Antibacterial Residue Excretion via Urine as an Indicator for Therapeutical Treatment Choice and Farm Waste Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Excretion of Sulfamethoxypyridazine via Urine
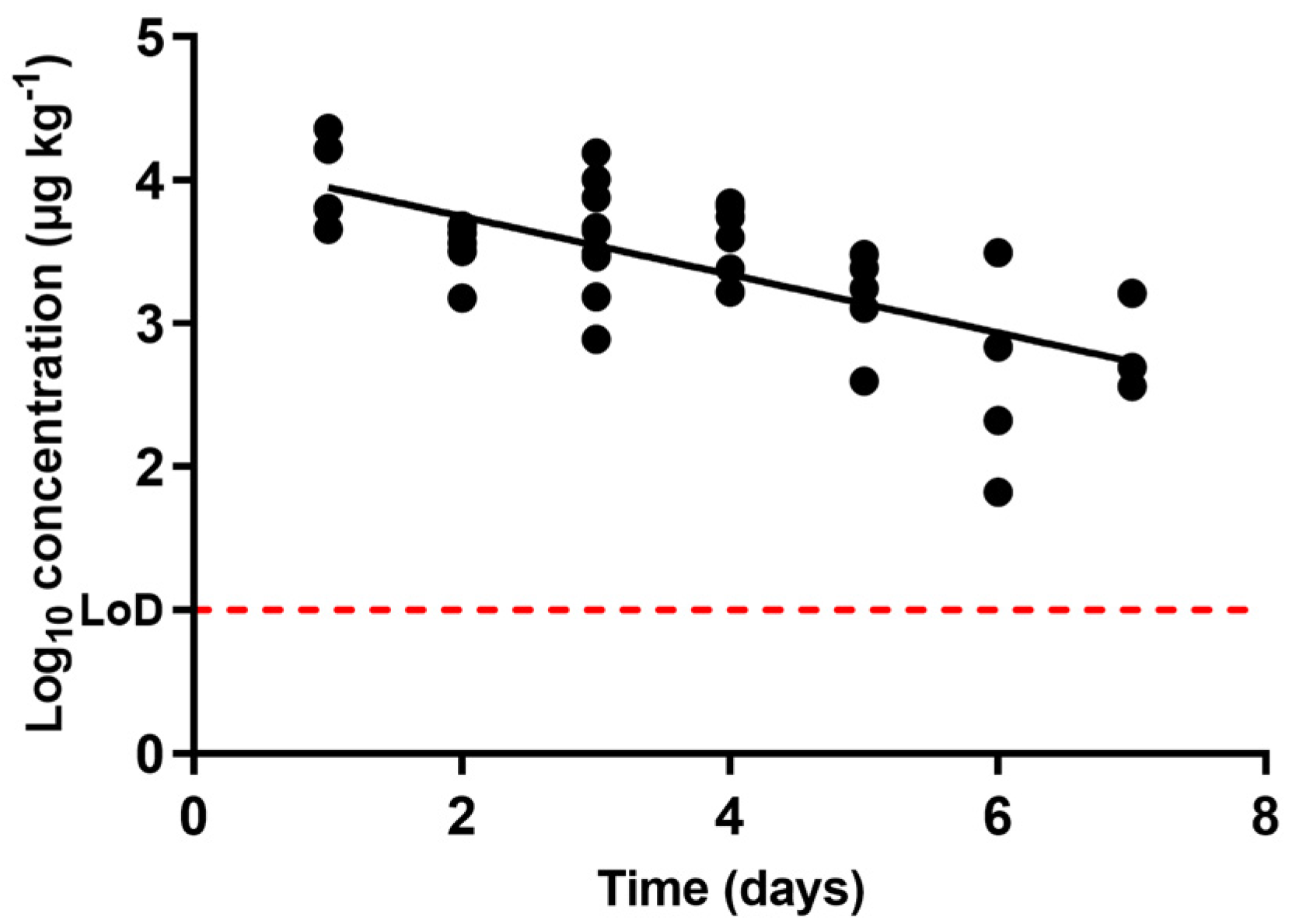
2.2. Excretion of Oxytetracycline via Urine
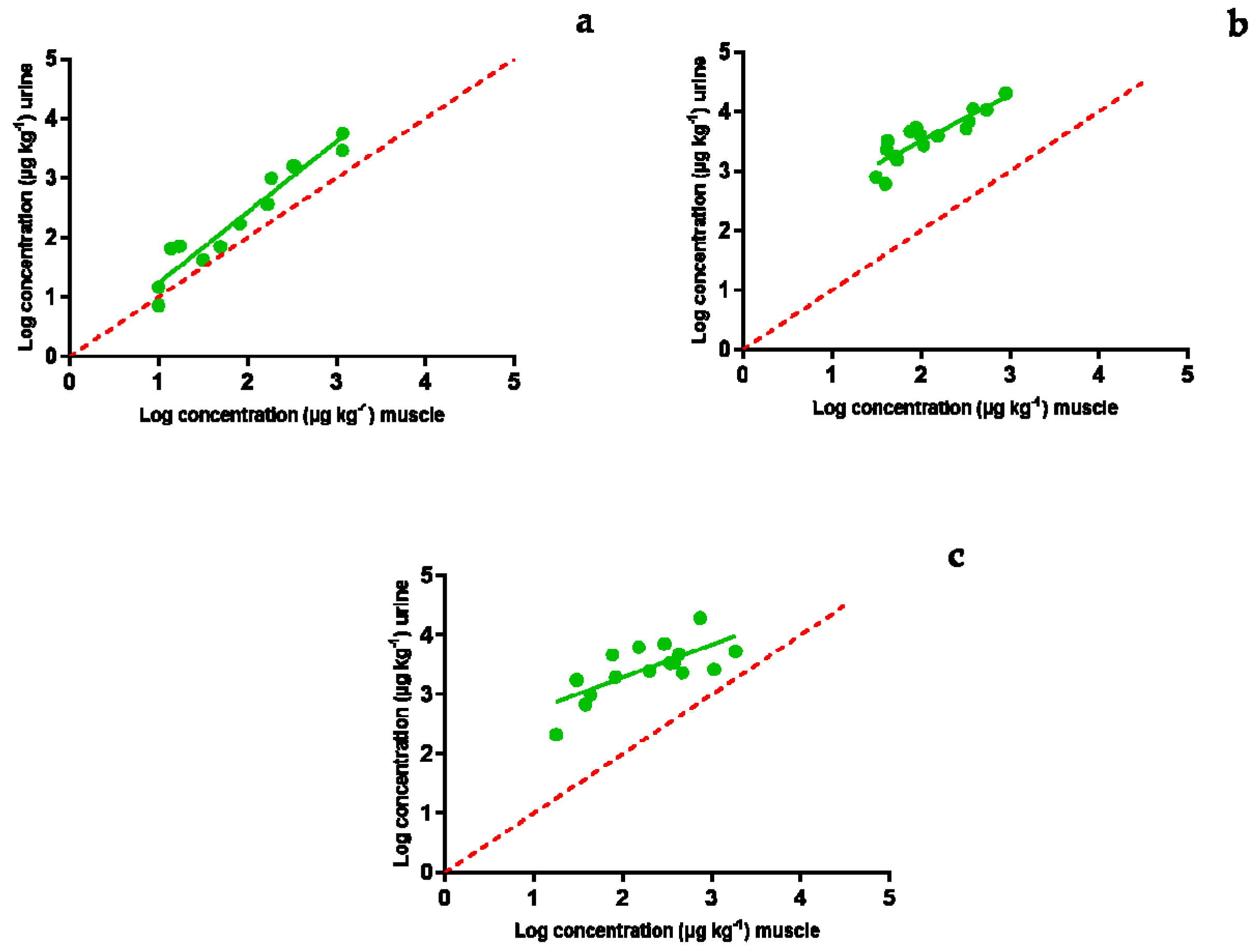
2.3. Excretion of Enrofloxacin via Urine
2.4. Comparative Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Urine Samples
3.1.1. Antimicrobials
3.1.2. Collection of Urine Samples Containing In Vivo Injected Antibiotics
3.1.3. Ethical Approval
3.2. LC-MS/MS Analysis
3.2.1. Standards and Reagents
3.2.2. Sample Preparation
3.2.3. LC-MS/MS Determination
3.3. Pharmacokinetic Parameters and Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, K.; Uwiera, R.R.; Kalmokoff, M.L.; Brooks, S.P.; Inglis, G.D. Antimicrobial growth promoter use in livestock: A requirement to understand their modes of action to develop effective alternatives. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2007, 49, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, A.; Santinello, M.; Penasa, M.; Scali, F.; Magni, E.; Alborali, G.L.; Bertocchi, L.; De Marchi, M. Use of antimicrobials in beef cattle: An observational study in the north of Italy. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 81, 105032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Glennon, E.E.; Chen, D.; Gilbert, M.; Robinson, T.P.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Reducing antimicrobial use in food animals. Science 2017, 357, 1350–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Neill, J. Antimicrobials in agriculture and the environment: Reducing unnecessary use and waste. In The Review on Antimicrobial Resistance; Wellcome Trust, HM Government: London, UK, 2015; pp. 1–44. Available online: https://amr-review.org/sites/default/files/Antimicrobials%20in%20agriculture%20and%20the%20environment%20-%20Reducing%20unnecessary%20use%20and%20waste.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Tang, K.L.; Caffrey, N.P.; Nobrega, D.B.; Cork, S.C.; Ronksley, P.E.; Barkema, H.W.; Polachek, A.J.; Ganshron, H.; Sharma, N.; Kellner, J.D.; et al. Restricting the use of antibiotics in food-producing animals and its associations with antibiotic resistance in food-producing animals and human beings: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Planet Health 2017, 1, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA (European Medicine Agency). Categorisation of Antibiotics for Use in Animals for Prudent and Responsible Use. 2020. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/infographic-categorisation-antibiotics-use-animals-prudent-responsible-use_en.pdf (accessed on 27 April 2021).
- Regulation (EU) 2019/4 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 11 December 2018 on the manufacture, placing on the market and use of medicated feed, amending Regulation (EC) No. 183/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council and repealing Council Directive 90/167/EEC. Off. J. Eur. Union 2019, L. 4, 1–23. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32019R0004 (accessed on 23 March 2021).
- Regulation (EU) 2019/6 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 11 December 2018 on veterinary medicinal products and repealing Directive 2001/82/EC. Off. J. Eur. Union 2019, L. 4, 43–167. Available online: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/eur/2019/6 (accessed on 23 March 2021).
- Riviere, J.E.; Spoo, J.W. Chapter 42. Tetracycline antibiotics. In Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 8th ed.; Adams, R.H., Ed.; Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 2001; pp. 828–940. [Google Scholar]
- Papich, M.G.; Riviere, J.E. Chapter 45. Fluoroquinolone antimicrobial drugs. In Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 8th ed.; Adams, R.H., Ed.; Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 2001; pp. 898–917. [Google Scholar]
- Vaden, S.L.; Riviere, J.E. Chapter 41. Penicillins and related β-lactam antibiotics. In Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 8th ed.; Adams, R.H., Ed.; Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 2001; pp. 818–827. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J.; Zhao, T.; Liu, Q.; He, J.; He, D.; Wu, G.; Li, Y.; Jiang, C.; Xu, Z. Residual veterinary antibiotics in pig excreta after oral administration of sulfonamides. Environ. Geochem. Health 2016, 38, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, L.M.; Nobile, M.; Panseri, S.; Arioli, F. Antibiotic use in heavy pigs: Comparison between urine and muscle samples from food chain animals analysed by HPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2017, 235, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.S. Adsorptive removal of antibiotics from water and wastewater: Progress and challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 532, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.S.; Johir, M.A.H.; Sornalingam, K. Single and competitive sorption properties and mechanism of functionalized biochar for removing sulfonamide antibiotics from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 311, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Shi, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xu, J. Adsorption behavior and mechanism of chloramphenicols, sulfonamides, and nonantibiotic pharmaceuticals on multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 310, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Jiang, Y.S.; Li, F.Y.; Yang, D.Y. Preparation of biochar by simultaneous carbonization, magnetization and activation for norfloxacin removal in water. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 233, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.S.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Xu, J. Progress in the biological and chemical treatment technologies for emerging contaminant removal from wastewater: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 274–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifrtová, M.; Nováková, L.; Lino, C.; Pena, A.; Solich, P. An overview of analytical methodologies for the determination of antibiotics in environmental waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 649, 158–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, M.Y.; Müller, S.R.; McArdell, C.S.; Alder, A.C.; Suter, M.J.F. Quantification of veterinary antibiotics (sulfonamides and trimethoprim) in animal manure by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 952, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlüsener, M.P.; Bester, K.; Spiteller, M. Determination of antibiotics such as macrolides, ionophores and tiamulin in liquid manure by HPLC–MS/MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 375, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Lu, C.; Liao, Q.; Gudda, F.O.; Ling, W. Antibiotics in animal manure and manure-based fertilizers: Occurrence and ecological risk assessment. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 127006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling-Sørensen, B.; Nors Nielsen, S.; Lanzky, P.F.; Ingerslev, F.; Holten Lutzhoft, H.C.; Jorgensen, S.E. Occurrence, fate and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment-a review. Chemosphere 1998, 36, 357–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Guo, M.; Yates, S.R. Degradation kinetics of manure derived sulfadimethoxine in amended soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolls, J. Sorption of veterinary pharmaceuticals in soils: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 3397–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamscher, G.; Pawelzick, H.T.; Höper, H.; Nau, H. Different behavior of tetracyclines and sulfonamides in sandy soils after repeated fertilization with liquid manure. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmah, A.K.; Meyer, M.T.; Boxall, A.B.A. A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolpin, D.W.; Furlong, E.T.; Meyer, M.T.; Thurman, E.M.; Zaugg, S.D.; Barber, L.B.; Buxton, H.T. Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in US streams, 1999–2000: A national reconnaissance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baran, W.; Adamek, E.; Ziemianska, J.; Sobczak, A. Effects of the presence of sulfonamides in the environment and their influence on human health. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 196, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Khalil, S.; Bayen, S. Effect of thermal treatments on the degradation of antibiotic residues in food. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3760–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, L.; Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Shen, Y. Degradation of antibiotics and inactivation of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in Cephalosporin C fermentation residues using ionizing radiation, ozonation and thermal treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 121058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gros, M.; Marti, E.; Balcázar, J.L.; Boy-Roura, M.; Busquets, A.; Colon, J.; Sanchez-Melsio, A.; Lekunberri, I.; Borrego, C.M.; Ponsá, S.; et al. Fate of pharmaceuticals and antibiotic resistance genes in a full-scale on-farm livestock waste treatment plant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 378, 120716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, X.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qian, M.; Chen, X.; Zhao, H.; Sheng, M.; Cao, G.; et al. Removal of veterinary antibiotics from swine wastewater using anaerobic and aerobic biodegradation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurmessa, B.; Pedretti, E.F.; Cocco, S.; Cardelli, V.; Corti, G. Manure anaerobic digestion effects and the role of pre-and post-treatments on veterinary antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes removal efficiency. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; He, L.Y.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhao, J.L.; Liu, W.R.; Zhang, J.N.; Chen, J.; He, L.K.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Ying, G.G. Fate of veterinary antibiotics during animal manure composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti, E.; Gros, M.; Boy-Roura, M.; Ovejero, J.; Busquets, A.M.; Colón, J.; Petrovic, M.; Ponsá, S. Pharmaceuticals removal in an on-farm pig slurry treatment plant based on solid-liquid separation and nitrification-denitrification systems. J. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Moya, M.; Graells, M.; Castells, G.; Amigó, J.; Ortega, E.; Buhigas, G.; Pérez, L.M.; Mansilla, H.D. Characterization of the degradation performance of the sulfamethazine antibiotic by photo-Fenton process. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2533–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruden, A.; Larsson, D.J.; Amézquita, A.; Collignon, P.; Brandt, K.K.; Graham, D.W.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Suzuki, S.; Silley, P.; Snape, J.R.; et al. Management options for reducing the release of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes to the environment. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, G.K.; Millar, R.G.; Anstis, P.W. Stability of sulfonamide antibiotics in spiked pig liver tissue during frozen storage. J. AOAC Int. 1997, 80, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berendsen, B.J.A.; Elbers, I.J.W.; Stolker, A.A.M. Determination of the stability of antibiotics in matrix and reference solutions using a straightforward procedure applying mass spectrometric detection. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2011, 28, 1657–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spoo, J.W.; Riviere, J.E. Chapter 40. Sulfonamides. In Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 8th ed.; Adams, R.H., Ed.; Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 2001; pp. 796–817. [Google Scholar]
- Benchaoui, H.A.; Nowakowski, M.; Sherington, J.; Rowan, T.G.; Sunderland, S.J. Pharmacokinetics and lung tissue concentrations of tulathromycin in swine. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 27, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengelers, M.J.B.; van Gogh, E.R.; Huveneers, M.B.M.; Hougee, P.E.; Kuiper, H.A.; Pijpers, A.; Verheijden, J.H.; Van Miert, A.S. Pharmacokinetics of sulfadimethoxine and sulfamethoxazole in combination with trimethoprim after oral single-and multiple-dose administration to healthy pigs. Vet. Res. Commun. 2001, 25, 461–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengelers, M.J.B.; Van Gogh, E.R.; Kuiper, H.A.; Pijpers, A.; Verheijden, J.H.; Van Miert, A.S. Pharmacokinetics of sulfadimethoxine and sulfamethoxazole in combination with trimethoprim after intravenous administration to healthy and pneumonic pigs. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 1995, 18, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhao, J.L.; Liu, W.R.; He, L.Y.; Zhang, J.N.; Chen, J.; He, L.K.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Ying, G.G. Occurrence, fate and mass loadings of antibiotics in two swine wastewater treatment systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziółkowski, H.; Grabowski, T.; Jasiecka, A.; Zuśka-Prot, M.; Barski, D.; Jaroszewski, J.J. Pharmacokinetics of oxytetracycline in broiler chickens following different routes of administration. Vet. J. 2016, 208, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Korchi, G.; Prats, C.; Arboix, M.; Pérez, B. Disposition of oxytetracycline in pigs after administration of two long-acting formulations. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 24, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, S.; Shen, S.; Zhou, J.; Ding, G.; Zhang, K. Systematic analysis of occurrence, density and ecological risks of 45 veterinary antibiotics: Focused on family livestock farms in Erhai Lake basin, Yunnan, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee-Sanford, J.C.; Aminov, R.I.; Krapac, I.J.; Garrigues-Jeanjean, N.; Mackie, R.I. Occurrence and diversity of tetracycline resistance genes in lagoons and groundwater underlying two swine production facilities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1494–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mackie, R.I.; Koike, S.; Krapac, I.; Chee-Sanford, J.; Maxwell, S.; Aminov, R.I. Tetracycline residues and tetracycline resistance genes in groundwater impacted by swine production facilities. Anim. Biotechnol. 2006, 17, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, S.; Krapac, I.G.; Oliver, H.D.; Yannarell, A.C.; Chee-Sanford, J.C.; Aminov, R.I.; Mackie, R.I. Monitoring and source tracking of tetracycline resistance genes in lagoons and groundwater adjacent to swine production facilities over a 3-year period. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4813–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, P.; Gyrd-Hansen, N. Bioavailability of enrofloxacin after oral administration to fed and fasted pigs. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1997, 80, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messenger, K.M.; Papich, M.G.; Blikslager, A.T. Distribution of enrofloxacin and its active metabolite, using an in vivo ultrafiltration sampling technique after the injection of enrofloxacin to pigs. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 35, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, M.J.; Mitjana, O.; Bonastre, C.; Laborda, A.; Falceto, M.V.; García-Gonzalo, D.; Abilleira, E.; Elorduy, J.; Bousquet-Melou, A.; Mata, L.; et al. Is blood a good indicator for detecting antimicrobials in meat? Evidence for the development of in vivo surveillance methods. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seymour, E.H.; Jones, G.M.; McGilliard, M.L. Comparisons of on-farm screening tests for detection of antibiotic residues. J. Dairy Sci. 1988, 71, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EU) No. 37/2010 of 22 December 2009 on pharmacologically active substances and their classification regarding maximum residue limits in foodstuffs of animal origin. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, L. 15, 1–72. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/sites/default/files/files/eudralex/vol-5/reg_2010_37/reg_2010_37_en.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2021).
- De la Torre, A.; Iglesias, I.; Carballo, M.; Ramírez, P.; Muñoz, M.J. An approach for mapping the vulnerability of European Union soils to antibiotic contamination. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 414, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemper, N. Veterinary antibiotics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment. Ecol. Indic. 2008, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.L. Environmental pollution by antibiotics and by antibiotic resistance determinants. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2893–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jechalke, S.; Focks, A.; Rosendahl, I.; Groeneweg, J.; Siemens, J.; Heuer, H.; Smalla, K. Structural and functional response of the soil bacterial community to application of manure from difloxacin-treated pigs. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 87, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuer, H.; Schmitt, H.; Smalla, K. Antibiotic resistance gene spread due to manure application on agricultural fields. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-R.; Owens, G.; Kwon, S.-I.; So, K.-H.; Lee, D.-B.; Ok, Y.S. Occurrence and environmental fate of veterinary antibiotics in the terrestrial environment. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 214, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Guideline on Environmental Impact Assessment for Veterinary Medicinal Products in Support of the VICH Guidelines GL6 and GL38, EMA/CVMP/ERA/418282/2005-Rev.1-Corr; European Medicines Agency: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Livermore, D.M. Has the era of untreatable infections arrived? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 64, i29–i36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trobos, M.; Jakobsen, L.; Olsen, K.E.; Frimodt-Møller, N.; Hammerum, A.M.; Pedersen, K.; Agerso, Y.; Porsbo, L.J.; Olsen, J.E. Prevalence of sulphonamide resistance and class 1 integron genes in Escherichia coli isolates obtained from broilers, broiler meat, healthy humans and urinary infections in Denmark. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2008, 32, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekanmbi, A.O.; Adejoba, A.T.; Banjo, O.A.; Saki, M. Detection of sul1 and sul2 genes in sulfonamide-resistant bacteria (SRB) from sewage, aquaculture sources, animal wastes and hospital wastewater in south-west Nigeria. Gene Rep. 2020, 20, 100742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Sun, W.; Jin, D.; Yu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, P.; Ma, J. Effect of composting on the conjugative transmission of sulfonamide resistance and sulfonamide-resistant bacterial population. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 125483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempini, P.N.; Aly, S.S.; Karle, B.M.; Pereira, R.V. Multidrug residues and antimicrobial resistance patterns in waste milk from dairy farms in Central California. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 8110–8122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodhi, K.K.; Kumar, M.; Singh, D.K. Insight into the amoxicillin resistance, ecotoxicity, and remediation strategies. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 39, 101858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riviere, J.E. Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination. In Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 9th ed.; Riviere, J.E., Papich, M.G., Eds.; Willey Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2009; pp. 11–46. [Google Scholar]
- Real Decreto 53/2013, de 1 de febrero, por el que se establecen las normas básicas aplicables para la protección de los animales utilizados en experimentación y otros fines científicos, incluyendo la docencia. Boletín Oficial Estado 2013, 34, 11370–11421.
- Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, L. 276, 33–79. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32010L0063 (accessed on 23 March 2021).

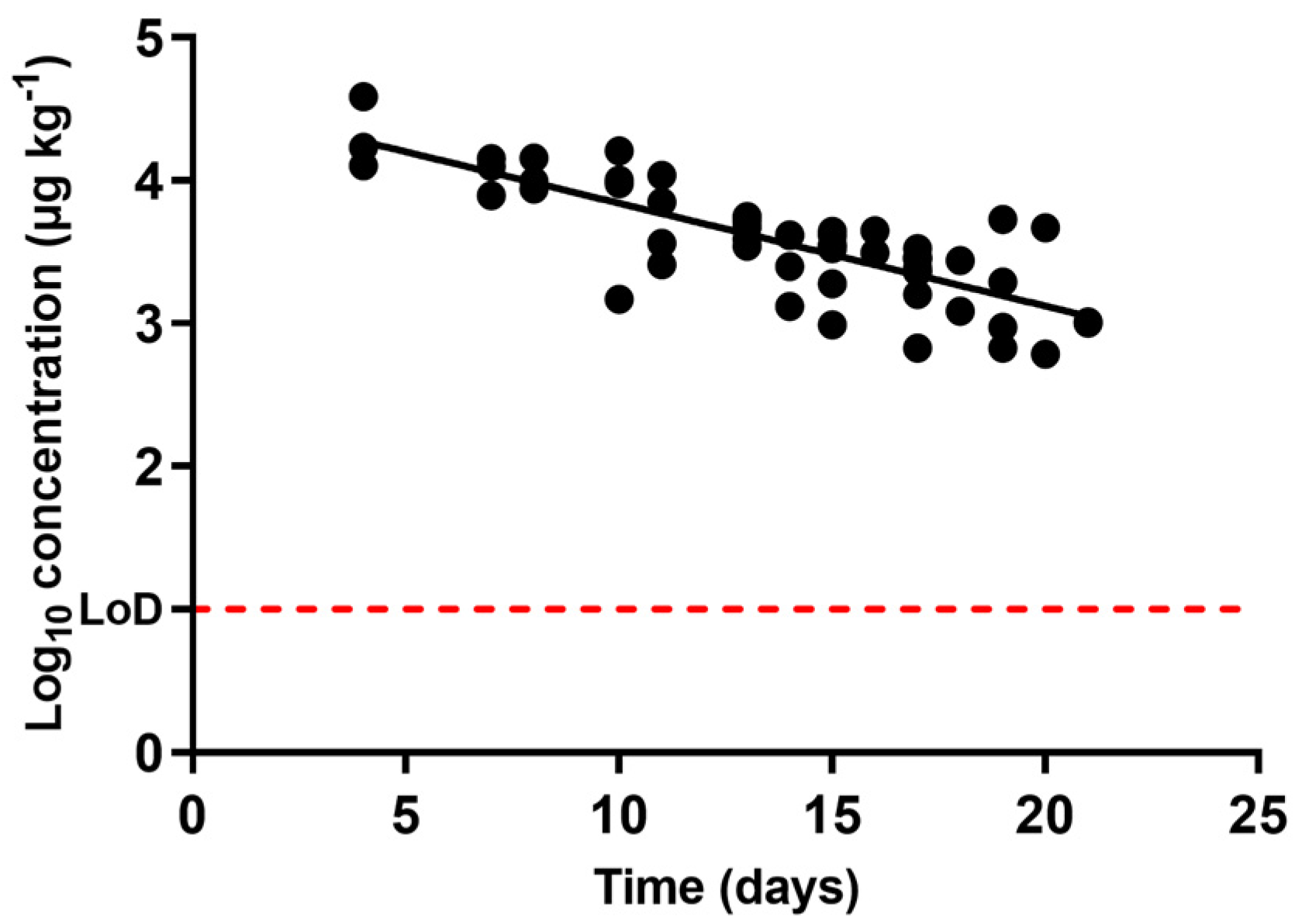
 ), oxytetracycline (
), oxytetracycline (  ), and enrofloxacin (
), and enrofloxacin (  ) in urine after animal treatment within the withdrawal period. The LoD dotted line represents the detection limit of the analytical technique for sulfamethoxypyridazine, oxytetracycline, and enrofloxacin.
) in urine after animal treatment within the withdrawal period. The LoD dotted line represents the detection limit of the analytical technique for sulfamethoxypyridazine, oxytetracycline, and enrofloxacin.
 ), oxytetracycline (
), oxytetracycline (  ), and enrofloxacin (
), and enrofloxacin (  ) in urine after animal treatment within the withdrawal period. The LoD dotted line represents the detection limit of the analytical technique for sulfamethoxypyridazine, oxytetracycline, and enrofloxacin.
) in urine after animal treatment within the withdrawal period. The LoD dotted line represents the detection limit of the analytical technique for sulfamethoxypyridazine, oxytetracycline, and enrofloxacin.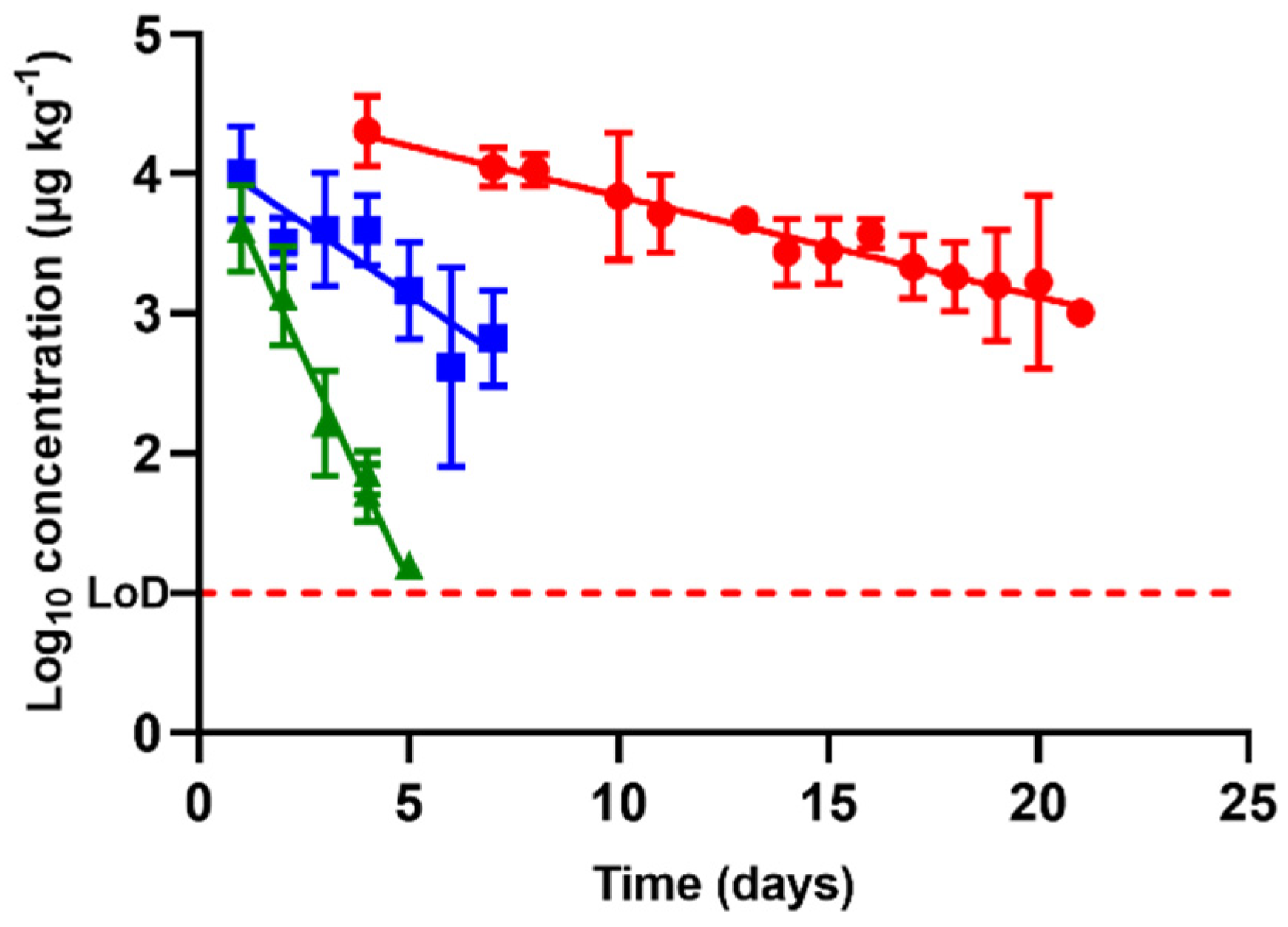
| Antibacterial Molecule | Slope | 1R2 | 2λz | T1/2 | Estimated Time for Complete Excretion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfamethoxypyridazine | 0.6144 ± 0.1052 | 0.99 | 0.71 | 0.49 | 6.89 |
| Oxytetracycline | 0.07194 ± 0.015 | 0.64 | 6.04 | 4.18 | 63.38 |
| Enrofloxacin | 0.2027 ± 0.0760 | 0.47 | 2.14 | 1.48 | 20.48 |
| Group | Active Compound | Commercial Name | Trading Company | Administration Pattern | Withdrawal Period (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfonamide | Sulfamethoxypyridazine | SULFAMETOX | S. P. VETERINARIA (Tarragona, Spain) | Attack dose of 40 mg kg−1 Maintenance dose 20 mg kg−1 for 5 days | 28 |
| Tetracycline | Oxytetracycline | ALAMYCIN L.A 300 | KARIZOO LAB (Barcelona, Spain) | Single dose of 30 mg kg−1 | 28 |
| Quinolone | Enrofloxacin | BAYTRILUNO 100 mg mL−1 | BAYER (Leverkusen, Germany) | 2 doses of 7.5 mg kg−1 separated 48 h | 12 |
| Compound | Precursor | Product | 1 DP (V) | 2 CE (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enrofloxacin | 360 | 342 | 72 | 30 |
| 266 | 72 | 50 | ||
| Ciprofloxacin | 332 | 314 | 61 | 30 |
| 231 | 61 | 50 | ||
| Ciprofloxacin-D8 (IS) | 340 | 322 | 61 | 30 |
| Sulfamethoxypyridazine | 281 | 156 | 60 | 25 |
| 108 | 60 | 35 | ||
| Sulfamethoxypyridazine-D3 (IS) | 284 | 156 | 60 | 25 |
| Oxytetracycline | 461 | 426 | 65 | 30 |
| Demeclocycline (IS) | 443 | 65 | 17 | |
| 465 | 154 | 65 | 40 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serrano, M.J.; García-Gonzalo, D.; Abilleira, E.; Elorduy, J.; Mitjana, O.; Falceto, M.V.; Laborda, A.; Bonastre, C.; Mata, L.; Condón, S.; et al. Antibacterial Residue Excretion via Urine as an Indicator for Therapeutical Treatment Choice and Farm Waste Treatment. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070762
Serrano MJ, García-Gonzalo D, Abilleira E, Elorduy J, Mitjana O, Falceto MV, Laborda A, Bonastre C, Mata L, Condón S, et al. Antibacterial Residue Excretion via Urine as an Indicator for Therapeutical Treatment Choice and Farm Waste Treatment. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(7):762. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070762
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerrano, María Jesús, Diego García-Gonzalo, Eunate Abilleira, Janire Elorduy, Olga Mitjana, María Victoria Falceto, Alicia Laborda, Cristina Bonastre, Luis Mata, Santiago Condón, and et al. 2021. "Antibacterial Residue Excretion via Urine as an Indicator for Therapeutical Treatment Choice and Farm Waste Treatment" Antibiotics 10, no. 7: 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070762
APA StyleSerrano, M. J., García-Gonzalo, D., Abilleira, E., Elorduy, J., Mitjana, O., Falceto, M. V., Laborda, A., Bonastre, C., Mata, L., Condón, S., & Pagán, R. (2021). Antibacterial Residue Excretion via Urine as an Indicator for Therapeutical Treatment Choice and Farm Waste Treatment. Antibiotics, 10(7), 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070762






