Pancreatic Lipase in Eutectogels as Emerging Materials: Exploring Their Properties and Potential Applications in Biosensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES)
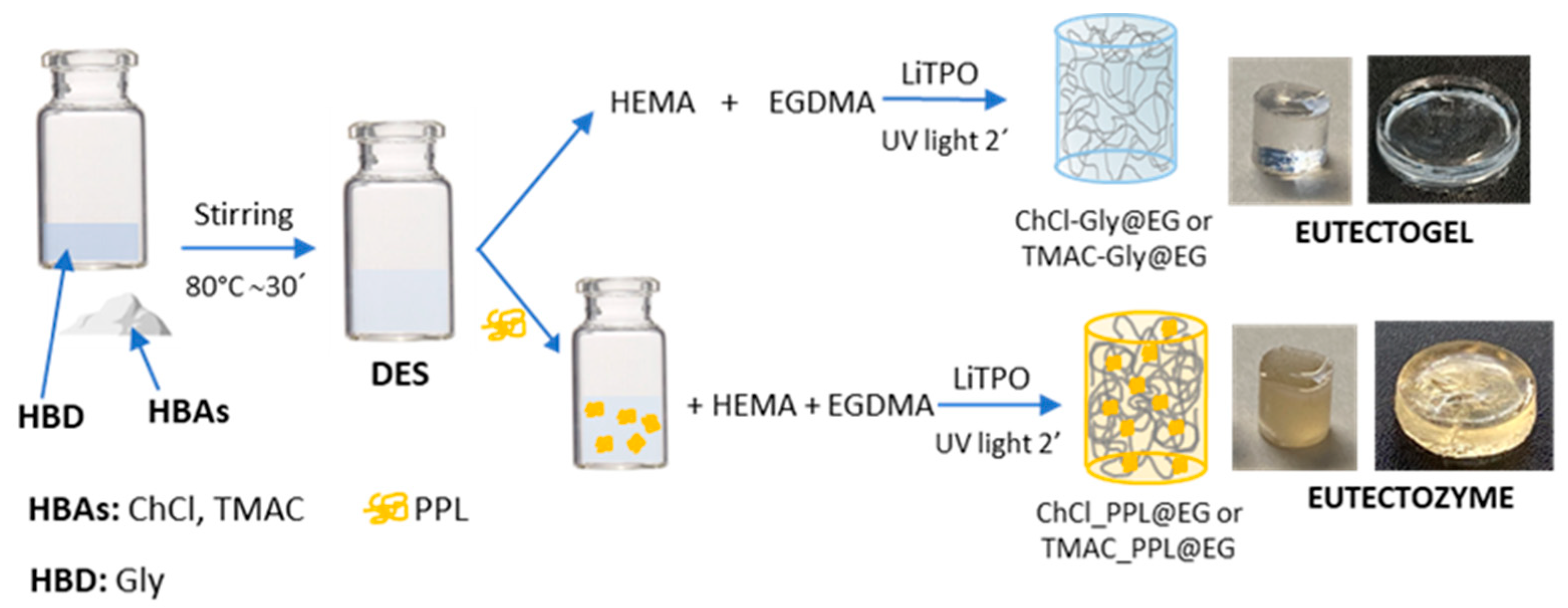
2.3. Preparation of Eutectogels (EGs) and Eutectozymes
2.4. Fluorescence Measurements
2.5. Activity Assay in Solution
2.6. Activity Assay in Eutectozymes
2.7. Inhibition Assays in Eutectozymes
2.8. Swelling Measurements
2.9. Rheological Measurements
2.10. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3. Results and Discussion
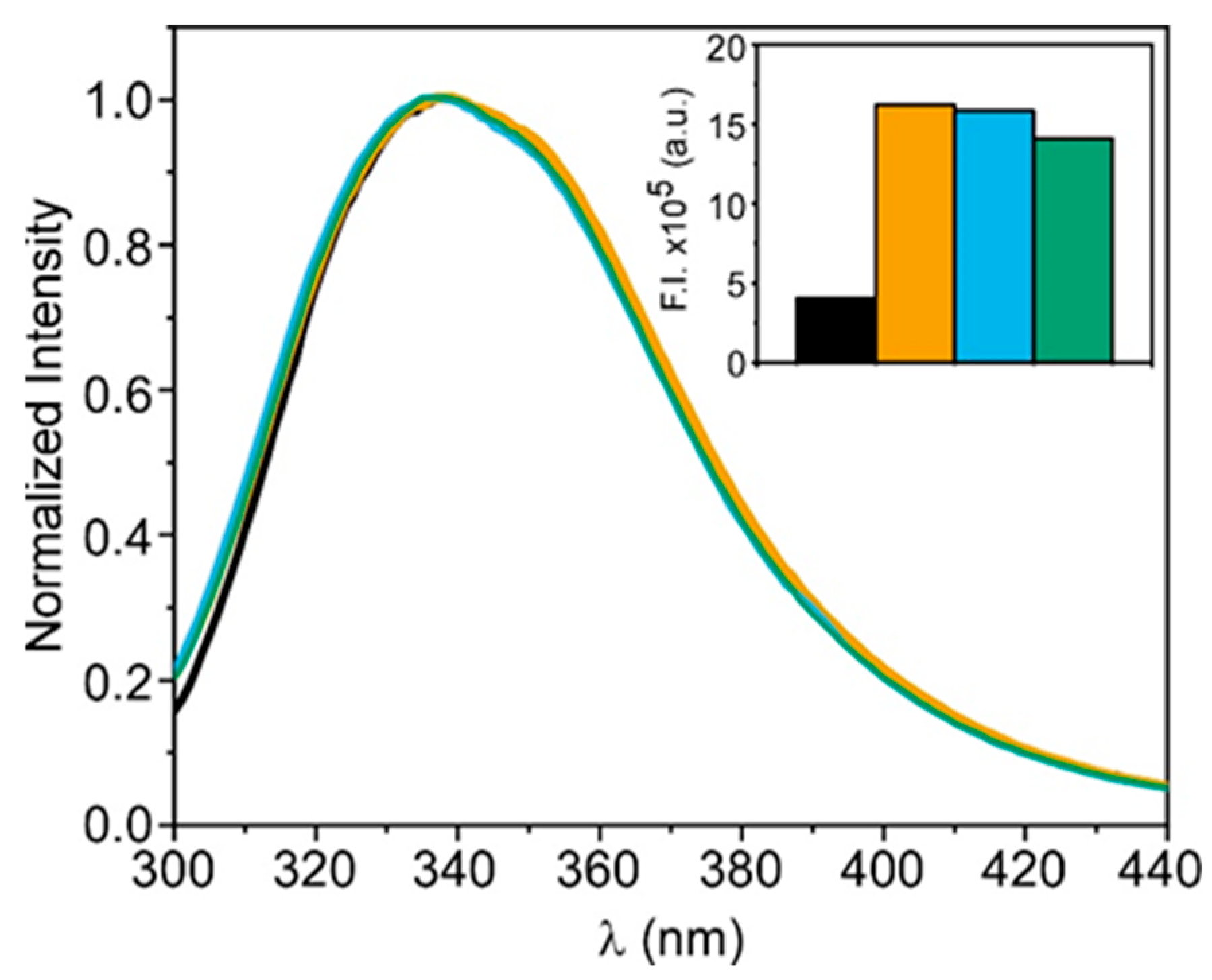
3.1. Conformational Stability of PPL in DES
3.2. Enzyme Activity of PPL in DES
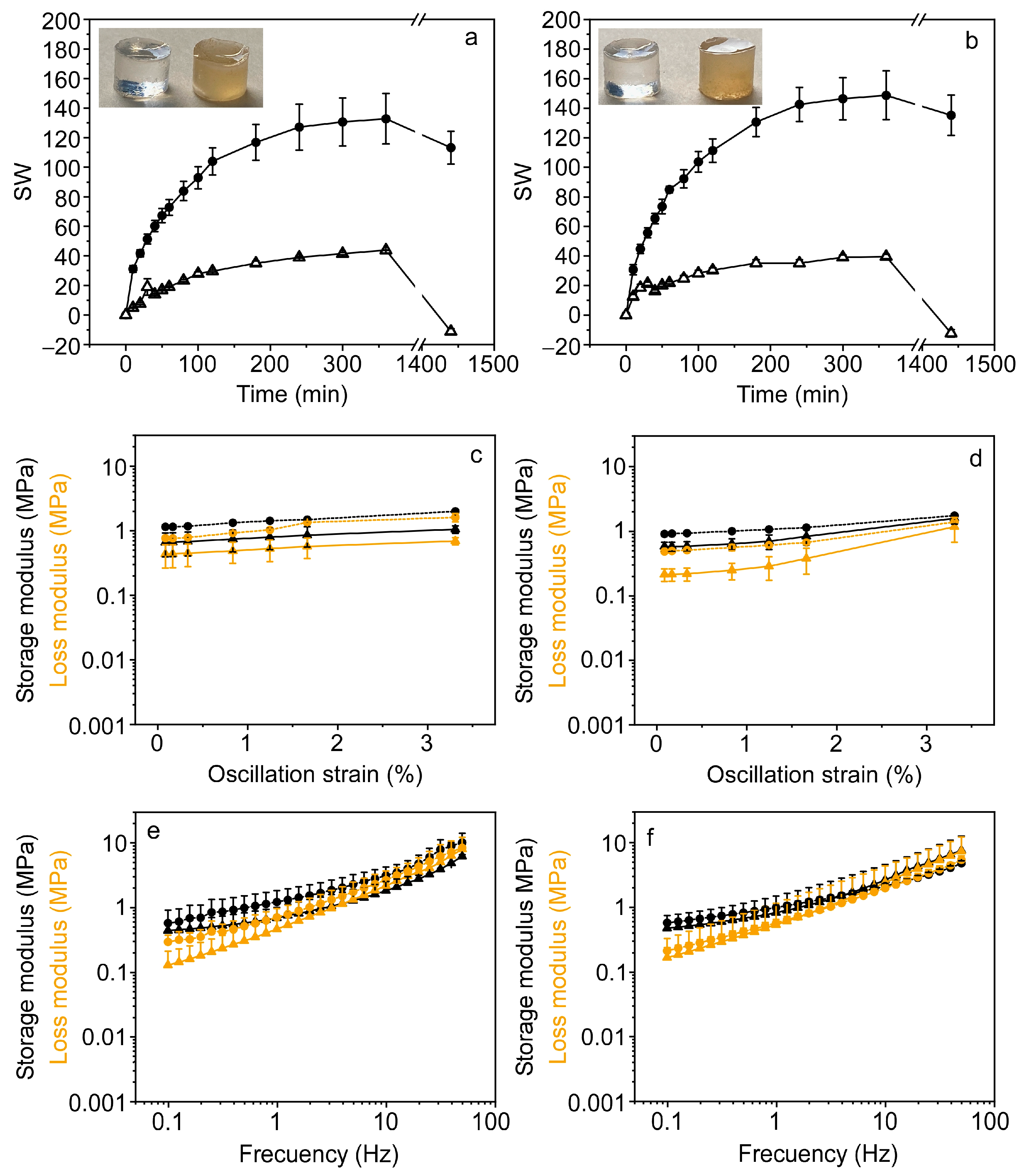
3.3. Characterization of PPL in Eutectogels
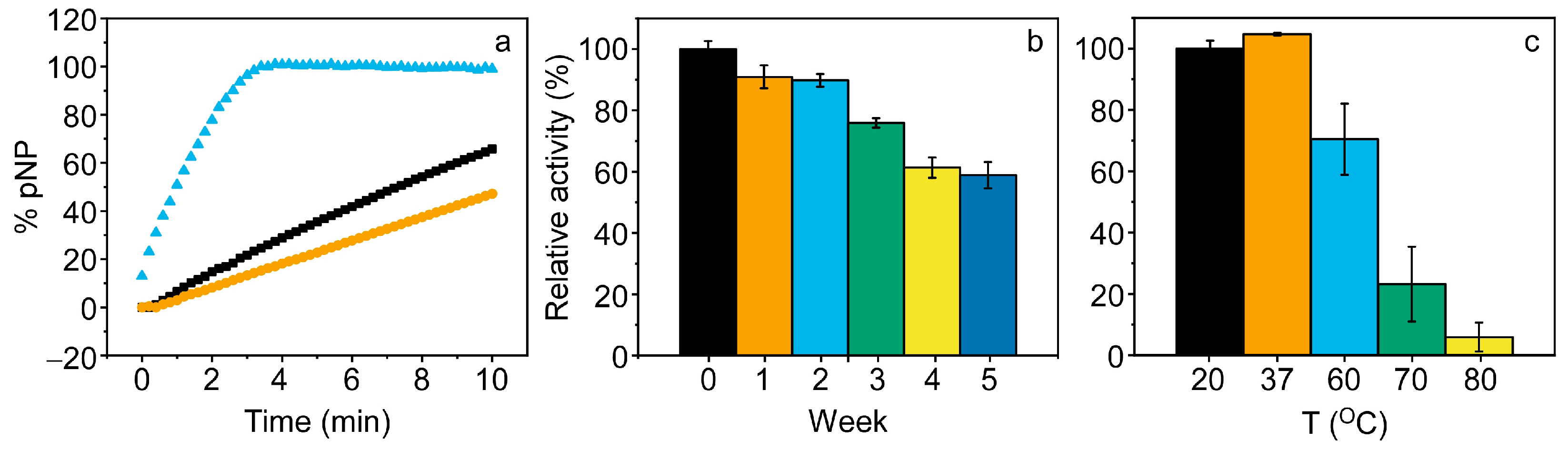
3.4. Enzyme Activity of PPL in Eutectogels
3.5. TMAC_PPL@EG as Platform for Biosensing Applications
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DES | Deep eutectic solvent |
| HBD | Hydrogen bond donor |
| HBA | Hydrogen bond aceptor |
| EG | Eutectogel |
| PL | Pancreatic lipase |
| PPL | Porcine pancreatic lipase |
| ChCl | Choline chloride |
| Gly | Glycerol |
| TMAC | Tetramethylammonium chloride |
| HEMA | 2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate |
| EGDMA | Ethylene glycol dimethacrylate |
| LiTPO | 2,4,6-Trimethylbenzoylphenylphosphinate lithium salt |
| pNPAc | p-Nitrophenyl acetate |
| pNPP | p-Nitrophenyl palmitate |
| pNP | p-Nitrophenol |
| W0 | Initial weight |
| Wt | Subsequent weight |
| SW | Degree of swelling |
| DMA | Dynamic mechanical analysis |
| E‘ | Storage modulus |
| E’’ | Loss modulus |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric analysis |
| DTG | Differential thermogravimetric analysis |
| Tm | Midpoint temperature |
| Tan δ | Damping factor |
References
- Hansen, B.B.; Spittle, S.; Chen, B.; Poe, D.; Zhang, Y.; Klein, J.M.; Horton, A.; Adhikari, L.; Zelovich, T.; Doherty, B.W.; et al. Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review of Fundamentals and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1232–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Ma, Z.; Yan, L. Deep Eutectic Solvents Eutectogels: Progress and Challenges. Green Chem. Eng. 2021, 2, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercadal, P.A.; González, A.; Beloqui, A.; Tomé, L.C.; Mecerreyes, D.; Calderón, M.; Picchio, M.L. Eutectogels: The Multifaceted Soft Ionic Materials of Tomorrow. JACS Au 2024, 4, 3744–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Sun, D.-W.; Tian, Y. Emerging Eutectogel Materials: Development, Synthesis, Properties, and Applications in Food Science. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 159, 104962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, B.; Du, X.; Shao, W.; Qian, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Z. Hydrophobic, Ionically Conductive, Self-Adhesive and Fully Recyclable Eutectogels for Stretchable Wearable Sensors and Triboelectric Nanogenerators. J. Mater. Chem. A 2025, 13, 12988–12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhan, J.; Pu, C.; Zhong, L.; Hou, H. Eutectogels: Recent Advances and Emerging Biological Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 2425778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noro, J.; Cabo, J.; Freitas, D.S.; Roque, C.S.; de Castro, M.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Silva, C. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Suitable Solvents for Lipase-Catalyzed Transesterification Reactions. ChemSusChem 2023, 16, e202300615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Chen, X.; Li, G.; Zhao, M.; Li, D. Effect of Deep Eutectic Solvents on Activity, Stability, and Selectivity of Enzymes: Novel Insights and Further Prospects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 284, 138148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taklimi, S.M.; Divsalar, A.; Ghalandari, B.; Ding, X.; Di Gioia, M.L.; Omar, K.A.; Saboury, A.A. Effects of Deep Eutectic Solvents on the Activity and Stability of Enzymes. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 377, 121562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquembre, R.; Sanz, J.M.; Wall, J.G.; Del Monte, F.; Mateo, C.R.; Ferrer, M.L. Thermal Unfolding and Refolding of Lysozyme in Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Aqueous Dilutions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 11248–11256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Calderón, M.; Beloqui, A.; Picchio, M.L. Eutectogels as Promising Materials in Biocatalysis. ChemCatChem 2024, 16, e202400204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Han, H.; Ma, Z. Carboxybetaine Methacrylate-Based Supramolecular Eutectogel: A High-Performance Antifouling Platform for Ultrasensitive Sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 444, 138419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alacid, Y.; Martínez-Baquero, R.; Esquembre, R.; Montilla, F.; Martínez-Tomé, M.J.; Mateo, C.R. Innovative Fluorescent Nanocomposite Eutectogels: Design and Characterization towards Biosensing Applications. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 424, 127123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.; Longo, M.A.; Deive, F.J.; Álvarez, M.S.; Rodríguez, A. Dual Role of a Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent as Lipase Extractant and Transesterification Enhancer. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 346, 131095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, C.; Ferreira, M.L.; Barbosa, O.; Dos Santos, J.C.S.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Briand, L.E.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Novozym 435: The “Perfect” Lipase Immobilized Biocatalyst? Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 2380–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, P.; Enespa; Singh, R.; Arora, P.K. Microbial Lipases and Their Industrial Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.N.C.; Palawat, S.; Paul, A.T. Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Molecular Modelling Studies of Indole Glyoxylamides as a New Class of Potential Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 85, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Hou, X.; Han, J.; Qin, X.; Yang, Y.; Song, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; et al. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Salicylanilides as Novel Allosteric Inhibitors of Human Pancreatic Lipase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2023, 91, 117413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skonta, A.; Gkantzou, E.; Spyrou, K.; Spyrou, S.; Polydera, A.; Gournis, D.; Stamatis, H. 3D Printed Polylactic Acid (PLA) Well Plates for Enzyme Inhibition Studies: The Case of Pancreatic Lipase. Catal. Res. 2022, 2, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, N.; Prabhu, N.P. Lid Closure Dynamics of Porcine Pancreatic Lipase in Aqueous Solution. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2016, 1860, 2313–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.I.; Lan, D.; Durrani, R.; Huan, W.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y. The Lid Domain in Lipases: Structural and Functional Determinant of Enzymatic Properties. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2017, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Caro, J.; Boudouard, M.; Bonicel, J.; Guidoni, A.; Desnuelle, P.; Rovery, M. Porcine Pancreatic Lipase. Completion of the Primary Structure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Protein Struct. 1981, 671, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, S.N.; Hayyan, A.; Hayyan, M.; Hashim, M.A.; Elgharbawy, A.A.M.; Sani, F.S.; Basirun, W.J.; Lee, V.S.; Alias, Y.; Mohammed, A.K.; et al. Ternary Glycerol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents: Physicochemical Properties and Enzymatic Activity. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2021, 169, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgharbawy, A.A.M.; Syed Putra, S.S.; Khan, H.W.; Azmi, N.A.N.; Sani, M.S.A.; Ab llah, N.; Hayyan, A.; Jewaratnam, J.; Basirun, W.J. Menthol and Fatty Acid-Based Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents as Media for Enzyme Activation. Processes 2023, 11, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, M.C.; Ferrer, M.L.; Mateo, C.R.; del Monte, F. Freeze-Drying of Aqueous Solutions of Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Suitable Approach to Deep Eutectic Suspensions of Self-Assembled Structures. Langmuir 2009, 25, 5509–5515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alacid, Y.; Martínez-Tomé, M.J.; Esquembre, R.; Herrero, M.A.; Mateo, C.R. Portable Alkaline Phosphatase–Hydrogel Platform: From Enzyme Characterization to Phosphate Sensing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Yu, H.; Wang, X.; Li, K.; Li, P. Effect of the Molecular Weight of Water-Soluble Chitosan on Its Fat-/Cholesterol-Binding Capacities and Inhibitory Activities to Pancreatic Lipase. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, C.V.T.; Luu, N.V.H.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Nguyen, T.T.; Ho, B.Q.; Nguyen, T.H.; Tran, T.D.; Nguyen, Q.T. Screening for Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitors: Evaluating Assay Conditions Using p-Nitrophenyl Palmitate as Substrate. All Life 2022, 15, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook-Chennault, K.; Anaokar, S.; Medina Vázquez, A.M.; Chennault, M. Influence of High Strain Dynamic Loading on HEMA–DMAEMA Hydrogel Storage Modulus and Time Dependence. Polymers 2024, 16, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezić Meštrović, I.; Somogyi Škoc, M.; Dragun, D.D.; Glagolić, P.; Meštrović, E. Sustainable Solutions for Producing Advanced Biopolymer Membranes—From Net-Zero Technology to Zero Waste. Polymers 2025, 17, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourbon-Freie, A.; Dub, R.E.; Xiao, X.; Lowe, M.E. Trp-107 and Trp-253 Account for the Increased Steady State Fluorescence That Accompanies the Conformational Change in Human Pancreatic Triglyceride Lipase Induced by Tetrahydrolipstatin and Bile Salt. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 14157–14164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, P.; Coste, T.; Piémont, E.; Lessinger, J.M.; Bousquet, J.A.; Chapus, C.; Kerfelec, B.; Férard, G.; Mély, Y. Time-Resolved Fluorescence Allows Selective Monitoring of Trp30 Environmental Changes in the Seven-Trp-Containing Human Pancreatic Lipase. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 12488–12496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, S.; Gupta, A.; Kashyap, H.K.; Kashyap, H.K. How Hydration Affects the Microscopic Structural Morphology in a Deep Eutectic Solvent. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 2230–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadyan, A.; Juneja, S.; Pandey, S. Photophysical Behavior and Fluorescence Quenching of l -Tryptophan in Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 7578–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaitanya, P.K.; Prabhu, N.P. Stability and Activity of Porcine Lipase Against Temperature and Chemical Denaturants. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 174, 2711–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanoli, V.; Pietrowska, J.; De, G.; Lima, A.; Souza, M.E.; Di, P.; Briatico Vangosa, F.; Mele, A.; Castiglione, F. Supramolecular Hydrophobic Eutectogels Based on Menthol-Thymol as Thermo- and PH-Responsive Drug Delivery Systems. ACS Appl. Eng. Mater. 2024, 2, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjunan, K.K.; Weng, C.Y.; Sheng, Y.J.; Tsao, H.K. Formation of Self-Healing Granular Eutectogels through Jammed Carbopol Microgels in Supercooled Deep Eutectic Solvent. Langmuir 2024, 40, 17081–17089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.H.; Liu, X.; Shen, M.Y.; Nie, S.P.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Gong, D.M.; Xie, M.Y. Purification, Physicochemical Characterisation and Anticancer Activity of a Polysaccharide from Cyclocarya Paliurus Leaves. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Mellado, N.; Larriba, M.; Navarro, P.; Rigual, V.; Ayuso, M.; García, J.; Rodríguez, F. Thermal Stability of Choline Chloride Deep Eutectic Solvents by TGA/FTIR-ATR Analysis. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 260, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldulaimi, M.D.; Omar, S.; Hasan, S.N.; Mohammed, I.; Murtaza, M.; Kamal, M.S.; Al-Yaseri, A. Formulation and Characterization of Quaternary Ammonium Compounds for Novel Application in Enhanced Oil Recovery. Energy Fuels 2024, 38, 21941–21955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Wang, Z. Tailoring the Swelling-Shrinkable Behavior of Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2303326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahveci, Z.; Martínez-Tomé, M.J.; Mallavia, R.; Mateo, C.R. Fluorescent Biosensor for Phosphate Determination Based on Immobilized Polyfluorene-Liposomal Nanoparticles Coupled with Alkaline Phosphatase. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, K.; Bhardwaj, S.; Kamboj, S.; Khatter, B. Method Development and Validation of Orlistat by Using RP-HPLC. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2025, 21, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Baquero, R.; Martínez-Tomé, M.J.; Gómez, J.; Esquembre, R.; Mateo, C.R. Pancreatic Lipase in Eutectogels as Emerging Materials: Exploring Their Properties and Potential Applications in Biosensing. Biosensors 2025, 15, 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090615
Martínez-Baquero R, Martínez-Tomé MJ, Gómez J, Esquembre R, Mateo CR. Pancreatic Lipase in Eutectogels as Emerging Materials: Exploring Their Properties and Potential Applications in Biosensing. Biosensors. 2025; 15(9):615. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090615
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Baquero, Raúl, María José Martínez-Tomé, Javier Gómez, Rocío Esquembre, and C. Reyes Mateo. 2025. "Pancreatic Lipase in Eutectogels as Emerging Materials: Exploring Their Properties and Potential Applications in Biosensing" Biosensors 15, no. 9: 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090615
APA StyleMartínez-Baquero, R., Martínez-Tomé, M. J., Gómez, J., Esquembre, R., & Mateo, C. R. (2025). Pancreatic Lipase in Eutectogels as Emerging Materials: Exploring Their Properties and Potential Applications in Biosensing. Biosensors, 15(9), 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090615




