Comparison of Immunological Profiles of SARS-CoV-2 Variants in the COVID-19 Pandemic Trends: An Immunoinformatics Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein Target Sequences
2.2. CTL and HTL Epitope Identification
2.2.1. CTL Epitope Prediction
2.2.2. HTL Epitope Prediction
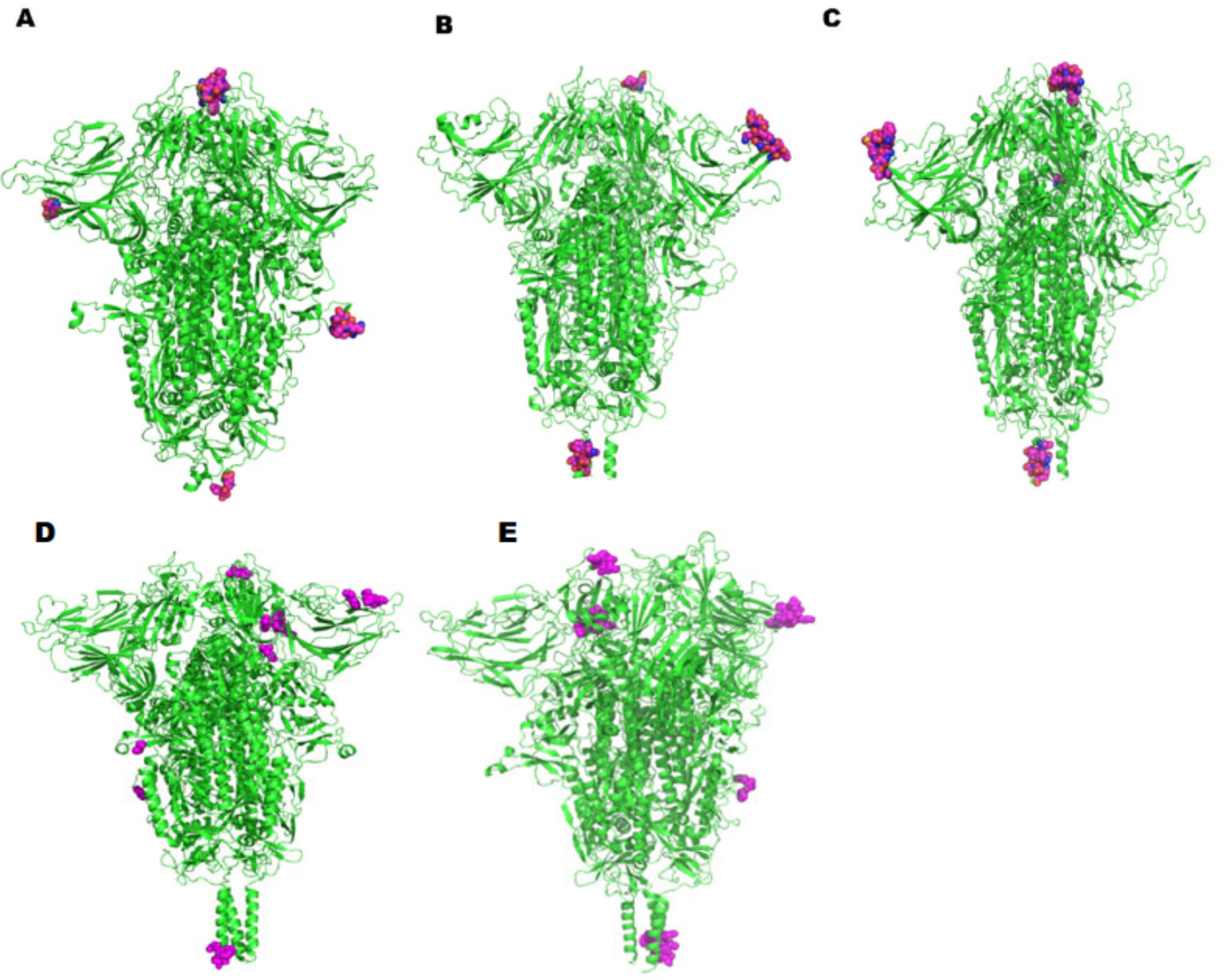
2.3. Analysis of Linear and Conformational B-Cell Epitopes
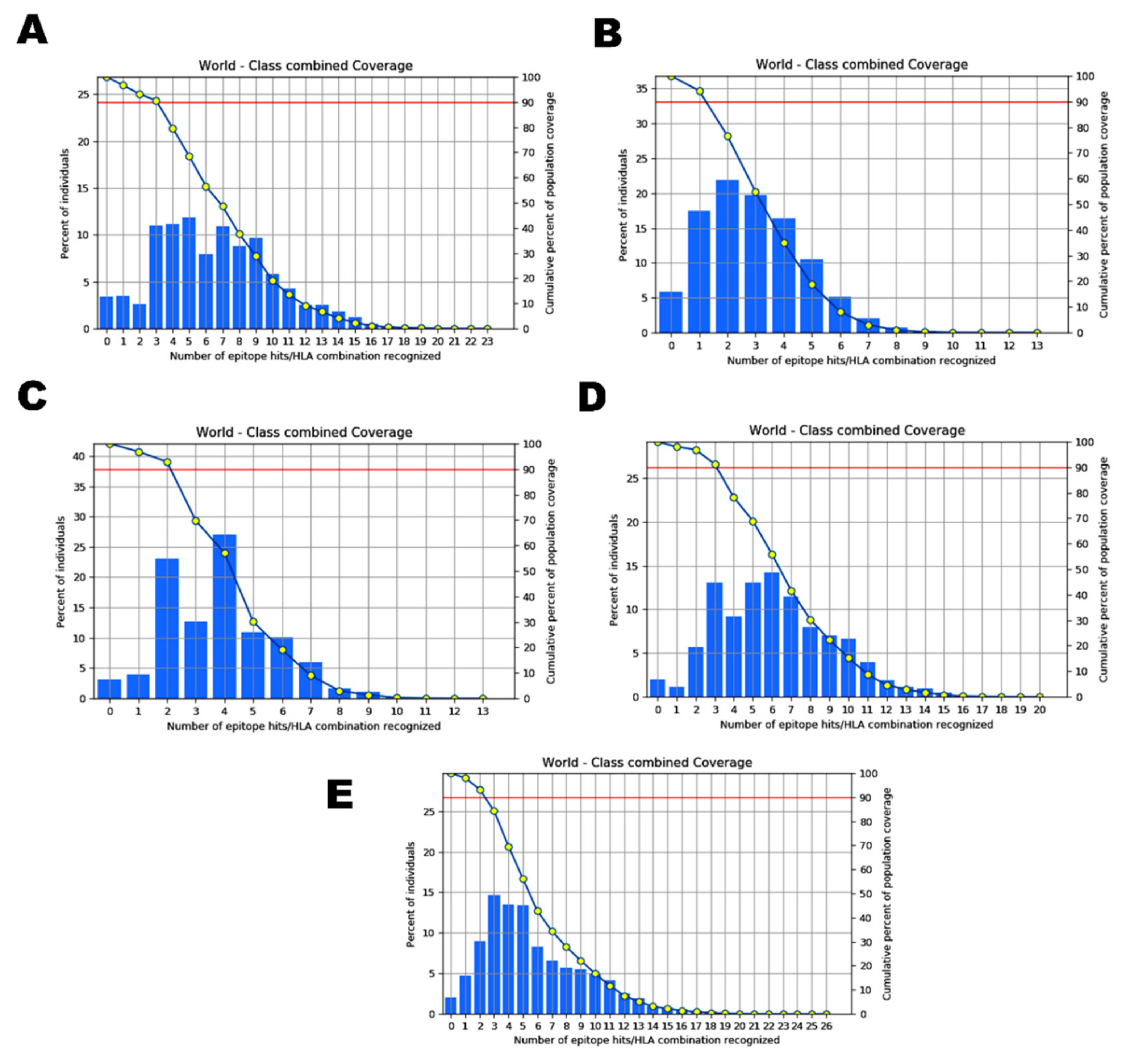
2.4. Analysis of Population Coverage
2.5. Binding Interactions of the Vaccine Peptides and the HLA Alleles
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Collection of Sequence Dataset
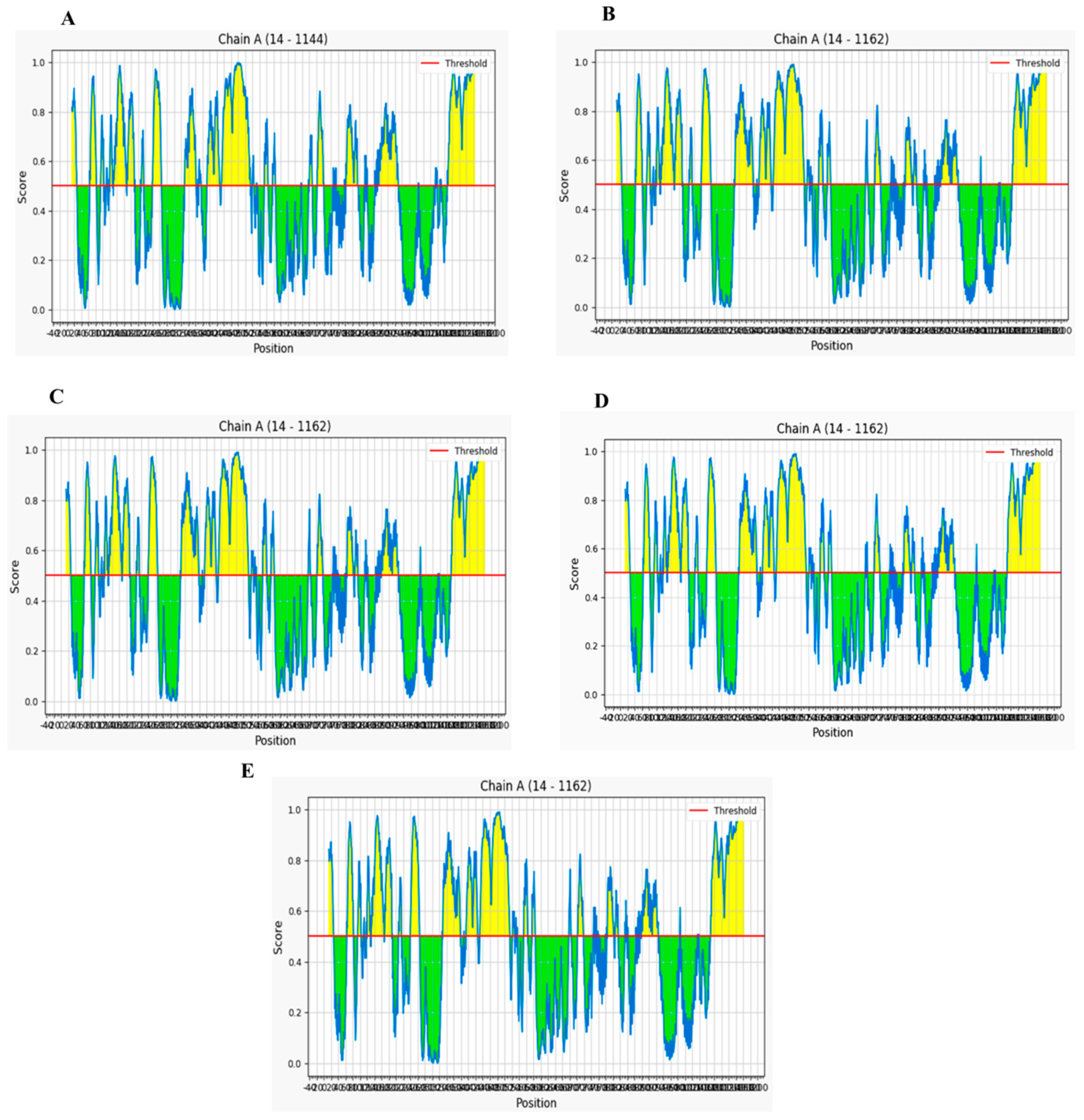
4.2. Sequence Variability Analysis of Spike Glycoprotein
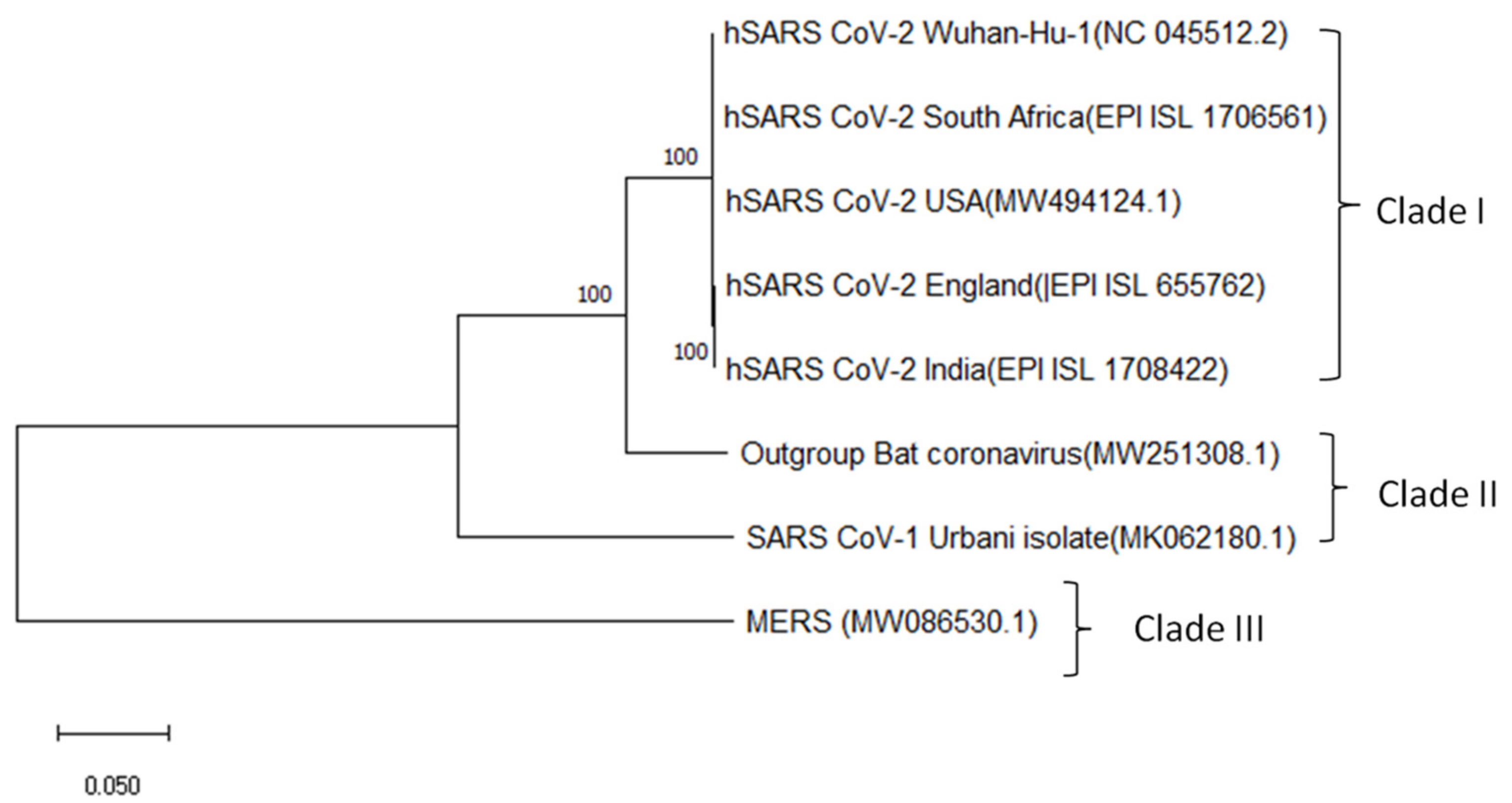
4.3. Phylogenetic Tree Construction
4.4. Prediction of Potential Cytotoxic and Helper T Lymphocyte Epitopes on Spike Glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2
4.5. B Lymphocyte Epitope Prediction in SARS-CoV-2 S Protein
4.6. Prediction of Protective Antigenic Epitopes
4.7. Conservancy Analysis
4.8. Population Coverage Analysis
4.9. Docking and Simulation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ejaz, H.; Alsrhani, A.; Zafar, A.; Javed, H.; Junaid, K.; Abdalla, A.E.; Abosalif, K.O.; Ahmed, Z.; Younas, S. COVID-19 and comorbidities: Deleterious impact on infected patients. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 1833–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Lancet Diabetes Endocrinology. COVID-19 and diabetes: A co-conspiracy? Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicenzi, M.; Di Cosola, R.; Ruscica, M.; Ratti, A.; Rota, I.; Rota, F.; Bollati, V.; Aliberti, S.; Blasi, F. The liaison between respiratory failure and high blood pressure: Evidence from COVID-19 patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Linde, N.A.; Sijbrands, E.J.; Boomsma, F.; van den Meiracker, A.H. Effect of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol on angiotensin II sensitivity: A randomized trial with fluvastatin. Hypertension 2006, 47, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro-Oliveira, A., Jr.; Nogueira, A.I.; Pereira, R.M.; Boas, W.W.; Dos Santos, R.A.; Simoes e Silva, A.C. The renin-angiotensin system and diabetes: An update. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 787–803. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Barker, T.A.; Berk, B.C. Angiotensin II and the endothelium: Diverse signals and effects. Hypertension 2005, 45, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzoni, A.; Maggi, L.; Capone, M.; Spinicci, M.; Salvati, L.; Colao, M.G.; Vanni, A.; Kiros, S.T.; Mencarini, J.; Zammarchi, L.; et al. Cell-mediated and humoral adaptive immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 are lower in asymptomatic than symptomatic COVID-19 patients. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 50, 2013–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, R.J.; Brokstad, K.A. Not just antibodies: B cells and T cells mediate immunity to COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 581–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, K.; Harris, T. An Effective COVID-19 Vaccine Needs to Engage T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 581807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.C.; Chen, C.H.; Wang, J.H.; Liao, H.C.; Yang, C.T.; Chen, C.W.; Lin, Y.C.; Kao, C.H.; Lu, M.Y.; Liao, J.C. Analysis of genomic distributions of SARS-CoV-2 reveals a dominant strain type with strong allelic associations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 30679–30686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khunti, K.; Singh, A.K.; Pareek, M.; Hanif, W. Is ethnicity linked to incidence or outcomes of covid-19? BMJ 2020, 369, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvizpour, S.; Pourseif, M.M.; Razmara, J.; Rafi, M.A.; Omidi, Y. Epitope-based vaccine design: A comprehensive overview of bioinformatics approaches. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korber, B.; Fischer, W.; Gnanakaran, S.G.; Yoon, H.; Theiler, J.; Abfalterer, W.; Foley, B.; Giorgi, E.E.; Bhattacharya, T.; Partridge, D.G.; et al. Spike mutation pipeline reveals the emergence of a more transmissible form of SARS-CoV-2. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentini, S.; Messali, S.; Zani, A.; Caccuri, F.; Giovanetti, M.; Ciccozzi, M.; Caruso, A. First detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein N501 mutation in Italy in August, 2020. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 00007-4. [Google Scholar]
- Mwenda, M.; Saasa, N.; Sinyange, N.; Busby, G.; Chipimo, P.J.; Hendry, J.; Kapona, O.; Yingst, S.; Hines, J.Z.; Minchella, P.; et al. Detection of B. 1.351 SARS-CoV-2 Variant Strain—Zambia, December 2020. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7008e2.htm (accessed on 27 February 2021).
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F. Structure, function, and evolution of coronavirus spike proteins. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2016, 3, 237–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulswit, R.J.; De Haan, C.A.; Bosch, B.J. Coronavirus spike protein and tropism changes. Adv. Virus Res. 2016, 96, 29–57. [Google Scholar]
- World Heath Organization (WHO). SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Available online: https://www.who.int/csr/don/31-december-2020-sars-cov2-variants/en/ (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Issues Policies to Guide Medical Product Developers Addressing Virus Variants. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-issues-policies-guide-medical-product-developers-addressing-virus (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Ong, E.; Wong, M.U.; Huffman, A.; He, Y. COVID-19 coronavirus vaccine design using reverse vaccinology and machine learning. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wu, J.; Nie, J.; Zhang, L.; Hao, H.; Liu, S.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, H.; Nie, L.; et al. The impact of mutations in SARS-CoV-2 spike on viral infectivity and antigenicity. Cell 2020, 182, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, T.; Cai, D.; Hu, Z.; Liao, H.; Zhi, L.; Wei, H.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Cytokine storm intervention in the early stages of COVID-19 pneumonia. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 53, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehl, P.; Levitt, M. Structure-based conformational preferences of amino acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 12524–12529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Zheng, D.; Liang, S.; Zhang, C. Conformational B-cell epitope prediction on antigen protein structures: A review of current algorithms and comparison with common binding site prediction methods. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Shang, J.; Graham, R.; Baric, R.S.; Li, F. Receptor recognition by the novel coronavirus from Wuhan: An analysis based on decade-long structural studies of SARS coronavirus. J. Virol. 2020, 94, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, T.; Platt, D.; Parida, L. Variant analysis of SARS-CoV-2 genomes. Bull. World Health Organ. 2020, 98, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftab, S.O.; Ghouri, M.Z.; Masood, M.U.; Haider, Z.; Khan, Z.; Ahmad, A.; Munawar, N. Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase as a potential therapeutic drug target using a computational approach. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Peng, Y.; Huang, B.; Ding, X.; Wang, X.; Niu, P.; Meng, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; et al. Genome composition and divergence of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) originating in China. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, S.; Teng, T.; Abdalla, A.E.; Zhu, W.; Xie, L.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X. Systematic comparison of two animal-to-human transmitted human coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV. Viruses 2020, 12, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Tworowski, D.; Detroja, R.; Mukherjee, S.B.; Frenkel-Morgenstern, M. Immunoinformatics and structural analysis for identification of immunodominant epitopes in SARS-CoV-2 as potential vaccine targets. Vaccines 2020, 8, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, V.; Bose, S. Immunoinformatics-aided identification of T cell and B cell epitopes in the surface glycoprotein of 2019-nCoV. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognan, D.; Zimmermann, N.; Jung, G.; Folkers, G. Molecular dynamics study of a complex between the human histocompatibility antigen HLA-A2 and the IMP58-66 nonapeptide from influenza virus matrix protein. Eur. J. Biochem. 1992, 208, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakib, A.; Sami, S.A.; Mimi, N.J.; Chowdhury, M.M.; Eva, T.A.; Nainu, F.; Paul, A.; Shahriar, A.; Tareq, A.M.; Emon, N.U.; et al. Immunoinformatics-guided design of an epitope-based vaccine against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 spike glycoprotein. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 124, 103967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frampton, D.; Rampling, T.; Cross, A.; Bailey, H.; Heaney, J.; Byott, M.; Scott, R.; Sconza, R.; Price, J.; Margaritis, M.; et al. Genomic characteristics and clinical effect of the emergent SARS-CoV-2 B. 1.1. 7 lineage in London, UK: A whole-genome sequencing and hospital-based cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 170–175. [Google Scholar]
- Baric, R.S. Emergence of a Highly Fit SARS-CoV-2 Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2684–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tough, R.H.; McLaren, P.J. Interaction of the host and viral genome and their influence on HIV disease. Front. Genet. 2019, 9, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant Upadhyay, R. Evolution of new variants/mutants of JE virus, its effect on neurovirulence, antigenicity, host immune responses and disease transmission in endemic areas. J. Viruses 2014, 2014, 516904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, T.M.; de Oliveira, M.T.; Watanabe, A.S.; Biselli-Périco, J.M.; Drumond, B.P.; Ribeiro, M.R.; Vedovello, D.; Araújo, J.P., Jr.; Pimenta, P.F.; Chaves, B.A.; et al. Viral immunogenicity determines epidemiological fitness in a cohort of DENV-1 infection in Brazil. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briney, B.; Sok, D.; Jardine, J.G.; Kulp, D.W.; Skog, P.; Menis, S.; Jacak, R.; Kalyuzhniy, O.; De Val, N.; Sesterhenn, F.; et al. Tailored immunogens direct affinity maturation toward HIV neutralizing antibodies. Cell 2016, 166, 1459–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Malik, D.; Raina, A. Immuno-informatics approach for B-cell and T-cell Epitope based peptide vaccine design against novel COVID-19 virus. Vaccine 2021, 39, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, U.K.; Tayebi, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Adhikari, U.K.; Tayebi, M.; Rahman, M.M. Immunoinformatics approach for epitope-based peptide vaccine design and active site prediction against polyprotein of emerging oropouche virus. J. Immunol. Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| SARS-CoV-2 Isolate | Length | Molecular Weight (Dalton) | Theoretical PI | Total no of −ve and +ve Aminoacids | Extinction Coefficient (M−1cm−1) | Estimated Half-Life (h) | Instability Index | Aliphatic Index | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wuhan | 1273 | 141,178.47 | 6.24 | 110/103 | 148,960 | 30 | 33.01 | 84.67 | −0.079 |
| England | 1273 | 141,169.51 | 6.32 | 109/103 | 150,450 | 30 | 33.03 | 84.67 | −0.075 |
| USA | 1273 | 141,120.43 | 6.32 | 109/103 | 148,960 | 30 | 32.86 | 84.67 | −0.77 |
| India | 1273 | 141,280.46. | 6.35 | 109/103 | 150,450 | 30 | 32.82 | 84.45 | −0.078 |
| South Africa | 1273 | 141,120.43 | 6.32 | 109/103 | 148,960 | 30 | 32.86 | 84.67 | −0.077 |
| SARS-CoV-2 Variant | Epitope | Position | Antigenicity Score | Immunogenicity Score | MHC I Alleles | No of MHC I Binding Alleles | Conservancy at 100% Sequence Identity | Allergenicity | Toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wuhan, China | ILDITPCSF | 584–592 | 1.184 | 0.02632 | HLA-B*15:01, HLA-A*01:01, HLA-A*02:06, HLA-B*35:01, HLA-B*08:01, HLA-A*02:01, HLA-A*32:01, HLA-A*24:02, HLA-A*23:01, HLA-A*30:02, HLA-B*58:01, HLA-B*53:01 | 12 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| STQDLFLPF | 50–58 | 0.662 | 0.06828 | HLA-A*32:01, HLA-B*57:01, HLA-B*15:01, HLA-A*26:01, HLA-B*58:01, HLA-B*35:01, HLA-A*30:02, HLA-A*23:01, HLA-A*24:02, HLA-A*01:01, HLA-A*11:01, HLA-B*53:01 | 12 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| VVFLHVTYV | 1060–1068 | 1.512 | 0.1278 | HLA-A*02:06, HLA-A*02:03, HLA-A*02:01, HLA-A*68:02, HLA-B*51:01, HLA-A*30:01, HLA-A*32:01, HLA-B*08:01, HLA-A*26:01 | 9 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| GVVFLHVTY | 1059–1067 | 1.410 | 0.20837 | HLA-B*15:01, HLA-A*30:02, HLA-A*26:01, HLA-B*35:01, HLA-A*32:01, HLA-B*57:01, HLA-A*11:01, HLA-A*01:01, HLA-B*58:01 | 9 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| WTAGAAAYY | 258–266 | 0.662 | 0.15259 | HLA-A*26:01, HLA-A*01:01, HLA-A*30:02, HLA-A*68:01, HLA-B*35:01, HLA-B*15:01, HLA-B*58:01, HLA-B*57:01 | 8 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| GAAAYYVGY | 261–269 | 0.660 | 0.09963 | HLA-A*30:02, HLA-B*15:01, HLA-B*35:01, HLA-A*26:01, HLA-A*01:01, HLA-A*11:01, HLA-B*58:01 | 7 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| RVVVLSFEL | 509–517 | 1.192 | 0.046 | HLA-A*32:01, HLA-A*02:06, HLA-B*57:01, HLA-B*58:01, HLA-A*02:01 | 5 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| England | WTAGAAAY | 258–266 | 0.826 | 0.15259 | HLA-A*26:01, HLA-A*01:01, HLA-A*30:02, HLA-A*68:01, HLA-B*35:01, HLA-B*15:01, HLA-B*58:01, HLA-B*53:01, HLA-B*57:01 | 9 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| QYIKWPWYI | 1208–1216 | 1.664 | 0.21624 | HLA-A*24:02, HLA-A*23:01, HLA-C*06:02, HLA-C*07:02, HLA-C*14:02, HLA-A*32:01, HLA-C*07:01 | 7 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| GVYFASTEK | 89–97 | 0.664 | 0.09023 | HLA-A*11:01, HLA-A*30:01, HLA-A*68:01, HLA-A*31:01 | 4 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| NGVEGFNCY | 481–489 | 1.182 | 0.22039 | HLA-B*35:01, HLA-A*26:01, HLA-C*12:02 | 3 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| PYRVVVLSF | 507–515 | 1.028 | 0.03138 | HLA-A*23:01, HLA-A*24:02, HLA-C*14:02 | 3 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| VYAWNRKRI | 350–358 | 0.813 | 0.12625 | HLA-A*24:02, HLA-C*14:02, HLA-A*23:01 | 3 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| SPRRARSVA | 680–688 | 0.511 | 0.0402 | HLA-B*07:02, HLA-B*08:01 | 2 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| USA | VVFLHVTYV | 1060–1068 | 1.51 | 0.1278 | HLA-A*02:06, HLA-A*02:03, HLA-A*02:01, HLA-A*68:02, HLA-B*51:01, HLA-A*30:01, HLA-A*30:02, HLA-A*32:01, HLA-B*08:01, HLA-A*26:01, HLA-A*33:01, HLA-A*03:01, HLA-A*31:01, HLA-B*57:01, HLA-B*15:01, HLA-A*68:01 | 16 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| ILDITPCSF | 584–592 | 1.184 | 0.02632 | HLA-B*15:01, HLA-A*01:01, HLA-A*02:06, HLA-B*35:01, HLA-B*08:01, HLA-A*02:01, HLA-A*32:01, HLA-A*24:02, HLA-A*23:01, HLA-A*30:02, HLA-B*58:01, HLA-B*53:01 | 12 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| GVVFLHVTY | 1059–1067 | 1.140 | 0.20837 | HLA-B*15:01, HLA-A*30:02, HLA-A*26:01, HLA-B*35:01, HLA-A*32:01, HLA-B*57:01, HLA-A*11:01, HLA-B*58:01 | 8 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| GAAAYYVGY | 1060–1068 | 0.661 | 0.09963 | HLA-A*30:02, HLA-B*15:01, HLA-B*35:01, HLA-A*26:01, HLA-A*01:01, HLA-A*11:01, HLA-B*58:01 | 7 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| WTAGAAAYY | 258–266 | 0.631 | 0.15259 | HLA-A*26:01, HLA-A*01:01, HLA-A*30:02, HLA-A*68:01, HLA-B*35:01, HLA-B*15:01, HLA-B*58:01 | 7 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| LPFNDGVYF | 84–92 | 0.559 | 0.11767 | HLA-B*35:01, HLA-B*53:01, HLA-B*51:01, HLA-B*07:02, HLA-A*26:01 | 5 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| IAIVMVTIM | 1225–1233 | 1.134 | 0.06312 | HLA-B*51:01, HLA-B*35:01 | 2 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| India | FTISVTTEI | 718–726 | 0.8535 | 0.04473 | HLA-A*68:02; HLA-A*02:06; HLA-A*02:03; HLA-A*02:01; HLA-B*51:01; HLA-A*26:01; HLA-B*58:01; HLA-A*32:01; HLA-B*53:01 | 9 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| VVFLHVTYV | 1060–1068 | 1.512 | 0.1278 | HLA-A*02:06; HLA-A*02:03; HLA-A*02:01; HLA-A*68:02; HLA-B*51:01; HLA-A*30:01; HLA-A*32:01; HLA-B*08:01; HLA-A*26:01 | 9 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| YQPYRVVVL | 505–513 | 0.5964 | 0.1409 | HLA-B*08:01; HLA-A*02:06; HLA-B*15:01; HLA-A*02:03; HLA-A*02:01; HLA-A*24:02; HLA-B*40:01; HLA-A*23:01 | 8 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| YSKHTPINL | 204–212 | 1.0547 | 0.9845 | HLA-B*57:01; HLA-A*30:01; HLA-B*08:01; HLA-B*58:01; HLA-A*68:02; HLA-B*51:01; HLA-B*15:01; HLA-A*32:01 | 8 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| WTAGAAAYY | 258–266 | 0.6306 | 0.1525 | HLA-A*26:01; HLA-A*01:01; HLA-A*30:02; HLA-A*68:01; HLA-B*35:01; HLA-B*15:01; HLA-B*58:01 | 7 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| LPFNDGVYF | 84–92 | 0.5593 | 0.11767 | HLA-B*35:01; HLA-B*53:01; HLA-B*51:01; HLA-B*07:02; HLA-A*26:01 | 5 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| GAAAYYVGY | 261–269 | 0.6604 | 0.9963 | HLA-A*30:02; HLA-B*15:01; HLA-B*35:01; HLA-A*26:01; HLA-A*01:01 | 5 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| South Africa | IAIPINFTI | 712–720 | 1.5131 | 0.27703 | HLA-B*51:01; HLA-B*58:01; HLA-B*57:01; HLA-A*02:06; HLA-A*68:02; HLA-B*53:01; HLA-A*32:01; HLA-A*02:01; HLA-A*23:01; HLA-B*35:01; HLA-A*24:02 | 11 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| FTISVTTEI | 718–726 | 0.8534 | 0.04473 | HLA-A*68:02; HLA-A*02:06; HLA-A*02:03; HLA-A*02:01; HLA-B*51:01; HLA-A*26:01; HLA-B*58:01; HLA-A*32:01; HLA-B*53:01 | 9 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| YQPYRVVVL | 505–513 | 0.5964 | 0.1409 | HLA-B*08:01; HLA-A*02:06; HLA-B*15:01; HLA-A*02:03; HLA-A*02:01; HLA-A*24:02; HLA-B*40:01 HLA-A*23:01 | 8 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| WTAGAAAYY | 258–266 | 0.6306 | 0.15259 | HLA-A*26:01; HLA-A*01:01; HLA-A*30:02; HLA-A*68:01; HLA-B*35:01; HLA-B*15:01; HLA-B*58:01 | 7 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| YSKHTPINL | 204–212 | 1.0547 | 0.09845 | HLA-B*57:01; HLA-A*30:01; HLA-B*08:01; HLA-B*58:01; HLA-A*68:02; HLA-B*51:01; HLA-A*32:01 | 7 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| LPFNDGVYF | 84–92 | 0.5593 | 0.11767 | HLA-B*35:01; HLA-B*53:01; HLA-B*51:01; HLA-B*07:02; HLA-A*26:01 | 5 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic | |
| GVVFLHVTY | 1059–1067 | 1.4104 | 0.20837 | HLA-B*15:01; HLA-A*30:02; HLA-A*26:01; HLA-B*35:01; HLA-A*32:01 | 5 | 100% | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| Sl. No. | Peptide | MHC II Binding Allele | Start | End | Method | Percentile Rank | Vaxijen Score | Allergenicity | Toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wuhan Isolate | |||||||||
| 1 | MFVFLVLLPLVSSQC | HLA-DRB1*01:01 | 1 | 15 | Consensus | 0.24 | Antigen (0.5741) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 2 | MFVFLVLLPLVSSQC | HLA-DPA1*03:01/DPB1*04:02 | 1 | 15 | Consensus | 0.34 | Antigen (0.5741) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 3 | VLLPLVSSQCVNLTT | HLA-DRB4*01:01 | 6 | 20 | Consensus | 1.5 | Antigen (0.8957) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 4 | LHSTQDLFLPFFSNV | HLA-DPA1*01:03/DPB1*02:01 | 48 | 62 | Consensus | 1.4 | Antigen (0.2110) | Allergen | Non-toxic |
| 5 | LFLPFFSNVTWFHAI | HLA-DPA1*01:03/DPB1*04:01 | 54 | 68 | NetMHCIIpan | 0.81 | Antigen (0.2477) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 6 | KTQSLLIVNNATNVV | HLA-DRB3*02:02 | 113 | 127 | NetMHCIIpan | 0.17 | Antigen (0.6303) | Allergen | Non-toxic |
| 7 | SFVIRGDEVRQIAPG | HLA-DRB3*01:01 | 399 | 413 | Consensus | 0.51 | Antigen (0.5882) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 8 | GNYNYLYRLFRKSNL | HLA-DRB1*11:01 | 447 | 461 | Consensus | 0.22 | Non-antigen (0.1808) | Allergen | Non-toxic |
| 9 | PYRVVVLSFELLHAP | HLA-DPA1*03:01/DPB1*04:02 | 507 | 521 | Consensus | 0.25 | Antigen (0.8161) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 10 | FNFNGLTGTGVLTES | HLA-DRB1*09:01 | 541 | 555 | Consensus | 0.75 | Antigen (0.7797) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 11 | DIPIGAGICASYQTQ | HLA-DQA1*05:01/DQB1*03:01 | 633 | 677 | Consensus | 1.2 | Antigen (1.1088) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 12 | IAIPTNFTISVTTEI | HLA-DRB1*07:01 | 712 | 726 | Consensus | 0.47 | Antigen (0.7719) | Allergen | Non-toxic |
| 133 | CSNLLLQYGSFCTQL | HLA-DRB1*15:01 | 749 | 763 | Consensus | 0.58 | Antigen (0.6336) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 14 | WYIWLGFIAGLIAIV | HLA-DQA1*05:01/DQB1*03:01 | 1214 | 1228 | Consensus | 0.58 | Antigen (0.5770) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 15 | IWLGFIAGLIAIVMV | HLA-DQA1*05:01/DQB1*03:01 | 1216 | 1230 | Consensus | 0.51 | Antigen (0.6150) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| England Variant | |||||||||
| 16 | FVFLVLLPLVSSQCV | HLA-DRB1*01:01 | 2 | 16 | Consensus | 0.24 | Antigen (0.7185) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 17 | KTQSLLIVNNATNVV | HLA-DRB1*13:02 | 113 | 127 | Consensus | 0.01 | Antigen (0.6303) | Allergen | Non-toxic |
| 18 | YRVVVLSFELLHAPA | HLA-DPA1*01:03/DPB1*04:01 | 508 | 522 | NetMHCIIpan | 0.95 | Antigen (0.7072) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 19 | VVLSFELLHAPATVC | HLA-DRB1*01:01 | 511 | 525 | Consensus | 0.03 | Antigen (0.8618) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 20 | DIPIGAGICASYQTQ | HLA-DQA1*05:01/DQB1*03:01 | 663 | 677 | Consensus | 1.2 | Antigen (1.1088) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 21 | PRRARSVASQSIIAY | HLA-DPA1*02:01/DPB1*14:01 | 681 | 695 | NetMHCIIpan | 1.2 | Non-antigen (0.2408) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 22 | YIWLGFIAGLIAIVM | HLA-DQA1*05:01/DQB1*03:01 | 1215 | 1229 | Consensus | 0.51 | Antigen (0.6090) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| USA Variant | |||||||||
| 23 | SSGWTAGAAAYYVGY | HLA-DQA1*05:01/DQB1*03:01 | 255 | 269 | Consensus | 0.94 | Antigen (0.6604) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 24 | SGWTAGAAAYYVGYL | HLA-DQA1*05:01/DQB1*03:01 | 256 | 270 | Consensus | 1.2 | Antigen (0.6604) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 25 | VVVLSFELLHAPATV | HLA-DPA1*03:01/DPB1*04:02 | 510 | 524 | Consensus | 0.9 | Antigen (0.8083) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 26 | DIPIGAGICASYQTQ | HLA-DQA1*05:01/DQB1*03:01 | 663 | 677 | Consensus | 1.2 | Antigen (1.1088) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 27 | IAIPTNFTISVTTEI | HLA-DRB1*07:01 | 712 | 726 | Consensus | 0.47 | Antigen (0.7719) | Allergen | Non-toxic |
| 28 | RSFIEDLLFNKVTLA | HLA-DPA1*02:01/DPB1*05:01 | 815 | 829 | Consensus | 1.4 | Non-antigen (−0.0341) | Allergen | Non-toxic |
| 29 | GWTFGAGAALQIPFA | HLA-DRB1*09:01 | 885 | 899 | Consensus | 0.35 | Non-antigen (0.4665) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 30 | PREGVFVSNGTHWFV | HLA-DRB1*13:02 | 1090 | 1104 | Consensus | 1.2 | Antigen (1.0165) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 31 | REGVFVSNGTHWFVT | HLA-DRB3*02:02 | 1091 | 1105 | NetMHCIIpan | 0.2 | Antigen (1.0165) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 32 | SGNCDVVIGIVNNTV | HLA-DRB1*13:02 | 1123 | 1137 | Consensus | 1.3 | Antigen (0.5968) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 33 | CDVVIGIVNNTVYDP | HLA-DRB1*13:02 | 1126 | 1140 | Consensus | 0.7 | Antigen (0.7320) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 34 | WYIWLGFIAGLIAIV | HLA-DQA1*05:01/DQB1*03:01 | 1214 | 1228 | Consensus | 0.58 | Antigen (0.5770) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| Indian Variant | |||||||||
| 35 | MFVFLVLLPLVSSQC | HLA-DRB1*01:01 | 1 | 15 | Consensus | 0.24 | Antigen (0.5741) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 36 | DLFLPFFSNVTWFHA | HLA-DRB1*04:01 | 53 | 67 | Consensus | 1.1 | Non-antigen (0.2472) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 37 | KTQSLLIVNNATNVV | HLA-DRB1*13:02 | 113 | 127 | Consensus | 0.01 | Antigen (0.6303) | Allergen | Non-toxic |
| 38 | REFVFKNIDGYFKIY | HLA-DRB5*01:01 | 190 | 204 | Consensus | 0.17 | Non-antigen (−0.1712) | Allergen | Non-toxic |
| 39 | TRFASVYAWNRKRIS | HLA-DPA1*02:01/DPB1*14:01 | 232 | 246 | Consensus | 0.52 | Non-antigen (0.4963) | Allergen | Non-toxic |
| 40 | NYNYLYRLFRKSNLK | HLA-DRB1*11:01 | 448 | 462 | Consensus | 0.42 | Non-antigen (0.1089) | Allergen | Non-toxic |
| 41 | PYRVVVLSFELLHAP | HLA-DPA1*01:03/DPB1*02:01 | 507 | 521 | Consensus | 0.36 | Antigen (0.8161) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 42 | AIPINFTISVTTEIL | HLA-DRB1*07:01 | 713 | 727 | Consensus | 0.29 | Antigen (1.1305) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 43 | LQIPFAMQMAYRFNG | HLA-DRB4*01:01 | 894 | 908 | Consensus | 0.73 | Antigen (0.7205) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 44 | QQLIRAAEIRASANL | HLA-DPA1*02:01/DPB1*14:01 | 1010 | 1024 | NetMHCIIpan | 0.2 | Non-antigen (0.1269) | Allergen | Non-toxic |
| 45 | REGVFVSNGTHWFVT | HLA-DRB3*02:02 | 1091 | 1195 | NetMHCIIpan | 0.2 | Non-antigen (0.4461) | Allergen | Non-toxic |
| 46 | IWLGFIAGLIAIVMV | HLA-DQA1*05:01/DQB1*03:01 | 1216 | 1230 | Consensus | 0.51 | Antigen (0.6150) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| South African Variant | |||||||||
| 47 | MFVFLVLLPLVSSQC | HLA-DRB1*01:01 | 1 | 15 | Consensus | 0.24 | Antigen (0.5741) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 48 | FVFLVLLPLVSSQCV | HLA-DRB1*01:01 | 2 | 16 | Consensus | 0.24 | Antigen (0.7185) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 49 | LHSTQDLFLPFFSNV | HLA-DPA1*01:03/DPB1*02:01 | 48 | 62 | Consensus | 1.4 | Non-antigen (0.2110) | Allergen | Non-toxic |
| 50 | KTQSLLIVNNATNVV | HLA-DRB1*13:02 | 113 | 127 | Consensus | 0.01 | Antigen (0.6303) | Allergen | Non-toxic |
| 51 | REFVFKNIDGYFKIY | HLA-DRB5*01:01 | 190 | 204 | Consensus | 0.17 | Non-antigen (−0.1712) | Allergen | Non-toxic |
| 52 | NITRFQTLLALHRSY | HLA-DRB5*01:01 | 234 | 248 | Consensus | 0.32 | Non-antigen (0.1775) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 53 | ATRFASVYAWNRKRI | HLA-DRB5*01:01 | 344 | 358 | Consensus | 0.49 | Non-antigen (0.3489) | Allergen | Non-toxic |
| 54 | NYNYLYRLFRKSNLK | HLA-DRB1*11:01 | 448 | 462 | Consensus | 0.42 | Non-antigen (0.1089) | Allergen | Non-toxic |
| 55 | PYRVVVLSFELLHAP | HLA-DPA1*02:01/DPB1*01:01 | 507 | 521 | Consensus | 0.3 | Antigen (0.8161) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 56 | IAIPTNFTISVTTEI | HLA-DRB1*07:01 | 712 | 726 | Consensus | 0.47 | Antigen (0.7719) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 57 | TSGWTFGAGAALQIP | HLA-DRB1*09:01 | 883 | 897 | Consensus | 0.34 | Non-antigen (−0.0178) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 58 | ALQIPFAMQMAYRFN | HLA-DRB4*01:01 | 893 | 907 | Consensus | 0.81 | Antigen (1.0112) | Allergen | Non-toxic |
| 59 | QQLIRAAEIRASANL | HLA-DPA1*02:01/DPB1*14:01 | 1010 | 1024 | NetMHCIIpan | 0.2 | Non-antigen (0.1269) | Allergen | Non-toxic |
| 60 | REGVFVSNGTHWFVT | HLA-DRB3*02:02 | 1091 | 1105 | NetMHCIIpan | 0.2 | Non-antigen (0.4461) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 61 | CDVVIGIVNNTVYDP | HLA-DRB1*13:02 | 1126 | 1140 | Consensus | 0.7 | Antigen (0.7320) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| 62 | YIWLGFIAGLIAIVM | HLA-DQA1*05:01/DQB1*03:01 | 1215 | 1229 | Consensus | 0.51 | Antigen (0.6090) | Non-allergen | Non-toxic |
| Position | Epitope Sequence | Score | Antigenicity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wuhan Isolate | |||
| 14–28 | QCVNLTTRTQLPPAY | 0.772 | 1.4548 |
| 109–114 | TLDSKT | 0.529 | 1.1073 |
| 1033–1039 | VLGQSKR | 0.523 | 1.6008 |
| England Isolate | |||
| 392–429 | FTNVYADSFVIRGDEVRQIAPGQTGKIADYNYKLPDDF | 0.695 | 0.5786 |
| 576–585 | VRDPQTLEIL | 0.644 | 0.5446 |
| 872–928 | QYTSALLAGTITSGWTFGAGAALQIPFAMQMAYRFNGIGVTQNVLYENQKLIANQFN | 0.649 | 0.5394 |
| USA Isolate | |||
| 392–429 | FTNVYADSFVIRGDEVRQIAPGQTGKIADYNYKLPDDF | 0.695 | 0.5786 |
| 553–565 | TESNKKFLPFQQF | 0.666 | 0.5056 |
| 872–928 | QYTSALLAGTITSGWTFGAGAALQIPFAMQMAYRFNGIGVTQNVLYENQKLIANQFN | 0.649 | 0.5394 |
| 576–585 | VRDPQTLEIL | 0.644 | 0.5449 |
| Indian Isolate | |||
| 239–265 | QTLLALHRSYLTPGDSSSGWTAGAAAY | 0.816 | 0.4822 |
| 14–27 | QCVNLTTRTQLPPA | 0.771 | 1.4983 |
| 64–83 | WFHAGASSGTNGTKRFDNPV | 0.763 | 0.4097 |
| 169–190 | EYVSQPFLMDLEGKQGNFKNLR LIVNNATNVVIKVCEFQFCNDPFLGVYYHKNNKSWMESEFRVYSSANNCT | 0.75 | 0.7830 |
| 118–167 | RFPNITNLCPFGEVFNATRFASVYAWNRKRISNCVADYSVLYNSASFSTFK | 0.732 | 0.3023 |
| South African Isolate | |||
| 239–265 | QTLLALHRSYLTPGDSSSGWTAGAAAY | 0.815 | 0.4822 |
| 14–27 | QCVNLTTRTQLPPA | 0.769 | 1.4983 |
| 64–83 | WFHAIHVSGTNGTKRFDNPV | 0.763 | 0.4100 |
| 169–190 | EYVSQPFLMDLEGKQGNFKNLR | 0.75 | 0.7830 |
| 118–167 | LIVNNATNVVIKVCEFQFCNDPFLGVYYHKNNKSWMESEFRVYSSANNCT | 0.731 | 0.1177 |
| 328–378 | RFPNITNLCPFGEVFNATRFASVYAWNRKRISNCVADYSVLYNSASFSTFK | 0.728 | 0.3023 |
| Residue Position | Residue Name | Contact Number | Propensity Score | DiscotopeScore |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wuhan Isolate | ||||
| 181 | GLY | 6 | 0.026 | −0.667 |
| 183 | GLN | 19 | 1.817 | −0.577 |
| 444 | LYS | 9 | 1.701 | 0.47 |
| 447 | GLY | 5 | 1.651 | 0.886 |
| 449 | TYR | 4 | −0.223 | −0.667 |
| 496 | GLY | 3 | 0.343 | −0.041 |
| 501 | ASN | 27 | 3.051 | −0.405 |
| 679 | ASN | 15 | 1.01 | −0.831 |
| 684 | ALA | 11 | 1.663 | 0.206 |
| 1144 | GLU | 7 | 0.215 | −0.615 |
| 1145 | LEU | 4 | −0.092 | −0.541 |
| England Isolate | ||||
| 72 | GLY | 11 | 0.723 | −0.625 |
| 75 | GLY | 10 | 1.381 | 0.072 |
| 147 | LYS | 10 | 1.503 | 0.18 |
| 148 | ASN | 13 | 1.34 | −0.309 |
| 149 | ASN | 17 | 1.084 | −0.996 |
| 152 | TRP | 14 | 2.444 | 0.553 |
| 498 | GLN | 6 | 0.354 | −0.377 |
| 499 | PRO | 9 | 1.027 | −0.126 |
| 1142 | GLN | 7 | 0.467 | −0.392 |
| 1144 | GLU | 3 | 1.177 | 0.697 |
| 1145 | LEU | 5 | 0.608 | −0.037 |
| 1147 | SER | 6 | 0.413 | −0.325 |
| 1148 | PHE | 5 | 0.591 | −0.052 |
| USA Isolate | ||||
| 72 | GLY | 11 | 0.718 | −0.629 |
| 75 | GLY | 10 | 1.379 | 0.071 |
| 147 | LYS | 10 | 1.502 | 0.179 |
| 148 | ASN | 13 | 1.336 | −0.313 |
| 150 | LYS | 10 | 2.307 | 0.891 |
| 152 | TRP | 14 | 2.443 | 0.552 |
| 154 | GLU | 2 | −0.24 | −0.442 |
| 444 | LYS | 9 | 0.883 | −0.253 |
| 447 | GLY | 6 | 0.901 | 0.107 |
| 496 | GLY | 4 | 0.289 | −0.204 |
| 498 | GLN | 6 | 1.323 | 0.481 |
| 499 | PRO | 9 | 1.995 | 0.731 |
| 501 | ASN | 24 | 3.012 | −0.095 |
| 1141 | LEU | 3 | −0.549 | −0.831 |
| 1142 | GLN | 7 | 0.466 | −0.393 |
| 1145 | LEU | 5 | 0.608 | −0.037 |
| 1147 | SER | 6 | 0.412 | −0.325 |
| 1148 | PHE | 5 | 0.59 | −0.053 |
| 1149 | LYS | 5 | 0.797 | 0.13 |
| Indian Isolate | ||||
| 147 | LYS | 10 | 4.318 | −0.682 |
| 149 | ASN | 9 | 4.399 | −0.101 |
| 153 | MET | 18 | 1.485 | −7.515 |
| 424 | LYS | 24 | 4.315 | −7.685 |
| 460 | ASN | 18 | 2.804 | −6.196 |
| 461 | LEU | 17 | 3.048 | −5.452 |
| 462 | LYS | 16 | 3.219 | −4.781 |
| 501 | TYR | 15 | 1.556 | −5.944 |
| 563 | GLN | 11 | 1.367 | −4.133 |
| 679 | ASN | 10 | 3.455 | −1.545 |
| 809 | PRO | 11 | 4.234 | −1.266 |
| 1158 | ASN | 10 | 4.027 | −0.973 |
| 1159 | HIS | 10 | 4.027 | −0.973 |
| 1160 | THR | 8 | 3.607 | −0.393 |
| 1161 | SER | 7 | 3.308 | −0.192 |
| South African Isolate | ||||
| 146 | HIS | 14 | 3.276 | 3.724 |
| 147 | LYS | 11 | 4.084 | −1.416 |
| 148 | ASN | 8 | 4.194 | 0.194 |
| 149 | ASN | 9 | 4.399 | −0.101 |
| 150 | LYS | 8 | 4.194 | 0.194 |
| 151 | SER | 13 | 4.108 | −2.392 |
| 152 | TRP | 18 | 3.747 | −5.253 |
| 409 | GLN | 20 | 2.989 | −7.011 |
| 414 | GLN | 18 | 2.979 | −6.021 |
| 424 | LYS | 9 | 4.399 | −0.101 |
| 498 | GLN | 21 | 3.461 | −7.039 |
| 499 | PRO | 20 | 3.536 | −6.464 |
| 501 | ASN | 15 | 2.768 | −4.732 |
| 679 | ASN | 9 | 3.115 | −1.385 |
| 680 | SER | 9 | 3.115 | −1.385 |
| 809 | PRO | 11 | 4.234 | −1.266 |
| 810 | SER | 13 | 3.958 | −0.542 |
| 811 | LYS | 12 | 3.646 | −2.354 |
| 1155 | TYR | 11 | 2.84 | −2.66 |
| 1156 | PHE | 12 | 3.55 | −2.45 |
| 1157 | LYS | 10 | 3.353 | −1.647 |
| 1158 | ASN | 10 | 4.027 | −0.973 |
| 1159 | HIS | 10 | 4.027 | −0.973 |
| 1160 | THR | 8 | 3.607 | −0.393 |
| 1160 | THR | 8 | 3.607 | −0.393 |
| 1161 | SER | 7 | 3.308 | −0.192 |
| Epitope | Country | Population Coverage |
|---|---|---|
| Wuhan Strain | ||
| ILDITPCSF STQDLFLPF VVFLHVTYV GVVFLHVTY WTAGAAAYY GAAAYYVGY | World | 93.65% |
| South Asia | 88.23% | |
| India | 80.22% | |
| England | 97.08% | |
| France | 96.42% | |
| Italy | 95.12% | |
| Sweden | 92.66% | |
| United States | 95.3 | |
| South Africa | 87.07% | |
| England Isolate | ||
| NGVEGFNCY QYIKWPWYI WTAGAAAYY VYAWNRKRI GVYFASTEK SPRRARSVA PYRVVVLSF | World | 94.15% |
| South Asia | 92.78% | |
| India | 89.3% | |
| England | 97.62% | |
| France | 97.36% | |
| Italy | 95.84% | |
| Sweden | 96.12% | |
| United States | 93.76% | |
| South Africa | 96.49% | |
| USA Isolate | ||
| VVFLHVTYV IAIVMVTIM LPFNDGVYF IAIPTNFTI | World | 91.98% |
| South Asia | 81.6% | |
| India | 73.8% | |
| England | 95.97% | |
| France | 96.2% | |
| Italy | 93.59% | |
| Sweden | 98.77% | |
| United States | 94.9% | |
| South Africa | 83.62% | |
| Indian Isolate | ||
| FTISVTTEI VVFLHVTYV YQPYRVVVL YSKHTPINL WTAGAAAYY LPFNDGVYF GAAAYYVGY | World | 97.98% |
| South Asia | 91.95% | |
| India | 85.34% | |
| England | 99.71% | |
| France | 99.21% | |
| Italy | 97.97% | |
| Sweden | 99.82% | |
| United States | 98.07% | |
| South Africa | 90.51% | |
| South African Isolate | ||
| IAIPINFTI FTISVTTEI YQPYRVVVL WTAGAAAYY YSKHTPINL GVVFLHVTY LPFNDGVYF | World | 97.48% |
| South Asia | 91.95% | |
| India | 85.34% | |
| England | 99.71% | |
| France | 99.21% | |
| Italy | 97.97% | |
| Sweden | 99.82% | |
| United States | 98.07% | |
| South Africa | 90.51% | |
| S.No. | Potential Peptide for Vaccine | Binding Alleles | Attractive vdW | Repulsive vdW | ACE | HB | Global Energy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wuhan Isolate | |||||||
| 1. | ILDITPCSF | HLA-B*51:01 | −28.64 | 7.59 | −9.54 | −2.23 | −58.28 |
| HLA-B*08:01 | −24.90 | 5.90 | −8.27 | −3.92 | −50.66 | ||
| HLA-A*02:06 | −24.14 | 10.32 | −9.30 | −2.48 | −49.01 | ||
| 2. | STQDLFLPF | HLA-A*32:01 | −19.73 | 14.97 | −11.66 | −1.83 | −44.18 |
| HLA-B*57:01 | −29.53 | 21.42 | −3.31 | −3.03 | −40.05 | ||
| HLA-B*15:01 | −3.50 | 0.00 | 0.36 | 0.00 | −8.53 | ||
| 3. | VVFLHVTYV | HLA-B*51:01 | −29.19 | 10.45 | −1.43 | −3.35 | −51.05 |
| HLA-A*02:03 | −18.26 | 2.58 | −9.10 | −4.13 | −42.85 | ||
| 4. | GVVFLHVTY | HLA-B*35:01 | −36.19 | 7.98 | −8.72 | −1.99 | −66.28 |
| HLA-A*01:01 | −32.13 | 6.50 | −7.59 | −2.76 | −55.83 | ||
| HLA-B*15:01 | −9.36 | 2.62 | 0.96 | −0.20 | −3.98 | ||
| 5. | WTAGAAAYY | HLA-B*35:01 | −27.77 | 4.34 | −2.83 | −3.28 | −54.98 |
| HLA-A*01:01 | −30.65 | 13.59 | −7.64 | −4.80 | −53.52 | ||
| 6. | GAAAYYVGY | HLA-A*30:02 | −25.83 | 3.78 | −4.26 | −4.52 | −51.90 |
| HLA-B*15:01 | −20.22 | 7.80 | −0.58 | −0.99 | −24.32 | ||
| England Isolate | |||||||
| 7. | QYIKWPWYI | HLA-A*23:01 | −25.46 | 8.91 | −13.16 | −0.95 | −57.28 |
| HLA-C*06:02 | −29.14 | 16.66 | −4.45 | −3.18 | −50.48 | ||
| 8. | GVYFASTEK | HLA-A*30:01 | −21.73 | 4.79 | 2.52 | −3.41 | −28.36 |
| 9. | NGVEGFNCY | HLA-B*35:01 | −37.69 | 6.42 | 2.02 | −2.25 | −46.33 |
| 10. | PYRVVVLSF | HLA-A*23:01 | −25.49 | 9.71 | −11.33 | −2.48 | −65.01 |
| HLA-C*14:02 | −25.48 | 5.04 | −1.94 | −0.95 | −41.16 | ||
| 11. | VYAWNRKRI | HLA-A*23:01 | −22.44 | 4.18 | −4.02 | −3.34 | −46.75 |
| 12. | SPRRARSVA | HLA-B*07:02 | −25.14 | 8.95 | 3.94 | −1.97 | −18.83 |
| USA Isolate | |||||||
| 13. | IAIVMVTIM | HLA-B*51:01 | −30.57 | 25.38 | −16.59 | −0.98 | −59.86 |
| 14. | LPFNDGVYF | HLA-B*35:01 | −35.26 | 47.18 | −3.06 | −3.78 | −30.68 |
| Indian Isolate | |||||||
| 15. | YQPYRVVVL | HLA-B*08:01 | −36.00 | 10.43 | −7.97 | −2.46 | −62.85 |
| 16. | YSKHTPINL | HLA-A*68:02 | −22.93 | 6.44 | −10.43 | −2.56 | −59.11 |
| 17. | FTISVTTEI | HLA-A*68:02 | −29.71 | 11.47 | −7.29 | −2.07 | −53.01 |
| 18. | WTAGAAAYY | HLA-A*26:01 | −31.19 | 8.71 | −0.08 | −1.66 | −44.75 |
| 19. | GAAAYYVGY | HLA-A*30:02 | −19.74 | 5.30 | −9.59 | −2.21 | −43.65 |
| South African Isolate | |||||||
| 20. | IAIPINFTI | HLA-B*51:01 | −22.76 | 6.82 | −13.73 | −0.80 | −54.96 |
| 21. | FTISVTTEI | HLA-B*51:01 | −22.68 | 11.47 | −7.29 | −7.29 | −53.01 |
| 22. | QLTPTWRVY | HLA-B*35:01 | −19.09 | 8.37 | −10.39 | 0.00 | −44.39 |
| 23. | YSKHTPINL | HLA-B*57:01 | −24.90 | 3.82 | −1.65 | −1.65 | −41.72 |
| 24. | YQPYRVVVL | HLA-B*08:01 | −21.47 | 10.07 | −9.41 | −0.98 | −38.80 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mallavarpu Ambrose, J.; Priya Veeraraghavan, V.; Kullappan, M.; Chellapandiyan, P.; Krishna Mohan, S.; Manivel, V.A. Comparison of Immunological Profiles of SARS-CoV-2 Variants in the COVID-19 Pandemic Trends: An Immunoinformatics Approach. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050535
Mallavarpu Ambrose J, Priya Veeraraghavan V, Kullappan M, Chellapandiyan P, Krishna Mohan S, Manivel VA. Comparison of Immunological Profiles of SARS-CoV-2 Variants in the COVID-19 Pandemic Trends: An Immunoinformatics Approach. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(5):535. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050535
Chicago/Turabian StyleMallavarpu Ambrose, Jenifer, Vishnu Priya Veeraraghavan, Malathi Kullappan, Poongodi Chellapandiyan, Surapaneni Krishna Mohan, and Vivek Anand Manivel. 2021. "Comparison of Immunological Profiles of SARS-CoV-2 Variants in the COVID-19 Pandemic Trends: An Immunoinformatics Approach" Antibiotics 10, no. 5: 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050535
APA StyleMallavarpu Ambrose, J., Priya Veeraraghavan, V., Kullappan, M., Chellapandiyan, P., Krishna Mohan, S., & Manivel, V. A. (2021). Comparison of Immunological Profiles of SARS-CoV-2 Variants in the COVID-19 Pandemic Trends: An Immunoinformatics Approach. Antibiotics, 10(5), 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050535






