Evaluation of the Cellsway Microfluidic CTC Enrichment and Identification Platform for CTC Detection in Metastatic NSCLC
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
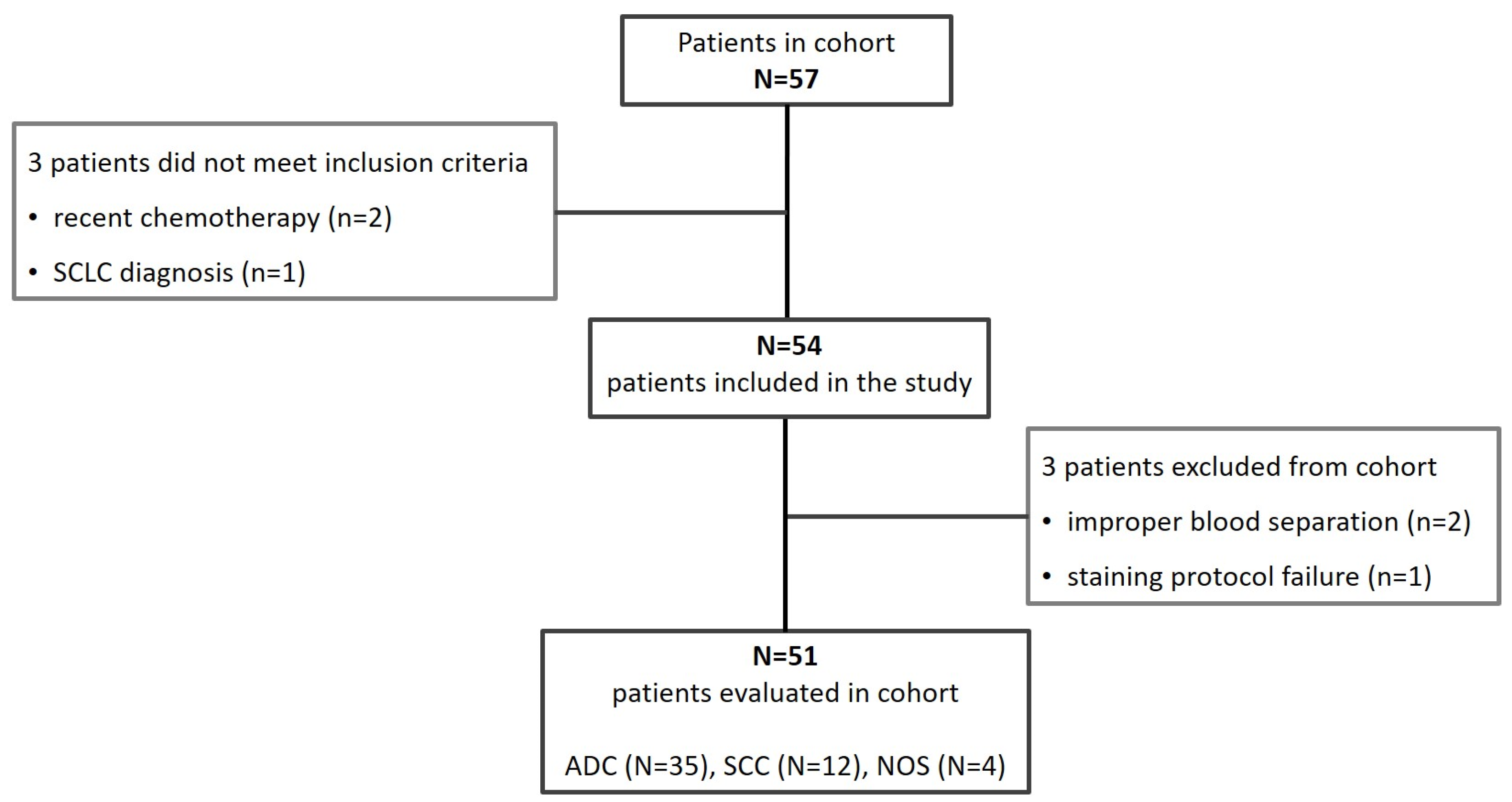
2.1. Patients Eligibility
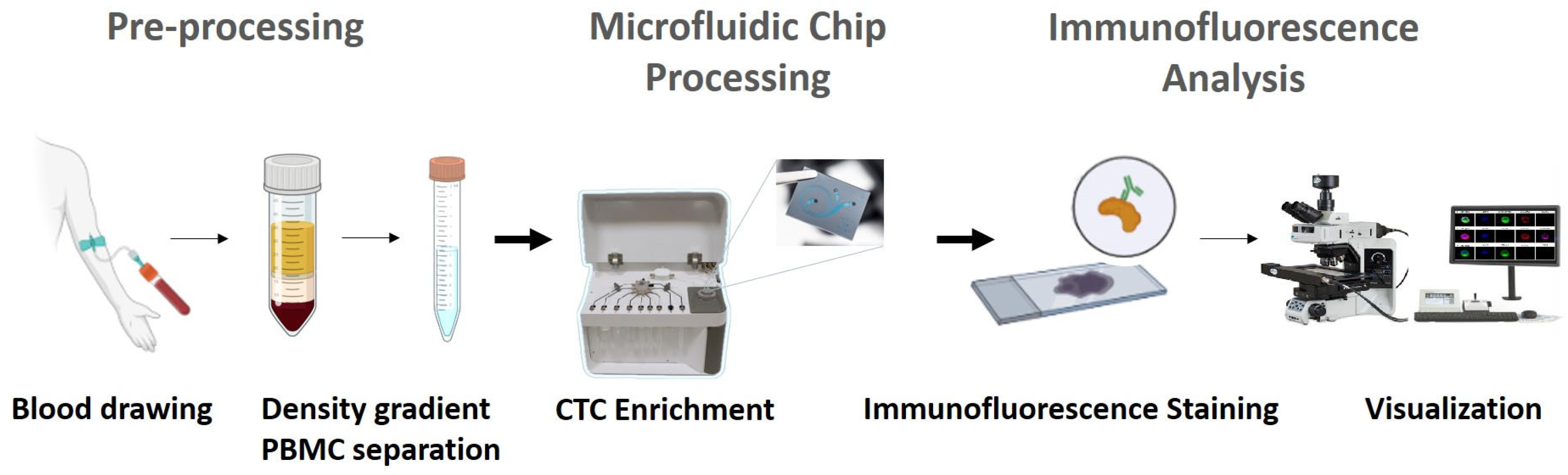
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Spiking Experiments
2.5. Blood Pre-Processing
2.6. Cellsway Microfluidic CTC Enrichment Platform
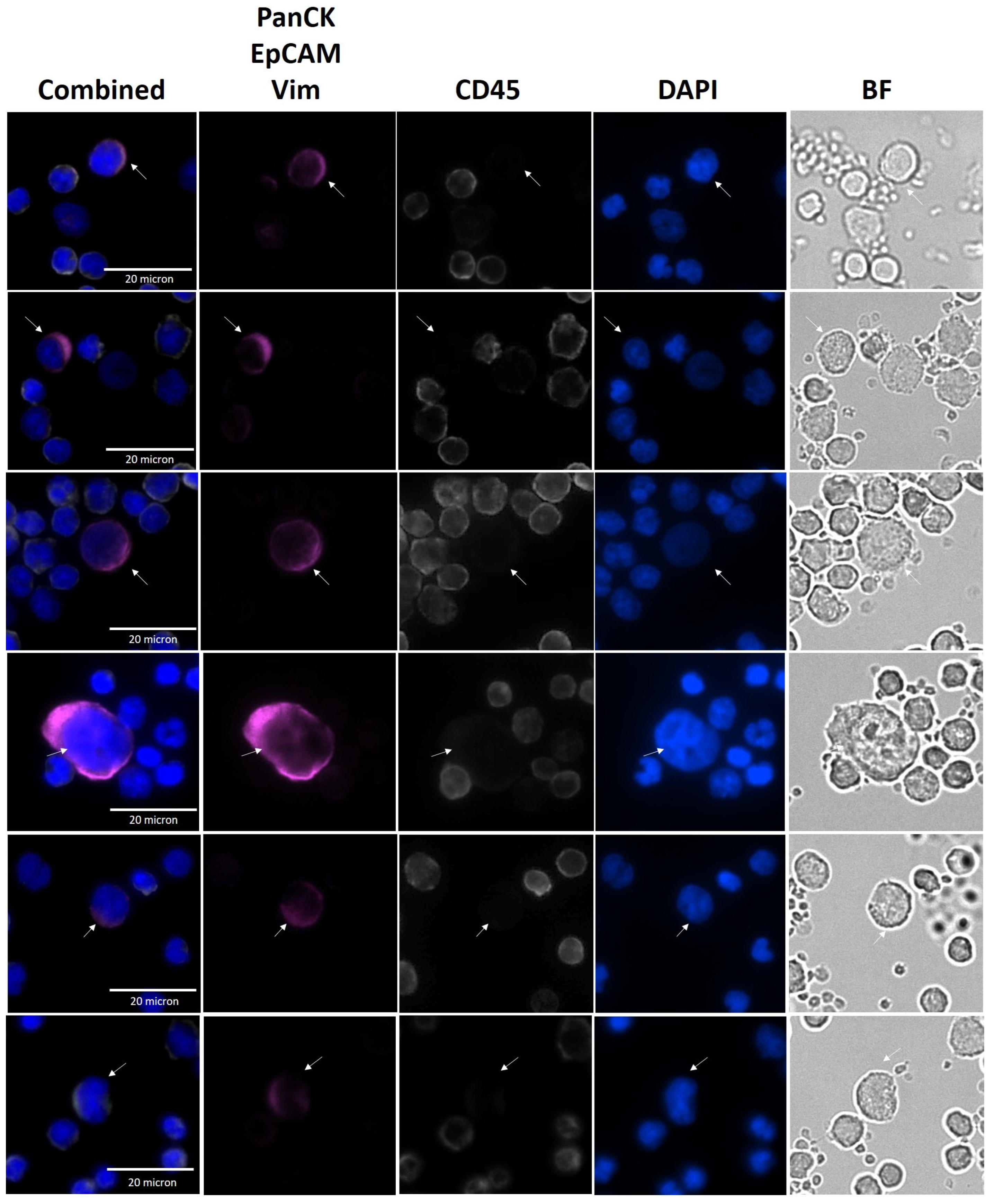
2.7. CTC Identification by Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.8. CTC and Cell Line Size Measurements
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analytical Validation of SwayBox Microfluidics (SwayChip Operated by SwayBox)
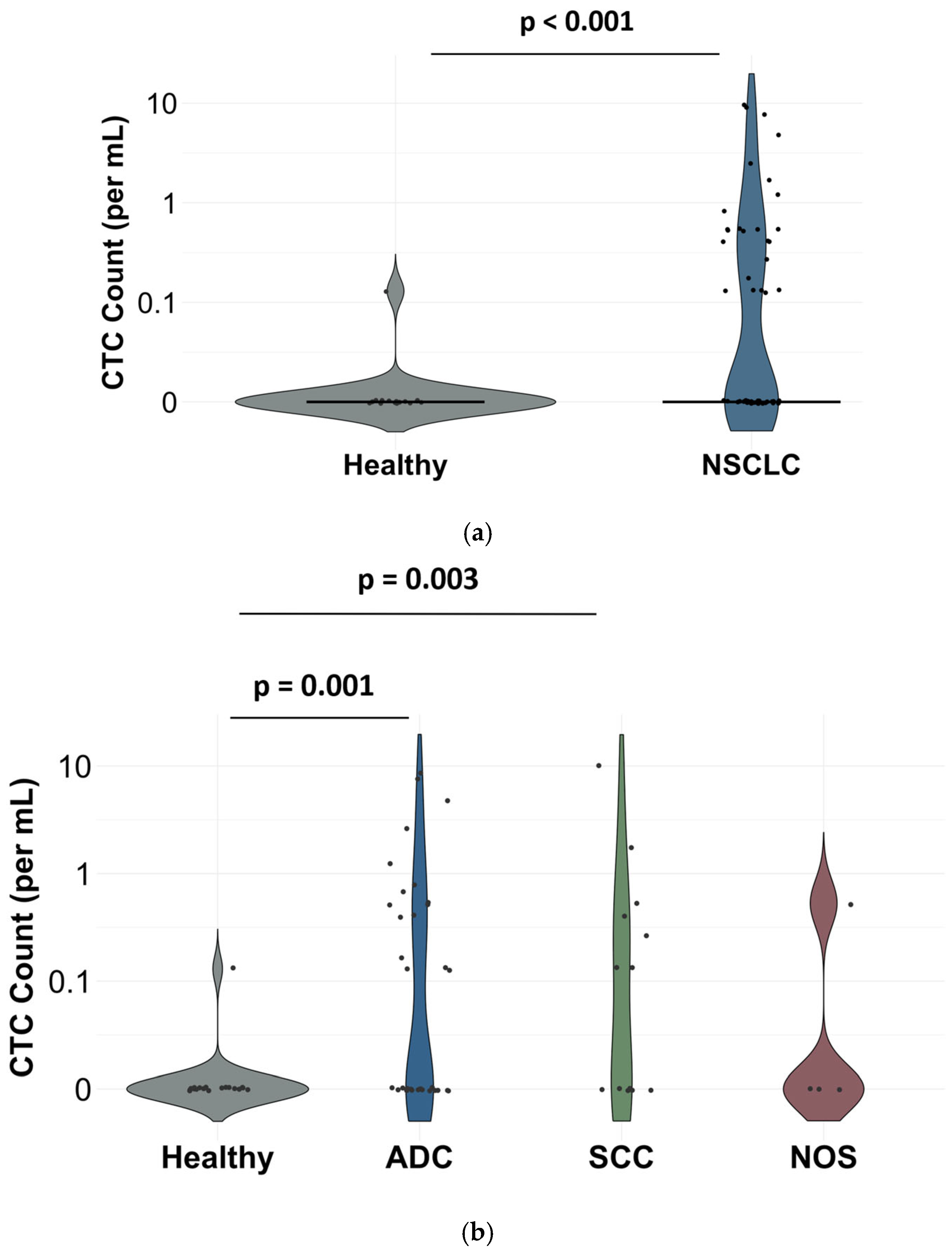
3.2. Clinical Performance of Cellsway Platform
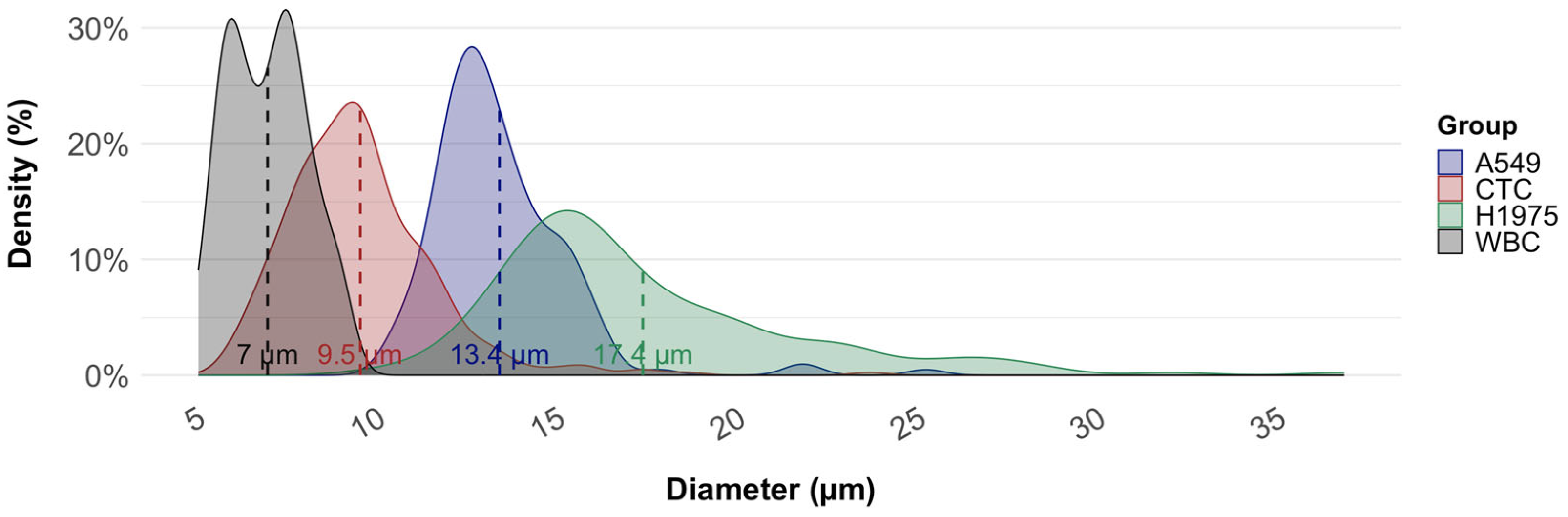
3.3. Average Diameter of CTCs from NSCLC Samples in Comparison with Cell Lines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; Feng, L.; Yu, J.; Chen, D. Global Burden of Lung Cancer in 2022 and Projections to 2050: Incidence and Mortality Estimates from GLOBOCAN. Cancer Epidemiol. 2024, 93, 102693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruano-Raviña, A.; Provencio, M.; Calvo De Juan, V.; Carcereny, E.; Moran, T.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; López-Castro, R.; Cuadrado Albite, E.; Guirado, M.; Gómez González, L.; et al. Lung Cancer Symptoms at Diagnosis: Results of a Nationwide Registry Study. ESMO Open 2020, 5, e001021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourlaba, G.; Gkiozos, I.; Kokkotou, E.; Stefanou, G.; Papaspiliou, A.; Syrigos, K. Lung Cancer Patients’ Journey from First Symptom to Treatment: Results from a Greek Registry. Cancer Epidemiol. 2019, 60, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, L.E.L.; Remon, J.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Garassino, M.C.; Heymach, J.V.; Kerr, K.M.; Tan, D.S.W.; Veronesi, G.; Reck, M. Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2024, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, N.; Bansal, J.G. Risk Factors of Lung Cancer in Nonsmoker. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2017, 41, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Herbst, R.S.; Boshoff, C. Toward Personalized Treatment Approaches for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilié, M.; Hofman, P. Pros: Can Tissue Biopsy Be Replaced by Liquid Biopsy? Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, L.; Tsao, M.S. Tumour Tissue Sampling for Lung Cancer Management in the Era of Personalized Therapy: What Is Good Enough for Molecular Testing? Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Guo, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Bu, J.; Sun, T.; Wei, J. Liquid Biopsy in Cancer Current: Status, Challenges and Future Prospects. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, J.B.; Hou, L.K.; Yu, F.; Zhang, J.; Wu, W.; Tang, X.M.; Sun, F.; Lu, H.M.; Deng, J.; et al. Liquid Biopsy in Lung Cancer: Significance in Diagnostics, Prediction, and Treatment Monitoring. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Fei, Q.; Qiu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, L. Liquid Biopsy Techniques and Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Monitoring and Evaluation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoli, E.; De Carlo, E.; Basile, D.; Zara, D.; Stanzione, B.; Schiappacassi, M.; Del Conte, A.; Spina, M.; Bearz, A. Liquid Biopsy in NSCLC: An Investigation with Multiple Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapeleris, J.; Ebrahimi Warkiani, M.; Kulasinghe, A.; Vela, I.; Kenny, L.; Ladwa, R.; O’Byrne, K.; Punyadeera, C. Clinical Applications of Circulating Tumour Cells and Circulating Tumour DNA in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer—An Update. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 859152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reina, C.; Šabanović, B.; Lazzari, C.; Gregorc, V.; Heeschen, C. Unlocking the Future of Cancer Diagnosis—Promises and Challenges of CtDNA-Based Liquid Biopsies in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Transl. Res. 2024, 272, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Leest, P.; Rozendal, P.; Rifaela, N.; van der Wekken, A.J.; Kievit, H.; de Jager, V.D.; Sidorenkov, G.; van Kempen, L.C.; Hiltermann, T.J.N.; Schuuring, E. Detection of Actionable Mutations in Circulating Tumor DNA for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Commun. Med. 2025, 5, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.G.; Lee, B.; Ha, C.; Lee, C.; Jung, H.A.; Sun, J.M.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, M.J.; Choi, Y.L.; Park, S.; et al. Clinical Utility of Circulating Tumor DNA Profiling in Detecting Targetable Fusions in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1463341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Ritterhouse, L.L. The Role of Plasma Genotyping in ALK- And ROS1-Rearranged Lung Cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 2557–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinello, A.; Tagliamento, M.; Pagliaro, A.; Conci, N.; Cella, E.; Vasseur, D.; Remon, J.; Levy, A.; Dall’Olio, F.G.; Besse, B. Circulating Tumor DNA to Guide Diagnosis and Treatment of Localized and Locally Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2024, 129, 102791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabon, J.J.; Hamilton, E.G.; Kurtz, D.M.; Esfahani, M.S.; Moding, E.J.; Stehr, H.; Schroers-Martin, J.; Nabet, B.Y.; Chen, B.; Chaudhuri, A.A.; et al. Integrating Genomic Features for Non-Invasive Early Lung Cancer Detection. Nature 2020, 580, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yuan, T.; Yuan, J.; Zhu, B.; Chen, D. Opportunities and Challenges of Using Circulating Tumor DNA to Predict Lung Cancer Immunotherapy Efficacy. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 150, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Capua, D.; Bracken-Clarke, D.; Ronan, K.; Baird, A.M.; Finn, S. The Liquid Biopsy for Lung Cancer: State of the Art, Limitations and Future Developments. Cancers 2021, 13, 3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahmaie, N.; Ozensoy Guler, O.; Simsek, E. A Revolutionary Era in Advancing Precision Immuno-Oncology; Role of Circulating Tumor Cells. J. Liq. Biopsy 2024, 6, 100169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Ulrich, B.C.; Supplee, J.; Kuang, Y.; Lizotte, P.H.; Feeney, N.B.; Guibert, N.M.; Awad, M.M.; Wong, K.K.; Janne, P.A.; et al. False-Positive Plasma Genotyping Due to Clonal Hematopoiesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4437–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; He, J.; Gao, W. Progress and Application of Circulating Tumor Cells in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2021, 22, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.S.; Mishra, A.; Edd, J.; Toner, M.; Maheswaran, S.; Haber, D.A. Circulating Tumor Cells: Blood-Based Detection, Molecular Biology, and Clinical Applications. Cancer Cell 2025, 43, 1399–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankhede, D.; Grover, S.; Hofman, P. Circulating Tumor Cells as a Predictive Biomarker in Resectable Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; De Luca, A.; Maiello, M.R.; D’Alessio, A.; Esposito, C.; Chicchinelli, N.; Forgione, L.; Piccirillo, M.C.; Rocco, G.; Morabito, A.; et al. Clinical Utility of Circulating Tumor Cells in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2017, 6, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, K.; Tartarone, A.; Santarpia, M.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, G. Circulating Tumor Cells Can Predict the Prognosis of Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer after Resection: A Retrospective Study. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cai, Y.; Mou, S. Liquid Biopsy in Lung Cancer: The Role of Circulating Tumor Cells in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prognosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 181, 117726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, K.; Xu, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, T. Prognostic Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinniah, C.; Aguarin, L.; Cheng, P.; Decesaris, C.; Cutillo, A.; Berman, A.T.; Frick, M.; Doucette, A.; Cengel, K.A.; Levin, W.; et al. Early Detection of Recurrence in Patients With Locally Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer via Circulating Tumor Cell Analysis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2019, 20, 384–390.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, P.; Xu, W.; Qiu, L.; Ren, J.; Fei, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Xing, Y.; Shen, M.; et al. Distinct CTC Specific RNA Profile Enables NSCLC Early Detection and Dynamic Monitoring of Advanced NSCLC. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2417849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kejík, Z.; Kaplánek, R.; Dytrych, P.; Masařík, M.; Veselá, K.; Abramenko, N.; Hoskovec, D.; Vašáková, M.; Králová, J.; Martásek, P.; et al. Circulating Tumour Cells (Ctcs) in Nsclc: From Prognosis to Therapy Design. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanssen, A.; Wagner, J.; Gorges, T.M.; Taenzer, A.; Uzunoglu, F.G.; Driemel, C.; Stoecklein, N.H.; Knoefel, W.T.; Angenendt, S.; Hauch, S.; et al. Characterization of Different CTC Subpopulations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdo, M.; Belloum, Y.; Heigener, D.; Welker, L.; von Weihe, S.; Schmidt, M.; Heuer-Olewinski, N.; Watermann, I.; Szewczyk, M.; Kropidlowski, J.; et al. Comparative Evaluation of PD-L1 Expression in Cytology Imprints, Circulating Tumour Cells and Tumour Tissue in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Mol. Oncol. 2023, 17, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Cai, S.; Yu, Z.; Guo, X. EP.11A.11 Application of Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) PD-L1 Detection in the Evaluation of Therapeutic Efficacy in Advanced NSCLC: A Retrospective Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2024, 19, S600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edd, J.F.; Mishra, A.; Smith, K.C.; Kapur, R.; Maheswaran, S.; Haber, D.A.; Toner, M. Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells. iScience 2022, 25, 104696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, A.J.; Nteliopoulos, G.; Shaw, J.A.; Coombes, R.C. A Review of Circulating Tumour Cell Enrichment Technologies. Cancers 2021, 13, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.F. A Review on Microdevices for Isolating Circulating Tumor Cells. Micromachines 2020, 11, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descamps, L.; Roy, D.L.; Deman, A.L. Microfluidic-Based Technologies for CTC Isolation: A Review of 10 Years of Intense Efforts towards Liquid Biopsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macaraniag, C.; Luan, Q.; Zhou, J.; Papautsky, I. Microfluidic Techniques for Isolation, Formation, and Characterization of Circulating Tumor Cells and Clusters. APL Bioeng. 2022, 6, 031501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pødenphant, M.; Ashley, N.; Koprowska, K.; Mir, K.U.; Zalkovskij, M.; Bilenberg, B.; Bodmer, W.; Kristensen, A.; Marie, R. Separation of Cancer Cells from White Blood Cells by Pinched Flow Fractionation. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 4598–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabacak, N.M.; Spuhler, P.S.; Fachin, F.; Lim, E.J.; Pai, V.; Ozkumur, E.; Martel, J.M.; Kojic, N.; Smith, K.; Chen, P.I.; et al. Microfluidic, Marker-Free Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells from Blood Samples. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 694–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warkiani, M.E.; Khoo, B.L.; Wu, L.; Tay, A.K.P.; Bhagat, A.A.S.; Han, J.; Lim, C.T. Ultra-Fast, Label-Free Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells from Blood Using Spiral Microfluidics. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, C.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Xianyu, Y.; Hu, G.; Jiang, X. Size-Based Hydrodynamic Rare Tumor Cell Separation in Curved Microfluidic Channels. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 011802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkiani, M.E.; Guan, G.; Luan, K.B.; Lee, W.C.; Bhagat, A.A.S.; Kant Chaudhuri, P.; Tan, D.S.W.; Lim, W.T.; Lee, S.C.; Chen, P.C.Y.; et al. Slanted Spiral Microfluidics for the Ultra-Fast, Label-Free Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Ma, D.; Mi, X. A High-Throughput Circular Tumor Cell Sorting Chip with Trapezoidal Cross Section. Sensors 2024, 24, 3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omrani, V.; Targhi, M.Z.; Rahbarizadeh, F.; Nosrati, R. High-Throughput Isolation of Cancer Cells in Spiral Microchannel by Changing the Direction, Magnitude and Location of the Maximum Velocity. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Kim, T.H.; Smith, K.J.; Delaney, R.; Park, G.S.; Guo, H.; Lin, E.; Plegue, T.; Kuo, N.; Steffes, J.; et al. New Labyrinth Microfluidic Device Detects Circulating Tumor Cells Expressing Cancer Stem Cell Marker and Circulating Tumor Microemboli in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkayar, G.; Mutlu, E.; Şahin, Ş.; Yalçın, Y.D.; Töral, T.; Külah, H.; Yıldırım, E.; Zorlu, Ö.; Özgür, E. A Novel Microfluidic Method Utilizing a Hydrofoil Structure to Improve Circulating Tumor Cell Enrichment: Design and Analytical Validation. Micromachines 2020, 11, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkayar, G.; Yildirim, E.; Zorlu, O. A Method of Microfluidic Particle Separation Enhancement and the Device Thereof. WIPO Patent WO/2020/139210, 2 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kilercik, M.; Özgür, E.; Şahin, Ş.; Doğan, B.Ş.; Mutlu, E.; Cihan, C.; Kolay, M.; Erkal, N.; Zorlu, Ö.; Doğanca, T.S.; et al. Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells in Non-Metastatic Prostate Cancer through Integration of a Microfluidic CTC Enrichment System and Multiparametric Flow Cytometry. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0312296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen-Dogan, B.; Demir, M.A.; Sahin, B.; Yildirim, E.; Karayalcin, G.; Sahin, S.; Mutlu, E.; Toral, T.B.; Ozgur, E.; Zorlu, O.; et al. Analytical Validation of a Spiral Microfluidic Chip with Hydrofoil-Shaped Pillars for the Enrichment of Circulating Tumor Cells. Biosensors 2023, 13, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M Saini, V.; Oner, E.; Ward, M.P.; Hurley, S.; Henderson, B.D.; Lewis, F.; Finn, S.P.; Fitzmaurice, G.J.; O’Leary, J.J.; O’Toole, S.; et al. A Comparative Study of Circulating Tumor Cell Isolation and Enumeration Technologies in Lung Cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2025, 19, 2014–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosokawa, M.; Kenmotsu, H.; Koh, Y.; Yoshino, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Naito, T.; Takahashi, T.; Murakami, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Tsuya, A.; et al. Size-Based Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells in Lung Cancer Patients Using a Microcavity Array System. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Kulasinghe, A.; Bogseth, A.; O’Byrne, K.; Punyadeera, C.; Papautsky, I. Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells in Non-Small-Cell-Lung-Cancer Patients Using a Multi-Flow Microfluidic Channel. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2019, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, S.H.; Edd, J.; Stoddard, A.E.; Wong, K.H.K.; Fachin, F.; Maheswaran, S.; Haber, D.A.; Stott, S.L.; Kapur, R.; Toner, M. Microfluidic Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cell Clusters by Size and Asymmetry. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loutherback, K.; D’Silva, J.; Liu, L.; Wu, A.; Austin, R.H.; Sturm, J.C. Deterministic Separation of Cancer Cells from Blood at 10 ML/Min. AIP Adv 2012, 2, 042107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.L.; Chiou, J.F.; Wang, P.Y.; Lu, L.S.; Shen, C.N.; Hsu, H.L.; Burnouf, T.; Ting, L.L.; Chou, P.C.; Chung, C.L.; et al. Ex Vivo Expansion and Drug Sensitivity Profiling of Circulating Tumor Cells from Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.; Vanharanta, S. Circulating Tumor Cells: Come Together, Right Now, over Metastasis. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, K.; Yang, Z.; Cui, J.; He, H.; Hoffman, A.R.; Hu, J.-F.; Li, W. Systematic Correlation Analyses of Circulating Tumor Cells with Clinical Variables and Tumor Markers in Lung Cancer Patients. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 3099–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, S.P.; Witte, M.H. Cancer Metastasis through the Lymphatic versus Blood Vessels. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2024, 41, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.-A.A.; Baum, C.; Xie, Y. Cancer Metastasis Through the Lymphatics: Invasion and Dissemination. Lymphatics 2025, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volovetsky, A.B.; Novikova, V.A.; Boloban, A.; Rzhevskiy, A.S.; Kapitannikova, A.; Ovchinnikova, E.G.; Klejmentjeva, T.P.; Grishin, V.A.; Pigareva, Y.; Zvyagin, A.V.; et al. Prognostic Value of the Number of Circulating Tumor Cells in Patients with Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Micromachines 2025, 16, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofman, V.; Ilie, M.I.; Long, E.; Selva, E.; Bonnetaud, C.; Molina, T.; Vénissac, N.; Mouroux, J.; Vielh, P.; Hofman, P. Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells as a Prognostic Factor in Patients Undergoing Radical Surgery for Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma: Comparison of the Efficacy of the CellSearch AssayTM and the Isolation by Size of Epithelial Tumor Cell Method. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, M.G.; Sloane, R.; Priest, L.; Lancashire, L.; Hou, J.M.; Greystoke, A.; Ward, T.H.; Ferraldeschi, R.; Hughes, A.; Clack, G.; et al. Evaluation and Prognostic Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1556–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamminga, M.; De Wit, S.; Hiltermann, T.J.N.; Timens, W.; Schuuring, E.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M.; Groen, H.J.M. Circulating Tumor Cells in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Are Associated with Worse Tumor Response to Checkpoint Inhibitors. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, T.; Murata, Y.; Oki, Y.; Sugiyama, T.; Kusumoto, S.; Ishida, H.; Shirai, T.; Nakashima, M.; Yamaoka, T.; Okuda, K.; et al. Relationship of Circulating Tumor Cells to the Effectiveness of Cytotoxic Chemotherapy in Patients with Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Oncol. Res. 2012, 20, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadaki, M.A.; Sotiriou, A.I.; Vasilopoulou, C.; Filika, M.; Aggouraki, D.; Tsoulfas, P.G.; Apostolopoulou, C.A.; Rounis, K.; Mavroudis, D.; Agelaki, S. Optimization of the Enrichment of Circulating Tumor Cells for Downstream Phenotypic Analysis in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Anti-Pd-1 Immunotherapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheampong, E.; Morici, M.; Abed, A.; Bowyer, S.; Asante, D.B.; Lin, W.; Millward, M.; Gray, E.S.; Beasley, A.B. Powering Single-Cell Genomics to Unravel Circulating Tumour Cell Subpopulations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asante, D.B.; Morici, M.; Mohan, G.R.K.A.; Acheampong, E.; Spencer, I.; Lin, W.; van Miert, P.; Gibson, S.; Beasley, A.B.; Ziman, M.; et al. Multi-Marker Immunofluorescent Staining and Pd-L1 Detection on Circulating Tumour Cells from Ovarian Cancer Patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 6225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinen, L.T.D.; de Carvalho, F.M.; Rocha, B.M.M.; Aguiar, C.M.; Abdallah, E.A.; Campanha, D.; Mingues, N.B.; de Oliveira, T.B.; Maciel, M.S.; Cervantes, G.M.; et al. Cytokeratin-Based CTC Counting Unrelated to Clinical Follow Up. J. Thorac. Dis. 2013, 5, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelaar, P.A.J.; Kraan, J.; Van, M.; Zeune, L.L.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M.; Oomen-de Hoop, E.; Martens, J.W.M.; Sleijfer, S. Defining the Dimensions of Circulating Tumor Cells in a Large Series of Breast, Prostate, Colon, and Bladder Cancer Patients. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenta, R.; Richert, J.; Muchlińska, A.; Senkus, E.; Suchodolska, G.; Łapińska-Szumczyk, S.; Domżalski, P.; Miszewski, K.; Matuszewski, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; et al. Measurable Morphological Features of Single Circulating Tumor Cells in Selected Solid Tumors—A Pilot Study. Cytom. Part A 2024, 105, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.J.; Kim, S.-H.; Kang, H.J.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.M.; Gurel, O.; Kim, S.Y.; Roh, H.R.; Lee, J.; et al. Continuous Centrifugal Microfluidics (CCM) Isolates Heterogeneous Circulating Tumor Cells via Full Automation. Theranostics 2022, 12, 3676–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Li, W.; Yang, D.; Lin, P.P.; Zhang, L.; Guo, H. The Presence of Small-Size Circulating Tumor Cells Predicts Worse Prognosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2025, 149, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.C.; Robinson, P.S.; Wagner, C.; O’Shannessy, D.J. The ParsortixTM Cell Separation System—A Versatile Liquid Biopsy Platform. Cytom. Part A 2018, 93, 1234–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollier-Christen, E.; Renier, C.; Kaplan, T.; Kfir, E.; Crouse, S.C. VTX-1 Liquid Biopsy System for Fully-Automated and Label-Free Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells with Automated Enumeration by BioView Platform. Cytom. Part A 2018, 93, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Features | N | % | N (CTC+) | CTC Positivity Rate (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort (range = 0–72) | 51 | 100% | 24 | 47% | ||
| Sex | 0.759 | |||||
| Female | 36 | 71% | 16 | 44% | ||
| Male | 15 | 29% | 8 | 53% | ||
| Age (median = 64, range = 45–82) | 0.427 | |||||
| ≤60 | 15 | 29% | 9 | 60% | ||
| >60 | 36 | 71% | 15 | 42% | ||
| Subtype | 0.808 | |||||
| ADC | 35 | 69% | 17 | 49% | ||
| SCC | 12 | 24% | 6 | 50% | ||
| NOS | 4 | 8% | 1 | 25% | ||
| Lymph node metastasis | 0.697 | |||||
| yes | 43 | 84% | 19 | 44% | ||
| no | 1 | 2% | 1 | 100% | ||
| n/a | 7 | 14% | 4 | 57% | ||
| Number of metastatic lymph node (median = 6) | 0.013 | |||||
| ≤6 | 23 | 45% | 14 | 61% | ||
| >6 | 15 | 29% | 4 | 27% | ||
| n/a | 13 | 25% | 6 | 46% | ||
| Number of metastatic organs (median = 2, range 1–4) | 0.044 | |||||
| 1 | 3 | 6% | 0 | 0% | ||
| 2 | 29 | 57% | 12 | 41% | ||
| 3 | 10 | 20% | 5 | 50% | ||
| 4 | 3 | 6% | 3 | 100% | ||
| n/a | 6 | 12% | 4 | 67% | ||
| Tumor diameter (mm) (median = 32.8, range = 14–120 mm) | 0.594 | |||||
| ≤32.8 | 20 | 39% | 9 | 45% | ||
| >32.8 | 20 | 39% | 8 | 40% | ||
| n/a | 11 | 22% | 7 | 64% | ||
| Blood Volume | ||||||
| 6 mL | 6 | 12% | 3 | 75% | ||
| 6.5 mL | 3 | 6% | 18 | 43% | ||
| 7.5 mL | 42 | 82% | 3 | 60% | ||
| Relapse | ||||||
| yes | 4 | 8% | 3 | 75% | ||
| no | 42 | 82% | 18 | 43% | ||
| n/a | 5 | 10% | 3 | 60% | ||
| Site of metastasis | ||||||
| Liver | 10 | 20% | 1 | 1 0% | ||
| Lung | 8 | 16% | 3 | 38% | ||
| Brain | 8 | 16% | 3 | 38% | ||
| Bone | 25 | 49% | 12 | 48% | ||
| Lymph node | 44 | 86% | 20 | 45% | ||
| Surrenal glands | 7 | 14% | 2 | 29% | ||
| Pleura | 7 | 14% | 3 | 43% | ||
| Neck | 1 | 2% | 0 | 0% | ||
| Cervix | 1 | 2% | 1 | 100% | ||
| Colon | 1 | 2% | 1 | 100% | ||
| Mediasten | 1 | 2% | 0 | 0% | ||
| LAP | 8 | 16% | 1 | 13% |
| Number of Cells Measure (n) | Cell Size (µm) | Std Dev | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1975 | 152 | 17.4 | 4.3 | <0.001 |
| A549 | 158 | 13.4 | 2.0 | <0.001 |
| WBC | 100 | 7.0 | 1.1 | <0.001 |
| NSCLC-CTC | 285 | 9.5 | 2.0 | - |
| CTC Isolation Technology | Approach | Blood Volume (mL) | Number of Patients | Number of CTC+ Patients (%) | Median (Range) CTC/mL | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microcavity assay (MCA) | Filtration based | 7.5 | 22 | 17 (77) | 13 (0–291) | [67] |
| CellSearch | EpCAM-based | 7 (32) | 0 (0–37) | |||
| CellSearch | EpCAM-based | 7.5 | 33 | 12 (36.4) | NA (0–19) | [68] |
| CellSearch | EpCAM-based | 7.5 | 104 | 33 (32) | 0 (0–141) | [69] |
| Parsortix | Size and deformability based | 8 | 46 | 16 (35) | NA (1–33) | [70] |
| Microfluidic chip | Size-based | 9 | 30 | 23 (76.6) | 5 (0–16) | [71] |
| CellSearch | EpCAM-based | 7 | 210 | 82 (39) | NA (1–23) | [72] |
| ISET | Size-based | 104 (50) | NA (1–150) | |||
| CellSearch | EpCAM-based | 7.5 | 60 (stage IV) | 19 (32) | 1 (0–146) | [73] |
| Parsortix | Size and deformability based | 10 | 15 | 9 (60) | NA (0–12) | [74] |
| ISET | Size-based | 5 (33) | NA (0–3) | |||
| Ficoll | Density gradient centrifugation | 2 (13) | NA (0–2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Özgür, E.; Çırçır, A.; Doğan, B.Ş.; Şahin, Ş.; Karayalçın, G.; Demir, M.A.; Erkek, B.; Demirtaş, E.; Zorlu, Ö.; Ceylan, F.; et al. Evaluation of the Cellsway Microfluidic CTC Enrichment and Identification Platform for CTC Detection in Metastatic NSCLC. Biosensors 2026, 16, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios16010034
Özgür E, Çırçır A, Doğan BŞ, Şahin Ş, Karayalçın G, Demir MA, Erkek B, Demirtaş E, Zorlu Ö, Ceylan F, et al. Evaluation of the Cellsway Microfluidic CTC Enrichment and Identification Platform for CTC Detection in Metastatic NSCLC. Biosensors. 2026; 16(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios16010034
Chicago/Turabian StyleÖzgür, Ebru, Ayça Çırçır, Begüm Şen Doğan, Şebnem Şahin, Gizem Karayalçın, Mehmet Alper Demir, Başak Erkek, Enes Demirtaş, Özge Zorlu, Furkan Ceylan, and et al. 2026. "Evaluation of the Cellsway Microfluidic CTC Enrichment and Identification Platform for CTC Detection in Metastatic NSCLC" Biosensors 16, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios16010034
APA StyleÖzgür, E., Çırçır, A., Doğan, B. Ş., Şahin, Ş., Karayalçın, G., Demir, M. A., Erkek, B., Demirtaş, E., Zorlu, Ö., Ceylan, F., Külah, H., Karadurmuş, N., Şendur, M. A. N., & Kılıçkap, S. (2026). Evaluation of the Cellsway Microfluidic CTC Enrichment and Identification Platform for CTC Detection in Metastatic NSCLC. Biosensors, 16(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios16010034







