Evaluation of 3-Chlorobenzoate 1,2-Dioxygenase Inhibition by 2- and 4-Chlorobenzoate with a Cell-Based Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Microorganism and Culture Conditions
2.2. Biosensor Determination of 3-Chlorobenzoate-1,2-Dioxygenase Activity
2.3. Evaluation of 3-CBDO Inhibition by 2- and 4-CBA
Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
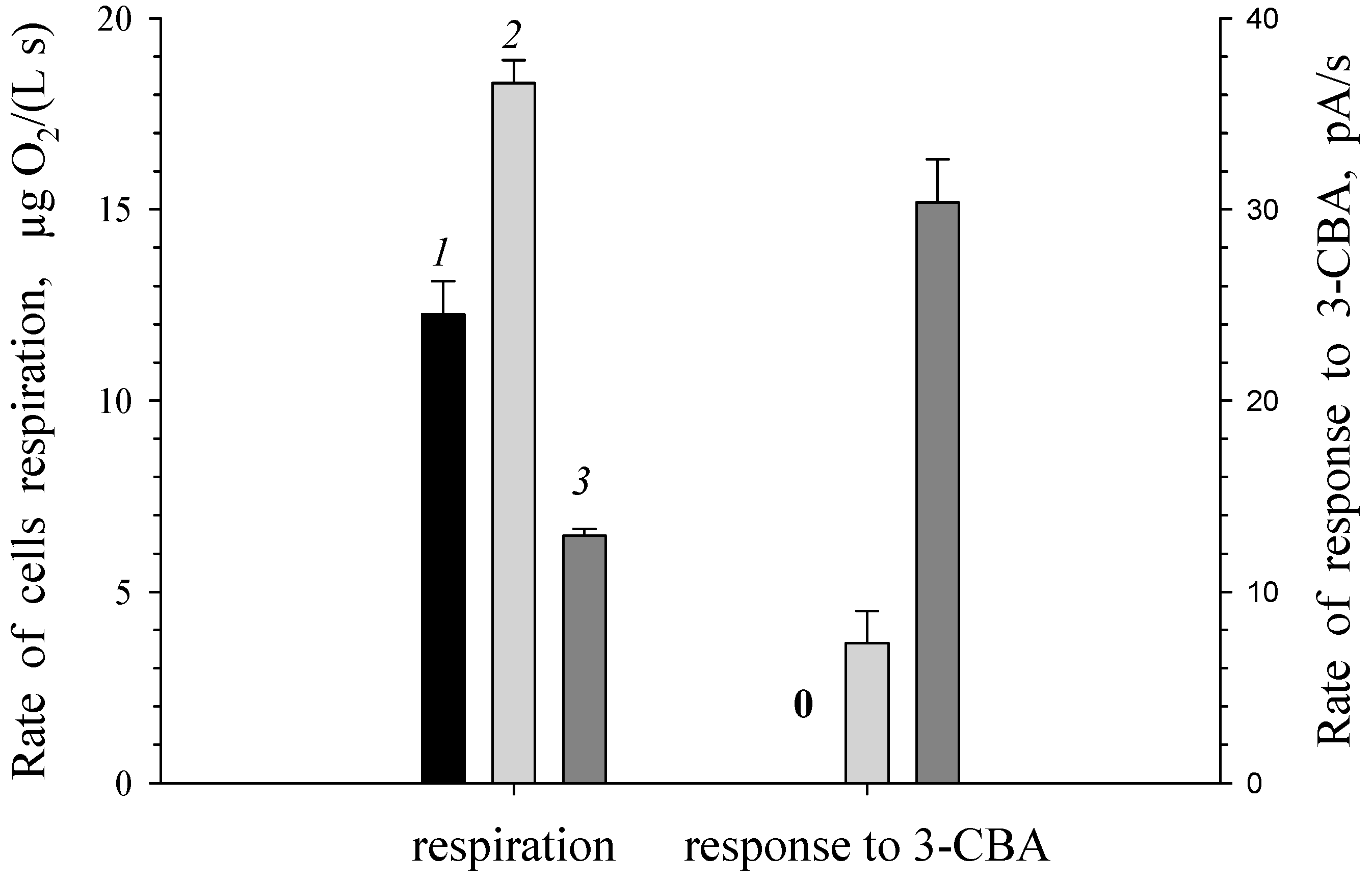
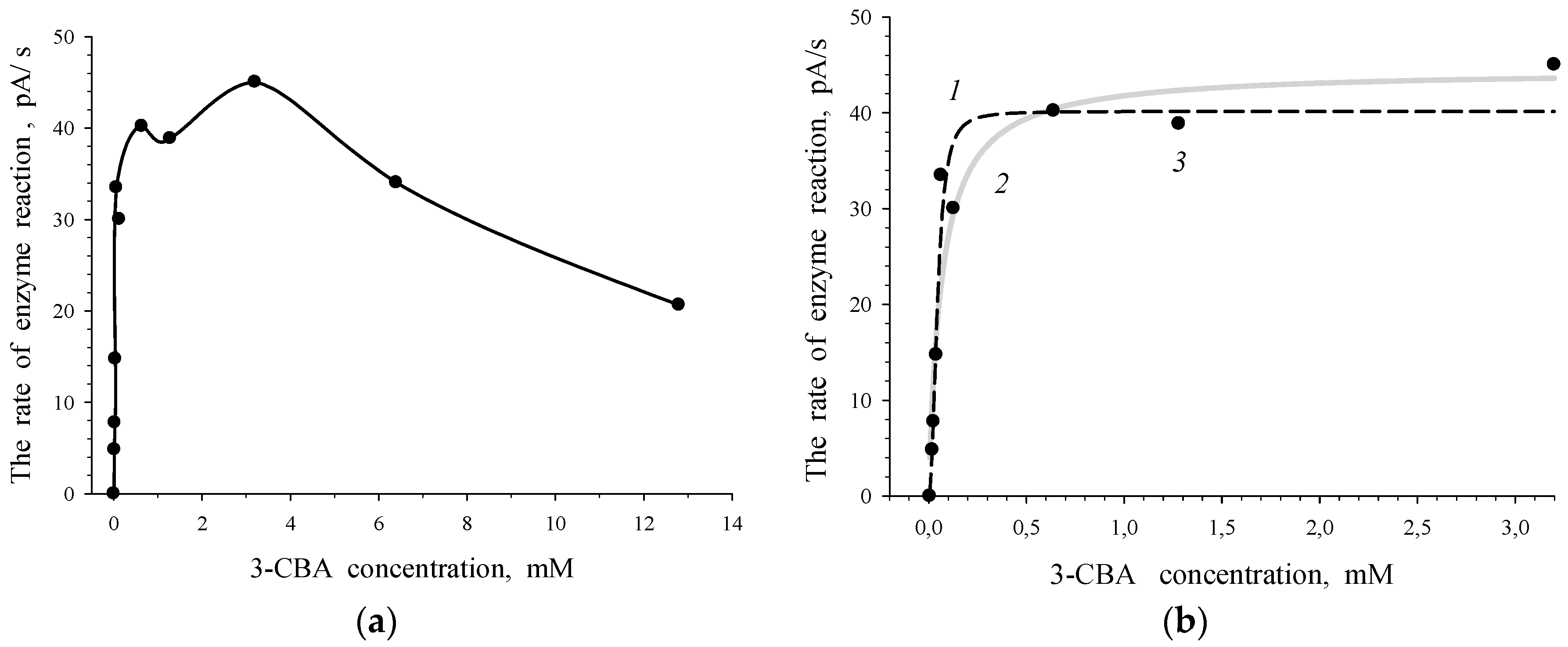
3.1. Estimation of 3-CBA-1,2-DO Activity
- Vmax was the maximum rate of the enzymatic reaction (maximal magnitude of the rate when S → ∞; a constant of catalytic activity);
- S0.5 was the substrate concentration (S) when V = 0.5Vmax (a Hill concentration constant);
- n was a Hill coefficient.
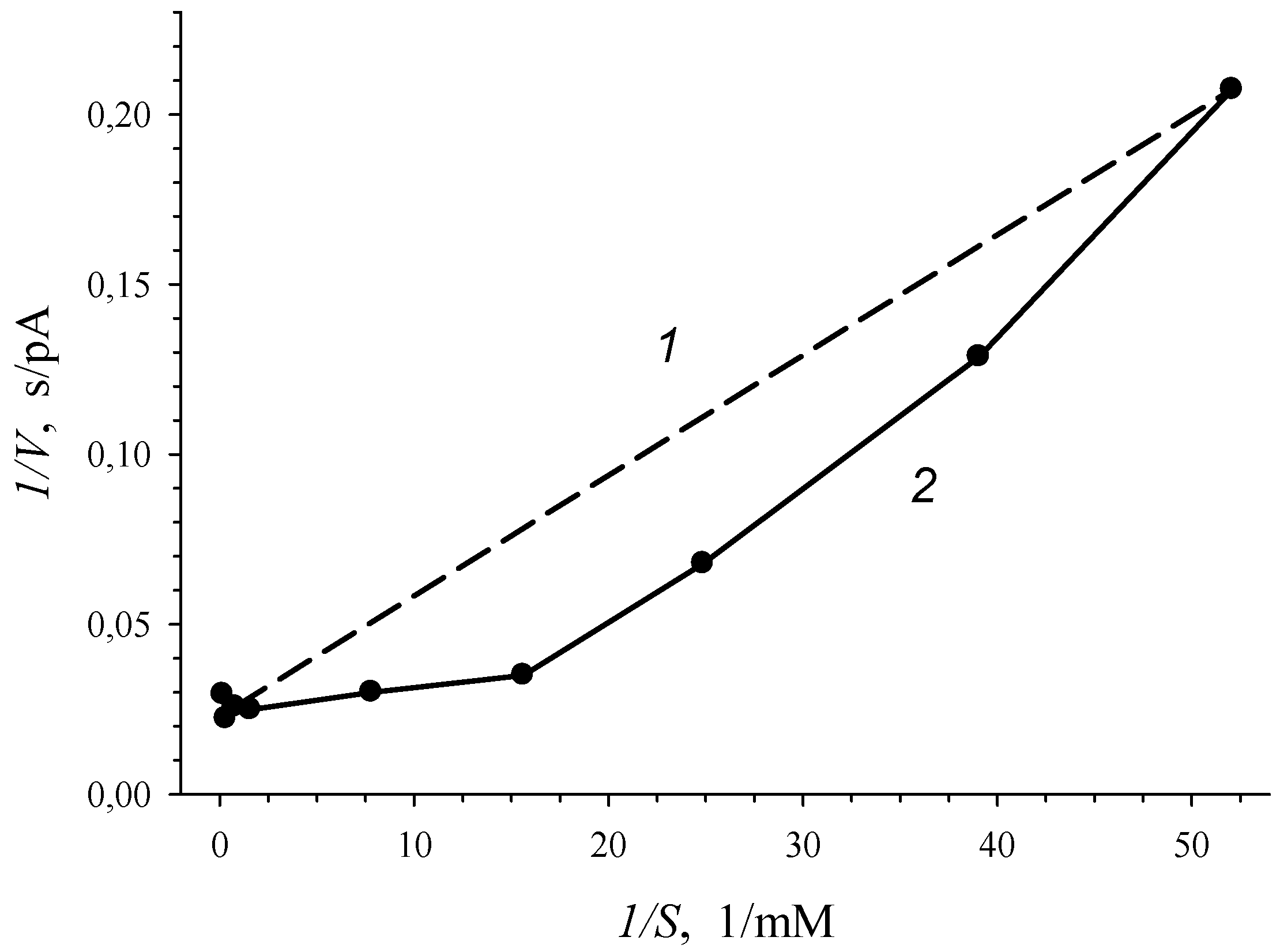
3.2. 3-Chlorobenzoate-1,2-Dioxygenase Inhibition by 2- and 4-Chlorobenzoate for R. opacus 1CP 3-CBA-Grown Cells
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hartmann, J.; Reineke, W.; Knackmuss, H.-J. Metabolism of 3-chloro-, 4-chloro-, and 3,5-dichlorobenzoate by a pseudomonad. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1979, 37, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baggi, G.; Zangrossi, M. Assessment of the biodegradative potential versus chlorobenzoates as single or mixed compounds in a stable microbial consortium. Ann. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 179–188. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Yang, X.; Xie, F.; Chao, Y.; Qian, S. Cometabolic degradation of mono-chloro benzoic acids by Rhodococcus sp. R04 grown on organic carbon sources. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 25, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribble, G.W. The abundant natural sources and uses of chlorinated chemicals. Am. J. Public Health. 1994, 84, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, E.; Hellwig, M.; Reineke, W.; Knackmuss, H.J. Isolation and characterization of a 3-chlorobenzoate degrading pseudomonad. Arch. Microbiol. 1974, 99, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, D.K.; Kellogg, S.T.; Hamada, S.; Chakrabarty, A.M. Plasmid specifying total degradation of 3-chlorobenzoate by a modified ortho pathway. J. Bacteriol. 1981, 146, 639–648. [Google Scholar]
- Plotnikova, E.G.; Solyanikova, I.P.; Egorova, D.O.; Shumkova, E.S.; Golovleva, L.A. Degradation of 4-chlorobiphenyl and 4-chlorobenzoic acid by the strain Rhodococcus ruber P25. Microbiology 2012, 81, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solyanikova, I.P.; Suzina, N.E.; Mulyukin, A.L.; El-Registan, G.I.; Golovleva, L.A. Effect of a dormant state on the xenobiotic-degrading strain Pseudomonas fluorescens 26K. Microbiology 2013, 82, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willes, R.F.; Nestmann, E.R.; Miller, P.A.; Orr, J.C.; Munro, I.C. Scientific principles for evaluating the potential for adverse effects from chlorinated organic chemicals in the environment. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1993, 18, 313–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, A.W.; Silvin, C.J.; Hassett, J.P.; Nakas, J.P.; Tanenbaum, S.W. Bacterial PCB biodegradation. Biodegradation 1992, 3, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harayama, S.; Rekik, M.; Bairoch, A.; Neidle, E.L.; Ornston, L.N. Potential DNA slippage structures acquired during evolutionary divergence of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus chromosomal benABC and Pseudomonas putida TOL pWW0 plasmid xylXYZ, genes encoding benzoate dioxygenases. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 7540–7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, W.; Miyauchi, K.; Masai, E.; Fukuda, M. Cloning and characterization of benzoate catabolic genes in the gram-positive polychlorinated biphenyl degrader Rhodococcus sp. strain RHA1. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 6598–6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solyanikova, I.P.; Emelyanova, E.V.; Shumkova, E.S.; Egorova, D.O.; Korsakova, E.S.; Plotnikova, E.G.; Golovleva, L.A. Peculiarities of the degradation of benzoate and its chloro- and hydroxy-substituted analogs by actinobacteria. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 100, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solyanikova, I.P.; Emelyanova, E.V.; Shumkova, E.S.; Travkin, V.M. Pathways of 3-chlorobenzoate degradation by Rhodococcus opacus strains 1CP and 6a. Microbiology 2019, 88, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neidle, E.L.; Hartnett, C.; Ornston, L.N.; Bairoch, A.; Rekik, M.; Harayama, S. Nucleotide sequences of the Acinetobacter calcoaceticus benABC genes for benzoate 1,2-dioxygenase reveal evolutionary relationships among multicomponent oxygenases. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 5385–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, J.A.; Sierra-Alvarez, R. Microbial transformation of chlorinated benzoates. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomburg, D.; Schomburg, I.; Chang, A. Handbook of Enzymes. In Class 1. Oxidoreductases XI: EC 1.14.11–1.14.14; Springer-Verlag Berlin and Heidelberg GmbH & Co. KG: Berlin, Germany, 2006; Volume 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, D.R.; Cain, R.B. Catechol oxygenase induction in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem. J. 1968, 106, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racek, J. Cell-Based Biosensors; Technomic Publishing Company: Lancaster, Basel, 1995; pp. 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Gorlatov, S.N.; Maltseva, O.V.; Shevchenko, V.I.; Golovleva, L.A. Degradation of chlorophenols by a culture of Rhodococcus erythropolis. Mikrobiologiya 1989, 58, 647–651. [Google Scholar]
- Krupyanko, V.I. Correction of Dixon plots. Eur. Chem. Bull. 2015, 4, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurganov, B.I. Allosteric Enzymes: Kinetic Behavior; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1982; ISBN 978-047110195. [Google Scholar]
- Emelyanova, E.V.; Solyanikova, I.P. Benzoate Concentration and Cooperativity by a Substrate for Benzoate 1,2-dioxygenase from Benzoate-degrading Rhodococcus Opacus 1CP. J. Biotechnol. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 1, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Katsumata, M.; Goldman, A.S. A mathematical analysis of the substrate effect observed in 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase reactions of rat testicular microsomes. J. Biochem. 1976, 79, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittenberger, C.L.; Fulco, J.G. Purification and allosteric properties of a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-linked D(-)-specific lactate dehydrogenase from Butyribacterium rettgeri. J. Biol. Chem. 1967, 242, 2917–2924. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Emelyanova, E.V.; Solyanikova, I.P. Evaluation of 3-Chlorobenzoate 1,2-Dioxygenase Inhibition by 2- and 4-Chlorobenzoate with a Cell-Based Technique. Biosensors 2019, 9, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030106
Emelyanova EV, Solyanikova IP. Evaluation of 3-Chlorobenzoate 1,2-Dioxygenase Inhibition by 2- and 4-Chlorobenzoate with a Cell-Based Technique. Biosensors. 2019; 9(3):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030106
Chicago/Turabian StyleEmelyanova, Elena V., and Inna P. Solyanikova. 2019. "Evaluation of 3-Chlorobenzoate 1,2-Dioxygenase Inhibition by 2- and 4-Chlorobenzoate with a Cell-Based Technique" Biosensors 9, no. 3: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030106
APA StyleEmelyanova, E. V., & Solyanikova, I. P. (2019). Evaluation of 3-Chlorobenzoate 1,2-Dioxygenase Inhibition by 2- and 4-Chlorobenzoate with a Cell-Based Technique. Biosensors, 9(3), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030106





