Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Implementation in a Saudi Medical City: An Exploratory Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Motives for ASP Adoption in the Medical City
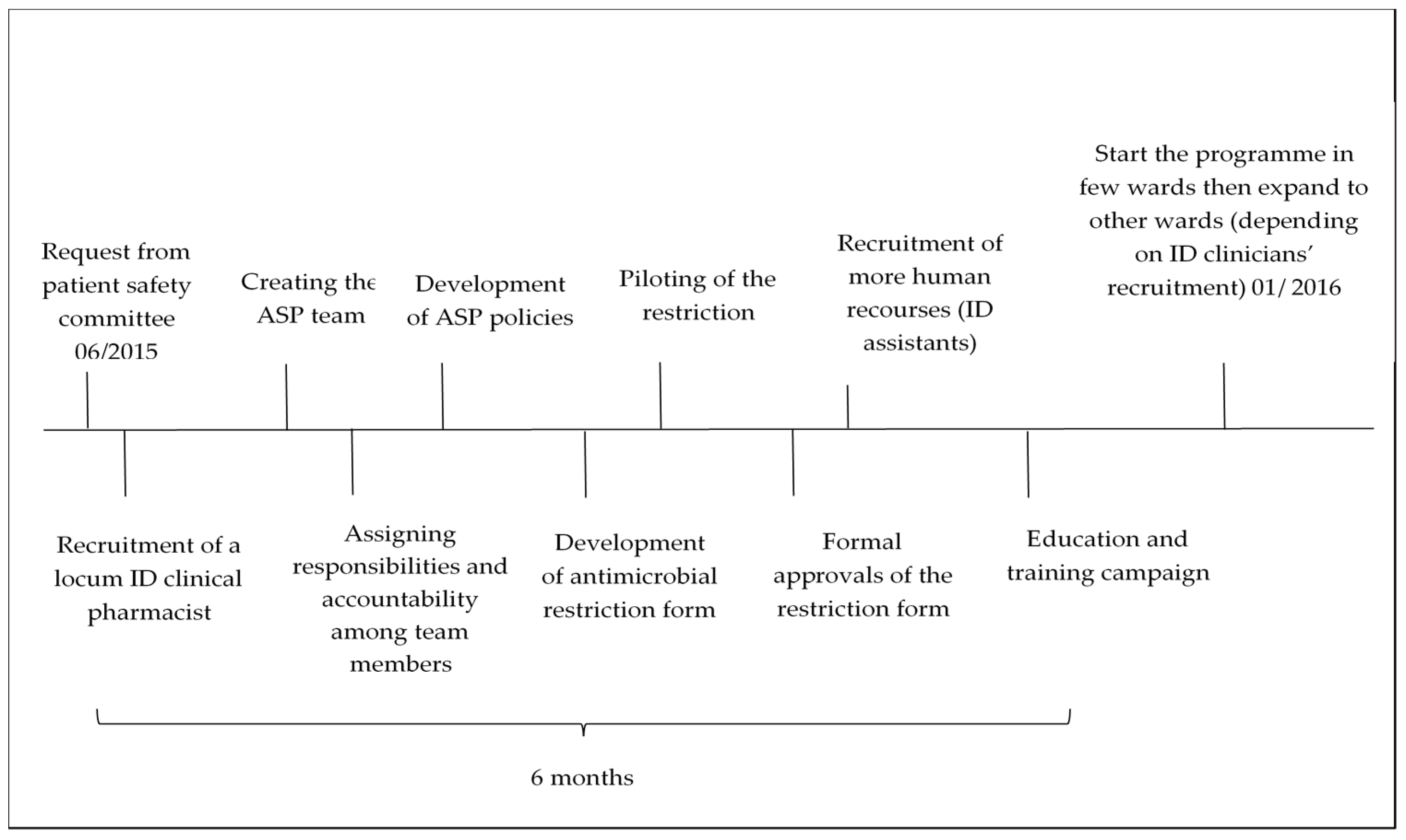
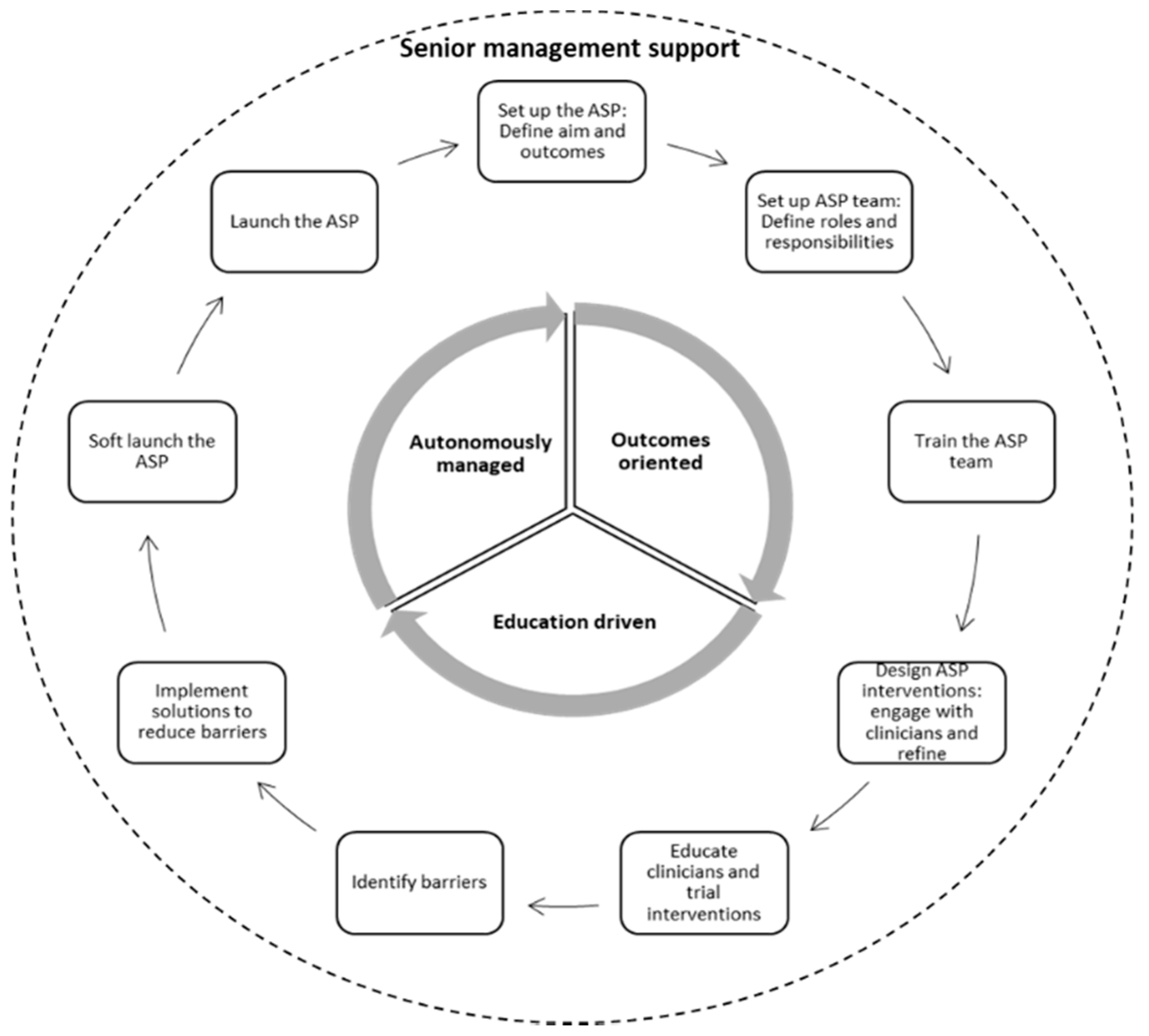
2.2. Development and Implementation of the Antimicrobial Stewardship Programme
Phases of ASP Implementation
- The ID consultant as the director of the ASP program and their ID team;
- The antimicrobial lead pharmacist as the manager of the ASP program and the clinical pharmacists’ team;
- Clinical pharmacists;
- Consultant clinical microbiologist and their team;
- The infection control consultant and their team.
2.3. ASP Implementation Challenges
2.3.1. Shortage of ASP Staff
2.3.2. Incompatible IT Systems
2.4. Critical Factors for the Sucessful Implementaion of ASP in the Medical City
2.4.1. Top Management Support
2.4.2. Project Management Training
2.4.3. A Dedicated ASP Team
2.4.4. Increased ID Clinicians’ Involvement in the Prescribing and Monitoring of Antimicrobials
2.5. Outcomes of ASP implementation
3. Discussion
4. Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Core Elements of Hospital Antibiotic Stewardship Programs. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/core-elements/hospital.html (accessed on 28 January 2021).
- Dyar, O.J.; Huttner, B.; Schouten, J.; Pulcini, C. What is antimicrobial stewardship? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, P.; Pulcini, C.; Hara, G.L.; West, R.M.; Gould, I.M.; Harbarth, S.; Nathwani, D. An international cross-sectional survey of antimicrobial stewardship programmes in hospitals. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallen, M.C.; Binda, F.; Oever, J.T.; Tebano, G.; Pulcini, C.; Murri, R.; Beovic, B.; Saje, A.; Prins, J.M.; Hulscher, M.E.J.L.; et al. Comparison of antimicrobial stewardship programmes in acute-care hospitals in four European countries: A cross-sectional survey. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 54, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scobie, A.; Budd, E.L.; Harris, R.J.; Hopkins, S.; Shetty, N. Antimicrobial stewardship: An evaluation of structure and process and their association with antimicrobial prescribing in NHS hospitals in England. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nhan, D.; Lentz, E.J.M.; Steinberg, M.; Bell, C.M.; Morris, A.M. Structure of antimicrobial stewardship programs in leading US hospitals: Findings of a nationwide survey. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, A.; Ebata, A.; Macgregor, H. Interventions to reduce antibiotic prescribing in LMICs: A scoping review of evidence from human and animal health systems. Antibiotics 2018, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, S.; Shebl, N.A.; Aslanpour, Z.; Shibl, A.; Berrou, I. Hospital Adoption of Antimicrobial Stewardship Programmes in Gulf Cooperation Council Countries: A Review of Existing Evidence. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 15, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akpan, M.R.; Isemin, N.U.; Udoh, A.E.; Ashiru-Oredope, D. Implementation of antimicrobial stewardship programmes in African countries: A systematic literature review. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 22, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.A.; Vlieghe, E.; Mendelson, M.; Wertheim, H.; Ndegwa, L.; Villegas, M.V.; Gould, I.; Hara, G.L. Antibiotic stewardship in low- and middle-income countries: The same but different? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijck, C.; Vlieghe, E.; Cox, J.A. Antibiotic stewardship interventions in hospitals in low-and middle-income countries: A systematic review. Bull. World Health Organ. 2018, 96, 266–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Intellectual Property Organization Antimicrobial Resistance—A Global Epidemic. Available online: https://www.wipo.int/meetings/en/doc_details.jsp?doc_id=350357 (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- Alghamdi, S.; Berrou, I.; Aslanpour, Z.; Mutlaq, A.; Haseeb, A.; Albanghali, M.; Hammad, M.A.; Shebl, N. Antimicrobial Stewardship Programmes in Saudi Hospitals: Evidence from a National Survey. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, T.U.; Alrodayyan, M.; Albladi, M.; Aldrees, M.; Siddique, M.I.; Aljohani, S.; Balkhy, H.H. Clonal diversity and genetic profiling of antibiotic resistance among multidrug/carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from a tertiary care hospital in Saudi Arabia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, S.; Atef-Shebl, N.; Aslanpour, Z.; Berrou, I. Barriers to implementing antimicrobial stewardship programmes in three Saudi hospitals: Evidence from a qualitative study. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 18, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaleh, N.A.; Al-Omar, H.A.; Mayet, A.Y.; Mullen, A.B. Evaluating the appropriateness of carbapenem and piperacillin-tazobactam prescribing in a tertiary care hospital in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 1492–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendelson, M.; Morris, A.M.; Thursky, K.; Pulcini, C. How to start an antimicrobial stewardship programme in a hospital. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellit, T.H.; Owens, R.C.; Mcgowan, J.E.; Gerding, D.N.; Weinstein, R.A.; Burke, J.P.; Huskins, W.C.; Paterson, D.L.; Fishman, N.O.; Carpenter, C.F.; et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America Guidelines for Developing an Institutional Program to Enhance Antimicrobial Stewardship. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannick, S.; Sevdalis, N.; Athanasiou, T. Beyond clinical engagement: A pragmatic model for quality improvement interventions, aligning clinical and managerial priorities. BMJ Qual. Saf. 2016, 25, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmann, K.E.; Lehnick, D.; Buettcher, M.; Schwendener-Scholl, K.; Daetwyler, K.; Fontana, M.; Morgillo, D.; Ganassi, K.; O’Neill, K.; Genet, P.; et al. Impact of empowering leadership on antimicrobial stewardship: A single center study in a neonatal and pediatric intensive care unit and a literature review. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzewuska, M.; Duncan, E.M.; Francis, J.J.; Morris, A.M.; Suh, K.N.; Davey, P.G.; Grimshaw, J.M.; Ramsay, C.R. Barriers and Facilitators to Implementation of Antibiotic Stewardship Programmes in Hospitals in Developed Countries: Insights From Transnational Studies. Front. Sociol. 2020, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan American Health Organization Recommendations for Implementing Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs in Latin America and the Caribbean: Manual for Public Health Decision-Makers. 2018. Available online: https://www.paho.org/en/documents/recommendations-implementing-antimicrobial-stewardship-programs-latin-america-and (accessed on 22 January 2021).
- Nachtigall, I.; Tafelski, S.; Heucke, E.; Witzke, O.; Staack, A.; Recknagel-Friese, S.; Geffers, C.; Bonsignore, M. Time and personnel requirements for antimicrobial stewardship in small hospitals in a rural area in Germany. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 1946–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brink, A.J.; Messina, A.P.; Feldman, C.; Richards, G.A.; Becker, P.J.; Goff, D.A.; Bauer, K.A.; Nathwani, D.; Van den Bergh, D. Antimicrobial stewardship across 47 South African hospitals: An implementation study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapadia, S.N.; Abramson, E.L.; Carter, E.J.; Loo, A.S.; Kaushal, R.; Calfee, D.P.; Simon, M.S. The Expanding Role of Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs in Hospitals in the United States: Lessons Learned from a Multisite Qualitative Study. Jt. Comm. J. Qual. Patient Saf. 2018, 44, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, A.; Cresswell, K.M.; Coleman, J.J.; Pontefract, S.K.; Slee, A.; Williams, R.; Sheikh, A. Investigating the ways in which health information technology can promote antimicrobial stewardship: A conceptual overview. J. R. Soc. Med. 2017, 110, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perozziello, A.; Lescure, F.X.; Truel, A.; Routelous, C.; Vaillant, L.; Yazdanpanah, Y.; Lucet, J.C. Prescribers’ experience and opinions on antimicrobial stewardship programmes in hospitals: A French nationwide survey. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 2451–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alawi, M.M.; Darwesh, B.M. A stepwise introduction of a successful antimicrobial stewardship program: Experience from a tertiary care university hospital in Western, Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med. J. 2016, 37, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathwani, D.; Varghese, D.; Stephens, J.; Ansari, W.; Martin, S.; Charbonneau, C. Value of hospital antimicrobial stewardship programs [ASPs]: A systematic review. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Bano, J.; Perez-Moreno, M.A.; Penalva, G.; Garnacho-Montero, J.; Pinto, C.; Salcedo, I.; Fernandez-Urrusuno, R.; Neth, O.; Gil-Navarro, M.V.; Perez-Milena, A.; et al. Outcomes of the PIRASOA programme, an antimicrobial stewardship programme implemented in hospitals of the Public Health System of Andalusia, Spain: An ecologic study of time-trend analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 26, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, J.P. Antibiotic Resistance—Squeezing the Balloon? JAMA 1998, 280, 1270–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Waele, J.J.; Schouten, J.; Beovic, B.; Tabah, A.; Leone, M. Antimicrobial de-escalation as part of antimicrobial stewardship in intensive care: No simple answers to simple questions—a viewpoint of experts. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moglad, E.H. Antibiotics profile, prevalence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL), and multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae from different clinical samples in Khartoum State, Sudan. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, R.J.; Bassetti, M.; Clancy, C.J.; Garey, K.W.; Greenberg, D.E.; Nguyen, M.-H.; Roblin, D.; Tillotson, G.S.; Wilcox, M.H. Combating resistance while maintaining innovation: The future of antimicrobial stewardship. Futur. Microbiol 2019, 14, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donadu, M.G.; Le, N.T.; Ho, D.V.; Doan, T.Q.; Le, A.T.; Raal, A.; Usai, M.; Marchetti, M.; Sanna, G.; Madeddu, S.; et al. Phytochemical compositions and biological activities of essential oils from the leaves, rhizomes and whole plant of hornstedtia bella Škorničk. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods (Applied Social Research Methods), 5th ed.; SAGE Publications: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 1452242569. [Google Scholar]

| Microorganisms | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotics | Year | E. coli | A. baumannii | Enterobacter spp. | S. epidermidis | S. aureus | MRSA |
| Amoxicillin/Clavulanic acid | 2015 | 37 | - | - | - | 28 | - |
| 2016 | 49 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Cefepime | 2015 | 45 | 28 | 39 | - | - | - |
| 2016 | 48 | 22 | 66 | - | - | - | |
| Ciprofloxacin | 2015 | 33 | 20 | 60 | 20 | 62 | 47 |
| 2016 | 36 | 22 | 75 | 20 | 75 | 69 | |
| Clindamycin | 2015 | - | - | - | 45 | - | |
| 2016 | - | - | - | 28 | 76 | 71 | |
| Colistin | 2015 | - | 69 | - | - | - | - |
| 2016 | - | 97 | - | - | - | - | |
| Gentamicin | 2015 | 71 | 24 | 56 | 46 | 75 | 55 |
| 2016 | 65 | 34 | 79 | 53 | 86 | 71 | |
| Piperacillin/Tazobactam | 2015 | 47 | - | 48 | - | - | - |
| 2016 | 77 | - | 64 | - | - | - | |
| Antibiotics | Total DOT (07–12/2015) | Total DOT (01–06/2016) |
|---|---|---|
| Tigecycline | 1039.8 | 624.5 |
| Colistin | 2080.9 | 1417.2 |
| Meropenem | 2287.2 | 2597.3 |
| Imipenem | 2365.6 | 1666.1 |
| TOTAL | 7773.5 | 6305.1 (−18.9%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alghamdi, S.; Berrou, I.; Bajnaid, E.; Aslanpour, Z.; Haseeb, A.; Hammad, M.A.; Shebl, N. Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Implementation in a Saudi Medical City: An Exploratory Case Study. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10030280
Alghamdi S, Berrou I, Bajnaid E, Aslanpour Z, Haseeb A, Hammad MA, Shebl N. Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Implementation in a Saudi Medical City: An Exploratory Case Study. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(3):280. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10030280
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlghamdi, Saleh, Ilhem Berrou, Eshtyag Bajnaid, Zoe Aslanpour, Abdul Haseeb, Mohamed Anwar Hammad, and Nada Shebl. 2021. "Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Implementation in a Saudi Medical City: An Exploratory Case Study" Antibiotics 10, no. 3: 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10030280
APA StyleAlghamdi, S., Berrou, I., Bajnaid, E., Aslanpour, Z., Haseeb, A., Hammad, M. A., & Shebl, N. (2021). Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Implementation in a Saudi Medical City: An Exploratory Case Study. Antibiotics, 10(3), 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10030280







