Universal Platform Based on Carbon Nanotubes Functionalised with Carboxylic Acid Groups for Multi-Analyte Enzymatic Biosensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrochemical Instrumentation
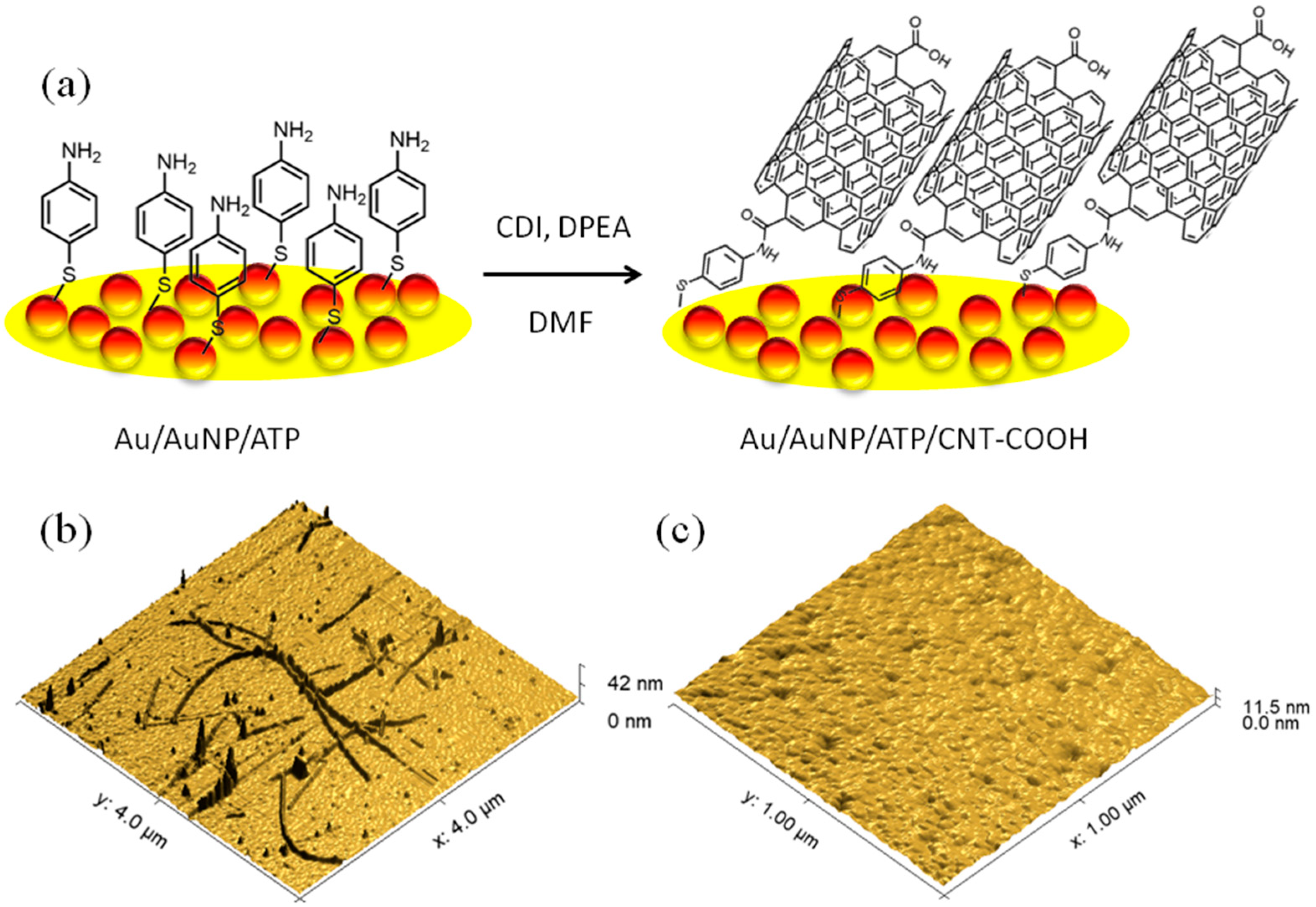
2.3. Construction of the Au/AuNP/CNT-COOH Bioelectrodes
2.4. Electrochemical Measurements
2.5. AFM Measurements
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Oxygen-Sensitive Electrode Preparation
3.2. Characterisation of the CNT-COOH on the Au Surface
3.3. Sensitivity to Molecular Oxygen of the Electrodes
3.4. Performance of the Bioelectrodes
3.5. Selectivity Assessment
3.6. Repeatability and Stability
3.7. Investigation of Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNT-COOH | Carbon nanotubes functionalised with carboxylic acid groups |
| CNTs | Carbon nanotubes |
| LOx | Lactate oxidase |
| GOx | Glucose oxidas |
| CAT | Catalase |
| LGOx | L-Glutamate oxidase |
| TYR | Tyrosinase |
| Lac | L-Lactate |
| ATP | 4-Aminothiophenol |
| CDI | 1,1′-Carbonyldiimidazole |
| DMF | Dimethylformamide |
| DIPEA | N,N-Diisopropylethylamine |
| PPB | Potassium phosphate buffer |
| AuNp | Gold nanoparticles |
| CV | Cyclic voltamperometry |
| CA | Chronoamperometry |
| Au | Gold electrode |
| SAM | Self-assembly monolayer |
| S | Slope derived from the linear concentration range |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| AFM | Atomic force microscopy |
| RSD | Relative standard deviation |
| GABA | γ-Aminobutyric acid |
| TRIS | Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane |
| FAD | Flavin adenine dinucleotide |
References
- Zhao, Y.; Jin, K.-Q.; Li, J.-D.; Sheng, K.-K.; Huang, W.-H.; Liu, Y.-L. Flexible and Stretchable Electrochemical Sensors for Biological Monitoring. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2305917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabnum, S.S.; Siranjeevi, R.; Raj, C.K.; Nivetha, P.; Benazir, K. A Comprehensive Review on Recent Progress in Carbon Nanotubes for Biomedical Application. Environ. Qual. Manag. 2025, 34, e70040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrier, D.C.; Honeychurch, K.C. Carbon Nanotube (CNT)-Based Biosensors. Biosensors 2021, 11, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Chen, X.; Ren, T.; Zhang, P.; Yang, D. Carbon Nanotube Based Biosensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 690–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, T.; Del Caño, R.; Mahato, K.; De la Paz, E.; Chen, C.; Ding, S.; Yin, L.; Wang, J. Wearable Electrochemical Glucose Sensors in Diabetes Management: A Comprehensive Review. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 7854–7889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, H.A.; Karim, M.M. Enzymatic and Enzyme-Free Electrochemical Lactate Sensors: A Review of the Recent Developments. Electrochem. Sci. Adv. 2025, 5, e202400021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, J.; Uddin, Z.; Singh, G.; Howlader, M.M.R. Glutamate Sensing in Biofluids: Recent Advances and Research Challenges of Electrochemical Sensors. Analyst 2020, 145, 321–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Yetisen, A.K. Biosensors for Psychiatric Biomarkers in Mental Health Monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 256, 116242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, R.A. The Blood-Brain Barrier and Glutamate123. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 867S–874S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaney, T.R.; Mabrouk, O.S.; Porter-Stransky, K.A.; Aragona, B.J.; Kennedy, R.T. Chemical Gradients within Brain Extracellular Space Measured Using Low Flow Push–Pull Perfusion Sampling in Vivo. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2013, 4, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Lopez de Alda, M.J.; Barceló, D. Advantages and Limitations of On-Line Solid Phase Extraction Coupled to Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Technologies versus Biosensors for Monitoring of Emerging Contaminants in Water. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1152, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakchin, P.S.; Nakhjavani, S.A.; Saber, R.; Ghanbari, H.; Omidi, Y. Recent Advances in Simultaneous Electrochemical Multi-Analyte Sensing Platforms. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 92, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klebes, A.; Ates, H.C.; Verboket, R.D.; Urban, G.A.; von Stetten, F.; Dincer, C.; Früh, S.M. Emerging Multianalyte Biosensors for the Simultaneous Detection of Protein and Nucleic Acid Biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 244, 115800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, U.; Gupta, V.; Arun, R.K.; Chanda, N. Recent Advances in Enzymatic Biosensors for Point-of-Care Detection of Biomolecules. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2022, 119, 3393–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-De-Corcuera, J.I.; Olstad, H.E.; García-Torres, R. Stability and Stabilization of Enzyme Biosensors: The Key to Successful Application and Commercialization. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 293–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollella, P. Enzyme-Based Amperometric Biosensors: 60 Years Later … Quo Vadis? Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1234, 340517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragauskaitė, E.; Marčiukaitis, S.; Radveikienė, I.; Bagdžiūnas, G. An Electrografted Monolayer of Polyaniline as a Tuneable Platform for a Glucose Biosensor. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 4647–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecelytė, G.; Dudkaitė, V.; Šedo, O.; Zdráhal, Z.; Bagdžiūnas, G. Tyrosine-Specific Bioconjugation Allowing Hole Hopping along Aromatic Chains of Glucose Oxidase. Mater. Horiz. 2025, 12, 6301–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, Y. Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes and Nanofibers for Biosensing Applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Xue, Y.; Qu, L.; Choi, H.-J.; Baek, J.-B. Metal-Free Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4823–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraman, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Santhanam, V. Monodisperse Sub-10 nm Gold Nanoparticles by Reversing the Order of Addition in Turkevich Method—The Role of Chloroauric Acid. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 361, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Nan, X.; Liu, Z. Toward the Chemistry of Carboxylic Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes by Chemical Force Microscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 4139–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berketa, K.; Mruga, D.; Dzyadevych, S.; Soldatkin, O. Development of a New Method of Improving the Oxidase-Based Biosensors’ Analytical Characteristics by Adding Catalase as an Auxiliary Enzyme. Electroanalysis 2023, 35, e202300190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes, T.I.; Moussy, F. In Vitro and In Vivo Degradation of Glucose Oxidase Enzyme Used for an Implantable Glucose Biosensor. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2000, 2, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bounegru, A.V.; Apetrei, C. Tyrosinase Immobilization Strategies for the Development of Electrochemical Biosensors—A Review. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radveikienė, I.; Palinauskas, D.; Ragauskaitė, E.; Bagdžiūnas, G. Self-Assembled Cyclodextrins-Based Nanostructures on Indium-Tin-Oxide for a Detection of Catecholamine Neurotransmitters. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 600, 154170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

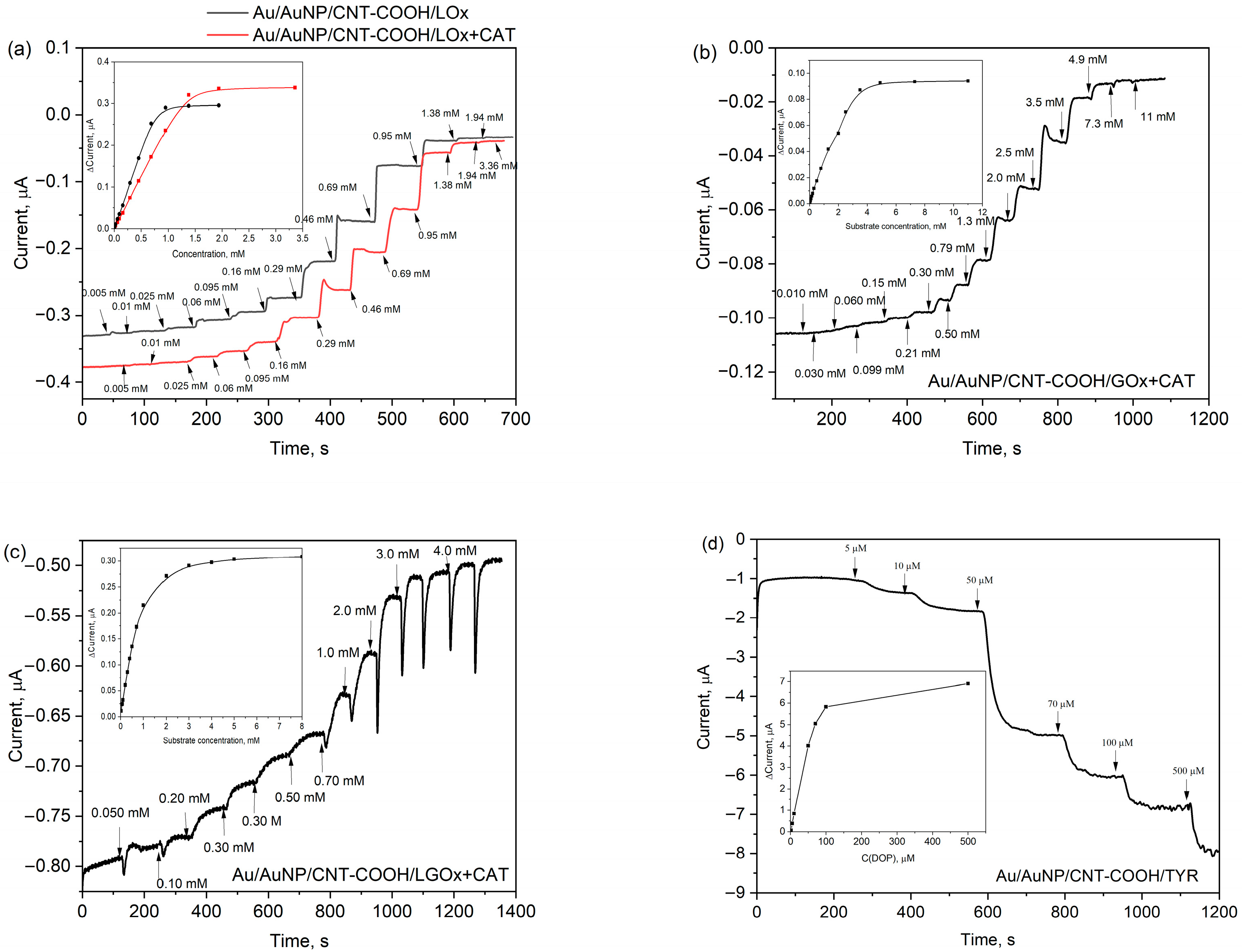
| Entry | Bioelectrode | Sensitivity, μA mM−1 cm−2 | Linear Range, μM | LOD, μM | Repeatability (RSD) a, % | Response time a, s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Au/AuNP/CNT-COOH/LOx | 12 | 10–690 | 15 | 5.2 | 30 |
| 2 | Au/AuNP/CNT-COOH/LOx+CAT | 7.5 | 10–1380 | 66 | 5.6 | 32 |
| 3 | Au/AuNP/CNT-COOH/GOx+CAT | 0.88 | 200–2500 | 250 | 6.8 | 52 |
| 4 | Au/AuNP/CNT-COOH/LGOx+CAT | 6.9 | 20–1000 | 130 | 3.8 | 72 |
| 5 | Au/AuNP/CNT-COOH/TYR | 2400 | 10–100 | 6.4 | 12 | 86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lukoševičius, E.; Kravčenko, J.; Mikėnaitė, G.; Markevičius, A.; Bagdžiūnas, G. Universal Platform Based on Carbon Nanotubes Functionalised with Carboxylic Acid Groups for Multi-Analyte Enzymatic Biosensing. Biosensors 2025, 15, 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100686
Lukoševičius E, Kravčenko J, Mikėnaitė G, Markevičius A, Bagdžiūnas G. Universal Platform Based on Carbon Nanotubes Functionalised with Carboxylic Acid Groups for Multi-Analyte Enzymatic Biosensing. Biosensors. 2025; 15(10):686. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100686
Chicago/Turabian StyleLukoševičius, Edmundas, Julija Kravčenko, Grėta Mikėnaitė, Augustas Markevičius, and Gintautas Bagdžiūnas. 2025. "Universal Platform Based on Carbon Nanotubes Functionalised with Carboxylic Acid Groups for Multi-Analyte Enzymatic Biosensing" Biosensors 15, no. 10: 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100686
APA StyleLukoševičius, E., Kravčenko, J., Mikėnaitė, G., Markevičius, A., & Bagdžiūnas, G. (2025). Universal Platform Based on Carbon Nanotubes Functionalised with Carboxylic Acid Groups for Multi-Analyte Enzymatic Biosensing. Biosensors, 15(10), 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100686






