Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes and the Electrocatalytic Activity of Gluconobacter oxydans as the Basis of a Biosensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
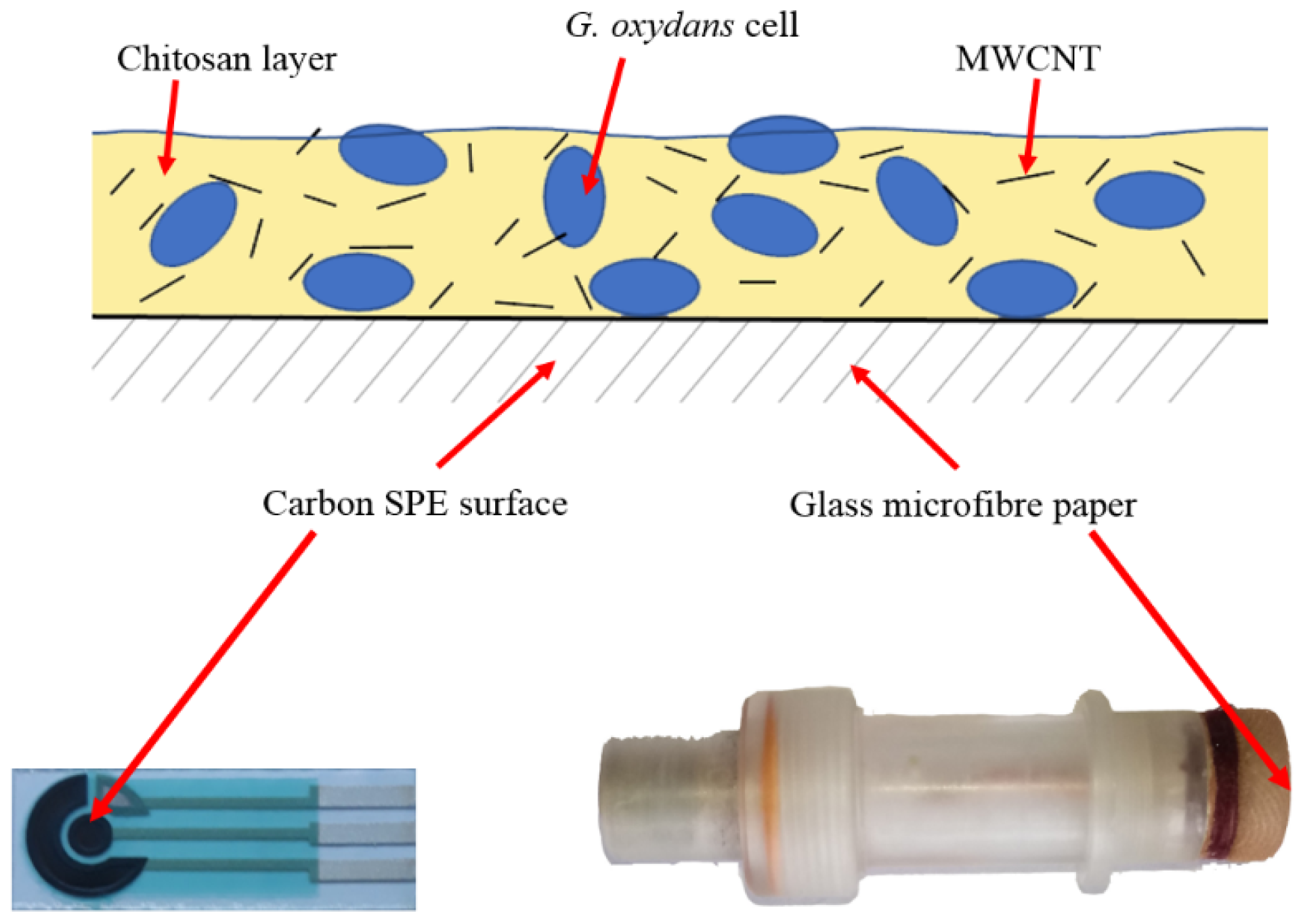
2.2. Formation of Biocomposites
2.3. Formation of Biosensors
3. Results and Discussion
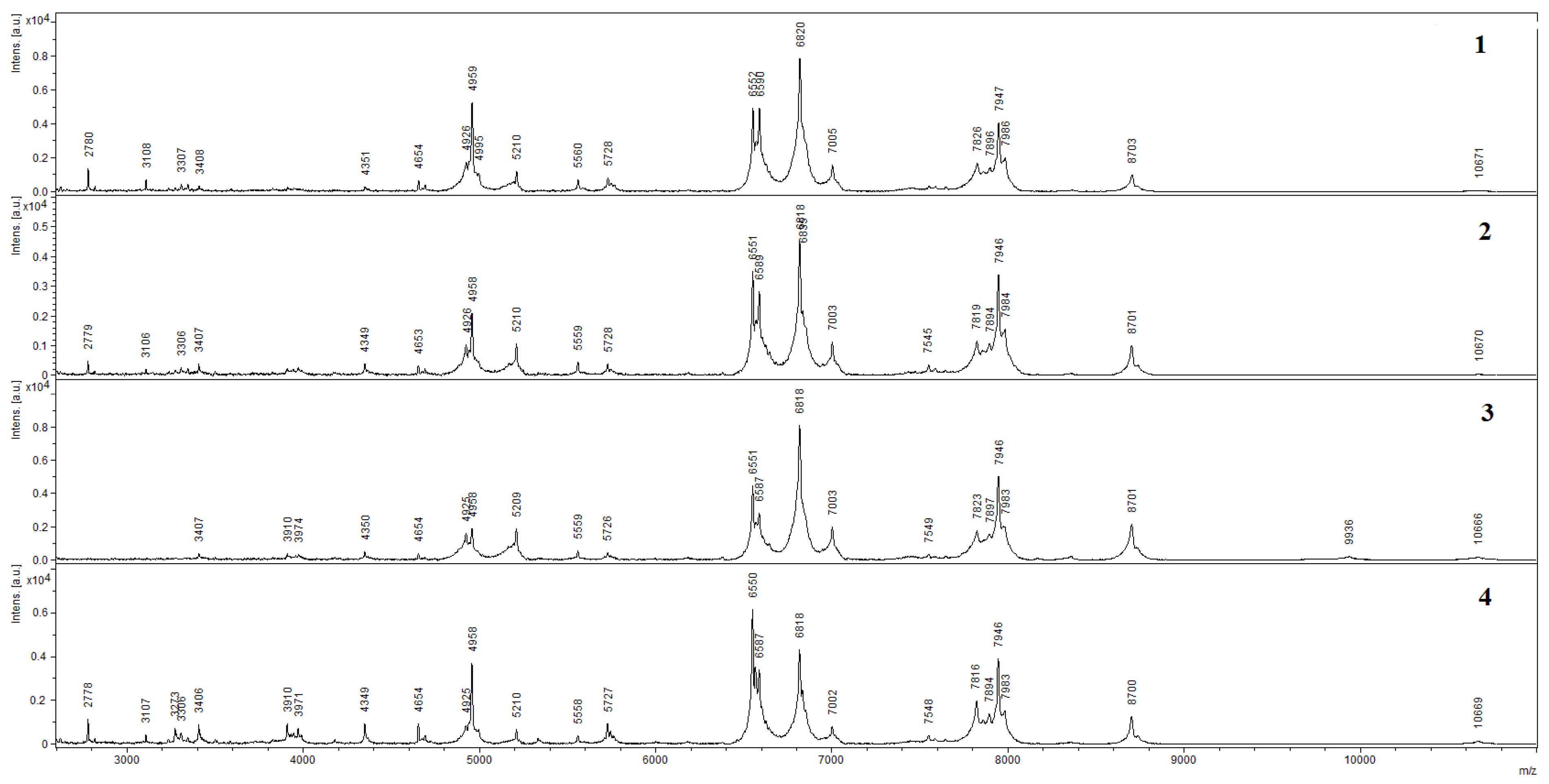
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization–Time of Flight Mass Spectroscopy (MALDI–TOF MS)
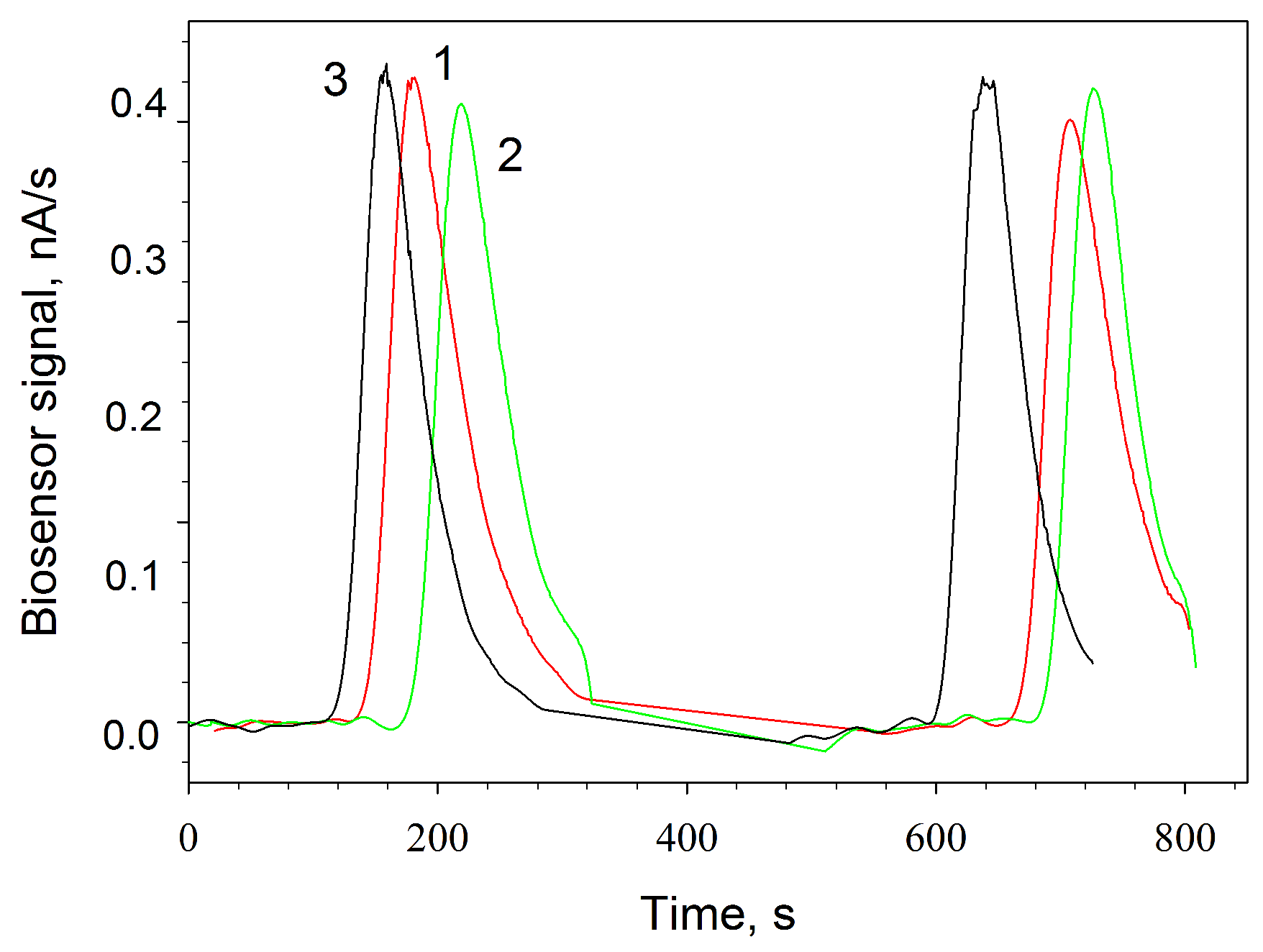
3.2. Respiratory Activity of G. oxydans
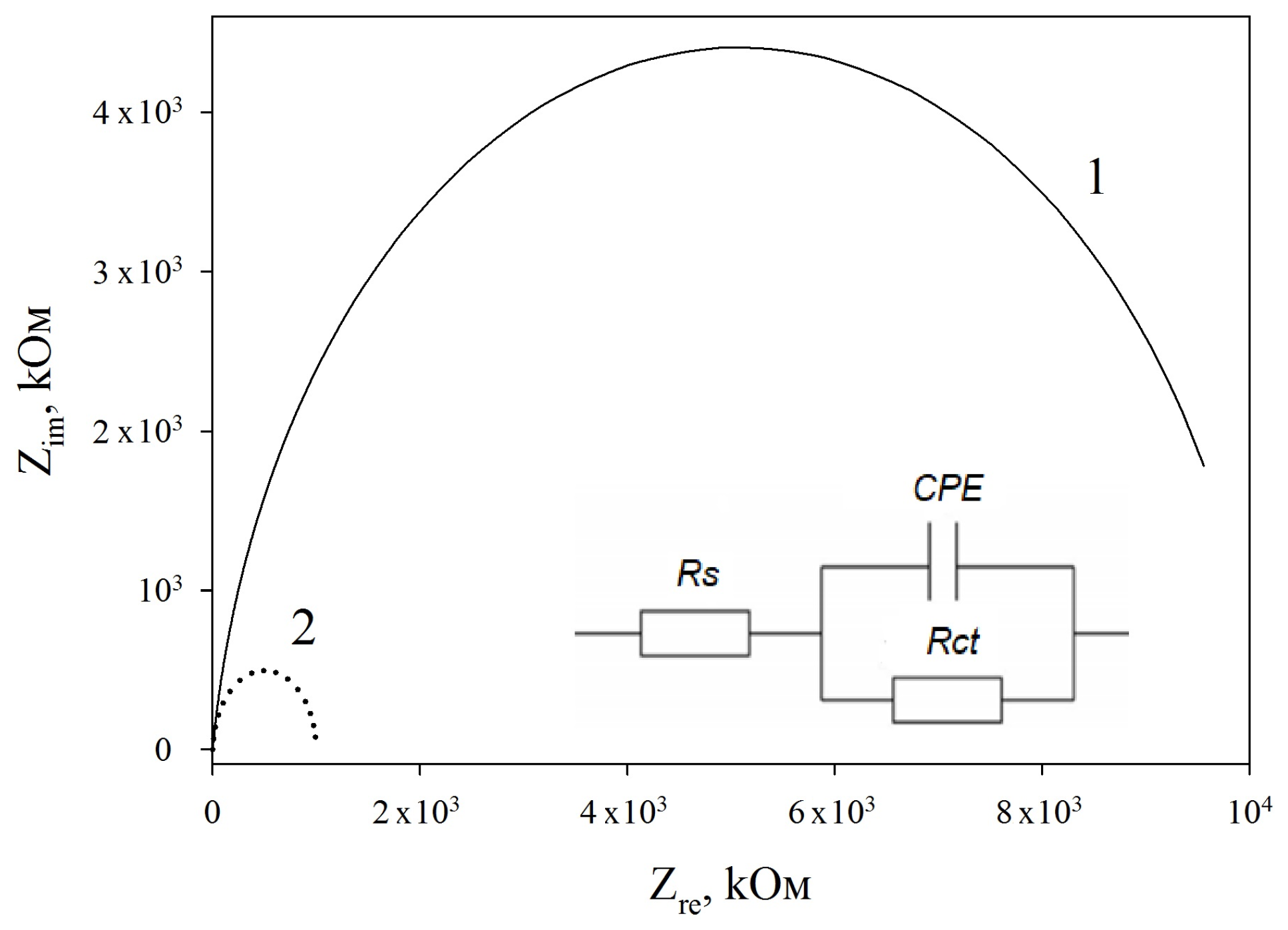
3.3. Impedance Spectra
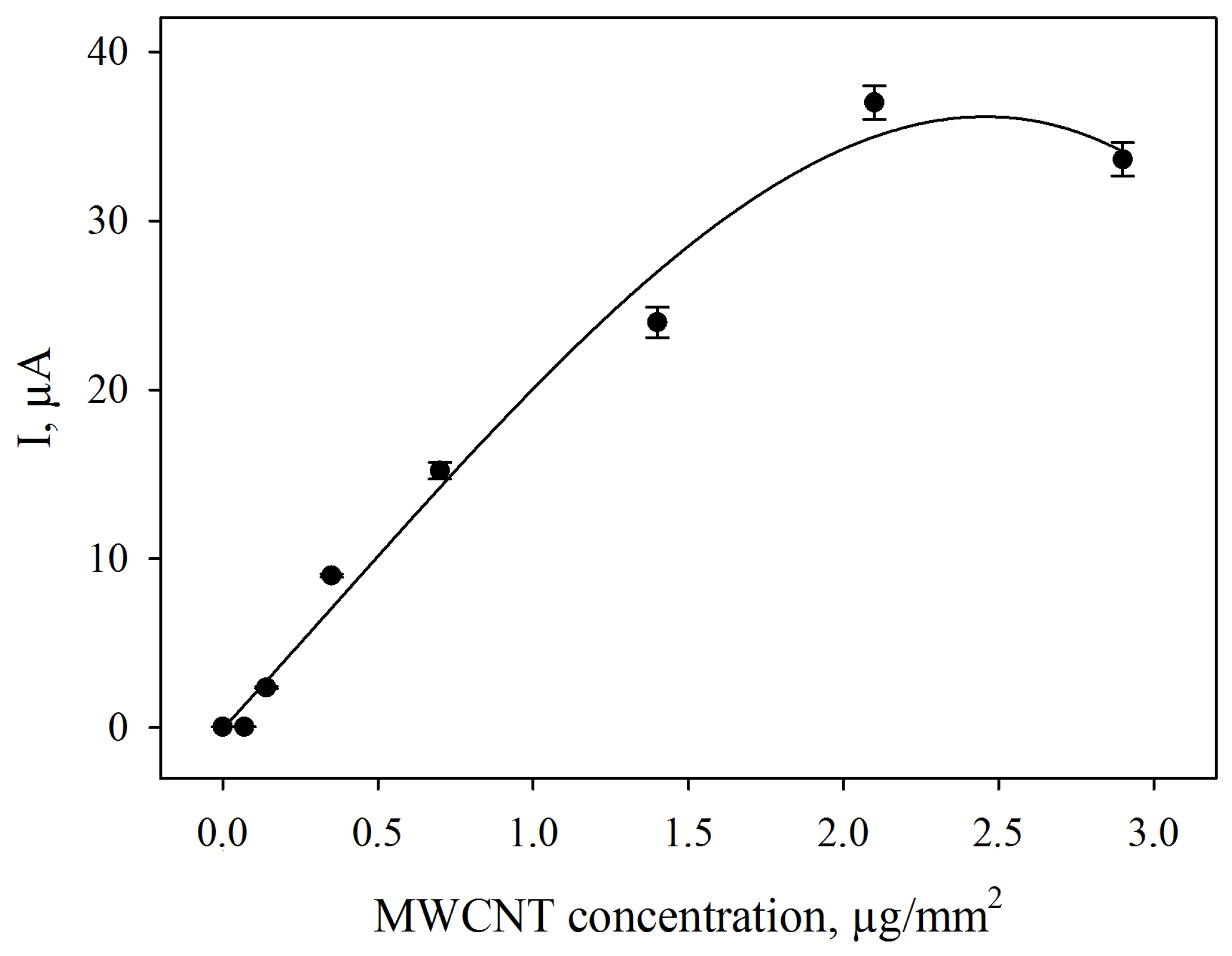
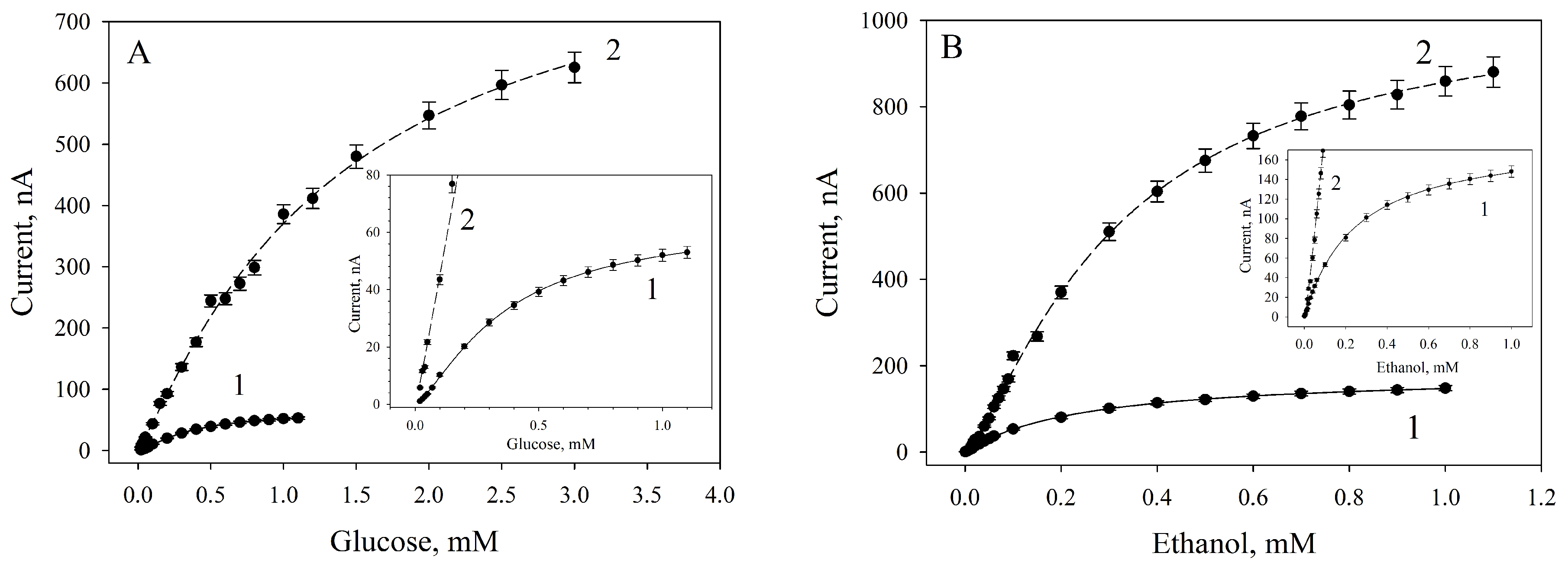
3.4. Amperometric Biosensors Based on G. oxydans/Chitosan and G. oxydans/MWCNTs/Chitosan Biocomposites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.; Pumera, M. Electrochemical catalysis at low dimensional carbons: Graphene, carbon nanotubes and beyond—A review. Appl. Mater. Today 2016, 5, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Murthy, C.N.; Prabha, C.R. Recent advances in carbon nanotube based electrochemical biosensors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girardello, R.; Baranzini, N.; Tettamanti, G.; De Eguileor, M.; Grimaldi, A. Cellular responses induced by multi-walled carbon nanotubes: In vivo and in vitro studies on the medicinal leech macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, G.; Yang, C.; Xu, P.; Yan, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W. Toxicity of carbon nanomaterials to plants, animals and microbes: Recent progress from 2015–present. Chemosphere 2018, 206, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Zhang, W.; Sun, J.; Chen, L.; Li, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, S.; Shen, S. Different modified multi-walled carbon nanotube-based anodes to improve the performance of microbial fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 22786–22795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, M.; Yan, M.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D. How do proteins ‘response’ to common carbon nanomaterials? Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 270, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, C. The nano-bio interaction and biomedical applications of carbon nanomaterials. Carbon N. Y. 2018, 138, 436–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharkova, A.S.; Arlyapov, V.A.; Turovskaya, A.D.; Avtukh, A.N.; Starodumova, I.P.; Reshetilov, A.N. Mediator BOD biosensor bBased on cells of microorganisms isolated from activated sludge. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2019, 55, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefcovicova, J.; Filip, J.; Gemeiner, P.; Tkac, J. Nanomaterial-based microbial biosensor for detection of ethanol in real samples. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 185, S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamanin, S.S.; Arlyapov, V.A.; Alferov, V.A.; Reshetilov, A.N. Enzyme-modified screen-printed electrodes for assaying glucose, ethanol, lactate and starch in fermentation media. Ferment. Technol. 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H. Current status of water environment and their microbial biosensor techniques—Part II: Recent trends in microbial biosensor development. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 3967–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Li, Y.; Gao, G.; Xia, S. A mediated BOD biosensor based on immobilized B. subtilis on three-dimensional porous graphene–polypyrrole composite. Sensors 2017, 17, 2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šefčovičová, J.; Tkac, J. Application of nanomaterials in microbial-cell biosensor constructions. Chem. Pap. 2015, 69, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plekhanova, Y.V.; Reshetilov, A.N.; Manolov, T.V.; Taranova, L.A. Biosensor monitoring of microbial treatment of wastewater from nonylphenol polyethoxylates under flow-through conditions. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2011, 47, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, P.; Ramprasath, T.; Selvam, G.S. A simple whole cell microbial biosensor to monitor soil pollution. N. Pestic. Soil Sens. 2017, 437–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonchar, M.; Smutok, O.; Karkovska, M.; Stasyuk, N.; Gayda, G. Yeast-based biosensors for clinical diagnostics and food control. In Biotechnology of Yeasts and Filamentous Fungi; Sibirny, A.A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 391–412. ISBN 9783319588292. [Google Scholar]
- Schenkmayerová, A.; Bertóková, A.; Šefčovičová, J.; Štefuca, V.; Bučko, M.; Vikartovská, A.; Gemeiner, P.; Tkáč, J.; Katrlík, J. Whole-cell Gluconobacter oxydans biosensor for 2-phenylethanol biooxidation monitoring. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 854, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, R.; Krishnaraj, N.; Selvam, A.; Wong, J.W.C.; Lee, P.K.H.; Leung, M.K.H.; Berchmans, S. Effect of composites based nickel foam anode in microbial fuel cell using Acetobacter aceti and Gluconobacter roseus as a biocatalysts. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 217, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkac, J.; Svitel, J.; Vostiar, I.; Navratil, M.; Gemeiner, P. Membrane-bound dehydrogenases from Gluconobacter sp.: Interfacial electrochemistry and direct bioelectrocatalysis. Bioelectrochemistry 2009, 76, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odaci, D.; Timur, S.; Telefoncu, A. A microbial biosensor based on bacterial cells immobilized on chitosan matrix. Bioelectrochemistry 2009, 75, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetilov, A.N.; Plekhanova, Y.V.; Tarasov, S.E.; Arlyapov, V.A.; Kolesov, V.V.; Gutorov, M.A.; Gotovtsev, P.M.; Vasilov, R.G. Effect of some carbon nanomaterials on ethanol oxidation by Gluconobacter oxydans bacterial cells. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2017, 53, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gu, H.; Yin, F.; Tu, Y. A glucose biosensor based on Prussian blue/chitosan hybrid film. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 1527–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plekhanova, Y.; Tarasov, S.; Bykov, A.; Reshetilov, A. Electrochemical assessment of the interaction of microbial living cells and carbon nanomaterials. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 13, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.C.; Siddiqui, N.A.; Marom, G.; Kim, J.K. Dispersion and functionalization of carbon nanotubes for polymer-based nanocomposites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 1345–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilmaciu, C.M.; Morris, M.C. Carbon nanotube biosensors. Front. Chem. 2015, 3, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marroquin, J.B.; Rhee, K.Y.; Park, S.J. Chitosan nanocomposite films: Enhanced electrical conductivity, thermal stability, and mechanical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1783–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, D.L.; Cox, M.M. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, 6th ed.; W.H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 1336. ISBN 978-1429234146. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.A.; Tsai, Y.C. Preparation of multiwalled carbon nanotube-chitosan-alcohol dehydrogenase nanobiocomposite for amperometric detection of ethanol. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 138, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Substrate | Glucose | Ethanol | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modification | G. oxydans/Chitosan | G. oxydans/MWCNTs/Chitosan | G. oxydans/Chitosan | G. oxydans/MWCNTs/Chitosan | |
| Parameter | |||||
| Vmax, nA | 64.55 ± 1.99 | 869.26 ± 76.02 | 181.36 ± 2.65 | 1048.31 ± 41.88 | |
| Km, мM | 0.36 ± 0.02 | 1.27 ± 0.22 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 0.32 ± 0.03 | |
| h | 1.36 ± 0.06 | 1.14 ± 0.09 | 1.02 ±0.02 | 1.30 ± 0.07 | |
| Linear range of detection, mM | 0.10–0.60 | 0.17–1.82 | 0.07–0.34 | 0.06–0.50 | |
| Regression equation for the linear segment | y = 65.80x + 6.89 | y = 259.06x + 92.18 | y = 240.94x + 30.57 | y = 1257.50x + 99.49 | |
| Correlation coefficient, R2 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | |
| Sensitivity coefficient, μA/mM | 65.80 | 259.06 | 240.94 | 1257.5 | |
| Minimal detection limit, mM | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.003 | 0.015 | |
| Detection range, mM | 0.04–1.00 | 0.04–2.50 | 0.003–0.700 | 0.015–1.000 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plekhanova, Y.; Tarasov, S.; Bykov, A.; Prisyazhnaya, N.; Kolesov, V.; Sigaev, V.; Signore, M.A.; Reshetilov, A. Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes and the Electrocatalytic Activity of Gluconobacter oxydans as the Basis of a Biosensor. Biosensors 2019, 9, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9040137
Plekhanova Y, Tarasov S, Bykov A, Prisyazhnaya N, Kolesov V, Sigaev V, Signore MA, Reshetilov A. Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes and the Electrocatalytic Activity of Gluconobacter oxydans as the Basis of a Biosensor. Biosensors. 2019; 9(4):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9040137
Chicago/Turabian StylePlekhanova, Yulia, Sergei Tarasov, Aleksandr Bykov, Natalia Prisyazhnaya, Vladimir Kolesov, Vladimir Sigaev, Maria Assunta Signore, and Anatoly Reshetilov. 2019. "Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes and the Electrocatalytic Activity of Gluconobacter oxydans as the Basis of a Biosensor" Biosensors 9, no. 4: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9040137
APA StylePlekhanova, Y., Tarasov, S., Bykov, A., Prisyazhnaya, N., Kolesov, V., Sigaev, V., Signore, M. A., & Reshetilov, A. (2019). Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes and the Electrocatalytic Activity of Gluconobacter oxydans as the Basis of a Biosensor. Biosensors, 9(4), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9040137






