Cnicin as an Anti-SARS-CoV-2: An Integrated In Silico and In Vitro Approach for the Rapid Identification of Potential COVID-19 Therapeutics
Abstract
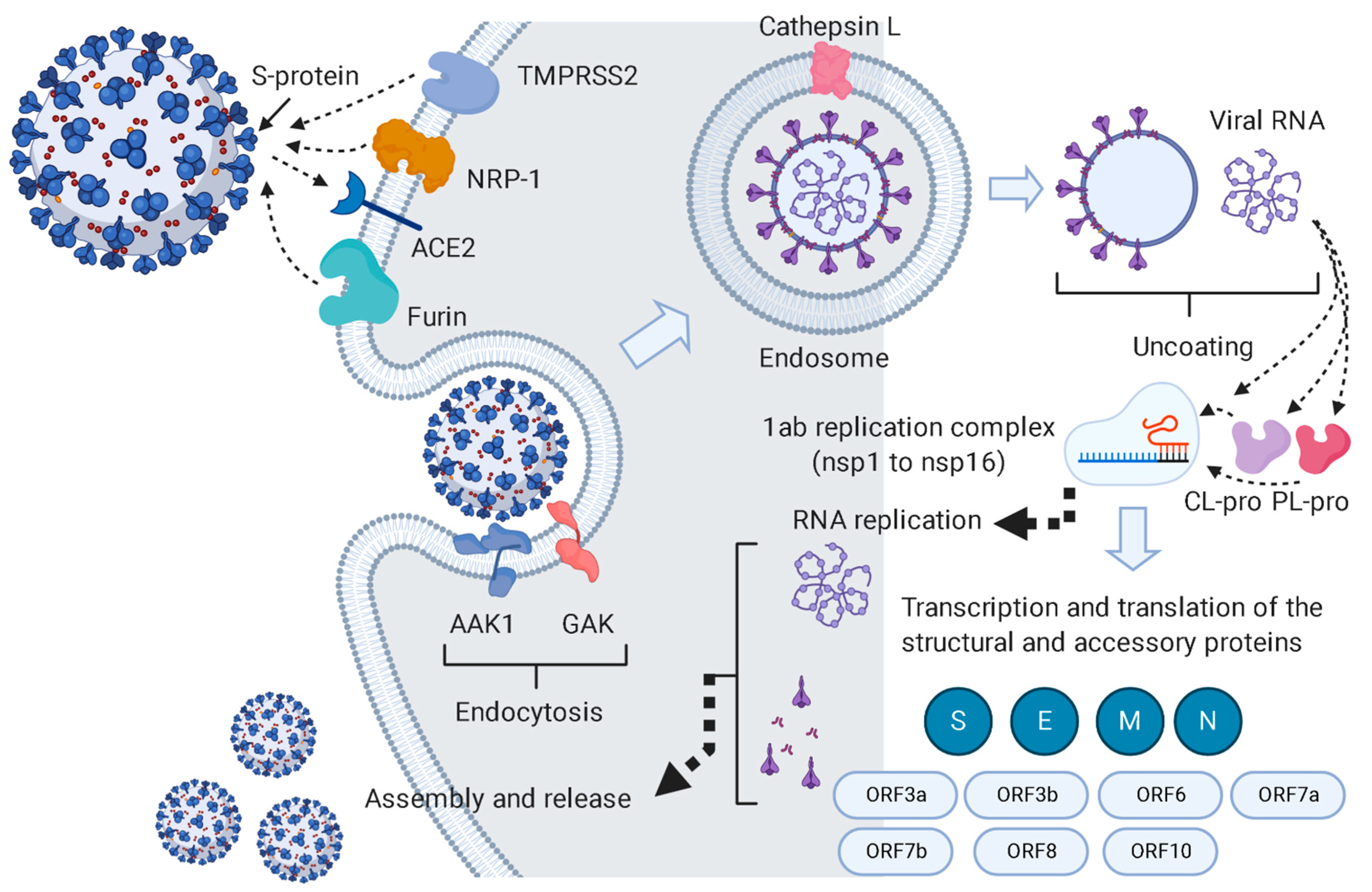
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Crude Extract
2.2. Preparation of C. benedictus’s Pure Compounds
2.3. Data Preparation
2.3.1. Compounds Preparation
2.3.2. Protein Structures Preparation
2.4. Ensemble Docking
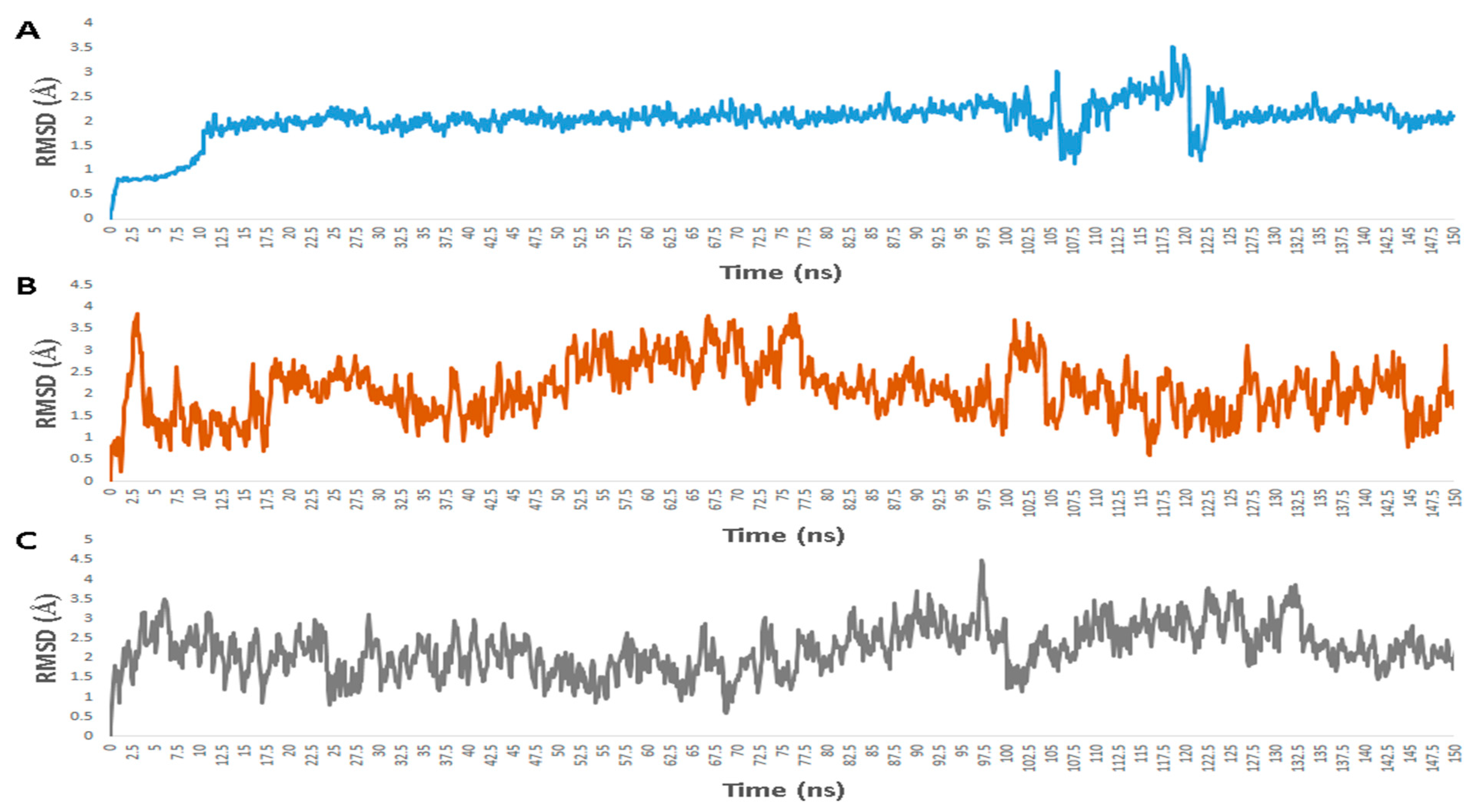
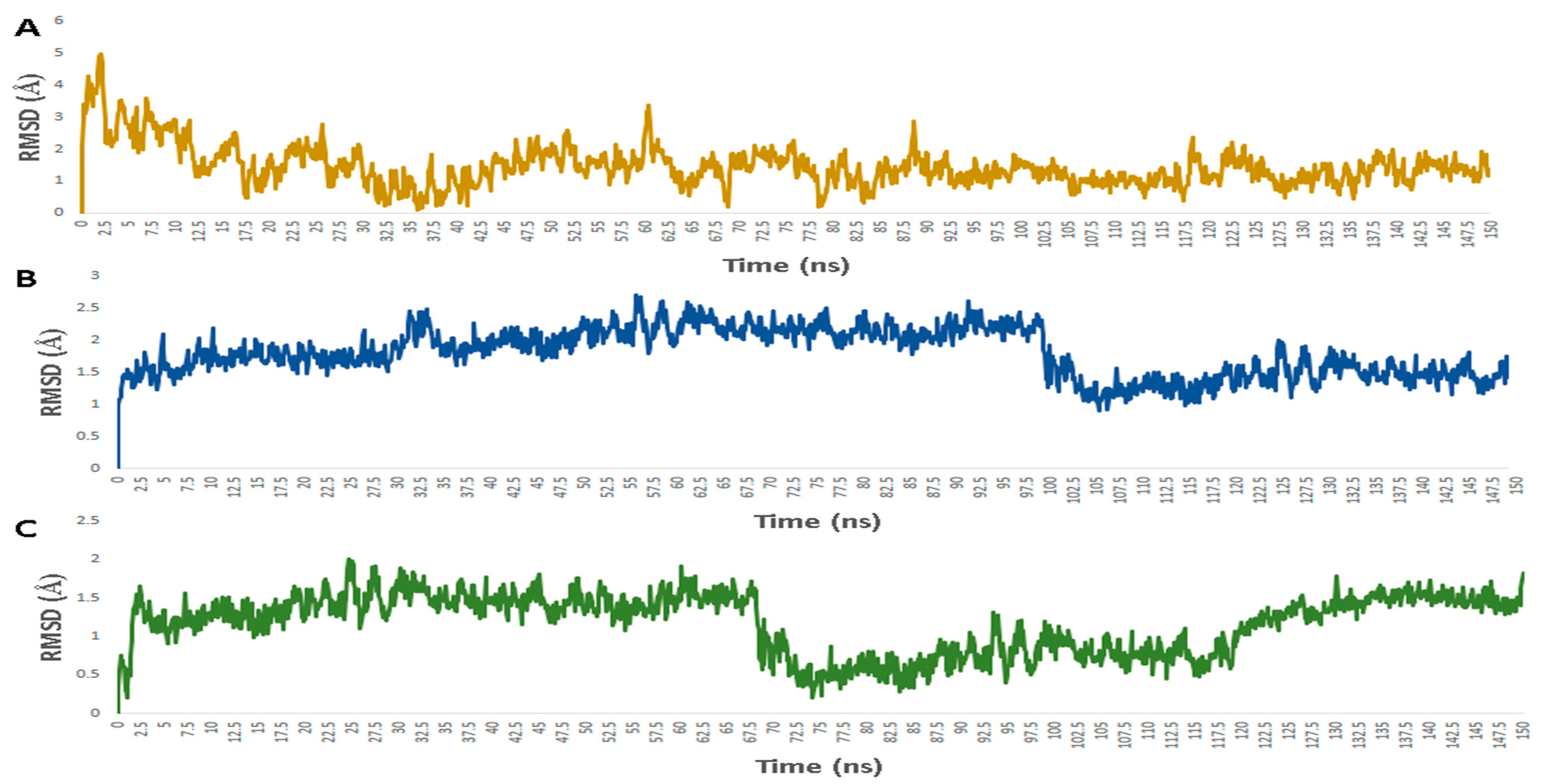
2.5. Molecular Dynamic Simulation
2.6. Networks Construction
2.7. In Silico Permeability Studies
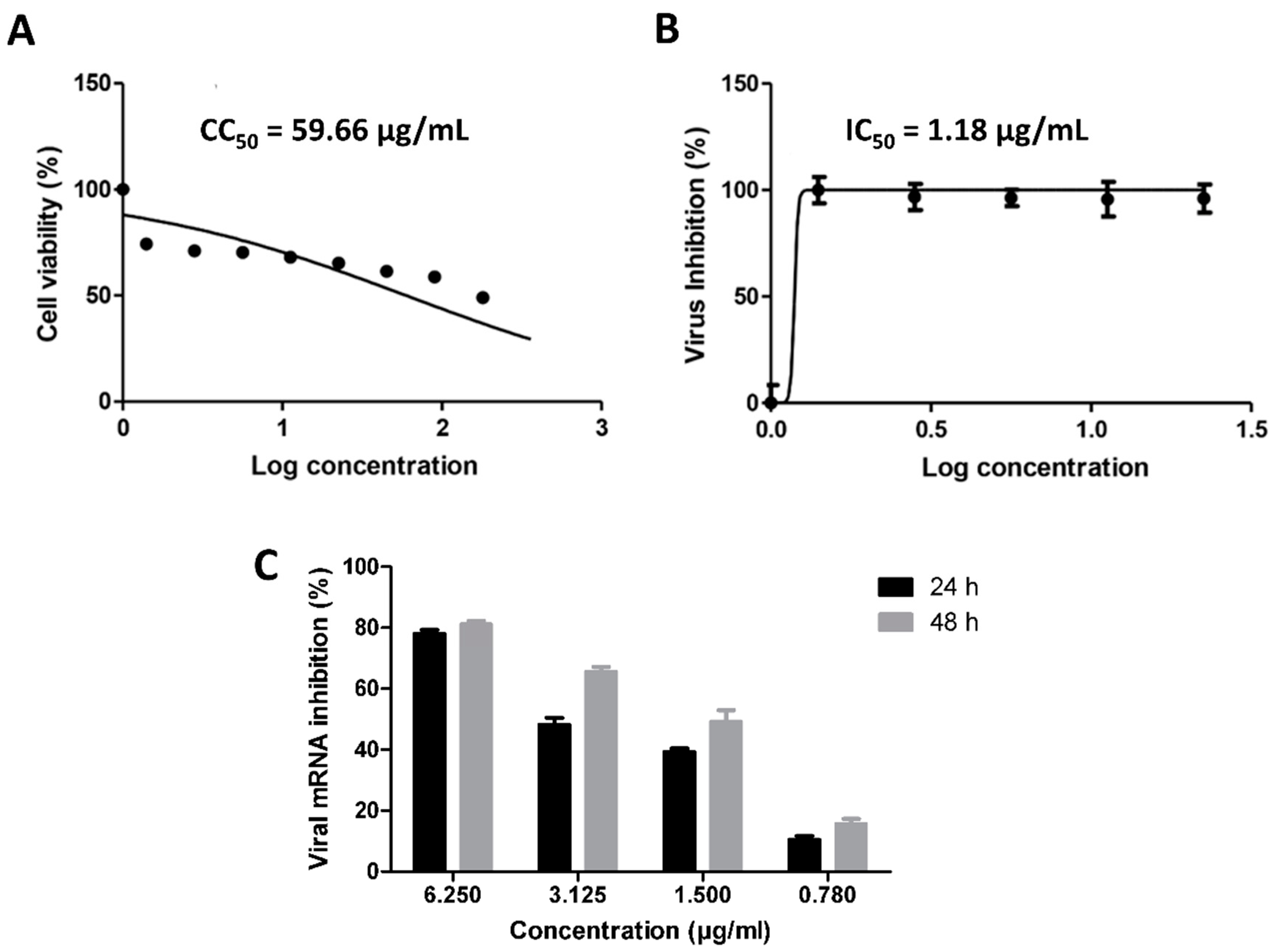
2.8. In Vitro Antiviral Assay
2.8.1. Virus and Cells
2.8.2. MTT Cytotoxicity Assay
2.8.3. Viral Inhibitory Concentration 50 (IC50) Determination
2.8.4. Quantitative Real Time Measurement of SARS CoV-2 mRNA Expression
2.9. Statistical Analysis
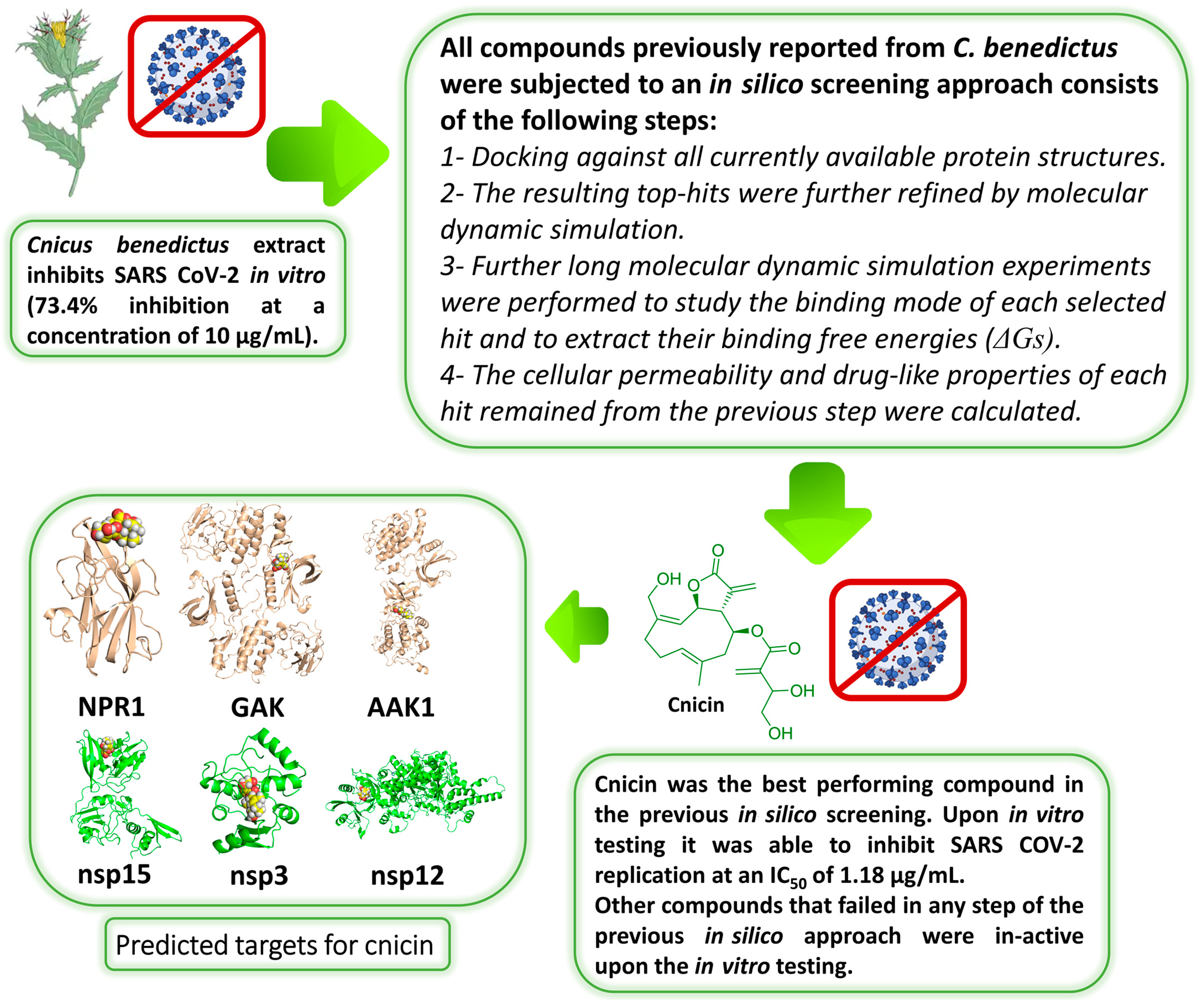
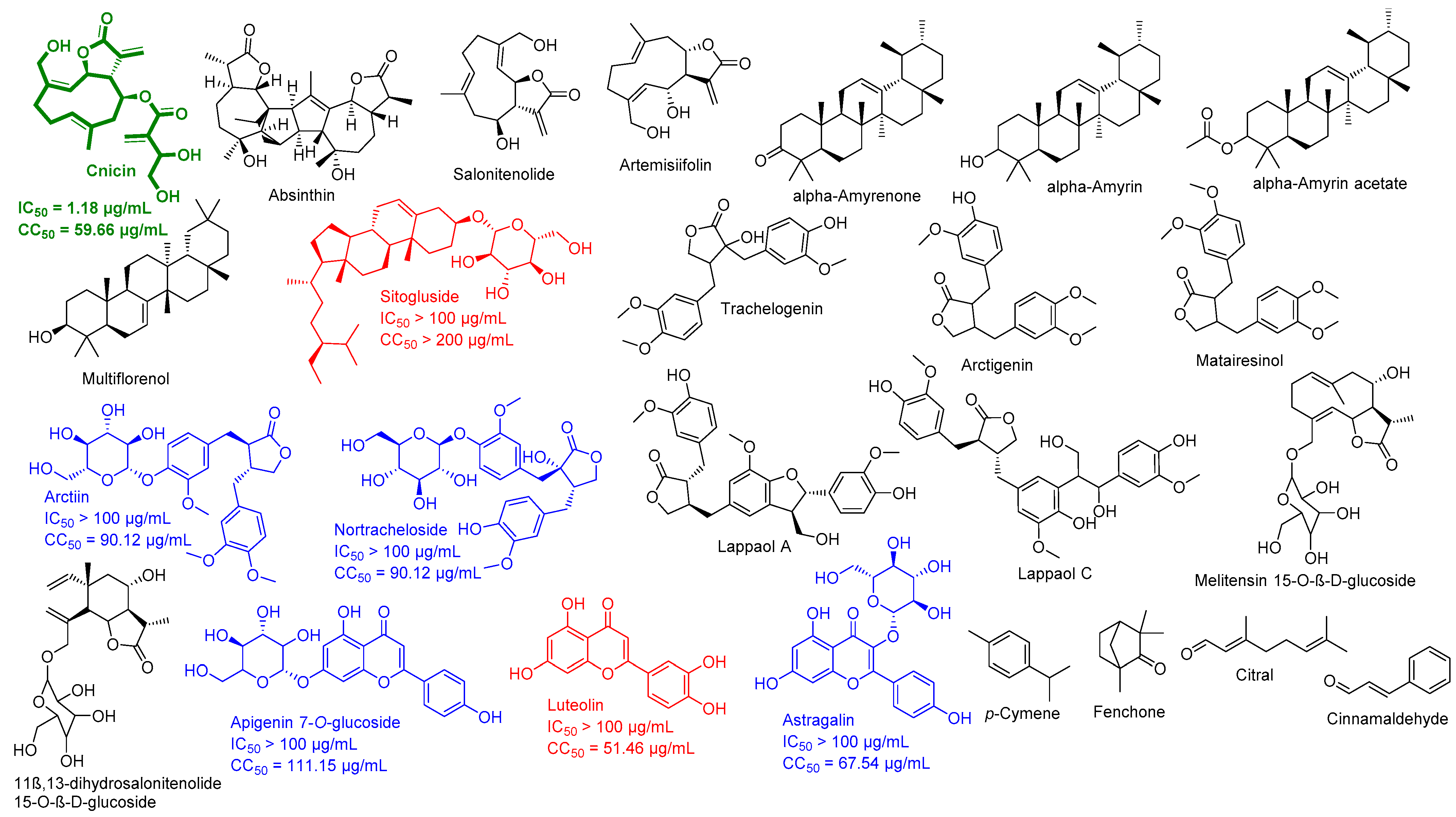
3. Results
3.1. Validation of In Silico Analysis
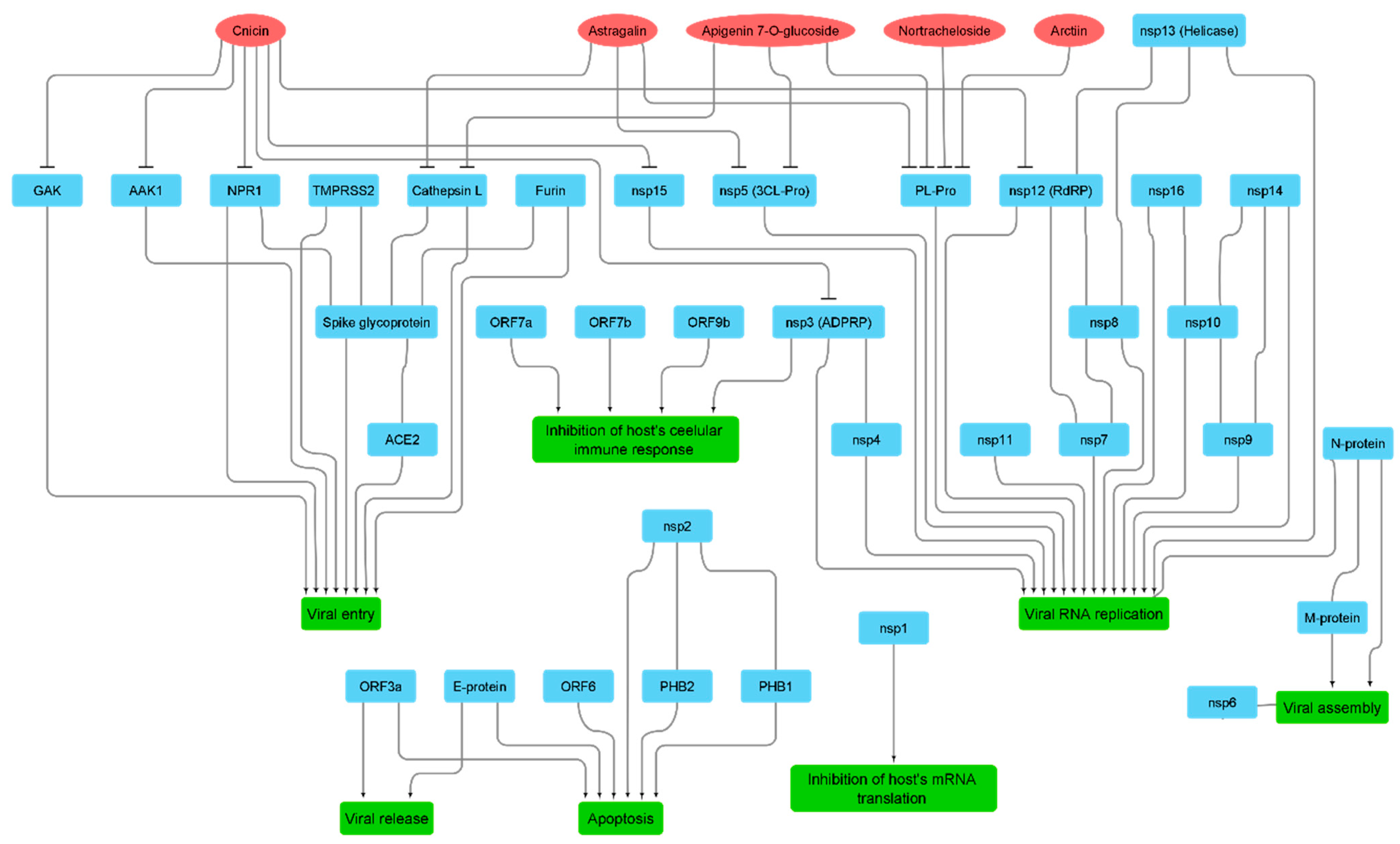
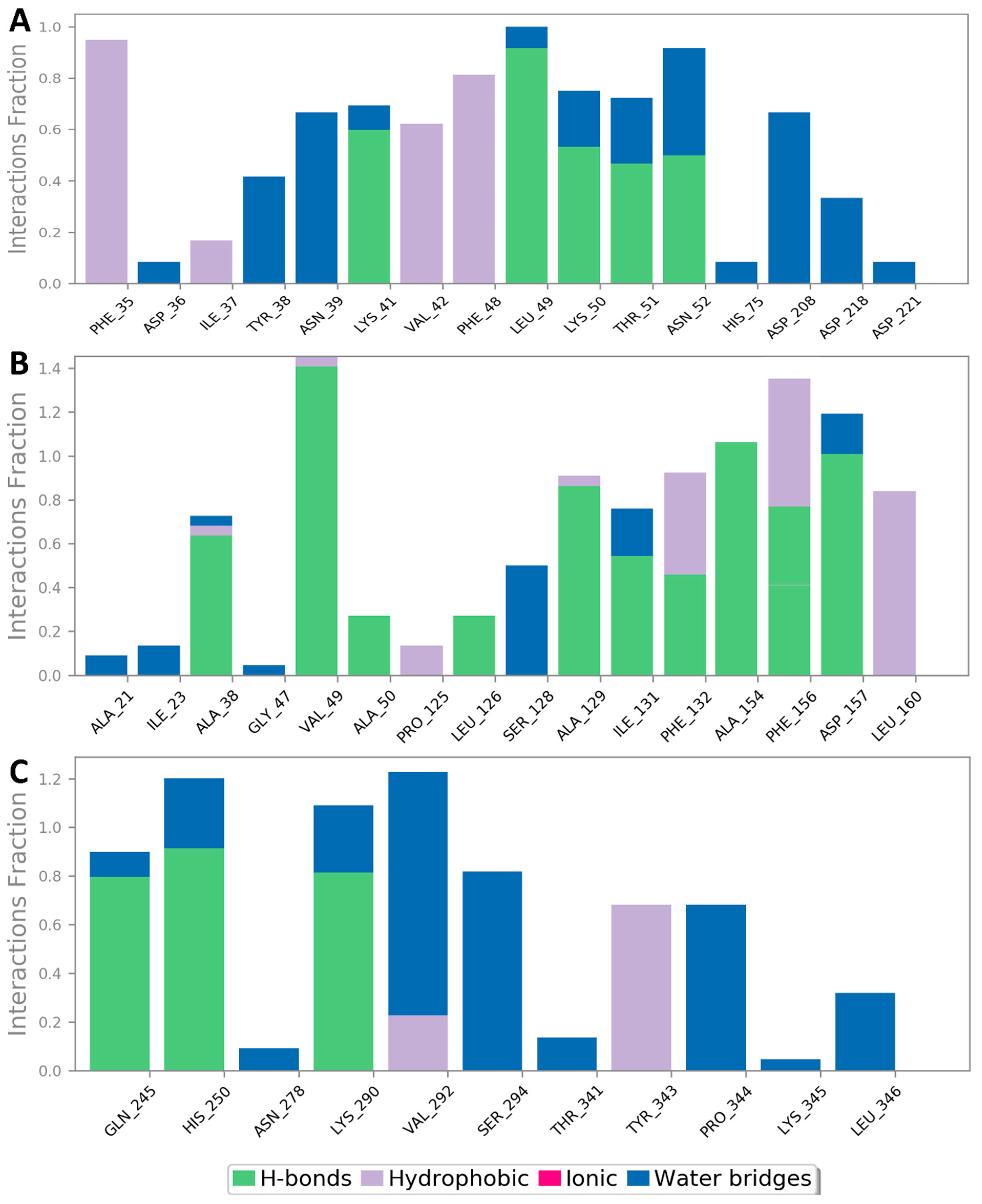
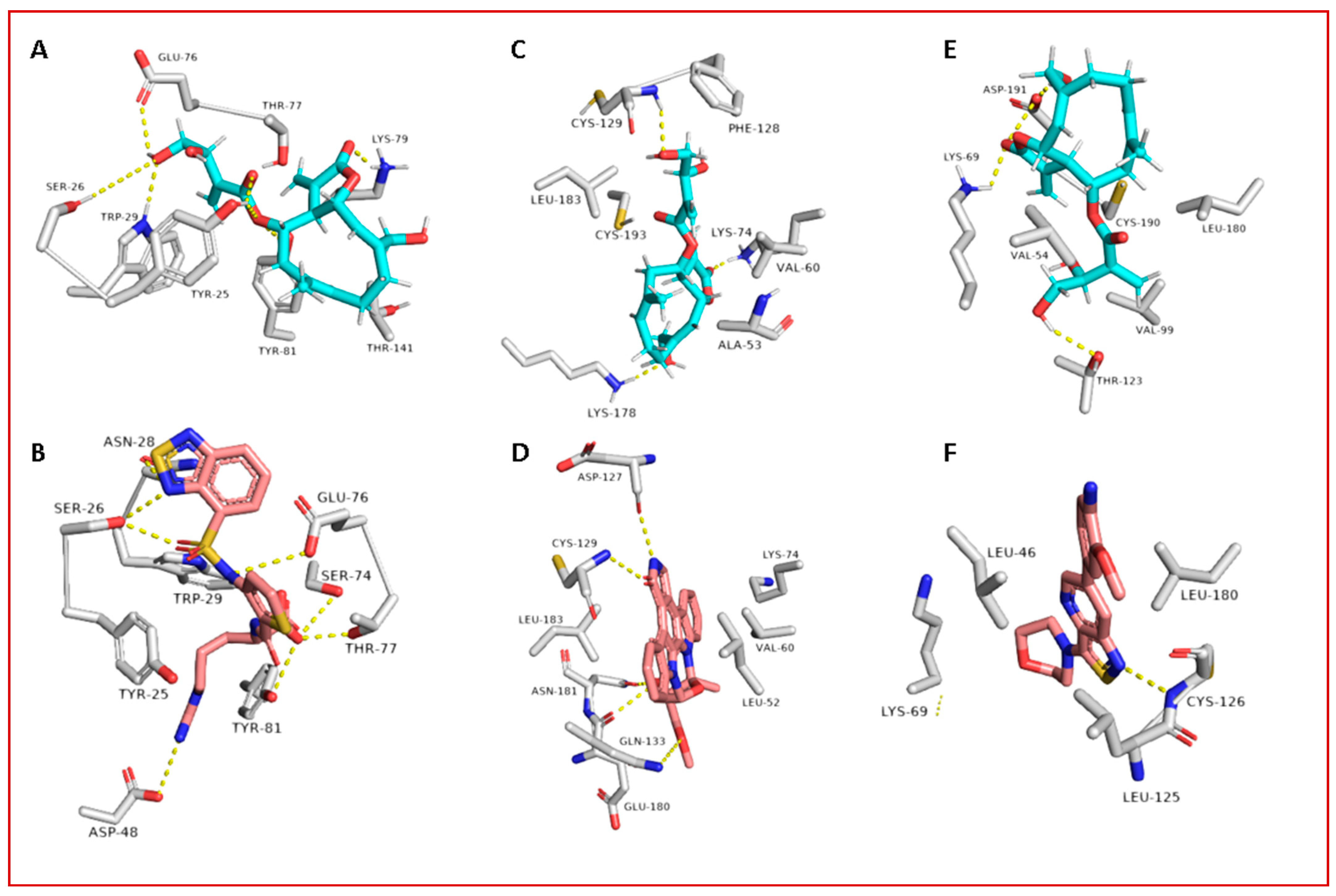
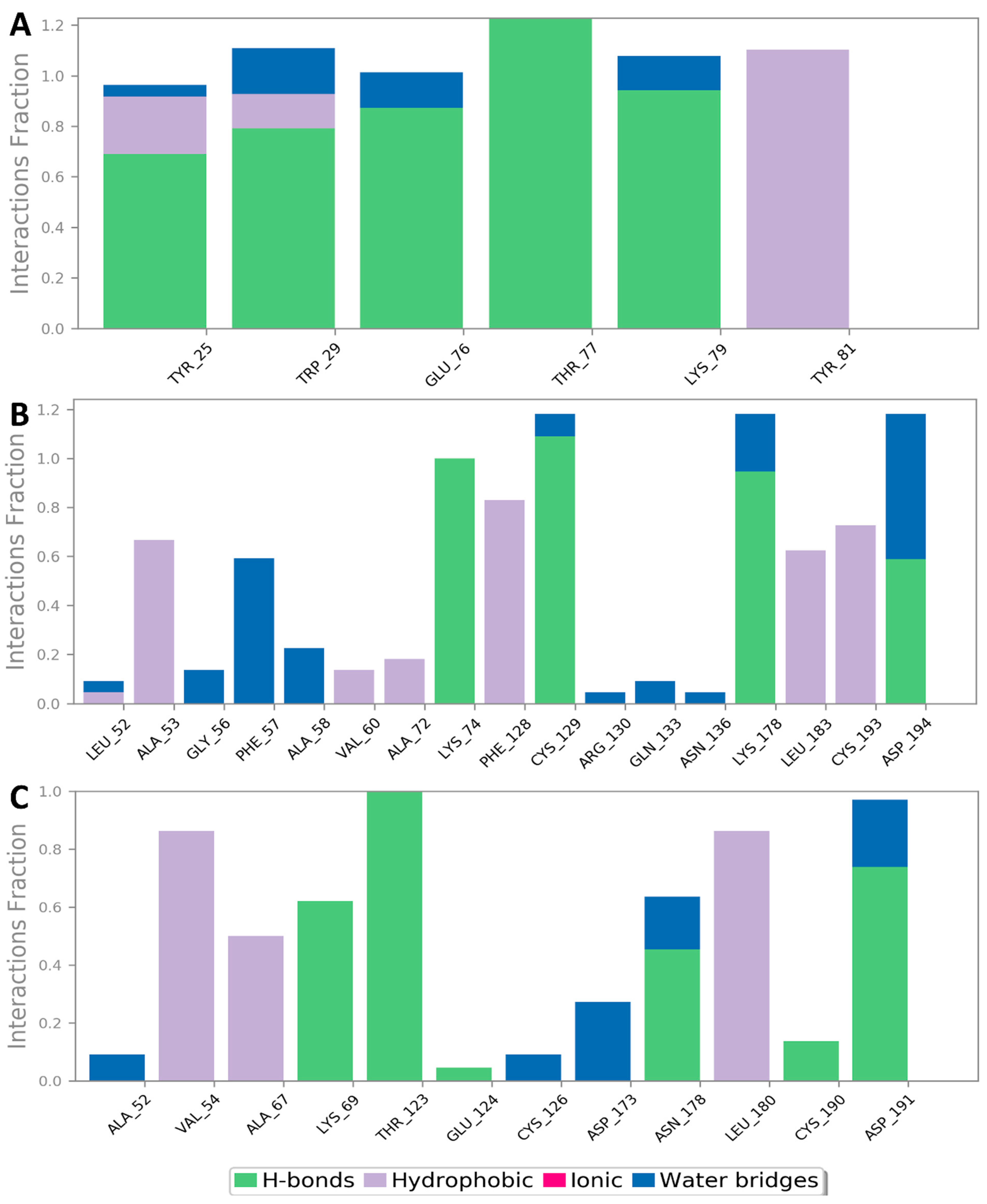
3.2. Molecular Interactions Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, D.; Chauhan, G.; Kalra, S.; Kumar, B.; Gill, M.S. A perspective on potential target proteins of COVID-19: Comparison with SARS-CoV for designing new small molecules. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 104, 104326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascella, M.; Rajnik, M.; Cuomo, A.; Dulebohn, S.C.; Di Napoli, R. Features, evaluation and treatment coronavirus (COVID-19). In Statpearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Mishra, N.; Singh, N.; Nisha, R.; Pal, R.R.; Singh, S.; Maurya, P.; Saraf, S.A. Credible Protein Targets and Curative Strategies for COVID-19: A Review. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2020, 2, 2067–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillaiyar, T.; Meenakshisundaram, S.; Manickam, M. Recent discovery and development of inhibitors targeting coronaviruses. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 668–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.K.; Feng, Y.; Chen, H.; Luk, H.K.; Yang, W.H.; Li, K.S.; Woo, P.C. Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus ORF8 protein is acquired from SARS-related coronavirus from greater horseshoe bats through recombination. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 10532–10547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Horby, P.W.; Hayden, F.G.; Gao, G.F. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet 2020, 395, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Fast identification of possible drug treatment of coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) through computational drug repurposing study. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 3277–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Islam, M.S.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, X. Traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of patients infected with 2019-new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): A review and perspective. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wondmkun, Y.T.; Mohammed, O.A. A Review on Novel Drug Targets and Future Directions for COVID-19 Treatment. Biol. Targets Ther. 2020, 14, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Mordy, F.M.; El-Hamouly, M.M.; Ibrahim, M.T.; Abd El-Rheem, G.; Aly, O.M.; Abd El-kader, A.M.; Youssif, K.A.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 main protease by phenolic compounds from Manilkara hexandra (Roxb.) Dubard assisted by metabolite profiling and in silico virtual screening. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 32148–32155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owis, A.I.; El-Hawary, M.S.; El Amir, D.; Aly, O.M.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Kamel, M.S. Molecular docking reveals the potential of Salvadora persica flavonoids to inhibit COVID-19 virus main protease. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 19570–19575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, A.M.; Khattab, A.R.; AboulMagd, A.M.; Hassan, H.M.; Rateb, M.E.; Zaid, H.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Nature as a treasure trove of potential anti-SARS-CoV drug leads: A structural/mechanistic rationale. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 19790–19802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, H.A.; Maulood, M.F.; Rasheed, A.M.; Fatak, D.F.; Kabah, K.K.; Abdulamir, A.S. Controlled randomized clinical trial on using Ivermectin with Doxycycline for treating COVID-19 patients in Baghdad, Iraq. MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbricht, C.; Basch, E.; Dacey, C.; Dith, S.; Hammerness, P.; Hashmi, S.; Weissner, W.; Seamon, E.; Vora, M. An evidence-based systematic review of blessed thistle (Cnicus benedictus) by the Natural Standard Research Collaboration. J. Diet. Suppl. 2008, 5, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Snafi, A.E. The constituents and pharmacology of Cnicus benedictus—A review. Pharm. Chem. J. 2016, 3, 129–135. [Google Scholar]
- Ulubelen, A.; Berkan, T. Triterpenic and steroidal compounds of Cnicus benedictus. Planta Med. 1977, 31, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sólyomváry, A.; Tóth, G.; Kraszni, M.; Noszál, B.; Molnár-Perl, I.; Boldizsár, I. Identification and quantification of lignans and sesquilignans in the fruits of Cnicus benedictus L.: Quantitative chromatographic and spectroscopic approaches. Microchem. J. 2014, 114, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Jian, Y.; Zulfiqar, A.; Li, B.; Zhang, K.; Long, F.; Peng, C.; Cai, X.; Khan, I.A.; Wang, W. Two new sesquiterpene lactone glycosides from Cnicus benedictus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 2211–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Thiessen, P.A.; Bolton, E.E.; Chen, J.; Fu, G.; Gindulyte, A.; Han, L.; He, J.; He, S.; Shoemaker, B.A.; et al. PubChem substance and compound databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D1202–D1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbe, S.; Buckland-Merrett, G. Data, disease and diplomacy: GISAID’s innovative contribution to global health. Glob. Chall. 2017, 1, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.E.; Jang, G.M.; Bouhaddou, M.; Xu, J.; Obernier, K.; White, K.M.; Tummino, T.A. A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature 2020, 583, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeliger, D.; de Groot, B.L. Ligand docking and binding site analysis with PyMOL and Autodock/Vina. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2010, 24, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, A.M.; Alhadrami, H.A.; El-Gendy, A.O.; Shamikh, Y.I.; Belbahri, L.; Hassan, H.M.; Rateb, M.E. Microbial natural products as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro). Microorganisms 2020, 8, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, K.J.; Chow, D.E.; Xu, H.; Dror, R.O.; Eastwood, M.P.; Gregersen, B.A.; Salmon, J.K.; Kolossvary, I.; Moraes, M.A.; Sacerdoti, F.D.; et al. Scalable algorithms for molecular dynamics simulations on commodity clusters. In Proceedings of the 2006 ACM/IEEE Conference on Supercomputing, Tampa, FL, USA, 11–17 November 2006; p. 43. [Google Scholar]
- Release, S. 3: Desmond molecular dynamics system, DE Shaw research, New York, NY, 2017. In Maestro-Desmond Interoperability Tools; Schrödinger: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Schrodinger LLC. Maestro, Version 9.0; Schrodinger LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lomize, A.L.; Pogozheva, I.D. Physics-Based Method for Modeling Passive Membrane Permeability and Translocation Pathways of Bioactive Molecules. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 3198–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: A web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.C.; Braun, R.; Wang, W.; Gumbart, J.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Villa, E.; Chipot, C.; Skeel, R.D.; Kalé, L.; Schulten, K. Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1781–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, M.; Wiese, S.; Warscheid, B. Cytoscape: Software for visualization and analysis of biological networks. In Data Mining in Proteomics; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 291–303. [Google Scholar]
- Lomize, A.L.; Hage, J.M.; Schnitzer, K.; Golobokov, K.; LaFaive, M.B.; Forsyth, A.C.; Pogozheva, I.D. PerMM: A Web Tool and Database for Analysis of Passive Membrane Permeability and Translocation Pathways of Bioactive Molecules. J. Chem. Inf. Modeling 2019, 59, 3094–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.X.; Yao, S.; Zhao, W.F.; Li, M.J.; Liu, J.; Shang, W.J.; Yu, K.Q. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 activities in vitro of Shuanghuanglian preparations and bioactive ingredients. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalska, K.; Kim, Y.; Jedrzejczak, R.; Maltseva, N.I.; Stols, L.; Endres, M.; Joachimiak, A. Crystal structures of SARS-CoV-2 ADP-ribose phosphatase (ADRP): From the apo form to ligand complexes. IUCrJ 2020, 7, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitiello, A.; La Porta, R.; Ferrara, F. Sacubitril, valsartan and SARS-CoV-2. BMJ Evid. Based Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, C.; Ginex, T.; Maestro, I.; Nozal, V.; Barrado-Gil, L.; Cuesta-Geijo, M.A.; Martínez, A.; Urquiza, J.; Alonso, C.; Campillo, N.E.; et al. COVID-19: Drug targets and potential treatments. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 12359–12386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Cao, W.; Xia, M.; Pan, S.; Xu, X. Study of structure and permeability relationship of flavonoids in Caco-2 cells. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 23, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veber, D.F.; Johnson, S.R.; Cheng, H.Y.; Smith, B.R.; Ward, K.W.; Kopple, K.D. Molecular properties that influence the oral bioavailability of drug candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Malone, B.; Llewellyn, E.; Grasso, M.; Shelton, P.M.; Olinares, P.D.B.; Kapoor, T.M. Structural basis for helicase-polymerase coupling in the SARS-CoV-2 replication-transcription complex. Cell 2020, 182, 1560–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Wower, J.; Maltseva, N.; Chang, C.; Jedrzejczak, R.; Wilamowski, M.; Joachimiak, A. Tipiracil binds to uridine site and inhibits Nsp15 endoribonuclease NendoU from SARS-CoV-2. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, A.; Allerston, C.K.; Jia, H.; Herzog, B.; Garza-Garcia, A.; Winfield, N.; Hartzoulakis, B.; Ellard, K.; Aqil, R.; Lynch, R.; et al. Small molecule inhibitors of the neuropilin-1 vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) interaction. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2215–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantuti-Castelvetri, L.; Ojha, R.; Pedro, L.D.; Djannatian, M.; Franz, J.; Kuivanen, S.; Smura, T. Neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and infectivity. Science 2020, 370, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, J. Covid-19: New coronavirus variant is identified in UK. BMJ 2020, 371, m4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiroz, L.S.; Ferreira, E.A.; Mengarda, A.C.; Almeida, A.D.C.; Pinto, P.D.F.; Coimbra, E.S.; de Moraes, J.; Denadai, Â.M.D.; Da Silva Filho, A.A. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of cnicin from blessed thistle (Centaurea benedicta) and its inclusion complexes with cyclodextrins against Schistosoma mansoni. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 1321–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbach, A.; Scheidig, A.J.; Klein, C.D. The unusual binding mode of cnicin to the antibacterial target enzyme MurA revealed by X-ray crystallography. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 5143–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caly, L.; Druce, J.D.; Catton, M.G.; Jans, D.A.; Wagstaff, K.M. The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Antivir. Res. 2020, 178, 104787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajter, J.C.; Sherman, M.S.; Fatteh, N.; Vogel, F.; Sacks, J.; Rajter, J.J. Use of Ivermectin Is Associated With Lower Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: The ICON Study. Chest 2020, 159, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jans, D.A.; Wagstaff, K.M. Ivermectin as a Broad-Spectrum Host-Directed Antiviral: The Real Deal? Cells 2020, 9, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alhadrami, H.A.; Sayed, A.M.; Hassan, H.M.; Youssif, K.A.; Gaber, Y.; Moatasim, Y.; Kutkat, O.; Mostafa, A.; Ali, M.A.; Rateb, M.E.; et al. Cnicin as an Anti-SARS-CoV-2: An Integrated In Silico and In Vitro Approach for the Rapid Identification of Potential COVID-19 Therapeutics. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050542
Alhadrami HA, Sayed AM, Hassan HM, Youssif KA, Gaber Y, Moatasim Y, Kutkat O, Mostafa A, Ali MA, Rateb ME, et al. Cnicin as an Anti-SARS-CoV-2: An Integrated In Silico and In Vitro Approach for the Rapid Identification of Potential COVID-19 Therapeutics. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(5):542. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050542
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlhadrami, Hani A., Ahmed M. Sayed, Hossam M. Hassan, Khayrya A. Youssif, Yasser Gaber, Yassmin Moatasim, Omnia Kutkat, Ahmed Mostafa, Mohamed Ahmed Ali, Mostafa E. Rateb, and et al. 2021. "Cnicin as an Anti-SARS-CoV-2: An Integrated In Silico and In Vitro Approach for the Rapid Identification of Potential COVID-19 Therapeutics" Antibiotics 10, no. 5: 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050542
APA StyleAlhadrami, H. A., Sayed, A. M., Hassan, H. M., Youssif, K. A., Gaber, Y., Moatasim, Y., Kutkat, O., Mostafa, A., Ali, M. A., Rateb, M. E., Abdelmohsen, U. R., & Gamaleldin, N. M. (2021). Cnicin as an Anti-SARS-CoV-2: An Integrated In Silico and In Vitro Approach for the Rapid Identification of Potential COVID-19 Therapeutics. Antibiotics, 10(5), 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050542










