Advances in the Direct Nanoscale Integration of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) with Transducers for the Development of High-Performance Nanosensors
Abstract
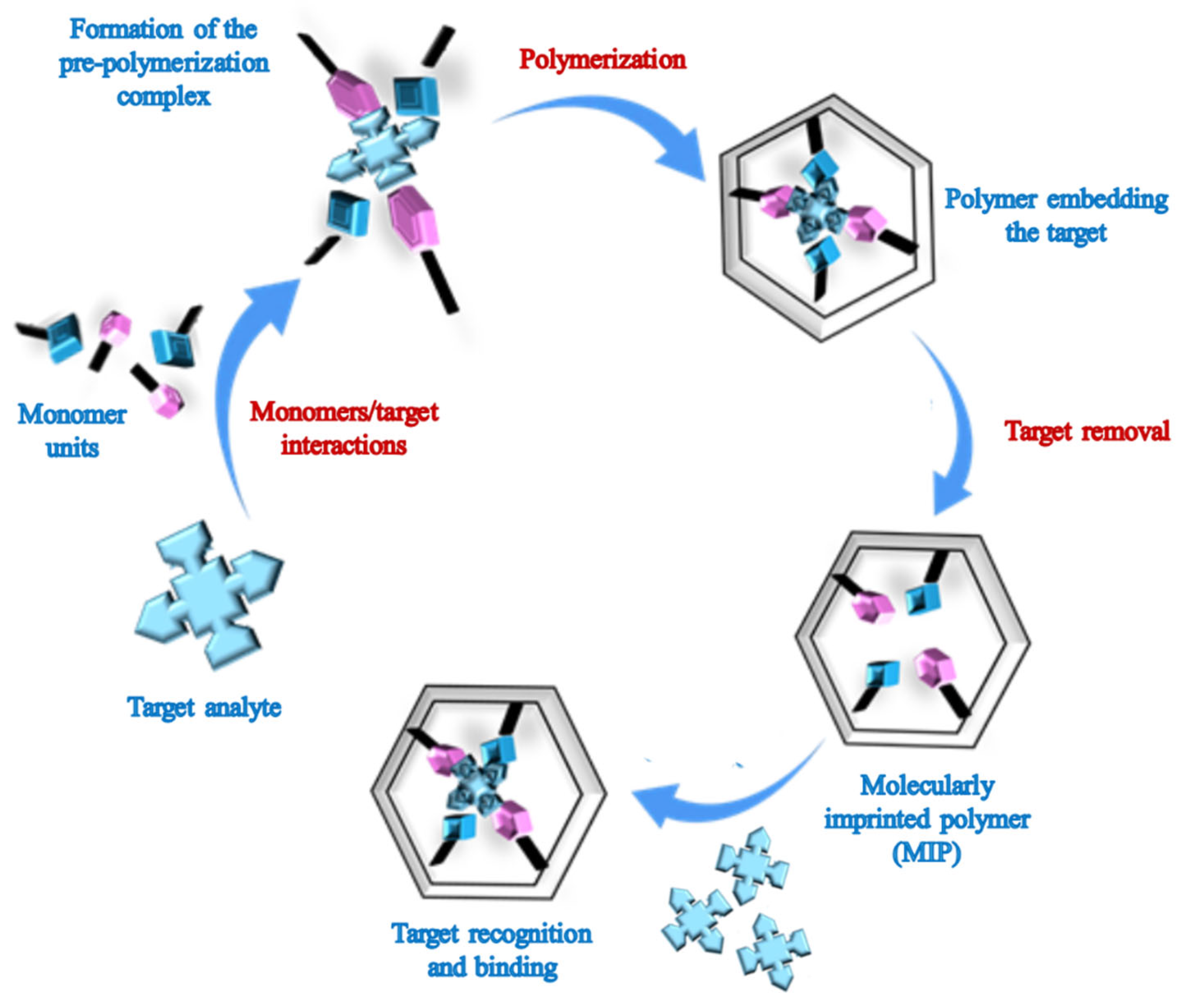
1. Introduction
2. Nanosized MIPs on Bulk Transducers
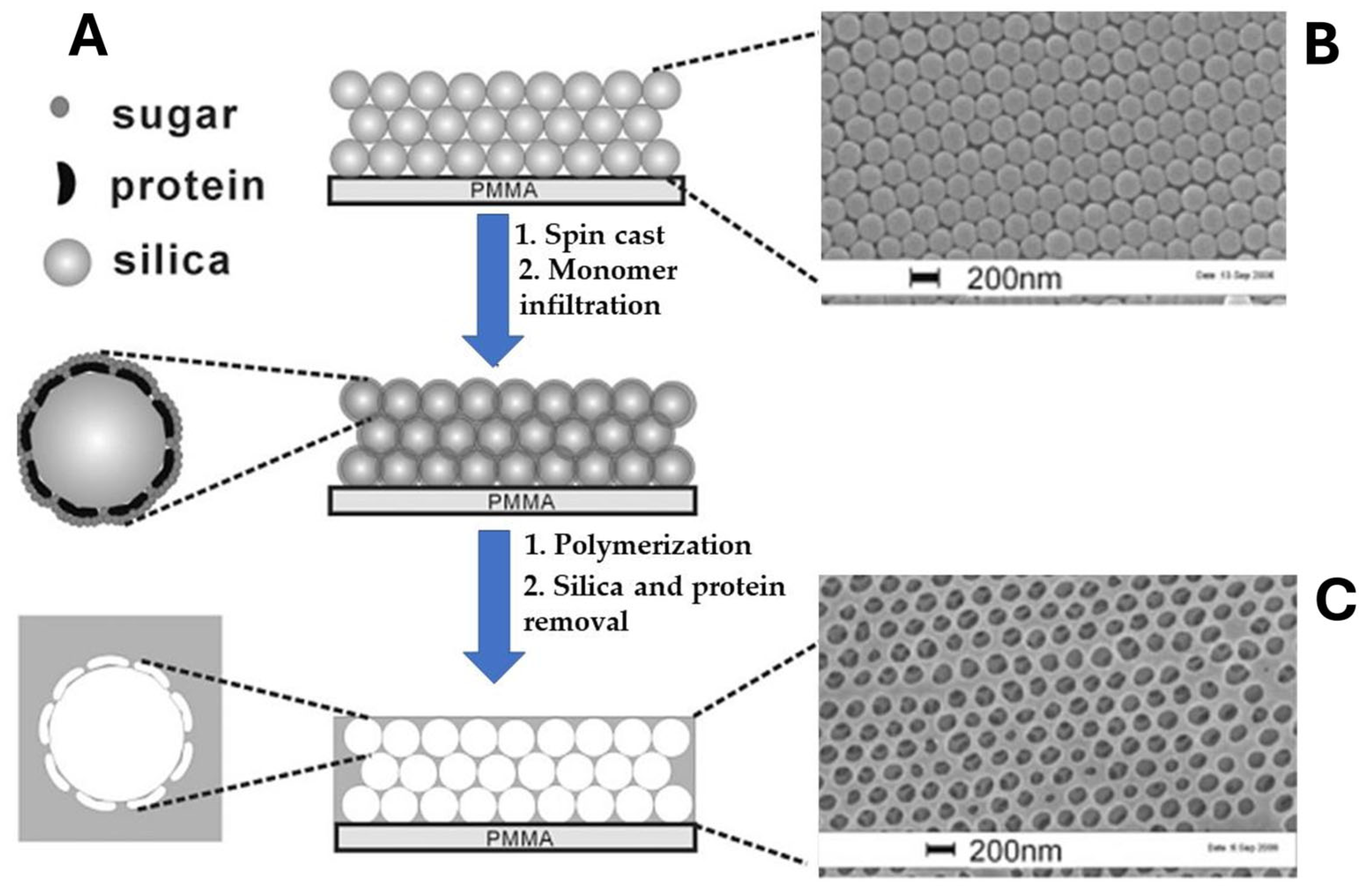
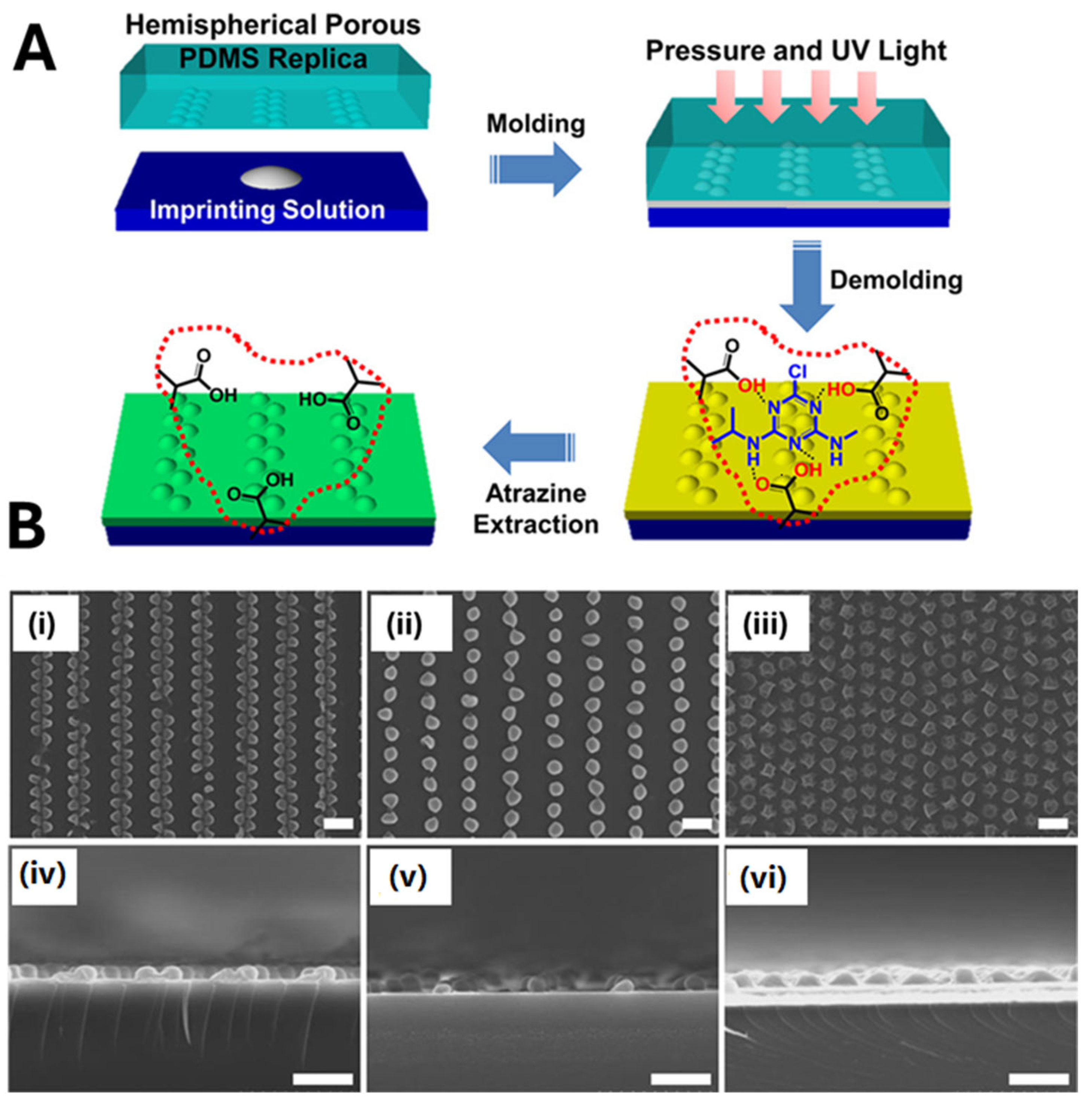
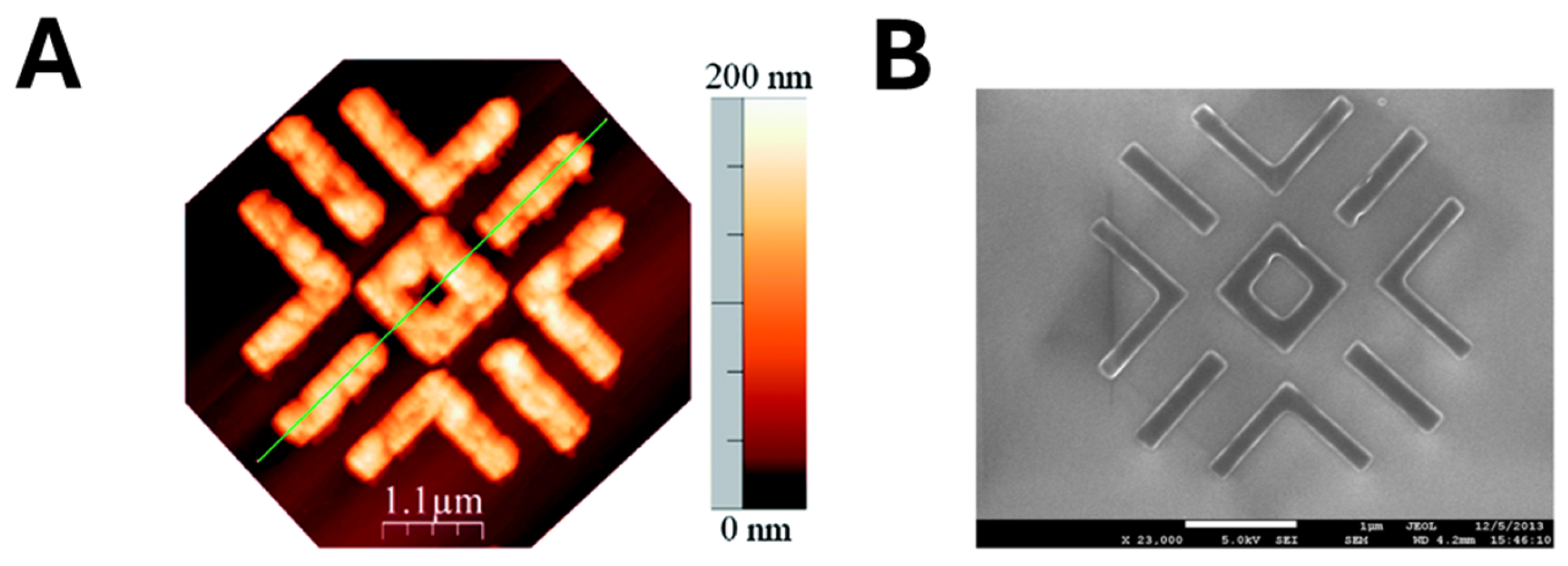
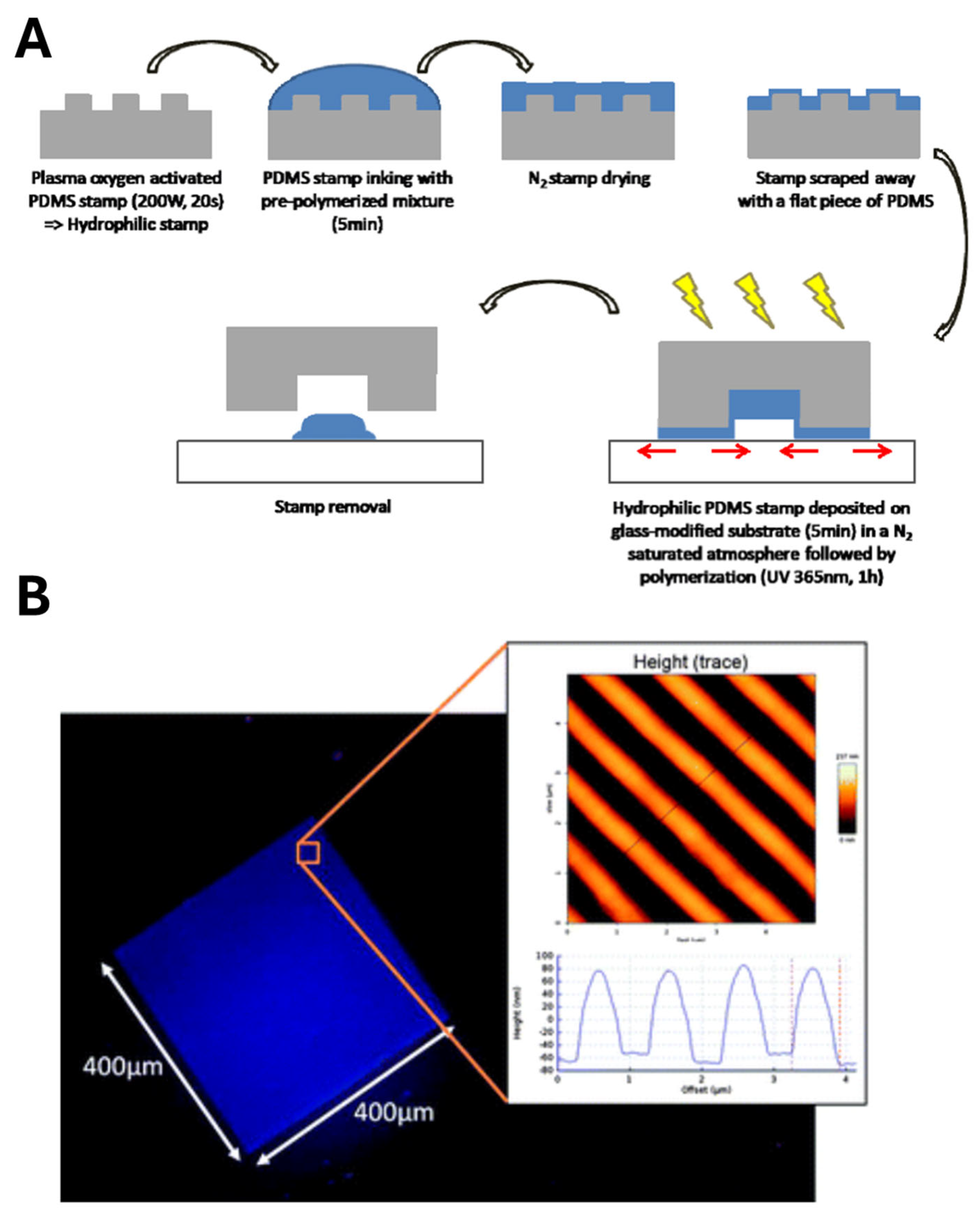
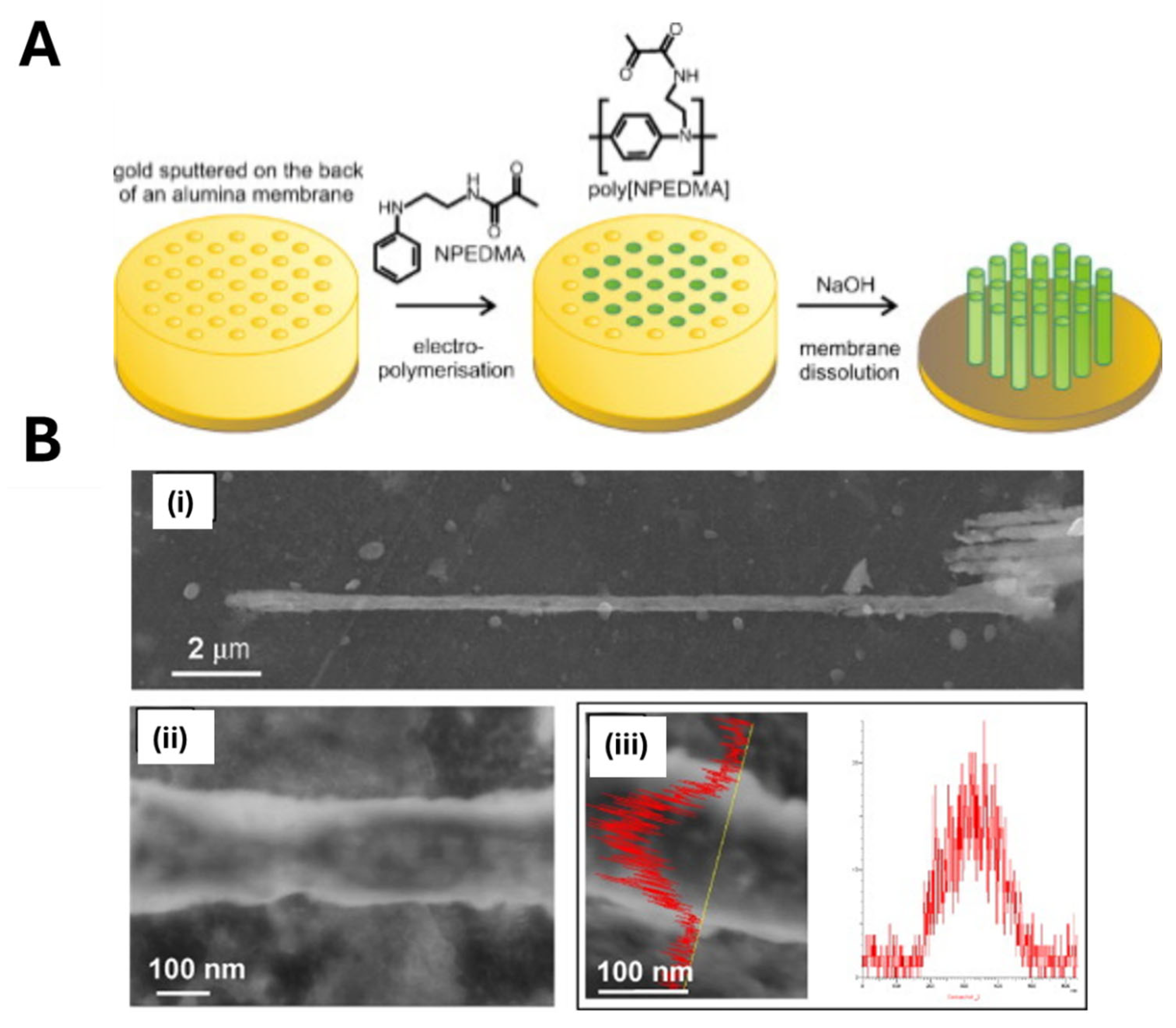
2.1. MIP Nanomolding
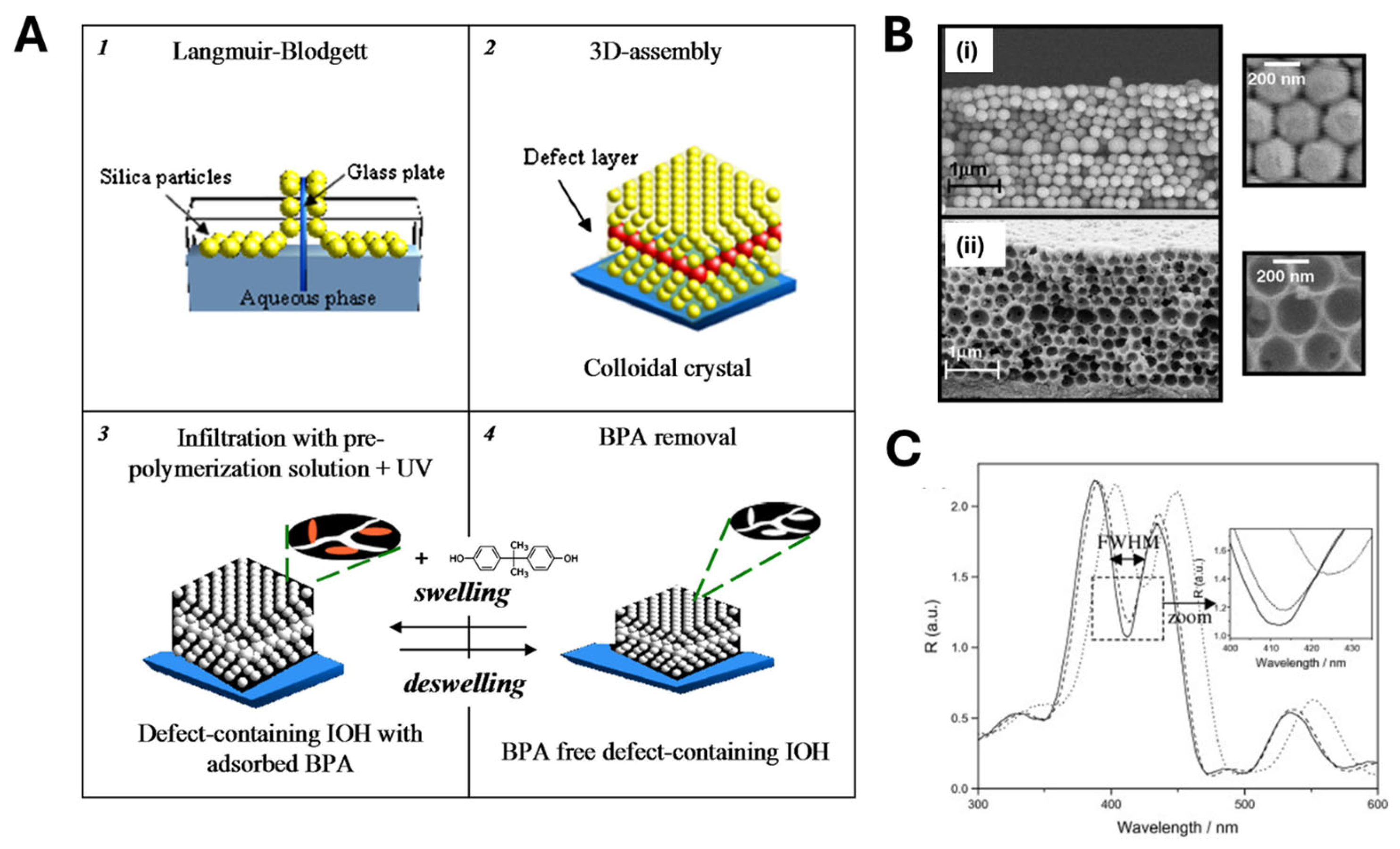
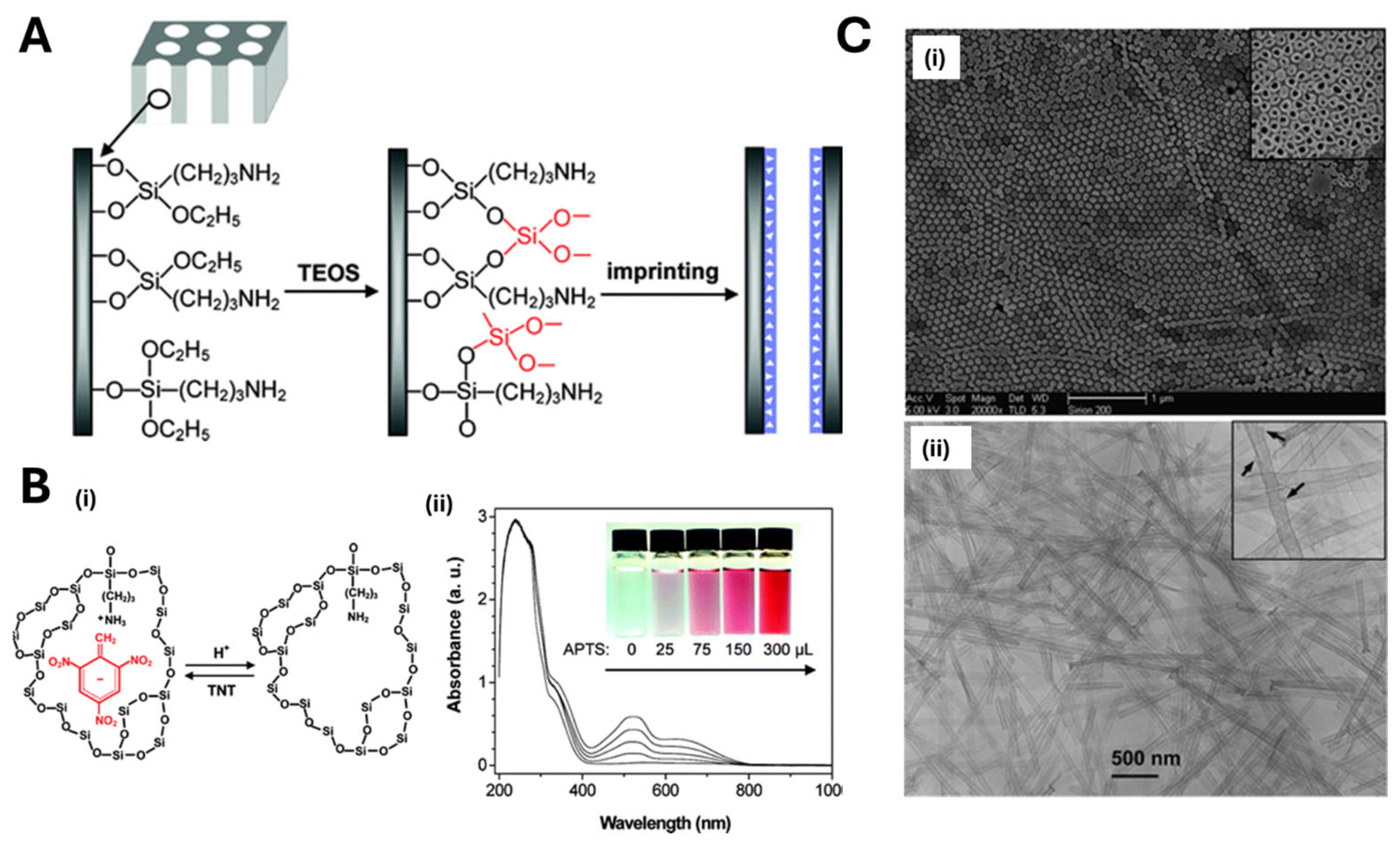
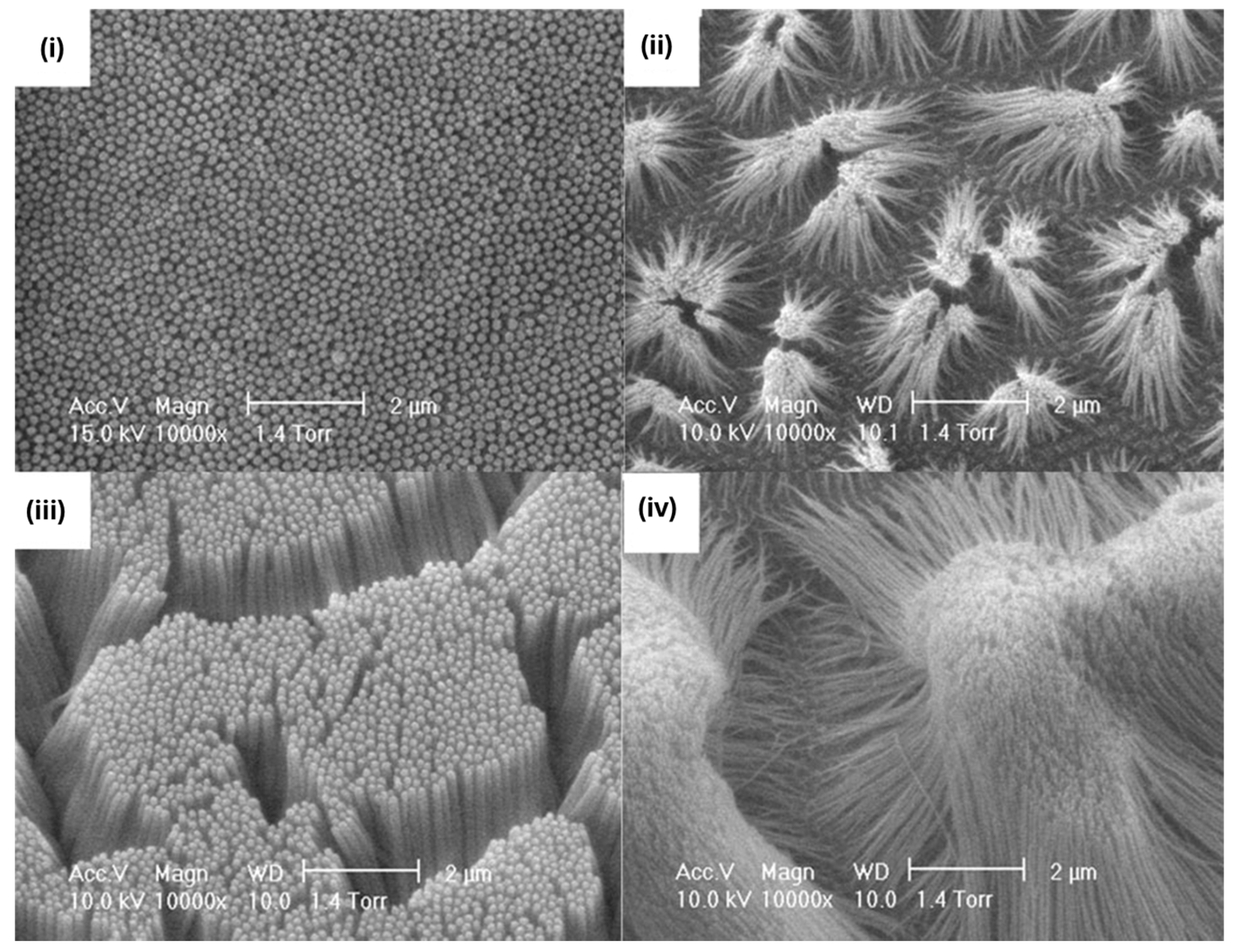
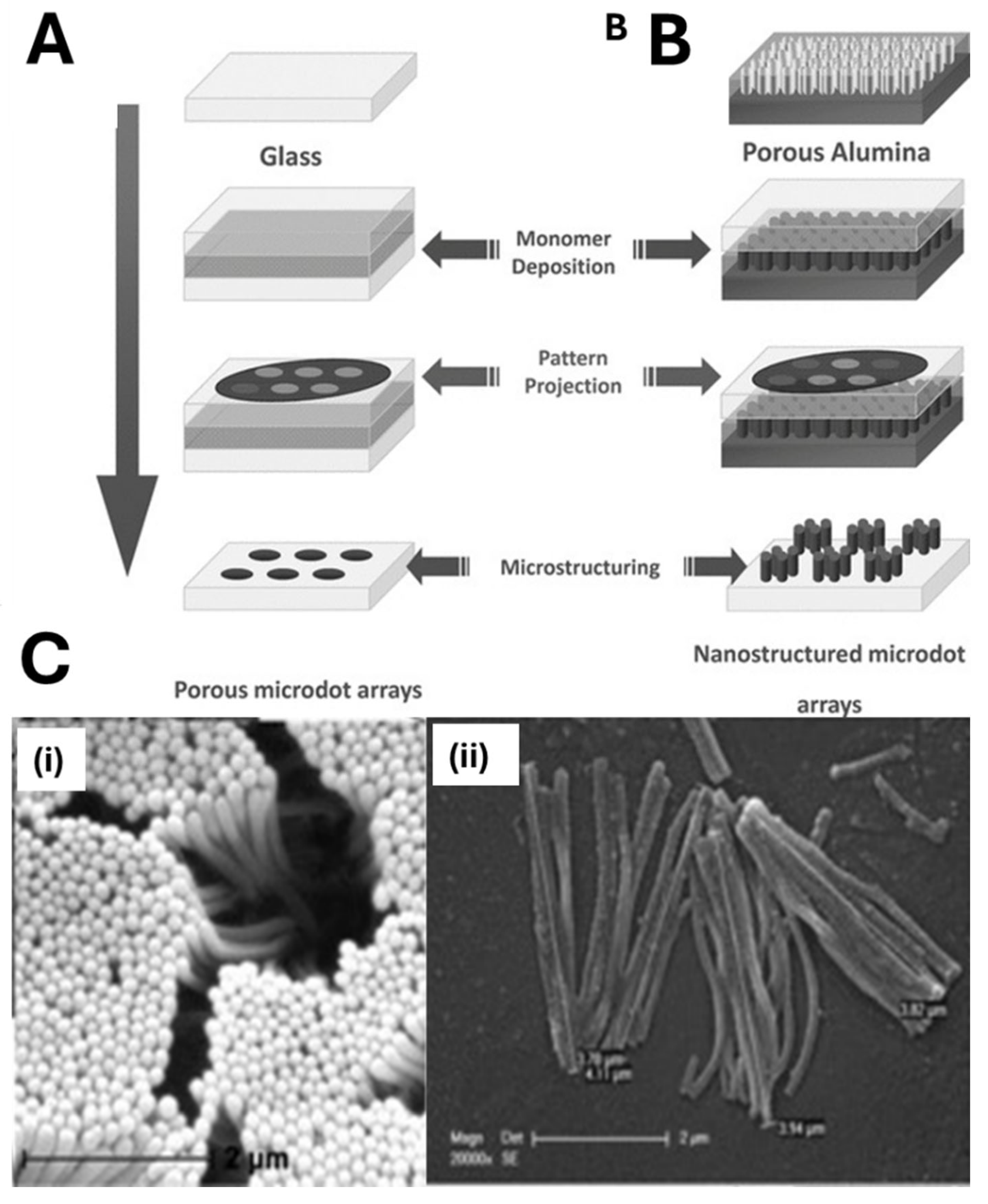
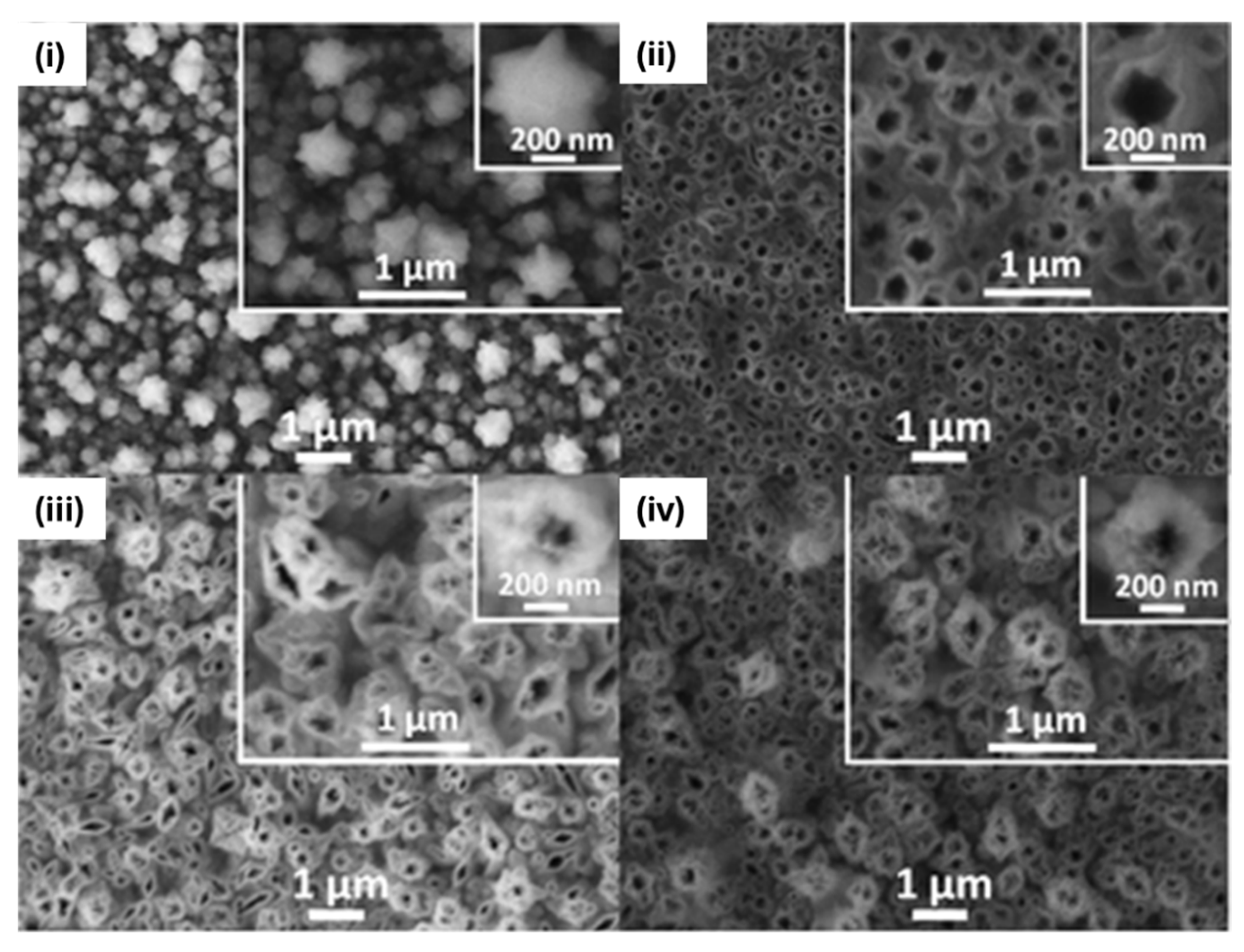
2.2. MIP Nanopatterning
3. Direct Integration of MIPs with Nanotransducers
3.1. MIP Electro-Polymerization
3.2. Dopamine Self-Polymerization
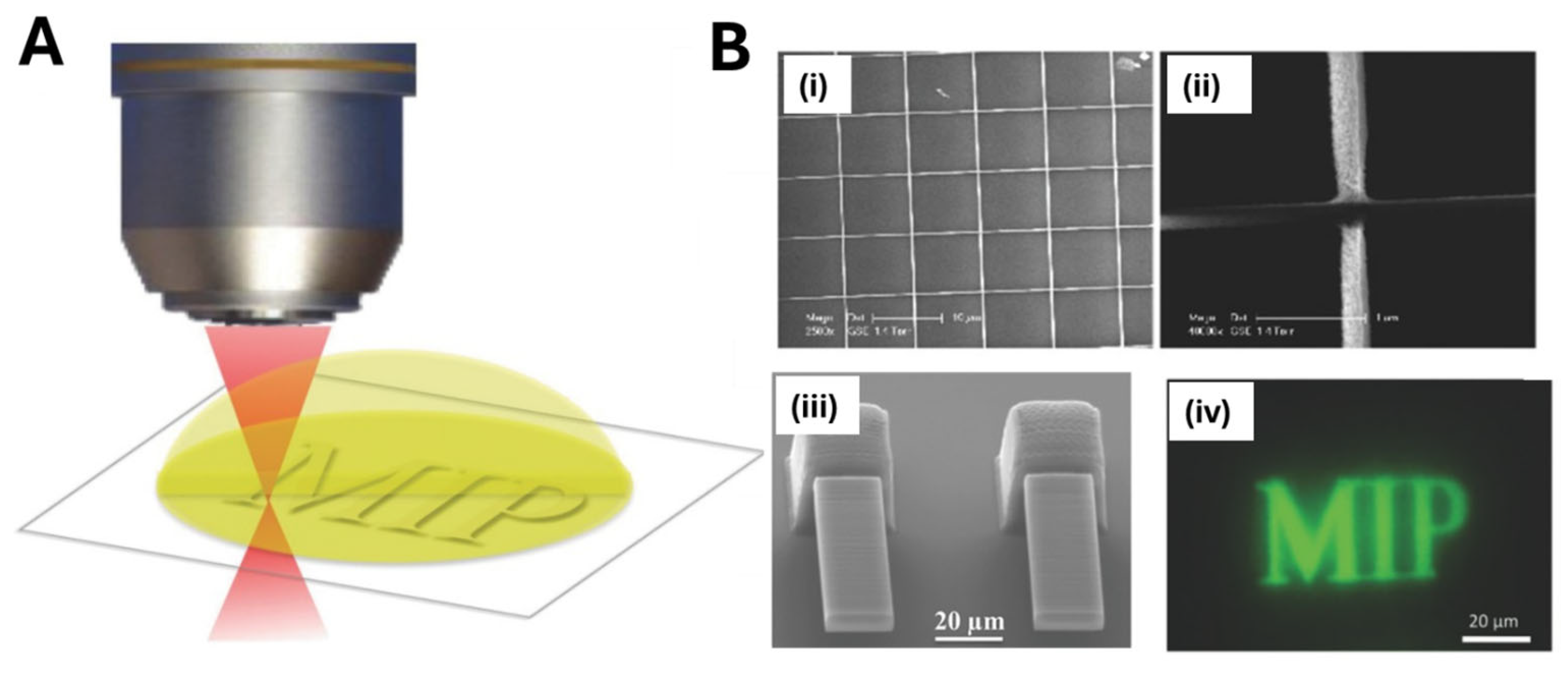
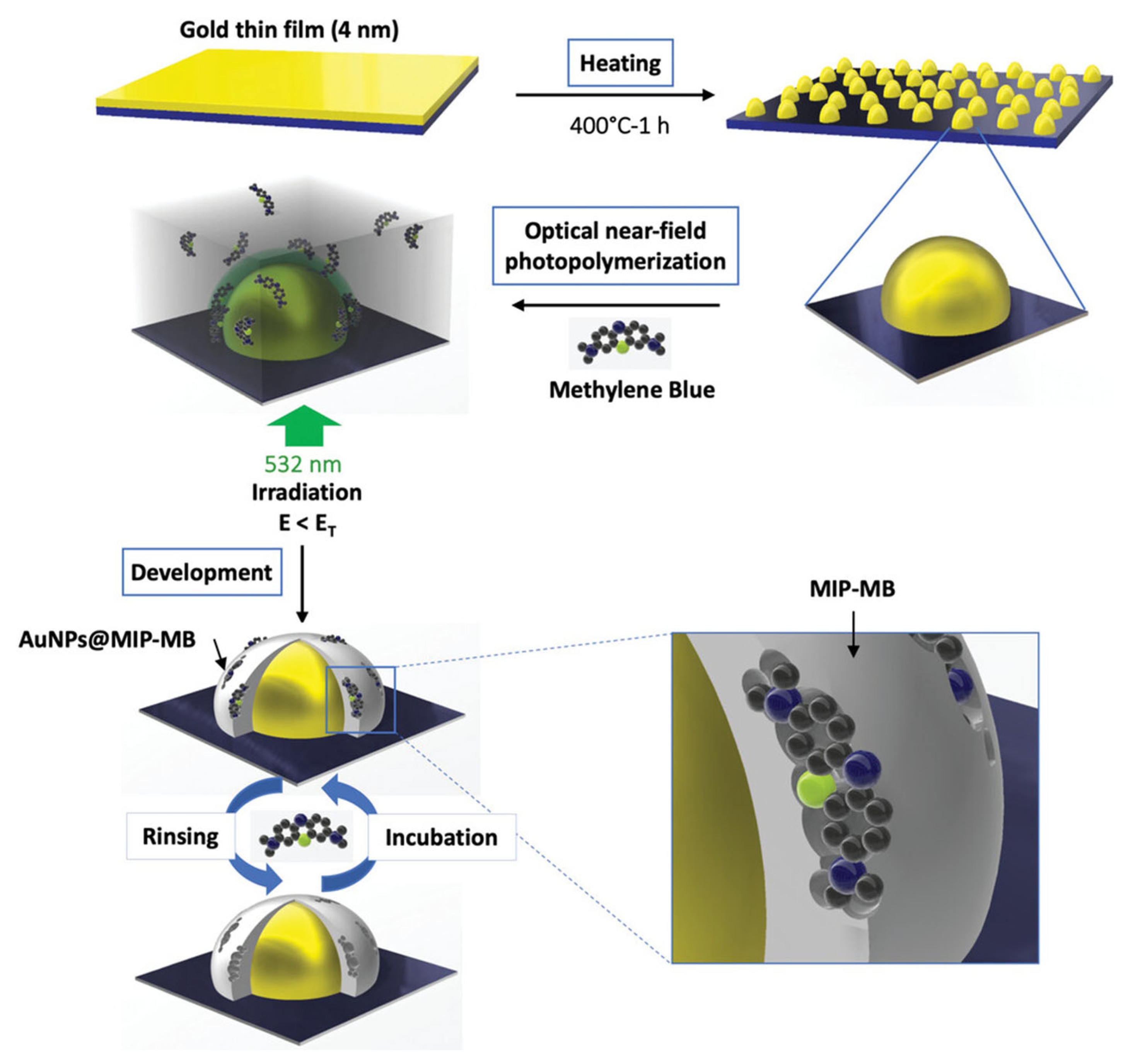
3.3. Localized Polymerization
3.4. Vapor-Phase Synthesis
| Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages | References |
| nanomolding |
|
| [41,42,58,69,70,72,73,74,75,76,77] |
| nanopatterning |
|
| [78,79,80,81,82,83,84] |
| electro-polymerization |
|
| [47,48,51,90,92,93,94,95] |
| dopamine self-polymerization |
|
| [101,102,103] |
| localized polymerization |
|
| [45,61,113,117,120,121] |
| vapor-phase synthesis |
|
| [43,44,127] |
4. MIP Applications in Nanosensors
4.1. Environmental Monitoring
4.2. Food Monitoring
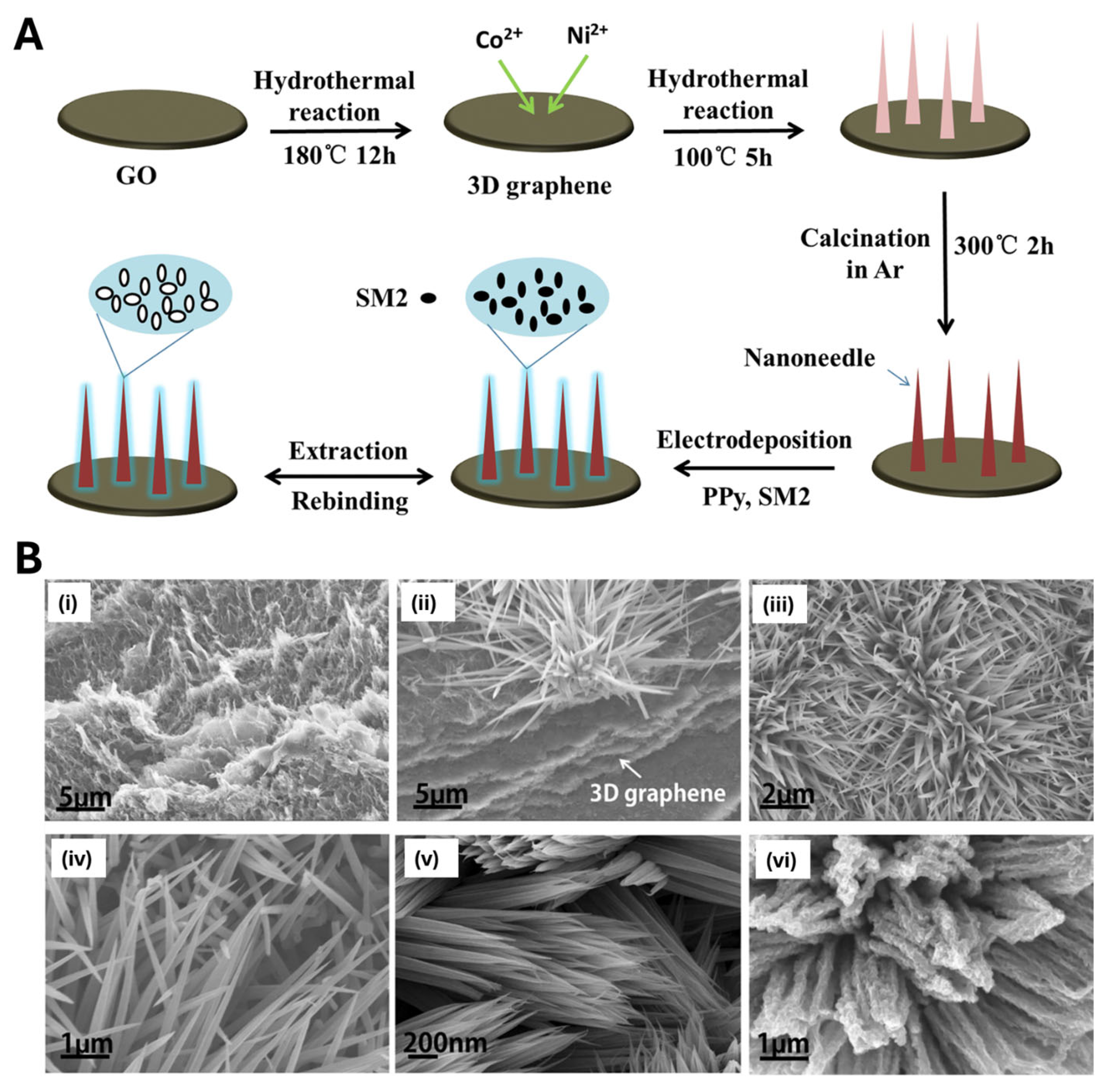
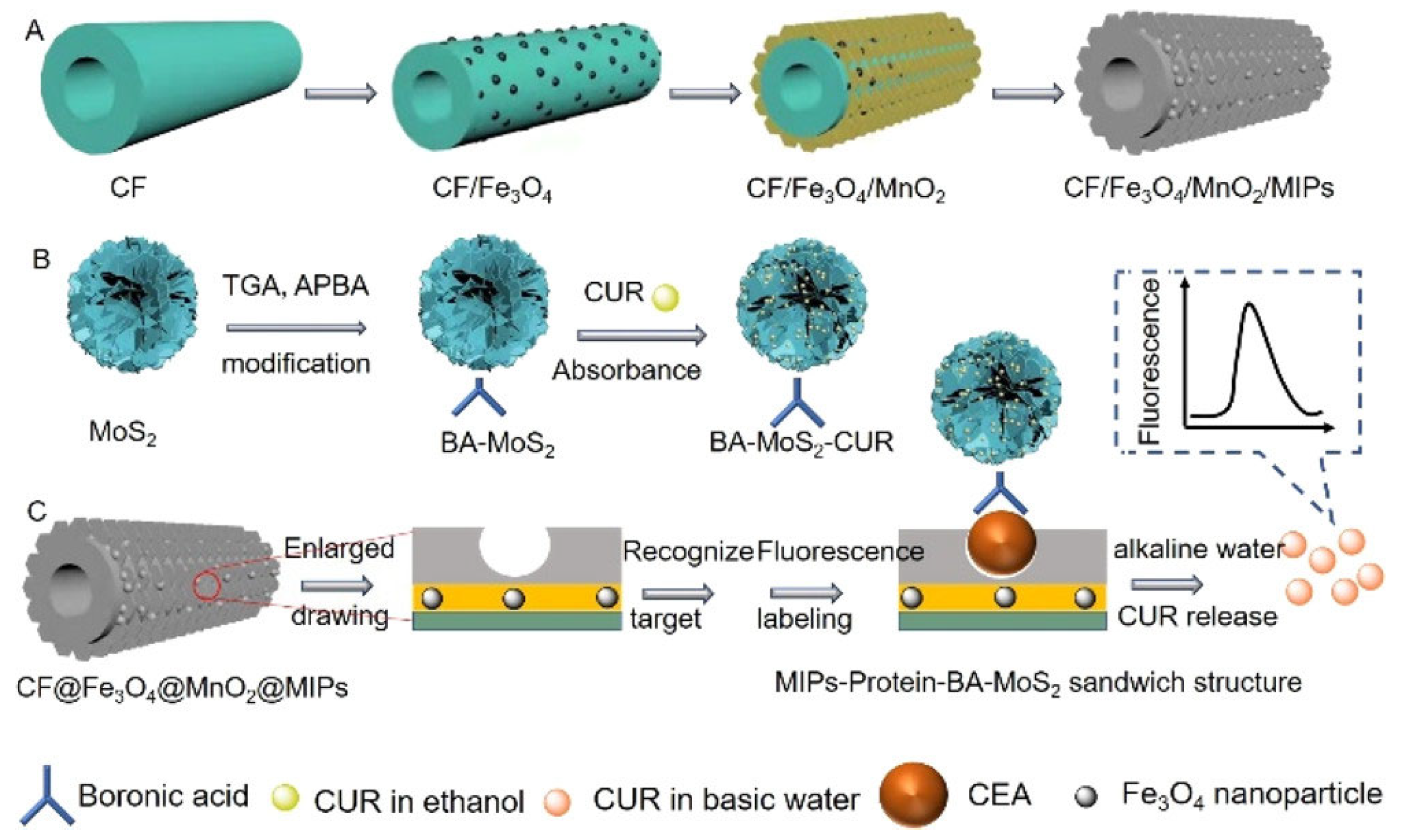
4.3. Biomarker Detection
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haupt, K.; Mosbach, K. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers and Their Use in Biomimetic Sensors. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Mosbach, K. Molecular Imprinting: Synthetic Materials As Substitutes for Biological Antibodies and Receptors. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüggemann, O.; Haupt, K.; Ye, L.; Yilmaz, E.; Mosbach, K. New configurations and applications of molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 889, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, K.; Linares, A.V.; Bompart, M.; Bernadette, T.S.B. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Mol. Impr. 2012, 325, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piletsky, S.A.; Turner, N.W.; Laitenberger, P. Molecularly imprinted polymers in clinical diagnostics—Future potential and existing problems. Med Eng. Phys. 2006, 28, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piletsky, S.; Canfarotta, F.; Poma, A.; Bossi, A.M.; Piletsky, S. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Cell Recognition. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 368–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossi, A.; Bonini, F.; Turner, A.P.; Piletsky, S.A. Molecularly imprinted polymers for the recognition of proteins: The state of the art. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossi, A.M.; Maniglio, D. BioMIPs: Molecularly imprinted silk fibroin nanoparticles to recognize the iron regulating hormone hepcidin. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, R.; Lei, J.; Ju, H.; Xue, Y. A Molecularly Imprinted Copolymer Designed for Enantioselective Recognition of Glutamic Acid. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 3223–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Liao, S. Organocatalytic, Stereoselective, Cationic Reversible Addition–Fragmentation Chain-Transfer Polymerization of Vinyl Ethers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 144, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliani, F.; Di Giulio, T.; Grecchi, S.; Benincori, T.; Arnaboldi, S.; Malitesta, C.; Mazzotta, E. Green Synthesis of a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based on a Novel Thiophene-Derivative for Electrochemical Sensing. Molecules 2024, 29, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamaoui, A.; Lahcen, A.A.; Amine, A. Unlocking the Potential of Molecularly Imprinted Polydopamine in Sensing Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwanza, C.; Zhang, W.-Z.; Mulenga, K.; Ding, S.-N. Advancing green chemistry in environmental monitoring: The role of electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensors. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 11490–11517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, G. Fourty years of molecular imprinting in synthetic polymers: Origin, features and perspectives. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, G.; Oberkobusch, D.; Minárik, M. Enzyme-analogue built polymers, 18 chiral cavities in polymer layers coated on wide-pore silica. React. Polym. Ion Exch. Sorbents 1985, 3, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, L.; Sellergren, B.; Mosbach, K. Imprinting of amino acid derivatives in macroporous polymers. Tetrahedron Lett. 1984, 25, 5211–5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibl, N.; Haupt, K.; Gonzato, C.; Duma, L. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Chemical Sensing: A Tutorial Review. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotta, E.; Di Giulio, T.; Malitesta, C. Electrochemical sensing of macromolecules based on molecularly imprinted polymers: Challenges, successful strategies, and opportunities. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 5165–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dong, X.; Yang, M. Development of separation materials using controlled/living radical polymerization. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 31, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Shao, M.; Xu, H.; Zhuo, S.; Liu, S.; Lee, S.-T. Molecularly imprinted polymer-coated silicon nanowires for protein specific recognition and fast separation. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 3990–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Jiang, S.; Liu, X. Efficient One-Pot Synthesis of Mussel-Inspired Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Coated Graphene for Protein-Specific Recognition and Fast Separation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 18448–18456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-J.; Zhou, W.-H.; Yin, X.-F.; Zhuang, Z.-X.; Yang, H.-H.; Wang, X.-R. Template Synthesized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanotube Membranes for Chemical Separations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 15954–15955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, L.; Turner, A.P. Molecularly-imprinted polymer sensors: Realising their potential. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, R.A.; Abu Hanifah, S.; Heng, L.Y. Advancements and prospects of molecularly imprinted polymers as chemical sensors: A comprehensive review. Talanta 2025, 287, 127592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justino, C.I.L.; Freitas, A.C.; Pereira, R.; Duarte, A.C.; Santos, T.A.P.R. Recent developments in recognition elements for chemical sensors and biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 68, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliani, F.; Di Giulio, T.; Asif, M.I.; Malitesta, C.; Mazzotta, E. Boosting Electrochemical Sensing Performances Using Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles. Biosensors 2024, 14, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Chacón, A.; Cetó, X.; del Valle, M. Molecularly imprinted polymers–towards electrochemical sensors and electronic tongues. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 6117–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cruz, A.; Ahmad, O.S.; Alanazi, K.; Piletska, E.; Piletsky, S.A. Generic sensor platform based on electro-responsive molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles (e-NanoMIPs). Microsystems Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lach, P.; Garcia-Cruz, A.; Canfarotta, F.; Groves, A.; Kalecki, J.; Korol, D.; Borowicz, P.; Nikiforow, K.; Cieplak, M.; Kutner, W.; et al. Electroactive molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for selective glyphosate determination. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 236, 115381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowski, M.; Lach, P.; Cieplak, M.; Kutner, W. Nanostructured molecularly imprinted polymers for protein chemosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyoti; Gonzato, C.; Żołek, T.; Maciejewska, D.; Kutner, A.; Merlier, F.; Haupt, K.; Sharma, P.S.; Noworyta, K.R.; Kutner, W. Molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles-based electrochemical chemosensors for selective determination of cilostazol and its pharmacologically active primary metabolite in human plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 193, 113542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinangeli, A.; Chianella, I.; Radicchi, E.; Maniglio, D.; Bossi, A.M. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Electrochemical Sensing: The Effect of Inhomogeneous Binding Sites on the Measurements. A Comparison between Imprinted Polyaniline versus nanoMIP-Doped Polyaniline Electrodes for the EIS Detection of 17β-Estradiol. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 4963–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, A.H.; Abd-Rabboh, H.S.M.; Hefnawy, A. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensors for monitoring the persistent organic pollutants chlorophenols. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 20163–20181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyazit, S.; Bui, B.T.S.; Haupt, K.; Gonzato, C. Molecularly imprinted polymer nanomaterials and nanocomposites by controlled/living radical polymerization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 62, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokonami, S.; Shiigi, H.; Nagaoka, T. Review: Micro- and nanosized molecularly imprinted polymers for high-throughput analytical applications. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 641, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, E.C.; Powell, J.M.; Clevinger, T.B.; Fairman, A.E.; Shukla, A. Advances in Biosensors and Diagnostic Technologies Using Nanostructures and Nanomaterials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2104126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, U.; Mujahid, A.; Zahid, M.; Mustafa, G.; Hayat, A. Nanostructured Molecularly Imprinted Photonic Polymers for Sensing Applications. Curr. Nanosci. 2020, 16, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappini, A.; Pasquardini, L.; Bossi, A.M. Molecular Imprinted Polymers Coupled to Photonic Structures in Biosensors: The State of Art. Sensors 2020, 20, 5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voicu, R.; Faid, K.; Farah, A.A.; Bensebaa, F.; Barjovanu, R.; Py, C.; Tao, Y. Nanotemplating for Two-Dimensional Molecular Imprinting. Langmuir 2007, 23, 5452–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Ying, Y.; Ping, J. Three-dimensional micro- and nanomanufacturing techniques for high-fidelity wearable bioelectronics. Nat. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2025, 2, 390–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, G.; Huang, J.; Zhang, D.; Qiu, Y. Construction of Self-Reporting Specific Chemical Sensors with High Sensitivity. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 4327–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, G.; Li, M.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Ultrasensitive Specific Stimulant Assay Based on Molecularly Imprinted Photonic Hydrogels. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotta, E.; Di Giulio, T.; Mariani, S.; Corsi, M.; Malitesta, C.; Barillaro, G. Vapor-Phase Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers on Nanostructured Materials at Room-Temperature. Small 2023, 19, e2302274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
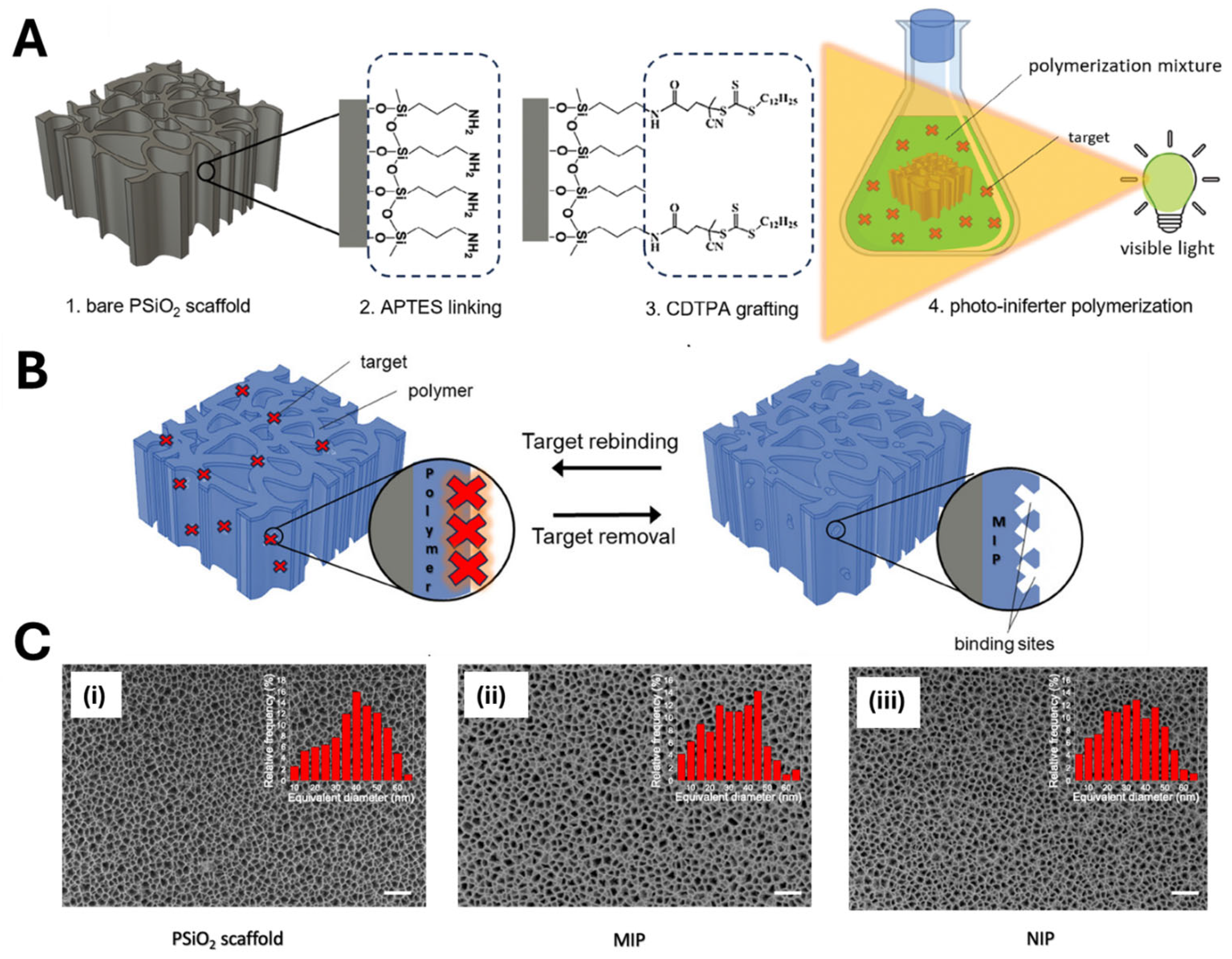
- Di Giulio, T.; Asif, I.M.; Corsi, M.; Rajpal, S.; Mizaikoff, B.; Ditaranto, N.; De Benedetto, G.E.; Malitesta, C.; Barillaro, G.; Mazzotta, E. A Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Porous Silicon Optical Sensor for Quercetin Detection in Wines. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 12663–12675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giulio, T.; Asif, M.I.; Corsi, M.; De Benedetto, G.E.; Malitesta, C.; Haupt, K.; Barillaro, G.; Gonzato, C.; Mazzotta, E. Visible-Light Photo-Iniferter Polymerization of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Direct Integration with Nanotransducers. Small Methods 2025, 9, e2401315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, H.C.; Chung, T.D. Electrochemical analysis based on nanoporous structures. Analyst 2012, 137, 3891–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, Q.; Liu, D.; Fang, F.; Mu, M.; Xie, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Wang, J.; Fang, G. Heterogeneous sensitization from nanoporous gold and titanium carbide (MXene) combining with molecularly imprinted polymers for highly sensitive and specific sensing detection of thiabendazole. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 367, 132159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, F.; Liu, J.; Song, H.; Liu, J.; Tang, H.; Ye, B.-C.; Sun, Z. Novel Electrochemical Sensing Platform Based on a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Decorated 3D Nanoporous Nickel Skeleton for Ultrasensitive and Selective Determination of Metronidazole. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 15474–15480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Wei, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, P.; Pan, J.; Zou, T.; Li, C.; Yan, Y. Highly-controllable imprinted polymer nanoshell at the surface of magnetic halloysite nanotubes for selective recognition and rapid adsorption of tetracycline. RSC Adv. 2013, 4, 7967–7978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fizir, M.; Richa, A.; He, H.; Touil, S.; Brada, M.; Fizir, L. A mini review on molecularly imprinted polymer based halloysite nanotubes composites: Innovative materials for analytical and environmental applications. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2020, 19, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhao, G.; Liu, M.; Zhu, Z. A novel photoelectrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer modified TiO2 nanotubes and its highly selective detection of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 1404–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajini, T.; Gigimol, M.; Mathew, B. A brief overview of molecularly imprinted polymers supported on titanium dioxide matrices. Mater. Today Chem. 2019, 11, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Dai, W.; Ge, L.; Yan, M.; Ge, S.; Yu, J. Visible light photoelectrochemical sensor based on Au nanoparticles and molecularly imprinted poly(o-phenylenediamine)-modified TiO2nanotubes for specific and sensitive detection chlorpyrifos. Analyst 2012, 138, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldara, M.; van Wissen, G.; Cleij, T.J.; Diliën, H.; van Grinsven, B.; Eersels, K.; Lowdon, J.W. Deposition Methods for the Integration of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) in Sensor Applications. Adv. Sens. Res. 2023, 2, 2200059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico-Yuste, A.; Carrasco, S. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Hybrid Materials for the Development of Optical Sensors. Polymers 2019, 11, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarepour, A.; Mohammadi, M.; Khosravi, A.; Soufi, G.J.; Hekmatnia, A.; Iravani, S.; Zarrabi, A. Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) in wearable and flexible sensors: Advancing healthcare monitoring. Microchem. J. 2025, 215, 114442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanci, S.N.; Ozcelikay-Akyildiz, G.; Ozkan, S.A. A review: Electrochemical analysis and application of anticancer drugs with MIP-based sensors and nanosensors. Essent. Chem 2025, 2, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, A.V.; Vandevelde, F.; Pantigny, J.; Falcimaigne-Cordin, A.; Haupt, K. Polymer Films Composed of Surface-Bound Nanofilaments with a High Aspect Ratio, Molecularly Imprinted with Small Molecules and Proteins. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1299–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malitesta, C.; Mazzotta, E.; Picca, R.A.; Poma, A.; Chianella, I.; Piletsky, S.A. MIP sensors–the electrochemical approach. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 402, 1827–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Dellatore, S.M.; Miller, W.M.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-Inspired Surface Chemistry for Multifunctional Coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khitous, A.; Molinaro, C.; Gree, S.; Haupt, K.; Soppera, O. Plasmon-Induced Photopolymerization of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Nanosensor Applications. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 10, 2201651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khitous, A.; Molinaro, C.; Thomas, C.; Haupt, K.; Soppera, O. Synthesis and Integration of Hybrid Metal Nanoparticles Covered with a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanolayer by Photopolymerization. Sensors 2023, 23, 3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, Y.; Soppera, O.; Haupt, K. Photopolymerization and photostructuring of molecularly imprinted polymers for sensor applications—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 717, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paruli, E.I.; Soppera, O.; Haupt, K.; Gonzato, C. Photopolymerization and Photostructuring of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 4769–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, S.; Frasco, M.F.; Freitas, P.P.; Sales, M.G.F. Detection of serum calprotectin based on molecularly imprinted photonic hydrogels: A novel approach for IBD diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2023, 13, 100313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.F.; Sales, M.G.F.; Frasco, M.F. A molecularly imprinted photonic polymer based on an inverse opal structure for sensing D-dimer at the point-of-care. Talanta 2022, 243, 123387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wei, J. Portable label-free inverse opal photonic hydrogel particles serve as facile pesticides colorimetric monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 1705–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Shi, D.; Qin, L.; Liu, S.; Chen, M. A facile approach for constructing molecularly imprinted photonic hydrogels with highly ordered and crack-free inverse-opal structure. J. Polym. Res. 2022, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Shi, W.; Cheng, M.; Liao, S.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Z. Molecularly imprinted photonic hydrogel sensor for optical detection of L-histidine. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffete, N.; Frederich, H.; Maître, A.; Schwob, C.; Ravaine, S.; Carbonnier, B.; Chehimi, M.M.; Mangeney, C. Introduction of a planar defect in a molecularly imprinted photonic crystal sensor for the detection of bisphenol A. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 364, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, R.; Lei, J.; Ju, H. Surface molecularly imprinted nanowire for protein specific recognition. Chem. Commun. 2008, 5761–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Liu, B.; Wang, Z.; Gao, D.; Guan, G.; Zhang, Z. Molecular Imprinting at Walls of Silica Nanotubes for TNT Recognition. Anal. Chem. 2007, 80, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandevelde, F.; Belmont, A.; Pantigny, J.; Haupt, K. Hierarchically Nanostructured Polymer Films Based on Molecularly Imprinted Surface-Bound Nanofilaments. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3717–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdunek, J.; Benito-Peña, E.; Linares, A.; Falcimaigne-Cordin, A.; Orellana, G.; Haupt, K.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Surface-Imprinted Nanofilaments for Europium-Amplified Luminescent Detection of Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics. Chem.–A Eur. J. 2013, 19, 10209–10216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernites, R.B.; Venkata, S.K.; Tiu, B.D.B.; Yago, A.C.C.; Advincula, R.C. Nanostructured, Molecularly Imprinted, and Template-Patterned Polythiophenes for Chiral Sensing and Differentiation. Small 2012, 8, 1669–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bognár, J.; Szűcs, J.; Dorkó, Z.; Horváth, V.; Gyurcsányi, R.E. Nanosphere Lithography as a Versatile Method to Generate Surface-Imprinted Polymer Films for Selective Protein Recognition. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 4703–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei, S.M.; Foudazi, R. Nanoconfined polymerization: Advantages of lyotropic liquid crystals as soft templates. Polym. Chem. 2025, 16, 1427–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, A.V.; Falcimaigne-Cordin, A.; Gheber, L.A.; Haupt, K. Patterning Nanostructured, Synthetic, Polymeric Receptors by Simultaneous Projection Photolithography, Nanomolding, and Molecular Imprinting. Small 2011, 7, 2318–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujahid, A.; Iqbal, N.; Afzal, A. Bioimprinting strategies: From soft lithography to biomimetic sensors and beyond. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1435–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Park, J.Y. Polymeric Colloidal Nanostructures Fabricated via Highly Controlled Convective Assembly and Their Use for Molecular Imprinting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 7381–7389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, S.; Canalejas-Tejero, V.; Navarro-Villoslada, F.; Barrios, C.A.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Cross-linkable linear copolymer with double functionality: Resist for electron beam nanolithography and molecular imprinting. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 1400–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalo, H.; Ayela, C.; Dague, E.; Vieu, C.; Haupt, K. Nanopatterning molecularly imprinted polymers by soft lithography: A hierarchical approach. Lab a Chip 2010, 10, 1316–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forchheimer, D.; Luo, G.; Montelius, L.; Ye, L. Molecularly imprinted nanostructures by nanoimprint lithography. Anal. 2010, 135, 1219–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, L.P.C.; Spangenberg, A.; Ton, X.; Fuchs, Y.; Bokeloh, F.; Malval, J.; Bui, B.T.S.; Thuau, D.; Ayela, C.; Haupt, K.; et al. Rapid Prototyping of Chemical Microsensors Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Synthesized by Two-Photon Stereolithography. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5931–5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.; Rastogi, C.K.; Rani, S.; Singh, G.P.; Saxena, S.; Shukla, S. Two decades of two-photon lithography: Materials science perspective for additive manufacturing of 2D/3D nano-microstructures. iScience 2023, 26, 106374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giulio, T.; Mazzotta, E.; Malitesta, C. Molecularly Imprinted Polyscopoletin for the Electrochemical Detection of the Chronic Disease Marker Lysozyme. Biosensors 2020, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldoni, R.; Thomaz, D.V.; Ottolini, M.; Di Giulio, S.; Di Giulio, T. Characterization of In situ electrosynthesis of polyaniline on pencil graphite electrodes through electrochemical, spectroscopical and computational methods. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 10287–10308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giulio, T.; Barca, A.; Verri, T.; De Gennaro, M.; Giancane, G.; Mazzotta, E.; Malitesta, C. Molecular imprinting based on metal-ion mediated recognition: Electrosynthesis of artificial receptors for the selective detection of peptides. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2023, 383, 133589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahcen, A.A.; Amine, A. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Sensors Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers and Nanomaterials. Electroanalysis 2018, 31, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanati, A.; Moakhar, R.S.; Hosseini, I.I.; Raeissi, K.; Karimzadeh, F.; Jalali, M.; Kharaziha, M.; Sheibani, S.; Shariati, L.; Presley, J.F.; et al. Gold Nano/Micro-Islands Overcome the Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Limitations to Achieve Ultrasensitive Protein Detection. ACS Sensors 2021, 6, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, D.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X. A facile electrochemical method for rapid determination of 3-chloropropane-1,2-diol in soy sauce based on nanoporous gold capped with molecularly imprinted polymer. Food Control. 2022, 134, 108750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhou, S.-F.; Al-Ghanim, K.A.; Mahboob, S.; Ye, B.-C.; Zhang, X. A novel sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer on a nanoporous gold leaf modified electrode for warfarin sodium determination. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 43724–43731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zhang, L.; Yu, F.; Ye, B.-C.; Li, Y. Molecularly imprinted polymer functionalized nanoporous Au-Ag alloy microrod: Novel supportless electrochemical platform for ultrasensitive and selective sensing of metronidazole. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 208, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xu, X. Synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymers/NiCo2O4 nanoneedle arrays on 3D graphene electrode for determination of sulfadimidine residue in food. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 54, 2066–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.; Correia, B.P.; Sharma, S.; Moreira, F.T.C. Molecular Imprinted Polymers on Microneedle Arrays for Point of Care Transdermal Sampling and Sensing of Inflammatory Biomarkers. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 39039–39044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladino, P.; Bettazzi, F.; Scarano, S. Polydopamine: Surface coating, molecular imprinting, and electrochemistry—successful applications and future perspectives in (bio)analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 4327–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladino, P.; Minunni, M.; Scarano, S. Cardiac Troponin T capture and detection in real-time via epitope-imprinted polymer and optical biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 106, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fan, L.; Dai, Y.; Kan, X. Recognition and determination of bovine hemoglobin using a gold electrode modified with gold nanoparticles and molecularly imprinted self-polymerized dopamine. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 2477–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamaoui, A.; Palacios-Santander, J.M.; Amine, A.; Cubillana-Aguilera, L. Molecularly imprinted polymers based on polydopamine: Assessment of non-specific adsorption. Microchem. J. 2021, 164, 106043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Li, W.; Shen, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, M.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Jing, T. Improving the sensitivity and selectivity of sulfonamides electrochemical detection with double-system imprinted polymers. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 864, 161173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Liu, Y.-J.; Liu, F.; Luo, M.-F.; Wan, Y.-C.; Huang, Z.; Liao, Q.; Mei, F.-S.; Wang, Z.-C.; Jin, A.-Y.; et al. Bio-inspired virus imprinted polymer for prevention of viral infections. Acta Biomater. 2017, 51, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.-Z.; Cheng, S.-W.; Xu, L.-B.; Liu, H.-Y.; Huang, K.; Li, L.; Zhai, Y.-Y.; Zeng, Y.-B.; Liu, H.-Q.; Shao, Y.; et al. Highly sensitive and selective sensor for sunset yellow based on molecularly imprinted polydopamine-coated multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Xu, S. Carbon Nanofibers Coated with Fe3O4 Nanoparticles and MnO2 Nanosheets further Modified with Molecularly Imprinted Polydopamine for Fluorescence Sensing of Carcinoembryonic Antigen. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 2532–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Gao, P.; Li, Y.; Qi, P.; Liu, J.; Shen, R.; Wang, L.; Huang, N.; Xiong, K.; Tian, W.; et al. Poly-dopamine, poly-levodopa, and poly-norepinephrine coatings: Comparison of physico-chemical and biological properties with focus on the application for blood-contacting devices. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakir, P.; Cutivet, A.; Resmini, M.; Bui, B.T.S.; Haupt, K. Protein-Size Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanogels as Synthetic Antibodies, by Localized Polymerization with Multi-initiators. Adv. Mater. 2012, 25, 1048–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizu, K.; Kobayakawa, N.; Takano, S.; Tokuno, Y.; Ozawa, M. Synthesis of polymer particles possessing radical initiating sites on the surface by emulsion copolymerization and construction of core–shell structures by a photoinduced atom transfer radical polymerization approach. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2007, 45, 1771–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, K.; Rangel, P.X.M.; Bui, B.T.S. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Antibody Mimics for Bioimaging and Therapy. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 9554–9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyazit, S.; Ambrosini, S.; Marchyk, N.; Palo, E.; Kale, V.; Soukka, T.; Bui, B.T.S.; Haupt, K. Versatile Synthetic Strategy for Coating Upconverting Nanoparticles with Polymer Shells through Localized Photopolymerization by Using the Particles as Internal Light Sources. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 8919–8923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameche, F.; Heni, W.; Telitel, S.; Ge, D.; Vidal, L.; Dumur, F.; Gigmes, D.; Lalevée, J.; Marguet, S.; Douillard, L.; et al. Plasmon-triggered living photopolymerization for elaboration of hybrid polymer/metal nanoparticles. Mater. Today 2020, 40, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soppera, O.; Jradi, S.; Ecoffet, C.; Lougnot, D.J.; Smith, G.B.; Cortie, M.B. Optical near-field patterning of photopolymer. NanoScience + Engineering. Proc. SPIE 2007, 6647, 66470I. [Google Scholar]
- Tasdelen, M.A.; Yagci, Y. Controlled/Living Radical Polymerization in the Presence of Iniferters; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2013; pp. 78–111. [Google Scholar]
- Suwier, D.R.; Monteiro, M.J.; Vandervelden, A.; Koning, C.E. The iniferter technique in radical polymerization under UV and thermal conditions: A comparative study. e-Polymers 2002, 2, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, F.; Todros, S.; Lakshmi, D.; Whitcombe, M.J.; Chianella, I.; Ferroni, M.; Piletsky, S.A.; Turner, A.P.; Marrazza, G. Quasi-monodimensional polyaniline nanostructures for enhanced molecularly imprinted polymer-based sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-F. Surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization for applications in sensors, non-biofouling surfaces and adsorbents. Polym. J. 2016, 48, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabibullin, A.; Mastan, E.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Zhu, S. Surface-Initiated Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2015, 270, 29–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, I.V.; Ek, J.I.; Ahn, E.C.; Sustaita, A.O. Molecularly imprinted polymers via reversible addition–fragmentation chain-transfer synthesis in sensing and environmental applications. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 9186–9201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Rana, S.; Mehra, P.; Kaur, K. Surface-Initiated Reversible Addition–Fragmentation Chain Transfer Polymerization (SI-RAFT) to Produce Molecularly Imprinted Polymers on Graphene Oxide for Electrochemical Sensing of Methylparathion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 49889–49901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrisson, S.; Whitfield, R.; Anastasaki, A.; Matyjaszewski, K. Atom transfer radical polymerization. Nat. Rev. Methods Prim. 2025, 5, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyjaszewski, K.; Xia, J. Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 2921–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.K.; Yang, J.C.; Hong, S.W.; Park, J. Molecular imprinting of polymer films on 2D silica inverse opal via thermal graft copolymerization for bisphenol A detection. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2020, 323, 128670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Pan, J.; Dai, J.; Cao, Z.; Hang, H.; Li, X.; Yan, Y. Magnetic ZnO surface-imprinted polymers prepared by ARGET ATRP and the application for antibiotics selective recognition. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 5571–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallas, P.; Georgakilas, V. Interfacial polymerization of conductive polymers: Generation of polymeric nanostructures in a 2-D space. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 224, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chondath, S.K.; Menamparambath, M.M. Interface-assisted synthesis: A gateway to effective nanostructure tuning of conducting polymers. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 918–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Zhang, T.; Feng, X. Interface-Assisted Synthesis of 2D Materials: Trend and Challenges. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 6189–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, A.T.; Wallace, G.G. Vapour phase polymerisation of conducting and non-conducting polymers: A review. Talanta 2014, 119, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, M.; Lahann, J. Vapor-based polymers: From films to nanostructures. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2219–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, G.O.; Armagan, E.; Erdogan, H.; Buyukserin, F.; Uzun, L.; Demirel, G. One-Dimensional Surface-Imprinted Polymeric Nanotubes for Specific Biorecognition by Initiated Chemical Vapor Deposition (iCVD). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 6447–6452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A, T.; M, D. Remediation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene Persistent in the Environment–A review. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2019, 29, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, X.; Chen, W. Recent advances in electrochemical sensors for the detection of 2, 4, 6-trinitrotoluene. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 17, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Falyouna, O.; Onyeaka, H.; Malloum, A.; Bornman, C.; AlKafaas, S.S.; Al-Sharify, Z.T.; Ahmadi, S.; Dehghani, M.H.; Mahvi, A.H.; et al. Recent progress on the remediation of metronidazole antibiotic as emerging contaminant from water environments using sustainable adsorbents: A review. J. Water Process. Eng. 2022, 51, 103405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, F. The enrofloxacin pollution control from fish to environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 199, 115923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Zekker, I.; Zhang, B.; Hendi, A.H.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, S.; Zada, N.; Ahmad, H.; Shah, L.A.; et al. Review on Methylene Blue: Its Properties, Uses, Toxicity and Photodegradation. Water 2022, 14, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Tan, X.; Tapas, S.; Zhang, J. Aim and shoot: Molecule-imprinting polymer coated MoO3 for selective SERS detection and photocatalytic destruction of low-level organic contaminants. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 36201–36207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subaihi, A.; Almanqur, L.; Muhamadali, H.; AlMasoud, N.; Ellis, D.I.; Trivedi, D.K.; Hollywood, K.A.; Xu, Y.; Goodacre, R. Rapid, Accurate, and Quantitative Detection of Propranolol in Multiple Human Biofluids via Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 10884–10892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Liao, P.; Li, W.; Hu, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Song, K.; Liu, J.; et al. Clinical Use of Propranolol Reduces Biomarkers of Proliferation in Gastric Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 628613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor, M.F.; Tariq, T.; Fatima, B.; Sahar, A.; Tariq, F.; Munir, S.; Khan, S.; Ranjha, M.M.A.N.; Sameen, A.; Zeng, X.-A.; et al. An insight into bisphenol A, food exposure and its adverse effects on health: A review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1047827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xie, C.; Li, S.; Xu, K. Electropolymerized molecular imprinting on gold nanoparticle-carbon nanotube modified electrode for electrochemical detection of triazophos. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 89, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, H.; Huang, Z.; Sun, D.-W.; Fu, H. Recent advances in the detection of 17β-estradiol in food matrices: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2144–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramasivam, A.; Murugan, R.; Jeraud, M.; Dakkumadugula, A.; Periyasamy, R.; Arjunan, S. Additives in Processed Foods as a Potential Source of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals: A Review. J. Xenobiotics 2024, 14, 1697–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugo, S.M.; Lu, W. Determination of β-Estradiol by Surface-Enhance Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) Using a Surface Imprinted Methacrylate Polymer on Nanoporous Biogenic Silica. Anal. Lett. 2021, 55, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.-Z.; Fang, B.; Pang, G.-F.; Ren, F.-Z. 3-Monochloropropane-1, 2-diol causes irreversible damage to reproductive ability independent of hormone changes in adult male rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 124, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciano, A.; Picariello, L.; Forino, M.; Moio, L.; Gambuti, A. Anthocyanins and nucleation seeds are key factors affecting quercetin precipitation in red wines. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 5163–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giulio, T.; De Benedetto, G.E.; Ditaranto, N.; Malitesta, C.; Mazzotta, E. Insights into Plastic Degradation Processes in Marine Environment by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strimbu, K.; Tavel, J.A. What Are Biomarkers? Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2010, 5, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozal-Palabiyik, B.; Uslu, B.; Marrazza, G. New Developments in Nanosensors for Pharmaceutical Analysis; Ozkan, S.A., Shah, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Chapter 11; pp. 327–380. ISBN 9780128161449. [Google Scholar]
- Zoltani, C.K. Cardiovascular Toxicity Biomarkers. In Biomarkers in Toxicology; Gupta, R.C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Chapter 12; pp. 209–228. ISBN 9780128146552. [Google Scholar]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asif, I.M.; Di Giulio, T.; Gagliani, F.; Malitesta, C.; Mazzotta, E. Advances in the Direct Nanoscale Integration of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) with Transducers for the Development of High-Performance Nanosensors. Biosensors 2025, 15, 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080509
Asif IM, Di Giulio T, Gagliani F, Malitesta C, Mazzotta E. Advances in the Direct Nanoscale Integration of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) with Transducers for the Development of High-Performance Nanosensors. Biosensors. 2025; 15(8):509. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080509
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsif, Ibrar Muhammad, Tiziano Di Giulio, Francesco Gagliani, Cosimino Malitesta, and Elisabetta Mazzotta. 2025. "Advances in the Direct Nanoscale Integration of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) with Transducers for the Development of High-Performance Nanosensors" Biosensors 15, no. 8: 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080509
APA StyleAsif, I. M., Di Giulio, T., Gagliani, F., Malitesta, C., & Mazzotta, E. (2025). Advances in the Direct Nanoscale Integration of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) with Transducers for the Development of High-Performance Nanosensors. Biosensors, 15(8), 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080509






