Matrix Optical Biosensor for Determining YKL-40/CHI3L1—A Biomarker Potentially Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Biological Material
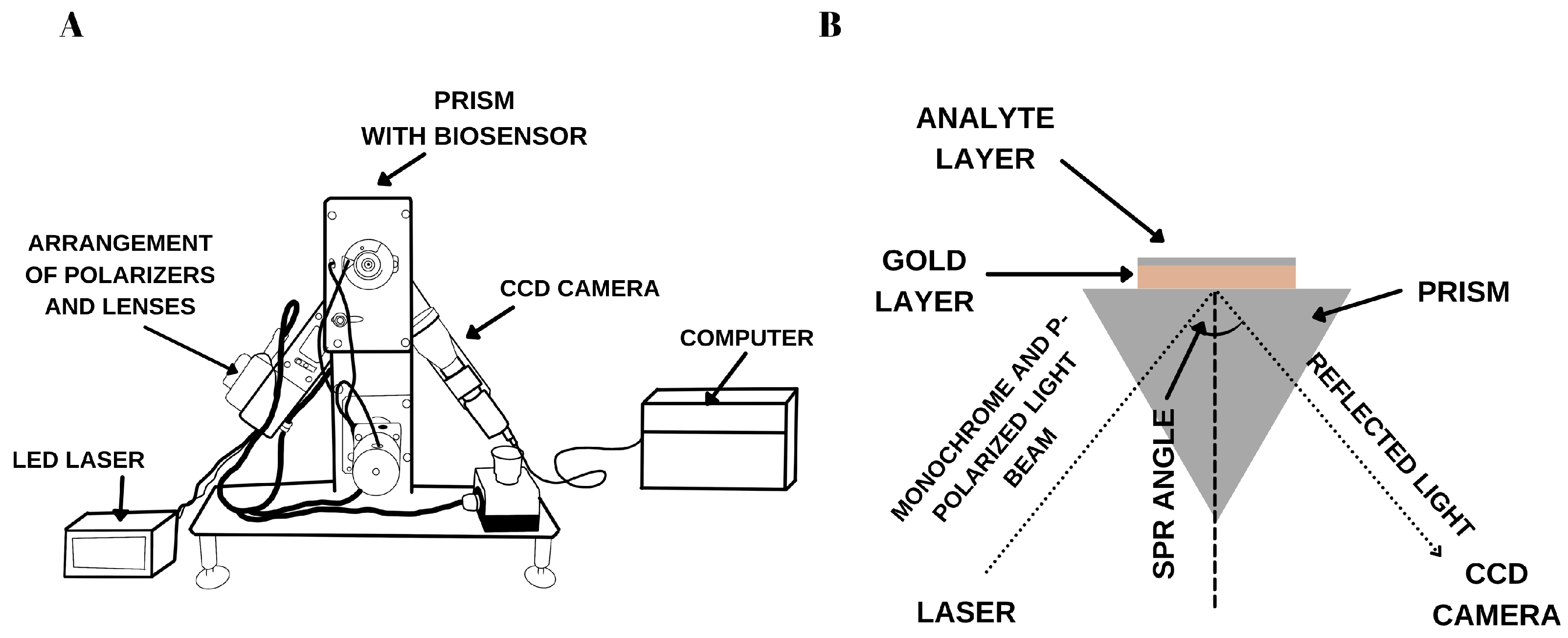
2.3. SPRi Instrumentation
2.4. Sensor Design
3. Experimental
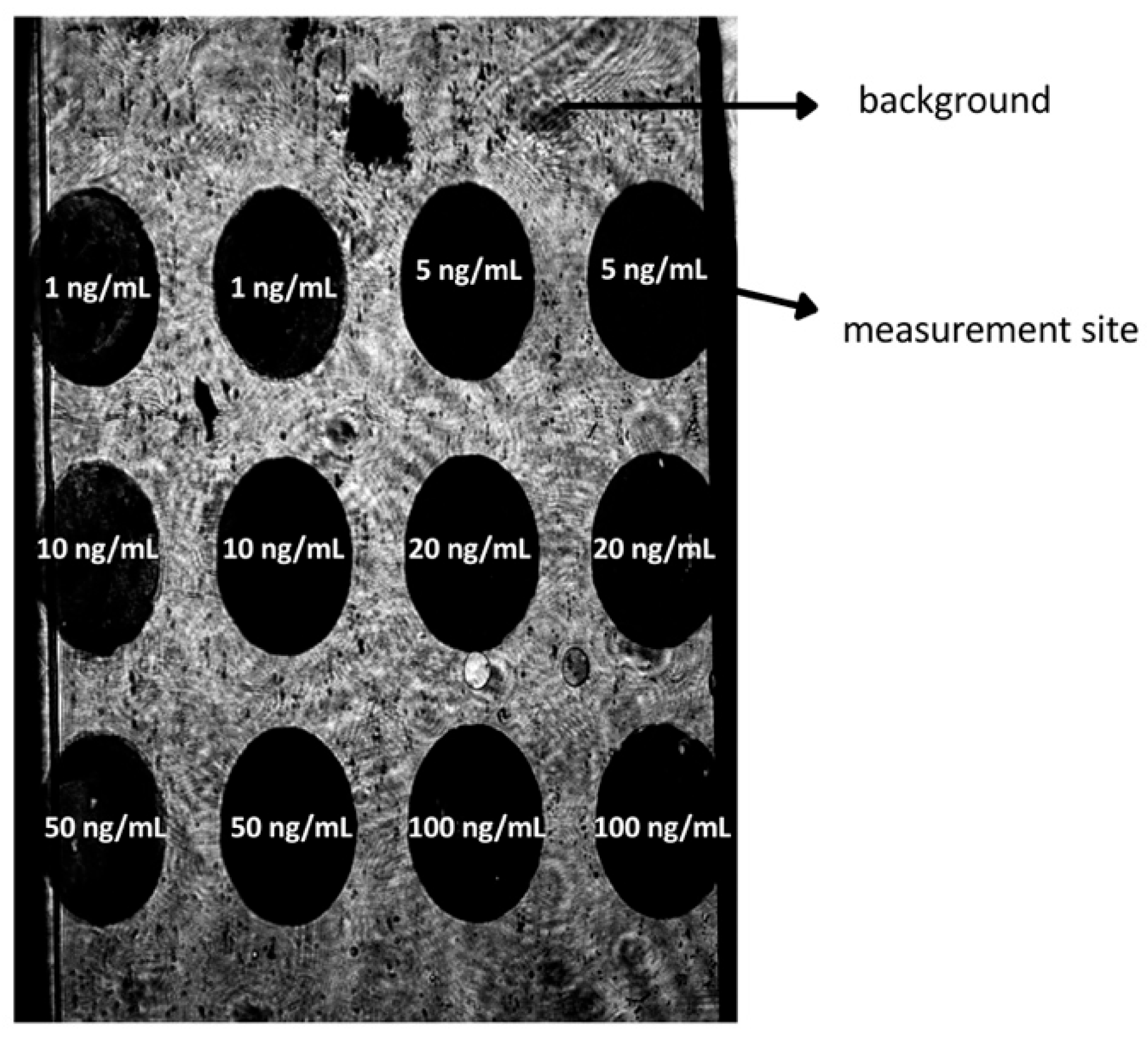
3.1. Selection of the Appropriate Ligand–Antibody Concentration. Calculation of the Surface Ligand Concentration
3.2. Selection of Rinse Frequency
3.3. Model SPR Curves—Evidence Confirming the Formation of Layers on the Surface of the Gold Plate
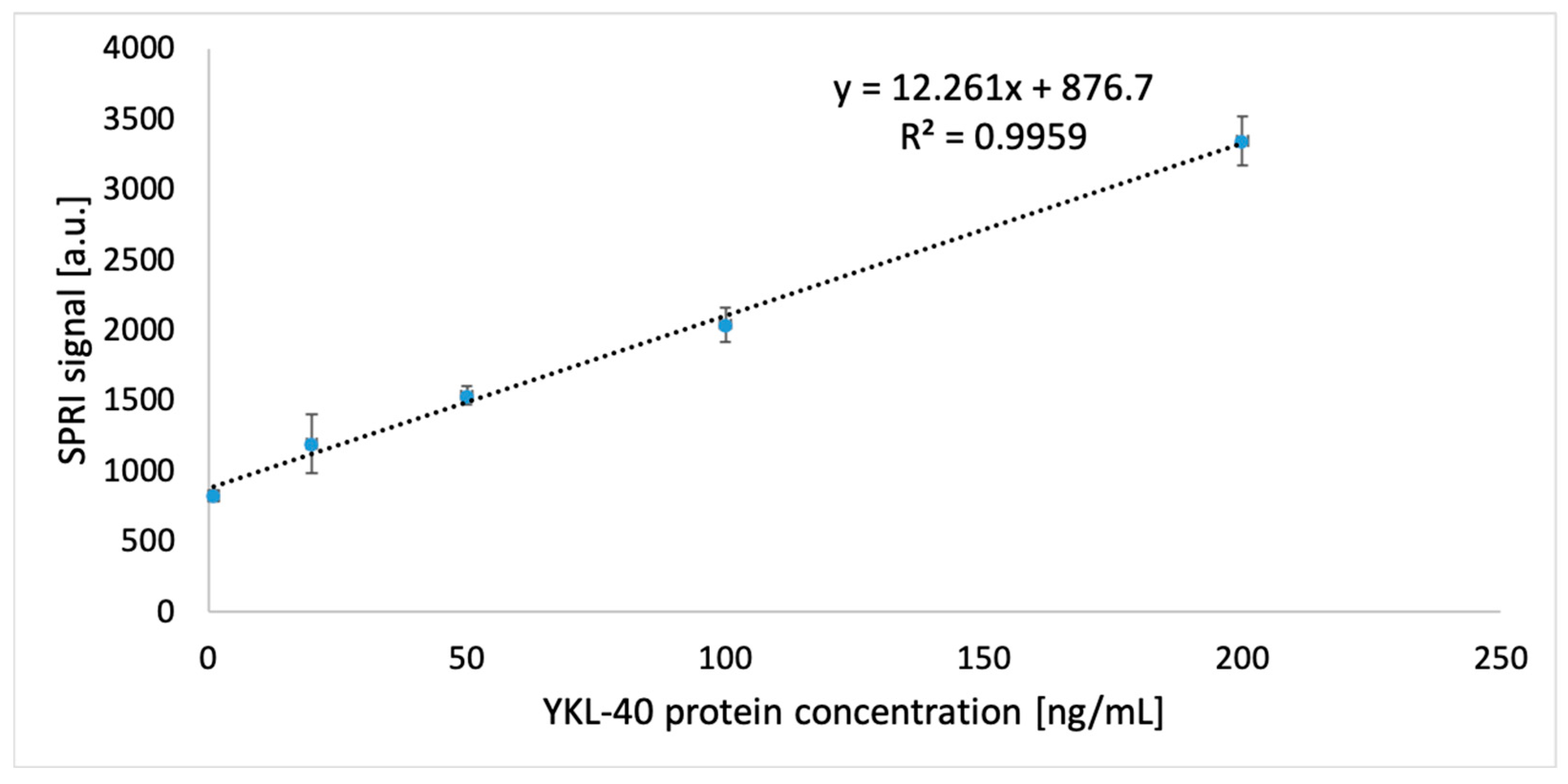
3.4. Analytical Response Study of the Biosensor: Limit of Detection and Quantification
3.5. Precision and Accuracy of the Method
3.6. Repeatability and Selectivity
3.7. Stability of the Biosensor
- − 24 h at room temperature,
- − 2 h at room temperature,
- − 2 h in a refrigerator,
- − four freeze–thaw cycles.
3.8. Determination YKL-40 in Real Samples
4. Discussion and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Sample Number | Concentration of YKL-40 in Plasma Samples from Patients with Alzheimer Disease [ng/mL] | Concentration of YKL-40 in Plasma Samples in Control Group Patients with Prostatitis [ng/mL] | Concentration of YKL-40 in Plasma Samples in Control Group Smokers [ng/mL] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 300.29 | 79.81 | 30.24 |
| 2 | 386.88 | 39.87 | 65.85 |
| 3 | 335.65 | 102.49 | 2.46 |
| 4 | 357.22 | 87.67 | 15.53 |
| 5 | 271.17 | 48.44 | 10.91 |
| 6 | 397.56 | 30.43 | 110.33 |
| 7 | 291.73 | 94.47 | 60.05 |
| 8 | 365.65 | 69.82 | 128.39 |
| 9 | 303.45 | 66.87 | 33.38 |
| 10 | 338.52 | 43.24 | 47.32 |
| 11 | 307.17 | 91.59 | 40.35 |
| 12 | 281.46 | 41.43 | 93.85 |
| 13 | 345.19 | 64.73 | 69.59 |
| 14 | 410.36 | 87.24 | 91.33 |
| 15 | 386.70 | 54.69 | 24.19 |
| 16 | 102.60 | 127.43 | 36.34 |
| 17 | 284.16 | 131.92 | 54.54 |
| 18 | 340.61 | 61.13 | 79.92 |
References
- Tizaoui, K.; Yang, J.W.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.; Yoon, S.; Jung, Y.; Park, J.B.; An, K.; Choi, H.; et al. The role of YKL-40 in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 3731–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroudis, I.; Chowdhury, R.; Petridis, F.; Karantali, E.; Chatzikonstantinou, S.; Balmus, I.M.; Luca, I.S.; Ciobica, A.; Kazis, D. YKL-40 as a Potential Biomarker for the Differential Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Medicina 2021, 58, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faibish, M.; Francescone, R.; Bentley, B.; Yan, W.; Shao, R. A YKL-40-neutralizing antibody blocks tumor angiogenesis and progression: A potential therapeutic agent in cancers. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, J.S.; Høyer, P.E.; Larsen, L.A.; Price, P.A.; Møllgård, K. YKL-40 Protein Expression in the Early Developing Human Musculoskeletal System. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2007, 55, 1213–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkyilmaz, A.; Devrimsel, G.; Kirbas, A.; Cicek, Y.; Karkucak, M.; Capkin, E. Gokmen, F. Relationship between pulse wave velocity and serum YKL-40 level in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2013, 3, 2751–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, J.; Matusiak, Ł.; Nowicka-Suszko, D.; Szepietowski, J. Chitinase-3-like protein 1 (YKL-40) is a biomarker of severity of joint involvement in psoriatic arthritis. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2018, 35, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltomaa, R.; Paimela, L.; Harvey, S.; Helve, T.; Leirisalo-Repo, M. Increased level of YKL-40 in sera from patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: A new marker for disease activity. Rheumatol. Int. 2001, 20, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wong, C.W.; Yan, M.; Li, L.; Liu, T.; Mei-Yu Or, P.; Kwok-Wing Tsui, S.; Miu-Yee Waye, M.; Man-Lok Chan, A. Differential regulation of the pro-inflammatory biomarker, YKL-40/CHI3L1, by PTEN/Phosphoinositide 3-kinase and JAK2/STAT3 pathways in glioblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2018, 429, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Jia, Z.; Hu, Y.; Cao, D.; Yang, M.; Liu, L.; Gao, L.; Qiu, S.; Yan, W.; et al. YKL-40 derived from infiltrating macrophages cooperates with GDF15 to establish an immune suppressive microenvironment in gallbladder cancer. Cancer Lett. 2023, 563, 216184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X. Tumor-recruited M2 macrophages promote gastric and breast cancer metastasis via M2 macrophage-secreted CHI3L1 protein. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zeng, J.; Xu, Y.; Su, Z.; Chong, Y.; Ling, T.; Xu, H.; Shi, H.; Zhu, M.; Mo, Q.; et al. Chitinase-3 like-protein-1 promotes glioma progression via the NF-κB signaling pathway and tumor microenvironment reprogramming. Theranostics 2022, 12, 6989–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Barger, S.; Barnum, S.; Bradt, B.; Bauer, J.; Cole, G.M.; Cooper, N.R.; Eikelenboom, P.; Emmerling, M.; Fiebich, B.L.; et al. Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2010, 21, 383–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkoe, D.J. Alzheimer’s disease: Genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 81, 741–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, K.; Dubois, B.; Fagan, A.M.; Lewczuk, P.; de Leon, M.J.; Hampel, H. Clinical utility of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in the diagnosis of early Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2015, 11, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.V.; Leitner, W.P.; Rivest, A.J.; Staples, M.K.; Radeke, M.J.; Anderson, D.H. The Alzheimer’s A beta-peptide is deposited at sites of complement activation in pathologic deposits associated with aging and age-related macular degeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11830–11835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonneh-Barkay, D.; Bissel, S.J.; Wang, G.; Fish, K.N.; Nicholl, G.C.; Darko, S.W.; Medina-Flores, R.; Murphey-Corb, M.; Rajakumar, P.A.; Nyaundi, J.; et al. YKL-40, a Marker of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Encephalitis, Modulates the Biological Activity of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonneh-Barkay, D.; Wang, G.; Starkey, A.; Hamilton, R.L.; A Wiley, C. In vivo CHI3L1 (YKL-40) expression in astrocytes in acute and chronic neurological diseases. J. Neuroinflamm. 2010, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonneh-Barkay, D.; Zagadailov, P.; Zou, H.; Niyonkuru, C.; Figley, M.; Starkey, A.; Wang, G.; Bissel, S.J.; Wiley, C.A.; Wagner, A.K. YKL-40 Expression in Traumatic Brain Injury: An Initial Analysis. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comabella, M.; Fernández, M.; Martin, R.; Rivera-Vallvé, S.; Borrás, E.; Chiva, C.; Julià, E.; Rovira, A.; Cantó, E.; Alvarez-Cermeño, J.C.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid chitinase 3-like 1 levels are associated with conversion to multiple sclerosis. Brain 2010, 133, 1082–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorens, F.; Thüne, K.; Tahir, W.; Kanata, E.; Diaz-Lucena, D.; Xanthopoulos, K.; Kovatsi, E.; Pleschka, C.; Garcia-Esparcia, P.; Schmitz, M.; et al. YKL-40 in the brain and cerebrospinal fluid of neurodegenerative dementias. Mol. Neurodegener. 2017, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pase, M.P.; Himali, J.J.; Puerta, R.; Beiser, A.S.; Gonzales, M.M.; Satizabal, C.L.; Yang, Q.; Aparicio, H.J.; Kojis, D.J.; Decarli, C.S.; et al. Association of Plasma YKL-40 With MRI, CSF, and Cognitive Markers of Brain Health and Dementia. Neurology 2024, 102, e208075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinuevo, J.L.; Ayton, S.; Batrla, R.; Bednar, M.M.; Bittner, T.; Cummings, J.; Fagan, A.M.; Hampel, H.; Mielke, M.M.; Mikulskis, A.; et al. Current state of Alzheimer’s fluid biomarkers. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 821–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaocharoen, W.; Suginta, W.; Limbut, W.; Ranok, A.; Numnuam, A.; Khunkaewla, P.; Kanatharana, P.; Thavarungkul, P.; Schulte, A. Electrochemical detection of the disease marker human chitinase-3-like protein 1 by matching antibody-modified gold electrodes as label-free immunosensors. Bioelectrochemistry 2015, 101, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Ke, Q.; Cai, F.; Gong, S.; Huang, R.; Fan, C. Platinum nanozyme-mediated temperature sensor for sensitive photothermal immunoassay of YKL-40 under near-infrared light. Sensors Diagn. 2023, 2, 1605–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naglot, S.; Aggarwal, P.; Dey, S.; Dalal, K. Estimation of Serum YKL-40 by Real-Time Surface Plasmon Resonance Technology in North-Indian Asthma Patients. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2016, 31, e22028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirco, A.; Zielinska, Z.; Gorodkiewicz, E.; Meacci, E.; Margheri, G. Detection of erythropoietin in blood plasma through an SPRi-based biosensor. Talanta 2025, 295, 128301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Y. Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensors: A Review of Molecular Imaging with High Spatial Resolution. Biosensors 2024, 14, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschm, E.; Raether, H. Radiative Decay of Non Radiative Surface Plasmons Excited by Light. Z. Für Naturforschung A 2014, 23, 2135–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homola, J. Present and future of surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 377, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarano, S.; Scuffi, C.; Mascini, M.; Minunni, M. Surface plasmon resonance imaging (SPRi)-based sensing: A new approach in signal sampling and management. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1380–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Devireddy, R.; Gartia, M.R. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Sensor for Cancer Biomarker Detection. Biosensors 2023, 13, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezabakhsh, A.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Fathi, F. Surface plasmon resonance biosensors for detection of Alzheimer’s biomarkers; an effective step in early and accurate diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 167, 112511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Javaid, M.; Singh, R.P.; Suman, R.; Rab, S. Biosensors applications in medical field: A brief review. Sensors Int. 2021, 2, 100100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczyńska, K.; Waszkiewicz, N. Diagnostic Utility of Selected Serum Dementia Biomarkers: Amyloid β-40, Amyloid β-42, Tau Protein, and YKL-40: A Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig-Schapiro, R.; Perrin, R.J.; Roe, C.M.; Xiong, C.; Carter, D.; Cairns, N.J.; Mintun, M.A.; Peskind, E.R.; Li, G.; Galasko, D.R.; et al. YKL-40: A Novel Prognostic Fluid Biomarker for Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 68, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Lee, H.-W.; Suk, K. Plasma level of chitinase 3-like 1 protein increases in patients with early Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurol. 2011, 258, 2181–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, Z.; Sankiewicz, A.; Kalinowska, N.; Zelazowska-Rutkowska, B.; Guszcz, T.; Ambroziak, L.; Kondratiuk, M.; Gorodkiewicz, E. Carboxymethyl Dextran-Based Biosensor for Simultaneous Determination of IDO-1 and IFN-Gamma in Biological Material. Biosensors 2025, 15, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalenberg, M.; Beaudoin, C.; Bulst, L.; Steubl, D.; Luppa, P.B. Magnetic bead fluorescent immunoassay for the rapid detection of the novel inflammation marker YKL40 at the point-of-care. J. Immunol. Methods 2015, 427, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, Z.; Oldak, L.; Guszcz, T.; Hermanowicz, A.; Gorodkiewicz, E. SPRi Biosensor for Simultaneous Determination of HIF-1α, Angiopoietin-2, and Interleukin-1β in Blood Plasma. Sensors 2024, 24, 5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagnucci, A.H., Jr.; Li, W.W. Alzheimer’s disease and angiogenesis. Lancet 2003, 361, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouyafar, A.; Heydarabad, M.Z.; Mahboob, S.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Rahbarghazi, R. Angiogenic potential of YKL-40 in the dynamics of tumor niche. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 100, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muszyński, P.; Groblewska, M.; Kulczyńska-Przybik, A.; Kułakowska, A.; Mroczko, B. YKL-40 as a Potential Biomarker and a Possible Target in Therapeutic Strategies of Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kester, M.I.; Teunissen, C.E.; Sutphen, C.; Herries, E.M.; Ladenson, J.H.; Xiong, C.; Scheltens, P.; van der Flier, W.M.; Morris, J.C.; Holtzman, D.M.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid VILIP-1 and YKL-40, candidate biomarkers to diagnose, predict and monitor Alzheimer’s disease in a memory clinic cohort. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2015, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deming, Y.; Black, K.; Carrell, D.; Cai, Y.; Del-Aguila, J.L.; Fernandez, M.V.; Budde, J.; Ma, S.; Saef, B.; Howells, B.; et al. Chitinase-3-like 1 protein (CHI3L1) locus influences cerebrospinal fluid levels of YKL-40. BMC Neurol. 2016, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| LOD | Detection Method |
|---|---|
| 0.002 ng/mL | SPRi method (this article) |
| 0.07 ng/mL [23] | Electrochemical sensor using polyclonal antibodies immobilized on gold electrodes, an electrochemical flow system with capacitive signal generation [23] |
| 0.014 ng/mL [24] | Photothermal YKL-40 screening platform by coupling platinum nanoparticles (PtNPs) excited by near-infrared (NIR) light with a handheld digital thermometer, using an antibody as a receptor layer [24] |
| 0.33 ng/mL [25] | Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) using a commercially available BIAcore 2000 device with antibodies in the receptor layer [25] |
| 2.9 ng/mL [38] | Fluorescent immunoenzymatic assay using magnetic beads [38] |
| Standard Solution Concentration [ng/mL] | Mean Concentration from 4 Analysis [ng/mL] | SD [ng/mL] | CV [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.0009 | 0.12 |
| 10.00 | 11.21 | 1.04 | 9.24 |
| 100.00 | 103.26 | 3.95 | 3.83 |
| 200.00 | 200.98 | 7.02 | 3.49 |
| Interferent | Concentration Ratio | Mean Concentration Marked [ng/mL] | Recovery [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| HIF-1α | 1:100 | 5.24 | 104.71 |
| 1:10 | 5.26 | 105.26 | |
| ANG-2 | 1:100 | 5.26 | 105.22 |
| 1:10 | 4.62 | 92.49 | |
| IL-1β | 1:100 | 5.43 | 108.63 |
| 1:10 | 5.21 | 104.26 | |
| Total tau | 1:100 | 5.83 | 116.52 |
| 1:10 | 5.64 | 112.82 | |
| Ptau-181 | 1:100 | 5.02 | 100.48 |
| 1:100 | 5.07 | 101.48 |
| Concentration of Control Sample C0 [ng/mL] | Analyte Storage Conditions | Concentration Marked Ci [ng/mL] | Δ [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 80 | 24 h at room temperature | 98.45 | 17.38 |
| 92.12 | |||
| 2 h at room temperature | 81.23 | 2.07 | |
| 82.12 | |||
| 2 h in a refrigerator | 80.23 | 0.81 | |
| 81.07 | |||
| four freeze–thaw cycles | 81.78 | 1.17 | |
| 80.11 | |||
| 314.18 | 24 h at room temperature | 320.42 | 1.61 |
| 319.34 | |||
| 2 h at room temperature | 315.16 | 0.09 | |
| 314.99 | |||
| 2 h in a refrigerator | 315.78 | 0.49 | |
| 316.89 | |||
| four freeze–thaw cycles | 321.11 | 1.64 | |
| 318.87 |
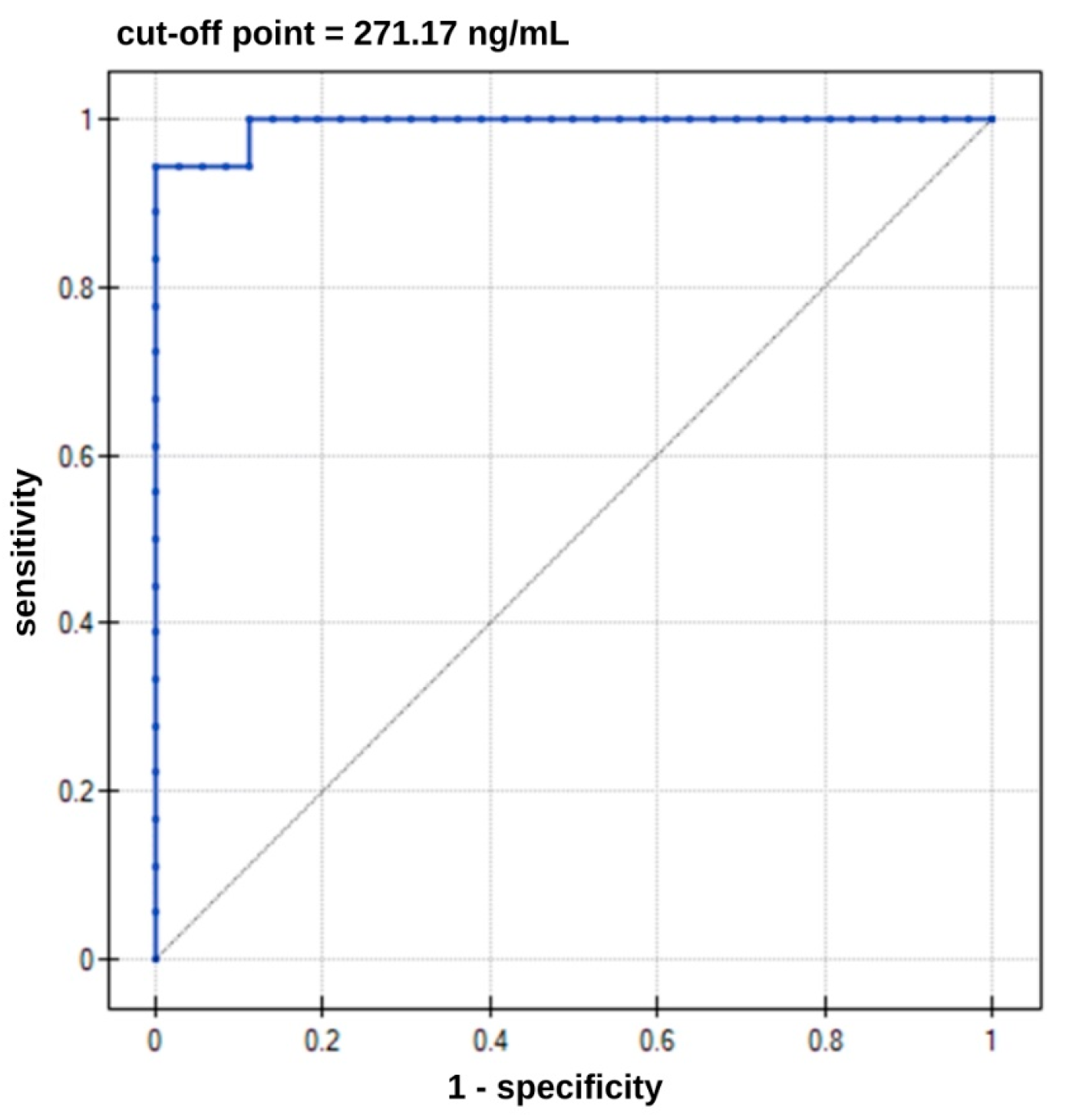
| Direction of the Diagnostic Variable | AUC | Sensitivity [%] | Specificity [%] | PPV [%] | NPV [%] | Cut-Off Point | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| stimulant | 0.99 | 94.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 97.00 | 271.17 ng/mL | <0.000001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zielinska, Z.; Ba Tarfi, A.; Gorodkiewicz, E. Matrix Optical Biosensor for Determining YKL-40/CHI3L1—A Biomarker Potentially Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease. Biosensors 2025, 15, 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100687
Zielinska Z, Ba Tarfi A, Gorodkiewicz E. Matrix Optical Biosensor for Determining YKL-40/CHI3L1—A Biomarker Potentially Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease. Biosensors. 2025; 15(10):687. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100687
Chicago/Turabian StyleZielinska, Zuzanna, Abdulelah Ba Tarfi, and Ewa Gorodkiewicz. 2025. "Matrix Optical Biosensor for Determining YKL-40/CHI3L1—A Biomarker Potentially Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease" Biosensors 15, no. 10: 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100687
APA StyleZielinska, Z., Ba Tarfi, A., & Gorodkiewicz, E. (2025). Matrix Optical Biosensor for Determining YKL-40/CHI3L1—A Biomarker Potentially Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease. Biosensors, 15(10), 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100687






