PEI-Fe3O4/PTA-AuNPs Hybrid System for Rapid DNA Extraction and Colorimetric LAMP Detection of E. faecium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
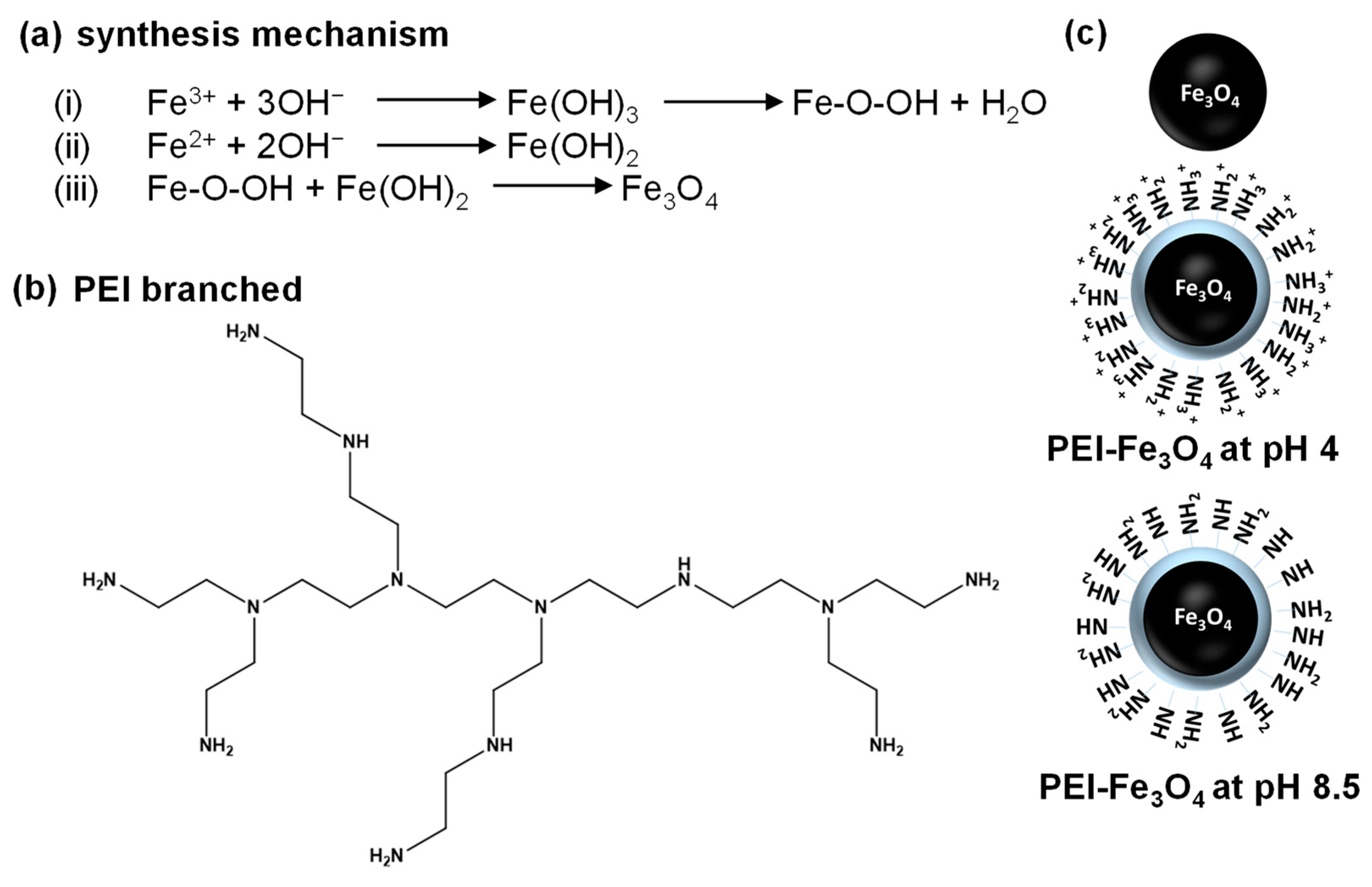
2.2. Synthesis of Fe3O4 and PEI-Fe3O4
2.3. Instruments and Characterizations
2.4. Preparation of Bacterial Samples
2.5. DNA Extraction Using Commercial Kit, Fe3O4, and PEI-Fe3O4
2.6. Primer Design
2.7. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay
2.8. Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
2.9. Colorimetric Detection of LAMP Using PTA-AuNPs
2.10. Sensitivity and Selectivity Test
2.11. Smartphone-Based Detection of LAMP Using PTA-AuNPs
3. Results and Discussion
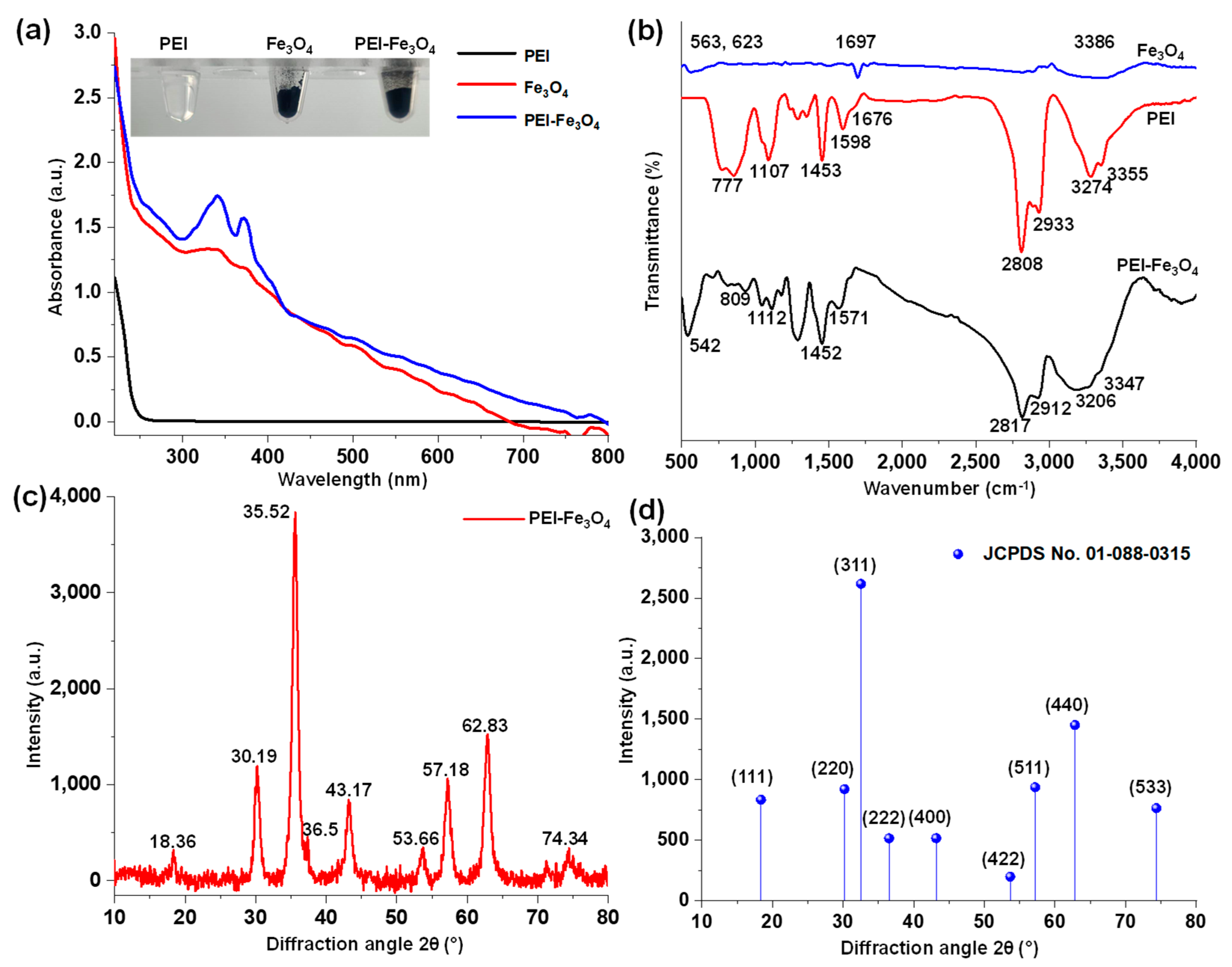
3.1. Absorption and Vibrational Spectra Analysis of PEI, Fe3O4, and PEI-Fe3O4
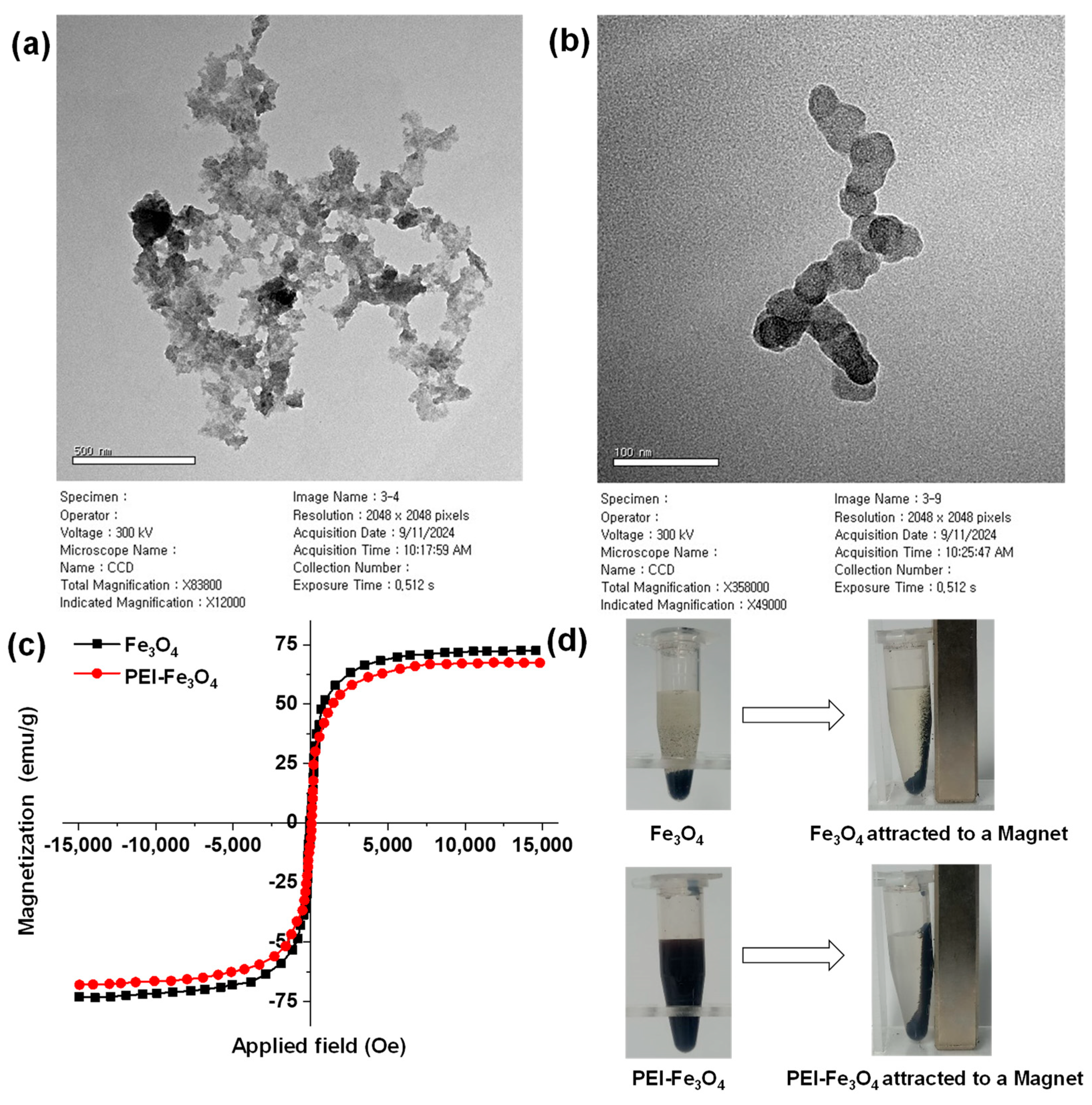
3.2. Structural Morphology Analysis of PEI-Fe3O4
3.3. Magnetic Properties of Fe3O4 and PEI-Fe3O4
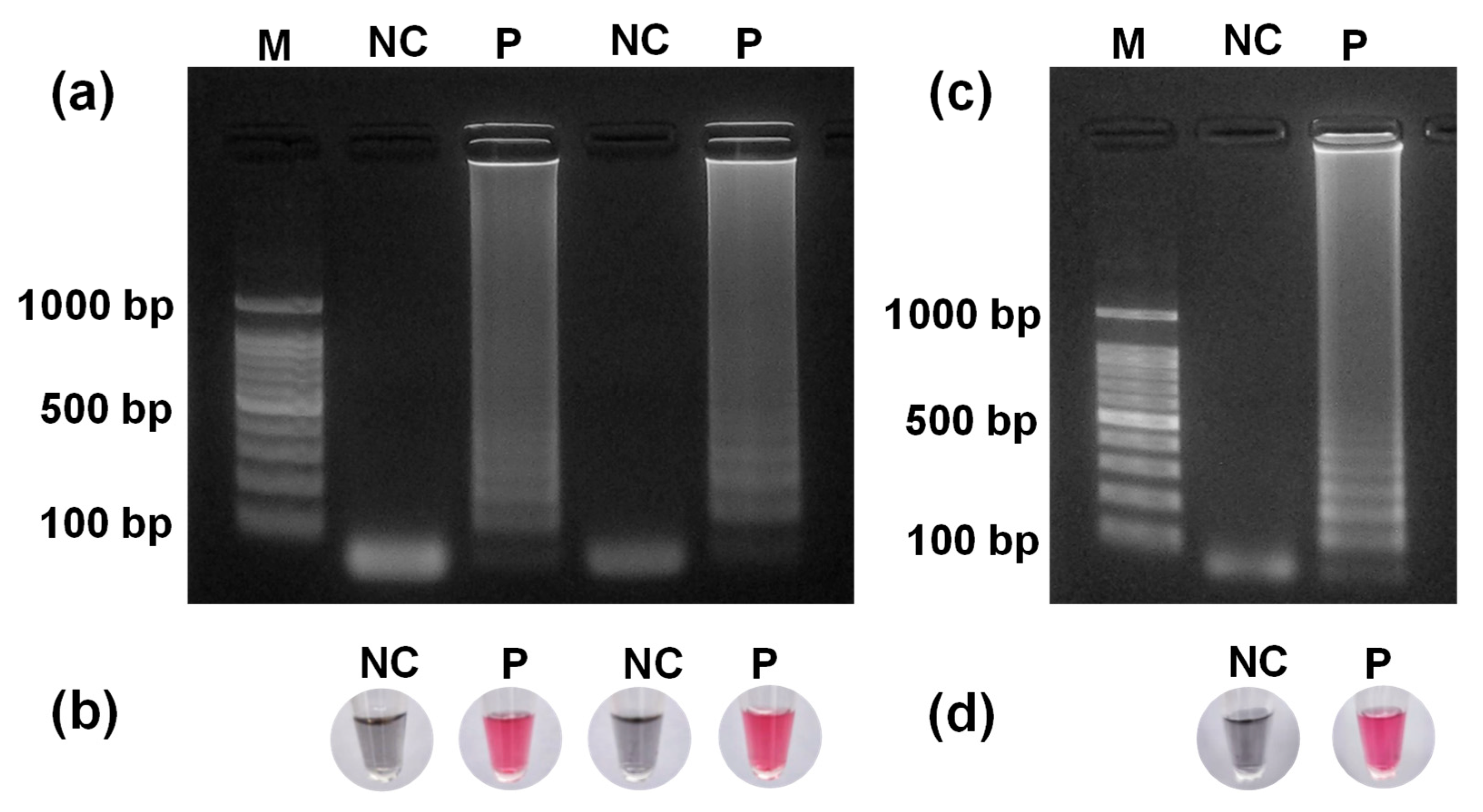
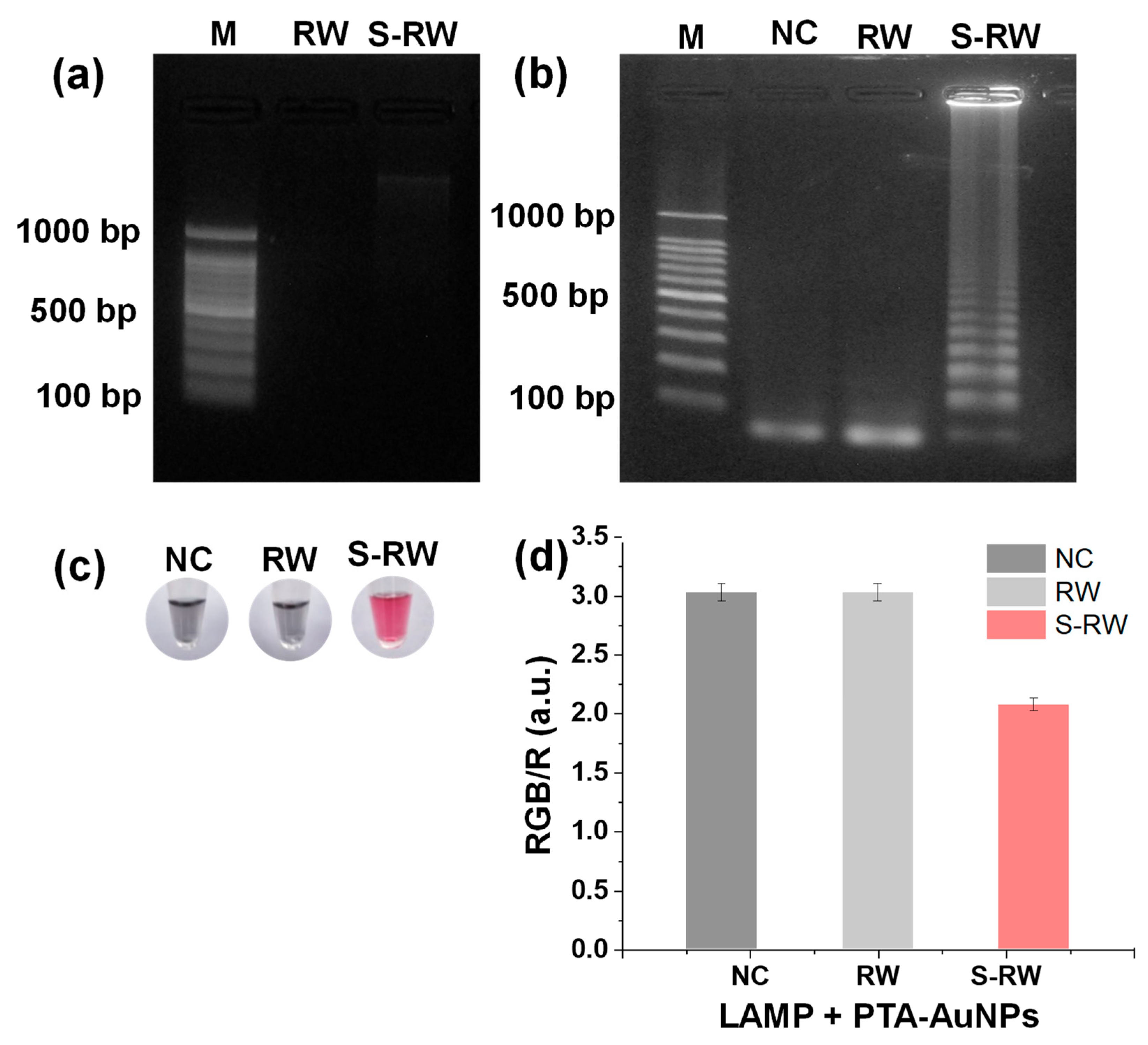
3.4. DNA Extraction from E. faecium
3.5. PTA-AuNPs Used as a Colorimetric Probe for LAMP Detection
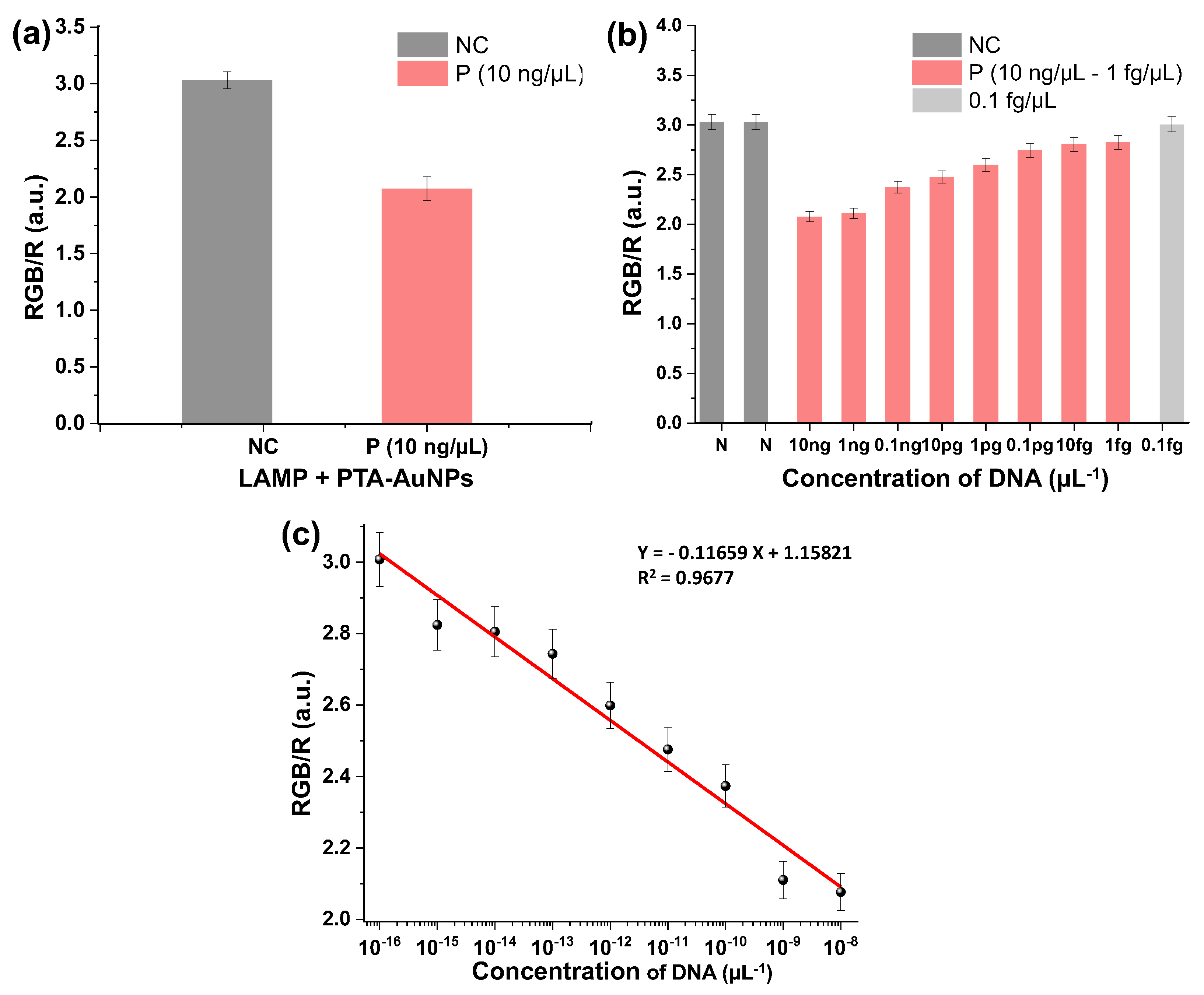
3.6. Results of the Sensitivity and Selectivity Assay
3.7. Smartphone-Based Detection of LAMP-Amplified DNA
3.8. Practical Application on Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, S.; Wei, Z.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, T.; Huang, X.; Shen, T.; Zhang, D.; Guo, Z.; Zou, X. Advancements in Magnetic Nanomaterial-Assisted Sensitive Detection of Foodborne Bacteria: Dual-Recognition Strategies, Functionalities, and Multiplexing Applications. Food Chem. 2025, 478, 143626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shioi, R.; Kool, E.T. Chemical Diversity of Reagents That Modify RNA 2′-OH in Water: A Review. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 15968–15982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, A.; Abbasian, F.; Ayala-Charca, G.; Tabrizi, H.O.; Roshanfar, A.; Ghafar-Zadeh, M.; Movahed, M.; Tahernezhad, Y.; Magierowski, S.; Ghafar-Zadeh, E. A Portable and Cost-Effective System for Electronic Nucleic Acid Mass Measurement. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Xiao, L.; Jun, Y.W.; Onishi, Y.; Kool, E.T. Reversible 2′-OH Acylation Enhances RNA Stability. Nat. Chem. 2023, 15, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaway, E. Biggest-Ever AI Biology Model Writes DNA on Demand. Nature 2025, 638, 868–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhat, J.; Alzyoud, L.; AlWahsh, M.; Acharjee, A.; Al-Omari, B. Advancing Precision Medicine: The Role of Genetic Testing and Sequencing Technologies in Identifying Biological Markers for Rare Cancers. Cancer Med. 2025, 14, e70853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velema, W.A.; Lu, Z. Chemical RNA Cross-Linking: Mechanisms, Computational Analysis, and Biological Applications. JACS Au 2023, 3, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikutis, S.; Bernardes, G.J.L. Technologies for Targeted RNA Degradation and Induced RNA Decay. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 13301–13330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Rampazzo, R.D.C.P.; Costa, A.D.T.; Krieger, M.A. Current Nucleic Acid Extraction Methods and Their Implications to Point-of-Care Diagnostics. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 1, 9306564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruthupandi, M.; Lee, N.Y. A Colorimetric POCT Mediated by Poly(Tannic Acid)-Capped AgNPs for the Detection of Hazardous H2S: Applications in Meat Spoilage Monitoring and Halitosis Diagnosis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 493, 138323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; He, N.; Deng, Y.; Chen, Z. Research on a Magnetic Separation-Based Rapid Nucleic Acid Extraction System and Its Detection Applications. Biosensors 2023, 13, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berensmeier, S. Magnetic Particles for the Separation and Purification of Nucleic Acids. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 73, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.; Huang, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, S.; Zhang, M. Chitosan-Crosslinked Low Molecular Weight PEI-Conjugated Iron Oxide Nanoparticle for Safe and Effective DNA Delivery to Breast Cancer Cells. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schermant, D.; Demeneixt, B.; Behr, J. A Versatile Vector for Gene and Oligonucleotide Transfer into Cells in Culture and in Vivo: Polyethylenimine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7297–7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T.; Tanaka, T.; Niwa, D.; Osaka, T.; Takeyama, H.; Matsunaga, T. Fabrication of Amino Silane-Coated Microchip for DNA Extraction from Whole Blood. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 116, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Easley, C.J.; Ferrance, J.P.; Landers, J.P. Chitosan as a Polymer for PH-Induced DNA Capture in a Totally Aqueous System. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 7222–7228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavandi, A.; Bekhit, A.E.A.; Sun, Z.; Ali, A.; Gould, M. A Novel Squid Pen Chitosan / Hydroxyapatite / β -Tricalcium Phosphate Composite for Bone Tissue Engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 55, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-gonzález, D.; Sena-torralba, A.; Wicaksono, W.P. Biosensors and Bioelectronics Iridium Oxide (IV) Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 132, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBain, S.C.; Yiu, H.H.P.; El Haj, A.; Dobson, J. Polyethyleneimine Functionalized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Agents for DNA Delivery and Transfection. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 2561–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Kaushik, G.; Verma, C.; Kumar, V.; Vashishtha, R. Polyethyleneimine-Functionalized Iron Oxide Nanoparticle-Based Method for Isolation of Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) from Saliva Samples in Forensic Investigations. Egypt. J. Forensic Sci. 2025, 15, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, Z.; Rouhanizadeh, M.; Nami, N.; Zareyee, D. Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles (MNPs) as an Effective Catalyst for Synthesis of Indole Derivatives. Nanochem Res. 2018, 3, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyth, N.; Yudovin-Farber, I.; Perez-Davidi, M.; Domb, A.J.; Weiss, E.I. Polyethyleneimine Nanoparticles Incorporated into Resin Composite Cause Cell Death and Trigger Biofilm Stress in Vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 22038–22043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosa-Acosta, J.R.; Silva, J.A.; Fernández-Izquierdo, L.; Díaz-Castañón, S.; Ortiz, M.; Zuaznabar-Gardona, J.C.; Díaz-García, A.M. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (IONPs) with Potential Applications in Plasmid DNA Isolation. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 545, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; The, K.; Trinh, L. One-Pot Colorimetric Nucleic Acid Test Mediated by Silver Nanoparticles for DNA Extraction and Detection. Biosensors 2025, 15, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D. Capture and Release of Genomic DNA by PEI Modified Fe3O4/Au Nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2010, 30, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Nagamine, K.; Tomita, N.; Notomi, T. Detection of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Reaction by Turbidity Derived from Magnesium Pyrophosphate Formation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 289, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammatikos, S.; Svoliantopoulos, I.; Gizeli, E. Naked-Eye Detection of LAMP-Produced Nucleic Acids in Saliva Using Chitosan-Capped AuNPs in a Single-Tube Assay. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 18514–18521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manalo, M.N.; Pérez, L.M.; LiWang, A. Hydrogen-Bonding and π-π Base-Stacking Interactions Are Coupled in DNA, as Suggested by Calculated and Experimental Trans-Hbond Deuterium Isotope Shifts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 11298–11299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaki, S.H.; Malek, T.J.; Chaudhary, M.D.; Tailor, J.P.; Deshpande, M.P. Magnetite Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Synthesis by Wet Chemical Reduction and Their Characterization. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 035009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Wanale, S.G.; Gacem, A.; Yadav, V.K.; Ahmed, I.A.; Algethami, J.S.; Kakodiya, S.D.; Modi, T.; Alsuhaibani, A.M.; Yadav, K.K.; et al. Nanostructured Iron Oxides: Structural, Optical, Magnetic, and Adsorption Characteristics for Cleaning Industrial Effluents. Crystals 2023, 13, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Gonzalez, C.; Gantz, S.; Ourry, L.; Mammeri, F.; Ammar-Merah, S.; Ponton, A. Elaboration and Rheological Investigation of Magnetic Sensitive Nanocomposite Biopolymer Networks. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 3136–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Jeevanandam, P. Synthesis of Self-Assembled Prismatic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles by a Novel Thermal Decomposition Route. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenda, K.; Idström, A.; Evenäs, L.; Persson, M.; Holmberg, K.; Bordes, R. An Analytical Approach to Elucidate the Architecture of Polyethyleneimines. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e51657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, K.R.; Pawar, A.R.; Salmote, A.D.; Shinde, S.A.; Undre, P.B. Exploring the Effect of Crystalline Phase on Photocatalytic, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Performance of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2024, 38, 101166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavamoorthi, R.; Raja, C.R. Structural and Magnetic Properties of Cobalt and Copper Ions Mixed Nickel Ferrite Nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2017, 30, 2535–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, S.V.; Suryawanshi, S.R.; Bhoraskar, S.V.; More, M.A.; Joag, D.S.; Mathe, V.L. Influence of Morphology and Crystallinity on Field Emission Properties of NiFe2O4 Nanoparticles Grown by High-Temperature Vapor Phase Condensation Route. Mater. Res. Express 2015, 2, 095001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badbedast, M.; Abdolmaleki, A.; Khalili, D. Copper-Decorated Magnetite Polydopamine Composite (Fe3O4@PDA): An Effective and Durable Heterogeneous Catalyst for Pyranopyrazole Synthesis. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202203199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maruthupandi, M.; Choi, H.S.; Lee, N.Y. PEI-Fe3O4/PTA-AuNPs Hybrid System for Rapid DNA Extraction and Colorimetric LAMP Detection of E. faecium. Biosensors 2025, 15, 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090601
Maruthupandi M, Choi HS, Lee NY. PEI-Fe3O4/PTA-AuNPs Hybrid System for Rapid DNA Extraction and Colorimetric LAMP Detection of E. faecium. Biosensors. 2025; 15(9):601. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090601
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaruthupandi, Muniyandi, Haang Seok Choi, and Nae Yoon Lee. 2025. "PEI-Fe3O4/PTA-AuNPs Hybrid System for Rapid DNA Extraction and Colorimetric LAMP Detection of E. faecium" Biosensors 15, no. 9: 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090601
APA StyleMaruthupandi, M., Choi, H. S., & Lee, N. Y. (2025). PEI-Fe3O4/PTA-AuNPs Hybrid System for Rapid DNA Extraction and Colorimetric LAMP Detection of E. faecium. Biosensors, 15(9), 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090601






