Recent Advances in Fluorescent Arylboronic Acids for Glucose Sensing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
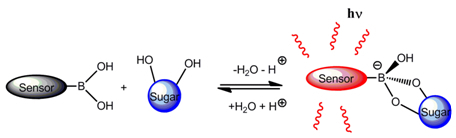
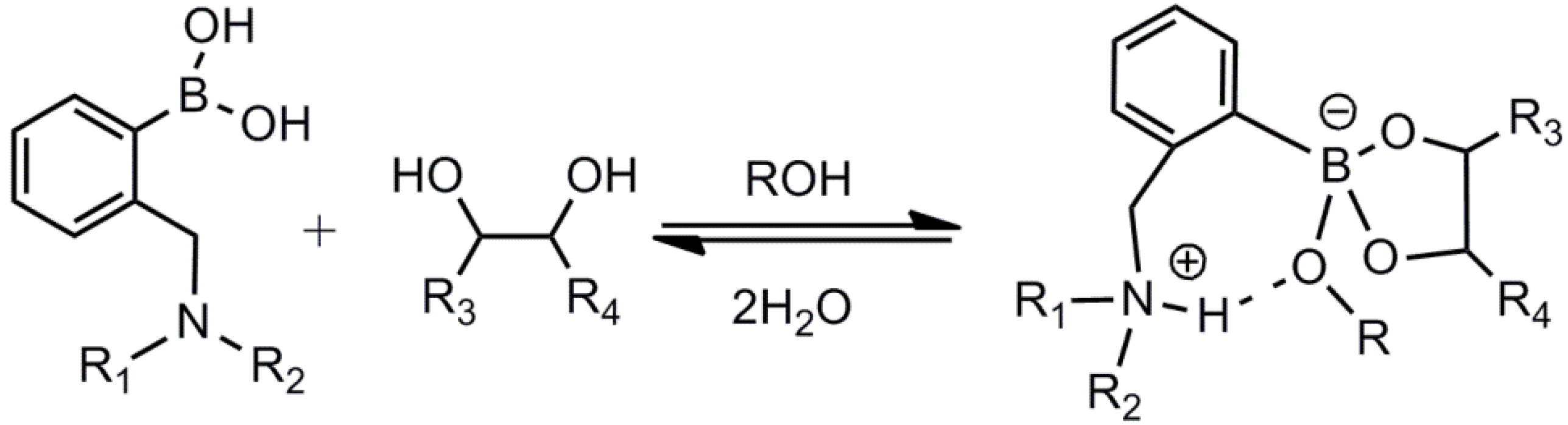
2. Fluorescent Arylboronic Acid Sensors
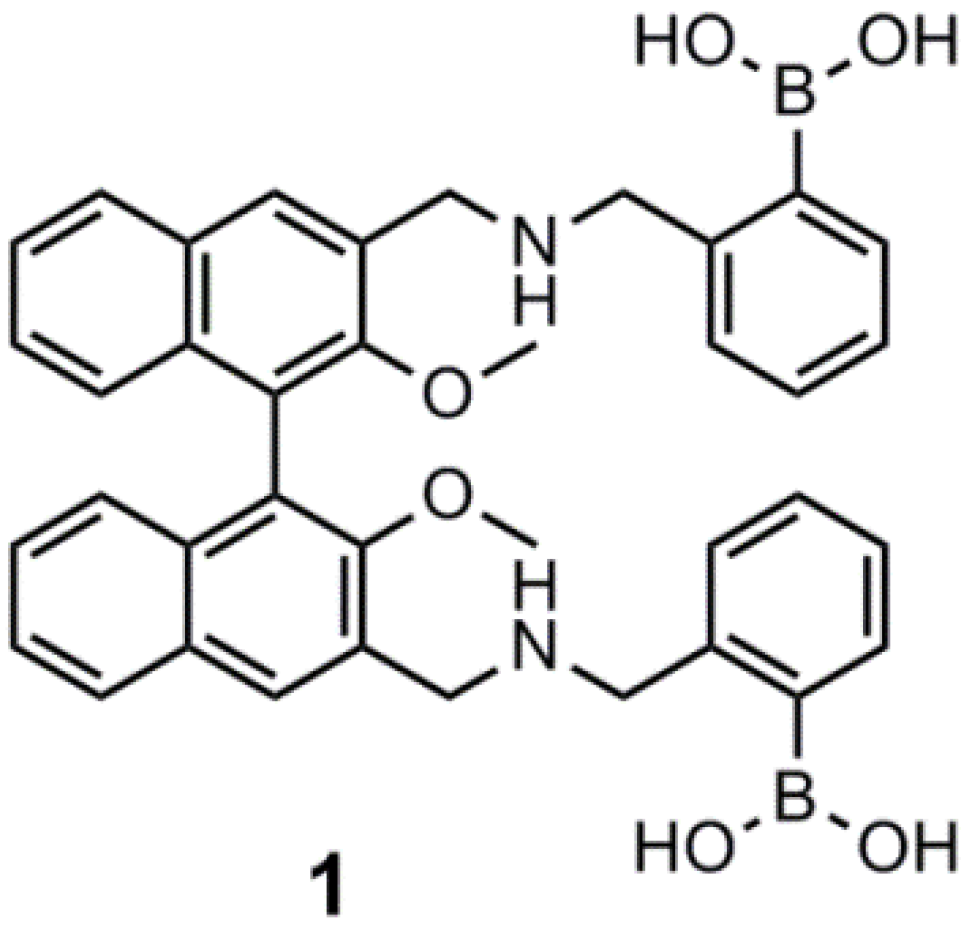
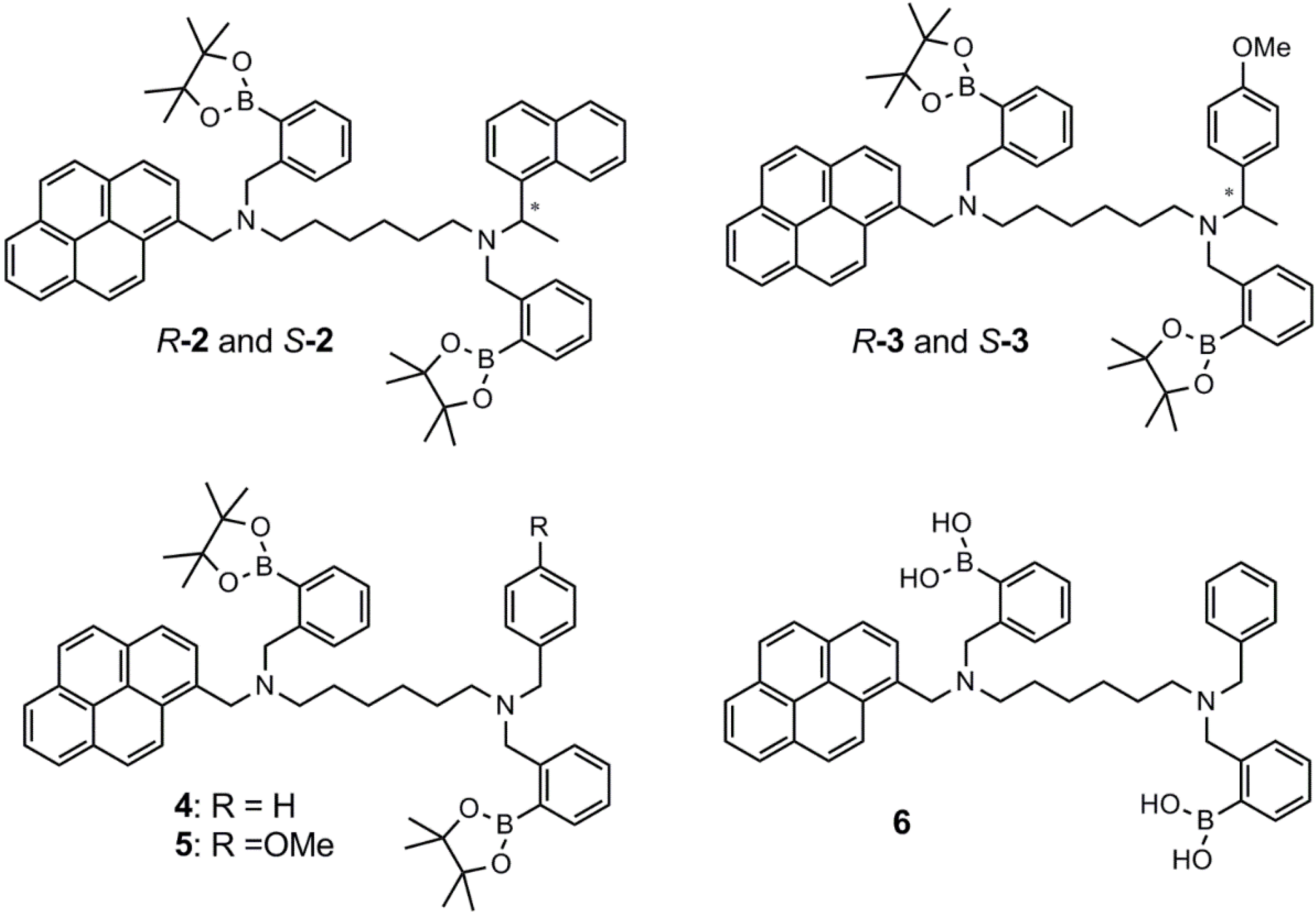
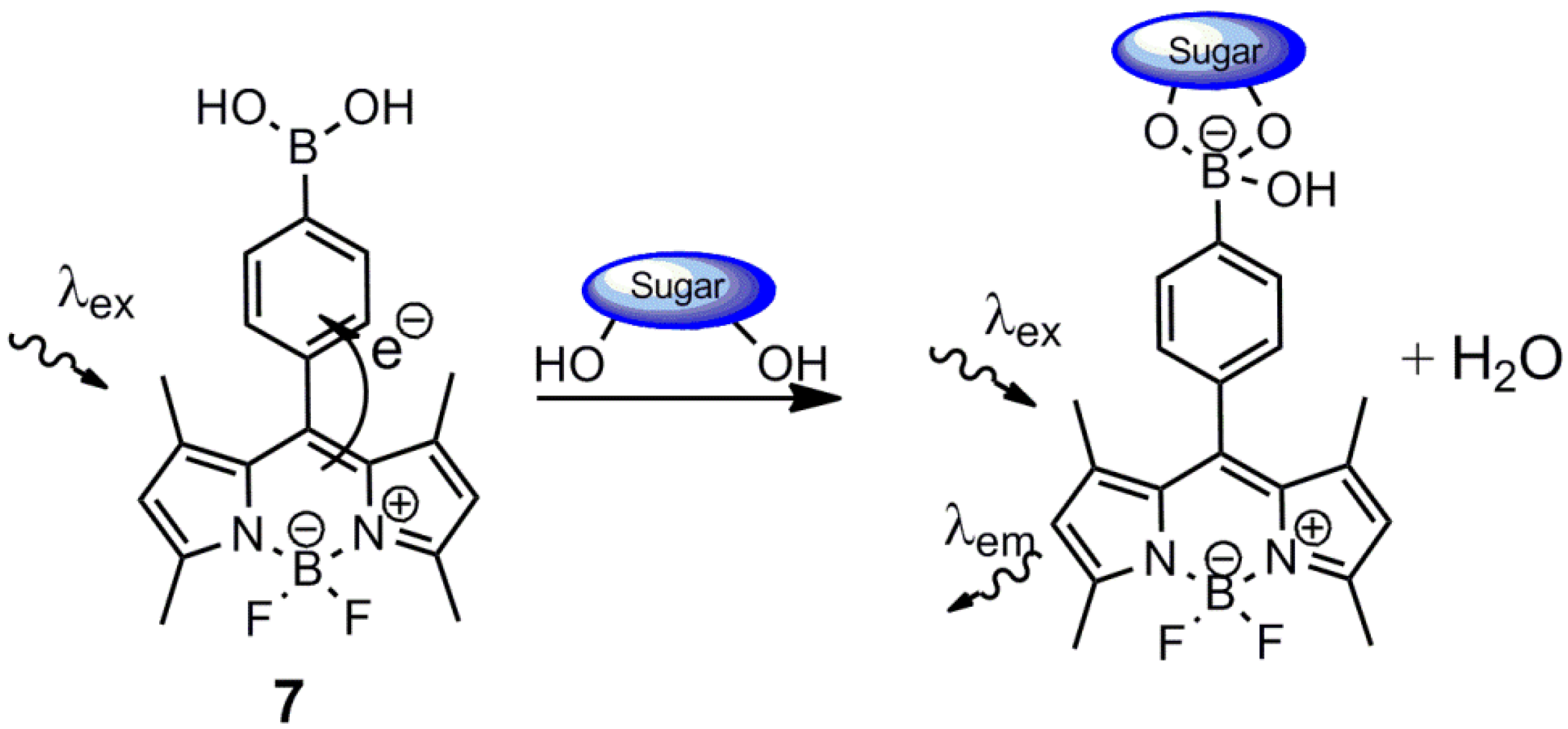
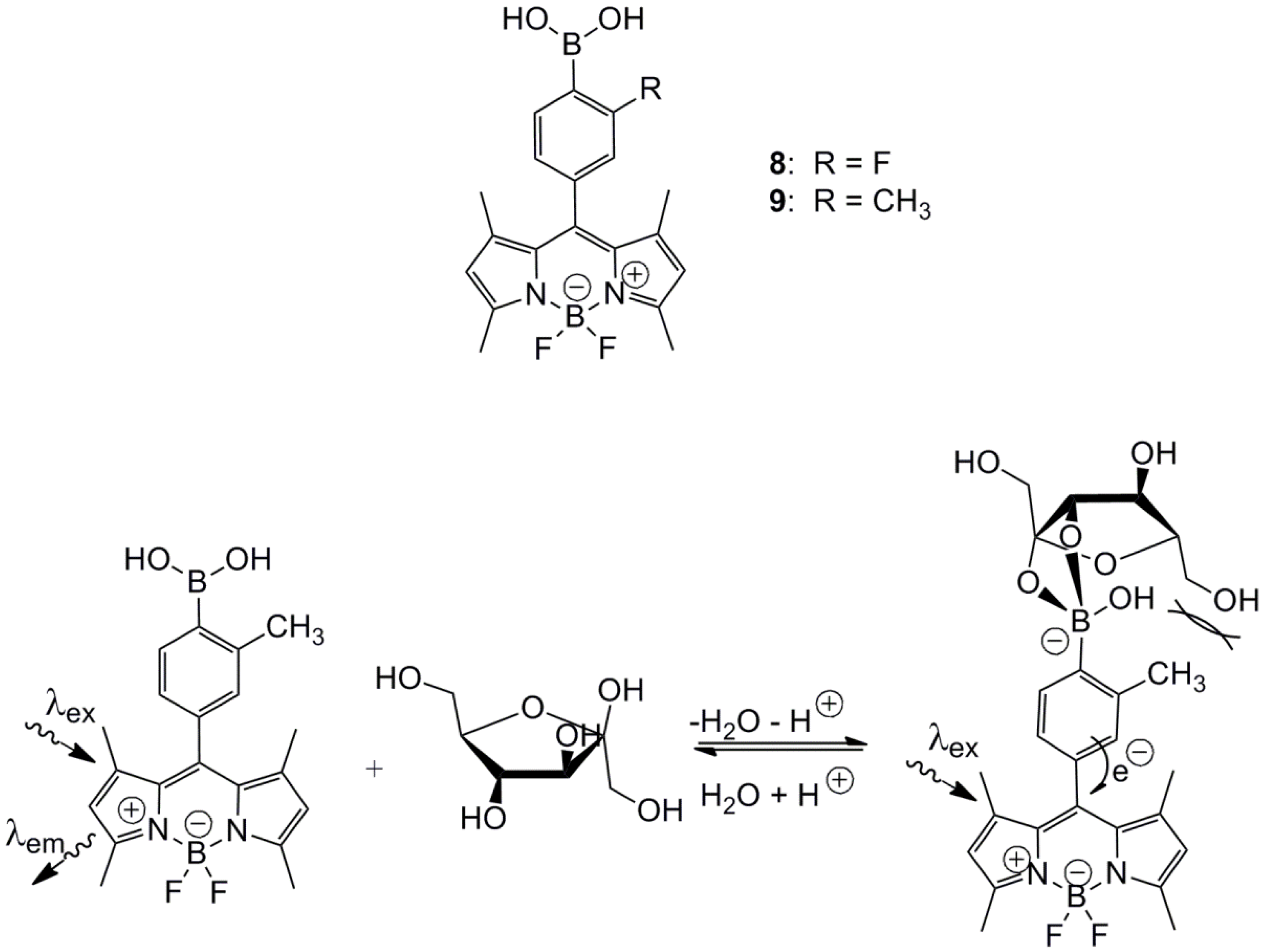
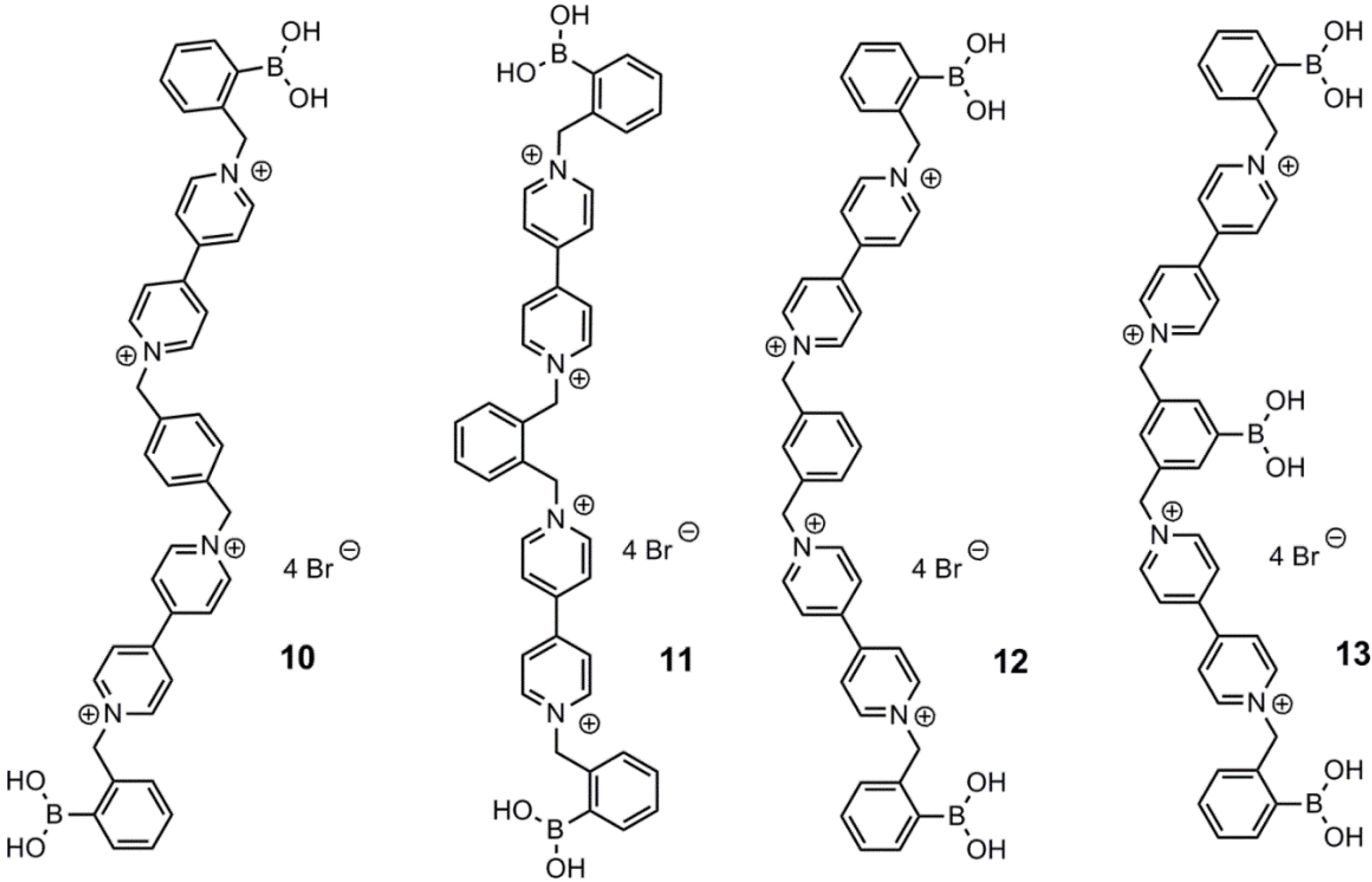
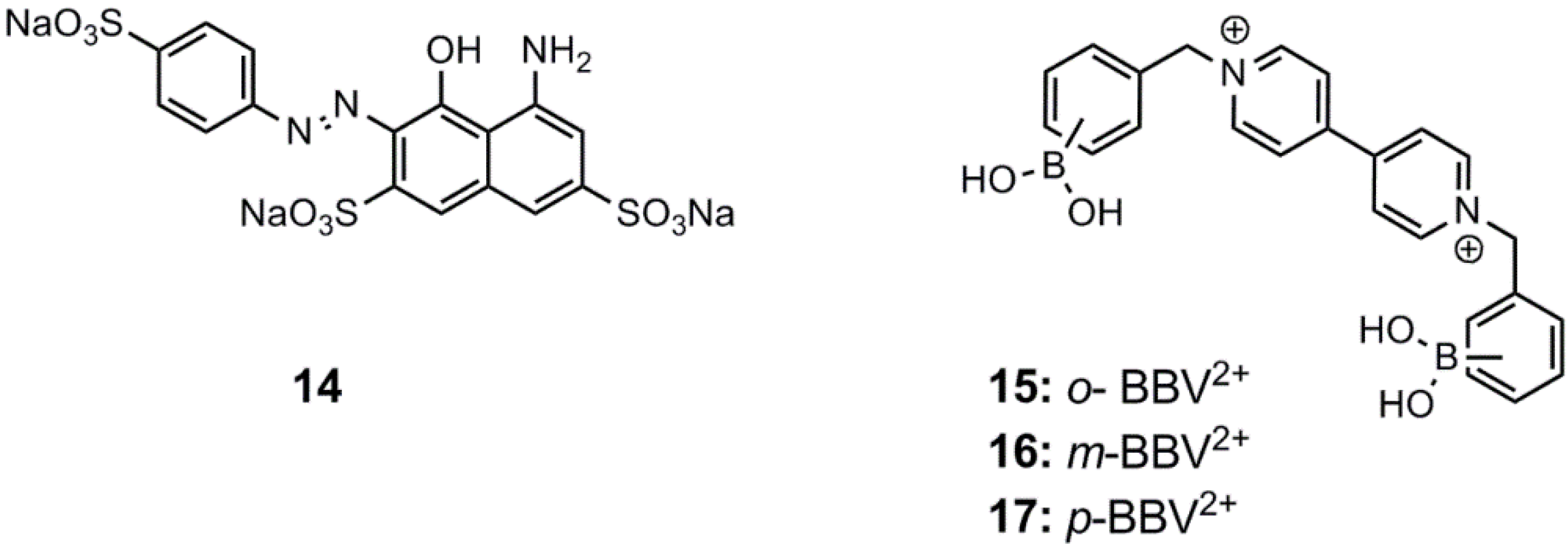
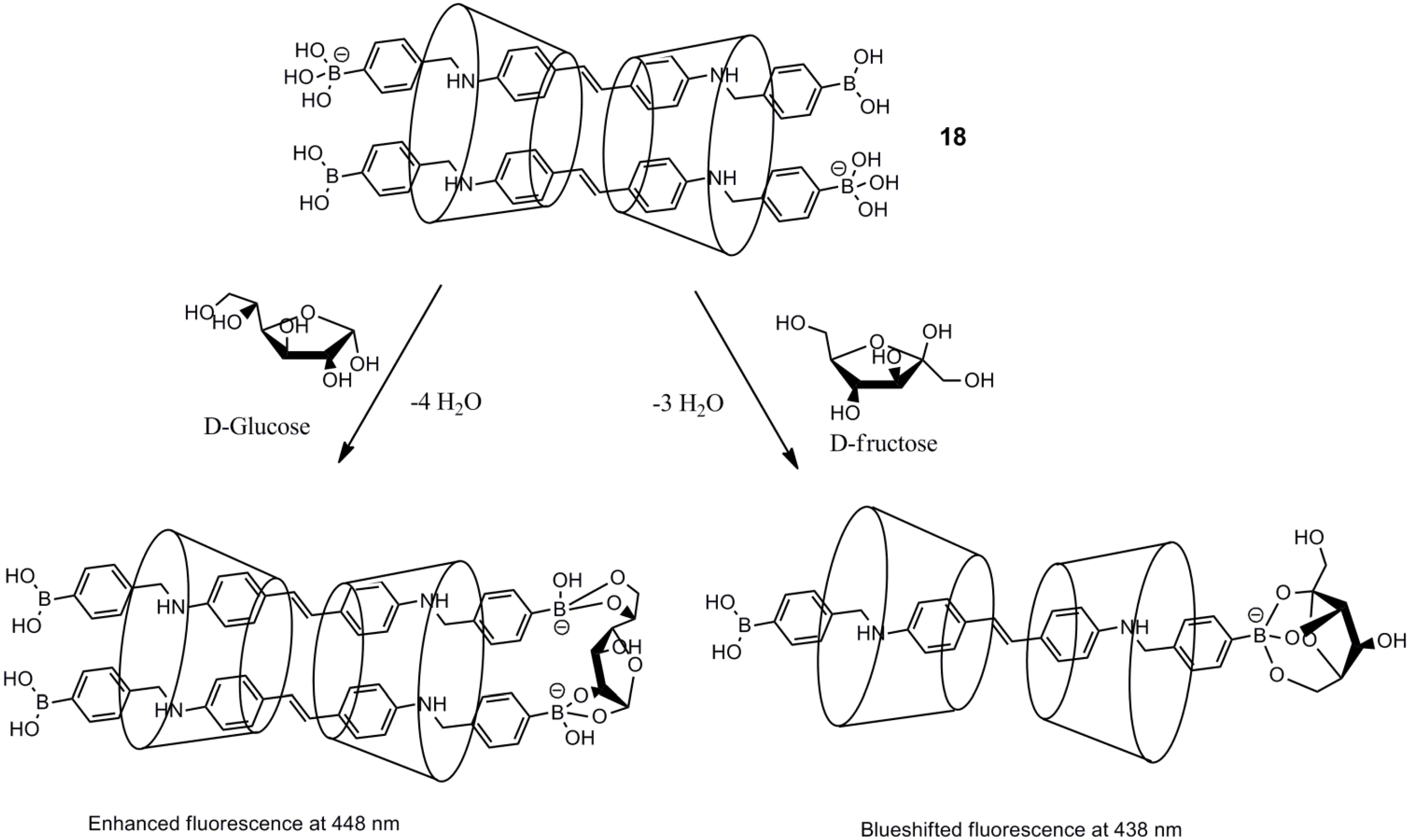
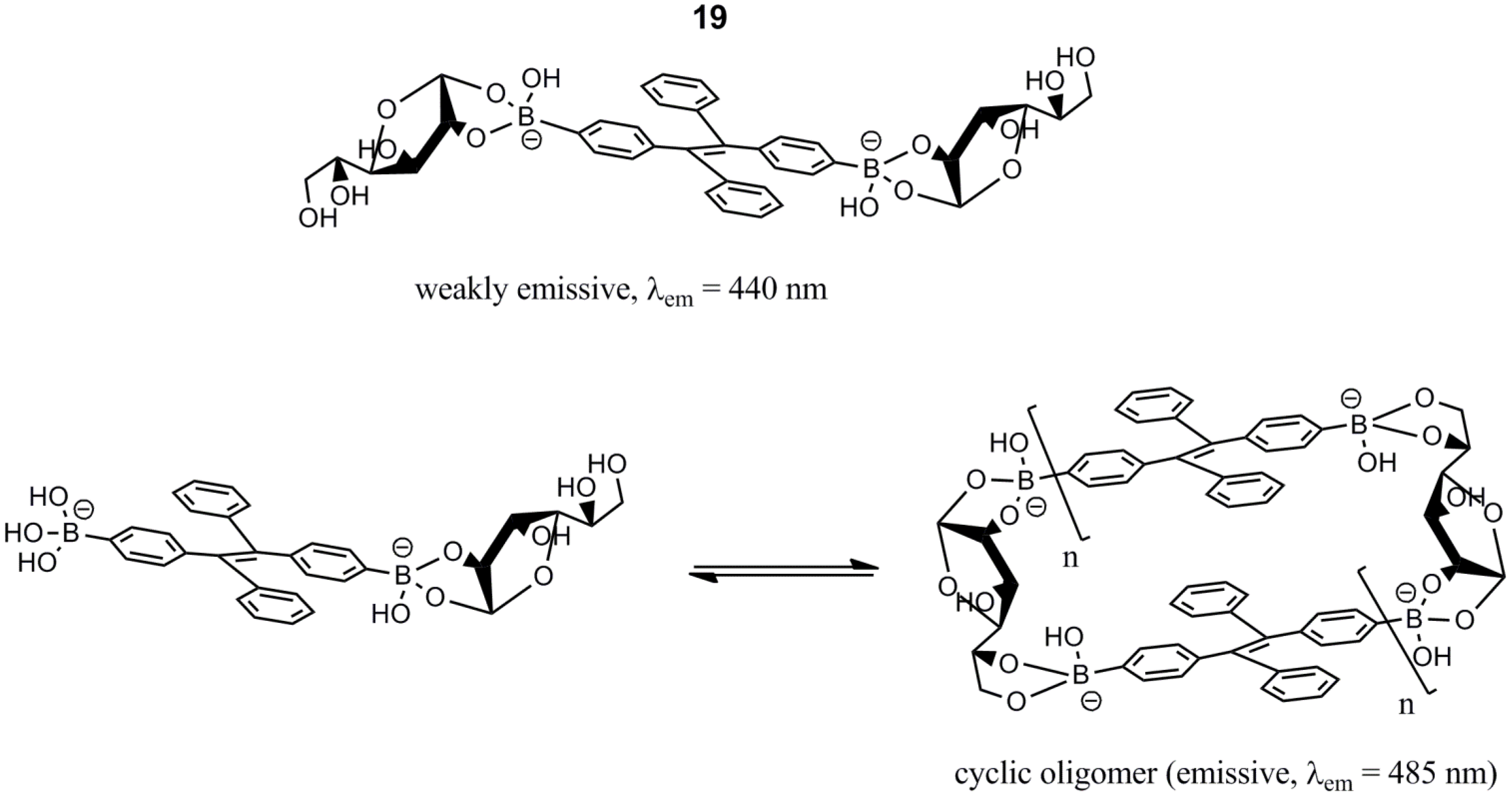
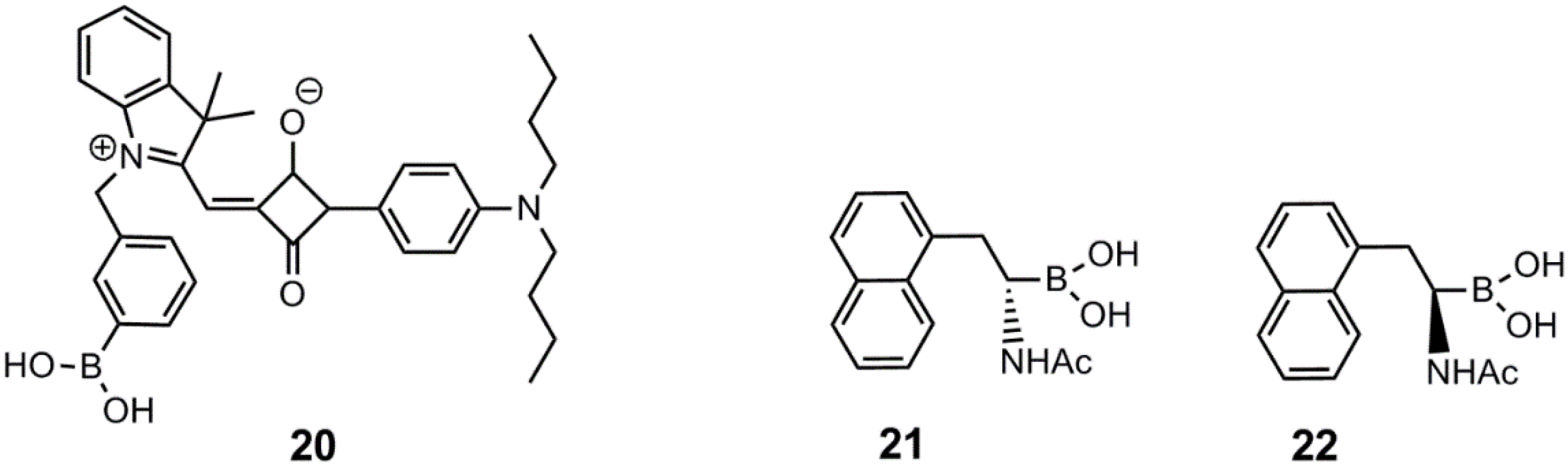
3. Immobilized Systems
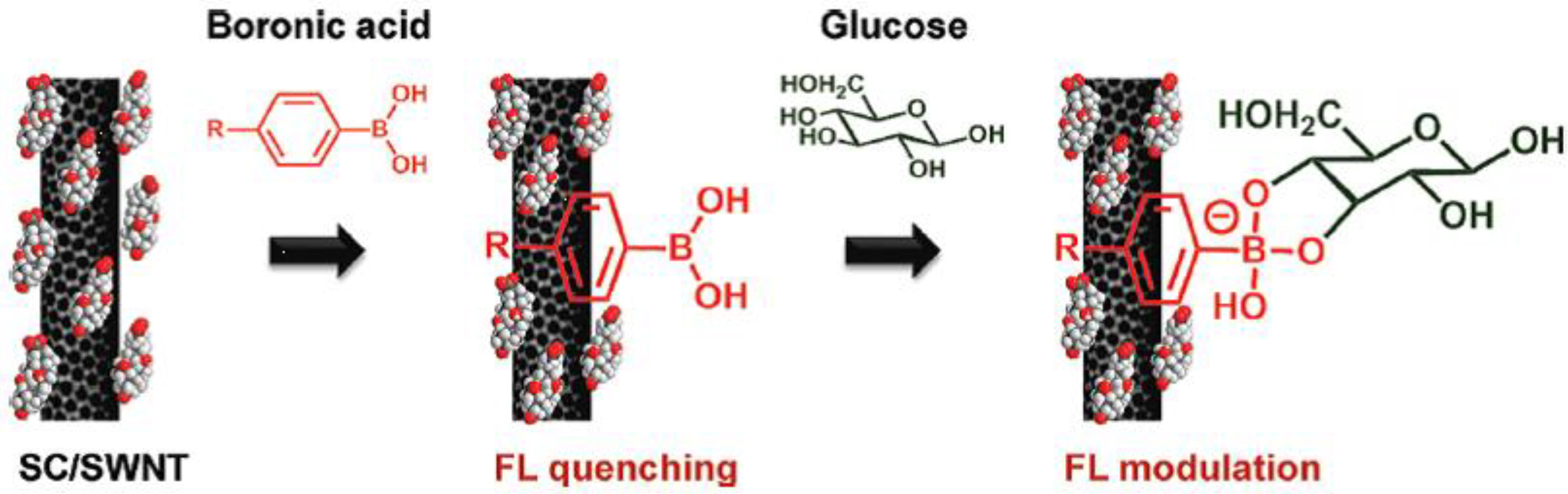
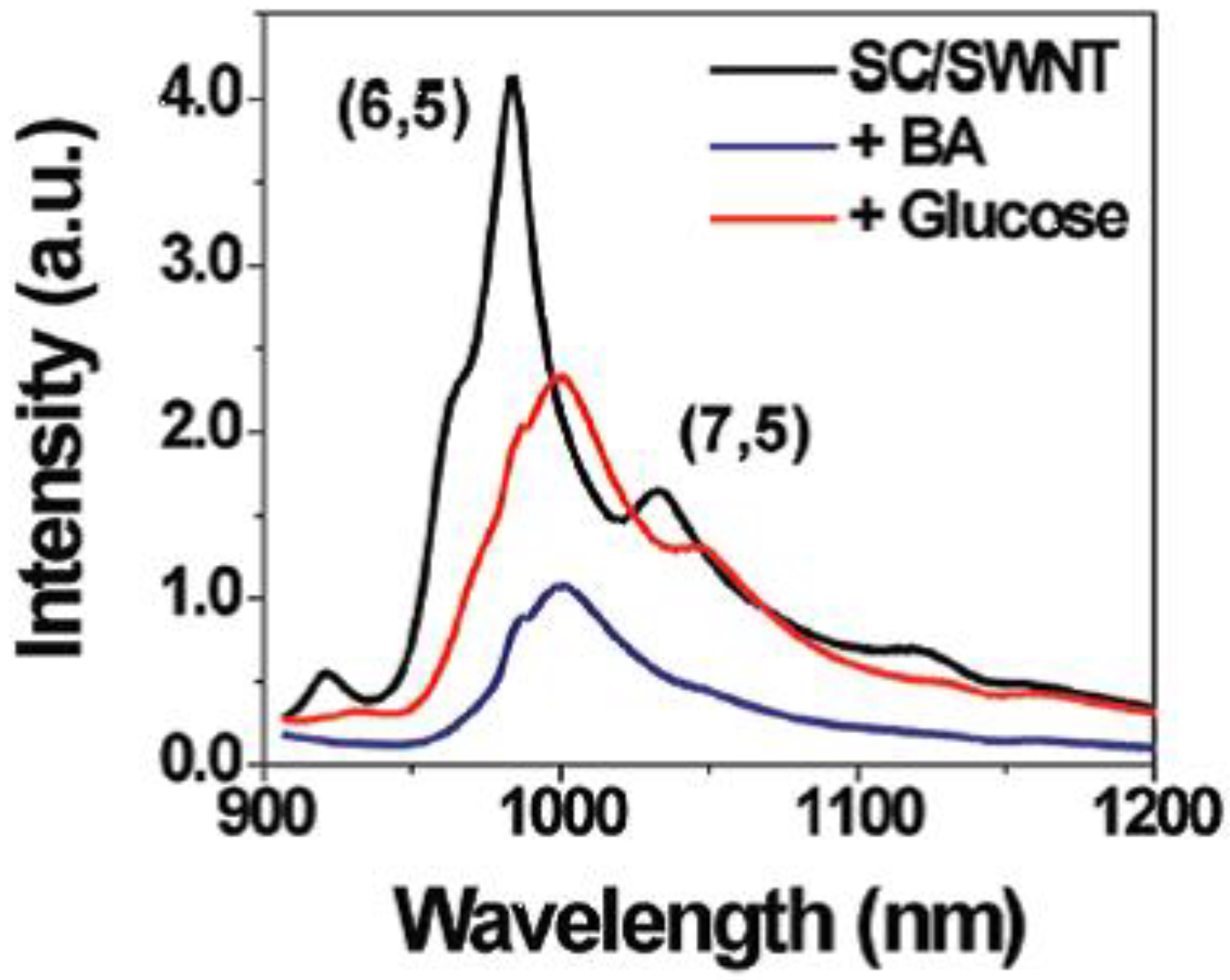
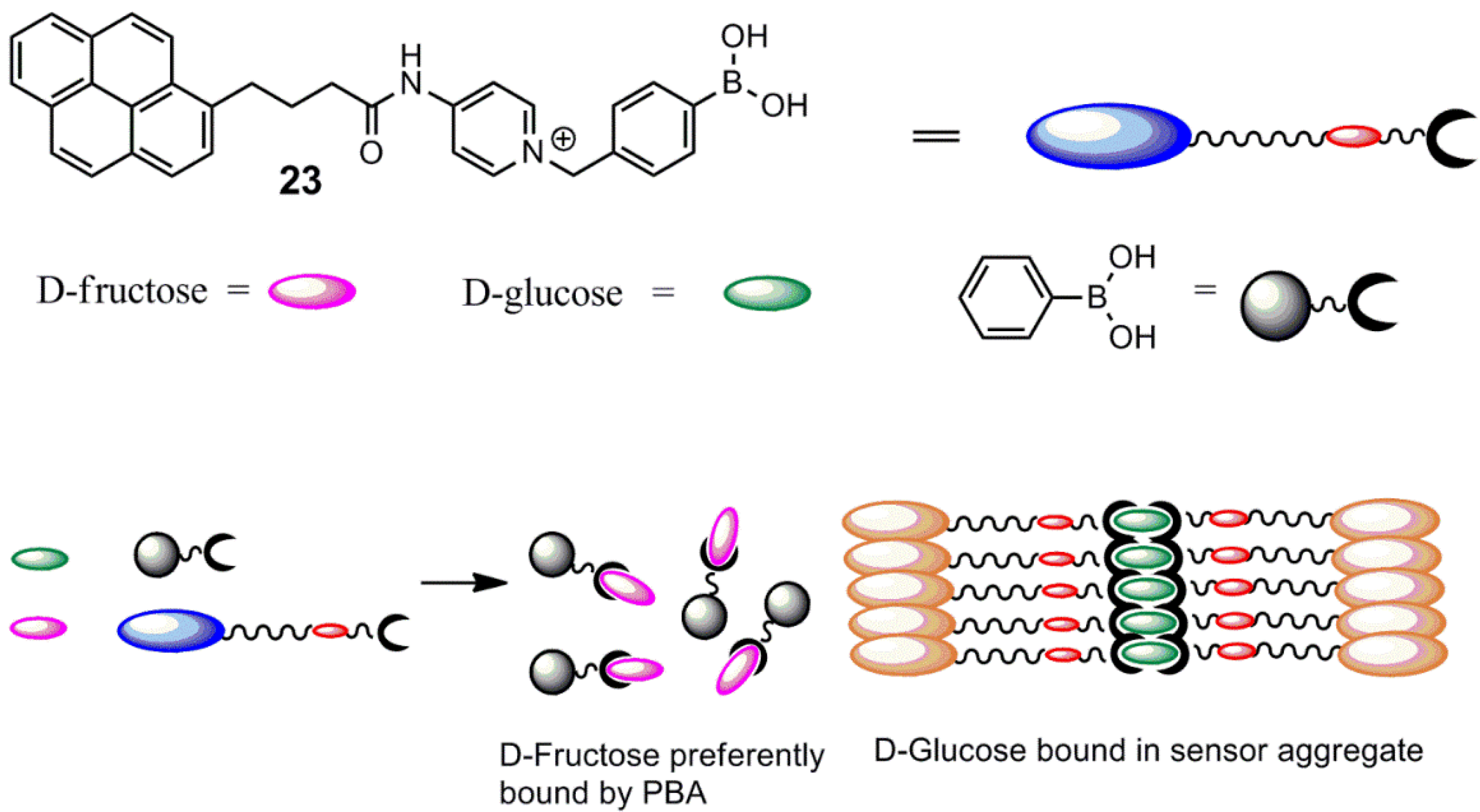
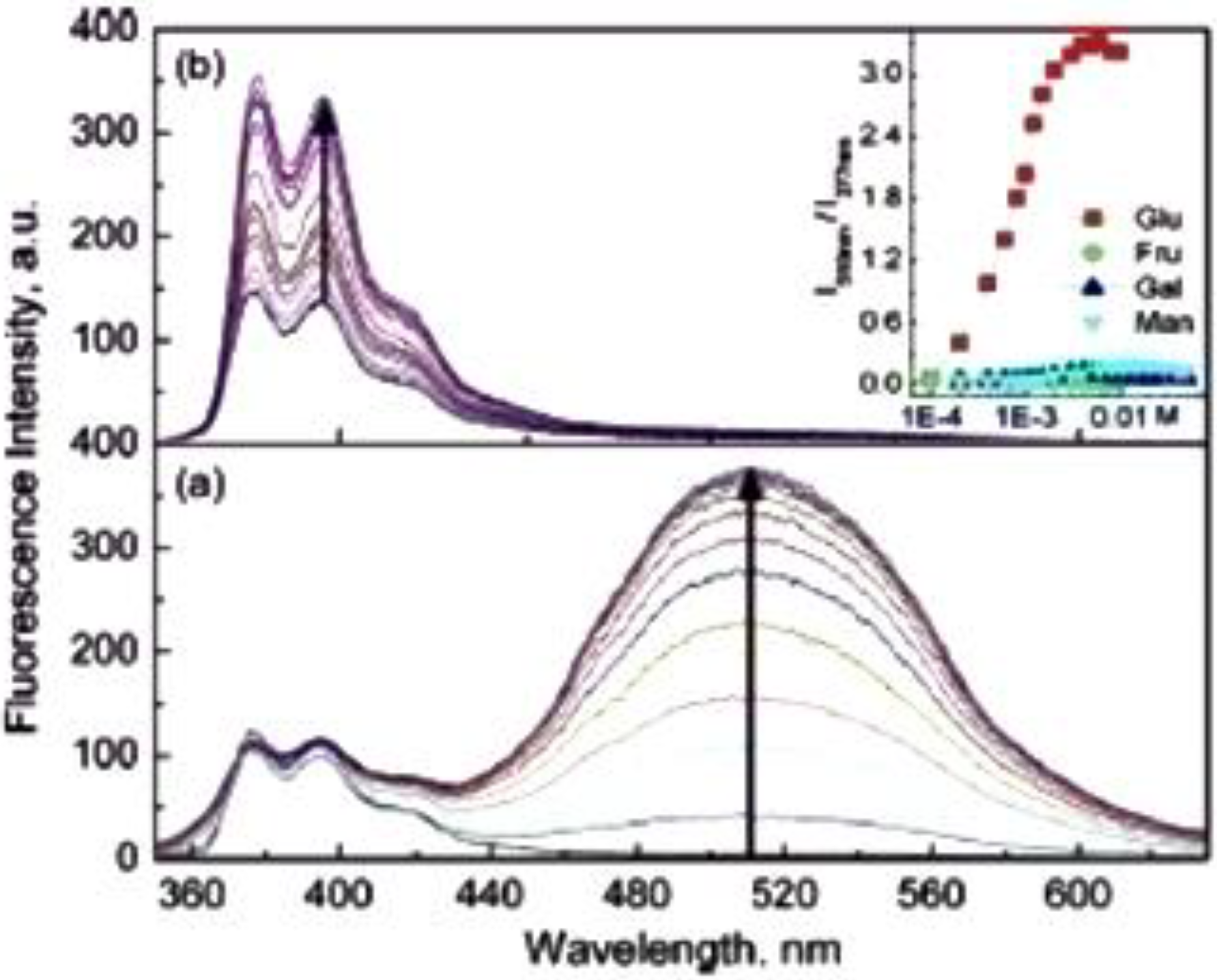
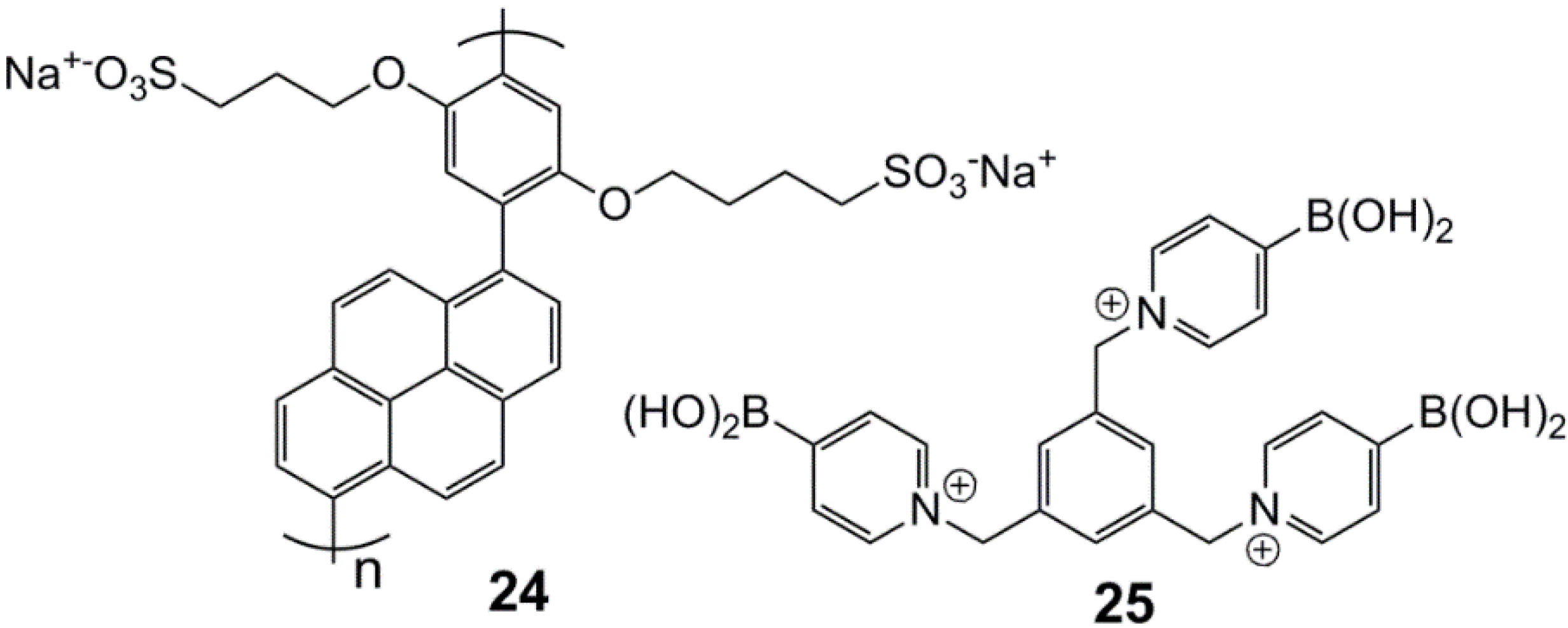
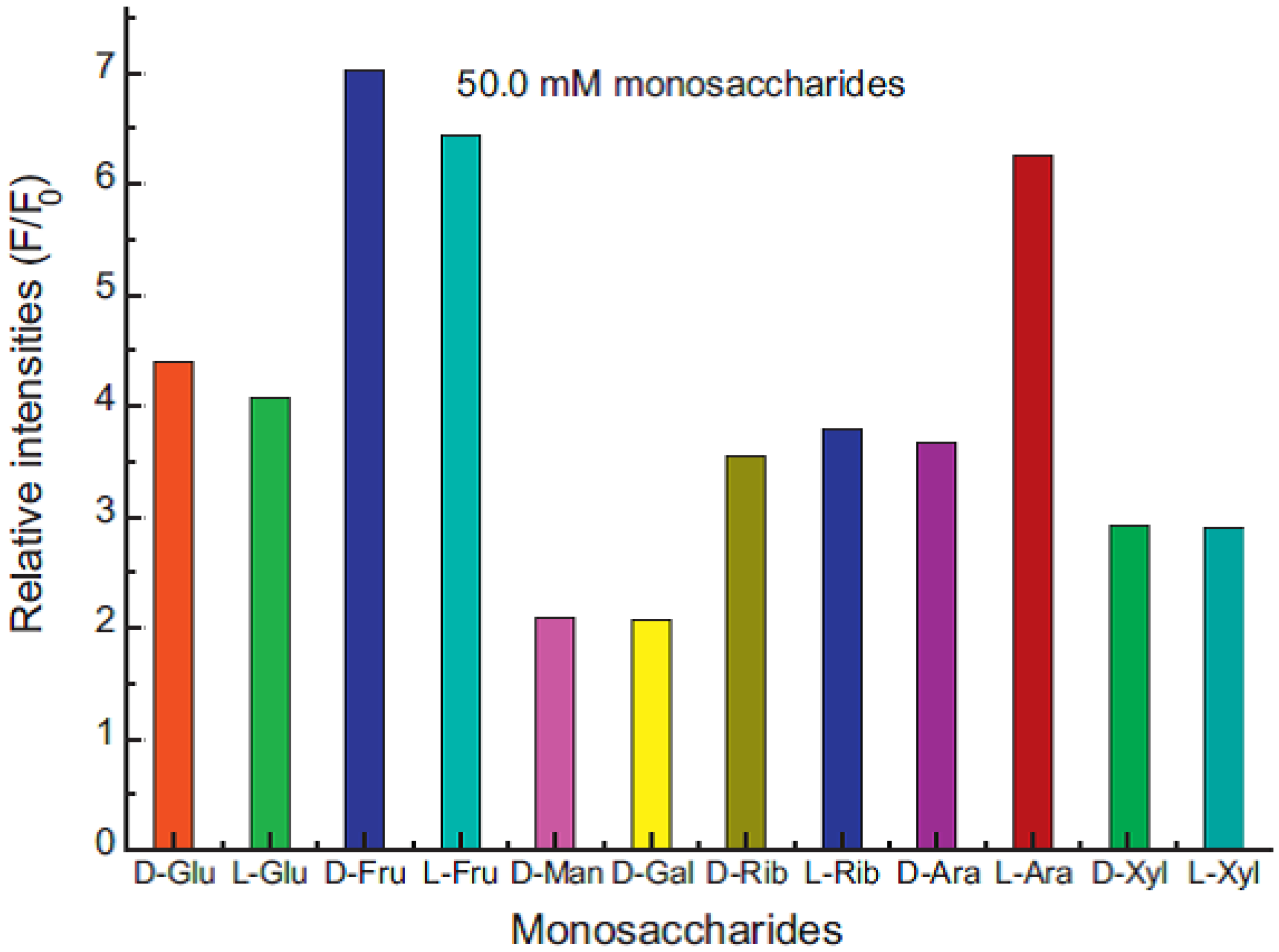
4. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mastrototaro, J.J. The minimed continuous glucose monitoring system. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2000, 2, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, B.A.; Beck, R.W.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Boland, E.A.; Chase, H.P.; Tansey, M.J.; Mauras, N.; Weinzimmer, S.A.; Ruedy, K.J.; Booth, A.D.; Kollman, C.; Diabetes Research in Children Network (DirecNet) Study Group. The accuracy of the CGMS in children with type 1 diabetes: Results of the diabetes research in children network (DirecNet) accuracy study. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2003, 5, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchinetti, A.; Sparacino, G.; Guerra, S.; Lujif, Y.M.; DeVries, J.H.; Mader, J.K.; Ellmerer, M.; Benesch, C.; Heinemann, L.; Bruttomesso, D.; Avogaro, A.; Cobelli, C. Real-time improvement of continuous glucose monitoring accuracy. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.L. The Pursuit of Noninvasive Glucose: Hunting the Deceitful Turkey. Available online: http://www.mendosa.com/noninvasive.glucose.pdf (accessed on 24 October 2013).
- Yoo, E.-H.; Lee, S.-Y. Glucose biosensors: An overview of use in clinical practice. Sensors 2010, 10, 4558–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, S.; Schultz, J.S. A miniature optical glucose sensor based on affinity binding. Biotechnology 1984, 2, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marcos, S.; Galindo, J.; Sierra, J.F.; Galban, J.; Castillo, J.R. An optical glucose biosensor based on derived glucose oxidase immobilised onto a sol-gel matrix. Sens. Actuator. B 1999, 57, 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- D’Auria, S.; Di Cesare, N.; Gryczynski, Z.; Rossi, M.; Lakowicz, J.R. A thermophilic apoglucose dehydrogenase as a nonconsuming glucose sensor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 274, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, H.; Maity, N.C.; Jarori, G.K. Time-resolved fluorescence of tryptophans in yeast hexokinase-PI: Effect of subunit dimerization and ligand binding. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2000, 55, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilardi, G.; Mei, G.; Rosato, N.; Agro, A.F.; Cass, A.E.G. Spectroscopic properties of an engineered maltose binding protein. Protein Eng. 1997, 10, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.G. Boronic Acids: Preparation, Application in Organic Synthesis and Medicine; Wiley-VCH: Berlin, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Electrochemical glucose biosensors. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reach, G.; Wilson, G.S. Can continuous glucose monitoring be used for the treatment of diabetes? Anal. Chem. 1992, 64, 381A–386A. [Google Scholar]
- Wickramasinghe, Y.; Yang, Y.; Spencer, S.A. Current problems and potential techniques in in vivo glucose monitoring. J. Fluoresc. 2004, 14, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.S.; Gifford, R. Biosensors for real-time measurements. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 2388–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadgama, P.; Desai, M.; Crump, P. Electrochemical transducers for in vivo monitoring. Electroanalysis 1991, 3, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, J.M.; Haas, C.E.; Vicente, G.; Colon, L.A. Evaluation of lacrimal fluid as an alternative for monitoring glucose in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med. 2005, 31, 1442–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baca, J.T.; Taormina, C.R.; Feingold, E.; Finegold, D.N.; Grabowski, J.J.; Asher, S.A. Mass spectral determination of fasting tear glucose concentrations in nondiabetic volunteers. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 1370–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baca, J.T.; Finegold, D.N.; Asher, S.A. Tear glucose analysis for the noninvasive detection and monitoring of diabetes mellitus. Ocul. Surf. 2007, 5, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Gao, X.; Wang, B. Boronic acids as potential pharmaceutical agents. Med. Res. Rev. 2003, 23, 346–368. [Google Scholar]
- Springsteen, G.; Wang, B. A detailed examination of boronic acid-diol complexation. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 5291–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Heagy, M.D. Fluorescent chemosensors for carbohydrates: A decade’s worth of bright spies for saccharides in review. J. Fluoresc. 2004, 14, 569–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, T.D.; Phillips, M.D.; Shinkai, S. Boronic Acids in Saccharide Recognition; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Pickup, J.C.; Hussain, F.; Evans, N.D.; Rolinsky, O.J.; Birch, D.S.J. Fluorescence based glucose sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 2555–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes, C.D. Reviews in Fluorescence; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- De Silva, A.P.; Gunaratne, H.Q.N.; Gunnlaugsson, T.; McCoy, C.P.; Maxwell, P.R.S.; Rademacher, J.T.; Rice, T.E. Photoionic devices with receptor-functionalized fluorophores. Pure Appl. Chem. 1996, 68, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, A.P.; Gunaratne, H.Q.N.; McCoy, C.P. Molecular photoionic and logic gates with bright fluorescence and off-on digital action. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 7891–7892. [Google Scholar]
- De Silva, A.P.; Gunaratne, H.Q.N.; Gunnlaugsson, T.; Huxley, A.J.M.; McCoy, C.P.; Rademacher, J.T.; Rice, T.E. Signaling recognition events with fluorescent sensors and switches. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 1515–1566. [Google Scholar]
- James, T.D.; Sandanayake, K.; Shinkai, S. Novel photoinduced electron-transfer sensor for saccharides based on the interaction of boronic acid and amine. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1994, 47, 477–478. [Google Scholar]
- James, T.D.; Sandanayake, K.R.A.S.; Iguchi, R.; Shinkai, S. Novel saccharide photoinduced electron transfer sensors based on the interaction between boronic acid and amine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 8982–8987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimori, S.; Bell, M.L.; Oh, C.S.; Frimat, K.A.; James, T.D. Modular fluorescence sensors for saccharides. Chem. Commun. 2001, 183, 1836–1837. [Google Scholar]
- Arimori, S.; Bell, M.L.; Oh, C.S.; Frimat, K.A.; James, T.D. Modular fluorescence sensors for saccharides. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 2002, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimori, S.; Bell, M.L.; Oh, C.S.; James, T.D. A modular fluorescence intramolecular energy transfer saccharide sensor. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 4249–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Davidson, M.G.; Mahon, M.F.; Kociak-Köhn, G.; James, T.D. An enantioselective fluorescent sensor for sugar acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 16179–16186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Fyles, T.M.; James, T.D. Chiral binol-bisboronic acid as fluorescence sensor for sugar acids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2004, 43, 3461–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; James, T.D.; Zhao, J. 6,6′-Bis-substituted binol boronic acids as enantioselective and chemoselective fluorescent chemosensors for d-sorbitol. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Wang, H.-C.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, C.; James, T.D.; Zhao, J. Selective saccharide recognition using modular diboronic acid fluorescent sensors. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, J.D.; Fossey, J.S.; James, T.D.; Brooks, B.R.; Bock, C.W. A computational investigation of the nitrogen-boron interaction in o-(N,N-dialkylaminomethyl)-arylboronate systems. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 12531–12539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, B.E.; Sorey, S.; Hargrove, A.E.; Shabbir, S.H.; Lynch, V.M.; Anslyn, E.V. Probing intramolecular B–N interactions in ortho-aminomethyl arylboronic acids. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 4055–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiCesare, N.; Lakowicz, J.R. Fluorescent probe for monosaccharides based on a functionalized boron-dipyrromethene with a boronic acid group. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 9105–9108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.S.; Petersen, J.F.; Hoeg-Jensen, T.; Christensen, J.B. Buffer and sugar concentration dependent fluorescence response of a BODIPY-based aryl monoboronic acid sensor. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 5852–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.S.; Ficker, M.; Petersen, J.F.; Christensen, J.B.; Hoeg-Jensen, T. Ortho-substituted fluorescent aryl monoboronic acid displays physiological binding of d-glucose. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 1849–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duin, M.; Peters, J.A.; Kieboom, A.P.G.; van Bekkum, H. Studies on borate esters 1: The pH dependence of the stability of esters of boric acid and in aqueous media as studied by 11B-NMR. Tetrahedron 1984, 40, 2901–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.S.; Christensen, J.B.; Solling, T.I.; Jakobsen, P.; Hoeg-Jensen, T. Ortho-substituted aryl monoboronic acids have improved selectivity for d-glucose relative to d-fructose and l-lactate. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 1334–1340. [Google Scholar]
- Camara, J.N.; Suri, J.T.; Cappucio, F.E.; Wessling, R.A.; Singaram, B. Boronic acid substituted viologen based optical sugar sensors: Modulated quenching with viologen as a method for monosaccharide detection. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 1139–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordes, D.B.; Gamsey, S.; Sharrett, Z.; Miller, A.; Thoniyot, P.; Wessling, R.A.; Singaram, B. The interaction of boronic acid-substituted viologens with pyranine: The effects of quencher charge on fluorescence quenching and glucose response. Langmuir 2005, 21, 6540–6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordes, D.B.; Miller, A.; Gamsey, S.; Singaram, B. Simultaneous use of multiple fluorescent reporter dyes for glucose sensing in aqueous solution. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 2767–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharrett, Z.; Gamsey, S.; Levine, P.; Cunningham-Bryant, D.; Vilozny, B.; Schiller, A.; Wessling, R.A.; Singaram, B. Boronic acid-appended bis-viologens as a new family of viologens for glucose sensing. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoniyot, P.; Cappucio, F.E.; Gamsey, S.; Cordes, D.B.; Wessling, R.A.; Singaram, B. Continuous glucose detection with fluorescent thin-film hydrogels. 2. Fiber optic sensor fabrication and in vitro testing. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2006, 8, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamsey, S.; Suri, J.T.; Wessling, R.A.; Singaram, B. Continuous glucose sensing using boronic acid-substituted viologens in fluorescent hydrogels: Linker effects and extension to fiber optics. Langmuir 2006, 22, 9067–9074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharrett, Z.; Gamsey, S.; Fat, J.; Cunningham-Bryant, D.; Wessling, R.A.; Singaram, B. The effect of boronic acid acidity on performance of viologen-based boronic acids in a two-component optical glucose-sensing system. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 5125–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lei, H.; Zhou, C.; Liang, F.; Feng, L. Optical probe for d-glucose based on cationic polymer quencher/receptor and anionic dye in aqueous solution. Sens. Actuator. B 2012, 163, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Wang, Y.; Liang, F.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Detection of glucose based on reversible “on-off” fluorescence systems in aqueous solution. Sens. Actuator. B 2011, 156, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Wang, Y.; Liang, F.; Ming, X.; Wang, X. Highly selective recognition of monosaccharides based on two-component system in aqueous solution. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 3175–3180. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Liang, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. A facile probe for dfructose with fluorescence “on-off-on” switch ensemble. Sens. Actuator. B 2012, 173, 575–579. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Lin, L.-R.; Huang, Y.-J.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.-B. A 2:2 stilbeneboronic acid-γ-cyclodextrin fluorescent ensemble highly selective for glucose in aqueous solutions. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 4362–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, C.; Tang, L.; Qin, A.; Hu, R.; Sun, J.Z.; Tang, B.Z. Specific detection of d-glucose by a tetraphenylene-based fluorescent sensor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Massie, T.L.; Maeda, T.; Nakazumi, H.; Colyer, C.L. A long-wavelength fluorescent squarylium cyanine dye possessing boronic acid for sensing monosaccharides and glycoproteins with high enhancement in aqueous solution. Sensors 2012, 12, 5420–5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Zhu, C.; Li, M.; Wang, B. Identification of the first fluorescent a-amidoboronic acid that change fluorescent properties upon sugar binding. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumai, M.; Kozuka, S.; Samizo, M.; Hashimoto, T.; Suzuki, I.; Hayashita, T. Glucose recognition by a supramolecular complex of boronic acid fluorophore with boronic acid-modified cyclodextrin in water. Anal. Sci. 2012, 28, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzow, K.; Jazdzewska, D.; Wiczk, W. 3-[2-(Boronophenyl)benzoxazol-5-yl]alanine derivatives as fluorescent monosaccharide sensors. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 9240–9248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannajuk, K.; Jamkatoke, M.; Tuntulani, T.; Tomapatanaget, B. Highly specific-glucose fluorescence sensing based on boronic anthraquinone derivatives via the GOx enzymatic reaction. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 8899–8904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, N.; Laughlin, S.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, B. Probing the general time scale question of boronic acid binding with sugars in aqueous solution at physiological pH. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 2957–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yum, K.; Ahn, J.-H.; McNicholas, T.P.; Barone, P.W.; Mu, B.; Kim, J.-H.; Jain, R.M.; Strano, M.S. Boronic acid library for selective, reversible near-infrared fluorescence quenching of surfactant suspended single-walled carbon nanotubes in response to glucose. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 819–830. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, B.; McNicholas, T.P.; Zhang, J.; Hilmer, A.J.; Jin, Z.; Reuel, N.F.; Kim, J.-H.; Yum, K.; Strano, M.S. A structure-function relationship for the optical modulation of phenyl boronic acid-grafted, polyethylene glycol-wrapped single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 17620–17627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-H.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Liang, R.-P.; Qiu, J.-D. Fluorescent graphene quantum dots with a boronic acid appened bipyridinium salt to sense monosaccharides in aqueous solution. Chem. Commun. 2013, 5180–5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manju, S.; Sreenivasan, K. Detection of glucose in synthetic tear fluid using dually functionalized gold nanoparticles. Talanta 2011, 85, 2643–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-J.; Ouyang, W.-J.; Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Fossey, J.S.; James, T.D.; Jiang, Y.-B. Glucose sensing via aggregation and the use of “knock-out” binding to improve selectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1700–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-J.; Jiang, Y.-B.; Fossey, J.S.; James, T.D.; Marken, F. Assembly of N-hexadecyl-pyridinium-4-boronic acid hexafluorophosphate monolayer films with catechol sensing selectivity. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 8305–8310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-J.; Jiang, Y.-B.; Bull, S.D.; Fossey, J.S.; James, T.D. Diols and anions can control the formation of an exciplex between a pyridinium boronic acid with an aryl group connected via a propylene linker. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 8180–8182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngamdee, K.; Noipa, T.; Martwiset, S.; Tuntulani, T.; Ngeontae, W. Enhancement of sensitivity of glucose sensors from alizarin-boronic acid adducts in aqueous micelles. Sens. Actuator. B 2011, 160, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savsunenko, O.; Matondo, H.; Franceschi-Messant, S.; Perez, E.; Popov, A.F.; Rico-Lattes, I.; Lattes, A.; Karpichev, Y. Functionalized vesicles based on amphiphilic boronic acids: A system for recognizing biologically important polyols. Langmuir 2013, 29, 3207–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Yin, N.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z. Fluorescence probe for monosaccharide based on anionic polyelectrolyte and cationic pyridine quaternary ammonium salt. Sens. Actuator. B 2013, 181, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, S. A simple method to fabricate fluorescent glucose sensor based on dye-complexed microgels. Sens. Actuator. B 2013, 177, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.J.; Shibata, H.; Okitsu, T.; Kawanishi, T.; Takeuchi, S. Long-term in vivo glucose monitoring using fluorescent hydrogel fibers. PNAS 2011, 108, 13399–13403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hansen, J.S.; Christensen, J.B. Recent Advances in Fluorescent Arylboronic Acids for Glucose Sensing. Biosensors 2013, 3, 400-418. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios3040400
Hansen JS, Christensen JB. Recent Advances in Fluorescent Arylboronic Acids for Glucose Sensing. Biosensors. 2013; 3(4):400-418. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios3040400
Chicago/Turabian StyleHansen, Jon Stefan, and Jørn Bolstad Christensen. 2013. "Recent Advances in Fluorescent Arylboronic Acids for Glucose Sensing" Biosensors 3, no. 4: 400-418. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios3040400
APA StyleHansen, J. S., & Christensen, J. B. (2013). Recent Advances in Fluorescent Arylboronic Acids for Glucose Sensing. Biosensors, 3(4), 400-418. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios3040400