Development of a Polyphenol Oxidase Biosensor from Jenipapo Fruit Extract (Genipa americana L.) and Determination of Phenolic Compounds in Textile Industrial Effluents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Solutions
2.2. Vegetal Material and Crude Extract Preparation
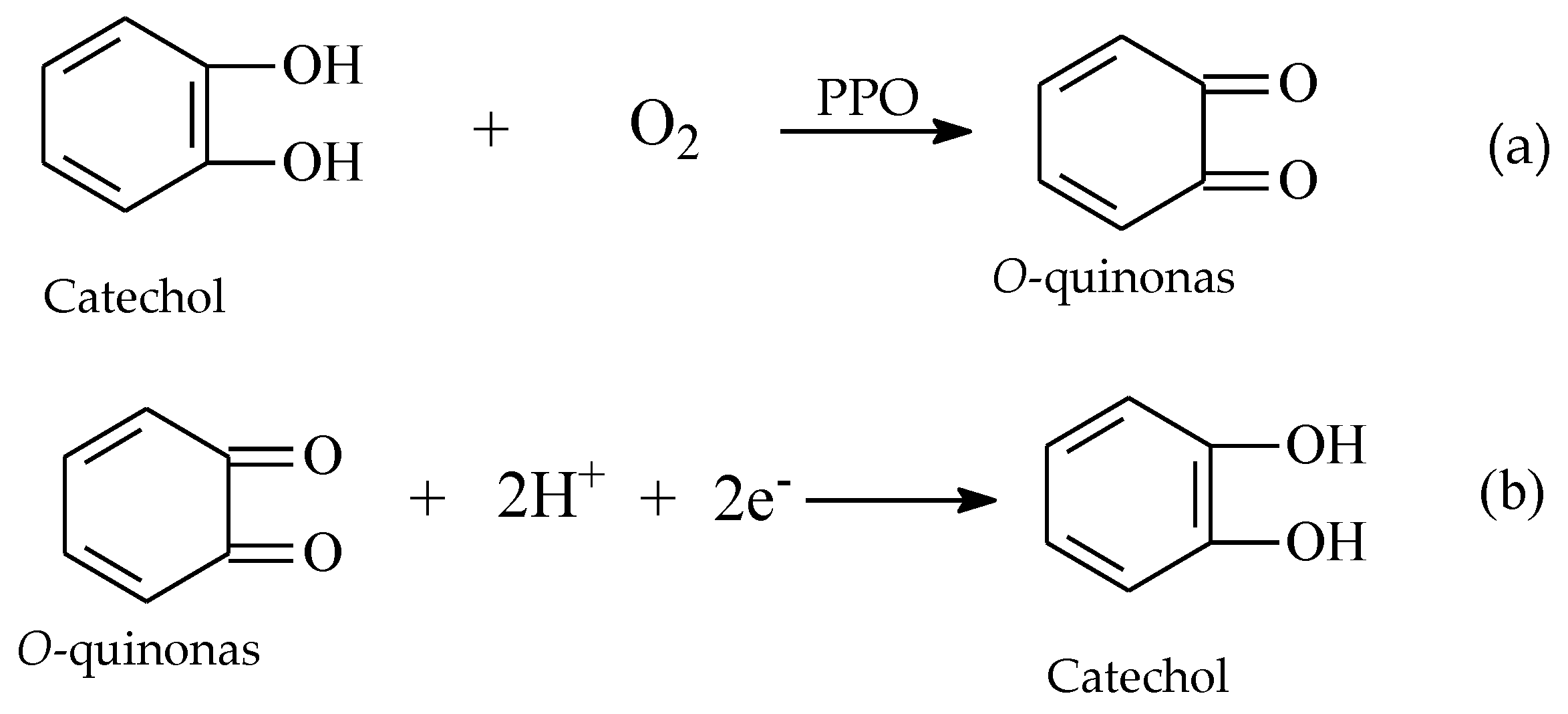
2.3. PPO Enzymatic Activity
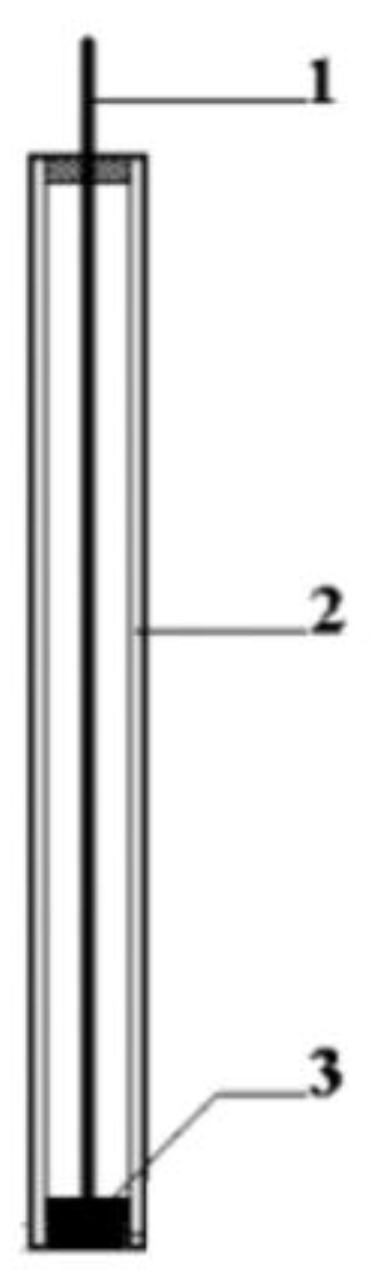
2.4. Biosensor Development
2.5. Electrochemical Analysis and Stability Assay
2.6. Analytical Curve, Limit of Detection and Recovery Test
2.7. Industrial Effluent Sample
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PPO Activity and JeEE Total Proteins
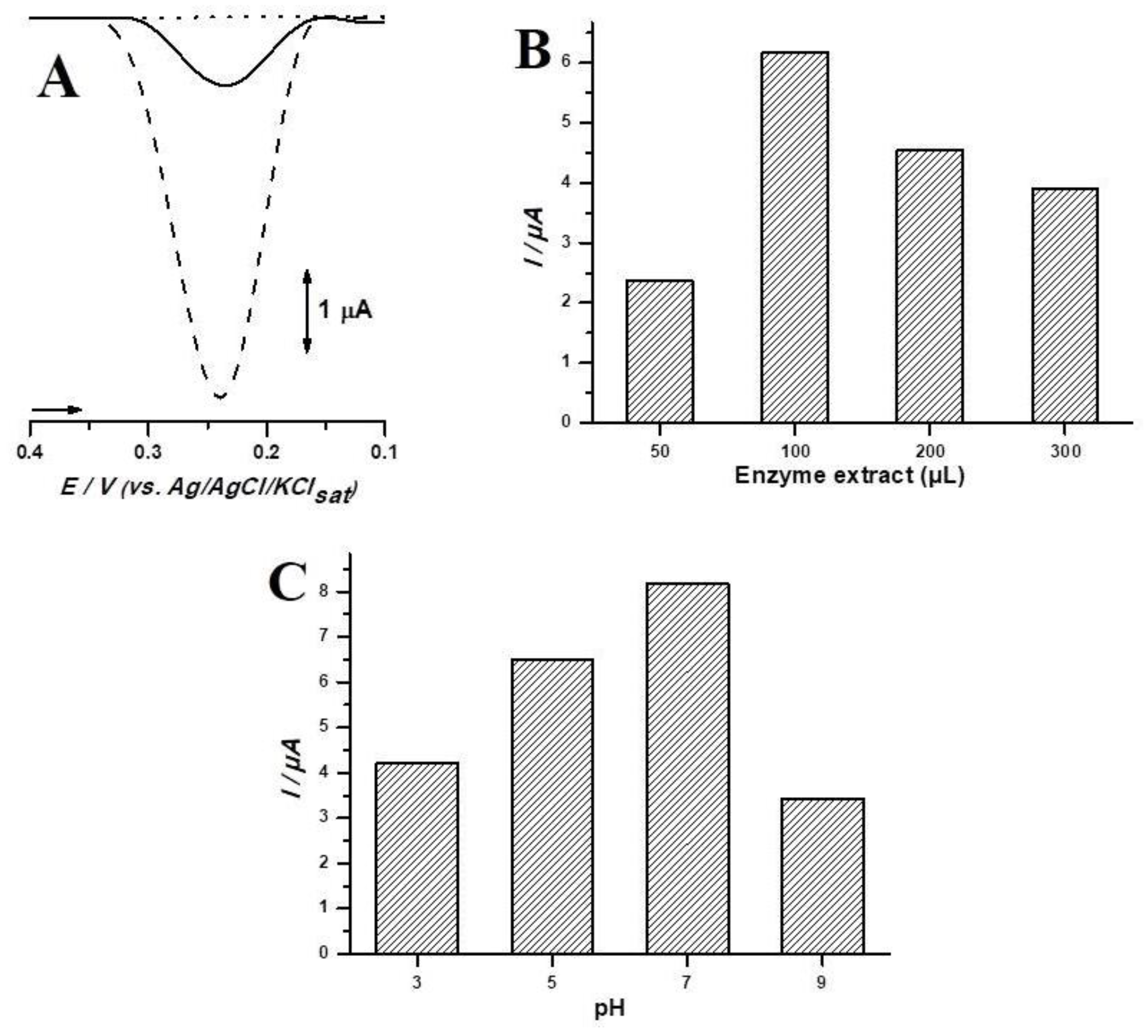
3.2. Biosensor Optimization
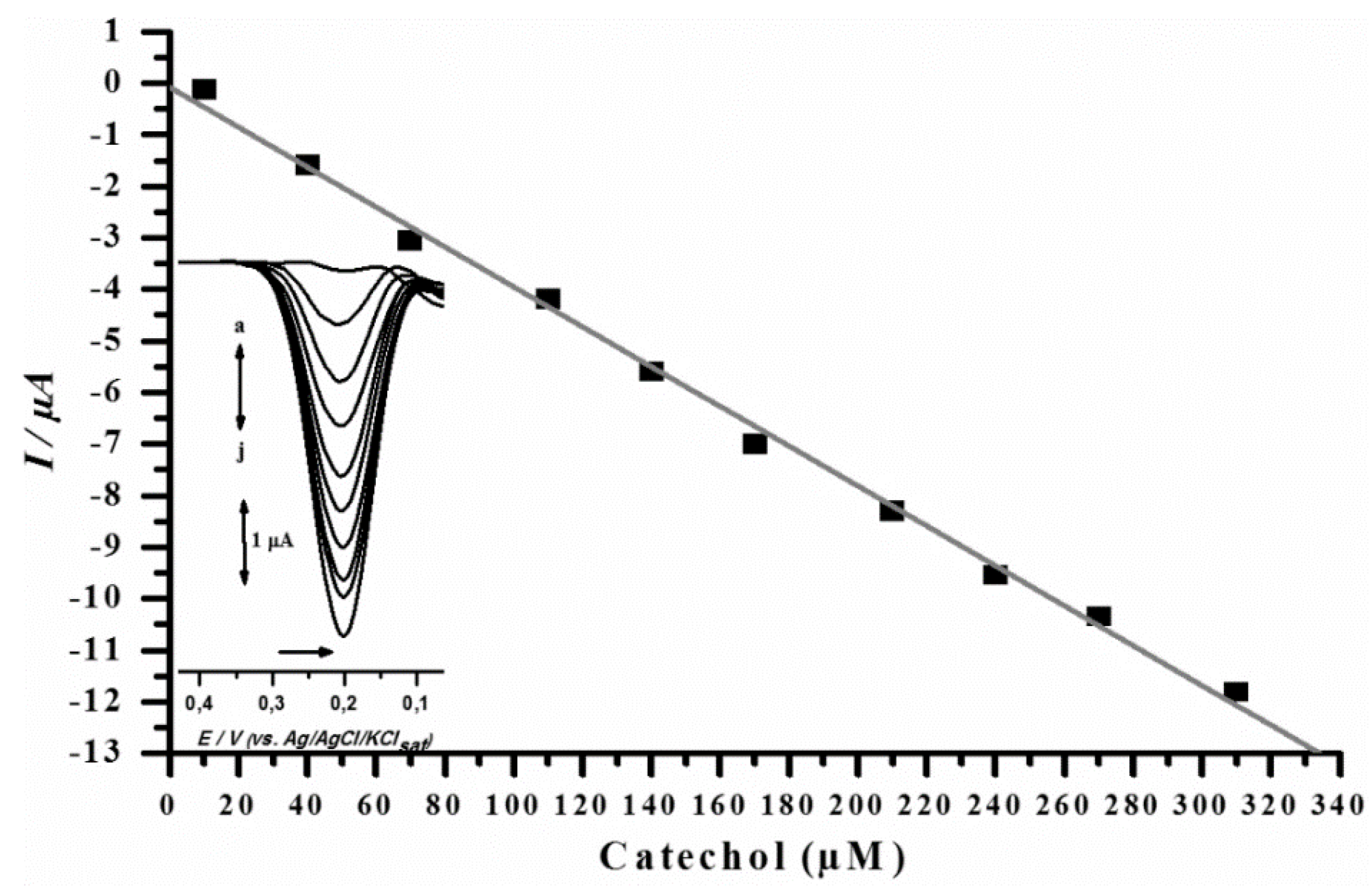
3.3. Analytical Curve for Catechol
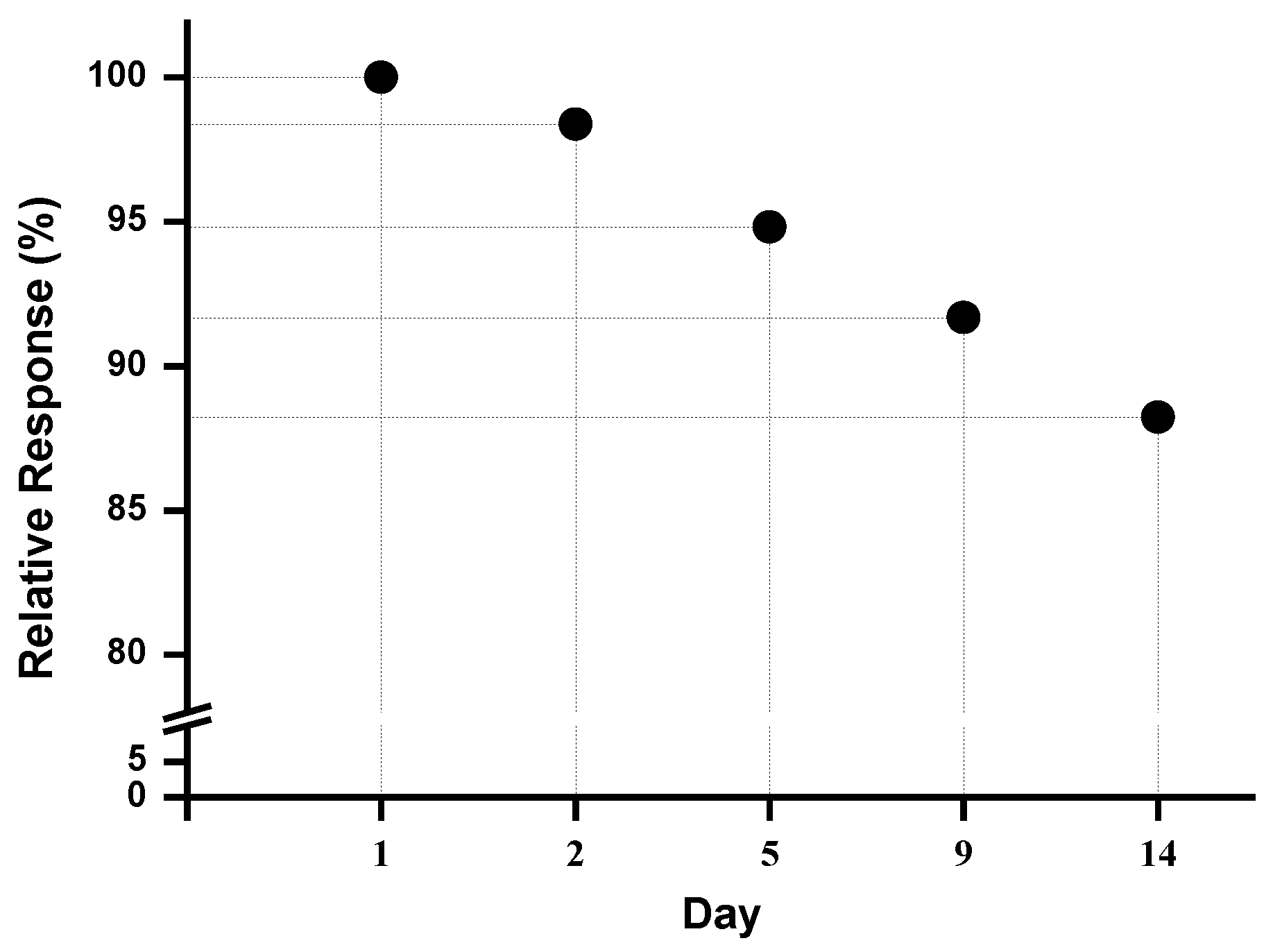
3.4. Stability Assay
3.5. Recovery Assay
3.6. Analysis of Phenolic Contaminants in the Industrial Sample
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lavilla, I.; Gil, S.; Costas, M.; Bendicho, C. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with microvolume spectrophotometry to turn green the 5530 APHA standard method for determining phenols in water and wastewater. Talanta 2012, 98, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Tian, L.; Li, Z.; Jia, L.; Zhang, X.; Xia, M.; Hu, Y. Whole-cell method for phenol detection based on the color reaction of phenol with 4-aminoantipyrine catalyzed by CotA laccase on endospore surfaces. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 69, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassiri, M.; Zahedi, M.M.; Pourmortazavi, S.M.; Yousefzade, M. Optimization of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for preconcentration and spectrophotometric determination of phenols in Chabahar Bay seawater after derivatization with 4-aminoantipyridine. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 86, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apetrei, I.M.; Apetrei, C. The biocomposite screen-printed biosensor based on immobilization of tyrosinase onto the carboxyl functionalised carbon nanotube for assaying tyramine in fish products. J. Food Eng. 2015, 149, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumana, G.; Das, M.; Srivasta, S.; Malhotra, B.D. A novel urea biosensor based on zirconia. Thin Solid Films 2010, 519, 1187–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BRASIL, Conselho Nacional de Meio Ambiente (CONAMA). Resolução RDC nº 397, 7 de Abril de 2008. Available online: http://www.mma.gov.br/port/conama/legiabre.cfm?codlegi=563 (accessed on 14 May 2018).
- Asan, A.; Isildak, I. Determination of major phenolic compounds in water by reversed-phase liquid chromatography after pre-column derivatization with benzoyl chloride. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 988, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Hu, L.; Hu, L.; Li, X.; Zou, H. Determining of phenolic compounds in river waterwith on-line coupling bisphenol A imprinted monolithic pre-column with high performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 2006, 69, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Zhao, L.; Lin, J.M. Molecularly imprinted polymer as micro-solid phase extraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography to determine phenolic compounds in environmental water samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 650, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pundir, S.; Chauhan, N.; Narang, J.; Pundir, C.S. Amperometric choline biosensor based on multiwalled carbon nanotubes/zirconium oxide nanoparticles electrodeposited on glassy carbon electrode. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 427, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, R.S.; Lopes, F.M.; Brito, A.O.; Garcia, L.F.; Sousa, D.F.; Gil, E.S. Enzimas vegetais: extração e aplicações biotecnológicas. Infarma 2017, 29, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apetrei, C.; Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L.; De Saja, J.A. Amperometrictyrosinase based biosensor using na electropolymerized phosphate-doped polypyrrole film as an immobilization support. Application for detection of phenolic compounds. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 8919–8925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Huan, S.; Shen, G.; Yu, R. A novel tyrosinase biosensor based on hydroxyapatite-chitosan nanocomposite for the detection of phenolic compounds. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 665, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, L.F.C.; Peixoto, J.V.M.; Oliveira, R.M.; Seleguini, A.; Nascimento, A.R. Propriedades físico-químicas de frutos de jurubeba de três regiões do Cerrado. Rev. Agric. Neotrop. 2015, 2, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Calas-Blanchard, C.; Istamboulié, G.; Bontoux, M.; Plantard, G.; Goetz, V.; Noguer, T. Biosensor-based real-time mornitoring of paracetamol photocatalytic degradation. Chemosphere 2015, 9, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, N.F.M.; Neto, S.Y.; Luz, R.C.S.; Damos, F.S.; Yamanaka, H. Ultrasensitive Determination of Malathion Using Acetylcholinesterase Immobilized on Chitosan-Functionalized Magnetic Iron Nanoparticles. Biosensors 2018, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terefe, N.S.; Delon, A.; Buckow, R.; Versteeg, C. Blueberry polyphenol oxidase: Characterization and the kinetics of thermal and high pressure activation and inactivation. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.F.; Benjamin, S.R.; Antunes, R.S.; Lopes, F.M.; Somerset, V.S.; Gil, E.S. Solanum melongena polyphenol oxidase biosensor for the electrochemical analysis of paracetamol. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 46, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanduri, V.; Sorokulova, I.B.; Samoylov, A.M.; Simonian, A.L.; Petrenko, V.A.; Vodyanoy, V. Phage as a molecular recognition elemento in biosensors immobilized by physical adsorption. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, H.V.S.; Noroozifar, M.; Kerman, K. Epigallocatechin Gallate-Modified Graphite Paste Electrode for Simultaneous Detection of Redox-Active Biomolecules. Sensors 2018, 18, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narang, J. A nylon membrane based amperometric biosensor for polyphenol determination. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2011, 72, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.B.; Gautam, S.; Sharma, A. Purification and characterization of polyphenol oxidase (PPO) from eggplant. Food Chem. 2012, 34, 1855–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polesel, D.N.; Sinhorini, A.L.C.; Perone, C.A.S. Caracterização cinética da enzima catecolase (Polifenoloxidase) em extratos brutos da polpa e da casca de berinjela (Solanum melongena L.). J. Health Sci. Inst. 2010, 28, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, N.M.; Abdullah, J.; Yusof, N.A.; Rashid, A.H.A.; Rahman, S.A.; Hasan, M.R. Amperometric Biosensor Based on Zirconium Oxide/Polyethylene Glycol/Tyrosinase Composite Film for the Detection of Phenolic Compounds. Biosensors 2016, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, R.S.; Garcia, L.F.; Somerset, V.S.; Gil, E.S.; Lopes, F.M. The Use of a Polyphenoloxidase Biosensor Obtained from the Fruit of Jurubeba (Solanum paniculatum L.) in the Determination of Paracetamol and Other Phenolic Drugs. Biosensors 2018, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Biosensor * | Graphite Powder (mg) | Vegetal Extract (µL) | Mineral Oil (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CP | 100 | - | 30 |
| CP-Jen50 | 100 | 50 | 30 |
| CP-Jen100 | 100 | 100 | 30 |
| CP-Jen200 | 100 | 200 | 30 |
| CP-Jen300 | 100 | 300 | 30 |
| Catechol (µM) 1 | Catechol Added (µM) 2 | Catechol Expected (µM) 3 | Catechol Recovery (µM) 4 | Catechol Recovery (%) 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 20 | 120 | 119 ± 0.93 | 95.00 |
| 100 | 30 | 130 | 127 ± 1.03 | 90.00 |
| 100 | 40 | 140 | 135 ± 0.77 | 87.50 |
| 100 | 50 | 150 | 148 ± 0.37 | 96.00 |
| 100 | 60 | 160 | 156 ± 1.22 | 93.33 |
| Method | Total Phenols (µM) (n = 4) | Student t Test |
|---|---|---|
| Spectrophotometry | 238.90 ± 0.99 | 0.15 |
| DPV using Jen100 biosensor | 240.46 ± 0.84 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antunes, R.S.; Ferraz, D.; Garcia, L.F.; Thomaz, D.V.; Luque, R.; Lobón, G.S.; Gil, E.D.S.; Lopes, F.M. Development of a Polyphenol Oxidase Biosensor from Jenipapo Fruit Extract (Genipa americana L.) and Determination of Phenolic Compounds in Textile Industrial Effluents. Biosensors 2018, 8, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8020047
Antunes RS, Ferraz D, Garcia LF, Thomaz DV, Luque R, Lobón GS, Gil EDS, Lopes FM. Development of a Polyphenol Oxidase Biosensor from Jenipapo Fruit Extract (Genipa americana L.) and Determination of Phenolic Compounds in Textile Industrial Effluents. Biosensors. 2018; 8(2):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8020047
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntunes, Rafael Souza, Denes Ferraz, Luane Ferreira Garcia, Douglas Vieira Thomaz, Rafael Luque, Germán Sanz Lobón, Eric De Souza Gil, and Flávio Marques Lopes. 2018. "Development of a Polyphenol Oxidase Biosensor from Jenipapo Fruit Extract (Genipa americana L.) and Determination of Phenolic Compounds in Textile Industrial Effluents" Biosensors 8, no. 2: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8020047
APA StyleAntunes, R. S., Ferraz, D., Garcia, L. F., Thomaz, D. V., Luque, R., Lobón, G. S., Gil, E. D. S., & Lopes, F. M. (2018). Development of a Polyphenol Oxidase Biosensor from Jenipapo Fruit Extract (Genipa americana L.) and Determination of Phenolic Compounds in Textile Industrial Effluents. Biosensors, 8(2), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8020047








