Fluorescent Nanosensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Coated on Graphene Quantum Dots for Fast Detection of Antibiotics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
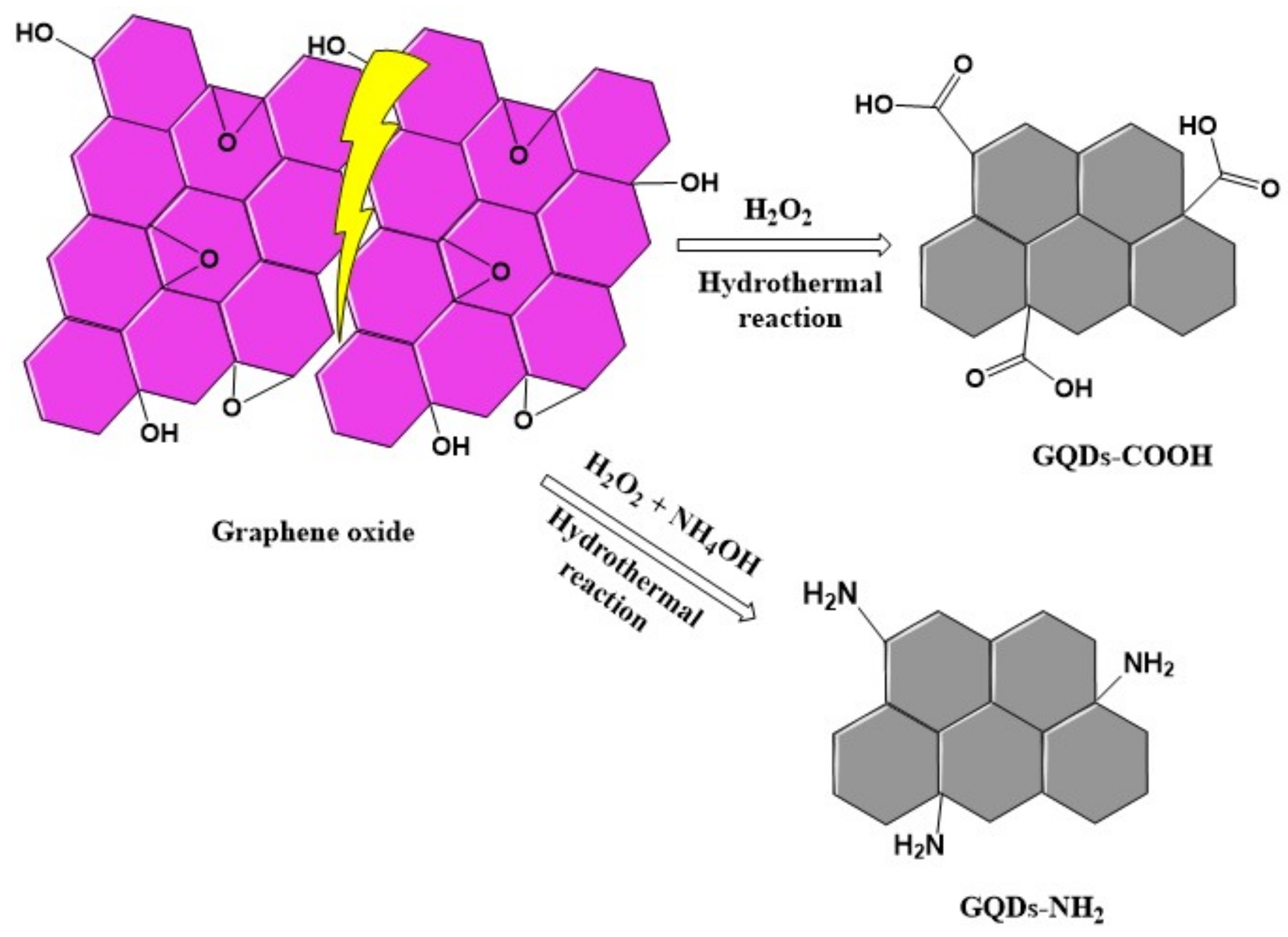
2.2. Synthesis of Two Kinds of Graphene Quantum Dots (GQDs)
2.2.1. Synthesis of Carboxylic Acid Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots (GQDs-COOH)
2.2.2. Synthesis of Amino Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots (GQDs-NH2)
2.3. Preparation of GQDs-MIPs from Sol-Gel Process
2.4. Characterization of GQDs-MIPs
2.5. Fluorescence Measurement of GQDs-MIPs
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Green Synthesis of GQDs
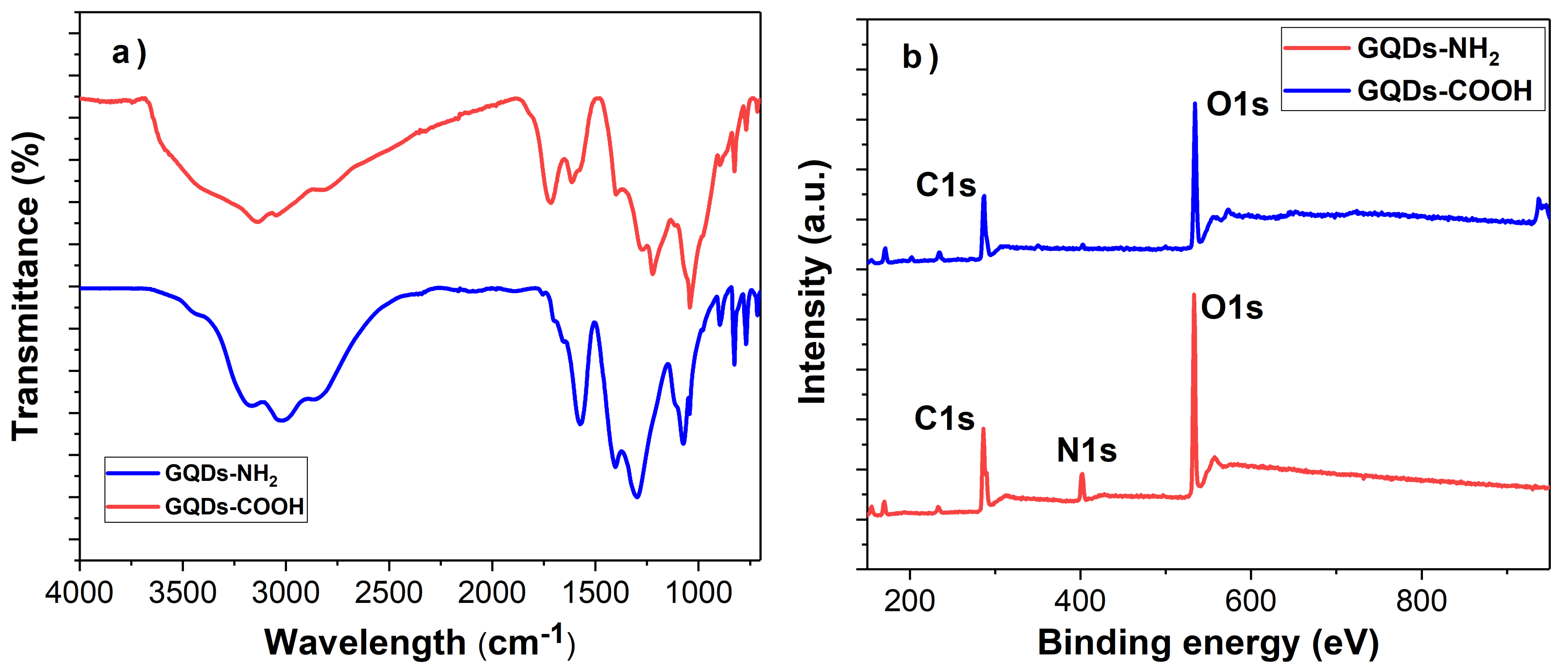
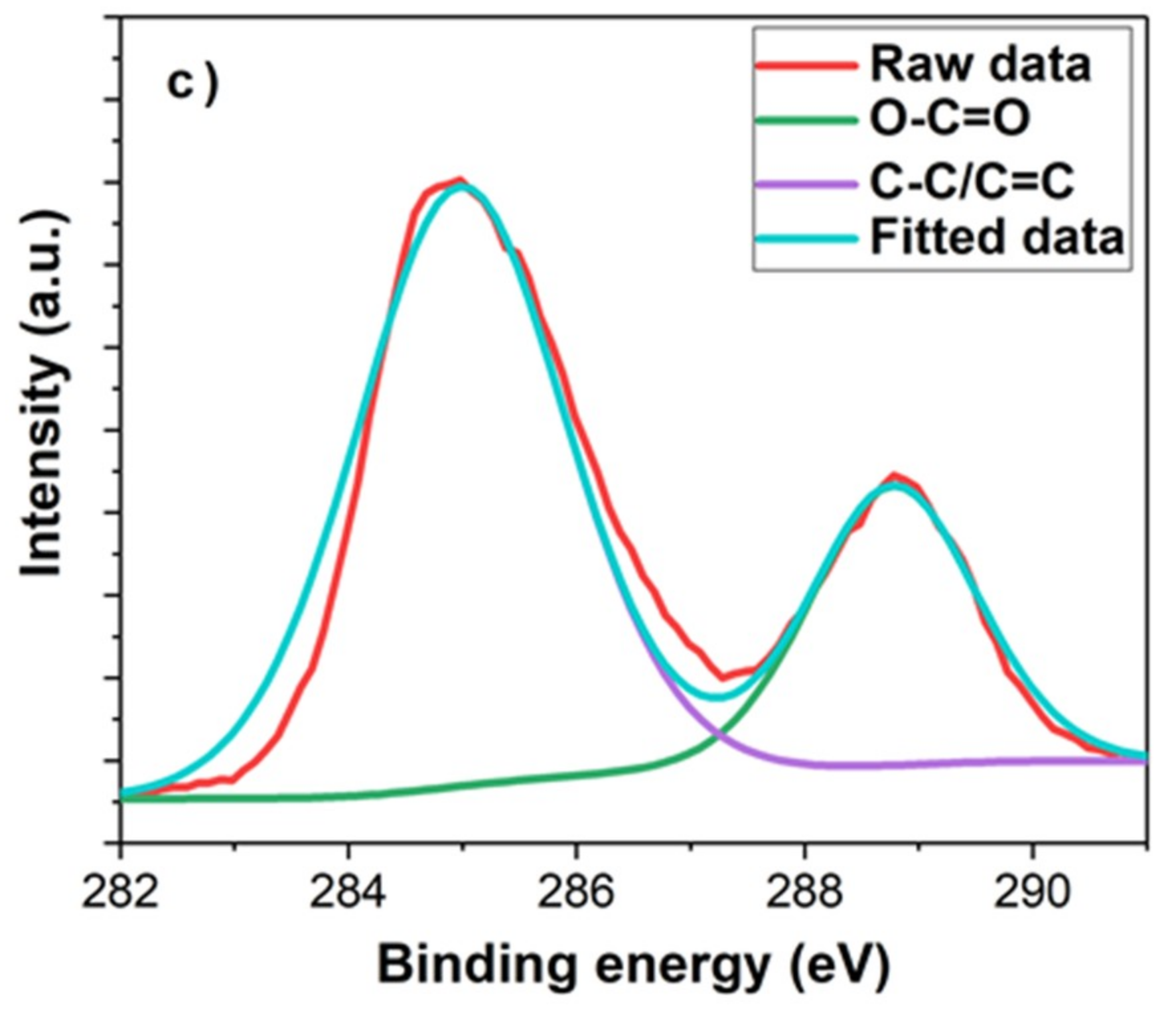
3.2. Comparison of GQDs with Different Functional Groups
3.3. TEM of GQDs-MIP and GQDs
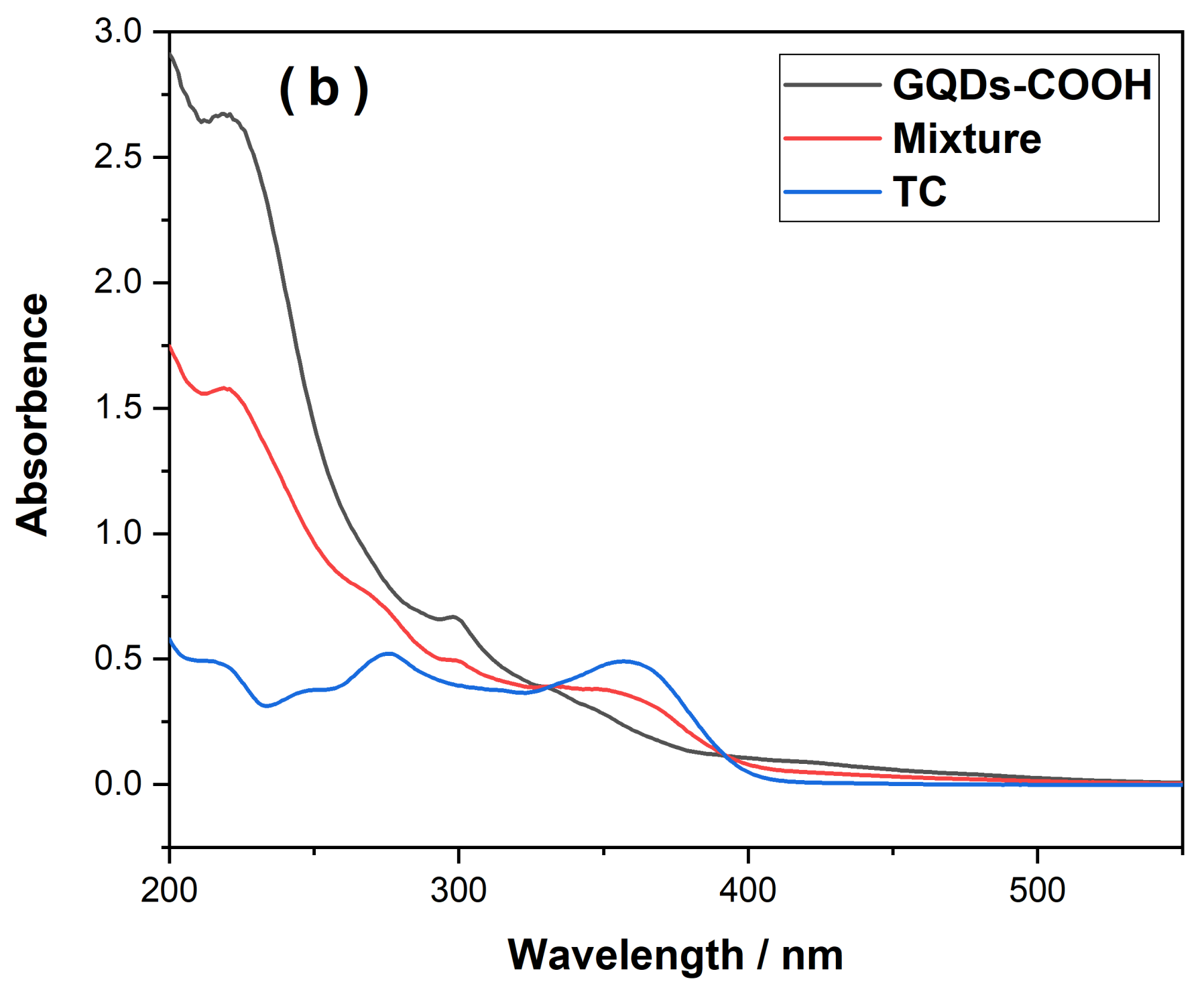
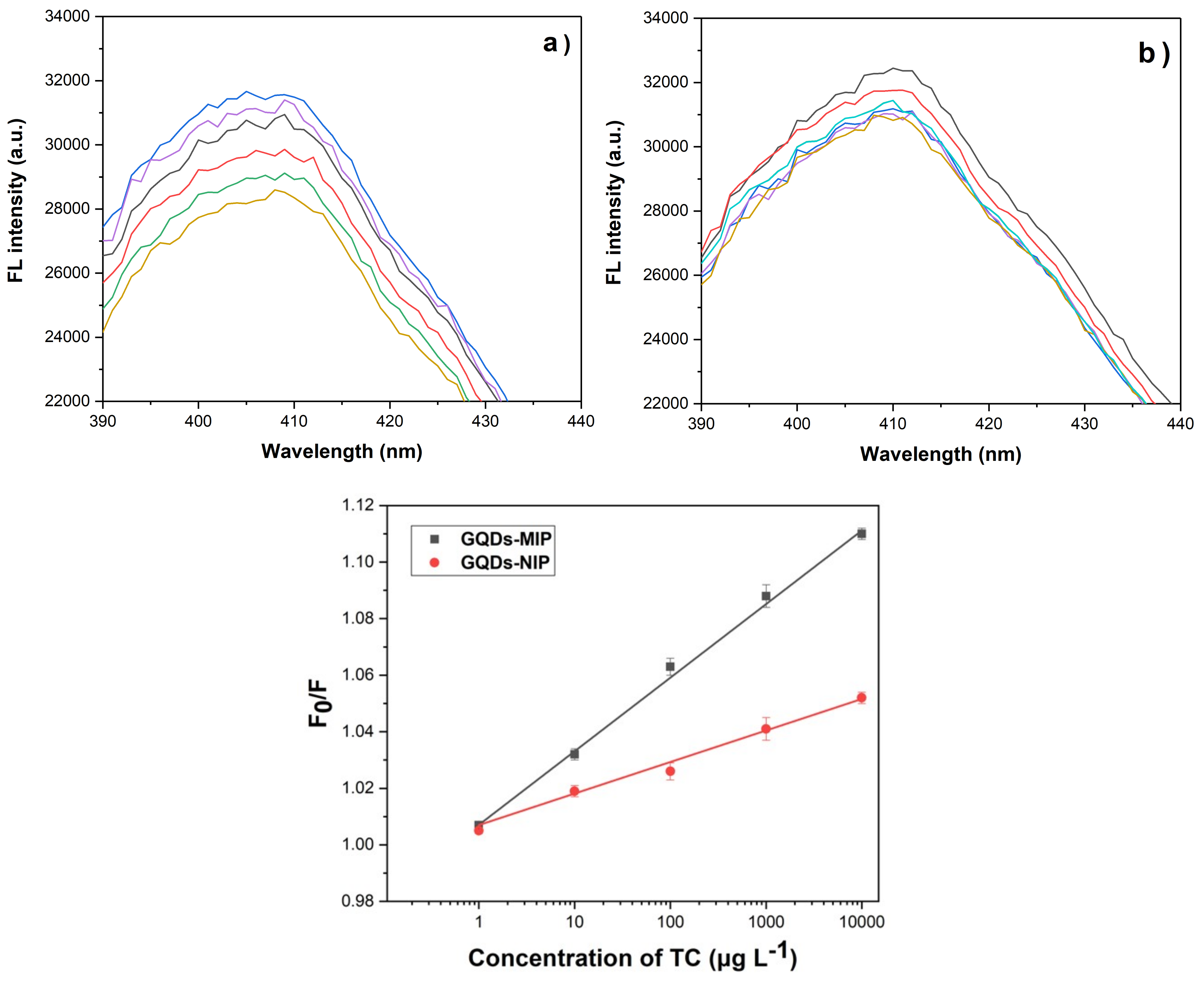
3.4. Determination of TC Using GQDs-MIPs
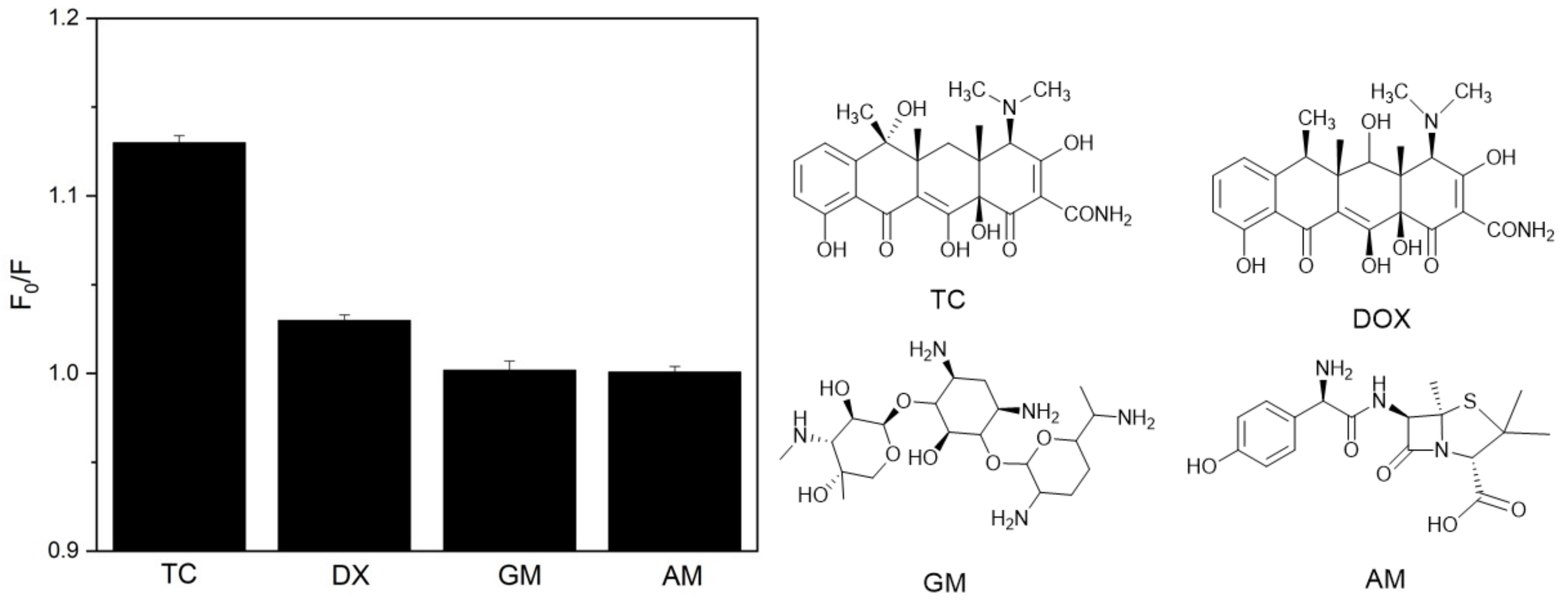
3.5. Selectivity of GQDs-MIPs
3.6. Real Sample Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chopra, I.; Roberts, M. Tetracycline Antibiotics: Mode of Action, Applications, Molecular Biology, and Epidemiology of Bacterial Resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2001, 65, 232–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiba, T.; Koyama, K.; Ishiki, Y. On the mechanism of the development of multiple-drug-resistant clones of Shigella. Jpn. J. Microbiol. 1960, 4, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M.C. Tetracycline Therapy: Update. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 36, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podhorniak, L.V.; Leake, S.; Schenck, F.J. Stability of tetracycline antibiotics in raw milk under laboratory storage conditions. J. Food Prot. 1999, 62, 547–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, H.; Yu, A.; Zhang, H.; Ding, L. Preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for the separation of tetracycline antibiotics from egg and tissue samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 3710–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, T.; Gao, X.D.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.F.; Hu, X.Z.; Hao, Q.L.; Zhou, Y.K.; Mei, S.R. Determination of trace tetracycline antibiotics in foodstuffs by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry coupled with selective molecular-imprinted solid-phase extraction. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 2009–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.K.; Zhao, C.X.; Li, P.; He, Y.D.; Yang, Z.R.; Sun, H.W. Preparation of doxycycline-imprinted magnetic microspheres by inverse-emulsion suspension polymerization for magnetic dispersion extraction of tetracyclines from milk samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 2656–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Svensson Bonde, J.; Kamra, T.; Bülow, L.; Leo, J.C.; Linke, D.; Ye, L. Bacterial imprinting at pickering emulsion interfaces. Angew. Chem Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 10687–10690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedwell, T.S.; Whitcombe, M.J. Analytical applications of MIPs in diagnostic assays: Future perspectives. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 1735–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yang, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Protein-imprinted material for the treatment of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 1890–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Wu, X.; Li, J. Molecular imprinting: Perspectives and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2137–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rechichi, A.; Cristallini, C.; Vitale, U.; Ciardelli, G.; Barbani, N.; Vozzi, G.; Giusti, P. New biomedical devices with selective peptide recognition properties. Part 1: Characterization and cytotoxicity of molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2007, 11, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morelli, I.; Chiono, V.; Vozzi, G.; Ciardelli, G.; Silvestri, D.; Giusti, P. Molecularly imprinted submicronspheres for applications in a novel model biosensor-film. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 150, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Biyikal, M.; Wagner, R.; Sellergren, B.; Rurack, K. Fluorescent sensory microparticles that “light-up” consisting of a silica core and a molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) shell. Angew. Chem Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7023–7027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley, J.; Feng, X.; Sun, Y. A multifunctional molecularly imprinted polymer-based biosensor for direct detection of doxycycline in food samples. Talanta 2018, 182, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yi, C.; Luo, J.; Liu, R.; Liu, J.; Jiang, J.; Liu, X. Glucose sensors based on electrodeposition of molecularly imprinted polymeric micelles: A novel strategy for MIP sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2607–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chullasat, K.; Nurerk, P.; Kanatharana, P.; Davis, F.; Bunkoed, O. A facile optosensing protocol based on molecularly imprinted polymer coated on CdTe quantum dots for highly sensitive and selective amoxicillin detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 254, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Lu, H. One-pot synthesis of mesoporous structured ratiometric fluorescence molecularly imprinted sensor for highly sensitive detection of melamine from milk samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 73, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; He, X.W.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K. Composite of CdTe quantum dots and molecularly imprinted polymer as a sensing material for cytochrome c. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2553–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.-Y.; He, X.-W.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-K. Novel Hybrid Structure Silica/CdTe/Molecularly Imprinted Polymer: Synthesis, Specific Recognition, and Quantitative Fluorescence Detection of Bovine Hemoglobin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 12609–12616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, T.T.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.S.; Zhang, Z.J.; Liu, P.; Zhang, C.C. Toxicity evaluation of CdTe quantum dots with different size on Escherichia coli. Toxicol. In Vitro 2012, 26, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Peng, H.; Xiong, H.; Chen, L. Strategies of molecular imprinting-based fluorescence sensors for chemical and biological analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 112, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravagnuolo, A.M.; Morales-Narváez, E.; Longobardi, S.; Da Silva, E.T.; Giardina, P.; Merkoçi, A. In situ production of biofunctionalized few-layer defect-free microsheets of graphene. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2771–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrzad-Samarin, M.; Faridbod, F.; Dezfuli, A.S.; Ganjali, M.R. A novel metronidazole fluorescent nanosensor based on graphene quantum dots embedded silica molecularly imprinted polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Li, X.; Qin, L.; Kang, S.-Z.; Li, G. Graphene quantum dots supported by graphene oxide as a sensitive fluorescence nanosensor for cytochrome c detection and intracellular imaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 6300–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, A.; Yu, C.; Wu, S.; Shen, J. Facile Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Graphene Quantum Dots for the Determination of Dopamine with Affinity-Adjustable. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 11741–11747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amjadi, M.; Jalili, R. Molecularly imprinted polymer-capped nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots as a novel chemiluminescence sensor for selective and sensitive determination of doxorubicin. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 86736–86743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, G.; Deng, L.; Hou, Y.; Qu, L. An electrochemical avenue to green-luminescent graphene quantum dots as potential electron-acceptors for photovoltaics. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Wu, D.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K. Bottom-up fabrication of photoluminescent graphene quantum dots with uniform morphology. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15221–15223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, T.; Ding, H.; Ding, L. Rapid microwave-assisted synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymers on carbon quantum dots for fluorescent sensing of tetracycline in milk. Talanta 2016, 146, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, M.R.; Hu, C.W.; Chen, J.L. Comparative syntheses of tetracycline-imprinted polymeric silicate and acrylate on CdTe quantum dots as fluorescent sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Spiked Amount (µg·L−1) | Measured Amount (µg·L−1) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.98 ± 0.049 | 98 ± 4.9 |
| 10 | 9.22 ± 0.57 | 92.2 ± 5.7 |
| 100 | 103.3 ± 3.7 | 103.3 ± 3.7 |
| 103 | (9.74 ± 0.72) × 102 | 97.4 ± 7.2 |
| 104 | (8.53 ± 0.61) × 103 | 85.3 ± 6.1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, T.; Halder, A.; Sun, Y. Fluorescent Nanosensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Coated on Graphene Quantum Dots for Fast Detection of Antibiotics. Biosensors 2018, 8, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8030082
Zhou T, Halder A, Sun Y. Fluorescent Nanosensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Coated on Graphene Quantum Dots for Fast Detection of Antibiotics. Biosensors. 2018; 8(3):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8030082
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Tongchang, Arnab Halder, and Yi Sun. 2018. "Fluorescent Nanosensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Coated on Graphene Quantum Dots for Fast Detection of Antibiotics" Biosensors 8, no. 3: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8030082
APA StyleZhou, T., Halder, A., & Sun, Y. (2018). Fluorescent Nanosensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Coated on Graphene Quantum Dots for Fast Detection of Antibiotics. Biosensors, 8(3), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8030082






