Discovery of Pyrrolidine-2,3-diones as Novel Inhibitors of P. aeruginosa PBP3
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Optimisation of the S2d Assay for Fluorescence-Based Screening
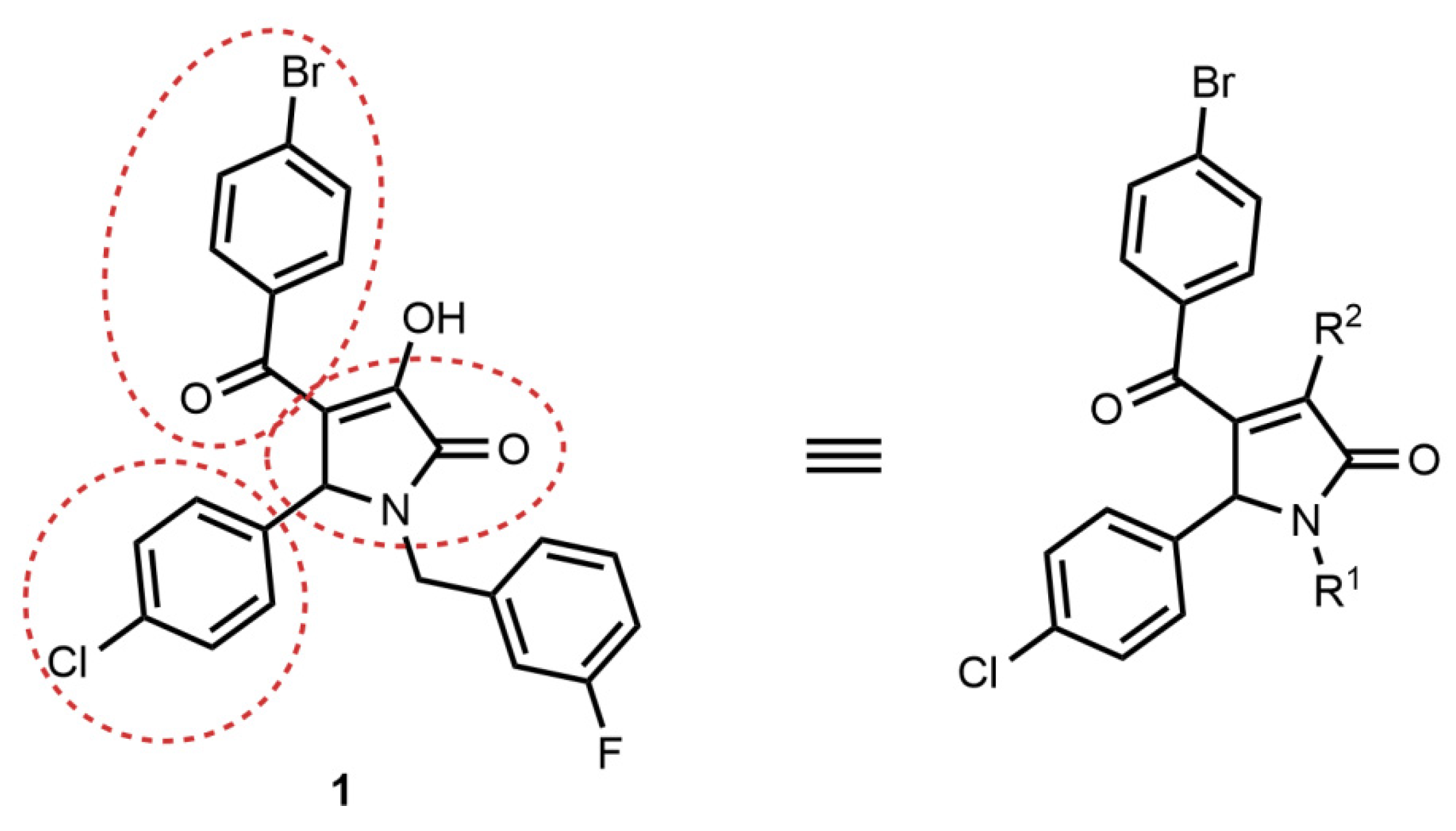
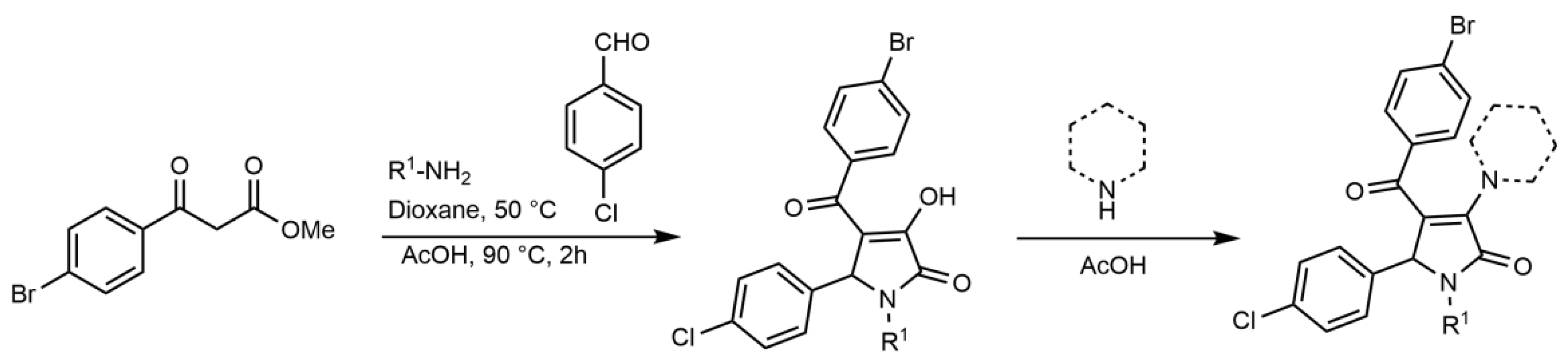
2.2. Synthesis of Compound 1 Analogues and Generation of the Pyrrolidine-2,3-dione Cluster
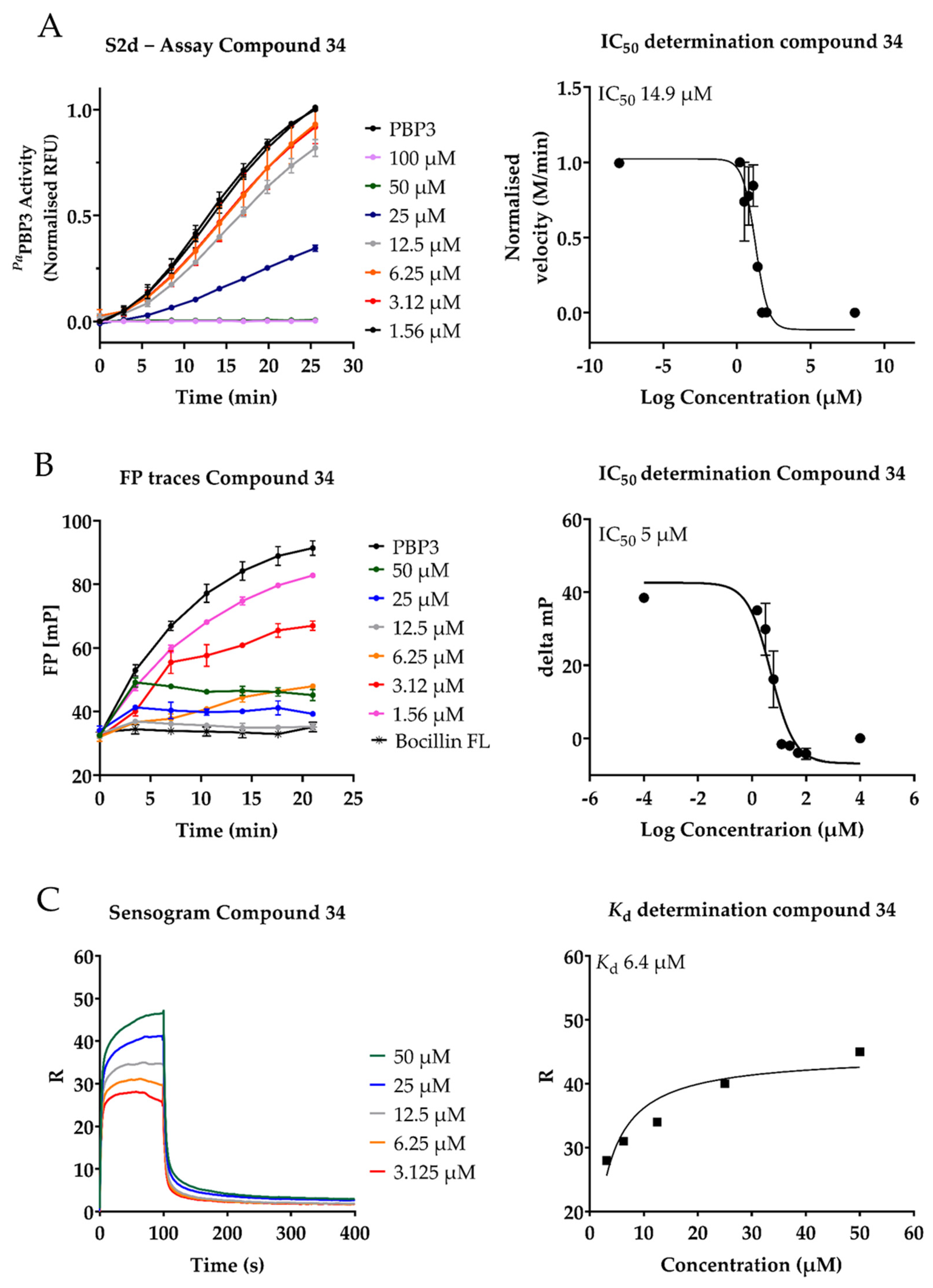
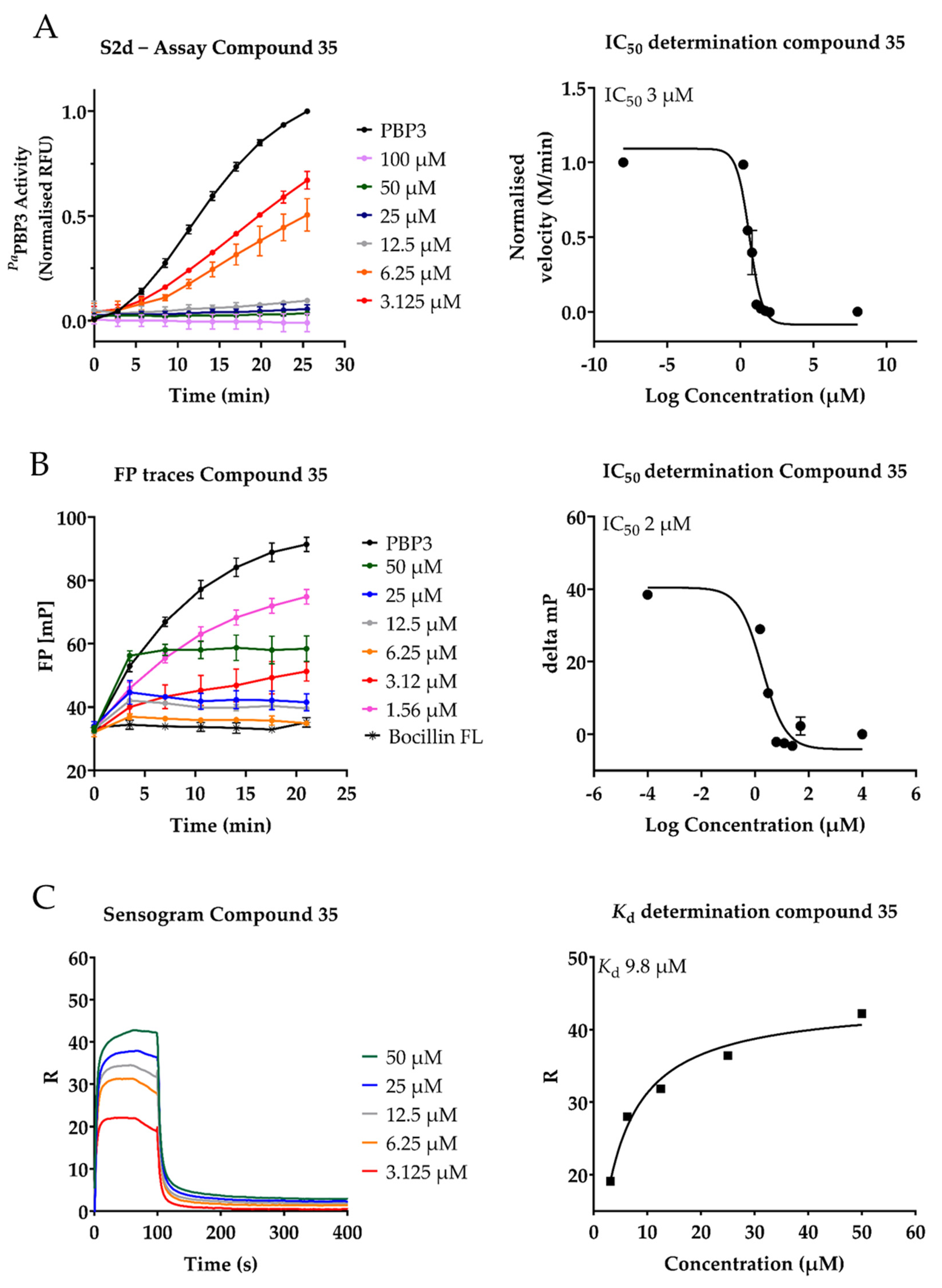
2.3. Inhibition of PaPBP3 by Pyrrolidine-2,3-dione Derivates
2.4. Antimicrobial Activities of Pyrrolidine-2,3-dione Derivates
2.5. Effect of the Pyrrolidine-2,3-diones on Eukaryotic Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Protein Expression and Purification
4.3. IC50 Determination by S2dfluo
4.4. IC50 Determination by the Bocillin FL Biochemical Assay
4.5. SPR Experiments
4.6. Bacterial Strains
4.7. MIC Determination
4.8. Cytotoxicity Assays
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Sandri, A.; Lleo, M.M.; Signoretto, C.; Boaretti, M.; Boschi, F. Protease inhibitors elicit anti-inflammatory effects in CF mice with Pseudomonas aeruginosa acute lung infection. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2021, 203, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonberg, R.; Gastmeier, P. Isolation of Infectious Cystic Fibrosis Patients: Results of a Systematic Review. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2005, 26, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, S.; Hayes, D.; Wozniak, D. Cystic Fibrosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: The Host-Microbe Interface. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00138-00118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klockgether, J.; Cramer, N.; Wiehlmann, L.; Davenport, C.; Tümmler, B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Genomic Structure and Diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, A.; Errington, J.; Vollmer, W. Regulation of peptidoglycan synthesis and remodelling. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmer, W.; Joris, B.; Charlier, P.; Foster, S. Bacterial peptidoglycan (murein) hydrolases. Fems Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 259–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmer, W.; Blanot, D.; de Pedro, M.A. Peptidoglycan structure and architecture. Fems Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, A.; Welsh, M.A.; Marmont, L.S.; Lee, W.; Sjodt, M.; Kruse, A.C.; Kahne, D.; Bernhardt, T.G.; Walker, S. FtsW is a peptidoglycan polymerase that is functional only in complex with its cognate penicillin-binding protein. Nat Microbiol 2019, 4, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeske, A.J.; Riley, E.P.; Robins, W.P.; Uehara, T.; Mekalanos, J.J.; Kahne, D.; Walker, S.; Kruse, A.C.; Bernhardt, T.G.; Rudner, D.Z. SEDS proteins are a widespread family of bacterial cell wall polymerases. Nature 2016, 537, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvage, E.; Kerff, F.; Terrak, M.; Ayala, J.A.; Charlier, P. The penicillin-binding proteins: Structure and role in peptidoglycan biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 234–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, S.; Derouaux, A.; Olatunji, S.; Fraipont, C.; Egan, A.J.; Vollmer, W.; Breukink, E.; Terrak, M. Interplay between Penicillin-binding proteins and SEDS proteins promotes bacterial cell wall synthesis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellini, D.; Koekemoer, L.; Newman, H.; Dowson, C.G. Novel and Improved Crystal Structures of H. influenzae, E. coli and P. aeruginosa Penicillin-Binding Protein 3 (PBP3) and N. gonorrhoeae PBP2: Toward a Better Understanding of beta-Lactam Target-Mediated Resistance. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 3501–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolo, J.; Worning, P.; Boye Nielsen, J.; Sobral, R.; Bowden, R.; Bouchami, O.; Damborg, P.; Guardabassi, L.; Perreten, V.; Westh, H.; et al. Evidence for the evolutionary steps leading to mecA-mediated β-lactam resistance in staphylococci. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, Y.; Ito, T.; Hiramatsu, K. A New Class of Genetic Element, Staphylococcus Cassette Chromosome mec, Encodes Methicillin Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 1549–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajavel, M.; Kumar, V.; Nguyen, H.; Wyatt, J.; Marshall, S.H.; Papp-Wallace, K.M.; Deshpande, P.; Bhavsar, S.; Yeole, R.; Bhagwat, S.; et al. Structural Characterization of Diazabicyclooctane beta-Lactam “Enhancers” in Complex with Penicillin-Binding Proteins PBP2 and PBP3 of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. mBio 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp-Wallace, K.; Bonomo, R. New β-Lactamase Inhibitors in the Clinic. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 2016, 30, 441–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zervosen, A.; Herman, R.; Kerff, F.; Herman, A.; Bouillez, A.; Prati, F.; Pratt, R.; Frère, J.M.; Joris, B.; Luxen, A.; et al. Unexpected Tricovalent Binding Mode of Boronic Acids within the Active Site of a Penicillin-Binding Protein. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 10839–10848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.; Wang, Y.; Stein, R. Kinetic and mechanistic studies of penicillin-binding protein 2x from Streptococcus Pneumoniae. Biochem. 2001, 40, 15811–15823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamin, M.; Adam, M.; Damblon, C.; Christiaens, L. Accumulation of acyl-enzyme in DD-peptidase-catalysed reactions with analogues of peptide substrates. Biochem. J. 1991, 280, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.; Damblon, C.; Plaitin, B.; Christiaens, L.; Frère, J.M. Chromogenic depsipeptide substrates for beta-lactamases and penicillin-sensitive DD-peptidases. Biochem. J. 1991, 270, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, M.; Damblon, C.; Jamin, M.; Zorzi, W.; Dusart, V.; Galleni, M.; el Kharroubi, A.; Piras, G.; Spratt, B.G.; Keck, W. Acyltransferase activities of the high-molecular-mass essential penicillin-binding proteins. Biochem. J. 1991, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, R.; Govardhan, C. Beta-Lactamase-catalyzed hydrolysis of acyclic depsipeptides and acyl transfer to specific amino acid acceptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 1302–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrak, M.; Ghosh, T.; Van Heijenoort, J.; Van Beeumen, J.; Lampilas, M.; Aszodi, J.; Ayala, J.; Ghuysen, J.; Nguyen-Distèche, M. The catalytic, glycosyl transferase and acyl transferase modules of the cell wall peptidoglycan-polymerizing penicillin-binding protein 1b of Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 34, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zervosen, A.; Lu, W.; Chen, Z.; White, R.; Demuth, T.; Frère, J.M. Interactions between Penicillin-Binding Proteins (PBPs) and Two Novel Classes of PBP Inhibitors, Arylalkylidene Rhodanines and Arylalkylidene Iminothiazolidin-4-ones. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adediran, S.A.; Sarkar, K.S.; Pratt, R.F. Kinetic Evidence for a Second Ligand Binding Site on Streptococcus pneumoniae Penicillin-Binding Protein 2x. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 1758–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Yeh, W.K.; Carnahan, R.H.; Flokowitsch, J.; Meier, T.I.; Alborn, W.E.; Becker, G.W.; Jaskunas, S.R. Biochemical characterization of penicillin-resistant and -sensitive penicillin-binding protein 2x transpeptidase activities of Streptococcus pneumoniae and mechanistic implications in bacterial resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zervosen, A.; Zapun, A.; Frère, J.M. Inhibition of Streptococcus pneumoniae Penicillin-Binding Protein 2x and Actinomadura; R39 DD-Peptidase Activities by Ceftaroline. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Chung, T.; Oldenburg, K. A Simple Statistical Parameter for Use in Evaluation and Validation of High Throughput Screening Assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 1999, 4, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.Y.; Shoichet, B.K. A detergent-based assay for the detection of promiscuous inhibitors. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoichet, B.K. Screening in a spirit haunted world. Drug Discov. Today 2006, 11, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedarovich, A.; Djordjevic, K.A.; Swanson, S.M.; Peterson, Y.K.; Nicholas, R.A.; Davies, C. High-throughput screening for novel inhibitors of Neisseria gonorrhoeae penicillin-binding protein 2. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoth, T.; Warburg, K.; Katzka, C.; Rai, A.; Wolf, A.; Brockmeyer, A.; Janning, P.; Reubold, T.; Eschenburg, S.; Manstein, D.; et al. The Ras Pathway Modulator Melophlin A Targets Dynamins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7240–7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.; Sutherland, J.B.; Rafii, F. beta-Lactam resistance development affects binding of penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) of Clostridium perfringens to the fluorescent penicillin, Bocillin FL. Anaerobe 2020, 62, 102179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.B.; Gu, R.F.; Gao, N.; Livchak, S.; Thresher, J. Continuous fluorescence anisotropy-based assay of Bocillin FL penicillin reaction with penicillin binding protein 3. Anal. Biochem. 2013, 439, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Meier, T.; Kahl, S.; Gee, K.; Blaszczak, L. BOCILLIN FL, a sensitive and commercially available reagent for detection of penicillin-binding proteins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1999, 43, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Lin, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, W.; Chen, D.; Gao, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, B.; Huang, H.; Lu, Y.; et al. Docking- and pharmacophore-based virtual screening for the identification of novel Mycobacterium tuberculosis protein tyrosine phosphatase B (MptpB) inhibitor with a thiobarbiturate scaffold. Bioorg Chem 2019, 85, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, R.; Erdmann, S.; Bovens, S.; Wolf, A.; Rose, M.; Hennig, S.; Waldmann, H.; Ottmann, C. Identification and structure of small-molecule stabilizers of 14-3-3 protein-protein interactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed Engl. 2010, 49, 4129–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, A.; Rose, R.; Hedberg, C.; Waldmann, H.; Ottmann, C. An optimised small-molecule stabiliser of the 14-3-3-PMA2 protein-protein interaction. Chemistry Eur. J. 2012, 18, 6520–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryabukhin, S.; Panov, D.; Plaskon, A.; Grygorenko, O. Approach to the Library of 3-Hydroxy-1,5-dihydro-2H-pyrrol-2-ones through a Three-Component Condensation. ACS Comb. Sci. 2012, 14, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, B.; Barcelo, I.; Bhagwat, S.; Patel, M.; Bou, G.; Papp-Wallace, K.; Bonomo, R.; Oliver, A. WCK 5107 (Zidebactam) and WCK 5153 Are Novel Inhibitors of PBP2 Showing Potent “β-Lactam Enhancer” Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02529-02516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp-Wallace, K.M.; Nguyen, N.; Jacobs, M.; Bethel, C.; Barnes, M.; Kumar, V.; Bajaksouzian, S.; Rudin, S.; Rather, P.; Bhavsar, S.; et al. Strategic Approaches to Overcome Resistance against Gram-Negative Pathogens Using β-Lactamase Inhibitors and β-Lactam Enhancers: Activity of Three Novel Diazabicyclooctanes WCK 5153, Zidebactam (WCK 5107), and WCK 4234. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 4067–4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, S.; Verlaine, O.; Gerards, T.; Zivec, M.; Humljan, J.; Sosic, I.; Amoroso, A.; Zervosen, A.; Luxen, A.; Joris, B.; et al. New noncovalent inhibitors of penicillin-binding proteins from penicillin-resistant bacteria. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosič, I.; Turk, S.; Sinreih, M.; Trošt, N.; Verlaine, O.; Amoroso, A.; Zervosen, A.; Luxen, A.; Joris, B.; Gobec, S. Exploration of the chemical space of novel naphthalene-sulfonamide and anthranilic Acid-based inhibitors of penicillin-binding proteins. Acta Chim. Slov. 2012, 59, 280–388. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spink, E.; Ding, D.; Peng, Z.; Boudreau, M.; Leemans, E.; Lastochkin, E.; Song, W.; Lichtenwalter, K.; O’Daniel, P.; Testero, S.; et al. Structure–Activity Relationship for the Oxadiazole Class of Antibiotics. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toney, J.; Hammond, G.; Leiting, B.; Pryor, K.; Wu, J.; Cuca, G.; Pompliano, D. Soluble Penicillin-Binding Protein 2a: β-Lactam Binding and Inhibition by Non-β-Lactams Using a 96-Well Format. Anal. Biochem. 1998, 255, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.; Gao, N.; Gu, R.; Thresher, J. Fluorescence anisotropy-based measurement of Pseudomonas aeruginosa penicillin-binding protein 2 transpeptidase inhibitor acylation rate constants. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 463, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraud, S.; Campigotto, A.J.; Chen, Z.; Poole, K. MexCD-OprJ Multidrug Efflux System of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Involvement in Chlorhexidine Resistance and Induction by Membrane-Damaging Agents Dependent upon the AlgU Stress Response Sigma Factor. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI. Performance Standars for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. In Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute Guideline M100; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018; Volume 28. [Google Scholar]
- CSLI. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically. Approved Standard. In Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute M07-A9; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]


| IC50 Determination with PaPBP3 a (µM) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | Source | PBP3 Inhibition at 100 µM (%) | S2dfluo Assay | FP-Bocillin FL Assay | |
| 1 |  | MPI b | ND b,c | 28 ± 9 | 7 ± 3 |
| 2 | 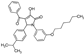 | ChemDiv 8015-0105 | 101 ± 0.4 | 4 ± 6 | 17 ± 9 |
| 3 |  | ChemDiv 8015-0104 | 100 ± 0.8 | 19 ±1 | >100 |
| 4 | 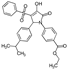 | ChemDiv F232-0415 | 101 | 24 ± 20 | >100 |
| 5 | 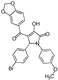 | MPI | ND b,c | 61 ± 1 | 69 ± 13 |
| 6 | 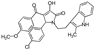 | ChemDiv 8015-3001 | 92 ± 7 | 63 ± 4 | 9 ± 6 |
| 7 | 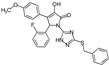 | ChemDiv C202-3660 | 62 | 65 ± 19 | 58 ± 21 |
| 8 |  | MPI [33] | ND b,c | 66 ± 16 | 93 ± 18 |
| 9 | 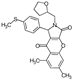 | ChemDiv D159-0900 | 60 | 99 ± 1 | 18 ± 3 |
| Biochemical Characterisation a | MIC (µM) against P. aeruginosa | Cytotoxicity CCRF-CEM (µM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nr | IC50 (µM) S2dfluo Assay | IC50 (µM) FP-Assay | Kd (µM) SPR | PAO1 b | K28926 c | |
| 1 | 28 ± 9 | 7 ± 3 | ND | >100 | 12.5 | >100 |
| 32 | >100 | >100 | ND | >100 | >100 | 94 ± 6 |
| 33 | >100 | >100 | ND | >100 | >100 | 58 ± 6 |
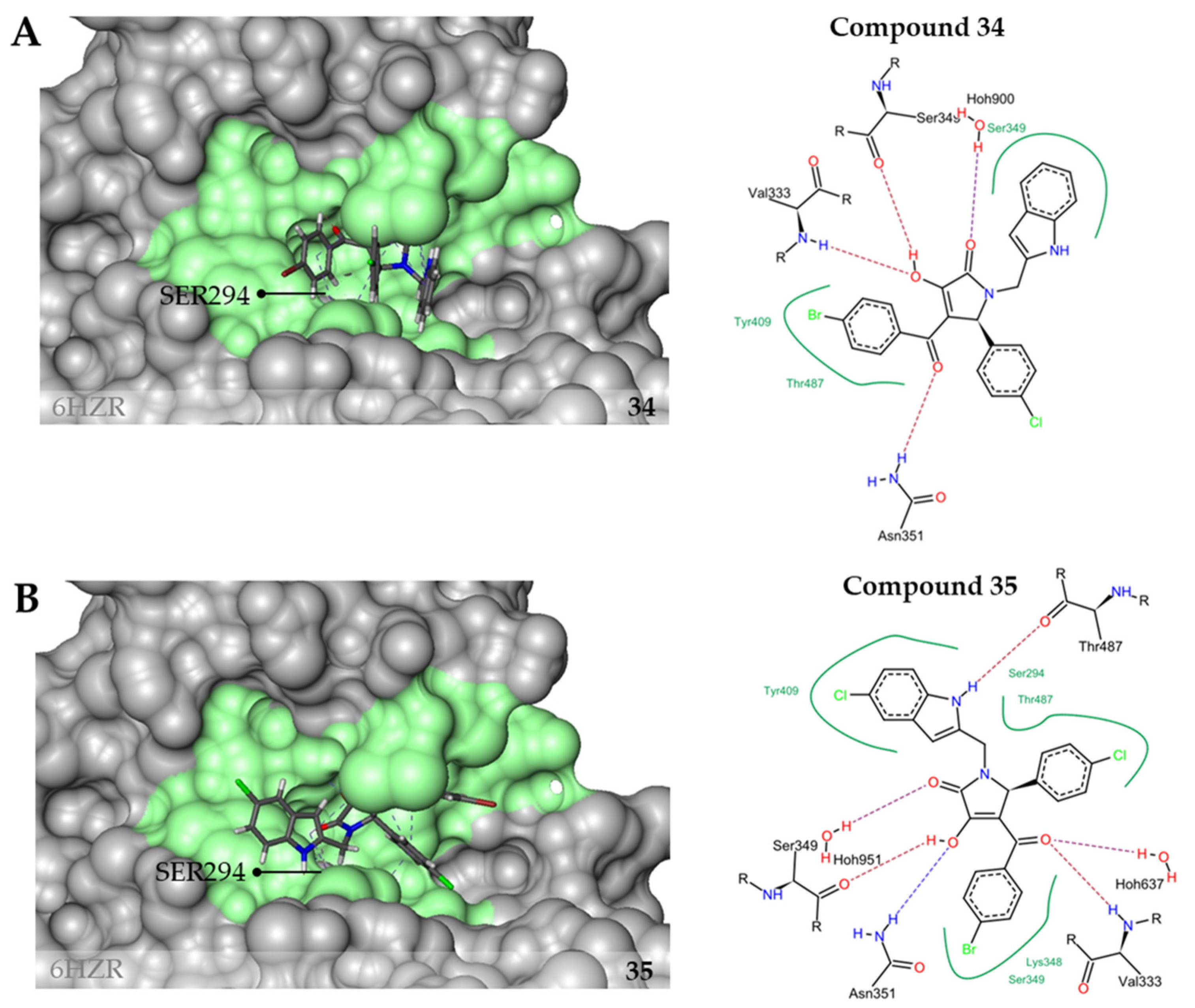
| 34 | 14 ± 9 | 4 ± 4 | 6.44 | 3.13 | 12.5 | >100 |
| 35 | 3 ± 1 | 0.6± 2 | 9.82 | 3.13 | 12.5 | 53 ± 5 |
| 36 | >100 | >100 | ND | >100 | 100 | 1 ± 2 |
| 37 | 16 ± 8 | 17 ± 3 | 454 | 6.25 | 12.5 | 8 ± 6 |
| 38 | 100 ± 11 | 117 ± 4 | 62.7 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 39 | 24 ± 7 | 11 ± 4 | ND | 6.25 | 25 | >100 |
| 40 | 8 ± 4 | 4 ± 2 | 22.9 | 25 | >100 | 93 ± 4 |
| 41 | >100 | >100 | ND | >100 | 25 | >100 |
| 42 | >100 | >100 | ND | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 43 | >100 | >100 | ND | >100 | >100 | 73 ± 9.2 |
| 44 | >100 | >100 | ND | >100 | >100 | 52 ± 3 |
| 45 | >100 | >100 | ND | >100 | >100 | 23 ± 11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-Pérez, A.; Freischem, S.; Grimm, I.; Weiergräber, O.; Dingley, A.J.; López-Alberca, M.P.; Waldmann, H.; Vollmer, W.; Kumar, K.; Vuong, C. Discovery of Pyrrolidine-2,3-diones as Novel Inhibitors of P. aeruginosa PBP3. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050529
López-Pérez A, Freischem S, Grimm I, Weiergräber O, Dingley AJ, López-Alberca MP, Waldmann H, Vollmer W, Kumar K, Vuong C. Discovery of Pyrrolidine-2,3-diones as Novel Inhibitors of P. aeruginosa PBP3. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(5):529. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050529
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-Pérez, Arancha, Stefan Freischem, Immanuel Grimm, Oliver Weiergräber, Andrew J. Dingley, María Pascual López-Alberca, Herbert Waldmann, Waldemar Vollmer, Kamal Kumar, and Cuong Vuong. 2021. "Discovery of Pyrrolidine-2,3-diones as Novel Inhibitors of P. aeruginosa PBP3" Antibiotics 10, no. 5: 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050529
APA StyleLópez-Pérez, A., Freischem, S., Grimm, I., Weiergräber, O., Dingley, A. J., López-Alberca, M. P., Waldmann, H., Vollmer, W., Kumar, K., & Vuong, C. (2021). Discovery of Pyrrolidine-2,3-diones as Novel Inhibitors of P. aeruginosa PBP3. Antibiotics, 10(5), 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050529






