Moorthy, I.G.; Suresh, R. Extraction and purification of an antimicrobial bioactive element from lichen associated Streptomyces olivaceus LEP7 against wound inhabiting microbial pathogens. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2020, 32, 2009–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, R.; Jadeja, V. Isolation, characterization and chromatography based purification of antibacterial compound isolated from rare endophytic actinomycetes Micrococcus yunnanensis. J. Pharm. Anal. 2017, 7, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvin, J.; Shanmughapriya, S.; Gandhimathi, R.; Kiran, G.S.; Ravji, T.R.; Natarajaseenivasan, K.; Hema, T.A. Optimization and production of novel antimicrobial agents from sponge associated marine actinomycetes Nocardiopsis dassonvillei MAD08. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 83, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozzein, W.N.; Rabie, W.; Ali, M.I.A. Screening the Egyptian desert actinomycetes as candidates for new antimicrobial compounds and identification of a new desert Streptomyces strain. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 2295–2301. [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson, N.D.; Street, T.L.; Foster, D.; Swann, J.; Atkins, B.L.; Brent, A.J.; McNally, M.A.; Oakley, S.; Taylor, A.; Peto, T.E.A.; et al. Real-time analysis of nanopore-based metagenomic sequencing from infected orthopaedic devices. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapley, A.; Tanksale, H.; Sagarkar, S.; Prasad, A.; Kumar, R.A.; Sharma, N.; Qureshi, A.; Purohit, H.J. Antimicrobial activity of Alcaligenes sp. HPC 1271 against multidrug resistant bacteria. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2016, 16, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawawisit, K.; Bhoopong, P.; Phupong, W.; Lertcanawanichakul, M. 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenol, the bioactive compound produced by Streptomyces sp. KB1. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 7–12. [Google Scholar]








| Isolate Code | Gram Positive Test Organisms | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SE1 | SE2 | SE3 | VRSA1 | VRSA2 | VRSA3 | |
| SP1 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| SP2 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| SP3 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Isolate Code | Gram Negative Test Organisms | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | EC1 | EC2 | KP1 | KP2 | KP3 | |
| SP1 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| SP2 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| SP3 | - | - | - | ± | - | - |
| Isolate Code | Candida spp. Test Organisms | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA1 | CA2 | CA3 | CS1 | CS2 | CS3 | |
| SP1 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| SP2 | - | - | + | + | + | + |
| SP3 | ± | - | - | ± | - | - |
| Test Organisms | Mean Zone of Inhibition (mm) ± SD | |
|---|---|---|
| Dichloromethane Extract | Ethyl Acetate Extract | |
| S. aureus ATCC 25293 | 19 ± 1.0 | 13 ± 0.5 |
| VRSA2 | 15 ± 0.5 | 13 ± 1.0 |
| KP1 | 20 ± 1.0 | 11 ± 1.0 |
| KP2 | 14 ± 1.0 | 14 ± 0.5 |
| EC1 | 13 ± 0.5 | 13 ± 0.5 |
| EC2 | 14 ± 0.5 | 13 ± 0.5 |
| C. albicans ATCC 10231 | 11 ± 0.5 | 14 ± 1.0 |
| CA1 | 11 ± 1.0 | - |
| Gram-Positive | Gram-Negative | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Isolate Code | Resistance Pattern | Clinical Isolate Code | Resistance Pattern |
| SE1, SE2, SE3 | CLI, CN, FOX, CIP | KP1 | AMC, ATM, CTX, CAZ, CRO, FEP, CIP, SXT, TET, IMP, ETP, DOR, CT, PB, FF, RA, CN |
| VRSA1 | VAN, FOX | KP2 | AK, AMC, ATM, CTX, CAZ, CRO, FEP, CIP, SXT, TET, IMP, ETP, DOR, CT, FF, RA, CN |
| VRSA2, VSRA3 | VAN, CLI, CN, FOX, CIP | KP3 | AK, AMC, ATM, CTX, CAZ, CRO, FEP, CIP, SXT, TET, IMP, ETP, DOR, FF, RA, CN |
| EC1 | CTX, IMP | ||
| EC2 | AK, AMC, ATM, CTX, CAZ, CRO, FEP, CIP, SXT, TET, IMP, ETP, DOR, FF, RA, | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eltokhy, M.A.; Saad, B.T.; Eltayeb, W.N.; Yahia, I.S.; Aboshanab, K.M.; Ashour, M.S.E. Exploring the Nature of the Antimicrobial Metabolites Produced by Paenibacillus ehimensis Soil Isolate MZ921932 Using a Metagenomic Nanopore Sequencing Coupled with LC-Mass Analysis. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11010012
Eltokhy MA, Saad BT, Eltayeb WN, Yahia IS, Aboshanab KM, Ashour MSE. Exploring the Nature of the Antimicrobial Metabolites Produced by Paenibacillus ehimensis Soil Isolate MZ921932 Using a Metagenomic Nanopore Sequencing Coupled with LC-Mass Analysis. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleEltokhy, Mohamed A., Bishoy T. Saad, Wafaa N. Eltayeb, Ibrahim S. Yahia, Khaled M. Aboshanab, and Mohamed S. E. Ashour. 2022. "Exploring the Nature of the Antimicrobial Metabolites Produced by Paenibacillus ehimensis Soil Isolate MZ921932 Using a Metagenomic Nanopore Sequencing Coupled with LC-Mass Analysis" Antibiotics 11, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11010012
APA StyleEltokhy, M. A., Saad, B. T., Eltayeb, W. N., Yahia, I. S., Aboshanab, K. M., & Ashour, M. S. E. (2022). Exploring the Nature of the Antimicrobial Metabolites Produced by Paenibacillus ehimensis Soil Isolate MZ921932 Using a Metagenomic Nanopore Sequencing Coupled with LC-Mass Analysis. Antibiotics, 11(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11010012







