Using AuNPs-DNA Walker with Fluorophores Detects the Hepatitis Virus Rapidly
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Apparatus
2.2. Materials and Reagents
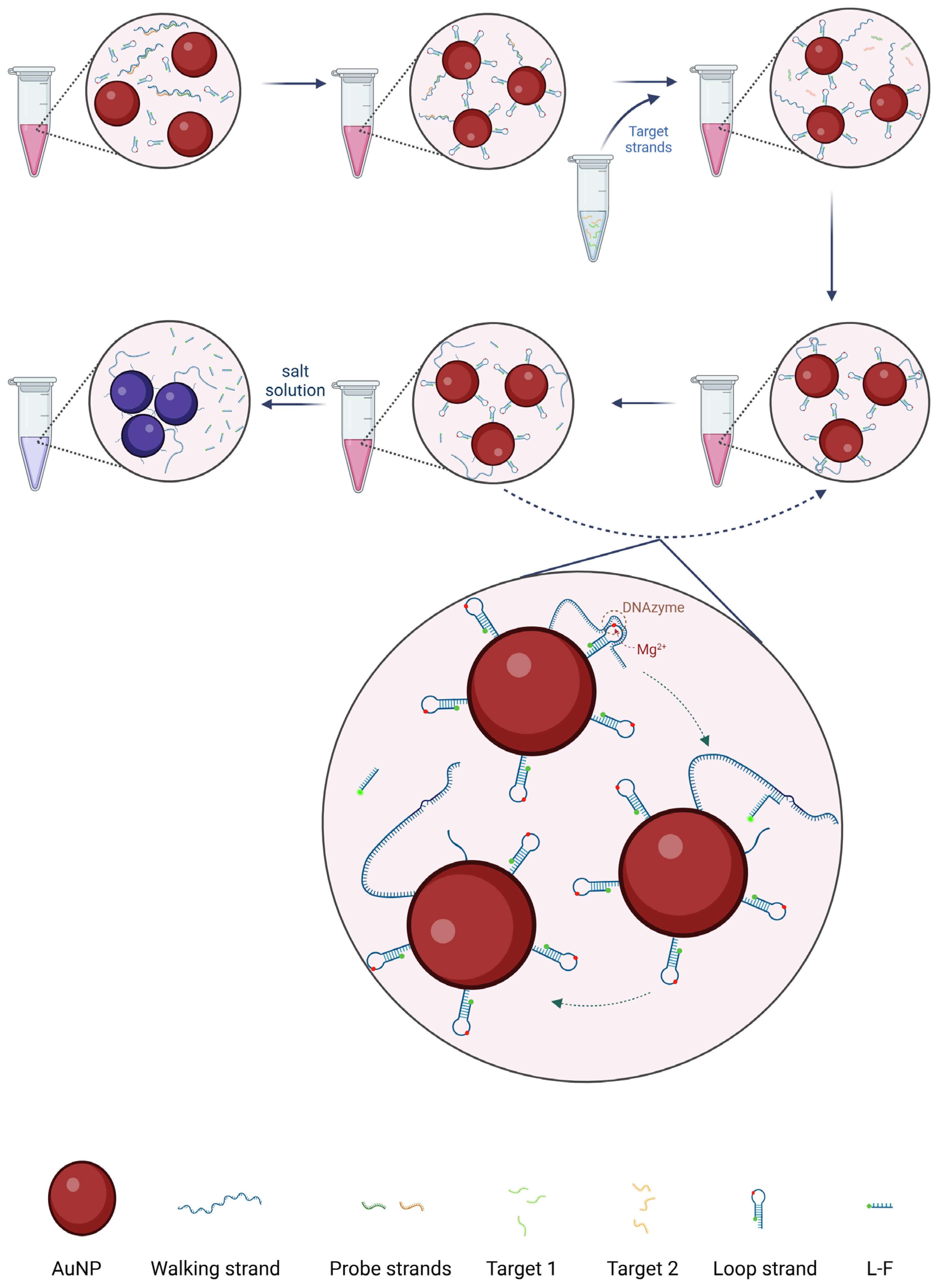
2.3. Preparation of DNA Walker
2.4. Preparation of AuNPs-DNA Walker
2.5. Colorimetric Detection and Fluorescence Detection of Virul Fragments
3. Results
3.1. Operating Principle of the AuNPs-DNA Walker
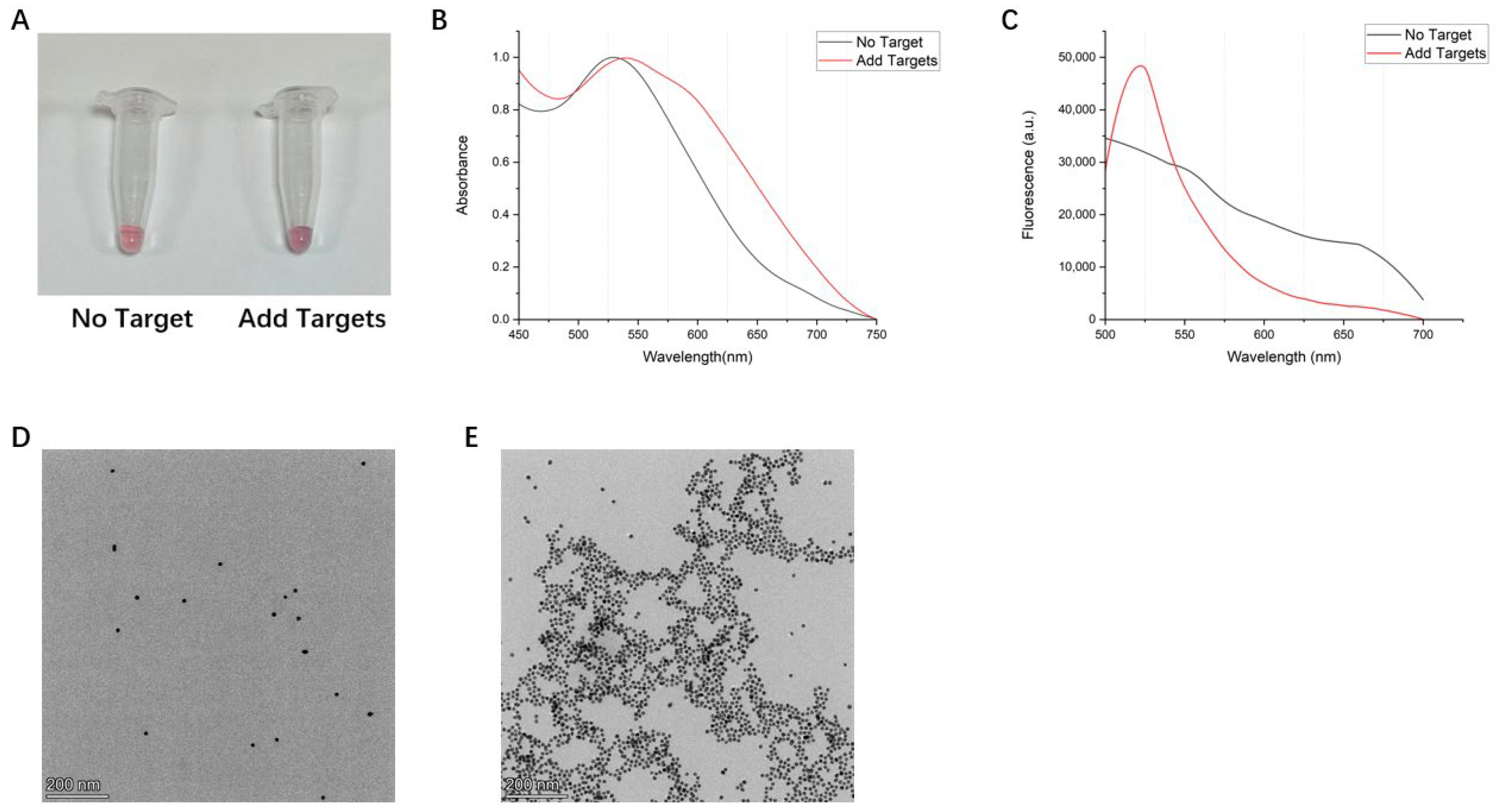
3.2. Colorimetric Response of the AuNPs-DNA Walker to HAV Target Sequences
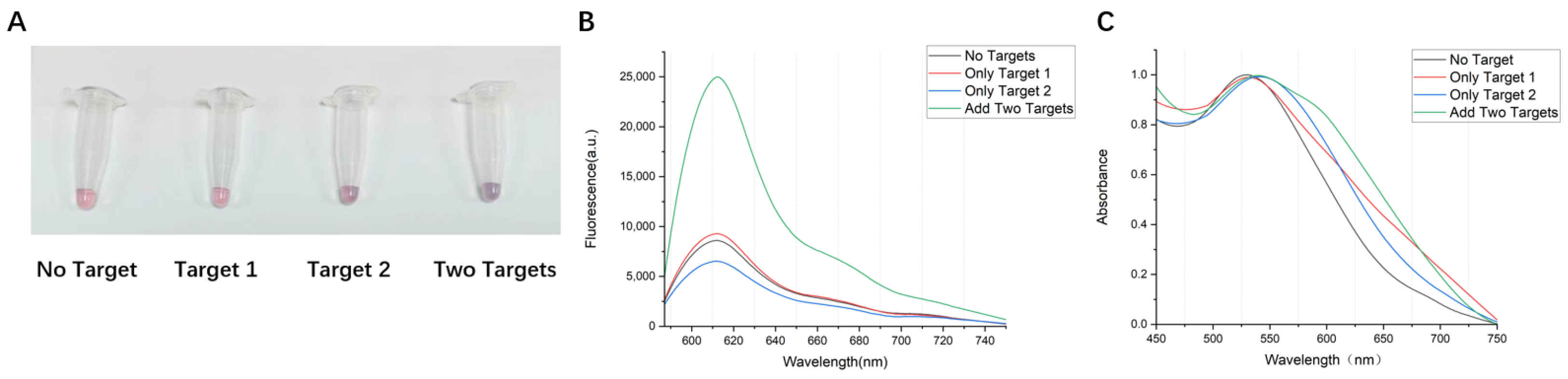
3.3. Specific Detection of the AuNPs-DNA Walker
3.4. Test of the AuNPs-DNA Walker to Virus Target Fragments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rasche, A.; Sander, A.-L.; Corman, V.M.; Drexler, J.F. Evolutionary biology of human hepatitis viruses. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 501–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorio, G.V.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Mowat, A.P. Viral hepatitis. Arch. Dis. Child. 1994, 70, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Feinstone, S.M. History of the Discovery of Hepatitis A Virus. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a031740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guvenir, M.; Arikan, A. Hepatitis B Virus: From Diagnosis to Treatment. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, W.J.; Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Lok, A.S.F. Hepatitis B. Lancet 2023, 401, 1039–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol, S.; Lagaye, S. The remarkable history of the hepatitis C virus. Genes Immun. 2019, 20, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nainan, O.V.; Xia, G.; Vaughan, G.; Margolis, H.S. Diagnosis of hepatitis a virus infection: A molecular approach. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trepo, C.; Chan, H.L.; Lok, A. Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 2014, 384, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinstone, S.M.; Kapikian, A.Z.; Purceli, R.H. Hepatitis A: Detection by immune electron microscopy of a viruslike antigen associated with acute illness. Science 1973, 182, 1026–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sadeq, D.W.; Taleb, S.A.; Zaied, R.E.; Fahad, S.M.; Smatti, M.K.; Rizeq, B.R.; Al Thani, A.A.; Yassine, H.M.; Nasrallah, G.K. Hepatitis B Virus Molecular Epidemiology, Host-Virus Interaction, Coinfection, and Laboratory Diagnosis in the MENA Region: An Update. Pathogens 2019, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delem, A.D. Comparison of modified HAVAB and ELISA for determination of vaccine-induced anti-HAV response. Biol. J. Int. Assoc. Biol. Stand. 1992, 20, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, R.H.; Wong, D.C.; Moritsugu, Y.; Dienstag, J.L.; Routenberg, J.A.; Boggs, J.D. A microtiter solid-phase radioimmunoassay for hepatitis A antigen and antibody. J. Immunol. 1976, 116, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritsugu, Y.; Dienstag, J.L.; Valdesuso, J.; Wong, D.C.; Wagner, J.; Routenberg, J.A.; Purcell, R.H. Purification of hepatitis A antigen from feces and detection of antigen and antibody by immune adherence hemagglutination. Infect. Immun. 1976, 13, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzin, M.A.; Abdoos, H.; Saber, R. AuNP-based biosensors for the diagnosis of pathogenic human coronaviruses: COVID-19 pandemic developments. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 7069–7084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; He, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J. Tetrahedron-Based Constitutional Dynamic Network for COVID-19 or Other Coronaviruses Diagnostics and Its Logic Gate Applications. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, P.; Pan, W.; Li, N.; Tang, B. AND Logic-Gate-Based CRISPR/Cas12a Biosensing Platform for the Sensitive Colorimetric Detection of Dual miRNAs. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 15839–15846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokni, M.; Tlili, A.; Attia, G.; Khaoulani, S.; Zerrouki, C.; Omezzine, A.; Othmane, A.; Bouslama, A.; Fourati, N. Novel sensitive immunosensor for the selective detection of Engrailed 2 urinary prostate cancer biomarker. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 217, 114678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, B.B.; Burkhardt, W., 3rd; Cebula, T.A. Identification of genetic variants of hepatitis A virus. J. Virol. Methods 1997, 65, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buti, M.; Jardí, R.; Bosch, A.; Rodríguez, F.; Sánchez, G.; Pinto, R.; Costa, X.; Sánchez-Avila, J.F.; Cotrina, M.; Esteban, R.; et al. Assessment of the PCR-Southern blot technique for the analysis of viremia in patients with acute hepatitis A. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2001, 24, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, J.; D’Souza, D.H.; Jaykus, L.A. Multiplex nucleic acid sequence-based amplification for simultaneous detection of several enteric viruses in model ready-to-eat foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 6603–6610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polish, L.B.; Robertson, B.H.; Khanna, B.; Krawczynski, K.; Spelbring, J.; Olson, F.; Shapiro, C.N. Excretion of hepatitis A virus (HAV) in adults: Comparison of immunologic and molecular detection methods and relationship between HAV positivity and infectivity in tamarins. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 3615–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, K.; Yokosuka, O.; Ehata, T.; Imazeki, F.; Saisho, H. PCR-SSCP analysis of 5′-nontranslated region of hepatitis A viral RNA: Comparison with clinicopathological features of hepatitis A. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2000, 45, 2422–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.P.; Yao, C.Y. Rapid and quantitative detection of hepatitis B virus. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11954–11963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikan, A.; Sayan, M.; Sanlidag, T.; Suer, K.; Akcali, S.; Guvenir, M. Evaluation of the pol/S Gene Overlapping Mutations in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients in Northern Cyprus. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayan, M.; Arikan, A.; Sanlidag, T. Comparison of Performance Characteristics of DxN VERIS System versus Qiagen PCR for HBV Genotype D and HCV Genotype 1b Quantification. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, E. Gold Nanoparticle-Based Plasmonic Biosensors. Biosensors 2023, 13, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medici, S.; Peana, M.; Coradduzza, D.; Zoroddu, M.A. Gold nanoparticles and cancer: Detection, diagnosis and therapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 76, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Radadi, N.S. Green Biosynthesis of Flaxseed Gold Nanoparticles (Au-NPs) as Potent Anti-cancer Agent Against Breast Cancer Cells. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021, 25, 101243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, F.; Kumar Dinda, A.; Kumar, A.; Koul, V. Investigation of ultrafine gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) based nanoformulation as single conjugates target delivery for improved methotrexate chemotherapy in breast cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 569, 118561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirkin, C.A.; Letsinger, R.L.; Mucic, R.C.; Storhoff, J.J. A DNA-based method for rationally assembling nanoparticles into macroscopic materials. Nature 1996, 382, 607–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, K.; Agasti, S.S.; Kim, C.; Li, X.; Rotello, V.M. Gold Nanoparticles in Chemical and Biological Sensing. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2739–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omabegho, T.; Sha, R.; Seeman, N.C. A bipedal DNA Brownian motor with coordinated legs. Science 2009, 324, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.; Allen, P.B.; Ellington, A.D. A stochastic DNA walker that traverses a microparticle surface. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Tang, D. Recent advances in DNA walker machines and their applications coupled with signal amplification strategies: A critical review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1171, 338523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, H.; Miao, P. Bipedal DNA Walker Based Electrochemical Genosensing Strategy. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4953–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Song, J.; Xu, X. Colorimetric detection of viral RNA fragments based on an integrated logic-operated three-dimensional DNA walker. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 217, 114714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Fang, J.; Guo, Y.; Tao, Y.; Han, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Jian, Y.; Xie, G. A target-triggered biosensing platform for detection of HBV DNA based on DNA walker and CHA. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 554, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Jin, M.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lou, Y. 3D-DNA walking nanomachine based on catalytic hairpin assembly and copper nanoclusters for sensitive detection of hepatitis C virus. Talanta 2024, 269, 125478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, P.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Cai, C. Ultrasensitive and selective electrochemical identification of hepatitis C virus genotype 1b based on specific endonuclease combined with gold nanoparticles signal amplification. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 4752–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shawky, S.M.; Guirgis, B.S.; Azzazy, H.M. Detection of unamplified HCV RNA in serum using a novel two metallic nanoparticle platform. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2014, 52, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawky, S.M.; Awad, A.M.; Allam, W.; Alkordi, M.H.; El-Khamisy, S.F. Gold aggregating gold: A novel nanoparticle biosensor approach for the direct quantification of hepatitis C virus RNA in clinical samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, O.J.; Goodall, B.L.; Hui, H.P.; Vats, N.; Brosseau, C.L. Development of a SERS-Based Rapid Vertical Flow Assay for Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Hu, F.; Yang, G.; Li, J.; Tian, H.; Peng, N. An LED-Driven AuNPs-PDMS Microfluidic Chip and Integrated Device for the Detection of Digital Loop-Mediated Isothermal DNA Amplification. Micromachines 2020, 11, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moitra, P.; Alafeef, M.; Dighe, K.; Frieman, M.B.; Pan, D. Selective Naked-Eye Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Mediated by N Gene Targeted Antisense Oligonucleotide Capped Plasmonic Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 7617–7627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alafeef, M.; Moitra, P.; Dighe, K.; Pan, D. RNA-extraction-free nano-amplified colorimetric test for point-of-care clinical diagnosis of COVID-19. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 3141–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Fan, Z.; Huang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Xie, M.; Wang, M. Hybridization chain reaction circuit-based electrochemiluminescent biosensor for SARS-CoV-2 RdRp gene assay. Talanta 2022, 240, 123207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, B.; Zheng, C.; Pan, D.; Shen, L.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Wen, Y.; Shi, Y. Using AuNPs-DNA Walker with Fluorophores Detects the Hepatitis Virus Rapidly. Biosensors 2024, 14, 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14080370
Sun B, Zheng C, Pan D, Shen L, Zhang W, Chen X, Wen Y, Shi Y. Using AuNPs-DNA Walker with Fluorophores Detects the Hepatitis Virus Rapidly. Biosensors. 2024; 14(8):370. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14080370
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Baining, Chenxiang Zheng, Dun Pan, Leer Shen, Wan Zhang, Xiaohua Chen, Yanqin Wen, and Yongyong Shi. 2024. "Using AuNPs-DNA Walker with Fluorophores Detects the Hepatitis Virus Rapidly" Biosensors 14, no. 8: 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14080370
APA StyleSun, B., Zheng, C., Pan, D., Shen, L., Zhang, W., Chen, X., Wen, Y., & Shi, Y. (2024). Using AuNPs-DNA Walker with Fluorophores Detects the Hepatitis Virus Rapidly. Biosensors, 14(8), 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14080370




