Development and Application of Colloidal Gold Test Strips for the Rapid Detection of Canine Brucellosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Cultural Medium, and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of B. canis LPS
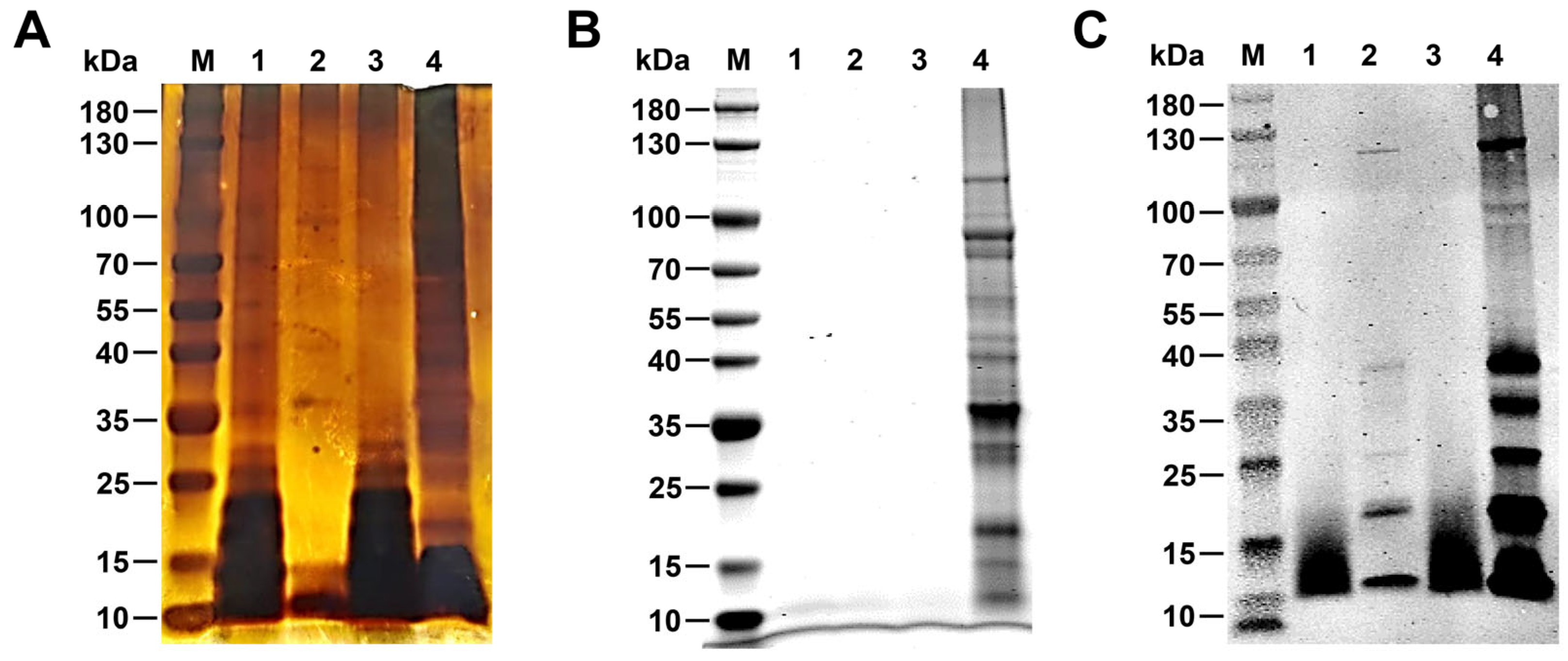
2.3. Silver Staining and Coomassie Brilliant Blue Stainin0067
2.4. Western Blotting
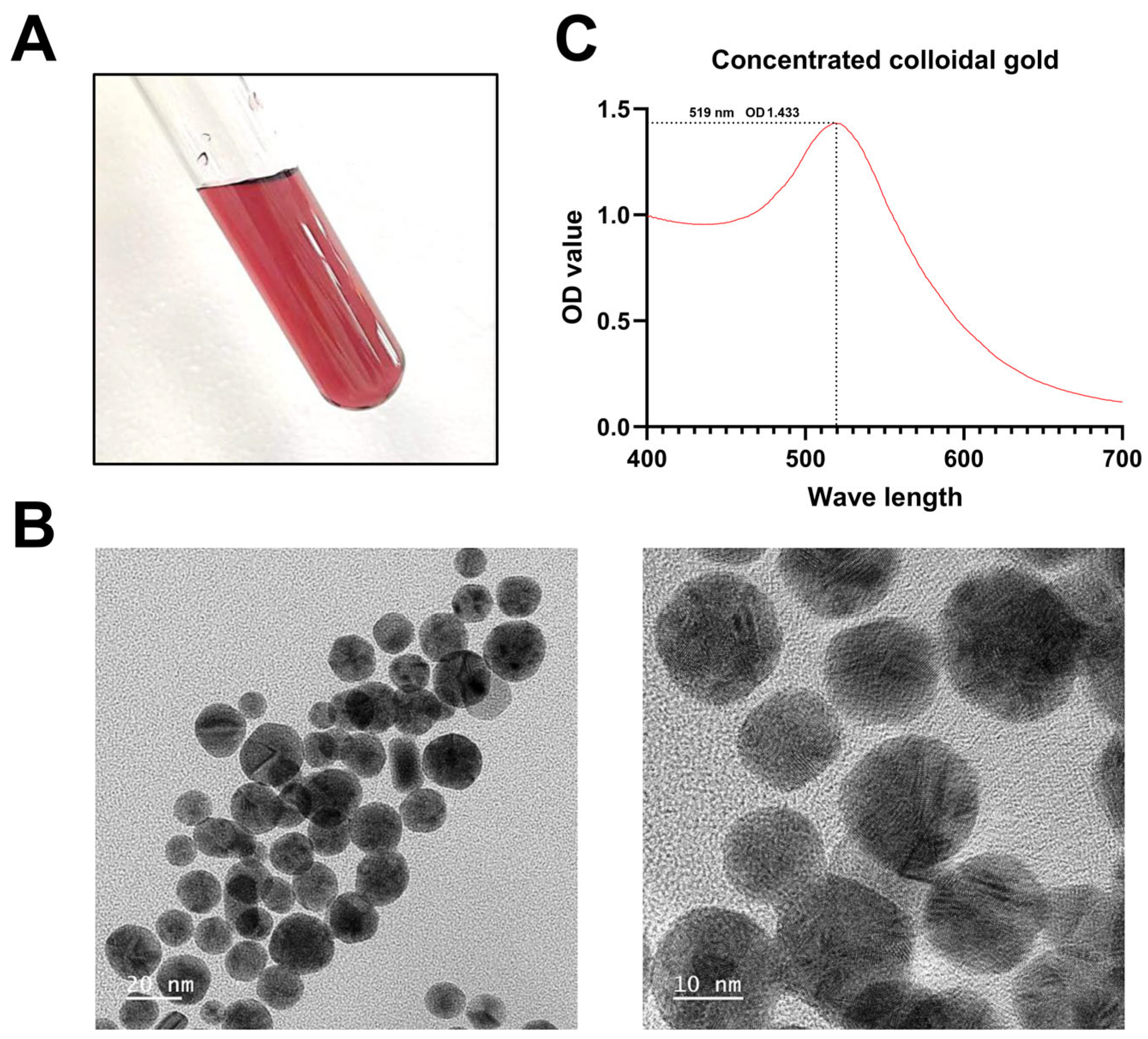
2.5. Synthesis of Concentrated Colloidal Gold
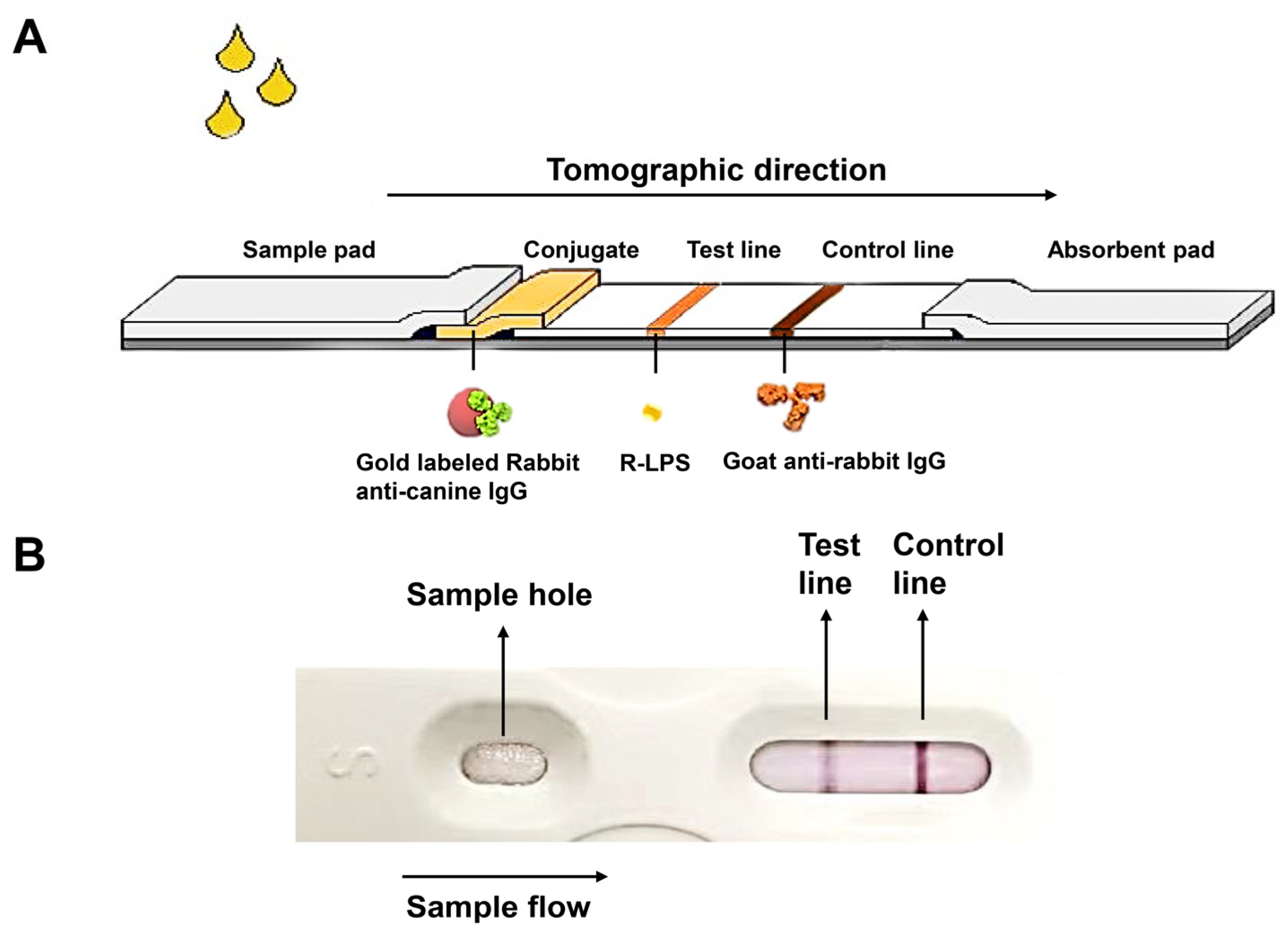
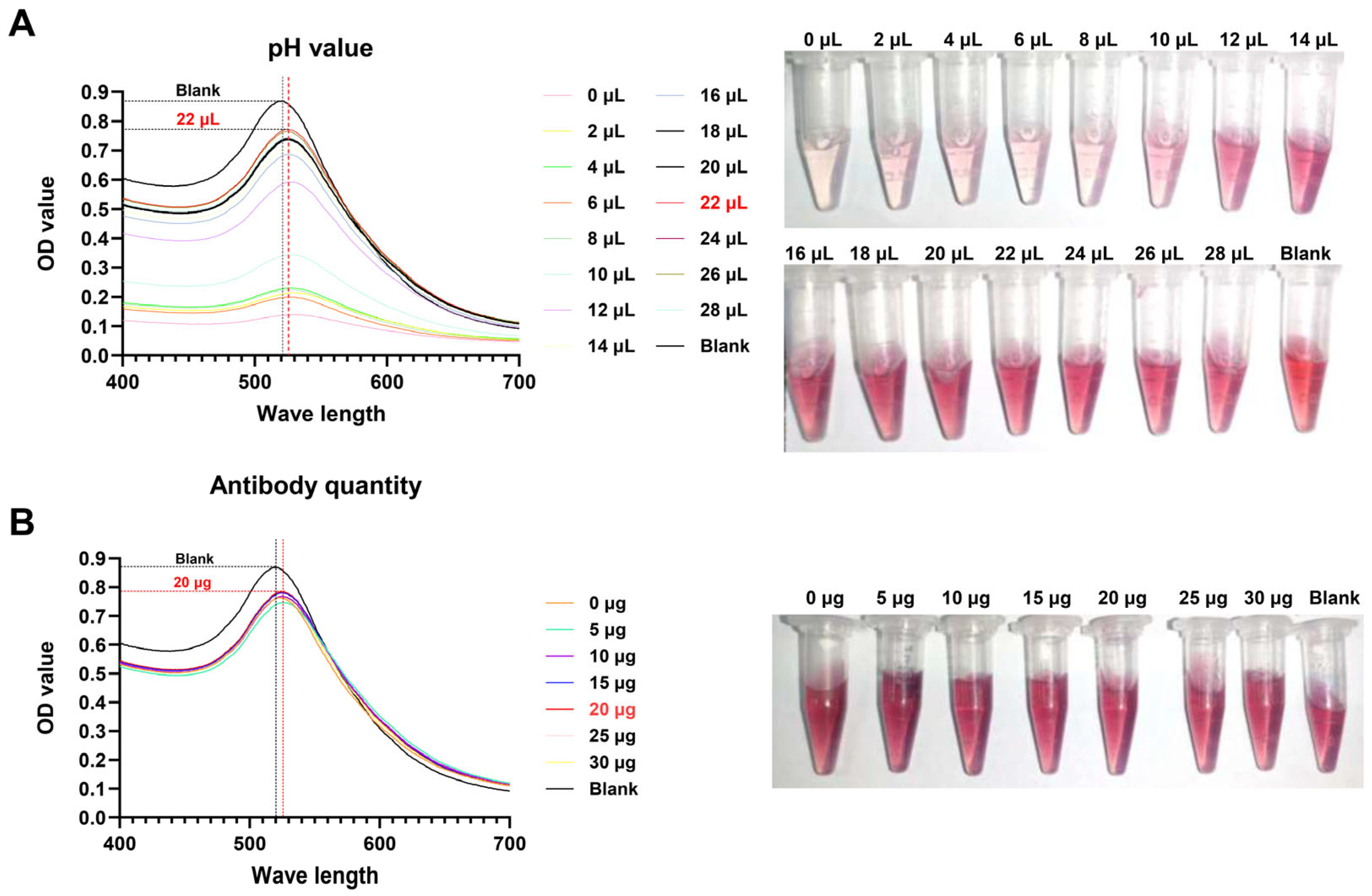
2.6. Optimization of the Colloidal Gold Test Strip
2.7. Preparation of the Test Strip Package
2.8. Specificity and Sensitivity of the Colloidal Gold Test Strip
2.9. Stability and Repeatability of the Colloidal Gold Test Strip
2.10. Clinical Evaluation of the Colloidal Gold Test Strip
3. Results
3.1. Identification R-LPS of B. canis
3.2. Identification of Colloidal Gold Solution
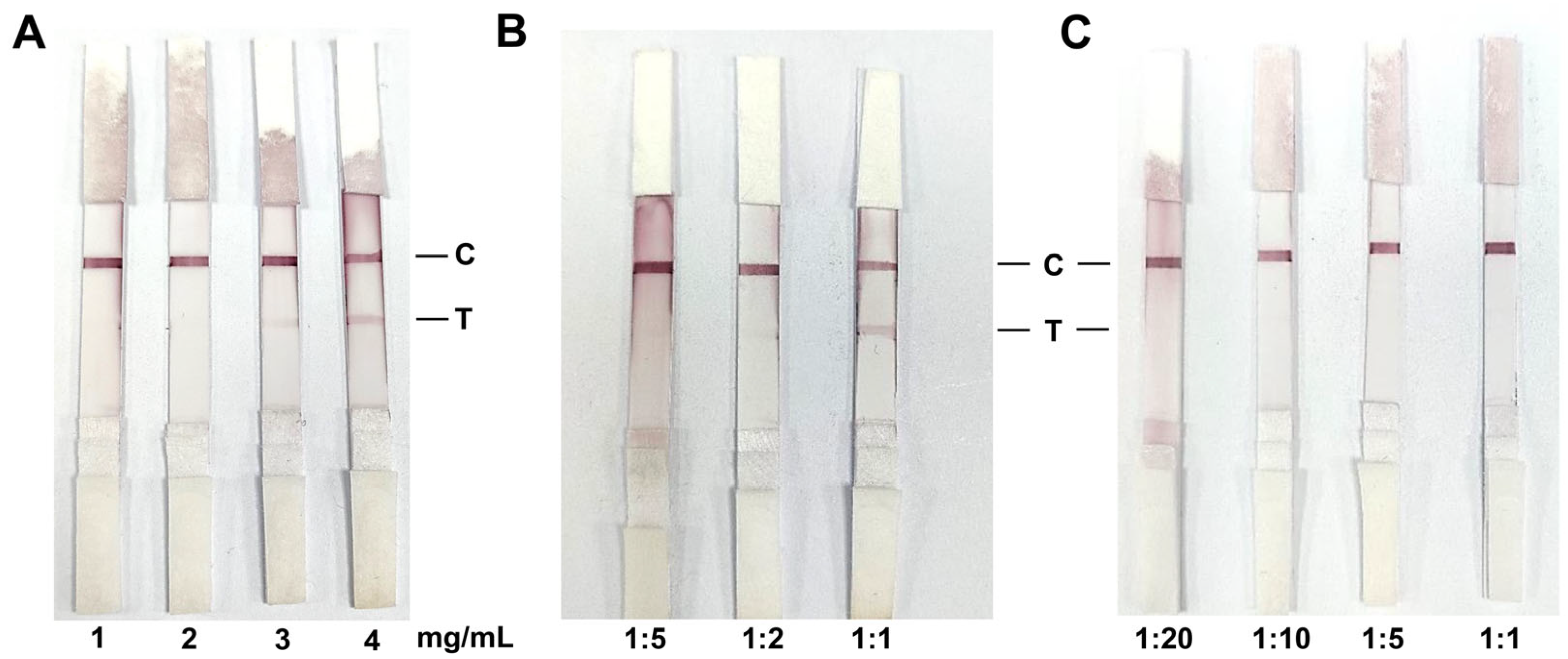
3.3. Optimal Labeling Conditions for Colloidal Gold
3.4. Optimal Antigen Coating and Serum Dilution for Colloidal Gold Test Strips
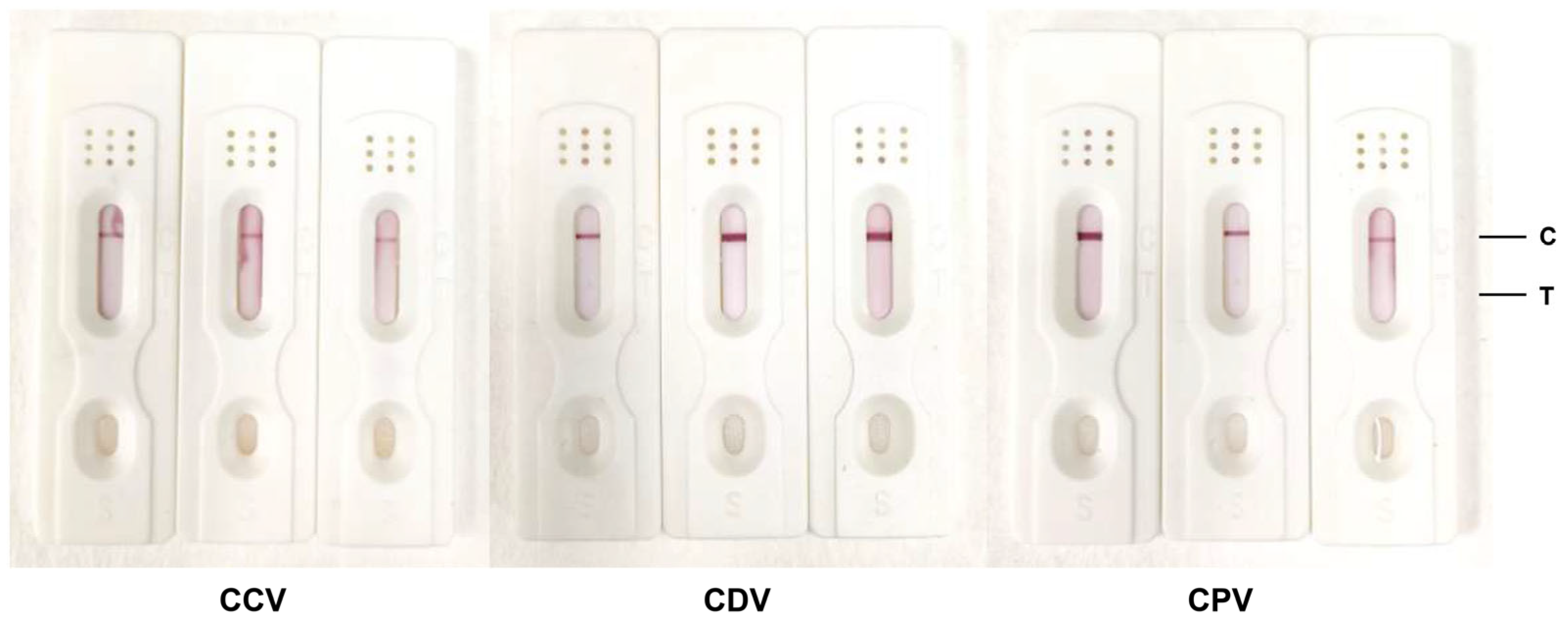
3.5. Evaluation of the Specificity of Colloidal Gold Test Strips
3.6. Comparative Analysis of Colloidal Gold Field Samples with Commercial iELISA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Celli, J. The intracellular life cycle of Brucella spp. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laverde, A.J.; Restrepo-Botero, D.; Hernández-Pulido, D.; Rodríguez-Bautista, J.L.; Sandoval, I.S. Seroprevalence of Brucella canis in canines from a dog shelter in Bogota, Colombia. Biomedica 2021, 41, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.A. Brucella canis infection in dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1969, 155, 2034–2037. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.A.; Gupta, B.N. Epizootiology, diagnosis, and control of Brucella canis. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1970, 156, 1737–1740. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Djokic, V.; Freddi, L.; de Massis, F.; Lahti, E.; van den Esker, M.H.; Whatmore, A.; Haughey, A.; Ferreira, A.C.; Garofolo, G.; Melzer, F.; et al. The emergence of Brucella canis as a public health threat in Europe: What we know and what we need to learn. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2249126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosford, K.L. Brucella canis: An update on research and clinical management. Can. Vet. J. 2018, 59, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Boeri, E.J.; Madariaga, M.J.; Dominguez, M.L.; Teijeiro, M.L.; Fernandez, N.M.; Elena, S.A.; Trangoni, M.D. Brucella canis Group 2 isolated in Argentina. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2021, 53, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.B.; Yang, J.H.; Li, D.L.; Hao, L.H.; Zhang, Z.; Mei, S.Y.; Zhang, H.; Du, F.Y.; Yv, L.H.; Liu, B.S.; et al. A specific reverse complement sequence for distinguishing Brucella canis from other Brucella species. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 983482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyuranecz, M.; Szeredi, L.; Rónai, Z.; Dénes, B.; Dencso, L.; Dán, Á.; Pálmai, N.; Hauser, Z.; Lami, E.; Makrai, L.; et al. Detection of Brucella canis-induced reproductive diseases in a kennel. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2011, 23, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Nan, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, P.; Chen, Y.; Mao, K.; Chen, Y. A novel approach for detection of brucella using a real-time recombinase polymerase amplification assay. Mol. Cell. Probes 2019, 48, 101451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Süer, K.; Güvenir, M.; Aykaç, A.; Güler, E.; Sayan, M.; Şanlıdağ, T.; Erdenliğ, G.S. Investigation of Brucella canis and Brucella abortus seropositivity by in-house rapid slide agglutination test and in-house ELISA in northern cyprus. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2023, 259, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, M.Z.; Vale, V.; Keid, L.; Freire, S.M.; Meyer, R.; Portela, R.W.; Barrouin-Melo, S.M. Validation of an ELISA method for the serological diagnosis of canine brucellosis due to Brucella canis. Res. Vet. Sci. 2011, 90, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuemmers, C.; Lüders, C.; Rojas, C.; Serri, M.; Castillo, C.; Espinoza, R. Detection of Brucella canis by immunochromatography method in vague dogs captured in Temuco city, Chile, 2011. Rev. Chil. Infectol. 2013, 30, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensel, M.E.; Negron, M.; Arenas-Gamboa, A.M. Brucellosis in dogs and public health risk. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1401–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Park, J.; Kim, S.J.; Soh, Y.M.; Kim, H.M.; Oh, B.H.; Song, J.J. Brucella immunogenic BP26 forms a channel-like structure. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Jiménez, M.; Ortiz-Román, L.F.; Castrillón-Salazar, L.L.; Giraldo-Echeverri, C.A.; Olivera-Angel, M. Application of a polymerase chain reaction test for the detection of Brucella canis from clinical samples of canines and humans. Rev. Colomb. Cienc. Pecu. 2014, 27, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keid, L.B.; Soares, R.M.; Vasconcellos, S.A.; Megid, J.; Salgado, V.R.; Richtzenhain, L.J. Comparison of agar gel immunodiffusion test, rapid slide agglutination test, microbiological culture and PCR for the diagnosis of canine brucellosis. Res. Vet. Sci. 2009, 86, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmichael, L.E.; Zoha, S.J.; Flores-Castro, R. Problems in the serodiagnosis of canine brucellosis: Dog responses to cell wall and internal antigens of Brucella canis. Dev. Biol. Stand. 1984, 56, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.B.; Ta, N.; Wang, L.P.; Fan, M.G.; Li, Y.X.; Zhang, C.H.; Zhang, L.J.; Wang, Z.J.; Jiang, H. Evaluation of colloidal gold immunochromatography for the diagnosis of human brucellosis caused by smooth Brucella. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2022, 35, 764–767. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, M.; Liu, M.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Wei, Y.R.; Liu, Y.; Yang, K.L.; Duan, X.; Shao, W.; et al. Comparison of BP26, Omp25 and Omp31 and a multiepitope-based fusion protein in the serological detection of canine brucellosis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 5301–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, T.; Yang, H.; Wang, N.; Wang, F.; Zhao, P.; Wang, H.; Mao, K.; Zhu, H.; Ding, J. Limitations of the BP26 protein-based indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of Brucellosis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 1410–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbel, M.J. Brucellosis: An overview. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1997, 3, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kianmehr, Z.; Ardestani, S.K.; Soleimanjahi, H.; Fotouhi, F.; Alamian, S.; Ahmadian, S. Comparison of biological and immunological characterization of lipopolysaccharides from Brucella abortus RB51 and S19. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2015, 8, e24853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fomsgaard, A.; Freudenberg, M.A.; Galanos, C. Modification of the silver staining technique to detect lipopolysaccharide in polyacrylamide gels. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 2627–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Chen, W.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X. Preparation of colloidal gold immunochromatographic strip for detection of Paragonimiasis skrjabini. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paek, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, Y.S. Development of rapid one-step immunochromatographic assay. Methods 2000, 22, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.Q.; Wan, Y.; Shi, Z.W.; Luo, J.C.; Li, H.Y.; Li, S.S.; Li, Y.Z.; Dai, X.Y.; Bai, X.; Tian, H.; et al. Colloidal gold and fluorescent immunochromatographic test strips for canine parvovirus detection. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 4903–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.; Smith, P.; Conde, S.; Draghi de Benitez, G.; Gall, D.; Halbert, G.; Kenny, K.; Massengill, C.; Muenks, Q.; Rojas, X.; et al. Rough lipopolysaccharide of Brucella abortus RB51 as a common antigen for serological detection of B. ovis, B. canis, and B. abortus RB51 exposure using indirect enzyme immunoassay and fluorescence polarization assay. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2004, 25, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keid, L.B.; Diniz, J.A.; Oliveira, T.M.; Ferreira, H.L.; Soares, R.M. Evaluation of an immunochromatographic test to the diagnosis of canine brucellosis caused by Brucella canis. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2015, 50, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, P.G.; Macedo, G.C.; Azevedo, V.; Oliveira, S.C. Brucella spp noncanonical LPS: Structure, biosynthesis, and interaction with host immune system. Microb. Cell Fact. 2006, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Colloidal Gold Detection | Positive | Negative | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test Positive | 20 (a) | 3 (b) | 23 (a + b) |
| Test Negative | 1 (c) | 239 (d) | 240 (c + d) |
| Total | 21 (a + c) | 242 (b + d) | 263 (a + b + c + d) |
| Evaluation Indicators | Formula for Assessment | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Positive | a + c | 21 |
| Negative | b + d | 242 |
| False Positive | b | 3 |
| False Negative | c | 1 |
| Sensitivity (A) | a/(a + c) × 100% | 95.23% |
| Specificity (B) | d/(b + d) × 100% | 98.76% |
| Misdiagnosis | b/(b + d) × 100% | 1.23% |
| Underdiagnosis | c/(a + c) × 100% | 4.70% |
| Diagnostic Compliance rate | (a + d)/(a + b + c + d) × 100% | 98.47% |
| Correctness Index (Youden) | A + B − 1 | 93.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, P.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Bao, Y.; Qi, J.; Han, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, S.; Tian, M. Development and Application of Colloidal Gold Test Strips for the Rapid Detection of Canine Brucellosis. Biosensors 2024, 14, 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14080388
Sun P, Yang X, Liu J, Bao Y, Qi J, Han X, Liu G, Wang S, Tian M. Development and Application of Colloidal Gold Test Strips for the Rapid Detection of Canine Brucellosis. Biosensors. 2024; 14(8):388. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14080388
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Pengxiang, Xinmei Yang, Jinyue Liu, Yanqing Bao, Jingjing Qi, Xiangan Han, Guanhui Liu, Shaohui Wang, and Mingxing Tian. 2024. "Development and Application of Colloidal Gold Test Strips for the Rapid Detection of Canine Brucellosis" Biosensors 14, no. 8: 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14080388
APA StyleSun, P., Yang, X., Liu, J., Bao, Y., Qi, J., Han, X., Liu, G., Wang, S., & Tian, M. (2024). Development and Application of Colloidal Gold Test Strips for the Rapid Detection of Canine Brucellosis. Biosensors, 14(8), 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14080388







