Abstract
The main objective of this study was to characterize using whole-genome sequencing analysis, a new variant of the qnrB gene (qnrB89) carried by a fluoroquinolone-susceptible bacterium isolated from mucus of farmed Salmo salar fingerling in Chile. Citrobacter gillenii FP75 was identified by using biochemical tests and 16S ribosomal gene analysis. Nucleotide and amino acid sequences of the qnrB89 gene exhibited an identity to qnrB of 81.24% and 91.59%, respectively. The genetic environment of qnrB89 was characterized by the upstream location of a sequence encoding for a protein containing a heavy metal-binding domain and a gene encoding for a N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase protein, whereas downstream to qnrB89 gene were detected the csp and cspG genes, encoding cold-shock proteins. The qnrB89 gene was located on a large chromosomal contig of the FP75 genome and was not associated with the 10-kb plasmid and class 1 integron harbored by the FP75 strain. This study reports for the first time the carriage of a qnrB gene by the C. gillenii species, and its detection in a bacterial strain isolated from farmed salmon in Chile.
1. Introduction
In Chilean salmon farming, the low availability of efficient vaccines and the high prevalence of bacterial infections, such as Piscirickettsiosis caused by the intracellular pathogen Piscirickettsia salmonis [1,2,3], have stimulated the use of large amounts of antimicrobials, accounting for a total consumption of 334.1 tons during 2019 [4]. During the last few years the main antibiotics used in Chilean salmon farming were florfenicol, oxytetracycline and erythromycin, and to a much lesser extent the first-generation fluoroquinolone flumequine [4,5].
Fluoroquinolones belong to a class of synthetic antimicrobial agents with a broad spectrum of activity [6,7,8] and are widely used in the treatment of infections caused by Gram negative bacteria [9]. However, due to the extensive use of these antibiotics, there has been an important increase in the resistance to these drugs [10]. The most effective fluoroquinolone resistance mechanism is chromosomal mutations that alter the antibiotic target proteins, DNA gyrase or DNA topoisomerase IV and their drug-binding affinity, commonly conferring high levels of resistance in several bacterial species [11,12]. Furthermore, the acquisition of plasmid-acquired resistance genes producing either target protection proteins, drug modifying enzymes or drug efflux pumps are other mechanisms of fluoroquinolone resistance [12,13,14]. Functions of several plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance (sometimes labeled PMQR) genes include protection of quinolone target proteins, which are mediated by qnr genes, encoding proteins that protect DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV against quinolones, thus preventing their activity [15,16].
It is well known that qnr-carrying bacteria exhibit only a low-level resistance to fluoroquinolones, but these bacteria can facilitate the emergence of resistant strains through the acquisition of other mechanisms of quinolone resistance, such as topoisomerase mutations and efflux action [8,17,18].
Currently, various studies report that prevalence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance, mainly encoded by the qnr genes is widespread, thus their occurrence among environmental bacteria is of high concern, but only a few studies addressing the occurrence of qnr genes among bacteria associated with aquaculture settings [19,20,21], or near fish farms [22] have been reported.
It must be noted that qnr gene carriage by bacteria isolated from reared fish in Chilean salmon farming has never been previously reported. Thus, this study adds important information on the detection of a qnr gene carried by bacteria of animal origin, and reporting for the first time the detection of a qnr gene in Citrobacter gillenii species.
It could be concluded that quinolone resistance genes could be detected among bacteria from reared salmon in Chile but not necessarily associated with plasmid elements with potential for horizontal transfer, thus not prompting an important risk to human public health.
The main aim of the study was to describe a new variant of the qnrB gene and its genomic environment carried by the multidrug resistant C. gillenii FP75 strain recovered from mucus of salmon reared in a Chilean salmon farm.
2. Results
2.1. Bacterial Identification
The bacterial strain FP75 was identified as Citrobacter gillenii by 16S ribosomal gene amplification (EMBL database accession number KX279662.1). The 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain FP75 was compared with all sequences currently available for members of the genus Citrobacter and related taxa. The results are presented as a phylogenetic dendrogram developed with the neighbor-joining method showing that FP75 strain is a member of the genus Citrobacter, where the most related species was C. gillenii (16S rRNA gene similarity 99.79%), as is depicted in Figure 1. In addition, identification of strain FP75 as C. gillenii was confirmed by specific biochemical characteristics, exhibiting important differences to the C. freundii species (Table 1).
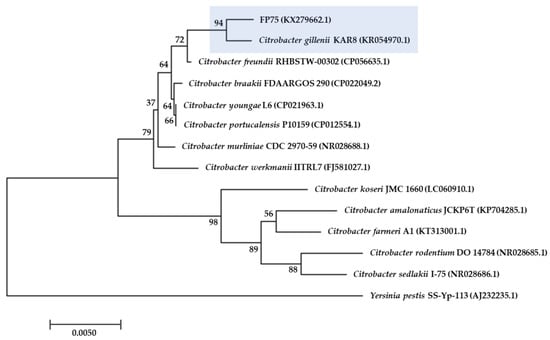
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree based on the 16S rDNA gene sequence constructed by the neighbor-joining method. Yersinia pestis was used as an outgroup. Horizontal branch lengths are proportional to evolutionary divergences. Bootstrap values (%) appear next to the corresponding branch.

Table 1.
Phenotypic differentiation between Citrobacter gillenii and Citrobacter freundii.
2.2. Molecular Analysis
A qnr gene was detected in the genome of C. gillenii FP75 strain. The gene sequence was submitted to Dr. George Jacoby, curator of the qnr database, and responsible for the assignment of novel variants of qnr genes. This group confirmed the submitted gene as a unique sequence, naming this new variant of the qnrB gene, as qnrB89 (EMBL database accession number MT544491.1).
The new variant qnrB89 showed a high identity to the sequences reported for the founding members of qnrB and qnrE genes included in the GenBank database (Table 2). Nucleotide sequence of qnrB89 gene exhibited an 81.24% and 75.04% identity with the qnrB and qnrE genes, respectively, whereas at the amino acid sequence level, QnrB89 presents an identity of 91.59% and 83.64% with QnrB and QnrE, respectively (Table 2).

Table 2.
Similarity of nucleotide and amino acid sequences of qnrB89 carried by Citrobacter gillenii FP75 with those of the alleles of the qnr gene.
The genetic environment of qnrB89 gene was characterized by the upstream location of a sequence encoding for a protein containing a heavy metal-binding domain (HMDP), a gene encoding a N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase protein, which is a peptidoglycan hydrolase (NALAP) and a gene encoding for a NAD(P)-dependent oxidoreductase protein (NAD(P)-DOP), whereas downstream of the qnrB89 gene were detected two genes encoding cold shock proteins (csp and cspG), a gene that encodes a lipoprotein (LP), and the artP gene, encoding an arginine transport ATP-binding protein (Figure 2). As shown in Figure 2, the genetic environment of qnrB89 is not typical of those commonly described for the chromosomal located qnrB genes carried by various Citrobacter species.
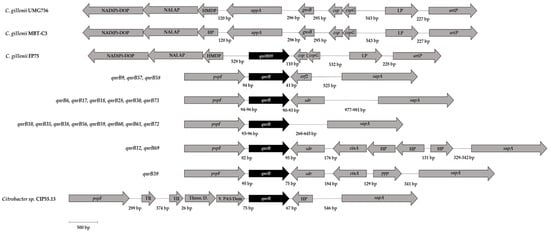
Figure 2.
Comparison of the genetic environment of the gene qnrB89, Schematic representation of the genetic environment of qnrB89 gene carried by Citrobacter gillenii FP75 with several chromosomally located qnrB genes carried by various Citrobacter species as described by Ribeiro et al. [28]. Numbers between ORFs indicate the size of the intergenic region in base pairs (bp). The sequences used in the scheme were those previously considered by Ribeiro et al. [28], and include the GenBank accession numbers KP339254 (qnrB6), KP339255 (qnrB9), ADLG01000026.1 (qnrB9), KP339256 (qnrB10), CP007557 (qnrB12), KP339257 (qnrB17), KP339258 (qnrB18), ACDJ02000027.1 (qnrB18), JTBV01000001.1 (qnrB28), JMUJ01000007.1 (qnrB28), JAPA01000008.1 (qnrB30), JN173057 (qnrB35), JN173060 (qnrB38), NZ_AMPE01000004.1 (qnrB38), NZ_AKTT01000018.1 (qnrB38), NZ_AOUE01000004.1 (qnrB38), JTBJ01000001.1 (qnrB38), JAPB01000002.1 (qnrB38), ABWL02000005.1 (qnrB39), KP339259 (qnrB56), KP339260 (qnrB57), KP339261 (qnrB58), KP339262 (qnrB59), AB734055 (qnrB60), AB734053 (qnrB61), BBMW01000005.1 (qnrB69), KP339263 (qnrB72), KP339264 (qnrB73), and CDHL01000019, corresponding to a new qnrB from strain CIP 55-13T, as described by Ribeiro et al. [28]. In addition, similar locus found in two available C. gillenii genomes belonging to the not-carrying qnr genes strains C. gillenii UMG736 (SUQN00000000.1) and C. gillenii MBT-C3 (QVEK00000000.1), are included in the scheme.
When the FP75 genome was compared to the two publicly available C. gilleni genomes, corresponding to C. gillenii UMG736 (SUQN00000000.1) and C. gillenii MBT-C3 (QVEK00000000.1), composed of 24 and 37 contigs, respectively, no qnr gene was detected. However, it is interesting to note that in both genomes the qnrB89 neighborhood was present, but instead of the qnrB89 gene, gene appA, encoding for an AppA family phytase/histidine-type acid phosphatase protein and gene gnsB, encoding for an addiction module toxin, GnsA/GnsB family protein, were observed, located in contigs 1 and 9 of C. gillenii UMG736 and C. gillenii MBT-C3 genomes, respectively (Figure 2).
2.3. Microbial Susceptibility Profile and Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs)
MIC values of flumequine and enrofloxacin of C. gillenii FP75 and Escherichia coli UC238 carrying the qnrB gene are shown in Table 3. Assayed strains exhibited low MICs of flumequine and ciprofloxacin, observing slight differences. These results confirmed that carriage of the qnrB89 gene is unable to confer resistance to quinolones in C. gillenii FP75 strain. Reference strain E. coli ATCC 25922, used for quality control exhibited a MIC value of flumequine and ciprofloxacin of 0.5 and 0.008 µg/mL, respectively, in agreement with the value recommended by CLSI [29].

Table 3.
Antimicrobial resistance patterns and minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of Citrobacter gillenii FP75 and Escherichia coli UC238.
Multidrug resistance of C. gillenii FP75 was demonstrated by performing a disk diffusion assay, showing resistance to the antibacterials amoxicillin, streptomycin, erythromycin, oxytetracycline, chloramphenicol, florfenicol, furazolidone, sulfisoxazole and trimethoprim and susceptibility to the antimicrobials cefotaxime, gentamicin, kanamycin, nalidixic acid, oxolinic acid, flumequine and ciprofloxacin (Table 3).
3. Discussion
The antimicrobials used in Chilean salmon farming are mainly florfenicol and oxytetracycline, accounting for the 90.8 and 99.8%, of used antibiotics during 2019 in freshwater and marine farms, respectively [4]. Thus, the use of oxolinic acid and flumequine, the unique quinolones authorized to be used in this industry is currently minimal [2,4,5].
Previous studies evidence Citrobacter as the origin of qnrB genes and suggest a divergent evolution of closely related qnrB genes [28,32]. Citrobacter are found in various clinical and environmental sources, including soil and water [33]. Furthermore, Citrobacter is currently considered an opportunistic pathogen in fish aquaculture, causing gastroenteritis of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss [34,35,36,37,38]. To date, a few studies have reported the isolation of C. gillenii from rainbow trout intestinal tract showing disease symptoms [24], and from the healthy fish intestine of rainbow trout and farmed grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) [39,40].
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of a qnr gene detected in the C. gillenii species, and prompts the necessity to investigate the carriage of qnr genes in farmed salmonid microbiota, and to provide a scientific basis of the prevalence of this opportunistic pathogen in farmed salmon to prevent potential secondary infections.
The higher similarity of nucleotide and amino acid sequence of qnrB89 with the qnrB allele, when compared to the qnrE sequences, determined that this gene was classified as qnrB89. As was stated by Jacoby et al. [32], qnrB is the most common of the five qnr families and has the greatest number of allelic variants, being mostly detected in the Citrobacter genus with several of them located on the bacterial chromosome. Among the qnrB alleles, qnrB89 variant exhibited the highest degree of amino acid (93.46%) sequence identity to the qnrB12 sequence from Citrobacter werkmanii isolated from poultry [41].
However, the genetic environment of the qnrB89 gene is very different to those reported for most of the other qnrB alleles, which consistently include the pspF (encoding a phage shock protein) and sapA (encoding a protein involved in antimicrobial peptide resistance) genes upstream and downstream of the qnrB genes, respectively [28], which are absent in the qnrB89 background. Furthermore, the qnrB89 genetic background is also very different to those of the qnrE1 gene, which is flanked by the genes araJ (encoding a arabinose efflux permease) and ppk (encoding a polyphosphate kinase) or tnp (encoding a transposase) [28,42]. Ribeiro et al. [28] characterized the genetic surroundings of various qnrB genes, observing eight different conserved genetic platforms for closely related qnrB genes carried by different Citrobacter species, demonstrating an association between the qnrB platforms carrying closely related qnrB genes and specific Citrobacter species. However, these genetic environments are highly different to that observed for the qnrB89 gene of C. gillenii FP75. However, it should be noted that C. gillenii species was not included in the referenced study.
In previous studies, qnrB genes have been commonly associated with integrons in clinic isolates belonging to the Citrobacter genus [43]. Lee et al. [44] studied the genetic context surrounding chromosomal qnrB62 gene carried by a C. freundii clinical isolate, observing an association with a complex class 1 integron. Furthermore, Ferreira et al. [45] isolated a clinical multiresistant C. freundii strain carrying a qnrB gene associated with a class 1 integron inserted in a large plasmid. In another study, several ciprofloxacin-resistant C. freundii recovered from wastewater treatment plants carried a qnrB gene as part of a complex integron [46]. Despite the previous finding that C. gillenii FP75 carries a class 1 integron [47], this study demonstrated that the harbored integron was not associated with the qnrB89 gene, which is in agreement with other previous studies of aquaculture associated bacteria carrying qnrB genes [48,49].
Otherwise, unlike qnrB89 gene, many reported qnrB alleles are associated with plasmid elements and are able to be horizontally transferred [50,51,52,53], but other qnrB variants have previously been described as non-transferable, such as the qnrB12 variant carried by Citrobacter werkmanii and a qnrB variant carried by Rhodococcus sp., which were unable to be horizontally mobilized [48,54]. However, the carriage of transferable determinants conferring resistance to florfenicol and oxytetracycline of C. gillenii FP75, which are associated with the 10-kb plasmid [47], suggest that intensive use of these antibiotics in Chilean salmon farming will exert a selective pressure on this bacteria, promoting the co-selection and persistence of the detected qnrB89 gene in the salmon mucus microbiota.
Despite the carriage of a variant of the qnrB gene by C. gillenii FP75, this strain is susceptible to quinolones. It is well known that resistance to quinolones is mainly due to chromosomal point mutations rather than being carried on any mobile genetic elements, but although qnr genes only confer low-level resistance to quinolones, these genes could favor the selection of additional chromosome-encoded quinolone resistance mechanisms. Furthermore, the study of qnr genes has an epidemiological relevance to advance a comprehensive understanding of the resistome associated with environmental settings, and to know their evolution and spread in these environments.
The chromosomal mutations exhibited by the C. gillenii FP75 strain leading to amino acid substitutions in the quinolone-resistance-determining regions of bacterial protein targets of quinolones were only a conserved change (Ser-83 to Thr) in the gyrase A protein, but not conferring resistance or low level susceptibility to quinolones, whereas the detected amino acid substitutions in GyrB (Leu-417 to His) and ParE (Ile-485 to Val) are located in protein regions not associated with changes in the susceptibility to quinolones.
In Chile in 2014 and 2015, the genes qnrA, qnrB, and qnrS, were described in strains isolated from uncontaminated sediments and sectors adjacent to a site affected by salmon farming [22,54]. However, this is the first report of a qnr gene detected in a bacterium directly associated with Chilean salmon farming, and most importantly, from farmed salmon mucus. The finding of this gene in a bacterial strain exhibiting susceptibility to quinolones suggest that incidence of qnr genes in these systems could be strongly underestimated when they are not associated with fluoroquinolone-resistant bacteria. Furthermore, these qnr-carrying bacteria are most frequently resistant to other antimicrobials, such as florfenicol and oxytetracycline, intensively used in Chilean aquaculture, thus favoring the prevalence of qnr genes in Chilean salmon farming, constituting a potential threat for salmon handlers and consumers, mostly considering that the chromosome of Citrobacter is the likely source of plasmid-mediated qnrB, as was suggested by Jacoby et al. [32].
Thus, the role of Chilean salmon farming as a potential reservoir of qnr genes must be elucidated, prompting the necessity of detecting qnr genes in a high number of representatives of reared salmon microbiota, including isolates exhibiting various levels of susceptibility to quinolones.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strain
The FP75 strain was recovered from mucus of reared salmon fingerling cultured in a freshwater farm located at the Puyehue Lake, in the South of Chile [47]. The purified strain stored at −85 °C in CryoBankTM vials (Mast Diagnostica, Reinfeld, Germany), was grown in Trypticase soy agar (TSA, Oxoid, Hants, UK) at 30 °C for 24 h prior to use.
4.2. Bacterial Identification
The phenotypic tests Gram staining, cell morphology, oxidase production and oxidation/fermentation (O/F) of glucose were determined according to the procedures described in Buller [55]. In addition, biochemical properties, urease production, ornithine decarboxylation, fermentation of sucrose, utilization of acetate and malonate were determined to phenotypically differentiate the FP75 strain from the Citrobacter freundii species [56], using the procedures described by Barrow and Feltham [57].
Furthermore, FP75 strain was identified by bacterial 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. DNA extraction and the amplification of the 16S ribosomal gene of the FP75 strain was performed as was previously described [47]. The sequence was edited and matched to the Ribosomal Database Project [58] to identify the bacterial isolate and deposited in the GenBank under accession number KX279662.1 as was previously reported [46]. The phylogenetic and molecular evolutionary analyses were conducted using MEGA version 7.0 [59].
4.3. Molecular Analysis of the qnrB89 Gene
Genomic DNA was extracted and purified using the commercial Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA), following the indications of the supplier. The characterization of the qnr gene and its genetic environment was carried out through the complete sequencing of the bacterium’s genome. The whole genomic DNA was sequenced by Macrogen USA (Rockville, MD, USA). The analysis of the qnr gene sequence and its genetic environment was based on the contigs derived from genomic sequencing. This analysis was performed with the BioEdit 7.2.5 software [60] and subsequent comparison by BLAST computational analysis with the sequences described in the GenBank database. The identification and classification of the detected qnr gene was complemented with the group of experts led by Dr. George Jacoby.
4.4. Antimicrobial Resistance Pattern
The antimicrobial susceptibility to 16 antimicrobials of strains C. gillenii FP75, E. coli DH5α and transconjugant strain E. coli FP75T was determined using a disk diffusion test according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guideline VET3-A [61] and previously described [62]. Briefly, bacterial suspensions in phosphate buffered saline at a turbidity corresponding to a 0.5 McFarland standard (bioMérieux, Marcy-l’Etoile, France) were streaked onto plates containing cation-adjusted Mueller–Hinton agar (CAMH, Difco Labs, NJ, USA) to which were added disks (Oxoid) containing the antibiotics amoxicillin (AML, 25 µg), cefotaxime (CTX, 30 μg), chloramphenicol (CM, 30 μg), florfenicol (FFC, 30 μg), streptomycin (S, 10 μg), gentamicin (CN, 10 μg), kanamycin (K, 30 μg), oxytetracycline (OT, 30 μg), erythromycin (E, 15 μg), nalidixic acid (NA, 30 μg), oxolinic acid (OA, 2 μg), flumequine (UB, 30 μg), ciprofloxacin (CIP, 5 μg), furazolidone (FR, 100 μg), sulfisoxazole (SFX, 300 μg) and trimethoprim (TMP, 5 μg). Plates were incubated at 28 °C for 24 h according to CLSI guidelines [61], and strains were considered resistant according to the criteria established by the CLSI [61,63]. As recommended by the CLSI guidelines [64], the reference strain E. coli ATCC 25922 was used as a quality control strain. All strains were re-examined to check the reproducibility of the assay.
4.5. Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs)
Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of flumequine and ciprofloxacin of C. gillenii FP75 and E. coli UC238 were determined by a microdilution method, as recommended by the CLSI guideline M07-A10 [65] and previously described [62]. Conical bottom microplates added with cation-adjusted Mueller–Hinton broth were inoculated with the antibiotic to obtain final series of two-fold concentrations in the range of 0.0625–128 µg/mL. Bacterial suspensions were prepared in sterile 0.85% saline and triplicate microplates were inoculated, delivering approximately 104 colony-forming units per well, and incubated for 24 h at 28 °C. The reference strain E. coli ATCC 25922 was included as quality control, as was recommended [65]. All assays were performed twice to check the reproducibility of the assay.
A breakpoint of ≤1.0 µg/mL was used to consider susceptibility to ciprofloxacin as stated by the CLSI [30] for enteric bacteria. Considering that no MIC breakpoints for flumequine are currently stated, we categorized the isolates using as a reference the flumequine epidemiological cut-off (ECOFF) value stated by the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) [31] for Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. (≤2.0 µg/mL for susceptible).
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the results of this study demonstrated for the first time the carriage of a new qnrB variant (qnrB89) by a bacterial strain isolated from reared fish in Chilean salmon farming, and the detection of a qnr gene in the Citrobacter gillenii species. The detection of a qnr gene carried by a quinolone susceptible strain strongly suggests that farmed fish is an important reservoir of these genes but are significantly underestimated considering that qnr genes are almost exclusively investigated among quinolone-resistant bacteria. Furthermore, the uncommon genetic environment of the qnrB89 gene, compared to other qnrB genes, and its non-association to integrons or plasmids suggest a most probable environmental origin, not related to a clinical source. This study shows important information on the characteristics of a qnr gene carried by quinolone susceptible bacteria from salmon farming, thus providing an important basis to advance the performing of genetic epidemiology studies on quinolone resistance genes in fish farm associated environments in Chile.
It can be concluded that quinolone resistance genes can be detected among bacteria from reared salmon in Chile but not necessarily associated with transferable elements, reducing their ability to be horizontally transferred, thus not significantly contributing to spread of these genes in these environments and not prompting an important risk to human public health.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.D.M. and C.C; methodology, C.C., R.R., F.A.G. and J.R.; software, C.C. and J.R.; validation, C.C. and C.D.M.; formal analysis, C.C., F.A.G. and C.D.M.; investigation, C.C., R.R., F.A.G. and J.R.; resources, C.D.M. and C.C.; writing—original draft preparation, C.D.M. and C.C.; writing—review and editing, C.D.M., C.C. and J.R.; visualization, C.C. and C.D.M.; supervision, C.D.M.; project administration, C.D.M.; funding acquisition, C.D.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially funded by the Science and Technology National Council (CONICYT) of Chile, grant number 1040924. CC was supported by the Postdoctoral Fund of the Universidad Católica del Norte, grant number 002.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Page: 10. Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, due to C. gillenii FP75 strain was obtained from the bacterial collection of the Aquatic Pathobiology Lab of the Universidad Católica del Norte.
Data Availability Statement
The whole-genome sequence of FP75 strain has been deposited at DDBJ/ENA/GenBank under the accession number JAFDOE000000000 (BioProjectPRJNA699318; BioSample SAMN17773723).
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge to Luz Hurtado for expert assistance with MIC assays. The authors acknowledge Gerardo González-Rocha, Chief of Laboratorio de Investigación en Agentes Antibacterianos of the Universidad de Concepción, Chile for providing the positive control of the qnrB gene, strain Escherichia coli UC238. The authors thank George Jacoby for his assistance in classifying the new variant of the qnrB gene.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Rozas, M.; Enríquez, R. Piscirickettsiosis and Piscirickettsia salmonis in fish: A review. J. Fish Dis. 2014, 37, 163–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avendaño-Herrera, R. Salmon aquaculture, Piscirickettsia salmonis virulence, and one health: Dealing with harmful synergies between heavy antimicrobial use and piscine and human health comment on. Aquaculture 2020, 532, 736062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SERNAPESCA. Informe Sanitario de Salmonicultura en Centros Marinos 2019; Servicio Nacional de Pesca y Acuicultura: Valparaíso, Chile, 2019; 38p, Available online: http://www.sernapesca.cl/sites/default/files/informe_sanitario_salmonicultura_2019_final_julio_2020.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2020).
- SERNAPESCA. Informe sobre Uso de Antimicrobianos en la Salmonicultura Nacional; Servicio Nacional de Pesca y Acuicul-tura: Valparaíso, Chile, 2019; 11p, Available online: http://www.sernapesca.cl/sites/default/files/informe_atb_2019.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2020).
- Miranda, C.D.; Godoy, F.A.; Lee, M.R. Current Status of the Use of Antibiotics and the Antimicrobial Resistance in the Chilean Salmon Farms. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfson, J.S.; Hooper, D.C. The fluoroquinolones: Structures, mechanisms of action and resistance, and spectra of activity in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1985, 28, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D.C. Mechanisms of Action and Resistance of Older and Newer Fluoroquinolones. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, S24–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldred, K.J.; Kerns, R.J.; Osheroff, N. Mechanism of Quinolone Action and Resistance. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appelbaum, P.; Hunter, P. The fluoroquinolone antibacterials: Past, present and future perspectives. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2000, 16, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, S.; Shen, P.; Lu, X.; Xiao, Y. Association between the rate of fluoroquinolones-resistant gram-negative bacteria and antibiotic consumption from China based on 145 tertiary hospitals data in 2014. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, S.; Poeta, P.; Hébraud, M.; Capelo, J.L.; Igrejas, G. Mechanisms of quinolone action and resistance: Where do we stand? J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redgrave, L.S.; Sutton, S.B.; Webber, M.A.; Piddock, L.J. Fluoroquinolone resistance: Mechanisms, impact on bacteria, and role in evolutionary success. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, J.; Pons, M.J.; Gomes, C. Transferable mechanisms of quinolone resistance. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 40, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, J.M.; Machuca, J.; Cano, M.E.; Calvo, J.; Martínez-Martínez, L.; Pascual, A. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance: Two decades on. Drug Resist. Updat. 2016, 29, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strahilevitz, J.; Jacoby, G.A.; Hooper, D.C.; Robicsek, A. Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance: A Multifaceted Threat. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 664–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, S.; Strahilevitz, J.; Hooper, D.C. Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.-Y.; Kim, E.S.; Choi, S.-H.; Kwon, H.-H.; Lee, S.-R.; Lee, S.-O.; Kim, M.-N.; Woo, J.H.; Kim, Y.S. Effects of a plasmid-encoded qnrA1 determinant in Escherichia coli strains carrying chromosomal mutations in the acrAB efflux pump genes. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 60, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinothkumar, K.; Kumar, G.N.; Bhardwaj, A.K. Characterization of Vibrio fluvialis qnrVC5 Gene in Native and Heterologous Hosts: Synergy of qnrVC5 with other Determinants in Conferring Quinolone Resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, Y.; Ahmed, A.M.; Mahfouz, N.B.; Kimura, T.; El-Khodery, S.A.; Moawad, A.A.; Shimamoto, T. Molecular Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistance in Gram-Negative Bacteria Isolated from Fish Farms in Egypt. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2010, 72, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.-X.; Tang, D.; Liu, Y.-H.; Zhang, X.-H.; Zeng, Z.-L.; Xu, L.; Hawkey, P.M. Prevalence and characteristics of -lactamase and plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in Escherichia coli isolated from farmed fish in China. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2350–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgueiro, V.; Manageiro, V.; Bandarra, N.M.; Reis, L.; Ferreira, E.; Caniça, M. Bacterial Diversity and Antibiotic Susceptibility of Sparus aurata from Aquaculture. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomova, A.; Ivanova, L.; Buschmann, A.H.; Rioseco, M.L.; Kalsi, R.K.; Godfrey, H.P.; Cabello, F.C. Antimicrobial resistance genes in marine bacteria and human uropathogenic Escherichia colifrom a region of intensive aquaculture. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2015, 7, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, D.J.; O’Hara, C.M.; Grimont, P.A.D.; Janda, J.M.; Falsen, E.; Aldova, E.; Ageron, E.; Schindler, J.; Abbott, S.L.; Steigerwalt, A.G. Biochemical Identification of Citrobacter Species Defined by DNA Hybridization and Description of Citrobacter gillenii sp. nov. (FormerlyCitrobacter Genomospecies 10) and Citrobacter murliniae sp. nov. (Formerly Citrobacter Genomospecies 11). J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 2619–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, M.; Saticioglu, I.B.; Buyukekiz, A.G.; Balta, F.; Altun, S. Molecular characterization and antimicrobial resistance profile of atypical Citrobacter gillenii and Citrobacter sp. isolated from diseased rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2017, 10, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L.; Cheung, W.K.; Hanson, D.F. Biochemical identification of citrobacteria in the clinical laboratory. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 1850–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/ (accessed on 28 November 2020).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information Protein Database. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/ (accessed on 5 October 2012).
- Ribeiro, T.G.; Novais, Â.; Branquinho, R.; Machado, E.; Peixe, L. Phylogeny and Comparative Genomics Unveil Independent Diversification Trajectories of qnrB and Genetic Platforms within Particular Citrobacter Species. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5951–5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Bacteria Isolated from Aquatic Animals; Second Informational Supplement; CLSI Document VET03/VET04-S2; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twenty Seventh Informational Supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Available online: https://mic.eucast.org/Eucast2/ (accessed on 22 November 2019).
- Jacoby, G.A.; Griffin, C.M.; Hooper, D.C. Citrobacter spp. as a Source of qnrB Alleles. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4979–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borenshtein, D.; Schauer, D.B. The Genus Citrobacter. In The Prokaryotes: A Handbook on the Biology of Bacteria: Proteo-Bacteria: Gamma Subclass; Dworkin, M., Falkow, S., Rosenberg, E., Scheleifer, K.H., Stackebrandt, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, N.; Yamane, N.; Kawamura, T. Systemic Citrobacter freundii infection among sunfish Mola mola in Matsushima Aquarium. Nippon. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1982, 48, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, F. Rainbow trout mortalities associated with a mixed infection with Citrobacter freundii and IPN virus. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 1991, 11, 222–224. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, B.; Stobie, M.; Robertson, P.A.W. Citrobacter freundii: The cause of gastroenteritis leading to progressive low level mortalities in farmed rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum, in Scotland. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 1992, 12, 166–167. [Google Scholar]
- Jeremić, S.; Jakić-Dimić, D.; Veljović, L.J. Citrobacter freundii as a cause of disease in fish. Acta Vet. 2003, 53, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeck, G.-W.; Kim, J.H.; Choresca, C., Jr.; Gómez, D.; Shin, S.P.; Han, J.E.; Park, S.-C. Mass mortality of doctor fish (Garra rufa obtusa) caused by Citrobacter freundii infection. J. Vet. Clin. 2009, 26, 150–154. [Google Scholar]
- Navarrete, P.; Magne, F.; Mardones, P.; Riveros, M.; Opazo, R.; Suau, A.; Pochart, P.; Romero, J. Molecular analysis of intestinal microbiota of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 71, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lü, A.; Hu, X.; Zheng, L.; Zhu, A.; Cao, C.; Jiang, J. Isolation and characterization of Citrobacter spp. from the intestine of grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idellus. Aquaculture 2011, 313, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehrenberg, C.; Friederichs, S.; Schwarz, S.; De Jong, A. Novel Variant of the qnrB Gene, qnrB12, in Citrobacter werkmanii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 52, 1206–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albornoz, E.; Tijet, N.; De Belder, D.; Gomez, S.; Martino, F.; Corso, A.; Melano, R.G.; Petroni, A. qnrE1, a Member of a New Family of Plasmid-Located Quinolone Resistance Genes, Originated from the Chromosome of Enterobacter Species. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02555-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga, M.P.; Andres, P.; Petroni, A.; Bistué, A.J.C.S.; Guerriero, L.; Vargas, L.J.; Zorreguieta, A.; Tokumoto, M.; Quiroga, C.; Tolmasky, M.E.; et al. Complex Class 1 Integrons with Diverse Variable Regions, Including aac(6′)-Ib-cr, and a Novel Allele, qnrB10, Associated with ISCR1 in Clinical Enterobacterial Isolates from Argentina. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 4466–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.; Kim, M.-N.; Park, K.S.; Lee, J.H.; Karim, A.M.; Park, M.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Complex Class 1 Integron Carrying qnrB62 and blaVIM-2 in a Citrobacter freundii Clinical Isolate. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6937–6940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.; Paradela, A.; Velez, J.; Ramalheira, E.; Walsh, T.R.; Mendo, S. Carriage of qnrA1 and qnrB2, blaCTX-M15, and complex class 1 integron in a clinical multiresistant Citrobacter freundii isolate. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 67, 188–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, G.; Kwong, W.; Davies, J.; Miao, V. Complex integrons containing qnrB4-ampC (blaDHA-1) in plasmids of multidrug-resistant Citrobacter freundii from wastewater. Can. J. Microbiol. 2013, 59, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez, M.; Miranda, C.D.; Fuentes, O.; De La Fuente, M.; Godoy, F.A.; Bello-Toledo, H.; González-Rocha, G. Occurrence of Transferable Integrons and sul and dfr Genes Among Sulfonamide-and/or Trimethoprim-Resistant Bacteria Isolated From Chilean Salmonid Farms. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Wu, X.; Yan, Q.; Ma, Y.; Huang, L.; Qin, Y.; Xu, X. Incidence of antimicrobial-resistance genes and integrons in antibiotic-resistant bacteria isolated from eels and aquaculture ponds. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2016, 120, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomova, A.; Ivanova, L.; Buschmann, A.H.; Godfrey, H.P.; Cabello, F.C. Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance (PMQR) Genes and Class 1 Integrons in Quinolone-Resistant Marine Bacteria and Clinical Isolates of Escherichia coli from an Aquacultural Area. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 75, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, G.A.; Walsh, K.E.; Mills, D.M.; Walker, V.J.; Oh, H.; Robicsek, A.; Hooper, D.C. qnrB, Another Plasmid-Mediated Gene for Quinolone Resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1178–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Jung, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, H.R.; Lee, J.N.; Chang, C.L. High Rates of Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance QnrB Variants Among Ciprofloxacin-Resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae from Urinary Tract Infections in Korea. Microb. Drug Resist. 2008, 14, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doma, A.O.; Popescu, R.; Mitulețu, M.; Muntean, D.; Dégi, J.; Boldea, M.V.; Radulov, I.; Dumitrescu, E.; Muselin, F.; Puvača, N.; et al. Comparative Evaluation of qnrA, qnrB, and qnrS Genes in Enterobacteriaceae Ciprofloxacin-Resistant Cases, in Swine Units and a Hospital from Western Romania. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halová, D.; Papousek, I.; Jamborova, I.; Masarikova, M.; Cizek, A.; Janecko, N.; Oravcova, V.; Zurek, L.; Clark, A.B.; Townsend, A.; et al. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in Enterobacteriaceae from American crows: High prevalence of bacteria with variable qnrB genes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 1257–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aedo, S.; Ivanova, L.; Tomova, A.; Cabello, F.C. Plasmid-Related Quinolone Resistance Determinants in Epidemic Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Uropathogenic Escherichia coli, and Marine Bacteria from an Aquaculture Area in Chile. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 68, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buller, N.B. Bacteriological Culture Techniques: Microscopy, Culture and Identification. In Bacteria from Fish and Other Aquatic Animals: A Practical Identification Manual, 1st ed.; Buller, N.B., Ed.; CABI Publishing: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 83–116. [Google Scholar]
- O’Hara, C.M.; Roman, S.B.; Miller, J.M. Ability of commercial identification systems to identify newly recognized species of Citrobacter. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrow, G.I.; Feltham, R.K.A. Cowan and Steel’s Manual for the Identification of Medical Bacteria, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993; 331p. [Google Scholar]
- Ribosomal Database Project. Available online: http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/ (accessed on 22 April 2013).
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Methods for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Testing of Bacteria Isolated from Aquatic Animals; Approved Guideline VET03-A; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, NJ, USA, 2006; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Concha, C.; Miranda, C.D.; Hurtado, L.; Romero, J. Characterization of Mechanisms Lowering Susceptibility to Flumequine among Bacteria Isolated from Chilean Salmonid Farms. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Test for Bacteria Isolated from Animals, 4th ed.; CLSI Supplement VET08; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Test, 12th ed.; Approved Standard M02-A12; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically, 10th ed.; Approved Standard M07-A10; CLSI Standards Centre: Wayne, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).