Comparison of Electrochemical Immunosensors and Aptasensors for Detection of Small Organic Molecules in Environment, Food Safety, Clinical and Public Security
Abstract
:1. Introduction
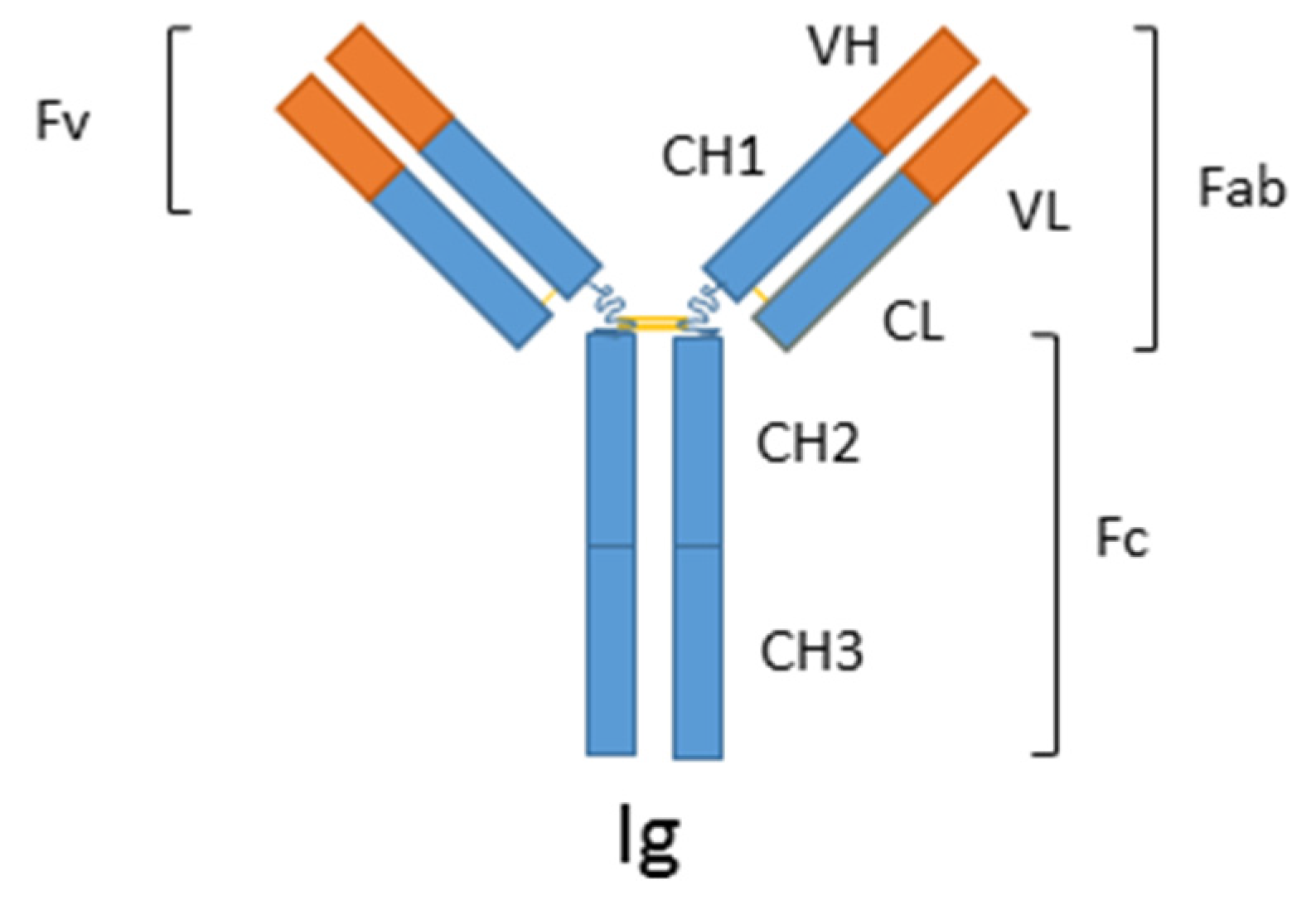
1.1. Immunosensors
1.2. Aptasensors
1.3. Peptide Sensors
2. Substances and Receptors
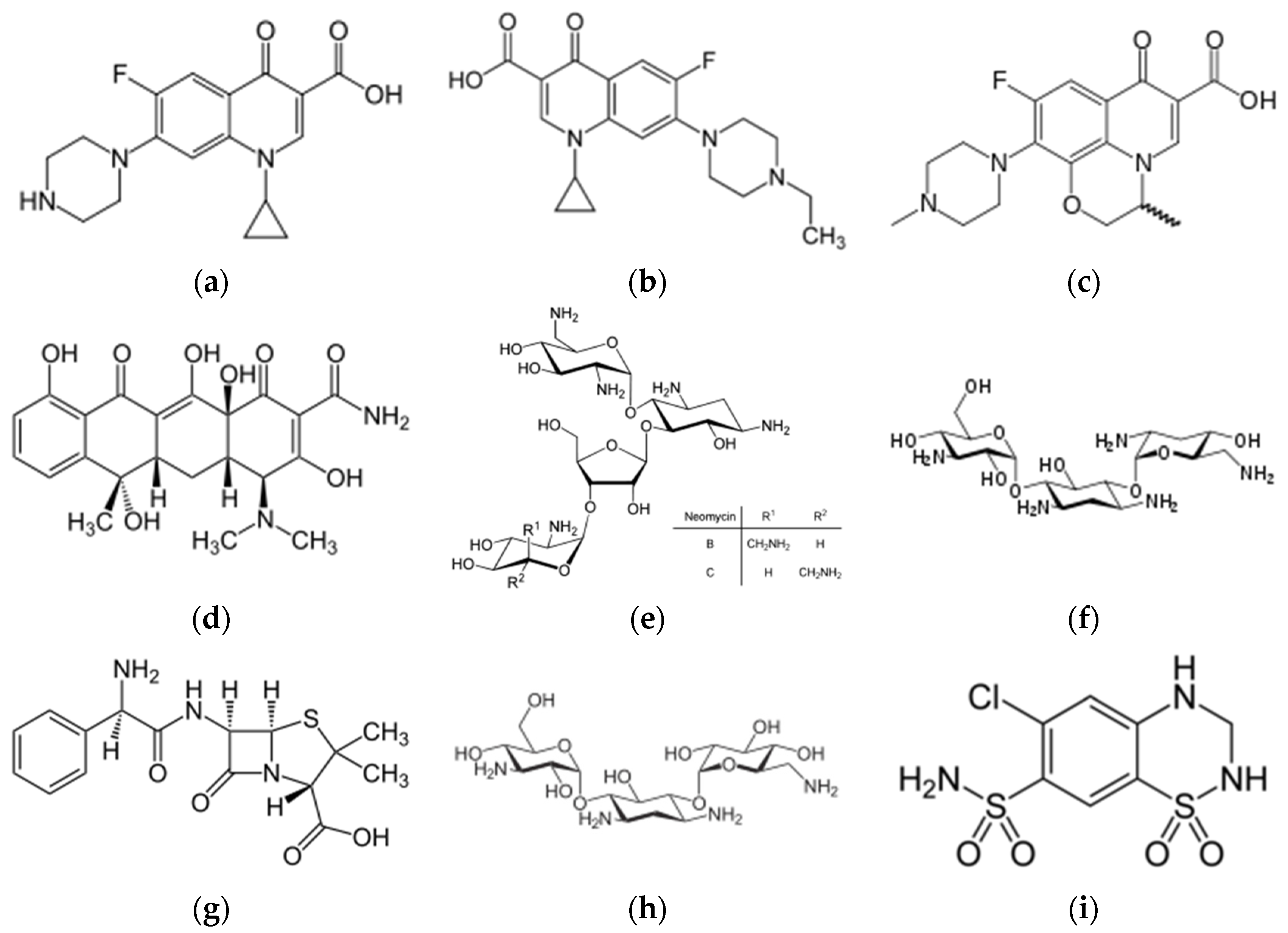
2.1. Antibiotics
2.1.1. Antibodies
2.1.2. Aptamers
2.2. Bisphenol A
2.2.1. Antibodies
2.2.2. Aptamers
2.2.3. Peptides
2.3. Cocaine
2.3.1. Antibodies
2.3.2. Aptamers
2.4. Ochratoxin A
2.4.1. Antibodies
2.4.2. Aptamers
2.4.3. Peptides
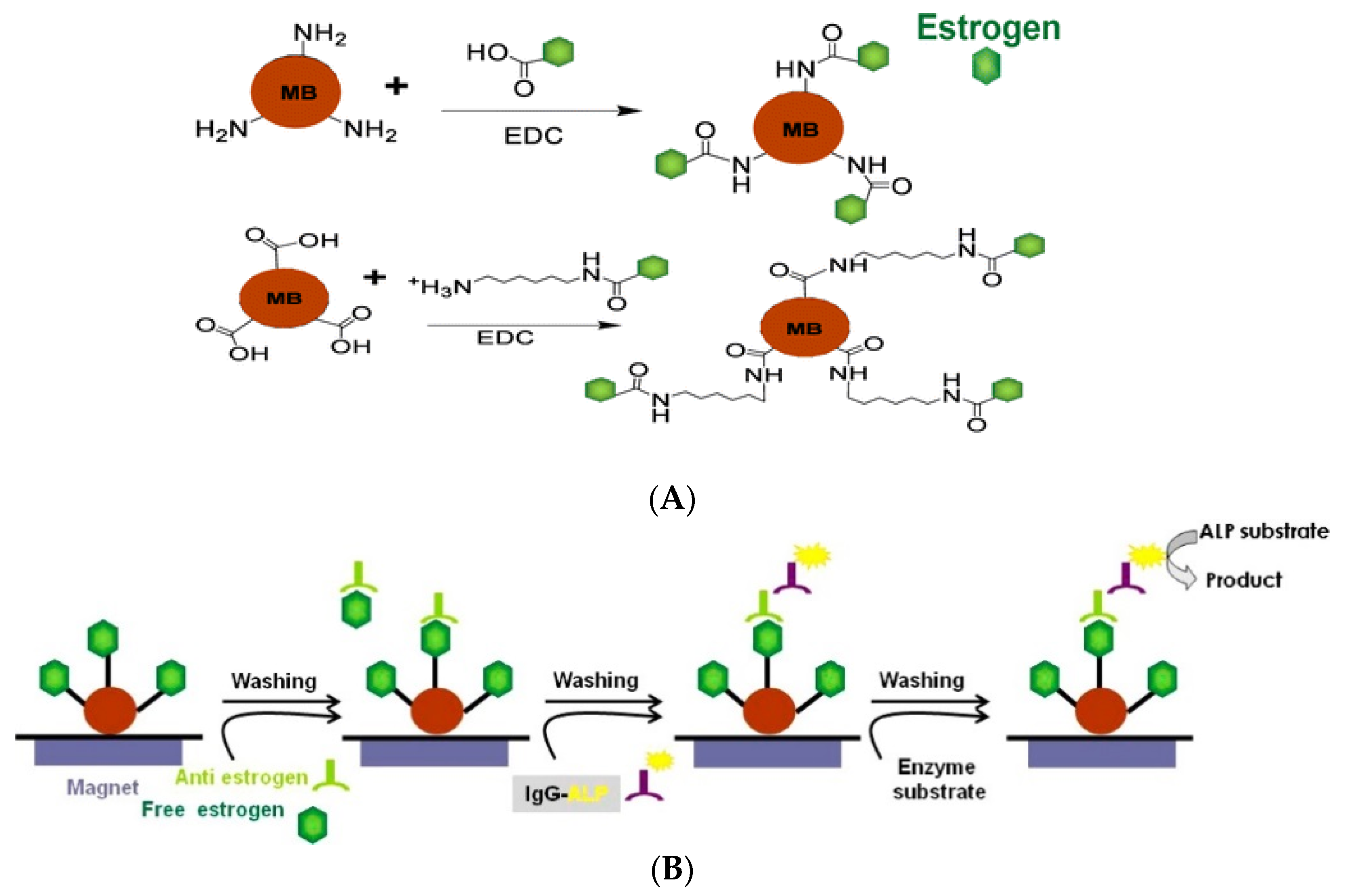
2.5. Estradiol
2.5.1. Antibodies
2.5.2. Aptamers
3. Conclusions and Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarma, V.R.; Silverton, E.W.; Davies, D.R.; Terry, W.D. The three-dimensional structure at 6 A resolution of a human gamma Gl immunoglobulin molecule. J. Biol. Chem. 1971, 246, 3753–3759. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Silverton, E.W.; Navia, M.A.; Davies, D.R. Three-dimensional structure of an intact human immunoglobulin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 5140–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antibodies-Online. Avaible online: http://xww.antibodies-online.com (accessed on 26 February 2016).
- Mascini, M.; Palchetti, I.; Tombelli, S. Nucleic Acid and Peptide Aptamers: Fundamentals and Bioanalytical Aspects. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1316–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
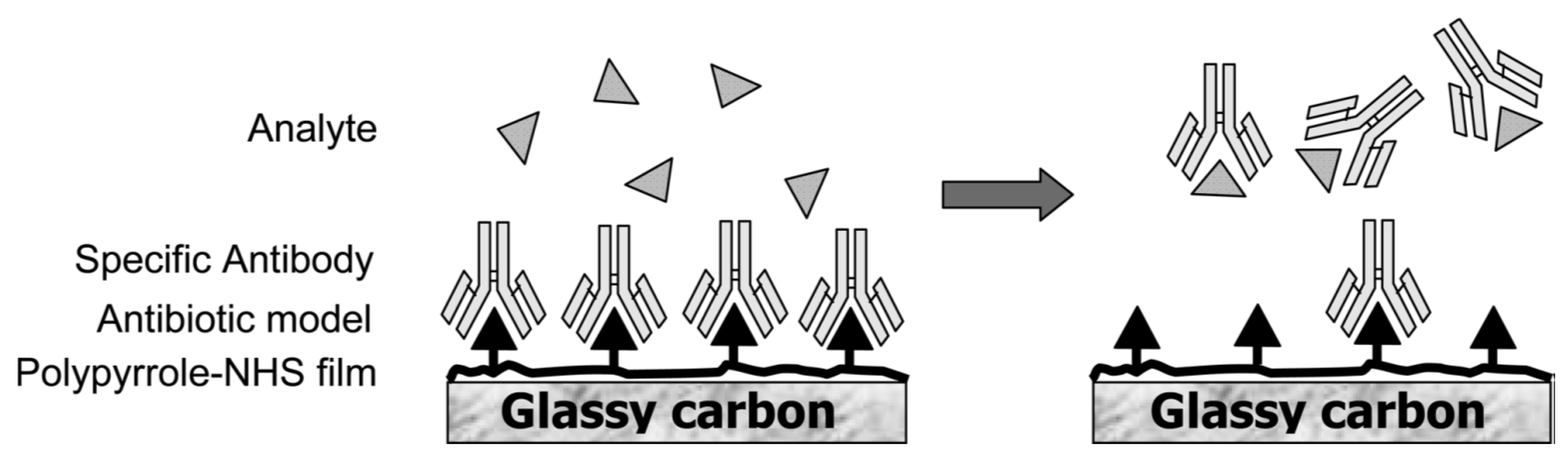
- Garifallou, G.Z.; Tsekenis, G.; Davis, F.; Higson, S.P.J.; Millner, P.A.; Pinacho, D.G.; Sanchez-Baeza, F.; Marco, M.P.; Gibson, T.D. Labeless immunosensor assay for fluoroquinolone antibiotics based upon an AC impedance protocol. Anal. Lett. 2007, 40, 1412–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, R.E.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Bouffier, L.; Gondran, C.; Cosnier, S.; Pinacho, D.G.; Marco, M.P.; Sanchez-Baeza, F.J.; Healy, T.; Martelet, C. Impedimetric immunosensor for the specific label free detection of ciprofloxacin antibiotic. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 23, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giroud, F.; Gorgy, K.; Gondran, C.; Cosnier, S.; Pinacho, D.G.; Marco, M.P.; Sánchez-Baeza, F.J. Impedimetric immunosensor based on a polypyrrole-antibiotic model film for the label-free picomolar detection of ciprofloxacin. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 8405–8409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.C.; Lin, C.H.; Wang, W.S. Development of an enrofloxacin immunosensor based on label-free electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Talanta 2009, 79, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, S.; Liu, Y.; Lin, M.; Kang, J.; Sun, Y.; Lei, H. A dual amplified electrochemical immunosensor for ofloxacin: Polypyrrole film-Au nanocluster as the matrix and multi-enzyme-antibody functionalized gold nanorod as the label. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 90, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacco, E.; Adrian, J.; Galve, R.; Marco, M.P.; Alegret, S.; Pividori, M.I. Electrochemical magneto immunosensing of antibiotic residues in milk. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2184–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centi, S.; Stoica, A.I.; Laschi, S.; Mascini, M. Development of an Electrochemical Immunoassay Based on the Use of an Eight-Electrodes Screen-Printed Array Coupled with Magnetic Beads for the Detection of Antimicrobial Sulfonamides in Honey. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conzuelo, A.F.; Gamella, M.; Campuzano, S.; Reviejo, A.J.; Pingarrón, J.M. Disposable amperometric magneto-immunosensor for direct detection of tetracyclines antibiotics residues in milk. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 737, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conzuelo, F.; Campuzano, S.; Gamella, M.; Pinacho, D.G.; Reviejo, A.J.; Marco, M.P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Integrated disposable electrochemical immunosensors for the simultaneous determination of sulfonamide and tetracycline antibiotics residues in milk. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 50, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Que, X.; Chen, X.; Fu, L.; Lai, W.; Zhuang, J.; Chen, G.; Tang, D. Platinum-catalyzed hydrogen evolution reaction for sensitive electrochemical immunoassay of tetracycline residues. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2013, 704, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Niazi, J.H.; Gu, M.B. Specific detection of oxytetracycline using DNA aptamer-immobilized interdigitated array electrode chip. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 634, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Niazi, J.H.; Gu, M.G. Electrochemical aptasensor for tetracycline detection. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2010, 33, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Li, D.J.; Gai, L.; Wang, J.P.; Li, Y.B. Electrochemical aptasensor for the detection of tetracycline with multi-walled carbon nanotubes amplification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 162, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Yao, D.; Xie, C.; Liu, D. Development of an aptasensor for electrochemical detection of tetracycline. Food Control 2014, 42, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Guo, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, X. Electrochemical Aptasensor Based on Prussian Blue-Chitosan-Glutaraldehyde for the Sensitive Determination of Tetracycline. Nano-Micro Lett. 2014, 6, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
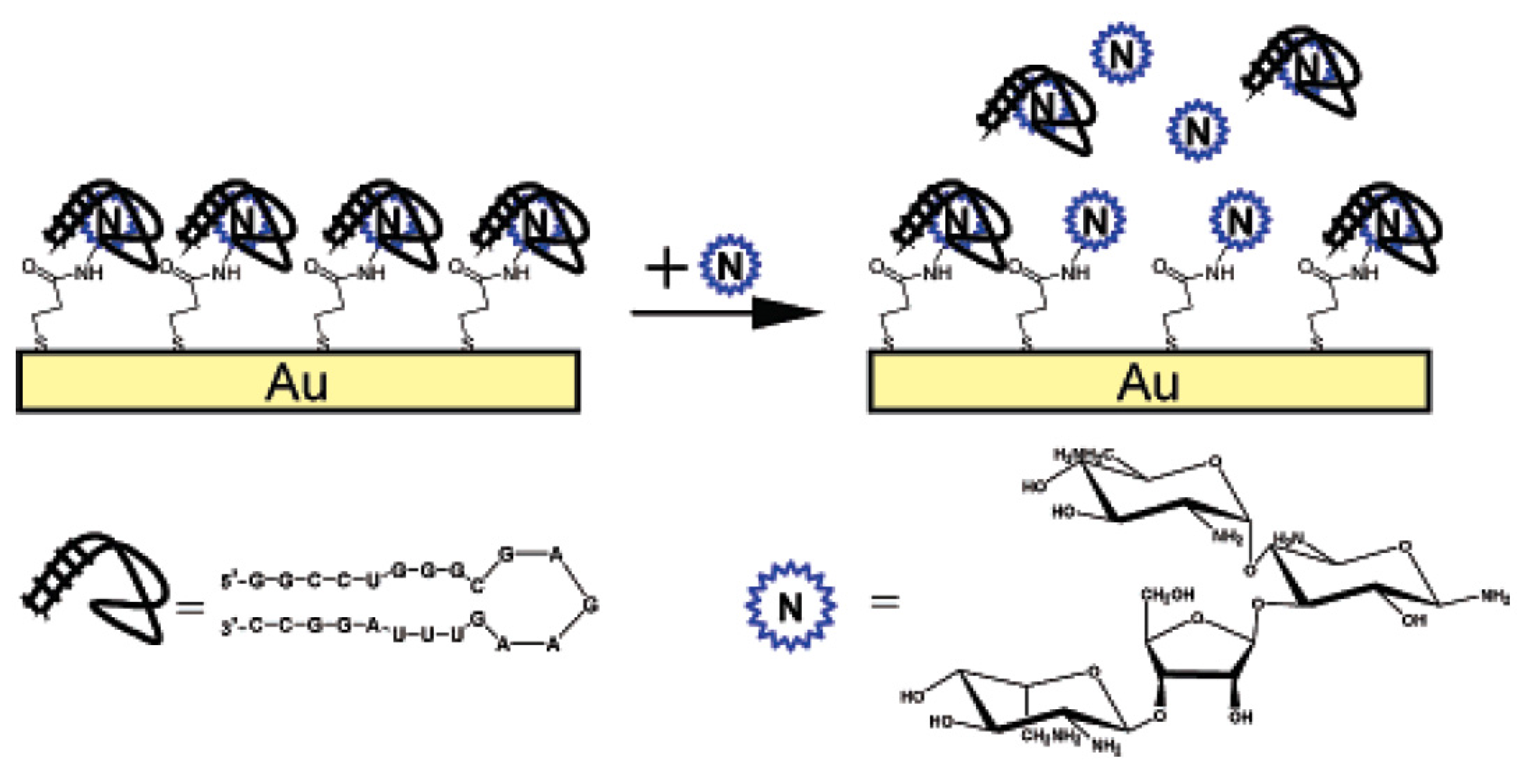
- De-los-Santos-Álvarez, N.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Tuñón-Blanco, P. Modified-RNA aptamer-based sensor for competitive impedimetric assay of neomycin B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 3808–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, A.A.; Miller, E.A.; Plaxco, K.W. Reagentless Measurement of Aminoglycoside Antibiotics in Blood Serum via an Electrochemical, Ribonucleic Acid Aptamer-Based Biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7090–7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wagan, S.; Morris, M.D.; Taylor, J.; White, R.J. Achieving Reproducible Performance of Electrochemical, Folding Aptamer-Based Sensors on Microelectrodes: Challenges and Prospects. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 11417–11424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Fernández, E.; de-los-Santos-Álvarez, N.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Tuñón-Blanco, P. Aptamer-Based Inhibition Assay for the Electrochemical Detection of Tobramycin Using Magnetic Microparticles. Electroanalysis 2011, 23, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fernández, E.; de-los-Santos-Álvarez, N.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J. Monovalent labeling system improves the sensitivity of aptamer-based inhibition assays for small molecule detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 182, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chandra, P.; Song, K.M.; Ban, C.; Shim, Y.B. Label-free detection of kanamycin based on the aptamer-functionalized conducting polymer/gold nanocomposite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 36, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daprà, J.; Lauridsen, L.H.; Nielsen, A.T.; Rozlosnik, N. Comparative study on aptamers as recognition elements for antibiotics in a label-free all-polymer biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 43, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragavan, K.V.; Rastogi, N.K.; Thakur, M.S. Sensors and biosensors for analysis of bisphenol-A. TRAC Trend Anal. Chem. 2013, 52, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Shiddiky, M.J.A.; Park, J.S.; Shim, Y.B. An impedimetric immunosensor for the label-free detection of bisphenol A. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2464–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, M.H.; Noh, H.B.; Rahman, M.A.; Won, M.S.; Shim, Y.B. Label-Free Detection of Bisphenol A Using a Potentiometric Immunosensor. Electroanalysis 2008, 20, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Reisberg, S.; Serradji, N.; Anquetin, G.; Pham, M.C.; Wu, W.; Dong, C.Z.; Piro, B. E-assay concept: Detection of bisphenol A with a label-free electrochemical competitive immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 53, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, F.; Wu, J.J.; Chu, H.Q.; Mei, Z.L.; Ye, Y.K.; Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Peng, C.F.; Zheng, L.; Chen, W. Electrochemical aptasensor for the determination of bisphenol A in drinking water. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Li, Y. An electrochemical aptasensor based on gold nanoparticles dotted graphene modified glassy carbon electrode for label-free detection of bisphenol A in milk samples. Food Chem. 2014, 162, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Kim, S.E.; Cho, M.; Yoo, I.K.; Choe, W.S.; Lee, Y. Highly sensitive and selective determination of bisphenol-A using peptide-modified gold electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.S.; Jang, J.R.; Choe, W.S.; Yoo, P.J. Electrochemical detection of Bisphenol A with high sensitivity and selectivity using recombinant protein-immobilized graphene electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, C.G.; Eremenko, A.V.; Kühn, A.; Kürzinger, K.; Makower, A.; Scheller, F.W. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 4624–4630.
- Suleiman, A.A.; Xu, Y.H. An amperometric immunosensor for cocaine. Electroanalysis 1998, 10, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Pan, J.Y.; Hua, W.J.; Tu, Y.F. An approach for the preparation of highly sensitive electrochemical impedimetric immunosensors for the detection of illicit drugs. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 726, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, S.A.; Kauffmann, J.M.; Zuman, P. Electrochemical Biosensors for Drug Analysis. In Electroanalysis in Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences; Springer: Verlag/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 141–186. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, B.R.; Lai, R.Y.; Wood, M.S.; Doctor, E.H.; Heeger, A.J.; Plaxco, K.W. An Electronic, Aptamer-Based Small-Molecule Sensor for the Rapid, Label-Free Detection of Cocaine in Adulterated Samples and Biological Fluids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 3138–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, X.; Xiao, Y.; Plaxco, K.W. High Specificity, Electrochemical Sandwich Assays Based on Single Aptamer Sequences and Suitable for the Direct Detection of Small-Molecule Targets in Blood and Other Complex Matrices. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6944–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golub, E.; Pelossof, G.; Freeman, R.; Zhang, H.; Willner, I. Electrochemical, Photoelectrochemical, and Surface Plasmon Resonance Detection of Cocaine Using Supramolecular Aptamer Complexes and Metallic or Semiconductor Nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 9291–9298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Chen, C.; Yin, J.; Li, B.; Zhou, M.; Dong, S.; Wang, E. Solid-State Probe Based Electrochemical Aptasensor for Cocaine: A Potentially Convenient, Sensitive, Repeatable, and Integrated Sensing Platform for Drugs. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 1556–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, B.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, R. Aptamer/quantum dot-based simultaneous electrochemical detection of multiple small molecules. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 688, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, M.; Li, P.; Li, L.; Huang, L.; Zhao, X.; Feng, Y.; Yang, Y. Quantum dots as immobilized substrate for electrochemical detection of cocaine based on conformational switching of aptamer. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2011, 662, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.W.; Zhang, F.T.; Cui, Y.R.; Deng, Q.P.; Krause, S.; Zhou, Y.L.; Zhang, X.X. A label-free aptasensor for the sensitive and specific detection of cocaine using supramolecular aptamer fragments/target complex by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Talanta 2012, 92, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roushani, M.; Shahdost-fard, F. A highly selective and sensitive cocaine aptasensor based on covalent attachment of the aptamer-functionalized AuNPs onto nanocomposite as the support platform. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 853, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roushani, M.; Shahdost-fard, F. A novel ultrasensitive aptasensor based on silver nanoparticles measured via enhanced voltammetric response of electrochemical reduction of riboflavin as redox probe for cocaine detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Xiang, Y. Highly sensitive electrochemical detection of cocaine on graphene/AuNP modified electrode via catalytic redox-recycling amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 32, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.W.; Sun, C.J.; Zhang, F.T.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Y.L.; Zhang, X.X. An electrochemical aptasensor based on enzyme linked aptamer assay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 31, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Li, J.; Cheng, W.; Yan, Y.; Tang, R.; Li, Y.; Ju, H.; Ding, S. Electrochemical aptasensor for highly sensitive determination of cocaine using a supramolecular aptamer and rolling circle amplification. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Simon, B.; Campas, M.; Marty, J.L.; Noguer, T. Novel highly-performing immunosensor-based strategy for ochratoxin A detection in wine samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radi, A.E.; Munoz-Berbel, X.; Cortina-Puig, M.; Marty, J.L. An electrochemical immunosensor for ochratoxin A based on immobilization of antibodies on diazonium-functionalized gold electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 2180–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radi, A.E.; Munoz-Berbel, X.; Lates, V.; Marty, J.L. Label-free impedimetric immunosensor for sensitive detection of ochratoxin A. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 1888–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamfir, L.G.; Geana, I.; Bourigua, S.; Rotariu, L.; Bala, C.; Errachid, A.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Highly sensitive label-free immunosensor for ochratoxin A based on functionalized magnetic nanoparticles and EIS/SPR detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 159, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heurich, M.; Abdul Kadir, M.K.; Tothill, I.E. An electrochemical sensor based on carboxymethylated dextran modified gold surface for ochratoxin A analysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 156, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrouda, A.; Sbartai, A.; Bessueille, F.; Renaud, L.; Maaref, A.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Electrically addressable deposition of diazonium functionalized antibodies on boron-doped diamond microcells for the detection of ochratoxin A. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 2444–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Gao, P.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Ma, H.; Du, B.; Wei, Q. Label-free photoelectrochemical immunosensor for sensitive detection of Ochratoxin A. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, H.; Chen, W.; Xu, D.; Xu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, L.; Chu, H.; Peng, C.; Xu, C.; Zhu, S. Fabricated aptamer-based electrochemical “signal-off” sensor of ochratoxin A. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakar, N.; Matharu, Z.; Malhotra, B.D. Polyaniline Langmuir–Blodgett film based aptasensor for ochratoxin A detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4006–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, P.; Zhang, L.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. Simply amplified electrochemical aptasensor of Ochratoxin A based on exonuclease-catalyzed target recycling. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 29, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, S. An electrochemical biosensor based on hairpin-DNA aptamer probe and restriction endonuclease for ochratoxin A detection. Electrochem. Commun. 2012, 25, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, A.; Andreescu, S.; Marty, J.L. Design of PEG-aptamer two piece macromolecules as convenient and integrated sensing platform: Application to the label-free detection of small size molecules. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 45, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazin, I.; Andreotti, N.; Hassine, A.I.; De Waard, M.; Sabatier, J.M.; Gonzalez, C. Peptide binding to ochratoxin A mycotoxin: A new approach in conception of biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heurich, M.; Altintas, Z.; Tothill, I.E. Computational Design of Peptide Ligands for Ochratoxin A. Toxins 2013, 5, 1202–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleri, R.; Demey, H.; Tria, S.A.; Guiseppi-Elie, A.; Hassine, A.I.; Gonzalez, C.; Bazin, I. Peptide conjugated chitosan foam as a novel approach for capture-purification and rapid detection of hapten—Example of ochratoxin A. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padeste, C.; Grubelnik, A.; Tiefenauer, L. Amperometric immunosensing using microperoxidase MP-11 antibody conjugates. Anal. Chim. Acta 1998, 374, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramitz, H.; Matsuda, M.; Thomas, J.H.; Sugawara, K.; Tanaka, S. Electrochemical immunoassay at a 17 beta-estradiol self-assembled monolayer electrode using a redox marker. Analyst 2003, 128, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pemberton, R.M.; Mottram, T.T.; Hart, J.P. Development of a screen-printed carbon electrochemical immunosensor for picomolar concentrations of estradiol in human serum extracts. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2005, 63, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, D.; Guilbault, G.G. Disposable amperometric immunosensor for the detection of 17-beta estradiol using screen-printed electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 113, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, G.; Fares, G.; Quadri, F.; delli Draisci, R.; Ferretti, G.; Marchiafava, C.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G. A disposable immunosensor for detection of 17beta-estradiol in non-extracted bovine serum. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 572, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wong, D.K.Y. Picogram-detection of estradiol at an electrochemical immunosensor with a gold nanoparticle vertical bar Protein G-(LC-SPDP)-scaffold. Talanta 2009, 77, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Duckworth, P.A.; Wong, D.K.Y. Square wave voltammetry versus electrochemical impedance spectroscopy as a rapid detection technique at electrochemical immunosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, N.A.; Schneider, R.J.; Messina, G.A.; Raba, J. Modified paramagnetic beads in a microfluidic system for the determination of ethinylestradiol (EE2) in river water samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1376–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.K.; Li, J.; Im, J.E.; Ahn, K.S.; Park, T.S.; Cho, S.I.; Kim, Y.R.; Lee, W.Y. Impedometric estrogen biosensor based on estrogen receptor alpha-immobilized gold electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2012, 671, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Feng, H.; Liu, X.; Wong, D.K.Y. Detection of estradiol at an electrochemical immunosensor with a Cu UPD vertical bar DTBP-Protein G scaffold. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 35, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojeda, I.; Lopez-Montero, J.; Moreno-Guzman, M.; Janegitz, B.C.; Gonzalez-Cortes, A.; Yanez-Sedeno, P.; Pingarron, J.M. Electrochemical immunosensor for rapid and sensitive determination of estradiol. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 743, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanso, H.; Barthelmebs, L.; Inguimbert, N.; Noguer, T. Immunosensors for Estradiol and Ethinylestradiol Based on New Synthetic Estrogen Derivatives: Application to Wastewater Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 2397–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaisuwan, N.; Xu, H.; Wu, G.; Liu, J. A highly sensitive differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry for determination of 17 beta-estradiol (E2) using CdSe quantum dots based on indirect competitive immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 46, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, S.; Yu, J.; Lian, W.; Cui, M.; Xu, W.; Huang, J. Electrochemical immunosensor based on graphene-polyaniline composites and carboxylated graphene oxide for estradiol detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, T.; Yan, L.; Wei, Q.; Du, B. An ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for determination of estradiol using coralloid Cu2S nanostructures as labels. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 6512–6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Du, B.; Li, H.; Xin, X.; Ma, H.; Wu, D.; Yan, L.; Wei, Q. Metal ions-based immunosensor for simultaneous determination of estradiol and diethylstilbestrol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 52, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monerris, M.J.; Arévalo, F.J.; Fernández, H.; Zon, M.A.; Molina, P.G. Development of a very sensitive electrochemical immunosensor for the determination of 17β-estradiol in bovine serum samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 208, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olowu, R.A.; Arotiba, O.; Mailu, S.N.; Waryo, T.T.; Baker, P.; Iwuoha, E. Electrochemical Aptasensor for Endocrine Disrupting 17 beta-Estradiol Based on a Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxylthiopene)-Gold Nanocomposite Platform. Sensors 2010, 10, 9872–9890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Q.; Qiu, B.; Cai, Z.; Chen, G. Label-free aptamer-based electrochemical impedance biosensor for 17 beta-estradiol. Analyst 2012, 137, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.J.; Liu, Y.J.; Shi, G.W.; Yang, X.R.; Liu, Y.M. Label-free aptamer sensor for 17 beta-estradiol based on vanadium disulfide nanoflowers and Au nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 201, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, H.; Liu, M.; Zhuang, L.; Li, Z.; Fan, L.; Zhao, G. A Fetomolar Level 17 beta-estradiol Electrochemical Aptasensor Constructed On Hierachical Dendritic Gold Modified Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 137, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Alsager, O.A.; Kumar, S.; Hodgkiss, J.M.; Travas-Sejdic, J. Label-free electrochemical aptasensor for femtomolar detection of 17 beta-estradiol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 70, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Zhao, G.; Shi, H.; Liu, M. A simple and label-free aptasensor based on nickel hexacyanoferrate nanoparticles as signal probe for highly sensitive detection of 17β-estradiol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, G.C.; Eissa, S.; Ng, A. Aptamer-Based Label-Free Impedimetric Biosensor for Detection of Progesterone. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



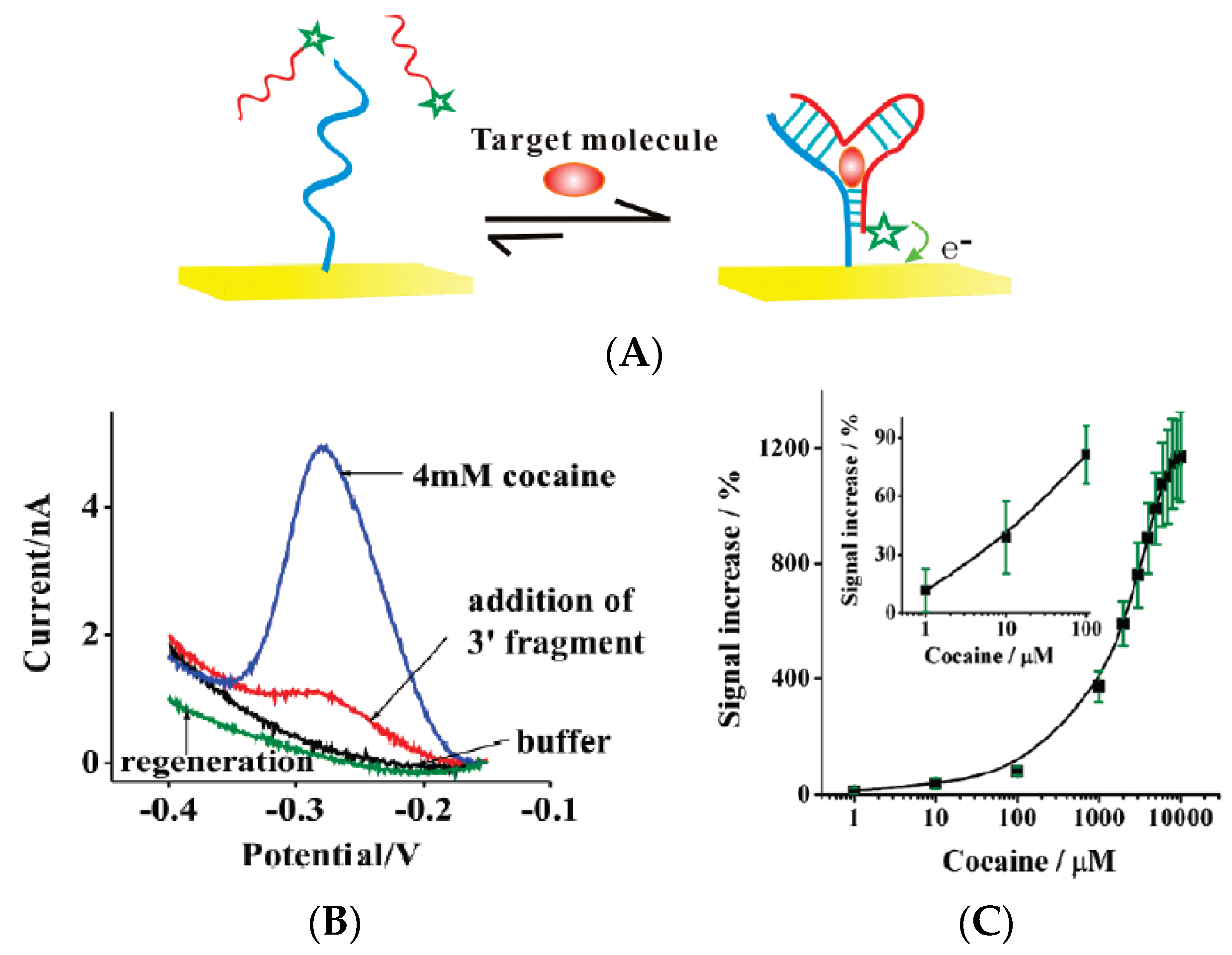
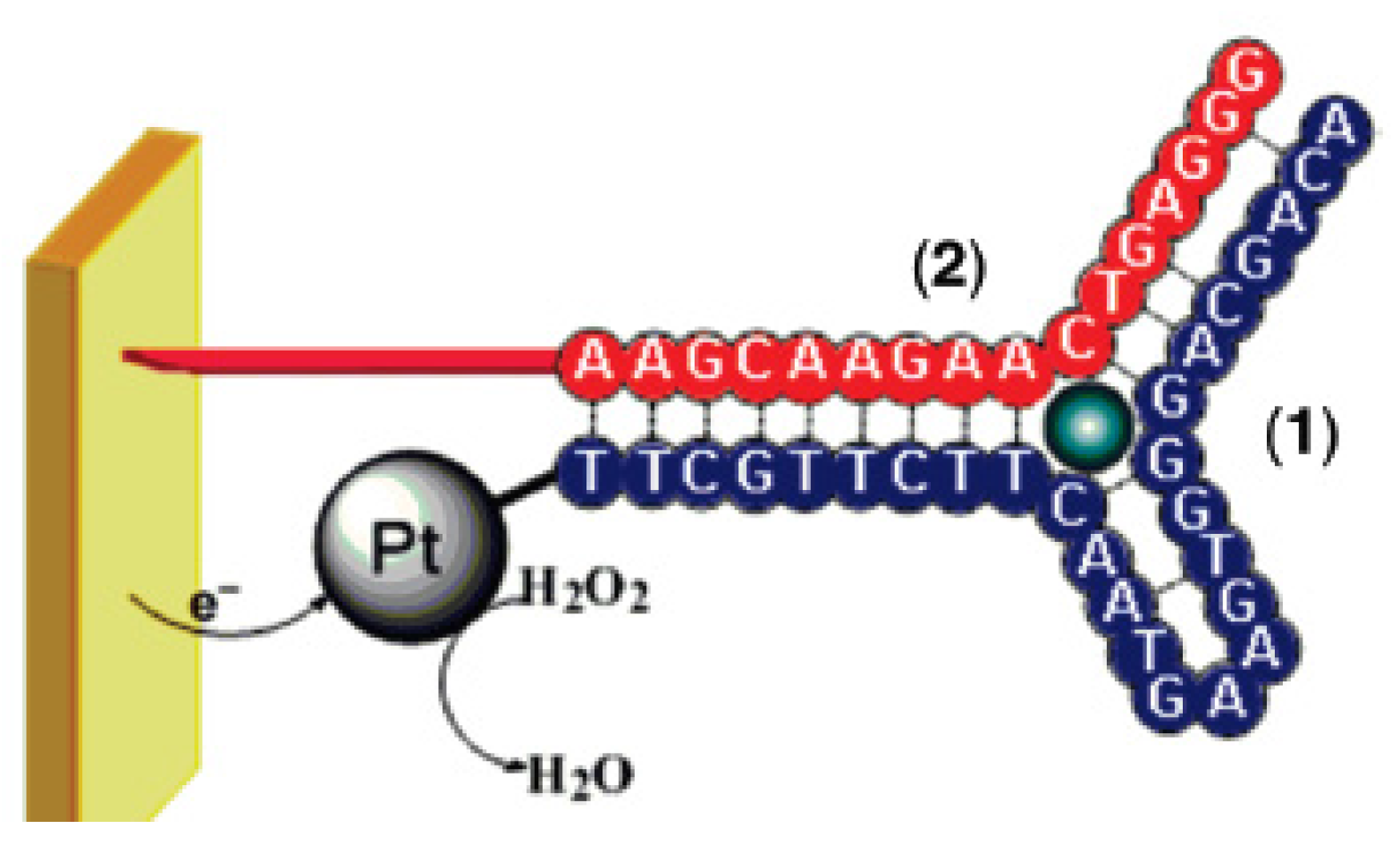
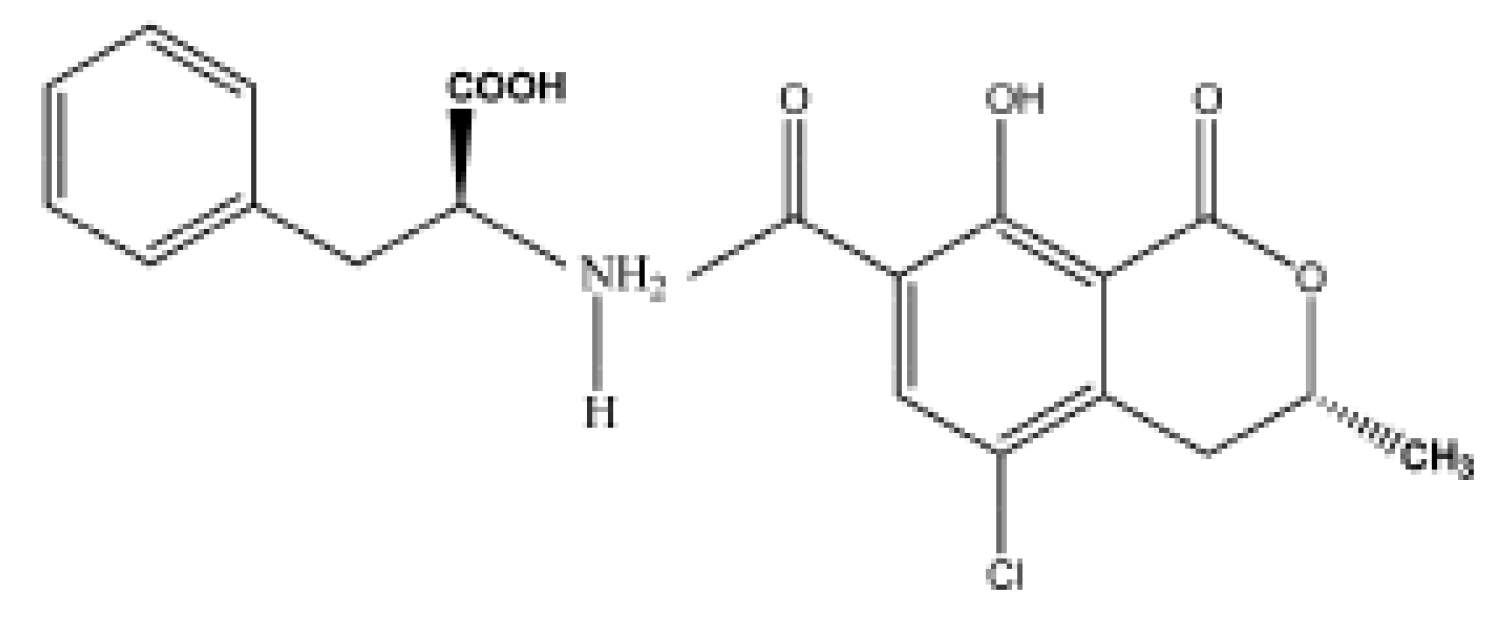
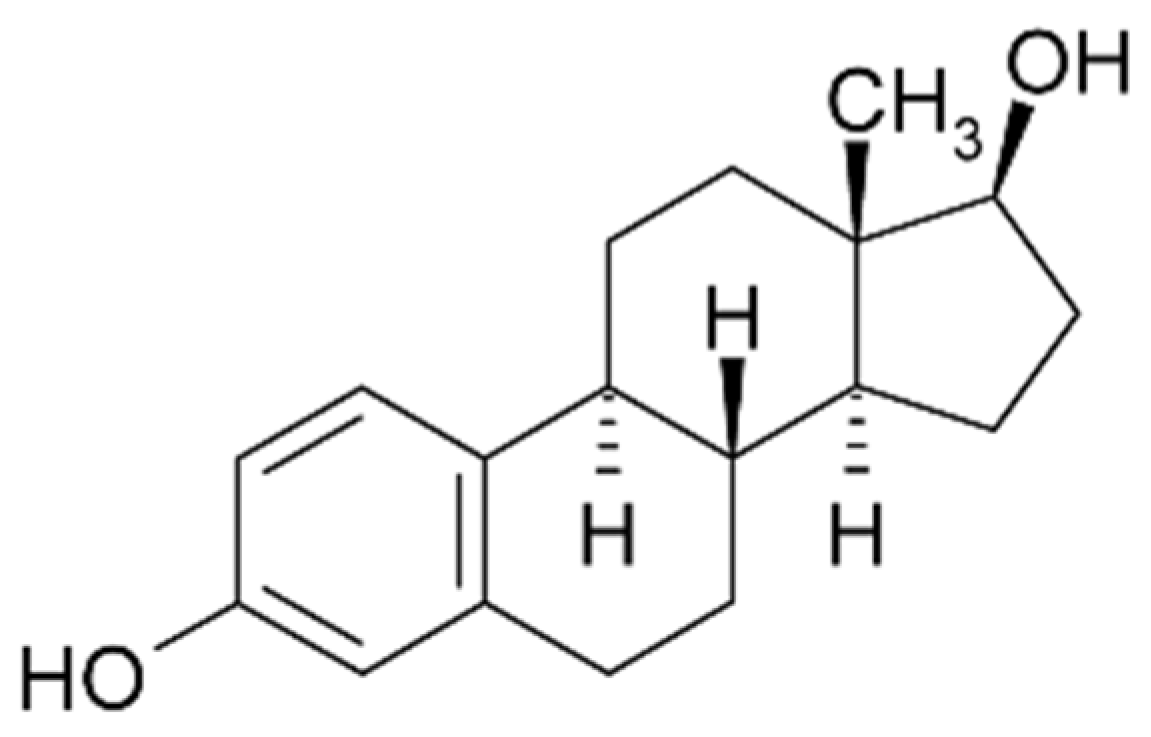
| Targets | Bioreceptors | LoD | Transduction & Analytical Methods | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF | Ab | 3 nM | EIS | [5] |
| CF | Ab | 30 pM | EIS | [6] |
| CF | Ab | 3 nM | EIS | [7] |
| CF | Ab | 3 nM | SAM/EIS | [8] |
| OFL | Ab | 0.1 nM | HRP/AuNPs/PPy/CV | [9] |
| SA | Ab | 6 nM | MBs/HRP/CV | [10] |
| TC | Ab | 4 nM | MBs/HRP/CV | [11] |
| TC | Ab | 1 nM | HRP/HQ/CV | [12] |
| TC | Ab | 13 pM | Platinum-catalyzed HER/CV | [14] |
| TC | Aptamer | 1 nM | Fe(CN)63−/4−/CV | [15] |
| TC | Aptamer | 10 nM | Fe(CN)63−/4−/CV/SWV | [16] |
| TC | Aptamer | 5 pM | CNTs/Fe(CN)63−/4−/DPV | [17] |
| TC | Aptamer | 2 nM | EIS | [18] |
| TC | Aptamer | 0.3 nM | PB/DPV | [19] |
| NEO | Aptamer | 1 μM | EIS | [20] |
| TOB | Aptamer | 2 μM | MB label/CV | [21] |
| TOB | Aptamer | 1 mM | AuNPs/MB label/CV | [22] |
| TOB | Aptamer | 5 μM | MBs/AlkP/CV | [23] |
| TOB | Aptamer | 0.1 μM | MBs/AlkP/CV | [24] |
| KAN | Aptamer | 10 nM | AuNPs/CV | [25] |
| KAN AMP | Aptamer Aptamer | 10 nM 100 pM | PEDOT/EIS PEDOT/EIS | [26] [26] |
| Bioreceptors | LoD | Transduction and Analytical Methods | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ab | 1.3 nM | Conducting polymer & EIS | [28,29] |
| Ab | 9 pM | Conducting polymer & SWV | [30] |
| Aptamer | 1 pM | Fe(CN)63−/4/EIS | [31] |
| Aptamer | 5 nM | Graphene/Fe(CN)63−/4/DPV | [32] |
| Peptide | 1 nM | SAM/Fe(CN)63−/4/DPV | [33] |
| Peptide | 100 fM | Graphene oxide/EIS | [34] |
| Bioreceptors | LoD | Transduction and Analytical Methods | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ab | 380 pM | AlkP-Ab/CV | [35] |
| Ab | 0.1 μM | HRP-Ab/CV | [36] |
| Ab | 33 fM | SAM/EIS | [37] |
| Aptamer | 10 μM | MB-labeled/CV | [39] |
| Aptamer | 1 μM | Two-strand aptamer/SWV | [40] |
| Aptamer | 1 μM | PtNPs-aptamer/H2O2/CV | [41] |
| Aptamer | 0.1 μM | Label-free/Two-strand aptamer/CV | [42] |
| Aptamer | 50 nM | Two-strand aptamer/QDs | [43] |
| Aptamer | 1 nM | Two-strand aptamer/QDs | [44] |
| Aptamer | 100 nM | Two-strand aptamer/EIS/[Fe(CN)6]3−/4− | [45] |
| Aptamer | 100 pM | Two-strand aptamer/AuNPs/DPV/[Fe(CN)6]3−/4− | [46] |
| Aptamer | 150 pM | Two-strand aptamer/AgNPs/CV/riboflavin | [47] |
| Aptamer | 1 nM | Two-strand aptamer/AlkP/CV | [48] |
| Aptamer | 20 nM | Two-strand aptamer/HRP/CV | [49] |
| Aptamer | 1 nM | RCA/AlkP/DPV | [50] |
| Bioreceptors | LoD | Transduction and Analytical Methods | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ab | 0.8 nM | AlkP- or HRP-Ab/CV | [51] |
| Ab | 30 nM | HRP/TMB/chronoamperometry | [52] |
| Ab | 1.3 nM | HRP/TMB/EIS | [53] |
| Ab | 25 pM | MBs/EIS | [54] |
| Ab | 0.12 nM | HRP/TMB/EIS | [55] |
| Ab | 17 pM | BDD/EIS | [56] |
| Ab | 5 pM | CdSe/TiO2/PEC | [57] |
| Aptamer | 80 pM | Multiple stem/MB-DNA/CV | [58] |
| Aptamer | 0.25 nM | LB/PANI/EIS | [59] |
| Aptamer | 2.5 pM | Fc-labeled aptamer/exonuclease/CV | [60] |
| Aptamer | 1 pM | HRP-labeled aptamer/exonuclease/CV | [61] |
| Aptamer | 0.3 pM | Fe(CN)63−/4−/EIS | [62] |
| Bioreceptors | LoD | Transduction and Analytical Methods | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ab | 0.1 nM | SAM/BQ/CV | [67] |
| Ab | 0.2 nM | AlkP-estradiol/DPV | [68] |
| Ab | 0.9 pM | AlkP-estradiol/amperometry | [69] |
| Ab | 0.15 nM | AlkP-estradiol/amperometry | [70] |
| Ab | 20 pM | AuNPs/HRP/BQ/CV | [71] |
| Ab | 65 pM | AuNPs/Protein G/[Fe(CN)6]3−/4−/SWV | [72] |
| Ab | 95 pM | AuNPs/Protein G/[Fe(CN)6]3−/4−/EIS | [72] |
| Ab | 1 pM | MBs/HRP-estradiol | [73] |
| Ab | 0.1 pM | HRP-estradiol/Catechol/CV | [74] |
| Ab | 45 pM | Protein G/Fc-MeOH/SWV | [75] |
| Ab | 2.8 pM | PABA/BQ | [76] |
| Ab | 3.6 pM | MBs/AlkP-αIgG/SWV | [77] |
| Ab | 0.2 nM | CdSe QDs/dissolution (SWASV) | [78] |
| Ab | 75 pM | Graphene/HRP-GO | [79] |
| Ab | 28 pM | Cu2S NPs/CV | [80] |
| Ab | 55 fM | Pb2+, Cd2+/porous Fe3O4/SWASV | [81] |
| Ab | 3 pM | AuNPs | [82] |
| Aptamer | 0.1 nM | PEDOT/AuNPs/Biot-Avidin/[Fe(CN)6]3−/4−/CV-SWV | [83] |
| Aptamer | 2 pM | SAM/Au/[Fe(CN)6]3−/4−/EIS | [84] |
| Aptamer | 1 pM | VS2/[Fe(CN)6]3−/4−/DPV | [85] |
| Aptamer | 5 fM | Au/BDD/[Fe(CN)6]3−/4−/EIS | [86] |
| Aptamer | 1 fM | Nanoporous electrode/[Fe(CN)6]3−/4−/EIS | [87] |
| Aptamer | 1 pM | Ni3+,Fe(CN)6]3−/AuNPs | [88] |
| Aptamer | 3 nM | SAM/Au/[Fe(CN)6]3−/4−/EIS | [89] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piro, B.; Shi, S.; Reisberg, S.; Noël, V.; Anquetin, G. Comparison of Electrochemical Immunosensors and Aptasensors for Detection of Small Organic Molecules in Environment, Food Safety, Clinical and Public Security. Biosensors 2016, 6, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6010007
Piro B, Shi S, Reisberg S, Noël V, Anquetin G. Comparison of Electrochemical Immunosensors and Aptasensors for Detection of Small Organic Molecules in Environment, Food Safety, Clinical and Public Security. Biosensors. 2016; 6(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6010007
Chicago/Turabian StylePiro, Benoit, Shihui Shi, Steeve Reisberg, Vincent Noël, and Guillaume Anquetin. 2016. "Comparison of Electrochemical Immunosensors and Aptasensors for Detection of Small Organic Molecules in Environment, Food Safety, Clinical and Public Security" Biosensors 6, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6010007
APA StylePiro, B., Shi, S., Reisberg, S., Noël, V., & Anquetin, G. (2016). Comparison of Electrochemical Immunosensors and Aptasensors for Detection of Small Organic Molecules in Environment, Food Safety, Clinical and Public Security. Biosensors, 6(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6010007






