Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on MWCNTs/GQDs for the Detection of Sulfamethazine in Aquaculture Seawater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Apparatus
2.2. MWCNTs/GQD Coating on the GCE
2.3. Preparation of Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor
2.4. Electrochemical Measurement
2.5. Real Sample Preparation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Preparation and Characteristics of the Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor
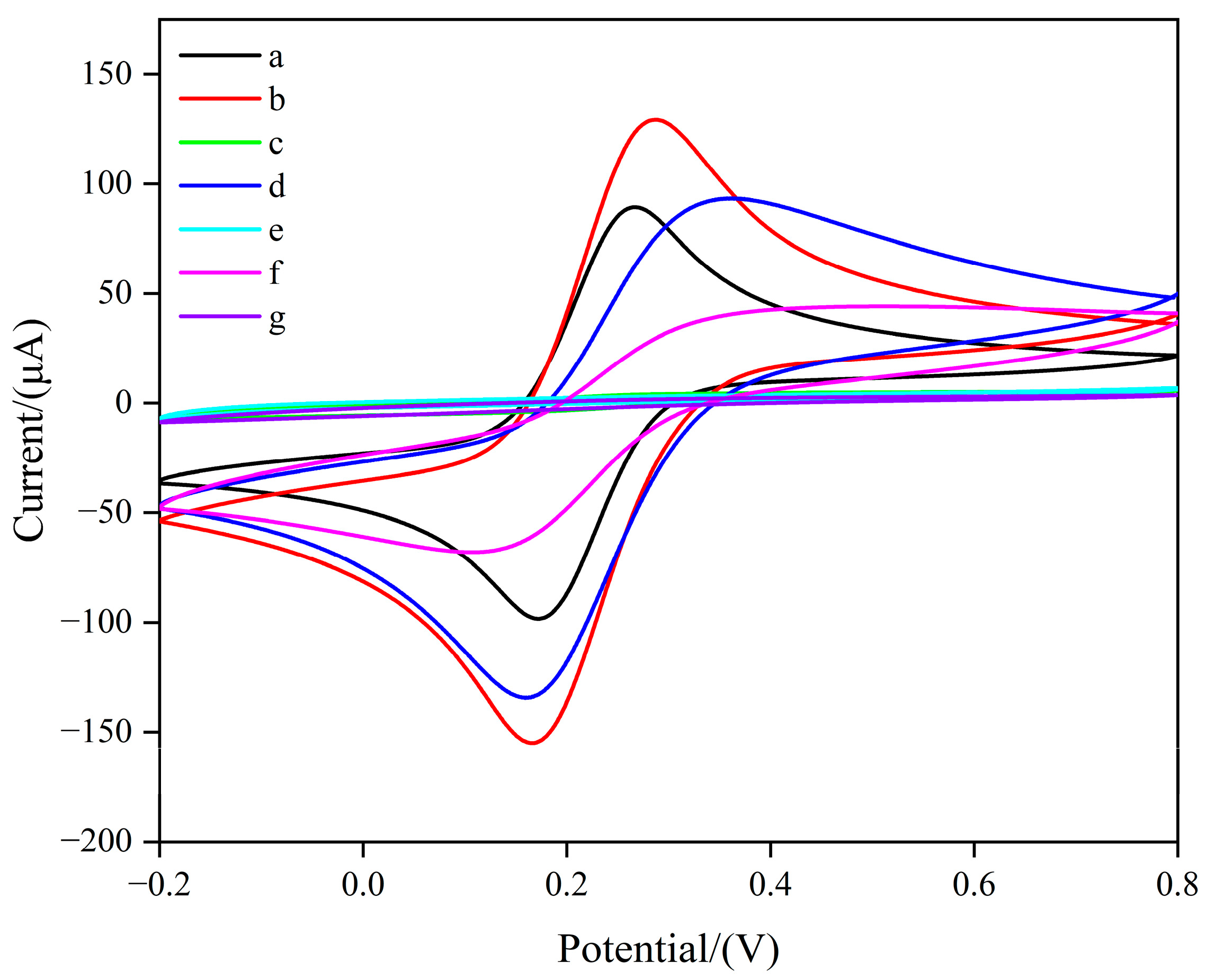
3.2. Electrochemical Behavior of the Modified Electrode
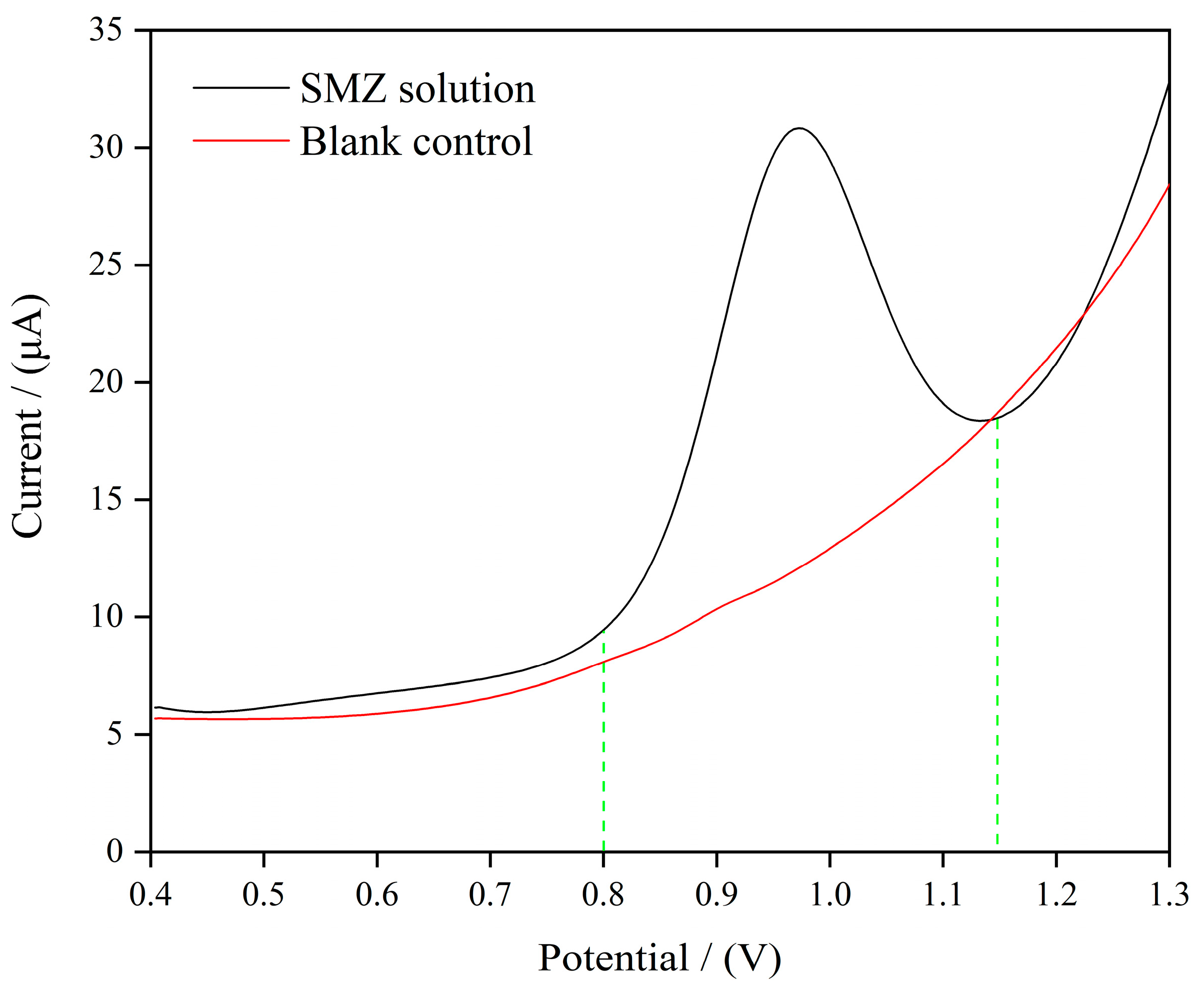
3.3. Electrochemical Action of the MIP/MWCNTs/GQDs/GCE During SMZ Oxidation
3.4. Optimization of the Modified Sensors and Determination
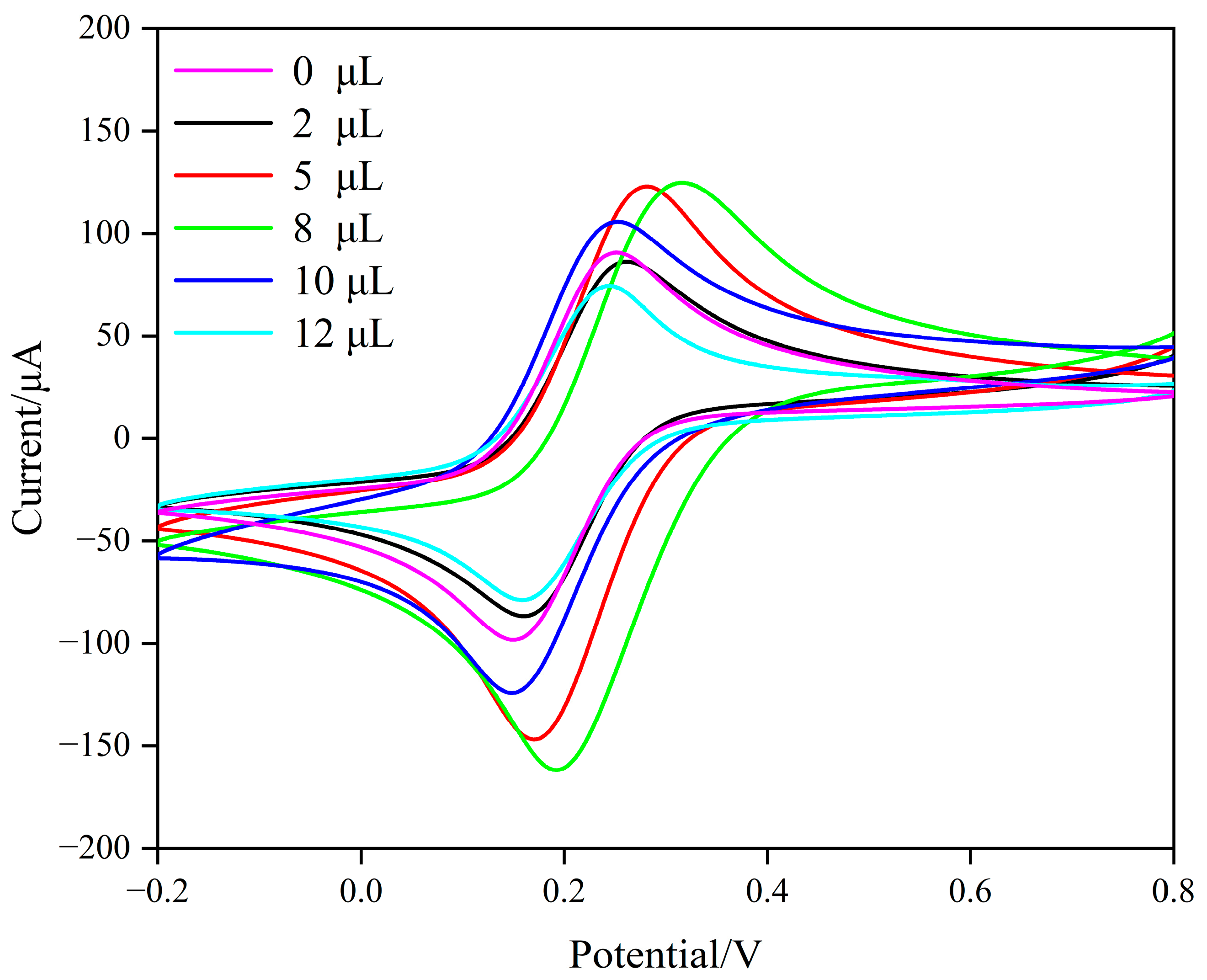
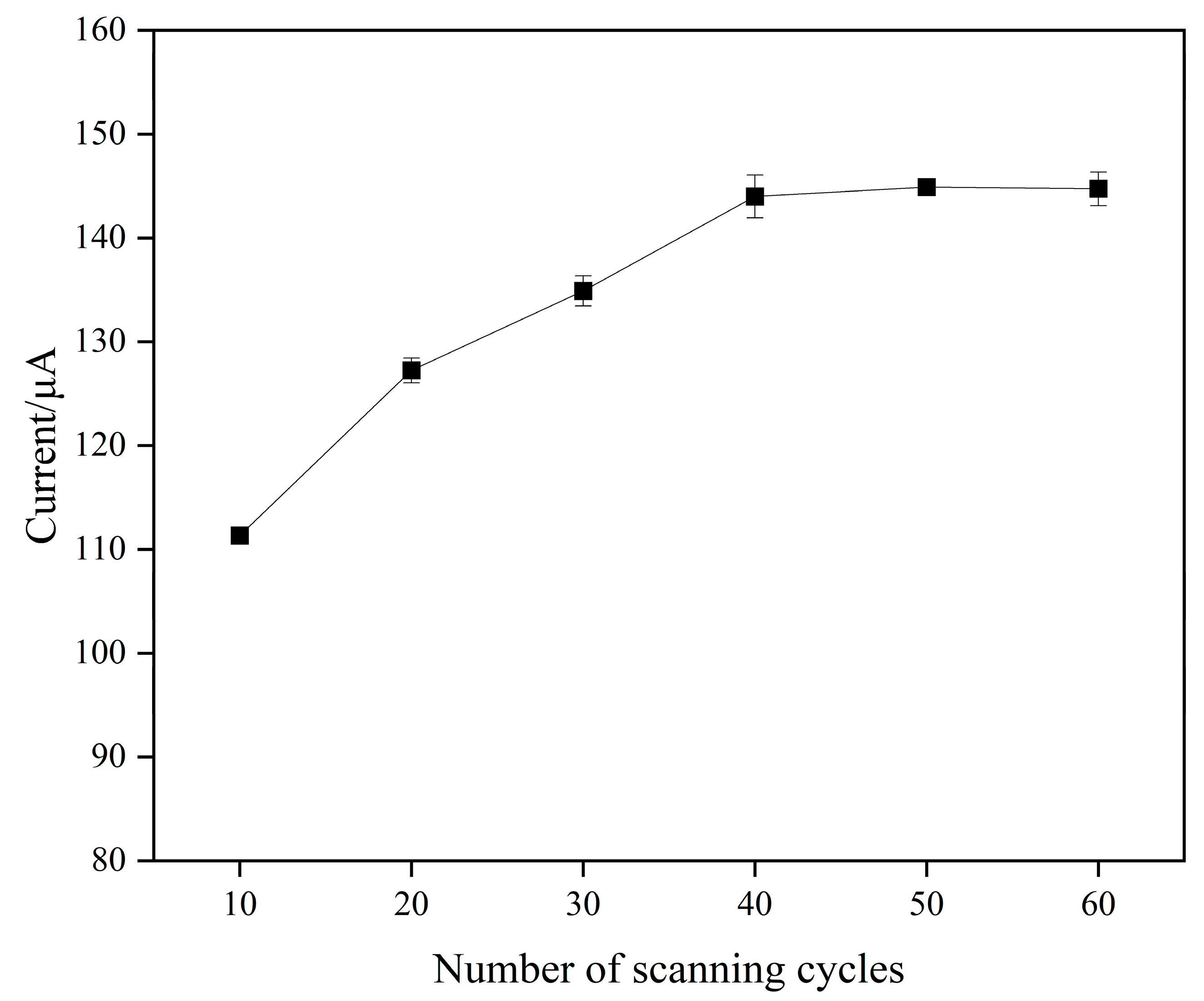
3.4.1. The Amount of Composite Carbon Nanomaterials
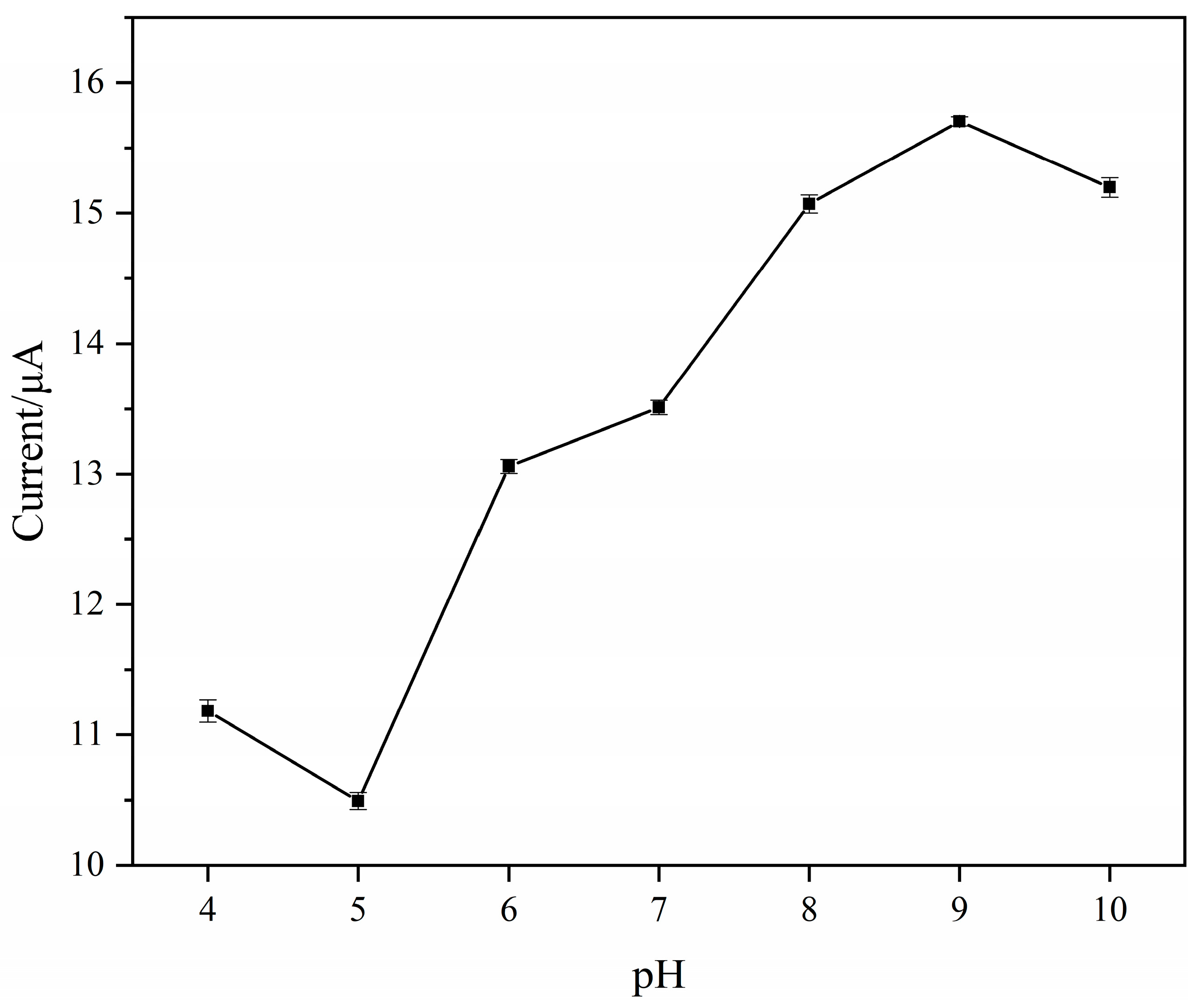
3.4.2. The pH of the Electrolyte
3.4.3. Optimization of Elution Method
3.4.4. Standard Solution Analysis
3.4.5. Selectivity of the Sensor
3.4.6. Reusability and Stability
3.4.7. Determination of Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Segura, P.A.; Takada, H.; Correa, J.A.; El Saadi, K.; Koike, T.; Onwona-Agyeman, S.; Ofosu-Anim, J.; Sabi, E.B.; Wasonga, O.V.; Mghalu, J.M.; et al. Global occurrence of anti-infectives in contaminated surface waters: Impact of income inequality between countries. Environ. Int. 2015, 80, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehab, O.R.; Mansour, A.M. New thiocyanate potentiometric sensors based on sulfadimidine metal complexes: Experimental and theoretical studies. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 57, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashile, P.P.; Munonde, T.S.; Nomngongo, P.N. Occurrence and adsorptive removal of sulfonamides and β-blockers in African and Asian water matrices: A comprehensive review. Environ. Adv. 2023, 13, 100435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xiong, W.; Zou, Y.; Lin, M.; Zhou, Q.; Xie, X.; Sun, Y. Evaluating the net effect of sulfadimidine on nitrogen removal in an aquatic microcosm environment. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, J.; Lou, Q.; Yang, P.; Fang, Y. Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of antibiotics in the surface water of Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.; Ramos, F. Analytical strategies for the detection and quantification of antibiotic residues in aquaculture fishes: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 52, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, J.; Baruah, J.B. Assemblies of Sulfathiazole- and Sulfamethazine-Derived Thiourea: Polymorphs, Solvates, and Fluoride Detection. Cryst. Growth Des. 2024, 24, 1910–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.J.; Liu, Y.W.; Li, X.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, M.; Yan, K.; Chen, H.X. Colorimetric detection of sulfamethazine based on target resolved calixarene derivative stabilized gold nanoparticles aggregation. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Wang, M.; Xue, Y.D.; Wang, A.J.; Mei, L.P.; Feng, J.J. Bimetallic PtNi nanozyme-driven dual-amplified photoelectrochemical aptasensor for ultrasensitive detection of sulfamethazine based on Z-scheme heterostructured CoS@In-CdS nanotubes. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2022, 371, 132519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tan, L.; Sun, S.; Lu, X.; Luo, Y. Land-derived wastewater facilitates antibiotic resistance contamination in marine sediment of semi-closed bay: A case study in Jiaozhou Bay, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 339, 117870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.L.; Yang, L.L.; Tang, J.M.; Wen, X.; Chen, X.Y.; Zheng, X.L.; Chen, L.L.; Li, J.Q.; Le, T. High-Sensitive FAM Labeled Aptasensor Based on FeO/Au/g-CN for the Detection of Sulfamethazine in Food Matrix. Biosensors 2022, 12, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalmalsawmi, J.; Tiwari, D.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, H. Efficient electrochemical sensor for trace detection of sulfamethazine in spring water: Use of novel nanocomposite material coated with Ag or Au nanoparticles. Microchem. J. 2022, 179, 107520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.V.; Sakthinathan, S.; Lee, D.; Chiu, T.W.; Muthukutty, B. Innovative Use of Carbon Nanofibers/Praseodymium Cobaltite for Targeted Detection of Hematologic Sulfamethazine. Langmuir 2024, 40, 21618–21628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, J.; Diao, X.; Altaf, M.M. Regional distribution differences of antibiotics in tropical marine aquaculture area: Insights into antibiotic management and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Tang, X.; Shi, X.; Zhang, C. Indirect photodegradation of sulfadimidine and sulfapyridine: Influence of CDOM components and main seawater factors. Chemosphere 2023, 333, 138821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Steele, J.C.; Meng, X.-Z. Usage, residue, and human health risk of antibiotics in Chinese aquaculture: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surya, R.; Sakthinathan, S.; Meenakshi, G.A.; Yu, C.L.; Chiu, T. Construction of CuYO/g-CN Novel Composite for the Sensitive and Selective Trace-Level Electrochemical Detection of Sulfamethazine in Food and Water Samples. Sensors 2024, 24, 5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xing, L.; Sun, X.; Li, Z.; Ding, T.; Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Ma, H.; Lin, T.; Yang, Q. Metabolites and metabolic pathway analysis of sulfadimidine in carp (Cyprinus carpio) based on UHPLC-Q-orbitrap HRMS. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Niu, Z.J.; Xu, C.C.; Zhan, M.H.; Koh, K.; Niu, J.F.; Chen, H.X. 2D MOF-enhanced SPR sensing platform: Facile and ultrasensitive detection of Sulfamethazine via supramolecular probe. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 456, 131642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.L.; Xiong, J.C.; Zhang, H.X.; He, Z.W.; Zheng, Y.J.; Jiang, H.Y.; Shen, J.Z. Adsorption and convenient ELISA detection of sulfamethazine in milk based on MOFs pretreatment. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.N.; Shi, B.Q.; Hu, X.T.; Li, W.T.; Huang, X.W.; Li, Z.H.; Zhang, X.N.; Zou, X.B.; Shi, J.Y. A ternary heterostructure aptasensor based on metal-organic framework and polydopamine nanoparticles for fluorescent detection of sulfamethazine. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.X.; Hu, X.L.; Dong, X.X.; Liu, P.; Zhang, N.; Gao, Z.; Wang, W.X.; Li, H.L.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.Y.; et al. A reliable fluorescence “turn-on” aptasensor based on dual-emitting europium metal-organic frameworks for ultrasensitive and selective detection of sulfamethazine. Food Chem. 2024, 454, 139756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.F.; Zou, M.Q.; Chen, Y.; Tang, F.; Dai, J.J.; Jin, Y.; Wang, C.; Xue, F. Ultrasensitive and selective detection of sulfamethazine in milk via a Janus-labeled Au nanoparticle-based surface-enhanced Raman scattering-immunochromatographic assay. Talanta 2024, 267, 125208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Shang, R.; Hong, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yu, K.; Kan, G.; Xiong, H.; Song, D.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, J. One-step online analysis of antibiotics in highly saline seawater by nano-based slug-flow microextraction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 134039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Tan, L.J.; Cui, Z.G.; Qu, K.M.; Wang, J.T. Graphene Oxide Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as Novel Adsorbents for Solid-Phase Microextraction for Selective Determination of Norfloxacin in the Marine Environment. Polymers 2022, 14, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Tan, L.J.; Qu, K.M.; Cui, Z.G.; Wang, J.T. Novel electrochemical sensor modified with molecularly imprinted polymers for determination of enrofloxacin in marine environment. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.P.; Zhang, M.; Guo, L.A.; Peng, K.F.; Man, Z.; Xie, S.L.; Liu, P.; Xie, D.; Wang, S.S.; Cheng, F.L. Photoelectrochemical aptasensor based on nanocomposite of CdSe@SnS for ultrasensitive and selective detection of sulfamethazine. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Yang, T.; Liu, P.; Tan, J.; Chen, S.; Lei, H.; Wei, X. Preparation of a V–COF@SWCNTs-COOH/SPCE supported molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for real-time detection of trace sulfadimidine. Talanta 2025, 282, 127046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wen, Y.; Hu, W.; Lu, X.; Chen, L.; Zhao, L.; Zeng, Q.; Tang, H.; Hong, Y.; Tang, K. A signal-amplified electrochemical immunosensor for the detection of sulfadimidine in crayfish using COOH-MWCNTs-Fe3O4-GO nanohybrids modified working electrode. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 134, 106501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Ling, Y.H.; Yuan, X.M.; Li, S.L.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Z.J.; Wang, G.X. P/N Junction TiO Nanotube-Polyaniline Molecular Imprinting Photoelectrochemistry Micro-Sensor with a Self-Elution Function Can Efficiently Detect Chloramphenicol. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 13988–13999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Wang, H.; Li, P.W.; Gao, W.K.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.L.; Jia, N.Q. In-site synthesis molecular imprinting NbO-based photoelectrochemical sensor for bisphenol A detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 121, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.G.; Huang, W.H.; Gao, M.M.; Yang, W.M.; Xu, W.Z. Novel photoresponsive molecularly imprinted polymers based on etched silicon core with enabling enhanced selectivity and sensitivity for the detection of sulfamethazine. Polym. Int. 2024, 73, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ying, H.; Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Luan, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, T.; Yu, S.; Yang, W. Synthesis of surface molecular imprinting polymer on SiO2-coated CdTe quantum dots as sensor for selective detection of sulfadimidine. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 404, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.Z.; Tang, S.Y.; Yuan, G.H.; Zhu, W.L.; Huang, Y.Y.; Li, S.J.; Lin, M.J. Tailored graphene quantum dots to passivate defects and accelerate charge extraction for all-inorganic CsPbIBr2 perovskite solar cells. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 895, 162529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.Z.; Xia, G.S.; Du, M.; Lu, Y.H.; Xu, H.B. Scotch-tape-like exfoliation effect of graphene quantum dots for efficient preparation of graphene nanosheets in water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 483, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.T.; Wang, J.L. Fe3O4-MWCNT Magnetic Nanocomposites as Efficient Fenton-Like Catalysts for Degradation of Sulfamethazine in Aqueous Solution. Chemistryselect 2017, 2, 10727–10735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalatbary, M.; Sayadi, M.H.; Hajiani, M.; Nowrouzi, M.; Homaeigohar, S. Green, sustainable synthesis of γ-Fe2O3/mwcnt/ag nano-composites using the viscum album leaf extract and waste car tire for removal of sulfamethazine and bacteria from wastewater streams. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.H.; Guo, R.; Pei, M.S.; Lin, W.Y. Construction of a novel GQD based ratiometric fluorescent composite probe for viscosity detection. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 14649–14652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.X.; Tian, C.L.; Cao, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, T.H.; Tang, J.N.; Zhang, F.; Chen, G.; Tang, J. Controllable functionalization of amino-functionalized graphene quantum dots as fluorescent probe for detection of Cu(II) ions detection. Mater. Lett. 2024, 364, 136393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.D.; Doong, R.A. Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of Nanomolar Ferric Ions Using Dopamine Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 21002–21010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, P.T.; Niu, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, J.H.; Lai, H.H.; Zhou, Q.; Zhai, H.Y. An Electrochemical Sensor Based on Cu-MOF-199@MWCNTs Laden with CuNPs for the Sensitive Detection of Creatinine. Langmuir 2023, 39, 13656–13667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.P.; Zhai, H.Y.; Chen, Z.G.; Zhou, Q.; Liang, Z.X.; Su, Z.H. Simultaneous Determination of Orange G and Orange II in Industrial Wastewater by a Novel FeO/MWCNTs-COOH/OP Modified Carbon Paste Electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 136, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.L.; Qiu, C.J.; Qu, W.; Zhuang, Y.; Han, X.C.; Tao, W.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Liu, H.Z.; Wang, W.H. Research on the Detection of Hg(II) in Seawater Using GR-MWCNTs/CeO-Modified Electrodes. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serag, E.; El-Maghraby, A.; Hassan, N.; El Nemr, A. CuO@MWCNTs nanocomposite as non-enzyme electrochemical sensor for the detection of Malathion in seawater. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 236, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.W.; Zhao, M.G.; Wang, X.T.; Qu, H.Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.G. Simultaneous electrochemical determination of catechol and hydroquinone in seawater using CoO/MWCNTs/GCE. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 234, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Pan, J.; Dai, J.; Cao, Z.; Hang, H.; Li, X.; Yan, Y. Magnetic ZnO surface-imprinted polymers prepared by ARGET ATRP and the application for antibiotics selective recognition. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 5571–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wu, M.; Wang, X.; Xu, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, X. 2 Development of Molecularly Imprinted Photonic Crystals Sensor for High-Sensitivity, Rapid Detection of Sulfamethazine in Food Samples. Polymers 2025, 17, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Qing, Y.; Wang, N.; Lu, Y.; Liu, T.; Liu, T.; Yang, W.; Li, S. Novel Thermosensitive Core–Shell Surface Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based on SiO2 for the Selective Adsorption of Sulfamethazine. Materials 2018, 11, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ren, H.; Yu, L. Development of molecularly imprinted photonic polymers for sensing of sulfonamides in egg white. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Liu, L.; Wan, Y.; Li, J.; Pi, F. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering based determination on sulfamethazine using molecularly imprinted polymers decorated with silver nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2023, 190, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Cheng, K.; Wu, Y.; Yu, P. Environment-friendly ZnO-based molecularly imprinting polymers fluorescence sensor for direct detection of sulfadimidine. J. Mate. Sci-Mate El. 2020, 31, 9550–9558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Liu, S.; Lv, Y.; Wang, S. DFT-assisted design of a electrochemical sensor based on MIP/CNT/MoS2-CoNi for the detection of sulfamethazine in meat. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 140, 107261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shao, K.; Hong, C.; Chen, S.; Lin, Z.; Huang, Z.; Lai, Z. Fluorimetric identification of sulfonamides by carbon dots embedded photonic crystal molecularly imprinted sensor array. Food Chem. 2023, 407, 135045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Li, L.; Fu, G.; Lai, Z.; Peng, A.; Huang, Z. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based photonic crystal sensor array for the discrimination of sulfonamides. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1101, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, M.; Li, M.; Zang, X. One-pot synthesis of a fluorescent molecularly imprinted nanosensor for highly selective detection of sulfapyridine in water. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Ying, H.; Zhang, B.; Cao, Y.; Li, S.; Huang, W.; Yang, W. Optimization and performance evaluation of a fluorescent sensor for residual sulfonamide antibiotics in honey samples. Polym. Advan. Technol. 2024, 35, e6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerome, R.; Sundramoorthy, A.K. Preparation of hexagonal boron nitride doped graphene flm modifed sensor for selective electrochemical detection of nicotine in tobacco sample. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1132, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.M.; Zhao, F.Q. Electrochemi cal sensor for chl oramphenico1 based on novel multiwalled carbon nanotubes@molecularly imprinted polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, Y.; Sun, L.; Zheng, J.; Dai, J.; Li, C.; Yan, Y. Convenient determination of sulfamethazine in milk by novel ratiometric fluorescence with carbon and quantum dots with on-site naked-eye detection and low interferences. Anal. Lett. 2018, 51, 2099–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, B.; Zhang, H.; Dong, X. HPLC determination of sulfamethazine in milk using surface-imprinted silica synthesized with iniferter technique. Talan. 2008, 76, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lida, F.; Masoume, Z. Electrochemical oxidation of sulfamethazine on multi-walled nanotube film coated glassy carbon electrode. J. Nanostruct. 2014, 4, 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, M.; Cesarino, I. Evaluation of a nanocomposite based on reduced graphene oxide and gold nanoparticles as an electrochemical platform for detection of sulfamethazine. J. Compos. Sci. 2019, 3, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Aquaculture Seawater Samples | Spiked Concentration (μM) | Detection Concentration (μM) | Rate of Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epinephelus fasciatus | Natural seawater | 0 | Nd a | / | / |
| 50 | 47.9 | 95.9 | 0.61 | ||
| Culture water | 0 | Nd | / | / | |
| 50 | 51.9 | 103.9 | 2.62 | ||
| Tailwater | 0 | Nd | / | / | |
| 50 | 50.6 | 101.2 | 2.02 | ||
| Epinephelus sp. | Natural seawater | 0 | Nd | / | / |
| 50 | 52.4 | 104.8 | 3.19 | ||
| Culture water | 0 | Nd | / | / | |
| 50 | 47.7 | 95.4 | 4.47 | ||
| Tailwater | 0 | Nd | / | / | |
| 50 | 49.7 | 99.4 | 3.11 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Zhang, T.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Cui, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Qu, K.; Cui, Z. Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on MWCNTs/GQDs for the Detection of Sulfamethazine in Aquaculture Seawater. Biosensors 2025, 15, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15030184
Chen J, Zhang T, Xu Y, Li H, Cui H, Zhao X, Zhou Y, Qu K, Cui Z. Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on MWCNTs/GQDs for the Detection of Sulfamethazine in Aquaculture Seawater. Biosensors. 2025; 15(3):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15030184
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jianlei, Tianruo Zhang, Yong Xu, Hao Li, Hongwu Cui, Xinguo Zhao, Yun Zhou, Keming Qu, and Zhengguo Cui. 2025. "Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on MWCNTs/GQDs for the Detection of Sulfamethazine in Aquaculture Seawater" Biosensors 15, no. 3: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15030184
APA StyleChen, J., Zhang, T., Xu, Y., Li, H., Cui, H., Zhao, X., Zhou, Y., Qu, K., & Cui, Z. (2025). Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on MWCNTs/GQDs for the Detection of Sulfamethazine in Aquaculture Seawater. Biosensors, 15(3), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15030184






