Rapid Detection of Staphylococcus aureus in Milk Samples by DNA Nanodendrimer-Based Fluorescent Biosensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Apparatus
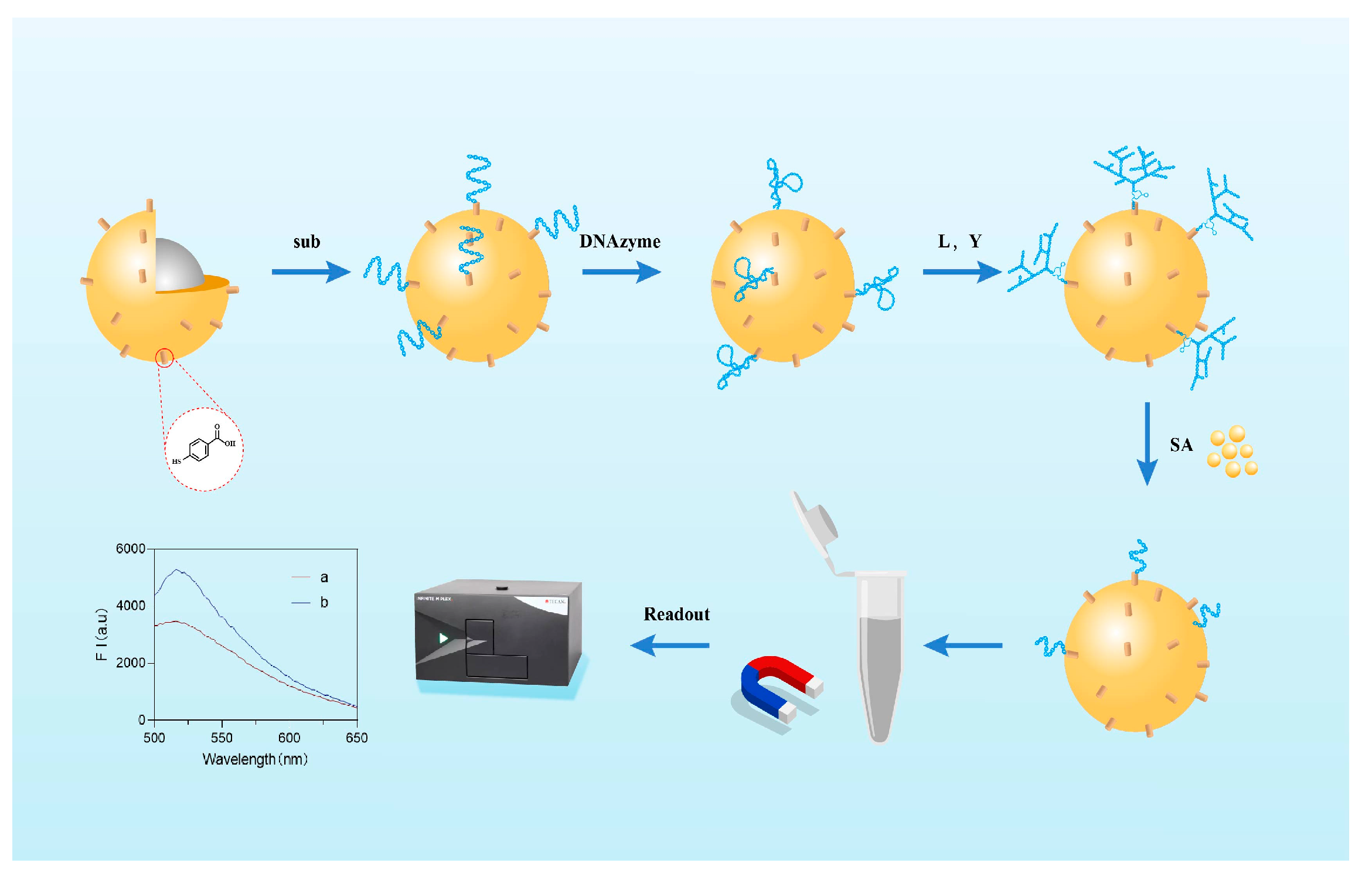
2.2. Preparation of Biosensors
- (1)
- Thiol reduction of substrate chain DNA
- (2)
- Coupling of Au@Fe3O4 nanoparticles with substrate chain
- (3)
- Fabrication of DNA nanodendrimer branches
- (4)
- Functionalization of Au@Fe3O4 nanoparticles
2.3. Gel Electrophoresis Protocol
2.4. Quantitative Detection of Staphylococcus aureus
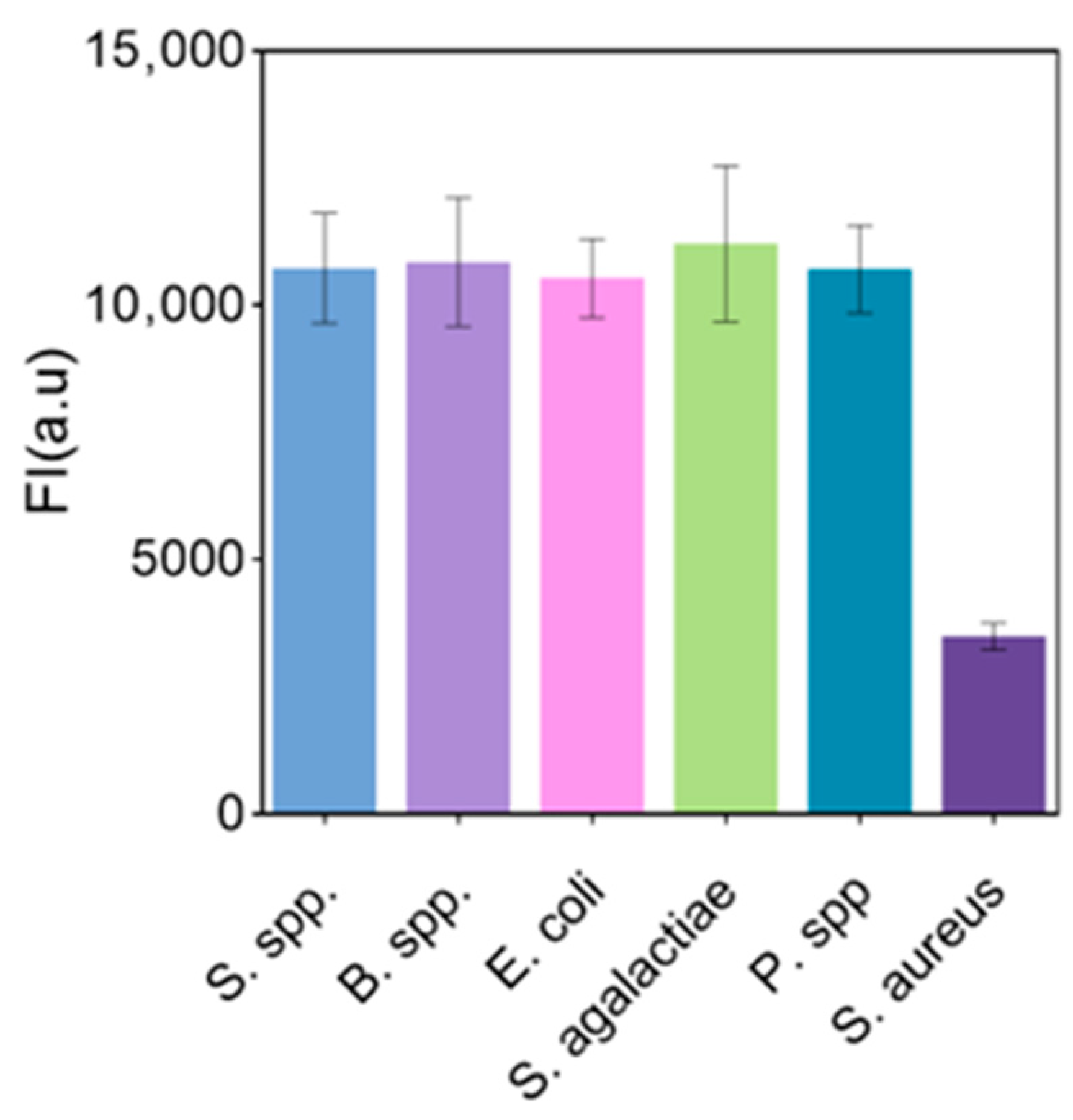
2.5. Specificity Assessment Against Non-Target Bacteria
2.6. Real-Sample Analysis in Complex Milk Matrix
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Detection Principle
3.2. DNA Gel Electrophoresis
3.3. Optimization of Conditions
3.4. Test Certificate
3.5. Sensor Performance Optimization
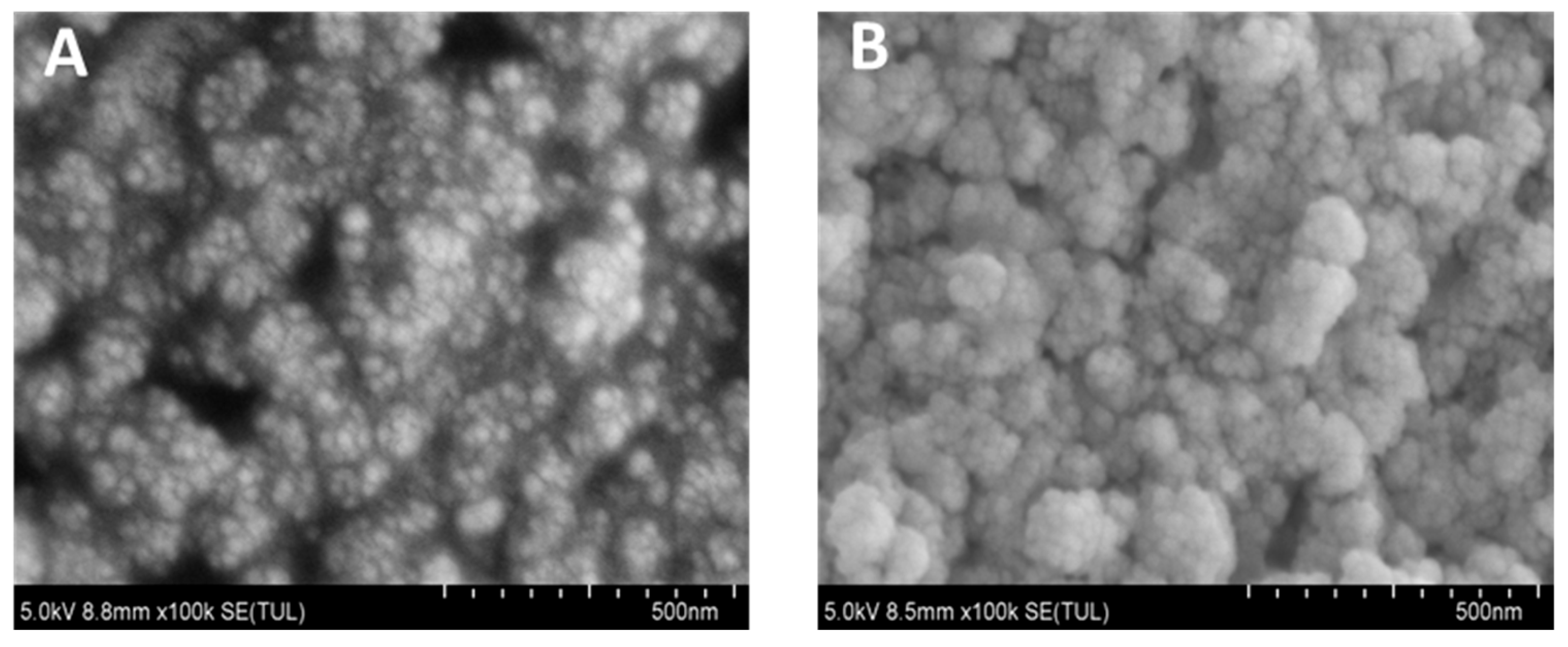
3.6. Morphological Characterization of Nanocomplex Assembly
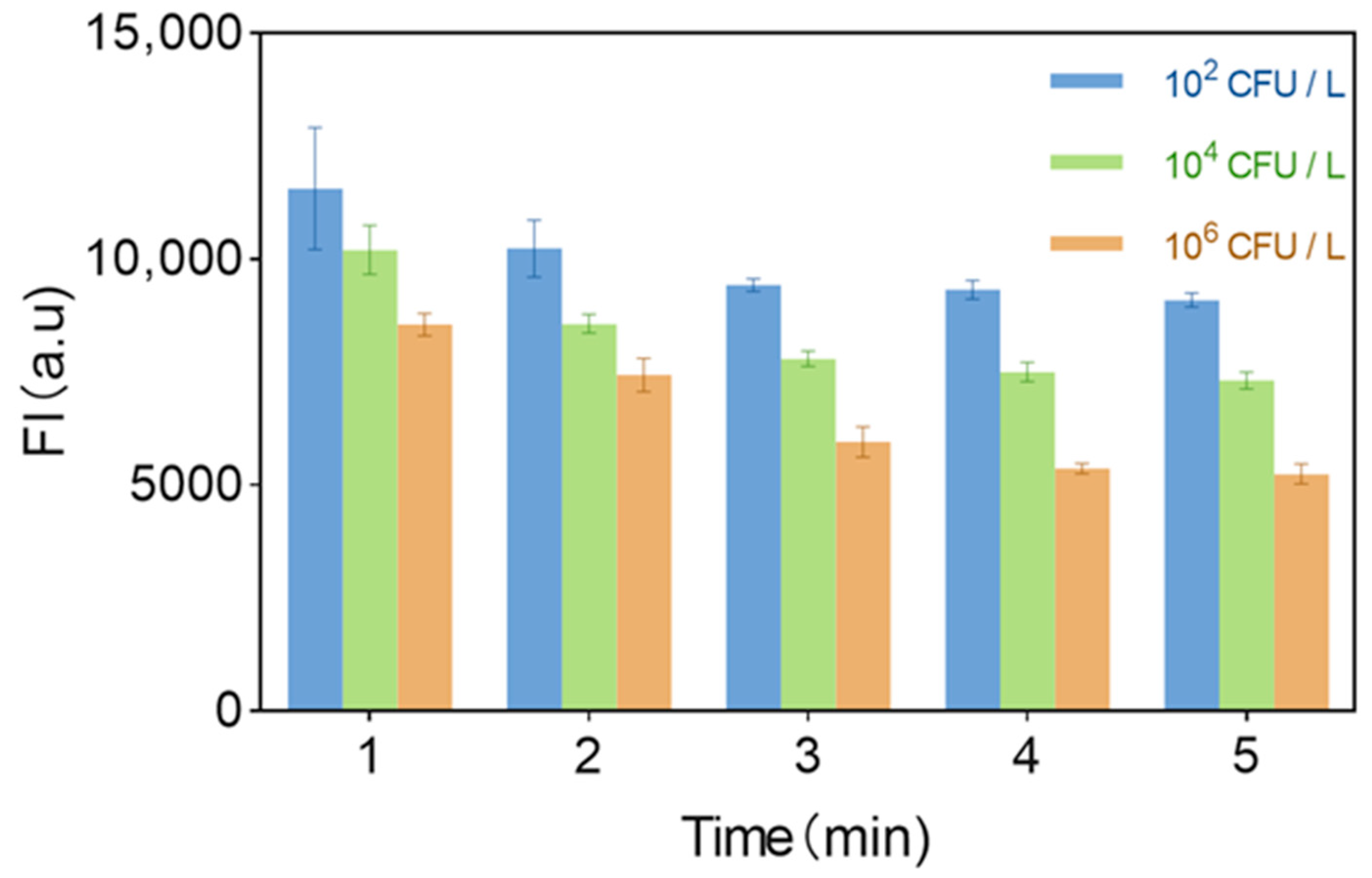
3.7. Optimization of Detection Time
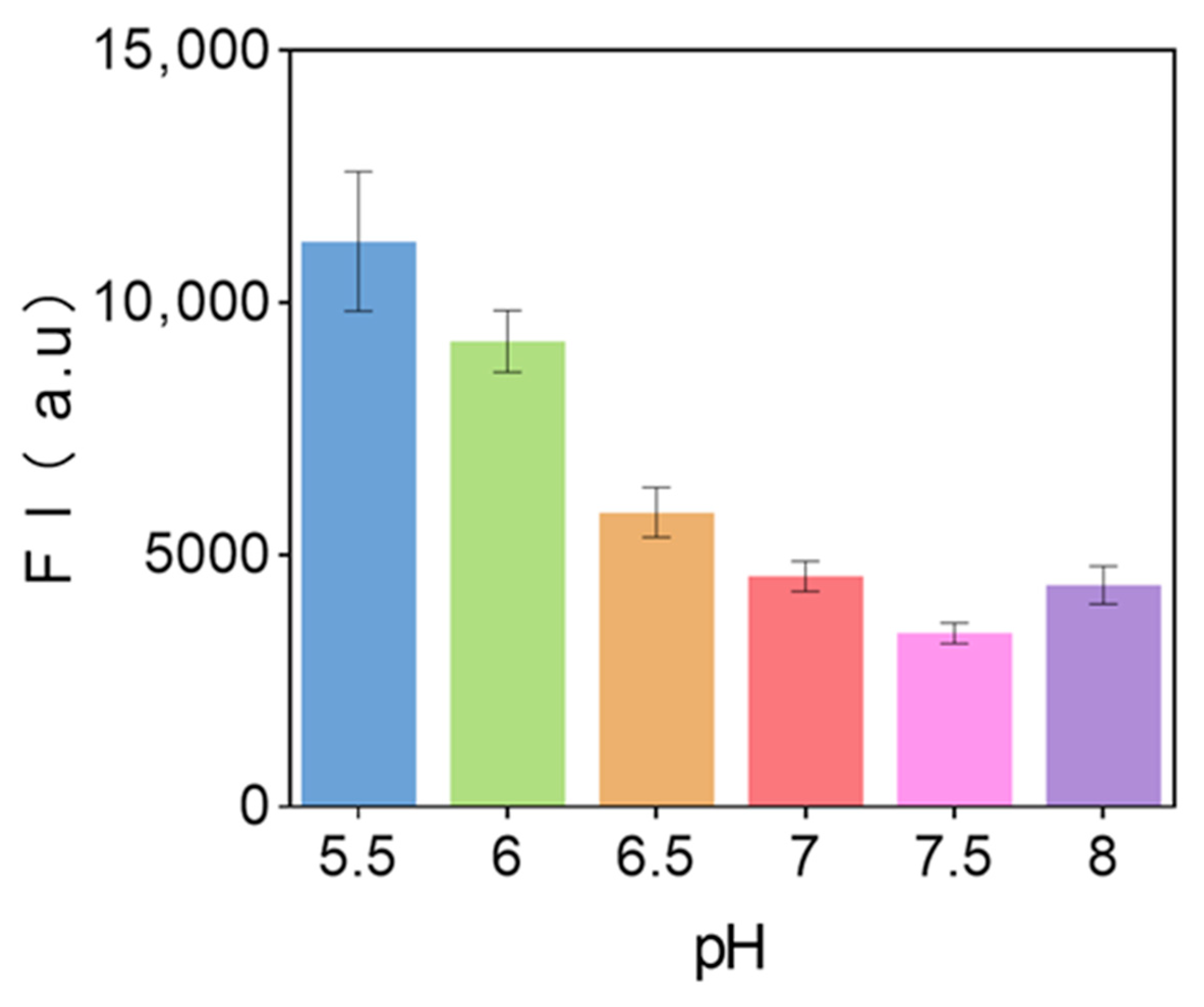
3.8. pH Value of Sensor Solution
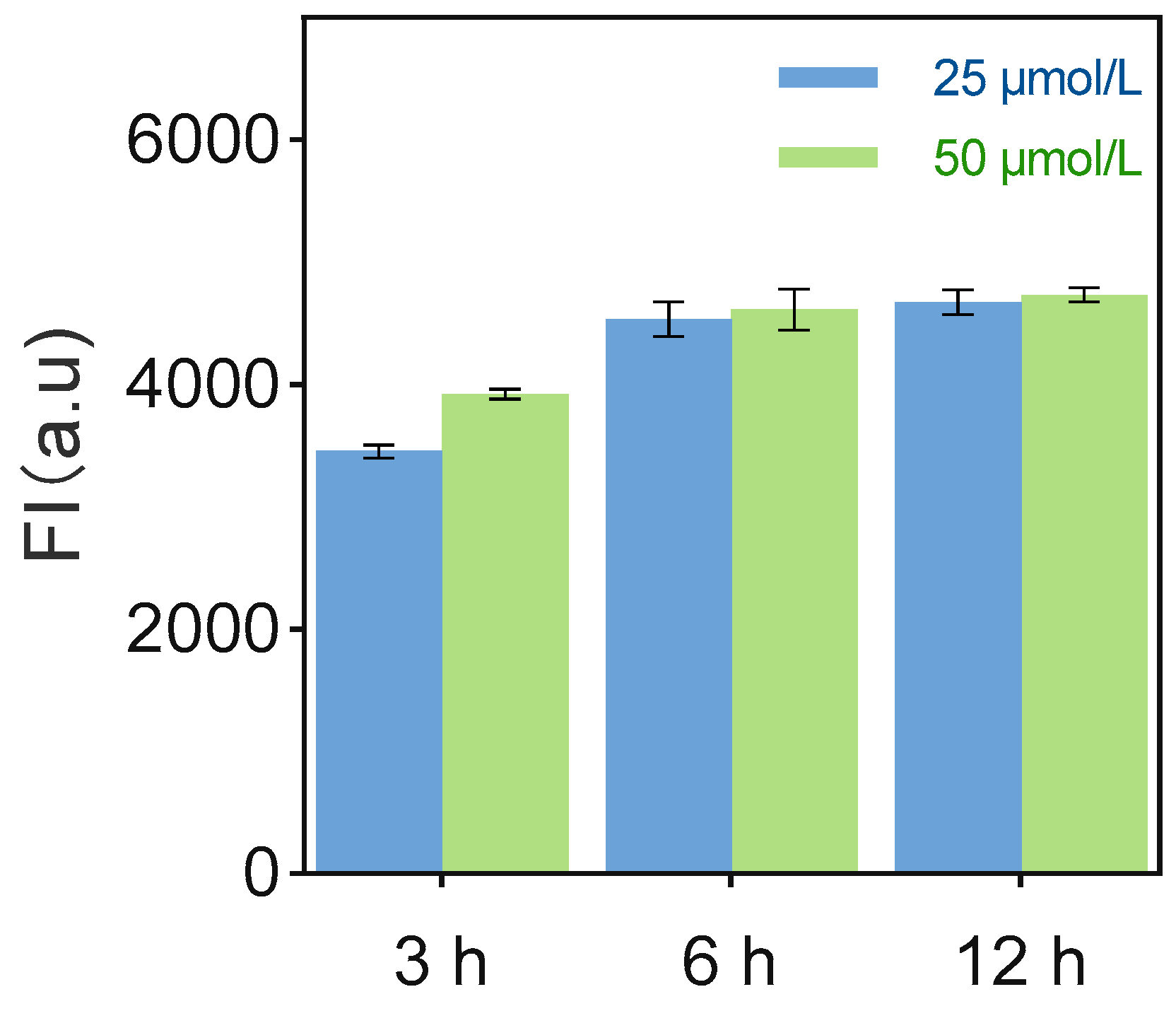
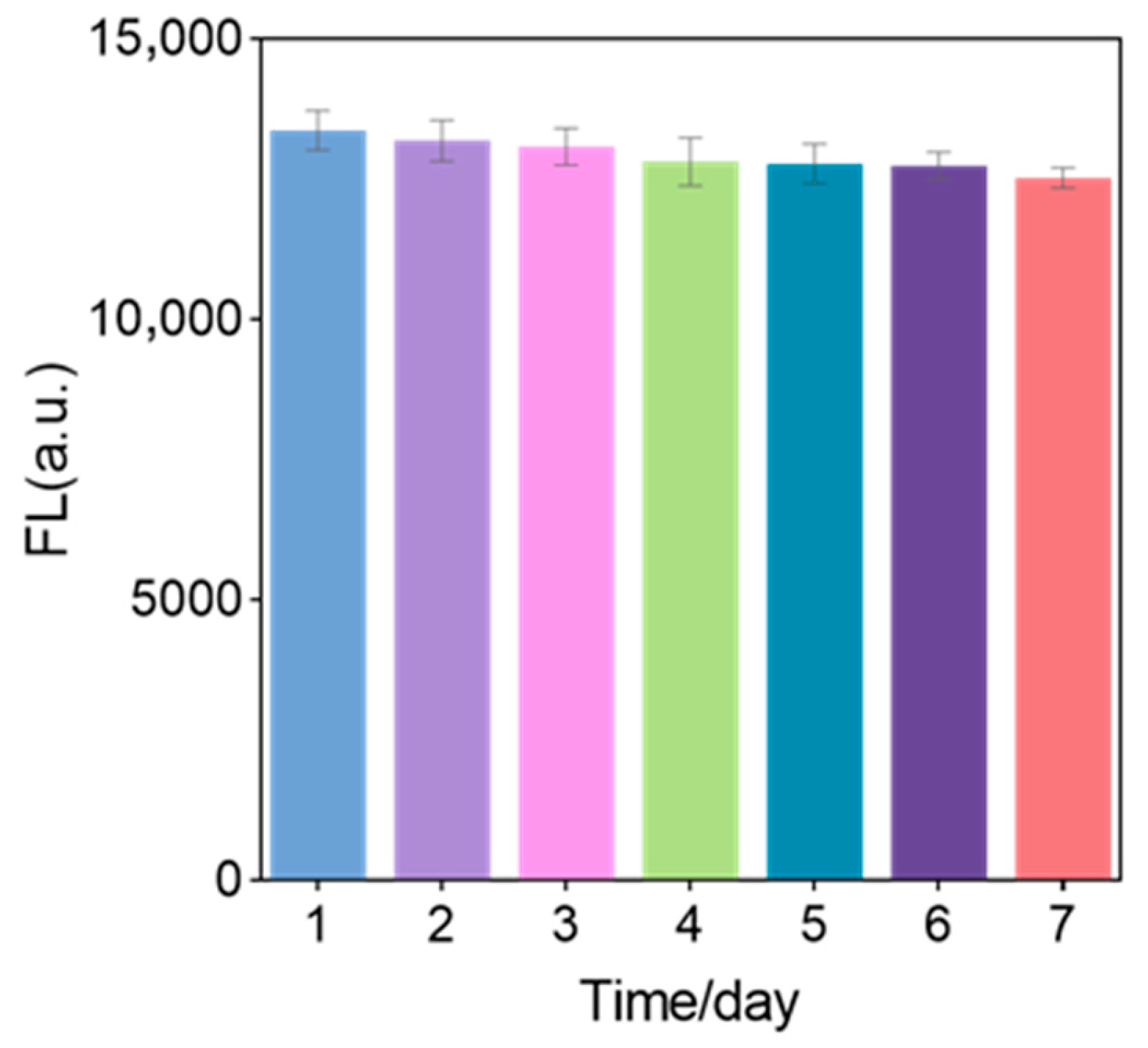
3.9. Stability of Sensor Solution
3.10. Linear Relationship
3.11. Anti-Interference
3.12. Analysis of the Actual Sample
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moody, M.; Sawyer, R. Is There a Community Microbial Community? A Comparison of Pathogens Between Two Hospital Surgical Intensive Care Units in a Single City. Surg. Infect. 2023, 24, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez-Delgado, A.; Mizrachi-Chávez, V.M.; Welti-Chanes, J.; Macher-Quintana, S.T.; Chuck-Hernández, C. Breast milk preservation: Thermal and non-thermal processes and their effect on microorganism inactivation and the content of bioactive and nutritional compounds. Front. Nutr. 2024, 10, 1325863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Abebe, R.; Hatiya, H.; Abera, M.; Megersa, B.; Asmare, K. Bovine mastitis: Prevalence, risk factors and isolation of Staphylococcus aureus in dairy herds at Hawassa milk shed, South Ethiopia. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ngassam-Tchamba, C.; Duprez, J.N.; Fergestad, M.; De Visscher, A.; L’Abee-Lund, T.; De Vliegher, S.; Wasteson, Y.; Touzain, F.; Blanchard, Y.; Lavigne, R.; et al. In vitro and in vivo assessment of phage therapy against Staphylococcus aureus causing bovine mastitis. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 22, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallam, K.I.; Abd-Elghany, S.M.; Elhadidy, M.; Tamura, T. Molecular Characterization and Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Retail Chicken. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 1879–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Lai, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. Recent Advances in Aptasensors For Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 889431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, L.; Sang, Y.; Hu, M. Recent advances in label-free fluorescent DNA sensors. Microchem. J. 2025, 208, 112351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhang, H.; Qi, X.; Miao, M.; Que, L.; Gu, X.; Chang, D.; Pan, H. CRISPR/Cas12a dual-mode biosensor for Staphylococcus aureus detection via enzyme-free isothermal amplification. Talanta 2025, 282, 127013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Bhardwaj, S.K.; Mehta, J.; Kim, K.H.; Deep, A. MOF-Bacteriophage Biosensor for Highly Sensitive and Specific Detection of Staphylococcus aureus. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 33589–33598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Hu, X.; Mei, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Liao, X.; Qiao, X.; Hong, C. PSA detection electrochemical immunosensor based on MOF-235 nanomaterial adsorption aggregation signal amplification strategy. Microchem. J. 2021, 171, 106870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jiang, M.; Cao, K.; Wu, M.; Zhao, C.; Li, H.; Hong, C. An electrochemical immunosensor for CEA detection based on Au-Ag/rGO@PDA nanocomposites as integrated double signal amplification strategy. Microchem. J. 2019, 151, 104223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Huang, C.; Sun, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, P.; Ge, S.; Yu, J. Electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on molybdenum disulfide-graphene quantum dots nanocomposites and DNA walker signal amplification for DNA detection. Mikrochim. Acta 2021, 188, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G. Advancing CRISPR/Cas Biosensing with Integrated Devices. ACS Sens. 2025, 10, 575–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, P.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Ni, S.; Jiang, P.; Sun, S.; Li, L. A novel and universal dual-channel signal amplification aptasensing platform for ultrasensitive and rapid detection of cardiac biomarkers based on the mutual regulation of bimetallic organic framework and silver nanoclusters. Talanta 2025, 288, 127745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Xu, W. Correction to “Functional Nucleic Acid Enzymes: Nucleic Acid-Based Catalytic Factories”. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 17879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Sun, W.; Fu, T.; Liu, X.; Chen, P.; Qiu, L.; Qu, F.; Tan, W. Aptamer-Based Targeted Delivery of Functional Nucleic Acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 7677–7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, M.; Zhu, T.F. Directed evolution and selection of biostable L-DNA aptamers with a mirror-image DNA polymerase. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lu, Y.; Li, Y. Functional Nucleic Acids for Analytical Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Silverman, S.K. Catalytic DNA: Scope, Applications, and Biochemistry of Deoxyribozymes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Wei, Y.; Gao, S. Functional nucleic acids for the treatment of diabetic complications. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, M.R.; McCloskey, C.M.; Buckley, P.; Rhea, K.; Chaput, J.C. Generating Biologically Stable TNA Aptamers that Function with High Affinity and Thermal Stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 7721–7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascetti, A.; Mirasoli, M.; Marchegiani, E.; Zangheri, M.; Costantini, F.; Porchetta, A.; Iannascoli, L.; Lovecchio, N.; Caputo, D.; de Cesare, G.; et al. Integrated chemiluminescence-based lab-on-chip for detection of life markers in extraterrestrial environments. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 123, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micura, R.; Höbartner, C. Fundamental studies of functional nucleic acids: Aptamers, riboswitches, ribozymes and DNAzymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 7331–7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, V.; Jaroslav, K.; Milan, K.; Pavel, S.; Václav, V.; Edward, A.C. Apollon: A deoxyribozyme that generates a yellow product. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 15, 9062–9075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, R.; Liu, J. A Silver DNAzyme. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 4014–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, E.M.; Cozma, I.; Mou, Q.; Brennan, J.D.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y. Biosensing with DNAzymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8954–8994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Qi, P.; Jia, L.; Yi, M.; Zhao, E.; Liu, Y.; Song, A.; Hao, J. Chemiluminescent gels of G-quadruplexes in deep eutectic solvents. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 655, 130319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nguyen, K.; Spitale, R.C.; Chaput, J.C. A biologically stable DNAzyme that efficiently silences gene expression in cells. Nat. Chem. 2021, 13, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donini, S.; Clerici, M.; Wengel, J.; Vester, B.; Peracchi, A. The advantages of being locked. Assessing the cleavage of short and long RNAs by locked nucleic acid-containing 8–17 deoxyribozymes. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 35510–35518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagopoulou, C.; Skotadis, E.; Aslanidis, E.; Tzourmana, G.; Rapesi, A.; Tsioustas, C.; Kainourgiaki, M.; Kleitsiotis, G.; Tsekenis, G.; Tsoukalas, D. Non-Faradaic Impedimetric Detection of Heavy Metal Ions via a Hybrid Nanoparticle-DNAzyme Biosensor. Biosensors 2024, 14, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Brindha, J.; Kaushik, C.; Balamurali, M.M. Biosensors for pathogen surveillance. Environ. Lett. 2018, 16, 1325–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zheng, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, G.; Yang, H.; Xiong, F.; Fan, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, C. Electrospun biosensors for biomarker detection. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2024, 59, 100767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yum, J.H.; Kumagai, T.; Hori, D.; Sugiyama, H.; Park, S. Histidine-DNA nanoarchitecture as laccase mimetic DNAzymes. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 10749–10754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, K.; Wu, C.; Guo, X.; Guan, F.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Yang, X.; Liu, N.; Dai, Q.; Zhang, S. Synthesized complex-frequency excitation for ultrasensitive molecular sensing. eLight 2024, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, D.; Zu, Y.; Zhang, L. Procalcitonin Detection Using Immunomagnetic Beads-Mediated Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Biosensors 2024, 14, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Neamu, B.V.; Irimie, A.; Popa, F.; Gabor, M.S.; Marinca, T.F.; Chicinaş, I. Soft magnetic composites based on oriented short Fe fibres coated with polymer. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 840, 155731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, M.; Riesgo, A. Intra-epithelial spicules in a homosclerophorid sponge. CellTissue Res. 2007, 328, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yuan, J.; Jin, N.; Yang, F.; Jiang, F.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Lin, J. One-step colorimetric immunosensing of foodborne bacteria using static magnet driven magnetophoretic separation and dual noble metal decorated magnetic nanobeads. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1349, 343831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lone, M.Y.; Kumar, A.; Ansari, N.; Husain, S.; Zulfequar, M.; Singh, R.C.; Husain, M. Enhancement of Sensor Response of as Fabricated SWCNT SensorwithGoldDecorated Nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 274, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, S.; Akmal, M.R.; Salek-Maghsoudi, A.; Rahmani, S.; Ganjali, M.R.; Norouzi, P.; Abdollahi, M. Novel label-free electrochemical aptasensor for determination of Diazinon using gold nanoparticles-modified screen-printed gold electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 120, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Sun, J.; Chen, Y.; Wen, K.; Wang, Z.; Shen, J.; Zhang, S.; Ke, Y.; Wang, Z. Highly sensitive SERS immunosensor for the detection of amantadine in chicken based on flower-like gold nanoparticles and magnetic bead separation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 118, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roushani, M.; Jalilian, Z.; Nezhadali, A. A novel electrochemical sensor based on electrode modified with gold nanoparticles and molecularly imprinted polymer for rapid determination of trazosin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 172, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Guo, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Zou, X.; Sun, Z. Ultrasensitive “On-Off” Ratiometric Fluorescence Biosensor Based on RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a for Detection of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 2167–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahdordizadeh, M.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Ansari, N.; Langroodi, F.A.; Abnous, K.; Ramezani, M. Aptamer based biosensors for detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 619–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Guan, M.; Mi, F.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, P.; Zhang, S.; Song, H.; Chen, G. A SERS/colorimetric biosensor based on AuNSs@Ag core–shell Prussian blue nanozyme for non-interference and rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus in milk. Microchim. Acta 2025, 192, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Tian, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Sun, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, F.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Coreactant-free electrochemiluminescent biosensor for detection of Staphylococcus aureus based on host–guest structure of Arg/ATT-AuNCs and DNA nanomachines. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 506, 160268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zou, Y.; Jiang, X.; Weng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, X.; Yang, G.; Lu, N. A high electron mobility transistor biosensor-based GaN for facile and sensitive detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Microchem. J. 2025, 211, 113124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Yang, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Pan, B.; Guo, W.; Wang, B. Click chemistry-enabled gold nanorods for sensitive detection and viability evaluation of copper(II)-reducing bacteria. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 30, 101453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]




| Name | Sequence and Modifications (From 5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| RL-Sub-SH-HS | CTAATGAGTACCTACTGTCTCTGGATGATCCTATGAACTGACT/rA/TGACCTCACTACCAAGGCGCTATCGGGAAG-FAM |
| RL-DNAzymes | FAM-ATGCCATCCTACCAACCACGAAGTACATTTCAAACTCATAACAATCCATCGGTTAGGTCCT GGTTGGAGCTCTGAACTCGAGACAGTAGGTACTCATTAG-FAM |
| Y-1 | FAM-CACGCAGAGTAACACATGACCGTCGAAGCTTCCCGATAGCGC-FAM |
| Y-2 | FAM-CTTCGACGGTCATGTACTAGATCAGAGGCTTCCCGATAGCGC-FAM |
| Y-3 | FAM-CCTCTGATCTAGTATGTTACTCTGCGTGCTTCCCGATAGCGC-FAM |
| L1 | FAM-TCTATTCGCATGAGAAGCGCTATCGGGAAG-FAM |
| L2 | FAM-TTCTCATGCGAATAGAGCGCTATCGGGAAG-FAM |
| Sensor | Method | Linear Range (CFU/mL) | Detection Limit (CFU/mL) | Testing Time (min) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a-Eu-MOF | Fluorescence | 7.9 × 100–7.9 × 108 | 3 | - | [43] |
| Aptamer-based Fluorescent LFB | Fluorescence | 2.8 × 101–2.8 × 107 | 1.65 | - | [44] |
| AuNSs@PB@Ag-Apt sensor | Colorimetric probe | 1 × 100–1 × 108 | 1 | - | [45] |
| ECL Biosensor | Electrochemi-luminescence | 1 × 101–1 × 109 | 1.16 | 40 | [46] |
| Aptamer-Modified GaN HEMT Sensor | GaN HEMT | 1 × 102–1 × 107 | 19 | 3.33 | [47] |
| AuNRs–BICC Click Chemistry Biosensor | click chemistry | 1 × 101–1 × 107 | 10 | 180 | [48] |
| DNA nanodendrimer-based fluorescent biosensor | Fluorescence | 1–1 × 107 | 1 | 3 | This work |
| Samples | Samples (CFU/mL) | Plate Counting Method ± SD (CFU/mL) | Fluorescent Biosensing ± SD (CFU/mL) | RSD (%) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milk-1 | 1 × 102 | (0.983 ± 0.064) × 102 | (0.967 ± 0.053) × 102 | 5.48 | 98.4 |
| 1 × 104 | (0.991 ± 0.058) × 104 | (1.012 ± 0.065) × 104 | 6.18 | 102.1 | |
| 1 × 106 | (1.061 ± 0.069) × 106 | (1.003 ± 0.057) × 106 | 5.34 | 94.5 | |
| Milk-2 | 1 × 102 | (1.045 ± 0.051) × 102 | (0.895 ± 0.043) × 102 | 4.80 | 85.6 |
| 1 × 104 | (1.026 ± 0.064) × 104 | (0.911 ± 0.048) × 104 | 5.27 | 88.8 | |
| 1 × 106 | (1.071 ± 0.035) × 106 | (1.006 ± 0.085) × 106 | 8.45 | 93.9 | |
| Milk-3 | 1 × 102 | (1.063 ± 0.052) × 102 | (0.987 ± 0.068) × 102 | 6.89 | 92.9 |
| 1 × 104 | (0.995 ± 0.047) × 104 | (0.965 ± 0.049) × 104 | 5.08 | 95.5 | |
| 1 × 106 | (1.039 ± 0.062) × 106 | (0.983 ± 0.069) × 106 | 7.02 | 94.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mijit, M.; Pan, D.; Wang, H.; Sun, C.; Yang, L. Rapid Detection of Staphylococcus aureus in Milk Samples by DNA Nanodendrimer-Based Fluorescent Biosensor. Biosensors 2025, 15, 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080527
Mijit M, Pan D, Wang H, Sun C, Yang L. Rapid Detection of Staphylococcus aureus in Milk Samples by DNA Nanodendrimer-Based Fluorescent Biosensor. Biosensors. 2025; 15(8):527. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080527
Chicago/Turabian StyleMijit, Mukaddas, Dongxia Pan, Hui Wang, Chaoqun Sun, and Liang Yang. 2025. "Rapid Detection of Staphylococcus aureus in Milk Samples by DNA Nanodendrimer-Based Fluorescent Biosensor" Biosensors 15, no. 8: 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080527
APA StyleMijit, M., Pan, D., Wang, H., Sun, C., & Yang, L. (2025). Rapid Detection of Staphylococcus aureus in Milk Samples by DNA Nanodendrimer-Based Fluorescent Biosensor. Biosensors, 15(8), 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080527





