Optical–Electronic Skin Based on Tea Polyphenol for Dual Signal Wearable Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Preparation of Fe3O4@C Nanoparticles
2.3. Preparation of TPC OE-Skins
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Biocompatibility Testing
2.6. Antimicrobial Testing
2.7. Electrical Testing and Human Motion Monitoring
3. Results and Discussion
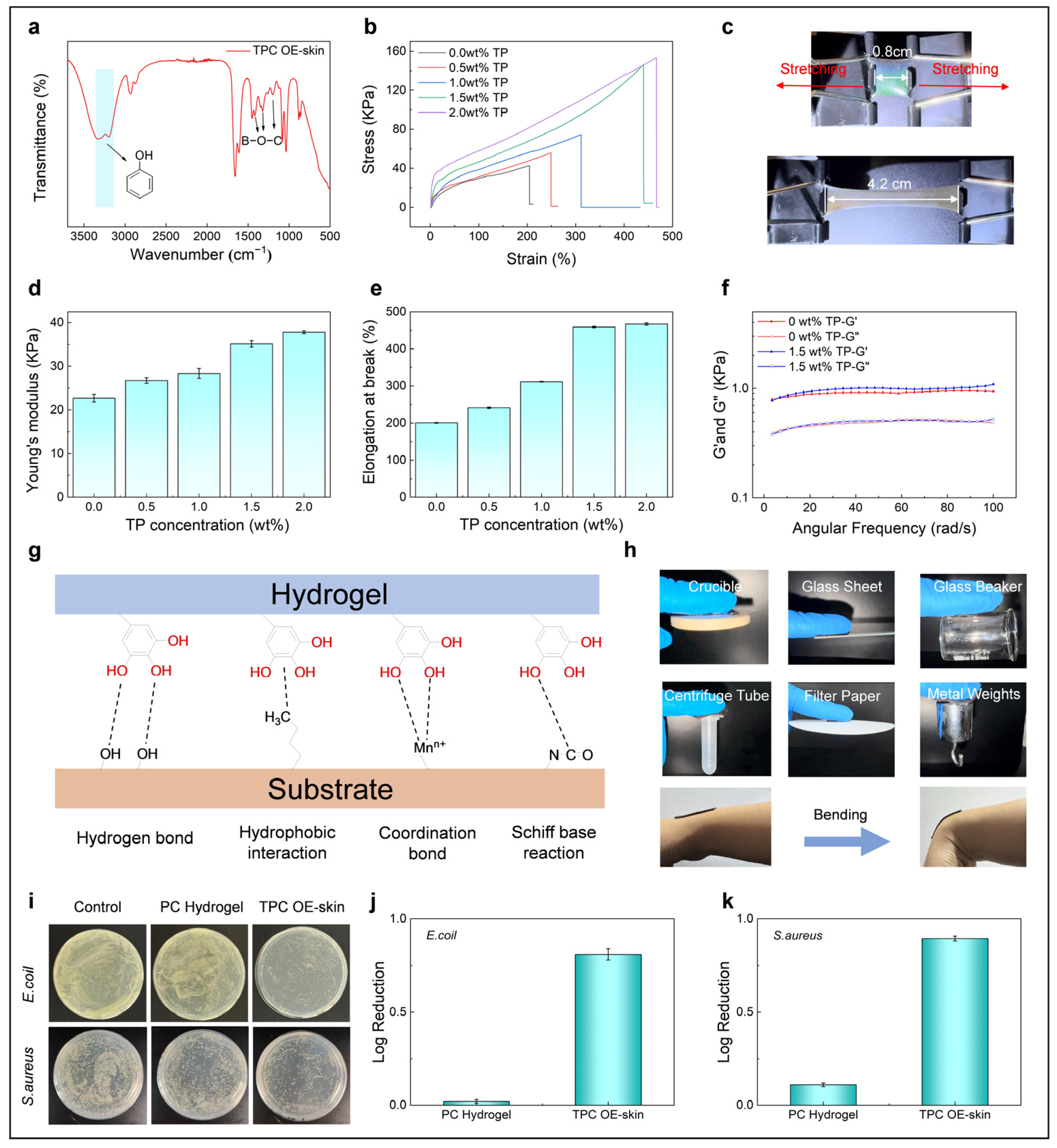
3.1. Fabrication of TPC OE-Skins
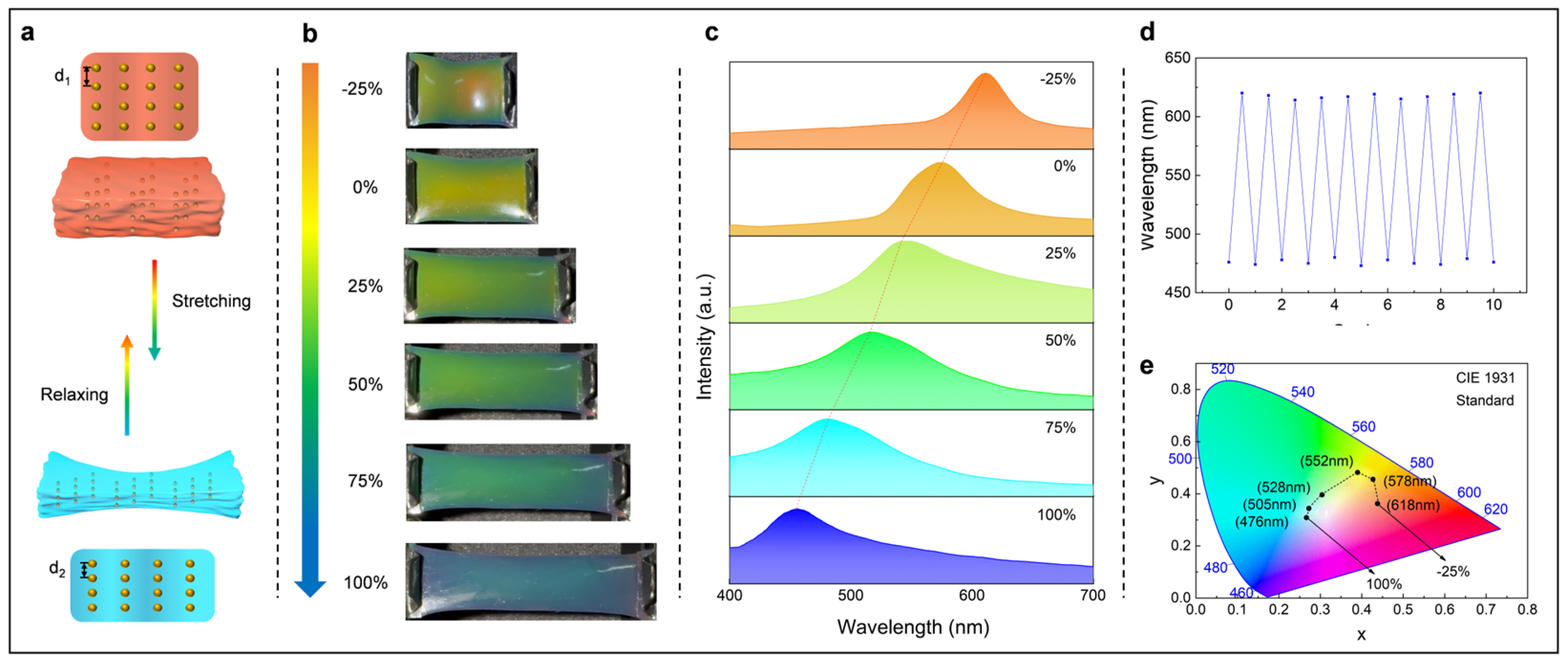
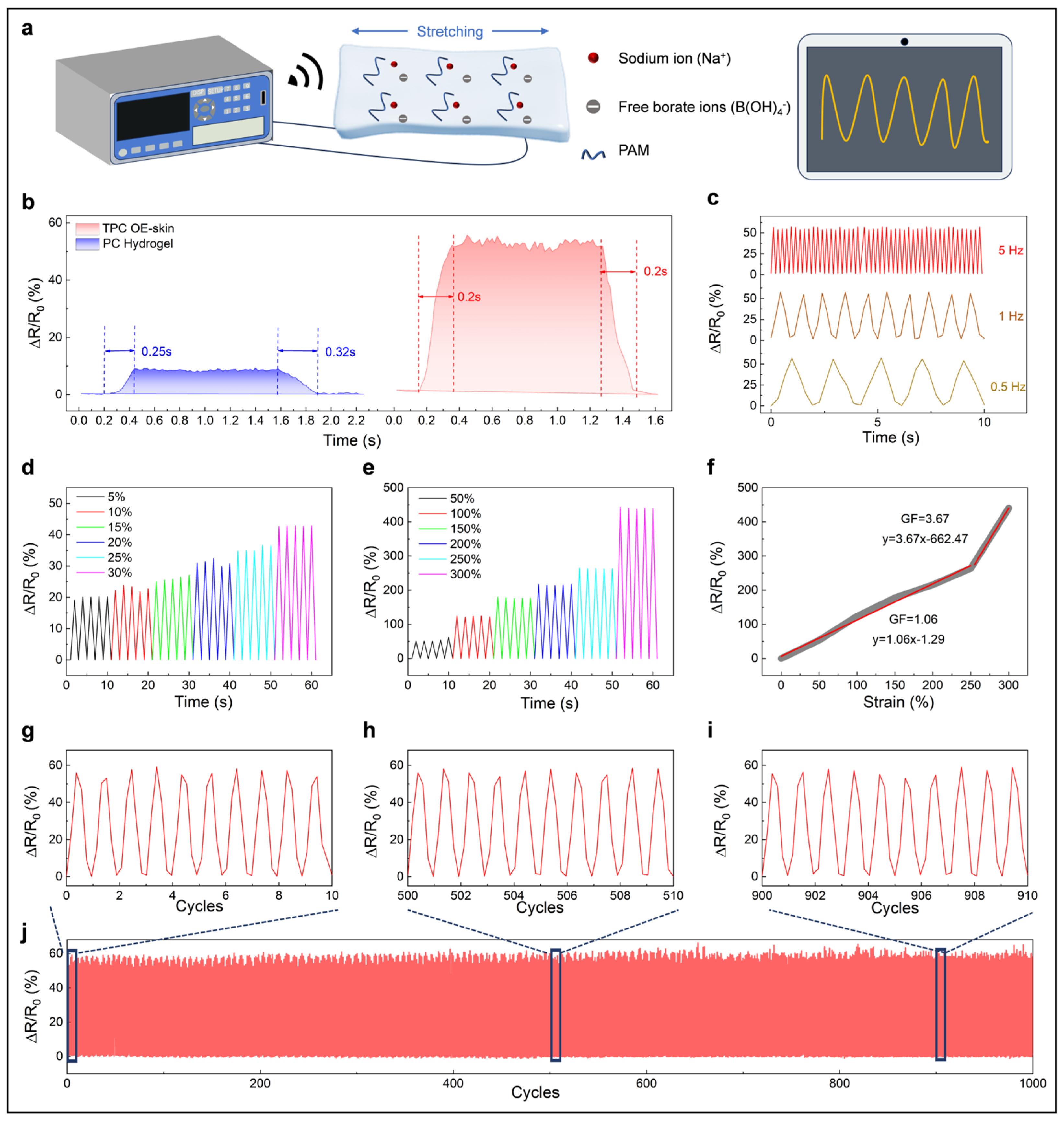
3.2. Optical and Electrical Sensing Performance of the TPC OE-Skin
3.3. Wearable Sensor for Human Motion Detection
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hong, W.; Guo, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, X.; He, J.; Zhang, R.; Yang, S.; Shao, Y.; Fang, Y.; et al. Fishbone and nettle fiber inspired stretchable strain sensor with high sensitivity and wide sensing range for wearable electronics. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 492, 152281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Liu, C.; Fan, W.; Sui, K. A Self-Detection Mechanism Toward Stable Multiple Perception of Ionic Skins. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 2423915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Long, Q.; Zhu, X.; He, L.; Li, Z.; Qian, X.; He, X.; Li, J.; Lv, C.; et al. Graphene/MXene/Cellulose cellulosic paper-based flexible bifunctional sensors utilizing molecular bridge strategy with tunable piezoresistive effect for Temperature-Pressure sensing. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 497, 154972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Ding, H.; Huang, W.; Gui, X.; Shi, W.; Shen, Y.; Tao, K.; Xie, X. Ultrasensitive and Stretchable Temperature Sensors Based on Thermally Stable and Self-Healing Organohydrogels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 19069–19079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katerinopoulou, D.; Zalar, P.; Sweelssen, J.; Kiriakidis, G.; Rentrop, C.; Groen, P.; Gelinck, G.H.; van den Brand, J.; Smits, E.C.P. Large-Area All-Printed Temperature Sensing Surfaces Using Novel Composite Thermistor Materials. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2018, 5, 1800605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.; Yiu, C.; Liu, Y.; Wong, T.H.; Huang, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Yao, K.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; et al. High Channel Temperature Mapping Electronics in a Thin, Soft, Wireless Format for Non-Invasive Body Thermal Analysis. Biosensors 2021, 11, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Yue, W.; Li, Y.; Yin, F.; Gao, S.; Zhang, C.; Kan, H.; Yao, Z.; Jiang, C.; Wang, C. Ultrafast-response/recovery capacitive humidity sensor based on arc-shaped hollow structure with nanocone arrays for human physiological signals monitoring. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2021, 334, 129637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; He, S.; Cui, D.; Chen, F. Bioinspired MXene-Based User-Interactive Electronic Skin for Digital and Visual Dual-Channel Sensing. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Wang, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, Z.; Deng, Y.; Tang, B.Z. From Fluorescence-Transfer-Lightening-Printing-Assisted Conductive Adhesive Nanocomposite Hydrogels toward Wearable Interactive Optical Information-Electronic Strain Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2400085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lin, W.; Gu, H. Carbon Quantum Dot-Functionalized Dermis-Derived Transparent Electronic Skin for Multimodal Human Motion Signal Monitoring and Construction of Self-Powered Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 46771–46788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alacid, Y.; Esquembre, R.; Montilla, F.; Martínez-Tomé, M.J.; Mateo, C.R. Fluorescent Nanocomposite Hydrogels Based on Conjugated Polymer Nanoparticles as Platforms for Alkaline Phosphatase Detection. Biosensors 2023, 13, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Niu, W.; Lo, C.Y.; Zhao, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S.; Ju, B.; Zhang, S. Interactively Full-Color Changeable Electronic Fiber Sensor with High Stretchability and Rapid Response. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.-L.; Tang, A.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, S. Robust and Durable Photonic Crystal with Liquid-Repellent Property for Self-Cleaning Coatings and Structural Colored Textiles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 35639–35650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Sun, J.; Ye, T.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, C. Bioinspired Low-Angle-Dependent Photonic Crystal Elastomer for Highly Sensitive Visual Strain Sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 41300–41309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Valenzuela, C.; Zhang, X.; Xue, P.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, L. Mechanochromic and Conductive Chiral Nematic Nanostructured Film for Bioinspired Ionic Skins. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 12829–12841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, K.; Ye, C.; Song, Y. Emerging interactively stretchable electronics with optical and electrical dual-signal feedbacks based on structural color materials. Nano Res. 2023, 17, 1837–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Ren, P.; Lyu, Q.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J. Adhesive photonic-ionic skins for visualizing wearable strain distributions. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 470, 143937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Tan, D.; Yang, X.; Xiong, L.; Li, G.; Lei, Y.; Xue, L. Fast Self-Assembly of Photonic Crystal Hydrogel for Wearable Strain and Temperature Sensor. Small Methods 2022, 6, 2200461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, C. Bioinspired conductive structural color hydrogels as a robotic knuckle rehabilitation electrical skin. Nanoscale Horiz. 2022, 7, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tian, H.; Liu, T.; Liu, H.; Zhao, F.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Shao, J. Chameleon-inspired active tunable structural color based on smart skin with multi-functions of structural color, sensing and actuation. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 2024–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.-L.; Liu, J.-T.; Xu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, Y. A High-performance Photonic-ionic E-skin with Synergistic Electronic/Optical Sensing for Motion Tracking. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 278, 117317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Q.; Wang, S.; Peng, B.; Chen, X.; Du, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J. Bioinspired Photonic Ionogels as Interactively Visual Ionic Skin with Optical and Electrical Synergy. Small 2021, 17, 2103271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Huang, C.; Li, Z.; Du, X. Bioinspired Ultra-Stretchable and Highly Sensitive Structural Color Electronic Skins. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 35, 2412703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y. Bio-Inspired Stretchable, Adhesive, and Conductive Structural Color Film for Visually Flexible Electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Yu, Y.; Fan, Q.; Wang, X.; Ye, F. Polyurethane-polypyrrole hybrid structural color films for dual-signal mechanics sensing. Smart Med. 2022, 1, e20220008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Chen, H.; He, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, Q.; Fu, Z.; Lu, C.; Lin, Z.; Caruso, F.; et al. Engineering Antimicrobial Metal–Phenolic Network Nanoparticles with High Biocompatibility for Wound Healing. Adv. Mater. 2023, 36, 230768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Pei, D.; Yang, Y.; Xu, K.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; He, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, A.; et al. Green Tea Derivative Driven Smart Hydrogels with Desired Functions for Chronic Diabetic Wound Treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2009442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, X.; Yao, J.; Hu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, H.; Wu, K. Enhancing under-urine adhesion and bladder adaptation of silk fibroin hydrogels with tea polyphenols for hemorrhagic cystitis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 283, 137487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Zhou, S.; Song, H.; Hu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, S.; Feng, X.; Pan, Y.; Gong, S.; et al. Green tea polyphenols-derived hybrid materials in manufacturing, environment, food and healthcare. Nano Today 2023, 52, 101990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Tang, T.; Gou, M. An adhesive hydrogel for the treatment of oral ulcers. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2025, 36, 110021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Lin, L.; Gan, Q.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Feng, C. Green Conductive Hydrogel Electrolyte with Self-Healing Ability and Temperature Adaptability for Flexible Supercapacitors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 39404–39419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Hu, Y.; Biasini, M.; Beyermann, W.P.; Yin, Y. Superparamagnetic magnetite colloidal nanocrystal clusters. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2007, 46, 4342–4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Q.; Wang, C.F.; Zhou, Z.F.; Chen, S. Robust Mechanochromic Elastic One-Dimensional Photonic Hydrogels for Touch Sensing and Flexible Displays. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2014, 2, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Zhao, J.; Ma, X.; Li, H.; Fan, D. Antibacterial Dual Network Hydrogels for Sensing and Human Health Monitoring. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2101089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.; Yuan, W. Biomimetic bilayer ionic conductive photoelectronic skin based on nano-structured photonic crystal film and flexible adhesive hydrogel for dual-signal motion detection and anti-disturbance temperature monitor. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 192, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daglia, M. Polyphenols as antimicrobial agents. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2012, 23, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenzl, C.; Hirsch, T.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Photonic Crystals for Chemical Sensing and Biosensing. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2014, 53, 3318–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.-L.; Zhao, G.; Wang, J.; Tang, A.; Liu, J.-T.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, Y. Optical–Electronic Skin Based on Tea Polyphenol for Dual Signal Wearable Sensing. Biosensors 2025, 15, 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050281
Xu J-L, Zhao G, Wang J, Tang A, Liu J-T, Zhu Z, Zhang Q, Tian Y. Optical–Electronic Skin Based on Tea Polyphenol for Dual Signal Wearable Sensing. Biosensors. 2025; 15(5):281. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050281
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jia-Li, Guangyao Zhao, Jiachen Wang, An Tang, Jun-Tao Liu, Zhijie Zhu, Qiang Zhang, and Yu Tian. 2025. "Optical–Electronic Skin Based on Tea Polyphenol for Dual Signal Wearable Sensing" Biosensors 15, no. 5: 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050281
APA StyleXu, J.-L., Zhao, G., Wang, J., Tang, A., Liu, J.-T., Zhu, Z., Zhang, Q., & Tian, Y. (2025). Optical–Electronic Skin Based on Tea Polyphenol for Dual Signal Wearable Sensing. Biosensors, 15(5), 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050281




