Quantitative Detection of Pyrene in Edible Oil via Plasmonic TLC-SERS Combined with Machine Learning Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
2.2. Preparation of Diatomite/Ag Composites
2.3. Preparation of PTLC Channel
2.4. TLC-SERS
2.5. Machine Learning and Analysis of Spectral Data
2.6. Instruments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SERS Properties of Diatomite/Ag
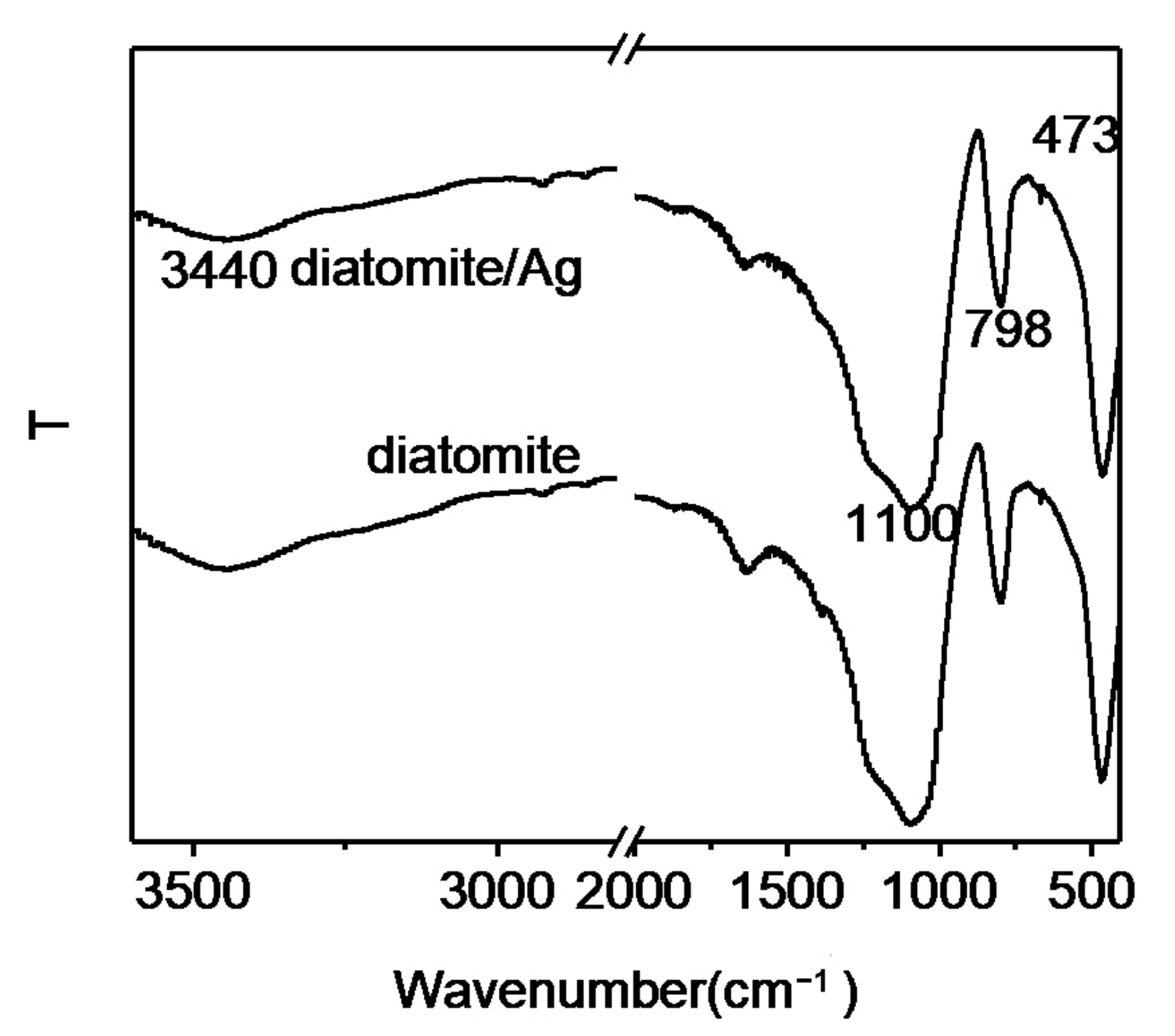
3.2. FTIR Spectra of the Substrate
3.3. Morphology and Characterization of Diatomite/Ag NPs
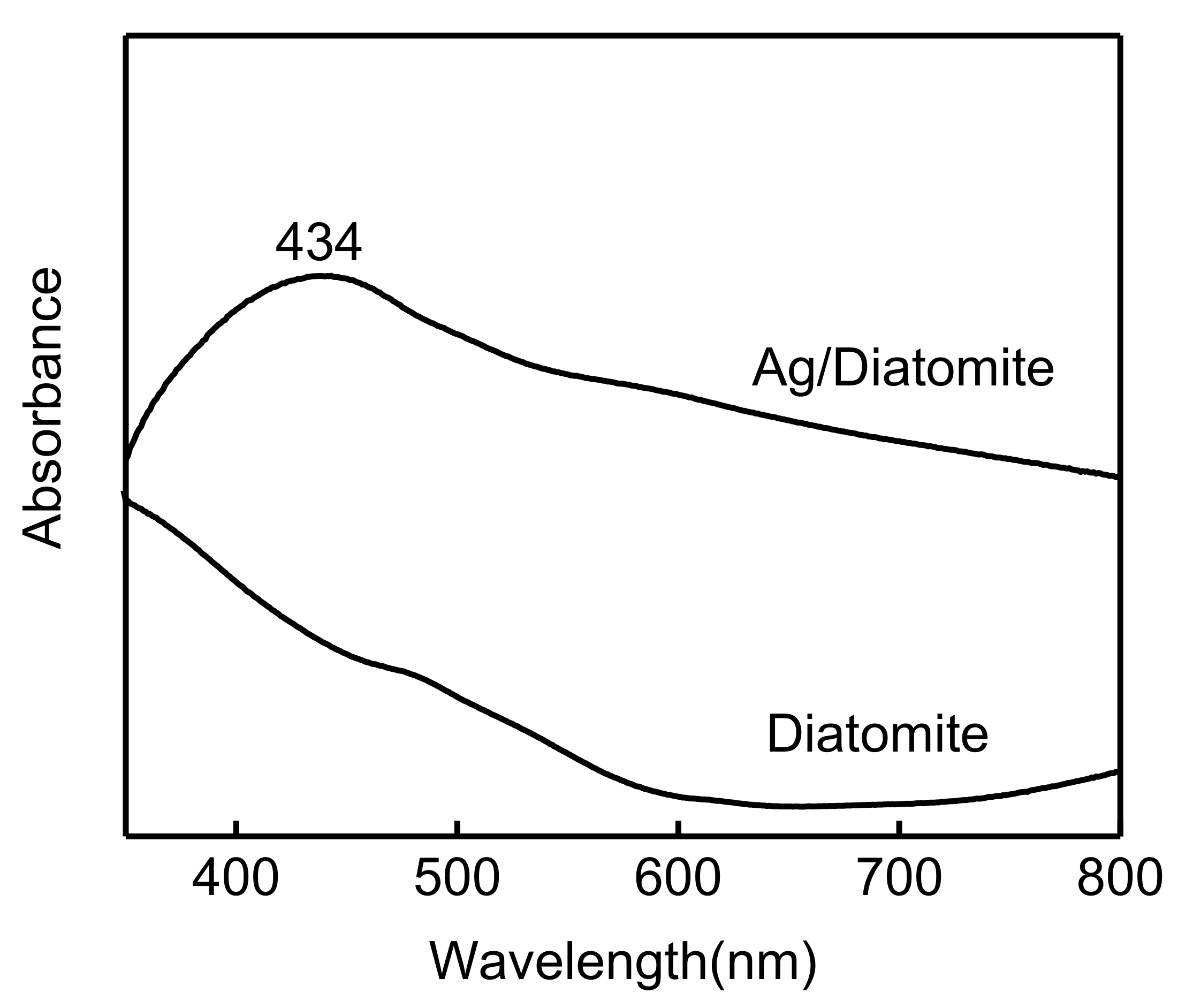
3.4. Plasmonic Feature of the Substrate
3.5. Uniformity of the Diatomite/Ag Channel
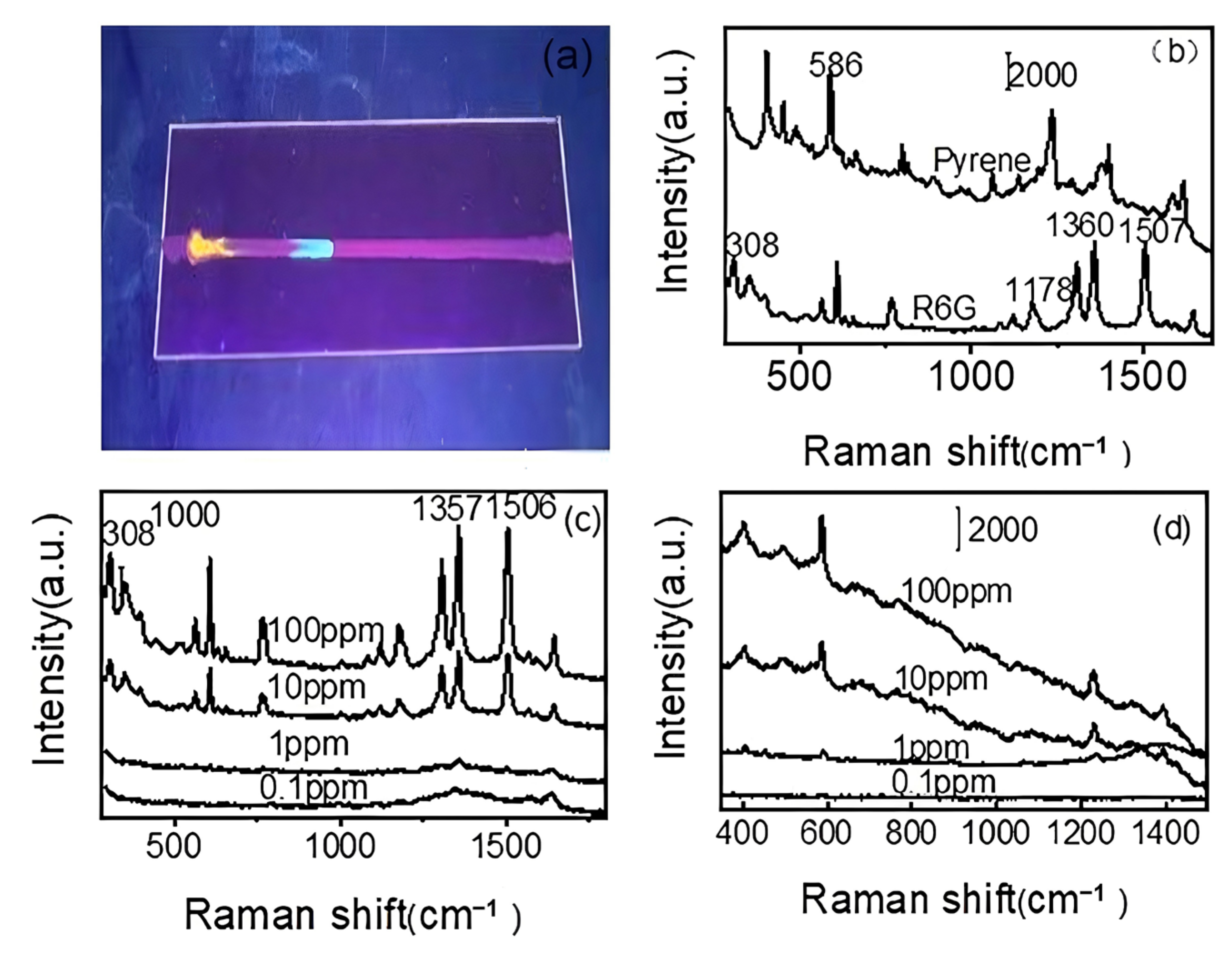
3.6. Separating and Detecting Pyrene from Mixtures
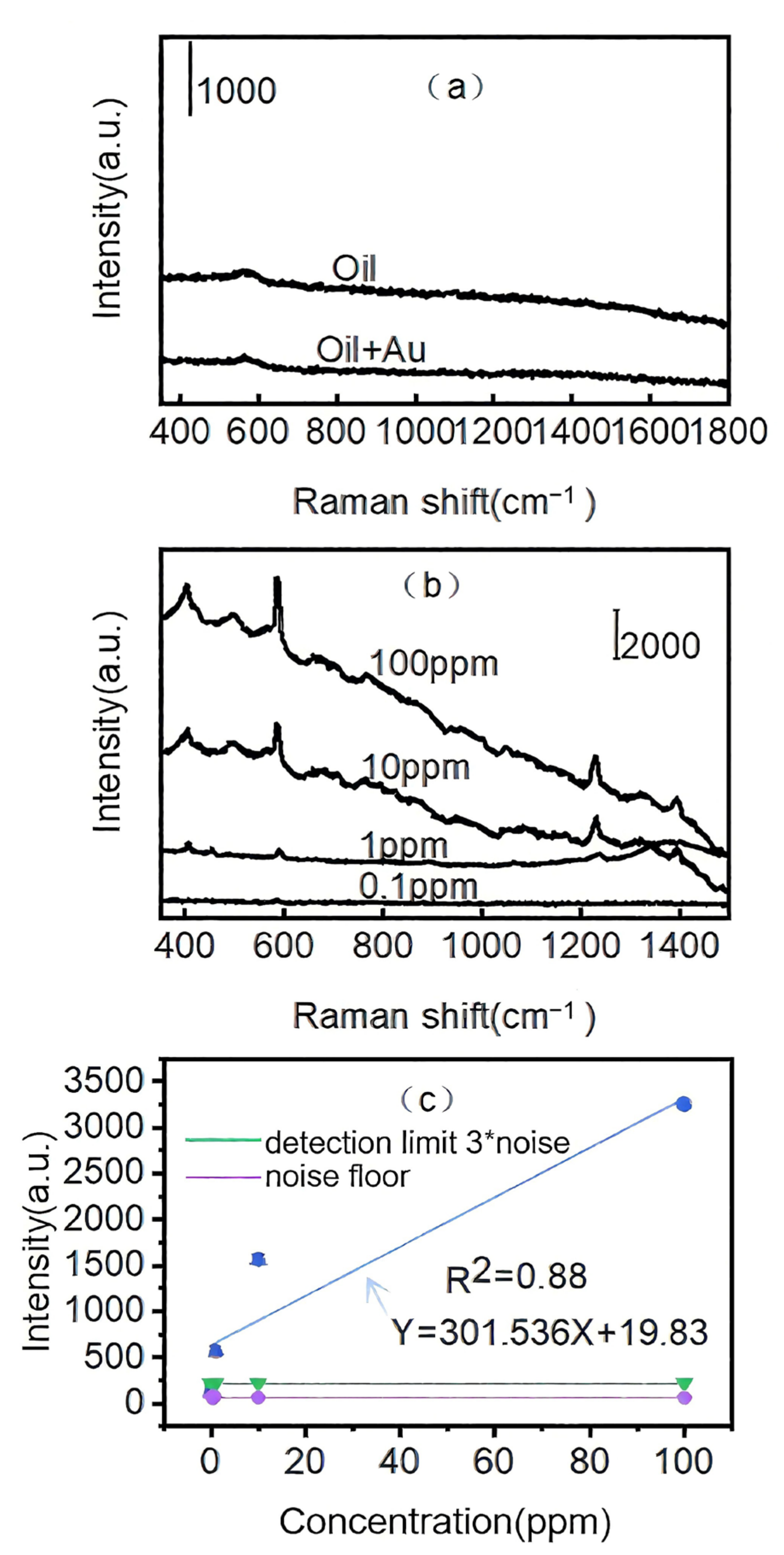
3.7. Identification of Pyrene from Edible Oil
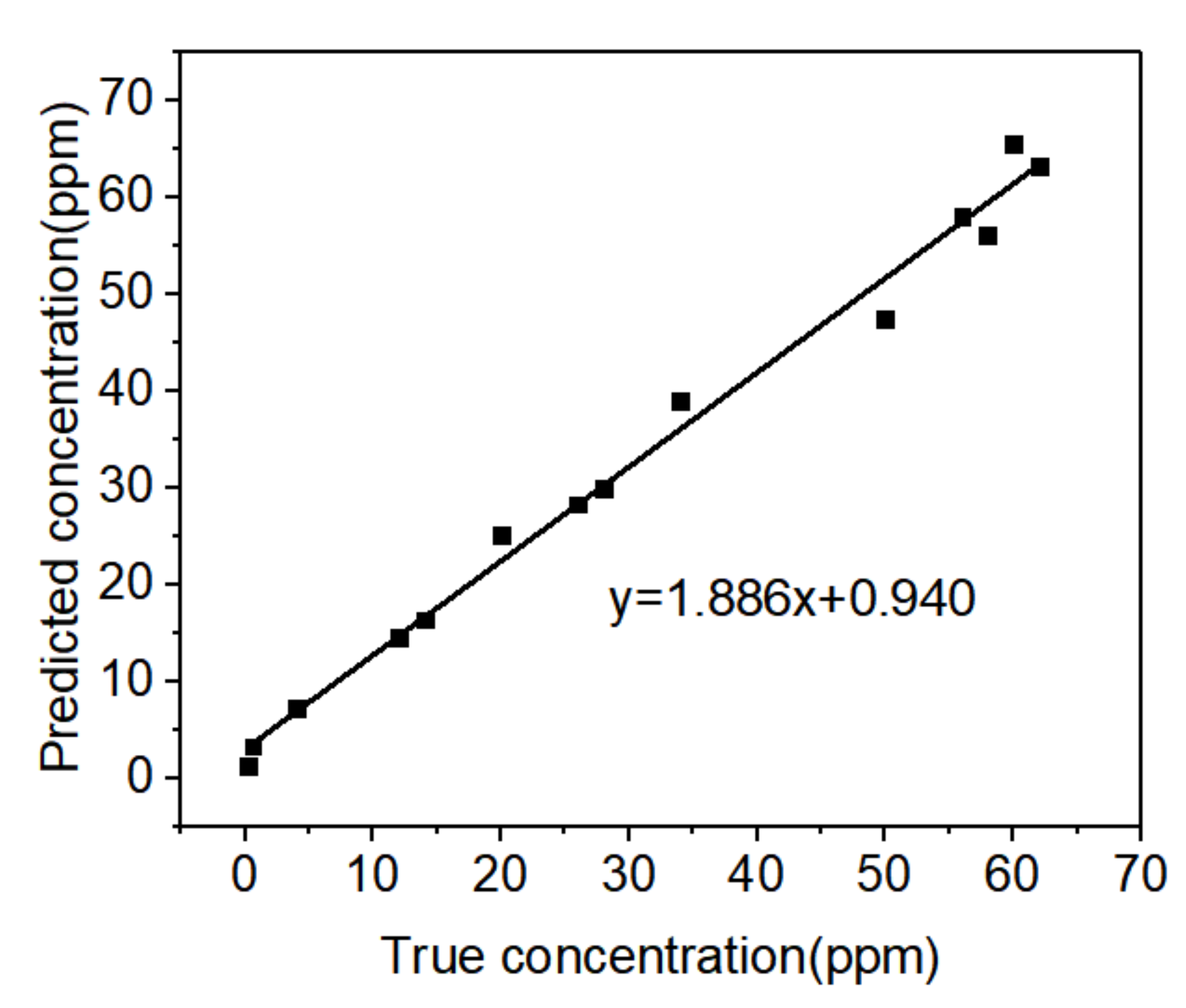
3.8. Establishment of the PCA-BP Model
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, X.-L.; Li, E.-K.; Cang, D.-Q.; Shi, Y.; Li, M.-J. Generation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons during coking. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2010, 17, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, A.T.; Fantke, P. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. A review. Cogent Environ. Sci. 2017, 3, 1339841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srogi, K. Monitoring of environmental exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2007, 5, 169–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.F.; Wang, X.; Han, X.X.; Xue, X.X.; Ji, W.; Qi, Z.H.; Liu, J.Q.; Zhao, B.; Ozaki, Y. Sensing of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with cyclodextrin inclusion complexes on silver nanoparticles by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Analyst 2010, 135, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eremina, O.E.; Sergeeva, E.A.; Ferree, M.V.; Shekhovtsova, T.N.; Goodilin, E.A.; Veselova, I.A. Dual-Purpose SERS Sensor for Selective Determination of Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds via Electron Donor-Acceptor Traps. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.-K.; Li, K.; Li, X.; Elbadry, S.; Raslan, A.A.; Li, Y.; Mulla, Z.S.; Tahoun, A.B.M.B.; El-Ghareeb, W.R.; Huang, X.-C. Levels of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in edible and fried vegetable oil: A health risk assessment study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 59784–59791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, M.-I.; Huang, S.-D. Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction method based on solidification of floating organic drop combined with gas chromatography with electron-capture or mass spectrometry detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1211, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavoltsos, S.; Sakellari, A.; Bakeas, E.; Bekiaris, G.; Plavšić, M.; Proestos, C.; Zinelis, S.; Koukoulakis, K.; Diakos, I.; Dassenakis, M.; et al. Trace elements, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, mineral composition, and FT-IR characterization of unrefined sea and rock salts: Environmental interactions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 10857–10868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cialla, D.; März, A.; Böhme, R.; Theil, F.; Weber, K.; Schmitt, M.; Popp, J. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS): Progress and trends. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 403, 27–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, K.; Cialla, D.; Ackermann, K.; Dörfer, T.; Möller, R.; Schneidewind, H.; Mattheis, R.; Fritzsche, W.; Rösch, P.; Popp, J. SERS: A versatile tool in chemical and biochemical diagnostics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 390, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.J.; Turner, J.W.; Idso, M.; Biryukov, S.V.; Rognstad, L.; Gong, H.; Trainer, V.L.; Wells, M.L.; Strom, M.S.; Yu, Q.M. In Situ Strain-Level Detection and Identification of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 2630–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markina, N.E.; Markin, A.V.; Weber, K.; Popp, J.; Cialla-May, D. Liquid-liquid extraction-assisted SERS-based determination of sulfamethoxazole in spiked human urine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1109, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Jin, L.; Xu, W.; Wu, Y. Disperse magnetic solid phase microextraction and surface enhanced Raman scattering (Dis-MSPME-SERS) for the rapid detection of trace illegally chemicals. Talanta 2018, 178, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zengin, A.; Tamer, U.; Caykara, T. Fabrication of a SERS based aptasensor for detection of ricin B toxin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markina, N.E.; Markin, A.V.; Zakharevich, A.M.; Goryacheva, I.Y. Calcium carbonate microparticles with embedded silver and magnetite nanoparticles as new SERS-active sorbent for solid phase extraction. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 3937–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowska, I.; Zydroń, M.; Szczepanik, K. TLC in the analysis of food additives. J. Planar Chromatogr.—Mod. TLC 2004, 17, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Fan, Q.; Yu, Q.; Wang, R.; Wang, H.; Kong, X. Facile detection of carbendazim in food using TLC-SERS on diatomite thin layer chromatography. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 247, 119037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hezel, U.B.; Zeiss, C. Chapter 8 Potential and experience in quantitative “high performance thin-layer chromatography” HPTLC. J. Chromatogr. Libr. 1977, 9, 147–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Chong, X.; Squire, K.; Wang, A.X. Microfluidic diatomite analytical devices for illicit drug sensing with ppb-Level sensitivity. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 259, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.Q.; Ji, S.Y.; Ren, Z.B.; Jiang, S.K.; Yu, Q.; Guo, J.Q.; Wang, A.X.; Kong, X.M. Rapid, convenient, and ultrasensitive point-of-care sensing of histamine from fish: A Portable chromatographic platform based on derivatization reaction. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1696, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, Q.; Guo, J.; Yuan, C.; Kong, X. On-site detection of pyrene from mixture with ppb level sensitivity by plasmonic TLC-DSERS. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 280, 121547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, N.S.; Ferreira, L.H.C.; Dutra, O.O. An Approach to Savitzky-Golay Differentiators. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 38, 4369–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.L.; Chen, Y.Q.; Xue, D.Y. Digital Fractional Order Savitzky-Golay Differentiator. Ieee Trans. Circuits Syst. Ii-Express Briefs 2011, 58, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Q.; Cai, K.Y. Time-domain analysis of the Savitzky-Golay filters. Digit. Signal Process. 2012, 22, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.Y.; Xu, J.L. Baseline estimation using optimized asymmetric least squares (O-ALS). Measurement 2024, 233, 114731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.W.; Zou, H. High-dimensional generalizations of asymmetric least squares regression and their applications. Ann. Stat. 2016, 44, 2661–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marukatat, S. Tutorial on PCA and approximate PCA and approximate kernel PCA. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 5445–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, R.C.; Cao, X.Y.; Zeng, B.; Shi, Z.D.; Ren, W.; Cao, X.X. Inception MLP: A vision MLP backbone for multi-scale feature extraction. Inf. Sci. 2025, 701, 121865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Wu, Y.; Tolba, A.; Li, T.F.; Ren, S.Q.; Ding, J.L. SA-MLP-Mixer: A Compact All-MLP Deep Neural Net Architecture for UAV Navigation in Indoor Environments. Ieee Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 21359–21371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Hu, H.; Zhang, L.Q.; Zhang, Y.A.; Li, J. Construction of Air Quality Level Prediction Model Based on STEPDISC-PCA-BP. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Huang, Y.L. Evaluation of mine water quality based on the PCA-PSO-BP model. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2024, 15, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.X.; Wang, H.J.; Li, W.M.; Zhan, D.P.; Li, X.Y.; Zang, X.M. Prediction Model of Endpoint Temperature of Converter Steelmaking Based on PCA-BP Neural Network. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2025, 78, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Hou, X.; Zhen, C.; Wang, A.X. Sub-Part-Per-Billion Level Sensing of Fentanyl Residues from Wastewater Using Portable Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Sensing. Biosensors 2021, 11, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, M. Validation of Nonlinear PCA. Neural Process. Lett. 2012, 36, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhu, K.; Yu, S. China Human Capital Prediction Based on the PCA-BP Artificial Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2009 Second International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation, Changsha, China, 10–11 October 2009; pp. 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Zhao, D.; Shen, T.; Ding, S.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, C. An optimized classification algorithm by BP neural network based on PLS and HCA. Appl. Intell. 2015, 43, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.W.; Sivashanmugan, K.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.X.; Wang, A.X. Multiplex sensing of complex mixtures by machine vision analysis of TLC-SERS images. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2022, 357, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.L.; Zhao, Y.; Sivashanmugan, K.; Squire, K.; Wang, A.X. Quantitative TLC-SERS detection of histamine in seafood with support vector machine analysis. Food Control 2019, 103, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Han, R.; Liu, Y.; Han, X.; Zhao, B. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) as a probe for detection of charge-transfer between TiO2 and CdS nanoparticles. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.E.J.; McCourt, M.R. SERS enhancement by aggregated Au colloids: Effect of particle size. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 7455–7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Fan, Q.Z.; Guo, J.Q.; Jiao, X.H.; Kong, X.M.; Yu, Q. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy tandem with derivatized thin-layer chromatography for ultra-sensitive on-site detection of histamine from fish. Food Control 2022, 138, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, J.; Jiao, X.; Guo, J.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Gu, G.; Sivashanmugan, K.; Kong, X. Quantitative Detection of Pyrene in Edible Oil via Plasmonic TLC-SERS Combined with Machine Learning Analysis. Biosensors 2025, 15, 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080477
Tian J, Jiao X, Guo J, Yu Q, Zhang S, Gu G, Sivashanmugan K, Kong X. Quantitative Detection of Pyrene in Edible Oil via Plasmonic TLC-SERS Combined with Machine Learning Analysis. Biosensors. 2025; 15(8):477. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080477
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Jiahui, Xianhe Jiao, Jiaqi Guo, Qian Yu, Shuqin Zhang, Guizhou Gu, Kundan Sivashanmugan, and Xianming Kong. 2025. "Quantitative Detection of Pyrene in Edible Oil via Plasmonic TLC-SERS Combined with Machine Learning Analysis" Biosensors 15, no. 8: 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080477
APA StyleTian, J., Jiao, X., Guo, J., Yu, Q., Zhang, S., Gu, G., Sivashanmugan, K., & Kong, X. (2025). Quantitative Detection of Pyrene in Edible Oil via Plasmonic TLC-SERS Combined with Machine Learning Analysis. Biosensors, 15(8), 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080477




