Possible Use of the SUDOSCAN Nephropathy Risk Score in Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis: Application in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. SUDOSCAN Measurements
2.3. Patient Clinical and Demographic Profile Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis of Data
3. Results
3.1. Comparison Between Different CKD Stages Groups
3.2. Relationships Between Variables
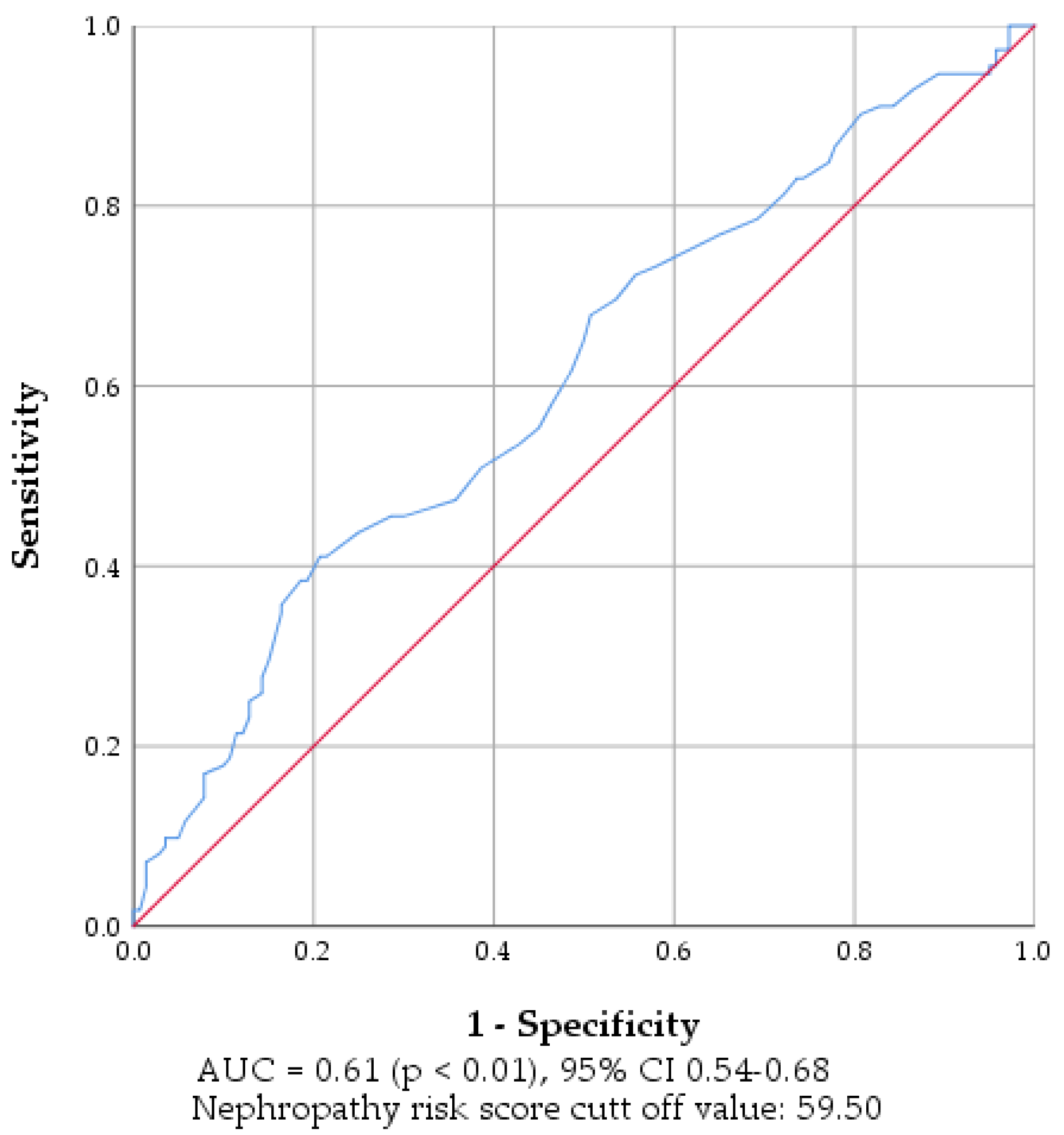
3.3. Effectiveness of SUDOSCAN to Predict Nephropathy Risk
3.4. Comparison Between Patients with or Without Diabetic Nephropathy According to SUDOSCAN Nephropathy-Risk
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Diabetes Federation About Diabetes. Available online: https://idf.org/about-diabetes/diabetes-facts-figures/?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- International Diabetes Federation Romania. Diabetes Country Report 2000–2050. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/data-by-location/country/romania/?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- Iglay, K.; Hannachi, H.; Howie, P.J.; Xu, J.; Li, X.; Engel, S.S.; Moore, L.M.; Rajpathak, S. Prevalence and co-prevalence of comorbidities among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr. Med Res. Opin. 2016, 32, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ozairi, E.; Jallo, M.K.; Hafidh, K.; Alhajeri, D.M.; Ashour, T.; Mahmoud, E.F.N.; ElAal, Z.A.; Loulou, M. Prevalence of Cardiovascular and Renal Co-morbidities in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in the Gulf, a Cross-sectional Observational Study. Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 1193–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacIsaac, R.J.; Ekinci, E.I.; Jerums, G. ‘Progressive diabetic nephropathy. How useful is microalbuminuria? Contra’. Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, F.; Liu, S.; Qiao, X.; Zheng, H.; Xiong, Q.; Wen, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, H.; Shi, H.; et al. SUDOSCAN, an effective tool for screening chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abenavoli, C.; Provenzano, M.; Ksiazek, S.H.; Hu, L.; Cuna, V.; La Manna, G.; Comai, G.; Baraldi, O. Role of Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate in Clinical Research: The Never-Ending Matter. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 25, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckardt, K.-U.; Berns, J.S.; Rocco, M.V.; Kasiske, B.L. Definition and Classification of CKD: The Debate Should Be About Patient Prognosis—A Position Statement From KDOQI and KDIGO. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Nica, A.; Rusu, E.; Dobjanschi, C.G.; Rusu, F.; A Parliteanu, O.; Vinereanu, I.V.; Sivu, C.; Radulian, G. Sudoscan’s Effectiveness in Identifying Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Cureus 2024, 16, e60344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eranki, V.; Santosh, R.; Rajitha, K.; Pillai, A.; Sowmya, P.; Dupin, J.; Calvet, J. Sudomotor function assessment as a screening tool for microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2013, 101, e11–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, V.A.; Sandroni, P.; Fealey, R.D.; Low, P.A. Detection of small-fiber neuropathy by sudomotor testing. Muscle Nerve 2006, 34, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, B.I.; Smith, S.C.; Bagwell, B.M.; Xu, J.; Bowden, D.W.; Divers, J. Electrochemical Skin Conductance in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2015, 41, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anghel, L.; Cobuz, C.; Benchea, L.-C.; Maciuc, V.; Cobuz, M.; Sascău, R.-A.; Stătescu, C. Sudomotor Dysfunction as an Early Marker of Autonomic and Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes: Insights from a Cross-Sectional Study Using SUDOSCAN. Biosensors 2025, 15, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toderean, R.; Cobuz, M.; Dimian, M.; Cobuz, C. From Evaluation to Prediction: Analysis of Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy Using Sudoscan and Artificial Intelligence. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinik, A.I.; Nevoret, M.-L.; Casellini, C. The New Age of Sudomotor Function Testing: A Sensitive and Specific Biomarker for Diagnosis, Estimation of Severity, Monitoring Progression, and Regression in Response to Intervention. Front. Endocrinol. 2015, 6, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, H.J.; Jaar, B.G.; Choi, M.J.; Palevsky, P.M.; Vassalotti, J.A.; Rocco, M.V. An Endorsement of the Removal of Race From GFR Estimation Equations: A Position Statement From the National Kidney Foundation Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2022, 80, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, S.R.; Aeddula, N.R. Chronic Kidney Disease; StatPearls Publishing: Oakland Park, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.-S.; Park, S.W.; Cho, Y.-W.; Kim, S.-K. Higher Prevalence and Progression Rate of Chronic Kidney Disease in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. J. 2018, 42, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramlage, P.; Lanzinger, S.; Hess, E.; Fahrner, S.; Heyer, C.H.J.; Friebe, M.; Buschmann, I.; Danne, T.; Holl, R.W.; Seufert, J. Renal function deterioration in adult patients with type-2 diabetes. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudman, L.; Vets, N.; Jansen, J.; De Smedt, A.; Billot, M.; Rigoard, P.; Cordenier, A.; Engelborghs, S.; Scafoglieri, A.; Moens, M. Electrochemical Skin Conductance Alterations during Spinal Cord Stimulation: An Experimental Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, M.; Ruzgas, T.; Svedenhag, P.; Anderson, C.D.; Ollmar, S.; Engblom, J.; Björklund, S. Skin hydration dynamics investigated by electrical impedance techniques in vivo and in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, B.I.; Bowden, D.W.; Smith, S.C.; Xu, J.; Divers, J. Relationships between electrochemical skin conductance and kidney disease in Type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2014, 28, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, L.-T.; Lin, Y.-L.; Wang, C.-H.; Hwu, C.-M.; Liou, H.-H.; Hsu, B.-G. Electrochemical Skin Conductance by Sudoscan in Non-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 13, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Zhu, X.; Lu, B.; Li, Y. Detection of relationships between SUDOSCAN with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2018, 138, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schold, J.D.; Navaneethan, S.D.; Jolly, S.E.; Poggio, E.D.; Arrigain, S.; Saupe, W.; Jain, A.; Sharp, J.W.; Simon, J.F.; Schreiber, M.J., Jr. Implications of the CKD-EPI GFR estimation equation in clinical practice. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, S.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Dyck, P.J.; Freeman, R.; Horowitz, M.; Kempler, P.; Lauria, G.; Malik, R.A.; Spallone, V.; Vinik, A.; et al. Diabetic Neuropathies: Update on Definitions, Diagnostic Criteria, Estimation of Severity, and Treatments. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2285–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Frequency | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Group | ||
| S1 (EGFR > 90 mL/min/1.73 m2) | 114 | 44.88 |
| S2 (EGFR between 60 and 90 mL/min/1.73 m2) | 112 | 44.09 |
| S3 (EGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2) | 28 | 11.02 |
| Sex | ||
| Men | 136 | 53.54 |
| Women | 118 | 46.46 |
| Diabetes duration | ||
| 0–5 years | 108 | 42.52 |
| 6–15 years | 87 | 34.25 |
| >15 years | 59 | 23.23 |
| Age | ||
| <50 years | 27 | 10.63 |
| 50–60 years | 89 | 35.04 |
| 61–70 years | 96 | 37.80 |
| >70 years | 42 | 16.54 |
| Group/ Characteristic | S1 | S2 | S3 | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std. Dev. | Mean | Std. Dev. | Mean | Std. Dev. | ||
| SUDOSCAN parameters | |||||||
| Right foot ESC value (μs) | 78.58 a | 7.57 | 80.08 a | 6.69 | 72.07 b | 14.55 | 0.00 |
| Left foot ESC value (μs) | 79.97 a | 5.79 | 80.23 a | 6.21 | 79.00 a | 6.79 | 0.69 |
| Right hand ESC value (μs) | 64.00 a | 14.39 | 64.91 a | 11.97 | 66.11 a | 13.25 | 0.73 |
| Left hand ESC value (μs) | 64.99 a | 13.76 | 65.82 a | 12.60 | 67.85 a | 11.79 | 0.59 |
| Nephropathy risk score | 65.61 a | 15.80 | 60.37 ab | 14.16 | 55.63 b | 11.45 | 0.00 |
| Clinical metabolic characteristics | |||||||
| HbA1c (%) | 8.47 a | 1.58 | 7.95 b | 1.33 | 7.98 b | 1.69 | 0.03 |
| Cholesterol total (mg/dL) | 181.10 a | 43.97 | 175.59 ab | 44.54 | 161.14 b | 38.88 | 0.10 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 146.87 a | 68.57 | 125.85 b | 53.21 | 146.83 a | 63.79 | 0.04 |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 123.61 a | 38.62 | 113.37 ab | 35.62 | 100.96 b | 31.28 | 0.01 |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 143.76 a | 17.58 | 140.47 a | 15.92 | 143.83 a | 6.64 | 0.30 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 82.07 a | 10.19 | 80.72 a | 11.33 | 78.79 a | 11.38 | 0.32 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.67 c | 0.12 | 0.90 b | 0.14 | 1.25 a | 0.22 | 0.00 |
| EGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 110.90 a | 18.70 | 75.78 b | 8.32 | 49.30 a | 8.41 | 0.00 |
| Patient characteristics | |||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 32.99 a | 5.75 | 31.44 a | 4.19 | 33.34 a | 5.90 | 0.04 |
| Diabetes duration (years) | 9.39 a | 9.33 | 9.12 a | 7.35 | 10.82 a | 8.34 | 0.63 |
| Age (years) | 58.01 b | 9.80 | 63.15 a | 7.40 | 65.89 a | 8.36 | 0.00 |
| Right Foot ESC Value | Left Foot ESC Value | Left Hand ESC Value | Right Hand ESC Value | Nephropathy Risk | Diabetes Duration | BMI | HbA1c | Cholesterol Total | Triglycerides | LDL Cholesterol | Systolic BP | Diastolic BP | Creatinine | EGFR | Age | Sex | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right foot ESC value value | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| Left foot ESC value | 0.91 ** | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||
| Left hand ESC value | 0.33 ** | 0.40 ** | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||
| Right hand ESC value | 0.30 ** | 0.37 ** | 0.90 ** | 1.00 | |||||||||||||
| Nephropathy risk | 0.62 ** | 0.60 ** | 0.37 ** | 0.41 ** | 1.00 | ||||||||||||
| Diabetes duration | 0.02 | 0.00 | −0.08 | −0.07 | −0.21 ** | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| BMI | 0.14 | 0.18 * | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.25 ** | −0.14 | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| HbA1c | 0.06 | 0.05 | −0.02 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.25 ** | 0.14 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| Cholesterol total | −0.03 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.06 | −0.01 | −0.10 | −0.04 | 0.11 | 1.00 | ||||||||
| Triglycerides | 0.01 | −0.04 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.39 ** | 1.00 | |||||||
| LDL cholesterol | −0.12 | −0.08 | −0.10 | −0.08 | −0.07 | −0.18 * | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.75 ** | 0.32 ** | 1.00 | ||||||
| Systolic BP | 0.02 | 0.08 | −0.06 | −0.10 | −0.08 | −0.03 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.06 | −0.01 | 0.08 | 1.00 | |||||
| Diastolic BP | 0.14 | 0.07 | −0.08 | −0.12 | 0.05 | −0.12 | 0.13 | −0.10 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.49 ** | 1.00 | ||||
| Creatinine | −0.12 | −0.04 | −0.09 | −0.11 | −0.33 ** | 0.13 | −0.04 | −0.05 | −0.24 ** | −0.03 | −0.13 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 1.00 | |||
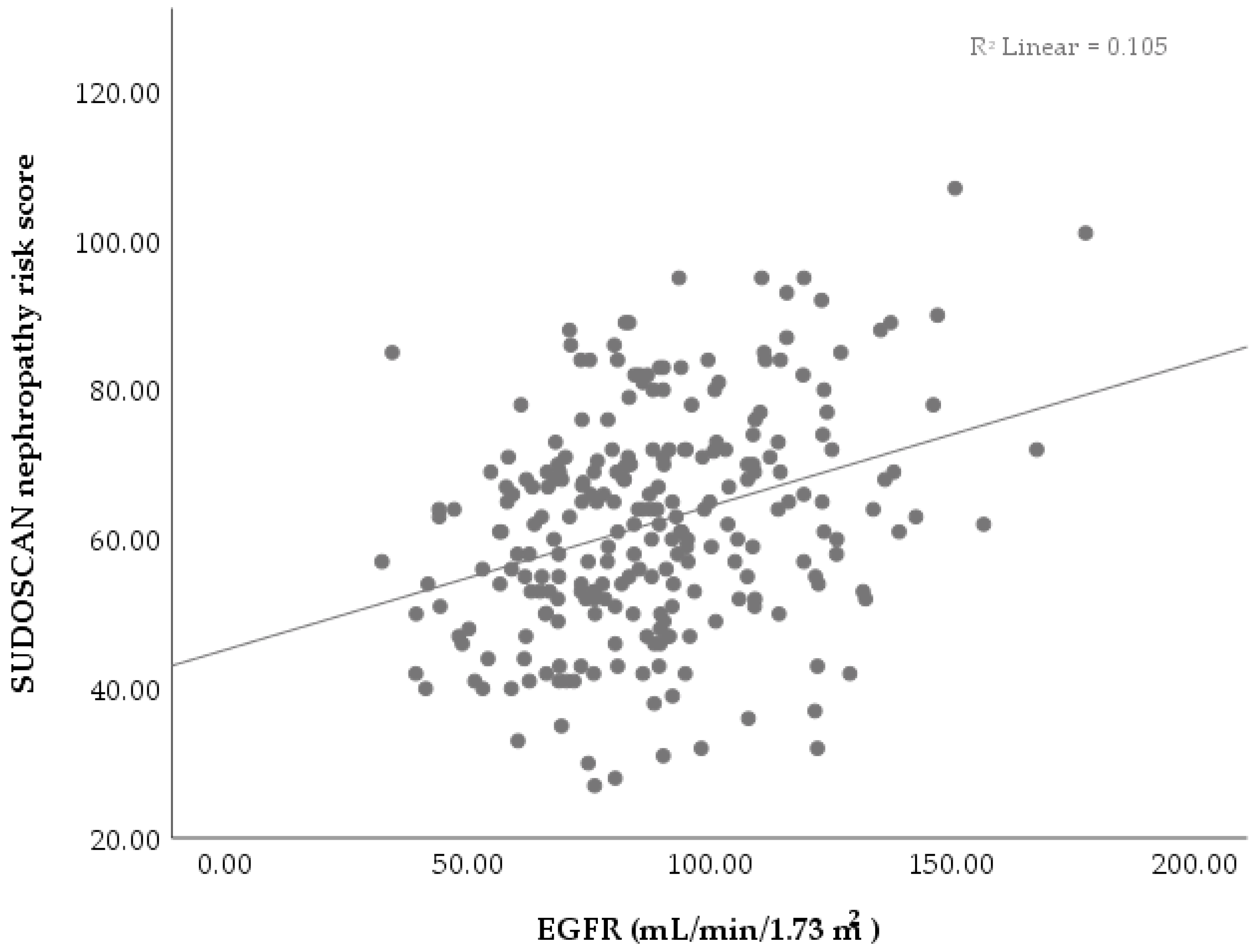
| EGFR | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.34 ** | −0.16 | −0.05 | 0.08 | 0.14 | −0.03 | 0.15 | −0.08 | 0.05 | −0.80 ** | 1.00 | ||
| Age | −0.15 | −0.14 | −0.19 * | −0.23 ** | −0.73 ** | 0.25 ** | −0.15 | −0.12 | −0.12 | −0.17 | −0.02 | 0.12 | −0.02 | 0.33 ** | −0.42 ** | 1.00 | |
| Sex | −0.04 | −0.02 | 0.15 | 0.21 * | 0.15 | −0.02 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.19 * | −0.06 | −0.10 | −0.17 * | −0.45 ** | −0.07 | −0.10 | 1.00 |
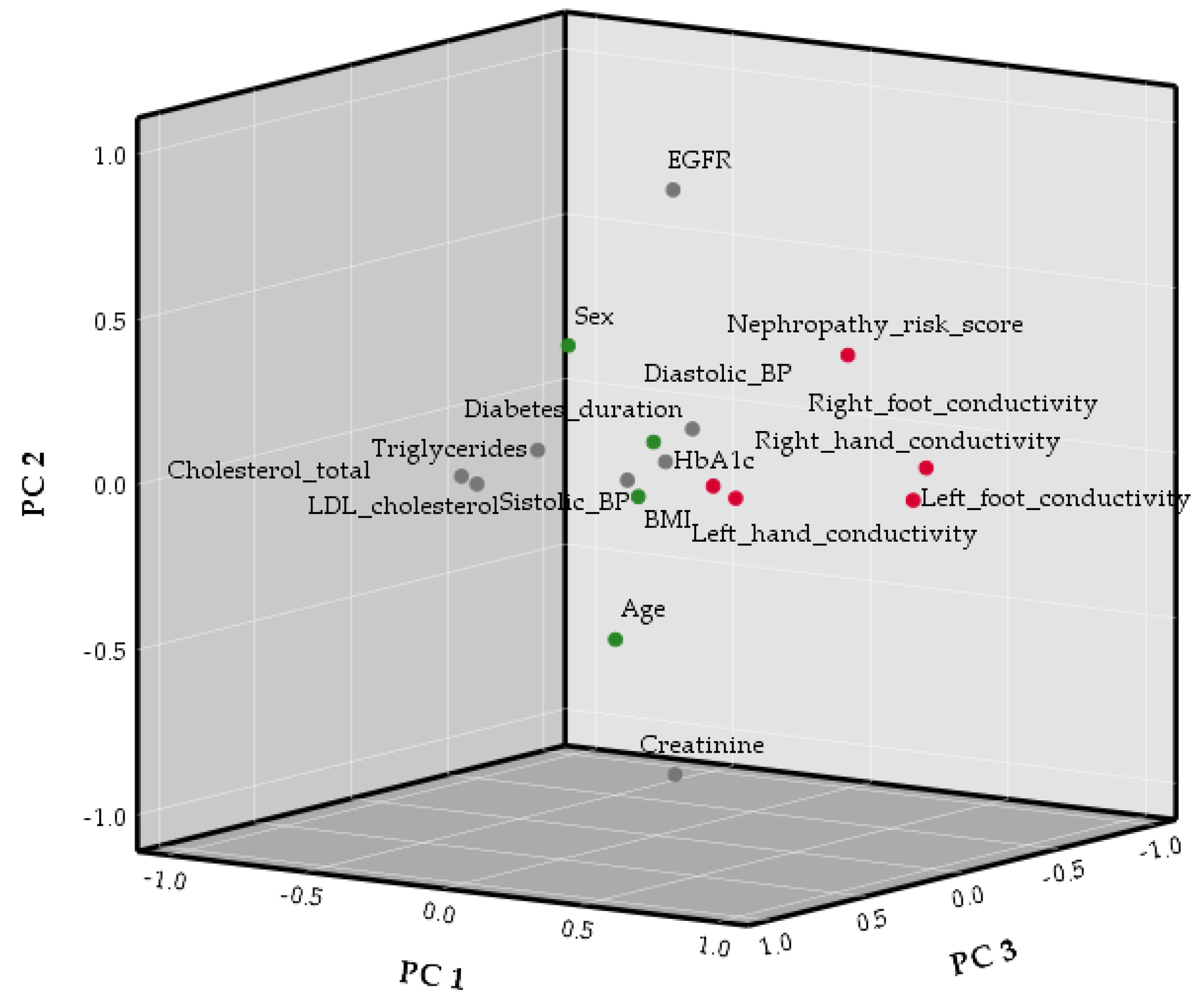
| Component | Eigenvalue | Variance (%) | Cumulative Variance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 3.72 | 21.88 | 21.88 |
| PC2 | 2.60 | 15.28 | 37.17 |
| PC3 | 1.92 | 11.31 | 48.47 |
| PC4 | 1.67 | 9.82 | 58.29 |
| PC5 | 1.31 | 7.73 | 66.02 |
| PC6 | 1.13 | 6.62 | 72.64 |
| PC7 | 1.09 | 6.39 | 79.02 |
| Source | Type III Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | p | Partial Eta Squared |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrected Model | 30,795.29 a | 6 | 5132.55 | 52.41 | 0.00 | 0.57 |
| Intercept | 30,145.41 | 1 | 30,145.41 | 307.80 | 0.00 | 0.57 |
| Age | 18,862.54 | 1 | 18,862.54 | 192.59 | 0.00 | 0.45 |
| Diabetes duration | 925.95 | 1 | 925.95 | 9.45 | 0.00 | 0.04 |
| BMI | 465.86 | 1 | 465.86 | 4.76 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| Sex | 252.77 | 1 | 252.77 | 2.58 | 0.11 | 0.01 |
| Group | 141.10 | 2 | 70.55 | 0.72 | 0.49 | 0.01 |
| SUDOSCAN Nephropathy Risk Score < 59.50 (G1) | SUDOSCAN Nephropathy Risk Score > 59.50 (G1) | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std. Dev. | Mean | Std. Dev. | ||
| SUDOSCAN parameters | |||||
| Right foot ESC value (μs) | 73.99 b | 9.59 | 80.98 a | 7.05 | 0.00 |
| Left foot ESC value (μs) | 76.50 b | 6.13 | 81.88 a | 5.15 | 0.00 |
| Right hand ESC value (μs) | 59.58 b | 13.36 | 68.37 a | 11.82 | 0.00 |
| Left hand ESC value (μs) | 61.74 b | 13.13 | 68.53 a | 12.23 | 0.00 |
| Nephropathy risk score | 48.14 b | 7.60 | 72.32 a | 10.01 | 0.00 |
| Clinical metabolic characteristics | |||||
| HbA1c (%) | 8.11 a | 1.55 | 8.25 a | 1.47 | 0.35 |
| Cholesterol total (mg/dL) | 172.12 a | 44.59 | 179.69 a | 43.30 | 0.21 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 129.49 a | 60.17 | 144.29 a | 63.68 | 0.05 |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 115.09 a | 35.10 | 117.76 a | 38.80 | 0.75 |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 143.46 a | 14.65 | 141.51 a | 17.38 | 0.27 |
| iastolic BP (mmHg) | 79.55 a | 11.44 | 82.22 a | 10.31 | 0.09 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.89 a | 0.25 | 0.79 b | 0.21 | 0.00 |
| EGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 81.17 b | 23.86 | 94.23 a | 25.73 | 0.00 |
| Patient characteristics | |||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 66.95 b | 8.05 | 56.78 a | 7.25 | 0.00 |
| Diabetes duration (years) | 12.30 a | 9.98 | 7.27 b | 6.15 | 0.00 |
| Age (years) | 30.86 b | 4.73 | 33.50 a | 5.25 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cobuz, C.; Ungureanu-Iuga, M.; Anton-Paduraru, D.-T.; Cobuz, M. Possible Use of the SUDOSCAN Nephropathy Risk Score in Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis: Application in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Biosensors 2025, 15, 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090620
Cobuz C, Ungureanu-Iuga M, Anton-Paduraru D-T, Cobuz M. Possible Use of the SUDOSCAN Nephropathy Risk Score in Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis: Application in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Biosensors. 2025; 15(9):620. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090620
Chicago/Turabian StyleCobuz, Claudiu, Mădălina Ungureanu-Iuga, Dana-Teodora Anton-Paduraru, and Maricela Cobuz. 2025. "Possible Use of the SUDOSCAN Nephropathy Risk Score in Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis: Application in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes" Biosensors 15, no. 9: 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090620
APA StyleCobuz, C., Ungureanu-Iuga, M., Anton-Paduraru, D.-T., & Cobuz, M. (2025). Possible Use of the SUDOSCAN Nephropathy Risk Score in Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis: Application in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Biosensors, 15(9), 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090620






