On-Site Pilot Testing of Hospital Wastewater Ozonation to Reduce Pharmaceutical Residues and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Drug Residues
2.2. Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
2.3. Energy Consumption of Ozonation System
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
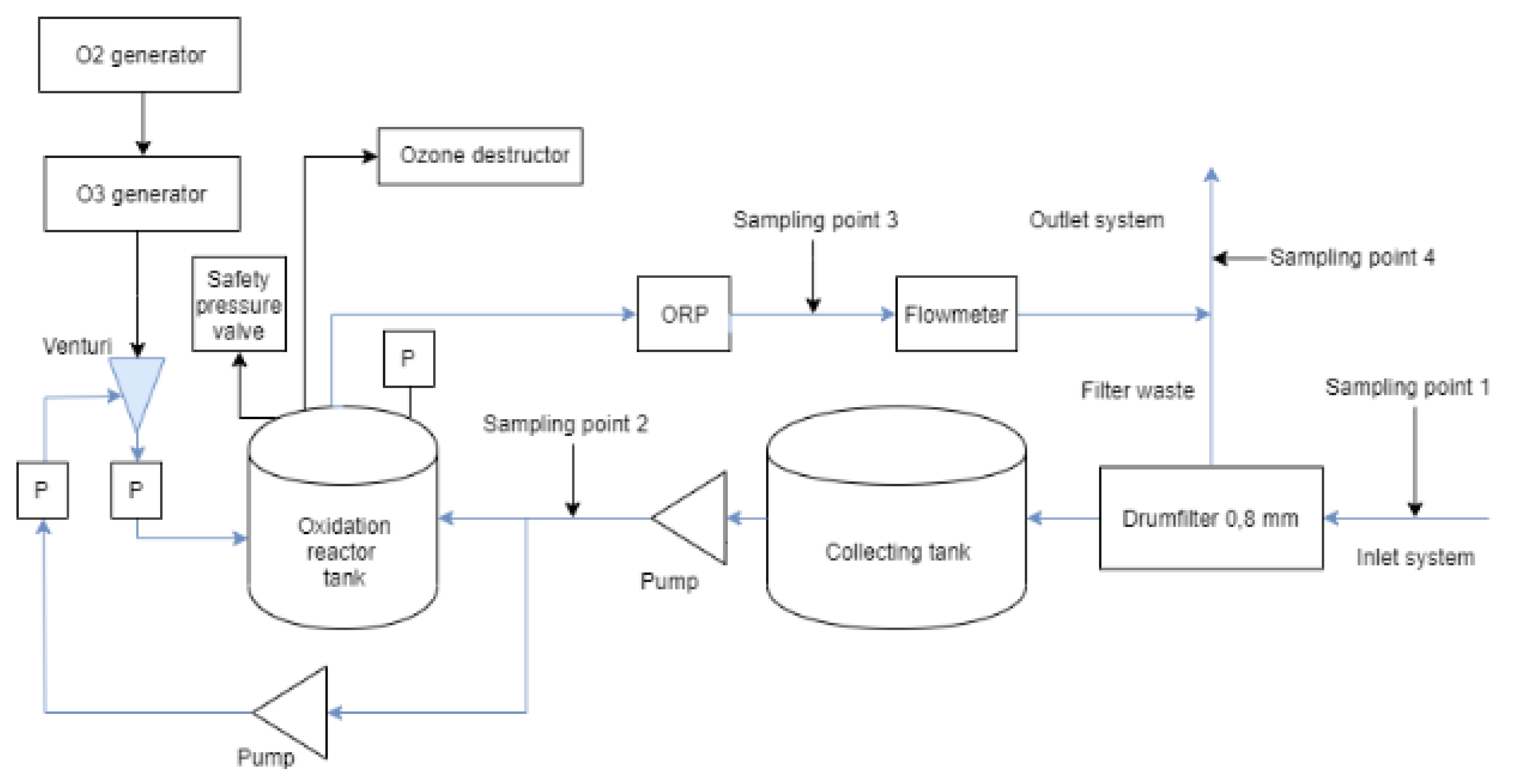
4.1. Study Site
4.2. Experimental Setup
4.3. Sampling
4.4. Analysis of Pharmaceuticals
4.5. Sampling for and Analysis of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
4.6. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Falås, P.; Andersen, H.R.; Ledin, A.; la Cour Jansen, J. Occurrence and reduction of pharmaceuticals in the water phase at Swedish wastewater treatment plants. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, K.V.; Dye, C.; Schlabach, M.; Langford, K.H. Source to sink tracking of selected human pharmaceuticals from two Oslo city hospitals and a wastewater treatment works. J. Environ. Monit. 2007, 9, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, K.M.S.; Spiliotopoulou, A.; Chhetri, R.K.; Casas, M.E.; Bester, K.; Andersen, H.R. Ozonation for source treatment of pharmaceuticals in hospital wastewater—Ozone lifetime and required ozone doze. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 290, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendz, D.; Paxéus, N.A.; Ginn, T.R.; Lodge, F.J. Occurence and fate of pharmaceutically active compounds in the environment, a case study: Höje River in Sweden. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 122, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Larsson, D.G.J. Concentrations of antibiotics predicted to select for resistant bacteria: Proposed limits for environmental regulation. Environ. Int. 2016, 86, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atterby, C.; Nykvist, M.; Lustig, U.; Andersson, D.I.; Jarhult, J.D.; Sandegren, L. Selection of resistant bacteria in Mallards exposed to subinhibitory concentrations of ciprofloxacin in their water environment. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, G.; Vega, S.R.; Fick, J.; Tysklind, M.; la cour Jansen, J.; Andersen, H.R. Removal of pharmaceuticals in WWTP effluents by ozone and hydrogen peroxide. Water SA 2014, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baresel, C.; Malmborg, J.; Ek, M.; Sehlén, R. Removal of pharmaceutical residues using ozonation as intermediate process step at Linköping WWTP, Sweden. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björlenius, B.; Beijer, K.; Shaik, S.; Lindberg, R.H.; Brunström, B.; Brandt, I. Removal of pharmaceuticals and unspecified contaminants in sewage treatment effluents by activated carbon filtration and ozonation: Evaluation using biomarker responses and chemical analysis. Chemosphere 2017, 176, 342–351. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, U.; Hastrup, C.; Klausen, M.M.; Pedersen, B.M.; Kristensen, G.H.; la cour Jansen, J.; Bak, S.N.; Tuerk, J. Removal of APIs and bacteria from hospital wastewater by MBR plus O3, O3+H2O2, PAC or ClO2. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 674, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorova, G.; Grabic, R.; Nyhlen, J.; Järhult, J.D.; Söderström, H. Fate of three anti-influenza drugs during ozonation of wastewater effluents: Degradation and formation of transformation products. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nöthe, T.; Fahlenkamp, H.; Von Sonntag, C. Ozonation of wastewater: Rate of ozone consumption and hydroxyl radical yield. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5990–5995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CWPharma. Evaluation and Experiences of Full-Scale Ozonation Followed by MBBR Post-Treatment and Comparisation with Previous Pilot Tests. GoA3.1: Pharmaceutical Removal at Full Scale. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/4032487/files/CWPharma_GoA3_1_Report_publ.pdf?download=1 (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- Lundström, E.; Adolfsson-Erici, M.; Alsberg, T.; Björlenius, B.; Eklund, B.; Lavén, M.; Breitholtz, M. Characterization of additional sewage treatment technologies: Ecotoxicological effects and levels of selected pharmaceuticals, hormones and endocrine disruptors. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korzeniewska, E.; Korzeniewska, A.; Harnisz, M. Antibiotic resistant Escherichia coli in hospital and municipal sewage and their emission to the environment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 91, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraupner, N.; Hutinel, M.; Schumacher, K.; Gray, D.A.; Genheden, M.; Fick, J.; Flach, C.-F.; Larsson, D.G.J. Evidence for selection of multi-resistant E. coli by hospital effluent. Environ. Int. 2021, 150, 106436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DHI Full Scale Advanced Wastewater Treatment at Herlev Hospital Treatment Performance and Evaluation. Available online: www.dhigroup.com/global/news/2016/08/hospital-wastewater-from-a-pollution-problem-to-new-water-resources (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- Larsson, D.G.J. Antibiotics in the environment. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 2014, 119, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindberg, R.H.; Olofsson, U.; Marcus, O.; Grabic, R.; Fick, J. Occurrence and behavior of 105 active pharmaceutical ingredients in sewage waters of a municipal sewer collection system. Water Res. 2014, 58, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, G.A.; Berglund, B.; Khan, K.M.; Lindgren, P.-E.; Fick, J. Occurrence and abundance of antibiotics and resistance genes in rivers, canal and near drug formulation facilities—A study in Pakistan. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabic, R.; Fick, J.; Lindberg, R.H.; Fedorova, G.; Tysklind, M. Multi-residue method for trace level determination of pharmaceuticals in environmental samples using liquid chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Talanta 2012, 100, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Low Flow | High Flow | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| API | LOQ | Pre-Ozonation | Difference | % Change | p-Value | Pre-Ozonation | Difference | % Change | p-Value |
| Alfuzosin | 4 | 70.7 | −20.5 | −29.0 | 0.0031 | 86.3 | −27.2 | −31.5 | 0.0604 |
| Amytriptyline | 15 | 79.8 | −6.0 | −7.5 | 96.7 | 4.8 | 5.0 | ||
| Atenolol | 15 | 1107.6 | 21.7 | 2.0 | 834.8 | 54.9 | 6.6 | ||
| Atorvastatin | 15 | 675.6 | −360.6 | −53.4 | <0.0001 | 898.8 | −604.9 | −67.3 | <0.0001 |
| Bisoprolol | 4 | 518 | −77.6 | −15.0 | 369.4 | 5.1 | 1.4 | ||
| Bupropion | 4 | 45.5 | −2.2 | −4.8 | 52.8 | 4.8 | 9.1 | ||
| Carbamazepin | 7.5 | 175.7 | −62.8 | −35.7 | 0.0156 | 168.2 | −13.1 | −7.8 | |
| Ceterizine | 15 | 358.4 | −90.1 | −25.1 | 0.0121 | 368.5 | −55.2 | −15.0 | |
| Ciprofloxacin | 15 | 48,695.3 | −12,400.2 | −25.5 | 66,815.3 | 1526.1 | 2.3 | ||
| Citalopram | 20 | 639 | −282 | −44.1 | 0.0816 | 550.3 | −140.3 | −25.5 | |
| Clarithromycine | 3 | 37.1 | −20.2 | −54.4 | 70.8 | −0.6 | −0.8 | ||
| Clindamycine | 3 | 523.6 | −119.3 | −22.8 | 0.0156 | 476.6 | −38.1 | −8.0 | |
| Codeine | 20 | 783.6 | −264.8 | −33.8 | <0.0001 | 901.6 | −138.9 | −15.4 | |
| Diclofenac | 15 | 411.2 | −61.8 | −15.0 | 0.0725 | 366.1 | −22.5 | −6.1 | |
| Fexofenadine | 10 | 104.9 | −17 | −16.2 | 101.5 | 9.6 | 9.5 | ||
| Flecainide | 2 | 160.8 | −10.4 | −6.5 | 257.1 | 32.9 | 12.8 | ||
| Fluconazole | 7.5 | 201.3 | −2.7 | −1.3 | 280.5 | 27.7 | 9.9 | ||
| Fluoxetine | 7.5 | 33.5 | −19 | −56.7 | <0.0001 | 48.5 | −15.3 | −31.5 | 0.0015 |
| Irbesartan | 3 | 97.3 | −17 | −17.5 | 58.6 | −2.1 | −3.6 | ||
| Metoprolol | 15 | 1224.9 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 1117.4 | 46.2 | 4.1 | ||
| Mirtazapine | 20 | 711.1 | −229.5 | −32.3 | 0.0249 | 521.7 | −35.2 | −6.7 | |
| Oxazepam | 10 | 191.4 | −39.8 | −20.8 | 209.4 | 3.9 | 1.9 | ||
| Paracetamol | 20 | 2,633,386 | −839,221.7 | −31.9 | 0.0499 | 2,501,226 | 72,804.2 | 2.9 | |
| Propranolol | 30 | 198.4 | −74.8 | −37.7 | 0.0014 | 178.1 | −13.7 | −7.7 | |
| Rosuvastatin | 3 | 554.5 | −133.5 | −24.1 | 650.6 | −35.2 | −5.4 | ||
| Tetracycline | 30 | 4511.2 | −2693.1 | −59.7 | <0.0001 | 3352.2 | −552.2 | −16.5 | |
| Tramadol | 20 | 242.1 | −16.5 | −6.8 | 195.8 | 14.8 | 7.6 | ||
| Trimethoprim | 4 | 617.6 | −261 | −42.2 | 0.0006 | 558.8 | −27.3 | −4.9 | |
| Venlafaxine | 20 | 1164.4 | −137.6 | −11.8 | 1073.1 | 65.8 | 6.1 | ||
| Mean all APIs | −25.2 | −6.0 | |||||||
| Mean antibiotics | −40.9 | −5.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Svebrant, S.; Spörndly, R.; Lindberg, R.H.; Olsen Sköldstam, T.; Larsson, J.; Öhagen, P.; Söderström Lindström, H.; Järhult, J.D. On-Site Pilot Testing of Hospital Wastewater Ozonation to Reduce Pharmaceutical Residues and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10060684
Svebrant S, Spörndly R, Lindberg RH, Olsen Sköldstam T, Larsson J, Öhagen P, Söderström Lindström H, Järhult JD. On-Site Pilot Testing of Hospital Wastewater Ozonation to Reduce Pharmaceutical Residues and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(6):684. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10060684
Chicago/Turabian StyleSvebrant, Sofia, Robert Spörndly, Richard H. Lindberg, Therese Olsen Sköldstam, Jim Larsson, Patrik Öhagen, Hanna Söderström Lindström, and Josef D. Järhult. 2021. "On-Site Pilot Testing of Hospital Wastewater Ozonation to Reduce Pharmaceutical Residues and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria" Antibiotics 10, no. 6: 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10060684
APA StyleSvebrant, S., Spörndly, R., Lindberg, R. H., Olsen Sköldstam, T., Larsson, J., Öhagen, P., Söderström Lindström, H., & Järhult, J. D. (2021). On-Site Pilot Testing of Hospital Wastewater Ozonation to Reduce Pharmaceutical Residues and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria. Antibiotics, 10(6), 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10060684






