Assessment of the Antibacterial Efficacy of Halicin against Pathogenic Bacteria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Bacterial Suspensions
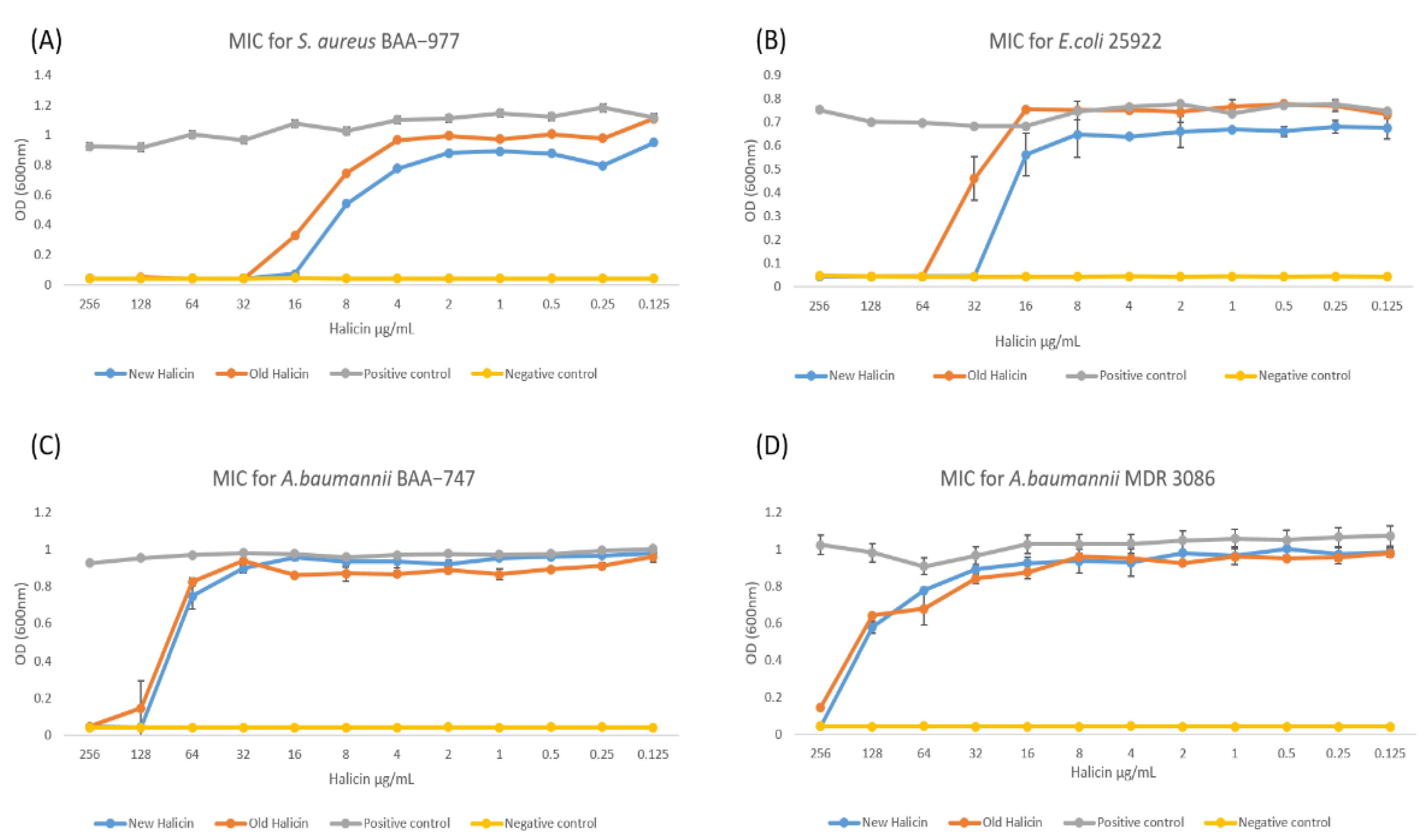
2.3. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Zone of Inhibition Assay
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antimicrobial Resistance Global Report on Surveillance (GLASS) Report: 2021 [Internet]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240027336 (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Kahlmeter, G.; Brown, D.F.J.; Goldstein, F.W.; MacGowan, A.P.; Mouton, J.; Österlund, A.; Rodloff, A.; Steinbakk, M.; Urbaskova, P.; Vatopoulos, A. European harmonization of MIC breakpoints for antimicrobial susceptibility testing of bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walker, A.S.; Pishchany, G.; Clardy, J. Parsing Molecules for Drug Discovery. Biochemistry 2020, 59, 1645–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stokes, J.M.; Yang, K.; Swanson, K.; Jin, W.; Cubillos-Ruiz, A.; Donghia, N.M.; Macnair, C.R.; French, S.; Carfrae, L.A.; Bloom-Ackermann, Z.; et al. A Deep Learning Approach to Antibiotic Discovery. Cell 2020, 180, 688–702.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masoudi-Sobhanzadeh, Y.; Omidi, Y.; Amanlou, M.; Masoudi-Nejad, A. Drug databases and their contributions to drug repurposing. Genomics 2020, 112, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, Y.; Erez, T.; Reynolds, I.J.; Kumar, D.; Ross, J.; Koytiger, G.; Kusko, R.; Zeskind, B.; Risso, S.; Kagan, E.; et al. Drug repurposing from the perspective of pharmaceutical companies. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farha, M.A.; Brown, E.D. Unconventional screening approaches for antibiotic discovery. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1354, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aburayan, W.S.; Booq, R.Y.; Binsaleh, N.S.; Alfassam, H.A.; Bakr, A.A.; Bukhary, H.A.; Alyamani, E.J.; Tawfik, E.A. The Delivery of the Novel Drug ‘Halicin’ Using Electrospun Fibers for the Treatment of Pressure Ulcer against Pathogenic Bacteria. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, D.A.; Barros, M.E.S.; Hamdan, J.S. Establishing a Method of Inoculum Preparation for Susceptibility Testing of Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kassim, A.; Omuse, G.; Premji, Z.; Revathi, G. Comparison of Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute and European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing guidelines for the interpretation of antibiotic susceptibility at a University teaching hospital in Nairobi, Kenya: A cross-sectional study. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2016, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonev, B.; Hooper, J.; Parisot, J. Principles of assessing bacterial susceptibility to antibiotics using the agar diffusion method. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 61, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ringertz, S.; Kronvall, G. On the theory of the disk diffusion test. Evidence for a Non-Linear Relationship between Critical Concentration and MIC, and Its Practical Implications for Susceptibility Testing of Haemophilus Influenzae. APMIS 1988, 96, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
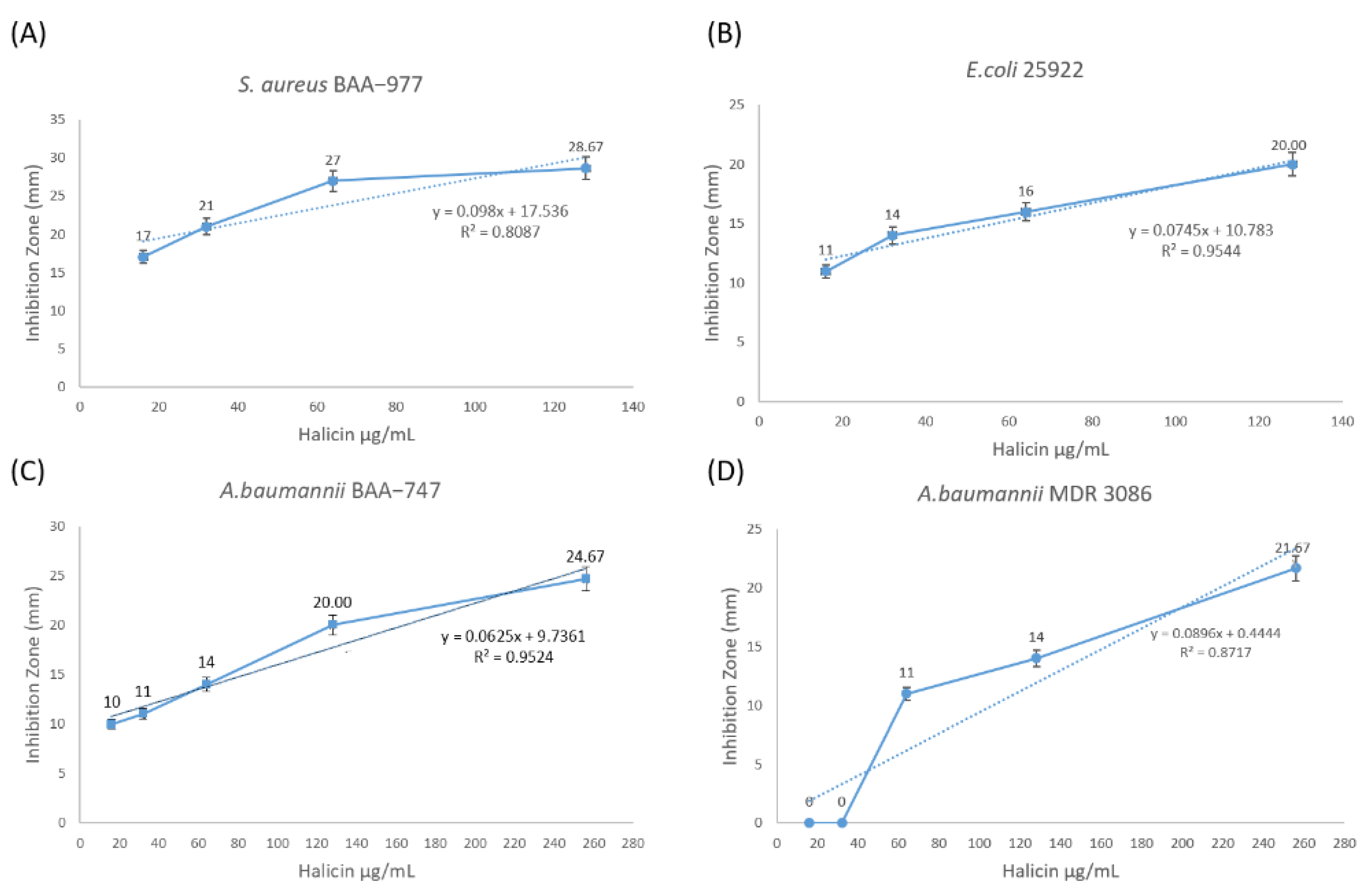
| Bacterial Strain | Halicin Concentration (μg/mL) | Zone of Inhibition (mm) Mean ± SD (n = 3) | Correlation Coefficient (R) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus ATCC BAA-977 | 16 | 17 ± 1 | 0.90 |
| 32 | 21 ± 0 | ||
| 64 | 27 ± 1 | ||
| 128 | 29 ± 1 | ||
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | 16 | 11 ± 1 | 0.98 |
| 32 | 14 ± 1 | ||
| 64 | 16 ± 1 | ||
| 128 | 20 ± 0 | ||
| A. baumannii ATCC BAA-747 | 16 | 10 ± 1 | 0.98 |
| 32 | 11 ± 1 | ||
| 64 | 14 ± 0 | ||
| 128 | 20 ± 0 | ||
| 256 | 25 ± 1 | ||
| A. baumannii MDR 3086 | 16 | 0 | 0.93 |
| 32 | 0 | ||
| 4 | 11 ± 1 | ||
| 128 | 14 ± 1 | ||
| 256 | 22 ± 1 |
| Bacterial Strain | MIC (μg/mL) | Sensitive (mm) | Resistant (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus ATCC BAA-977 | 16 | ≥17 | ≤15 |
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | 32 | ≥14 | ≤11 |
| A. baumannii ATCC BAA-747 | 128 | ≥20 | ≤14 |
| A. baumannii MDR 3086 | 256 | ≥22 | ≤14 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Booq, R.Y.; Tawfik, E.A.; Alfassam, H.A.; Alfahad, A.J.; Alyamani, E.J. Assessment of the Antibacterial Efficacy of Halicin against Pathogenic Bacteria. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10121480
Booq RY, Tawfik EA, Alfassam HA, Alfahad AJ, Alyamani EJ. Assessment of the Antibacterial Efficacy of Halicin against Pathogenic Bacteria. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(12):1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10121480
Chicago/Turabian StyleBooq, Rayan Y., Essam A. Tawfik, Haya A. Alfassam, Ahmed J. Alfahad, and Essam J. Alyamani. 2021. "Assessment of the Antibacterial Efficacy of Halicin against Pathogenic Bacteria" Antibiotics 10, no. 12: 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10121480
APA StyleBooq, R. Y., Tawfik, E. A., Alfassam, H. A., Alfahad, A. J., & Alyamani, E. J. (2021). Assessment of the Antibacterial Efficacy of Halicin against Pathogenic Bacteria. Antibiotics, 10(12), 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10121480






