Synergy between Indoloquinolines and Ciprofloxacin: An Antibiofilm Strategy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
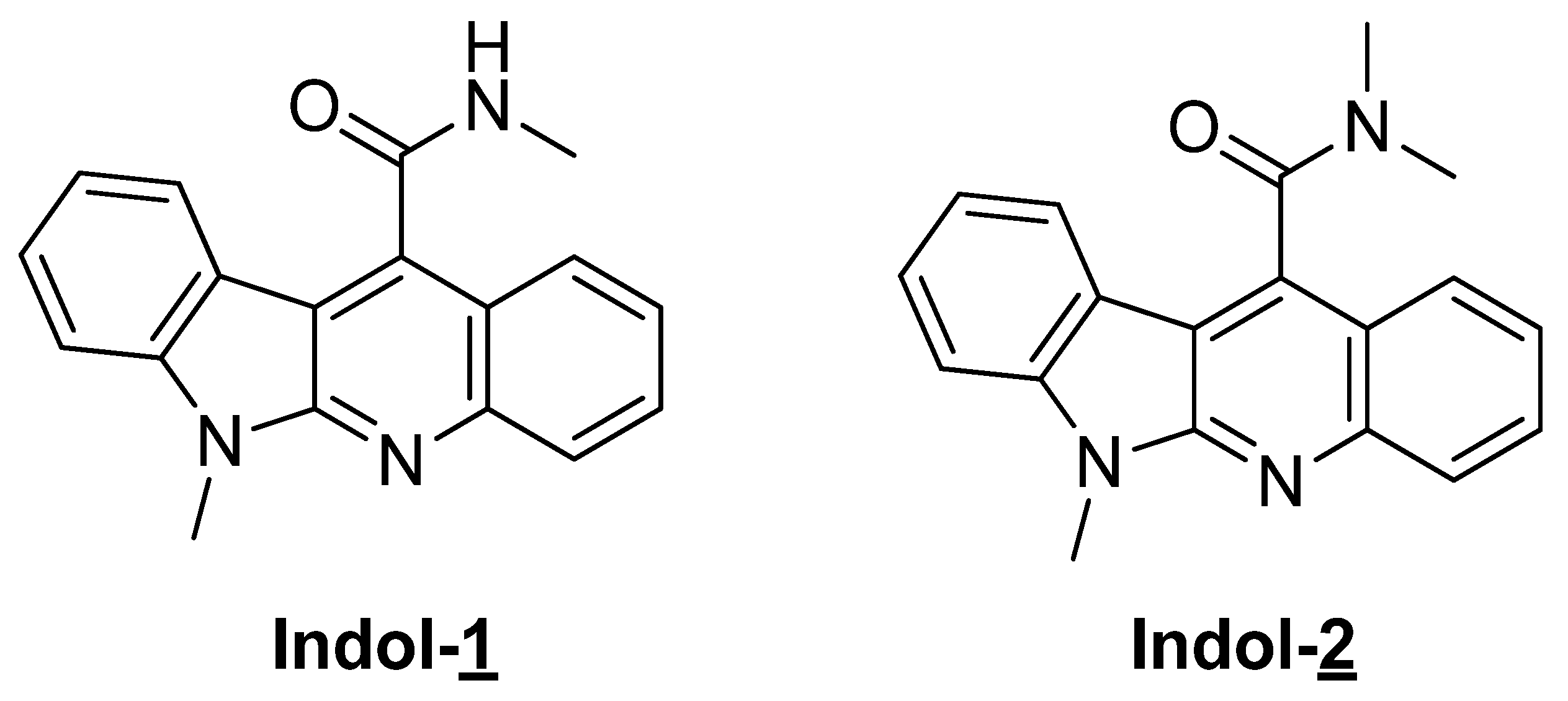
2.1. Preparation of Indoloquinoline Derivatives
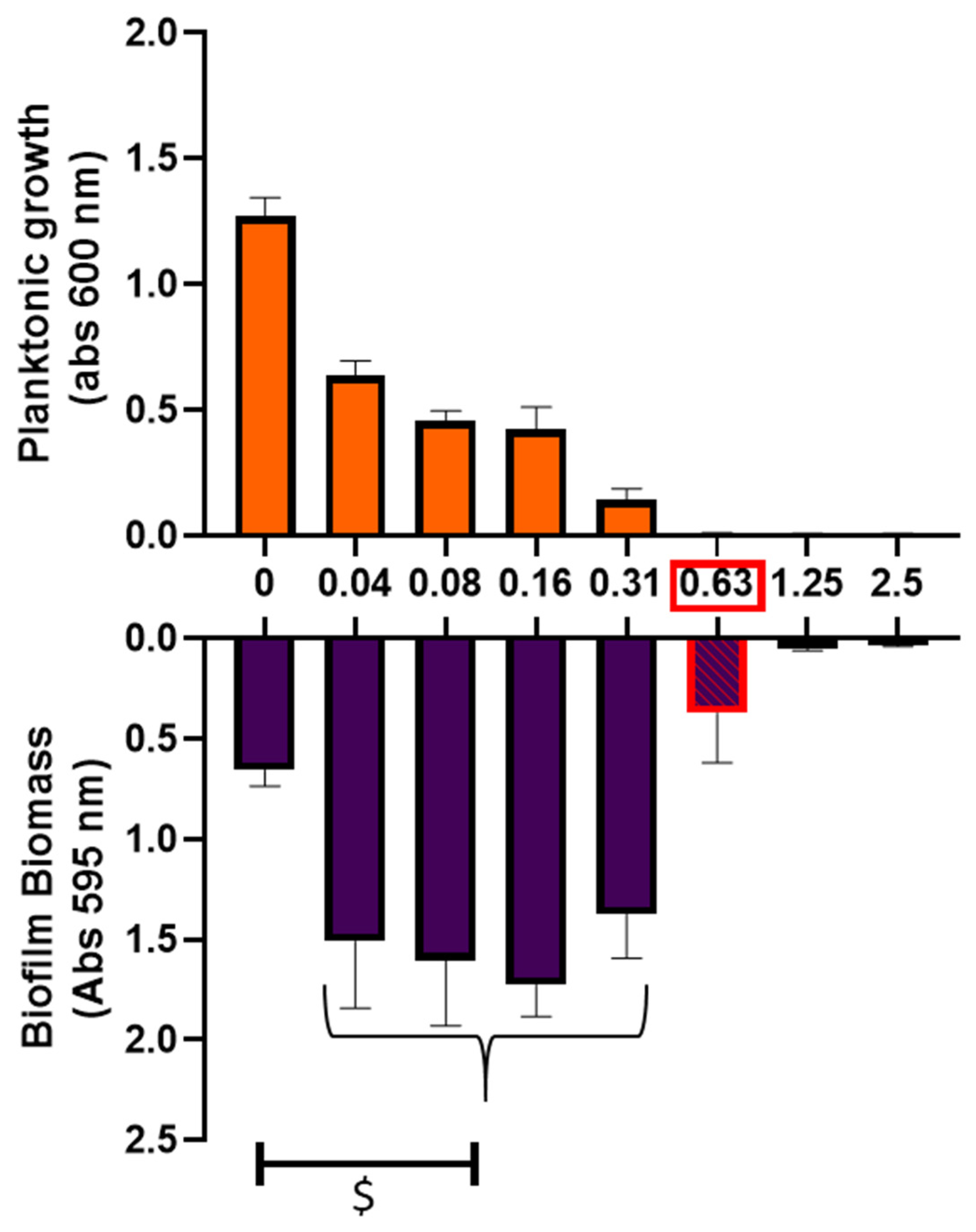
2.2. Impact of Ciprofloxacin on Biofilm Formation
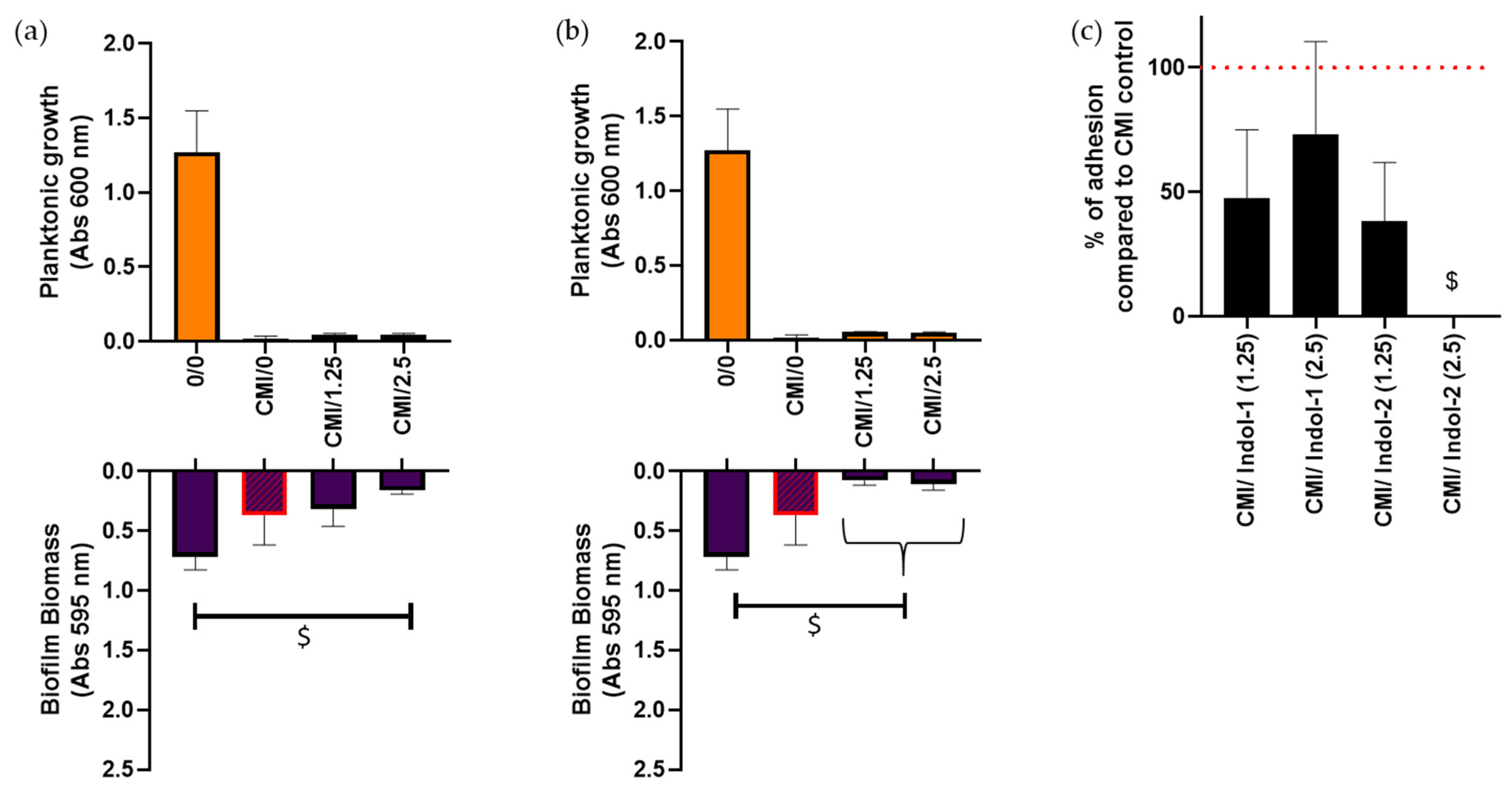
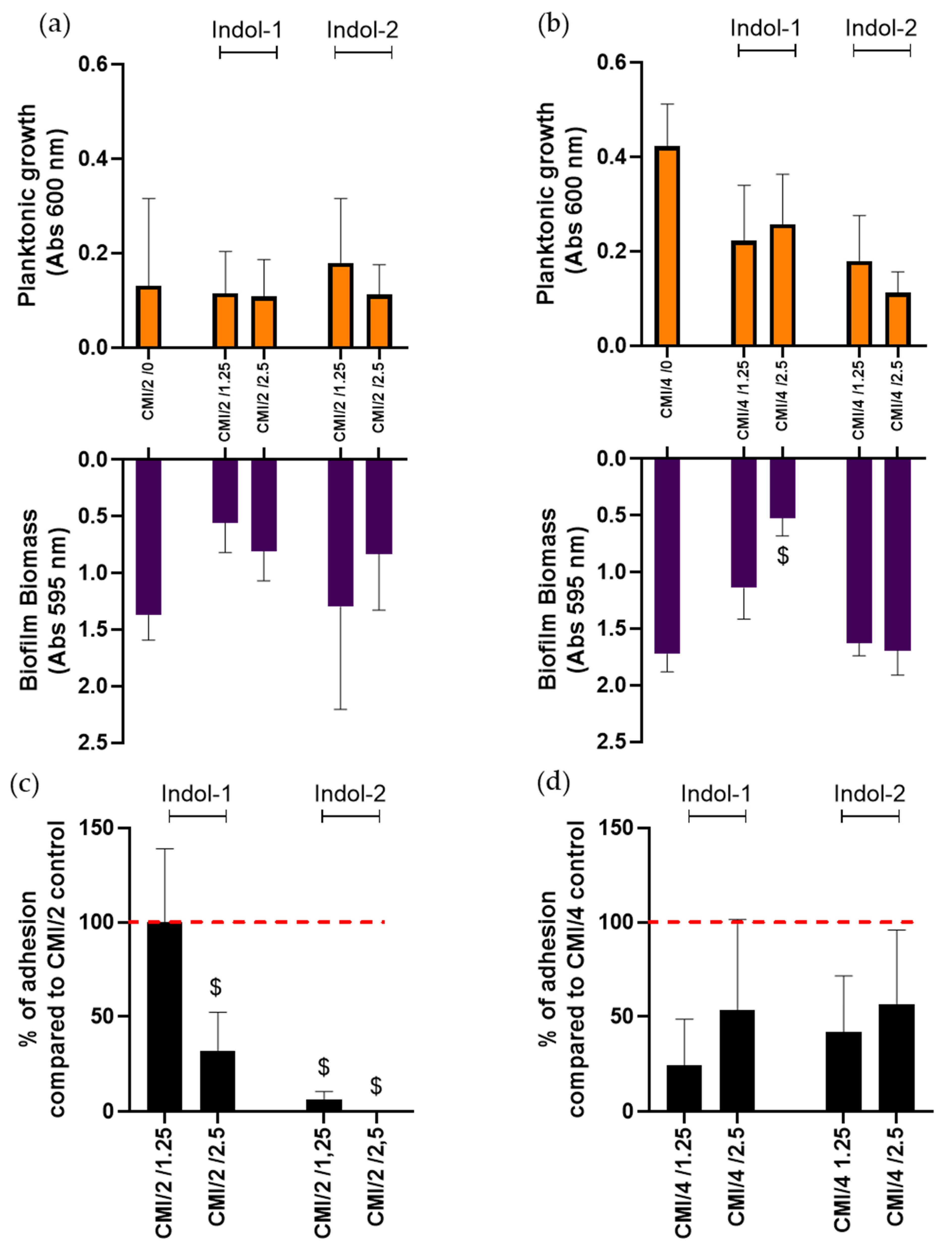
2.3. Combination of Ciprofloxacin and Indoloquinolines to Decrease Biofilm Biomass
2.4. Combination of Ciprofloxacin and Indoloquinoline to Decrease Adherent Bacteria Quantity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Indoloquinoline Derivatives
4.2. Bacterial Strains and Culture Media
4.3. Biofilm Formation
4.4. Crystal Violet Staining (Biofilm Evaluation)
4.5. Counting of Adhered Bacteria
4.6. Statistical Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stoodley, P.; Sauer, K.; Davies, D.G.; Costerton, J.W. Biofilms as Complex Differentiated Communities. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2002, 56, 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamret, F.; Colin, M.; Mongaret, C.; Gangloff, S.C.; Reffuveille, F. Antibiotic Tolerance of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm in Periprosthetic Joint Infections and Antibiofilm Strategies. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente-Núñez, C.; Reffuveille, F.; Fernández, L.; Hancock, R.E.W. Bacterial biofilm development as a multicellular adaptation: Antibiotic resistance and new therapeutic strategies. Curr. Opin Microbiol. 2013, 16, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, P. Antimicrobial Tolerance in Biofilms. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lima-e-Silva, A.A.; Silva-Filho, R.G.; Fernandes, H.M.Z.; Saramago, C.S.M.; Viana, A.S.; Souza, M.J. Sub-Inhibitory Concentrations of Rifampicin Strongly Stimulated Biofilm Production in [Abstract]. Open Microbiol. J. 2017, 11. Available online: https://openmicrobiologyjournal.com/VOLUME/11/PAGE/142/ABSTRACT/ (accessed on 20 March 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savage, V.J.; Chopra, I.; O’Neill, A.J. Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms Promote Horizontal Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1968–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.-F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Pan, B.; Liu, M.-L. Ciprofloxacin derivatives and their antibacterial activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 146, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CASFM/EUCAST AVRIL 2021 V1.0 [Internet]. Société Française de Microbiologie. 2021. Available online: https://www.sfm-microbiologie.org/2021/04/23/casfm-avril-2021-v1-0/ (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- Rehman, A.; Patrick, W.; Lamont, I.L. Mechanisms of ciprofloxacin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: New approaches to an old problem. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrado, J.; Moreira, R.; Paulo, A. Indoloquinolines as scaffolds for drug discovery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 2348–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Du, R.-L.; Zheng, Y.-Y.; Huang, B.-H.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, R.-F.; Wong, K.-Y.; Lu, Y.-J. Antibacterial activity of N -methylbenzofuro[3,2- b ]quinoline and N -methylbenzoindolo[3,2- b ]-quinoline derivatives and study of their mode of action. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 135, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Kamada, T.; Takeuchi, A.; Nishioka, H.; Kuroda, T.; Takeuchi, Y. Structure-activity relationship of indoloquinoline analogs anti-MRSA. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 5551–5554. Available online: https://okayama.pure.elsevier.com/en/publications/structure-activity-relationship-of-indoloquinoline-analogs-anti-m (accessed on 7 July 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Wisal, A.; Tahir, M.N.; Abdullah; Ali, A.; Hameed, S.; Ahmed, M.N. One-pot synthesis, crystal structure and antimicrobial activity of 6-benzyl-11-(p-tolyl)-6H-indolo[2,3-b]quinoline. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1210, 128035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, R.E.W.; Alford, M.A.; Haney, E.F. Antibiofilm activity of host defence peptides: Complexity provides opportunities. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Naseri, M.; He, Y.; Xu, C.; Walsh, L.J.; Ziora, Z.M. Non-antibiotic antimicrobial agents to combat biofilm-forming bacteria. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 21, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuama, O.C.; Ortiz, S.; Quirós-Guerrero, L.; Bouffartigues, E.; Tortuel, D.; Maillot, O.; Feuilloley, M.; Cornelis, P.; Lesouhaitier, O.; Grougnet, R.; et al. Tackling Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence by Mulinane-Like Diterpenoids from Azorella atacamensis. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahrioui, A.; Ortiz, S.; Azuama, O.C.; Bouffartigues, E.; Benalia, N.; Tortuel, D.; Maillot, O.; Chemat, S.; Kritsanida, M.; Feuilloley, M.; et al. Membrane-Interactive Compounds From Pistacia lentiscus L. Thwart Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudlo, M.; Allart-Simon, I.; Tinant, B.; Gérard, S.; Sapi, J. First domino radical cyclisation/Smiles rearrangement combination. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 2442–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khartabil, H.; Doudet, L.; Allart-Simon, I.; Ponce-Vargas, M.; Gérard, S.; Hénon, E. Mechanistic insights into Smiles rearrangement. Focus on π–π stacking interactions along the radical cascade. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 6840–6848. Available online: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2020/ob/d0ob01511c (accessed on 7 July 2021). [CrossRef]
- Prakash, T.P.; Perunninakulath, S.P.; Santosh, G.T. Isolation, Biological Activities and Synthesis of Indoloquinoline Alkaloids: Cryptolepine, Isocryptolepine and Neocryptolepine. Curr. Org. Chem. 2011, 15, 1036–1057. Available online: https://www.eurekaselect.com/73414/article (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- Holden, C.; Greaney, M.F. Modern Aspects of the Smiles Rearrangement. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 8992–9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allart-Simon, I.; Gérard, S.; Sapi, J. Radical Smiles Rearrangement: An Update. Molecules 2016, 21, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, A.R.P.; Kosowan, J.R.; Wood, T.E. The Truce–Smiles rearrangement and related reactions: A review. Available online: https://winnspace.uwinnipeg.ca/handle/10680/1777 (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- de la Fuente-Núñez, C.; Reffuveille, F.; Haney, E.F.; Straus, S.K.; Hancock, R.E.W. Broad-spectrum anti-biofilm peptide that targets a cellular stress response. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, D.; Joshi-Datar, A.; Lepine, F.; Bauerle, E.; Olakanmi, O.; Beer, K.; McKay, G.; Siehnel, R.; Schafhauser, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Active Starvation Responses Mediate Antibiotic Tolerance in Biofilms and Nutrient-Limited Bacteria. Science 2011, 334, 982–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reffuveille, F.; Josse, J.; Velard, F.; Lamret, F.; Varin-Simon, J.; Dubus, M.; Haney, E.F.; Hancock, R.; Mongaret, C.; Gangloff, S.C. Bone Environment Influences Irreversible Adhesion of a Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus Strain. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, K.B.; Ferreira, A.M.; Pereira, V.C.; Pinheiro, L.; Oliveira, A.D.; Cunha, M.D.L.R.D.S.D.; In Vitro Effects of Antimicrobial Agents on Planktonic and Biofilm Forms of Staphylococcus saprophyticus Isolated from Patients with Urinary Tract Infections. Front. Microbiol. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00040/full (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- Macia, M.; Rojo-Molinero, E.; Oliver, A. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing in biofilm-growing bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lutz, L.; Pereira, D.C.; Paiva, R.M.; Zavascki, A.P.; Barth, A.L. Macrolides decrease the minimal inhibitory concentration of anti-pseudomonal agents against Pseudomonas aeruginosa from cystic fibrosis patients in biofilm. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lebeaux, D.; Ghigo, J.-M.; Beloin, C. Biofilm-Related Infections: Bridging the Gap between Clinical Management and Fundamental Aspects of Recalcitrance toward Antibiotics. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 510–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Høiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S.; Ciofu, O. Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aka, S.T.; Haji, S.H. Sub-MIC of antibiotics induced biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the presence of chlorhexidine. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemati, S.; Kouhsari, E.; Sadeghifard, N.; Maleki, A.; Omidi, N.; Mahdavi, Z.; Pakzad, I. Sub-minimum inhibitory concentrations of biocides induced biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. New Microbes New Infect. 2020, 38, 100794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, G.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Bi, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhi, X.; Zhou, T.; Cao, J. Effects of sub-minimum inhibitory concentrations of ciprofloxacin on biofilm formation and virulence factors of Escherichia coli. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 23, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haney, E.F.; Trimble, M.J.; Cheng, J.T.; Vallé, Q.; Hancock, R.E.W. Critical Assessment of Methods to Quantify Biofilm Growth and Evaluate Antibiofilm Activity of Host Defence Peptides. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Charpentier, E.; Doudet, L.; Allart-Simon, I.; Colin, M.; Gangloff, S.C.; Gérard, S.; Reffuveille, F. Synergy between Indoloquinolines and Ciprofloxacin: An Antibiofilm Strategy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10101205
Charpentier E, Doudet L, Allart-Simon I, Colin M, Gangloff SC, Gérard S, Reffuveille F. Synergy between Indoloquinolines and Ciprofloxacin: An Antibiofilm Strategy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(10):1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10101205
Chicago/Turabian StyleCharpentier, Emilie, Ludovic Doudet, Ingrid Allart-Simon, Marius Colin, Sophie C. Gangloff, Stéphane Gérard, and Fany Reffuveille. 2021. "Synergy between Indoloquinolines and Ciprofloxacin: An Antibiofilm Strategy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa" Antibiotics 10, no. 10: 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10101205
APA StyleCharpentier, E., Doudet, L., Allart-Simon, I., Colin, M., Gangloff, S. C., Gérard, S., & Reffuveille, F. (2021). Synergy between Indoloquinolines and Ciprofloxacin: An Antibiofilm Strategy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics, 10(10), 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10101205





