Diazonium-Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes for Immunosensing Growth Hormone in Blood Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
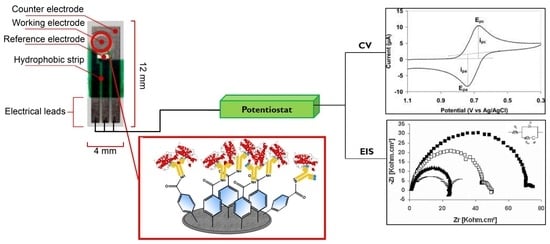
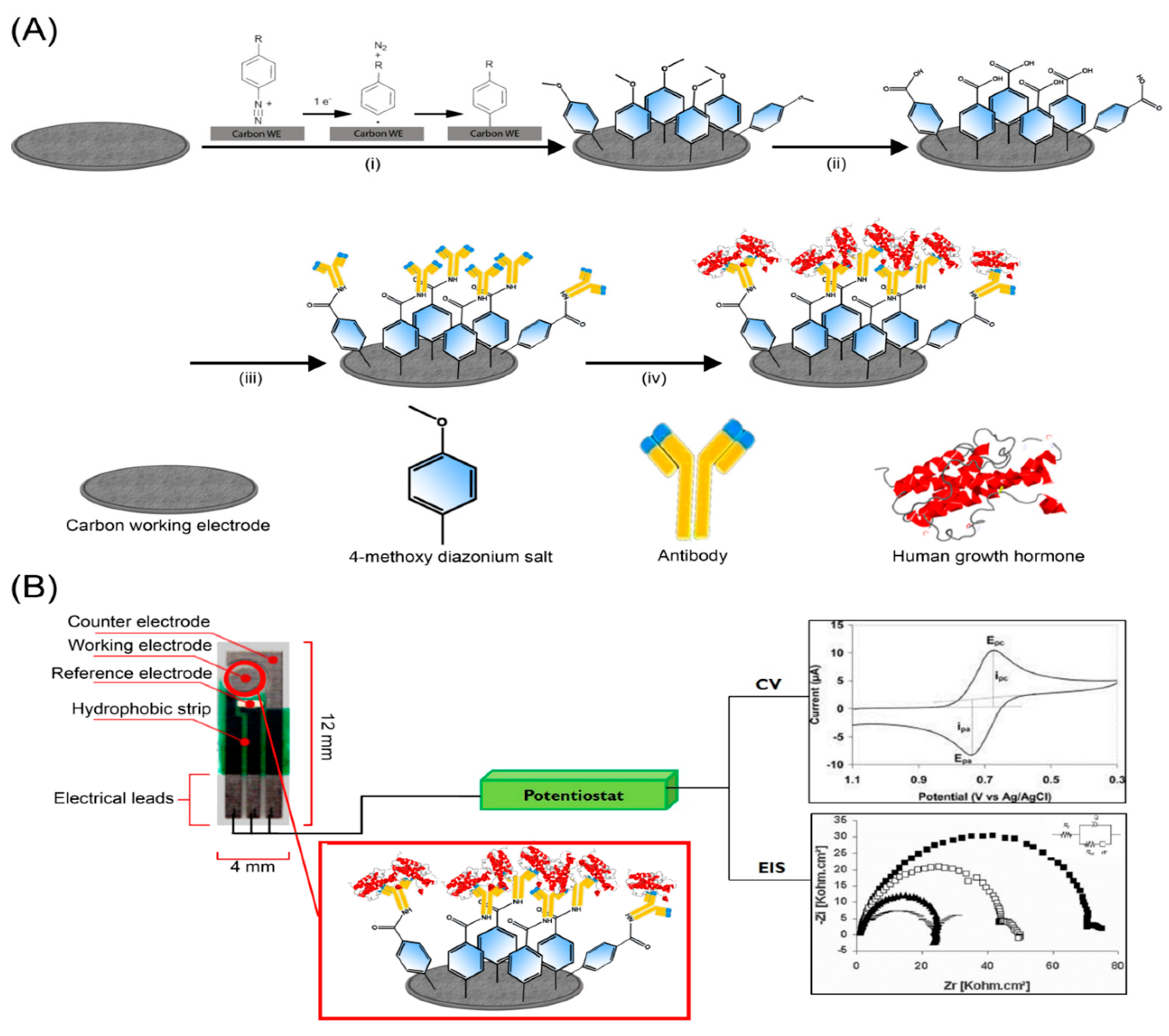
2.2. Electrode Preparation and Modification
2.3. Electrochemistry
2.4. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR)
2.5. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
2.6. Contact Angle Goniometry
2.7. ELISA-Based Detection
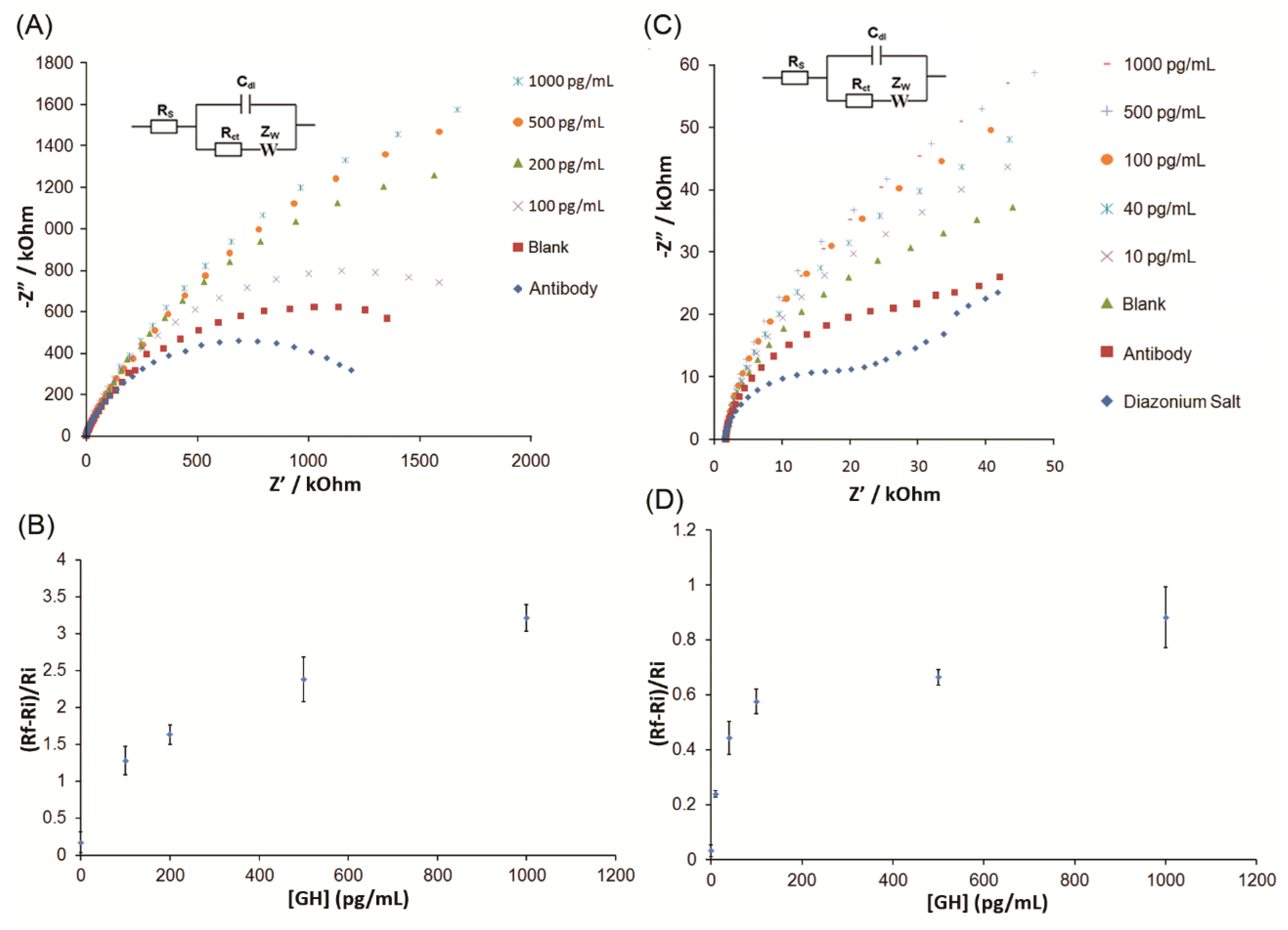
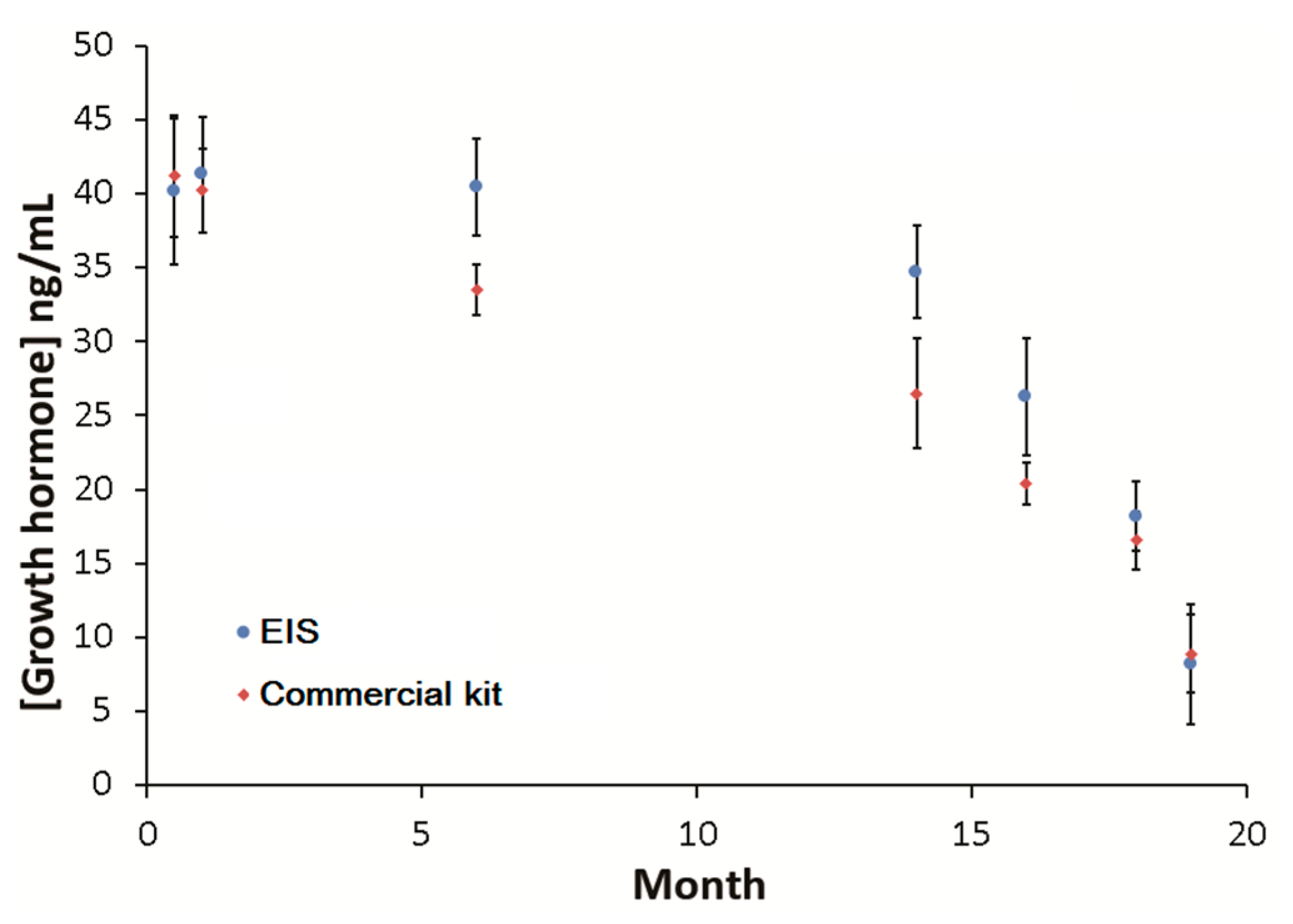
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gooding, J.J. Advances in interfacial design for electrochemical biosensors and sensors: Aryl diazonium salts for modifying carbon and metal electrodes. Electroanalysis 2007, 20, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooding, J.J.; Ciampi, S. The molecular level modification of surfaces: From self-assembled monolayers to complex molecular assemblies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2704–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Luais, E.; Gooding, J.J. The fabrication of stable gold nanoparticle-modified interfaces for electrochemistry. Langmuir 2011, 27, 4176–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Gooding, J.J. An interface comprising molecular wires and poly(ethylene glycol) spacer units self-assembled on carbon electrodes for studies of protein electrochemistry. Langmuir 2006, 22, 7421–7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, S.; Tlili, C.; L’Hocine, L.; Zourob, M. Electrochemical immunosensor for the milk allergen β-lactoglobulin based on electrografting of organic film on graphene modified screen-printed carbon electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 38, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, S.; Zourob, M. A Graphene-based electrochemical competitive immunosensor for the sensitive detection of okadaic acid in shellfish. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 7593–7599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, S.; L-Hocine, L.; Siaj, M.; Zourob, M. A graphene-based label-free voltammetric immunosensor for sensitive detection of the egg allergen ovalbumin. Analyst 2013, 138, 4378–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, Y.H.; Jang, H.S.; Kim, S.M.; Stach, E.; Ganesana, J.; Andreescu, S.; Stanciu, L.A. Biomagnetic glasses: Preparation, characterization, and biosensor applications. Langmuir 2010, 26, 4320–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolliopoulos, A.V.; Metters, J.P.; Banks, C.E. Electroanalytical sensing of selenium(IV) utilising screen printed graphite macro electrodes. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kang, A.; Wang, W.; Ho, S.V.; Gao, J.; Ma, G.; Su, Z. A novel sustained-release formulation of recombinant human growth hormone and its pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and safety profiles. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 2039–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.S.; Ahn, S.R.; Park, S.J.; Song, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.S.; Hong, J.Y.; Lee, J.S.; You, S.A.; Yoon, H.; et al. Ultrasensitive and selective recognition of peptide hormone using close-packed arrays of hPTHR-conjugated polymer nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5549–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bains, R.K.; Wells, S.E.; Flavell, D.M.; Fairhall, K.M.; Storm, M.; Le Tissier, P.; Robinson, I.C. Visceral obesity without insulin resistance in late-onset obesity rats. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 2666–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Higham, C.E.; Trainer, P.J. Growth hormone excess and the development of growth hormone receptor antagonists. Exp. Physiol. 2008, 93, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, M.L.; Tsai, Y.H.; Liu, X.; Wolfrum, C.; Seeberger, P.H. Synthetic inositol phosphoglycans related to GPI lack insulin-mimetic activity. ACS Chem. Biol. 2010, 5, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Li, H.; Mao, S.; Lin, J.M. Cell signaling analysis by mass spectrometry under coculture conditions on an integrated microfluidic device. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9306–9313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Schultz, P.G. Synthesis at the interface of chemistry and biology. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 12497–12515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mukhopadhyay, R. Deciphering cellular conversations. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 3963–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Delahaut, P.; Krug, O.; Schänzer, W.; Thevis, M. Metabolism of growth hormone releasing peptides. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 10252–10259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, R.I.G.; Soenksen, P.H. Growth hormone, IGF-I and insulin and their abuse in sport. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 542–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.E.; Ho, K.K. A robust test for growth hormone doping-present status and future prospects. Asian J. Androl. 2008, 10, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powrie, J.K.; Bassett, E.E.; Rosen, T.; Jørgensen, J.O.; Napoli, R.; Sacca, L.; Christiansen, J.S.; Bengtsson, B.A.; Sönksen, P.H. Detection of growth hormone abuse in sport. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2007, 17, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cung, L.; Baxter, R.C. Detection of growth hormone responsive proteins using SELDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2009, 19, 383–387. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.Y.; Yang, J.A.; Kim, E.S.; Jeon, G.; Oh, J.E.; Choi, W.Y.; Hahn, S.K.; Kim, J.K. Single-file diffusion of protein drugs through cylindrical nanochannels. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3817–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Shang, S.; Li, J.; Tan, Z.; Dean, T.; Maeda, A.; Gardella, T.J.; Danishefsky, S.J. Engineering of therapeutic polypeptides through chemical synthesis: Early lessons from human parathyroid hormone and analogues. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 15122–15129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausaite-Minkstimiene, A.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Kirlyte, J.; Ramanavicius, A. Comparative study of random and oriented antibody immobilization techniques on the binding capacity of immunosensor. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6401–6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, J.; Ellis, A.; Al-Sadie, R. Serum growth hormone measurements in clinical practice: An audit of performance from the UK national external quality assessment scheme. Horm. Res. 1993, 51, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauman, G.; Stolar, M.W.; Buchanan, T.A. The metabolic clearance, distribution, and degradation of dimeric and monomeric growth hormone (GH): Implications for the pattern of circulating GH forms. Endocrinology 1986, 119, 1497–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatelain, P.; Bouillat, B.; Coehn, R.; Sassolas, G.; Souberbielle, J.C.; Ruitton, A.; Joly, M.O.; Job, J.C. Assay of growth hormone levels in human plasma using commercial kits: Analysis of some factors influencing the results. Acta Paediatr. 1990, 370, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, E.O.; Morris, A.H.; Macgillivray, M.H.; Weber, D. Variable estimates of serum growth hormone concentrations by different radioassay systems. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1988, 66, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, T.; Shaw, M.A.; Baumann, G. Effects of growth hormone-binding proteins on serum growth hormone measurements. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1991, 72, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasca, F.; Harreither, W.; Ludwig, R.; Gooding, J.J.; Gorton, L. Cellobiose dehydrogenase aryl diazonium modified single walled carbon nanotubes: Enhanced direct electron transfer through a positively charged surface. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 3042–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, R.; Cui, L.; Tang, J.; Liu, Z.; Kong, Q.; Yang, W.; Gooding, J.J. Using molecular level modification to tune the conductivity of praphene papers. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 17939–17946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, S.; Barriere, F.; Leech, D. Designing stable redox-active surfaces: Chemical attachment of an osmium complex to glassy carbon electrodes prefunctionalized by electrochemical reduction of an in situ-generated aryl diazonium cation. Langmuir 2008, 24, 6351–6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Brahmendra, A.; Veloso, A.J.; Prashar, A.; Cheng, X.R.; Hung, V.W.S.; Guyard, C.; Terebiznik, M.; Kerman, K. Disposable immunochips for the detection of legionella pneumophila using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3485–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, N.; Le Tisser, P.; Grattan, D.; Kerman, K. Miniaturized electrochemical immunosensors for the detection of growth hormone. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Travas-Sejdic, J.; Williams, D.E. Water structure change-induced expansion and collapse of zwitterionic polymers surface-grafted onto carbon black. Langmuir 2012, 28, 8072–8083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Z.; Liu, J.Q.; Bocking, T.; Eggers, P.K.; Gooding, J.J. The modification of glassy carbon and gold electrodes with aryl diazonium salt: The impact of the electrode substrate on the rate of heterogeneous electron transfer. Chem. Phys. 2005, 319, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozhikandathil, J.; Packirisamy, M. Detection of recombinant growth hormone by evanescent cascaded waveguide coupler on silica-on-silicon. J. Biophotonics 2013, 6, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadabadi, H.; Badilescu, S.; Packirisamy, M.; Wüthrich, R. Integration of gold nanoparticles in PDMS microfluidics for lab-on-a-chip plasmonic biosensing of growth hormones. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 44, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, S.; Zeidan, E.; Henrich, V.C.; Sandros, M.G. Comparative analysis of human growth hormone in serum using SPRi, nano-SPRi and ELISA assays. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 7, e53508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Guerrero, A.B.; Maldonado, J.; Dante, S.; Grajales, D.; Lechuga, L.M. Direct and label-free detection of the human growth hormone in urine by an ultrasensitive bimodal waveguide biosensor. J. Biophotonics 2017, 10, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadabadi, H.; Packirisamy, M. Nano-integrated suspended polymeric microfluidics (SPMF) platform for ultra-sensitive biomolecular recognition of bovine growth hormones. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevino, J.; Calle, A.; Rodriguez-Frade, J.M.; Mellado, M.; Lechuga, L.M. Determination of human growth hormone in human serum samples by surface plasmon resonance immunoassay. Talanta 2009, 78, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevino, J.; Calle, A.; Rodriguez-Frade, J.M.; Mellado, M.; Lechuga, L.M. Surface plasmon resonance immunoassay analysis of pituatry hormones in urine and serum samples. Clin. Chim. Acta 2009, 403, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, B.; Khayamian, T.; Majidi, N.; Rahmani, H. Immobilization of specific monoclonal antibody on Au nanoparticles for hGH detection by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanaviciene, A.; German, N.; Kausaite-Minkstimiene, A.; Voronovic, J.; Kirlyte, J.; Ramanavicius, A. Comparative study of surface plasmon resonance, electrochemical and electroassisted chemiluminescence methods based immunosensor for the determination of antibodies against human growth hormone. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 36, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafin, V.; Ubeda, N.; Agui, L.; Yanez-Sedeno, P.; Pingarron, J.M. Ultrasensitive determination of human groth hormone (hGH) with a disposable electrochemical magneto-immunosensor. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Juan-Franco, E.; Caruz, A.; Pedrajas, J.R.; Lechuga, L.M. Site-directed antibody immobilization using a protein A-gold binding domain fusion protein for enhanced SPR immunosensing. Analyst 2013, 138, 2023–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, N.; Kausaite-Minkstimiene, A.; Kirlyte, J.; Makaraviciute, A.; Ramanavicius, A.; Mikoliunaite, L.; Ramanaviciene, A. Determination of antibodies against human growth hormone using a direct immunoassay format and different electrochemical methods. Analyst 2013, 138, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Juan-Franco, E.; Radriguez-Frade, J.M.; Mellado, M.; Lechuga, L.M. Implementation of a SPR immunosensor for the simultaneous detection of the 22K and 20K hGH isoforms in human serum samples. Talanta 2013, 114, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozhikandathil, J.; Badilescu, S.; Packirisamy, M. Plasmonic gold decorated MWCNT nanocomposite for localized plasmon resonance sensing. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespi, F. Central [CNS] and peripheral [Gastric tissue] selective monitoring of somatostatin (SRIF) with micro-sensor and voltammetry in rats: Influence of growth factors (GH, EGF). Biosensors 2017, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Biosensor Surface | Detection Technique | Limit of Detection | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silica-on-silicon (SOS) with a cascaded waveguide coupler | Evanescent wave-based fluoroimmunoassay | 25 ng/mL | [38] |
| Gold nanoparticles synthesized in a poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) microfluidic chip | LSPR-based immunoassay | 3.7 ng/mL | [39] |
| Anti-hGH coated with near-infrared quantum dots | SPRi (SPR imaging)- & Nano-SPRi-based immunoassay | 0.03 ng/mL–100 ng/mL | [40] |
| Anti-hGH-modified interferometer | Bimodal waveguide interferometry-based immunoassay | 10 pg/mL | [41] |
| Nano-integrated suspended polymeric microfluidics (SPMF) platform | Microcantilever-based immunoassay | 2 ng/mL | [42] |
| Anti-hGH modified gold surfaces | SPR-based immunoassay | 6 ng/mL | [43] |
| Anti-hGH modified gold surfaces | SPR-based immunoassay | 1-6 ng/mL | [44] |
| Gold nanoparticles immobilized on gold electrodes using 1,6-hexanedithiol | EIS-based immunoassay | 0.64 pg/mL | [45] |
| Sandwich-based immunoassay using horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labeled secondary antibody | SPR, pulsed amperometry (PA), electrochemically-assisted chemiluminescence (ECL), CV | 0.051 nM by SPR 0.027 nM by PA 0.061 nM by ECL 0.056 nM by CV | [46] |
| Tosyl-activated magnetic microparticles on screen-printed gold electrodes | Square-wave voltammetry (SWV) of 4-aminophenyl phosphate as the substrate of alkaline phosphatase | 0.005 ng/mL | [47] |
| Protein A-gold binding domain fusion protein | SPR-based immunoassay | 90 ng/mL | [48] |
| Anti-hGH immobilized on gold surfaces | PA & CV | 75 nM by PA 108 nM by CV | [49] |
| Oriented anti-hGH-modified gold surfaces using biotin-streptavidin | SPR-based immunoassay | 0.9 ng/mL for 22K and 20K hGH isoforms | [50] |
| Plasmonic gold decorated multi-walled carbon nanotube nanocomposite | LSPR-based immunoassay | 1 ng/mL | [51] |
| Carbon fiber microelectrode | Differential pulse voltammetry for in vivo and ex vivo measurements using rats | 2 µg/µL | [52] |
| Anti-GH modified SPCE | EIS-based immunoassay | 5 pg/mL | This work |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, N.; Chow, A.M.; Ganesh, H.V.S.; Ratnam, M.; Brown, I.R.; Kerman, K. Diazonium-Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes for Immunosensing Growth Hormone in Blood Samples. Biosensors 2019, 9, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030088
Li N, Chow AM, Ganesh HVS, Ratnam M, Brown IR, Kerman K. Diazonium-Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes for Immunosensing Growth Hormone in Blood Samples. Biosensors. 2019; 9(3):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030088
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Nan, Ari M. Chow, Hashwin V. S. Ganesh, Melanie Ratnam, Ian R. Brown, and Kagan Kerman. 2019. "Diazonium-Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes for Immunosensing Growth Hormone in Blood Samples" Biosensors 9, no. 3: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030088
APA StyleLi, N., Chow, A. M., Ganesh, H. V. S., Ratnam, M., Brown, I. R., & Kerman, K. (2019). Diazonium-Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes for Immunosensing Growth Hormone in Blood Samples. Biosensors, 9(3), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030088