Boosting Electrochemical Sensing Performances Using Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
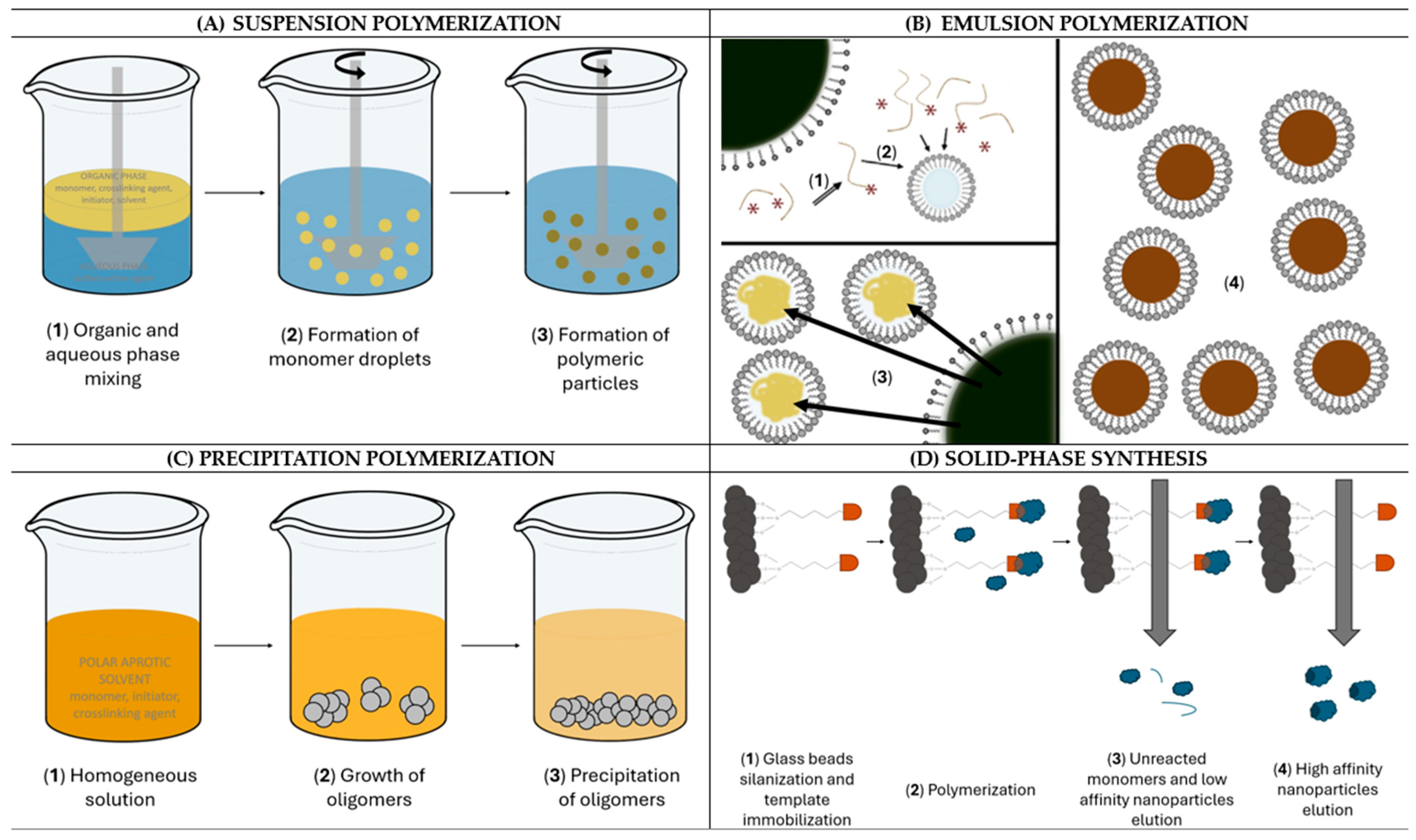
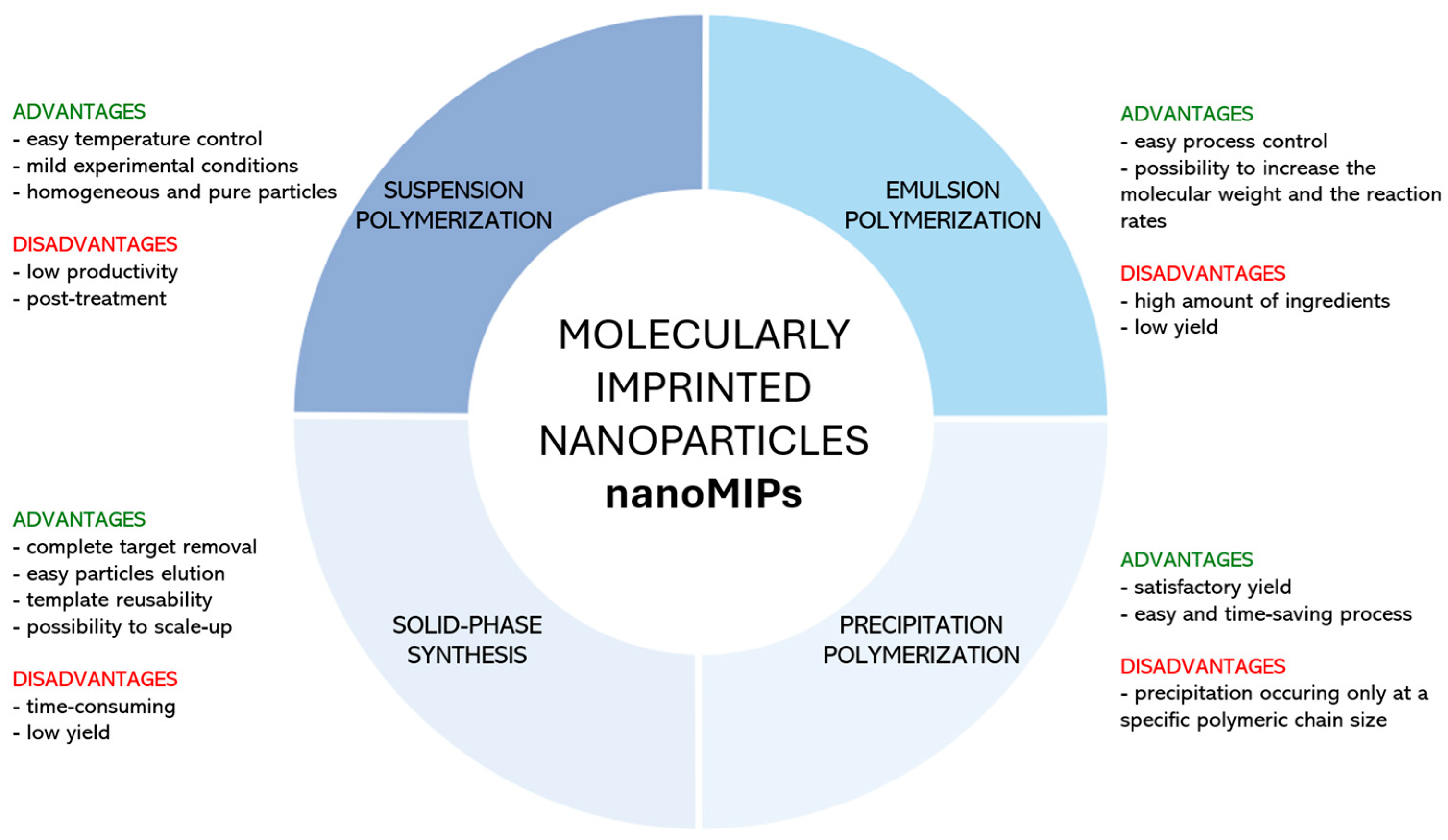
2. NanoMIPs Synthetic Strategies
2.1. Suspension Polymerization
2.2. Emulsion Polymerization
2.3. Precipitation Polymerization
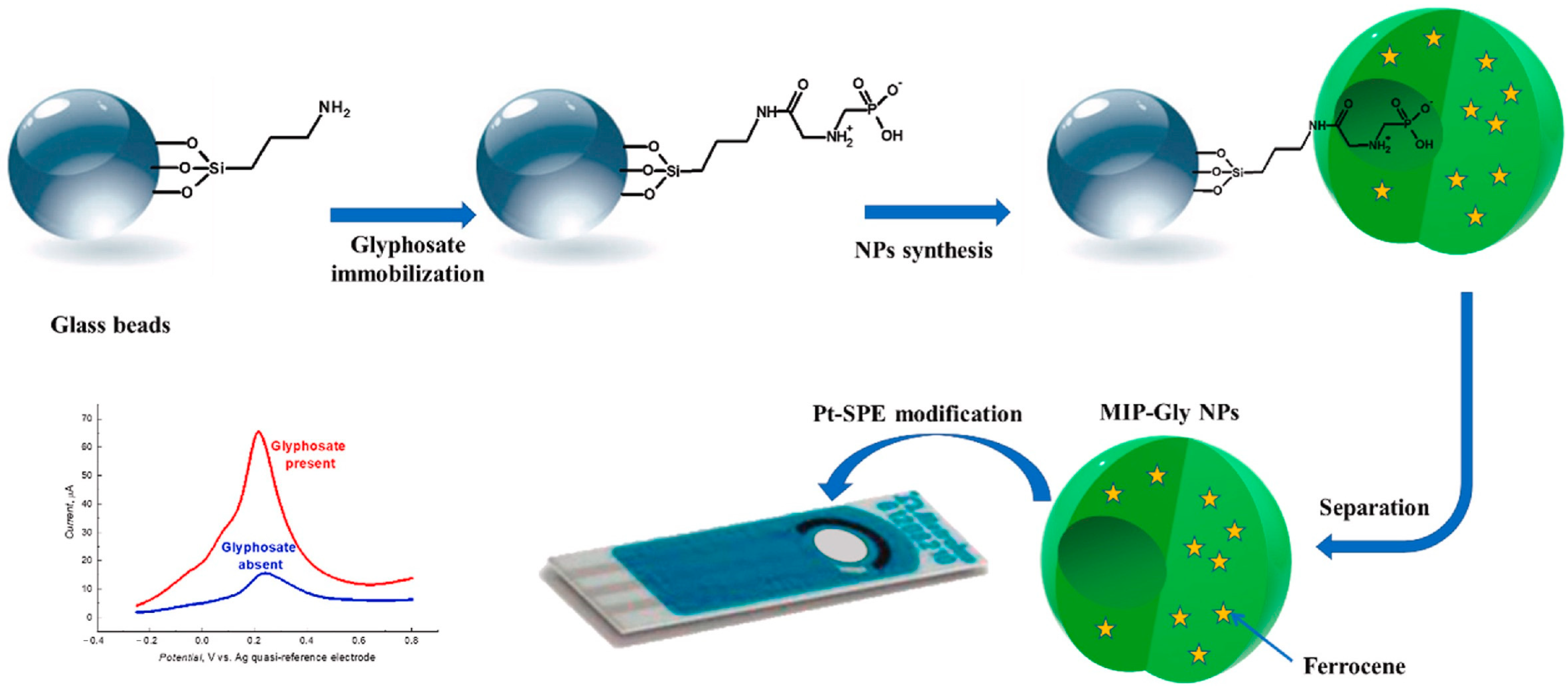
2.4. Solid-Phase Synthesis
3. Integration of NanoMIPs with Electrochemical Transducers for Sensing Purposes
3.1. NanoMIPs on the Electrode Surface
3.1.1. NanoMIPs Anchored to the Electrode Surface with Polymeric Films
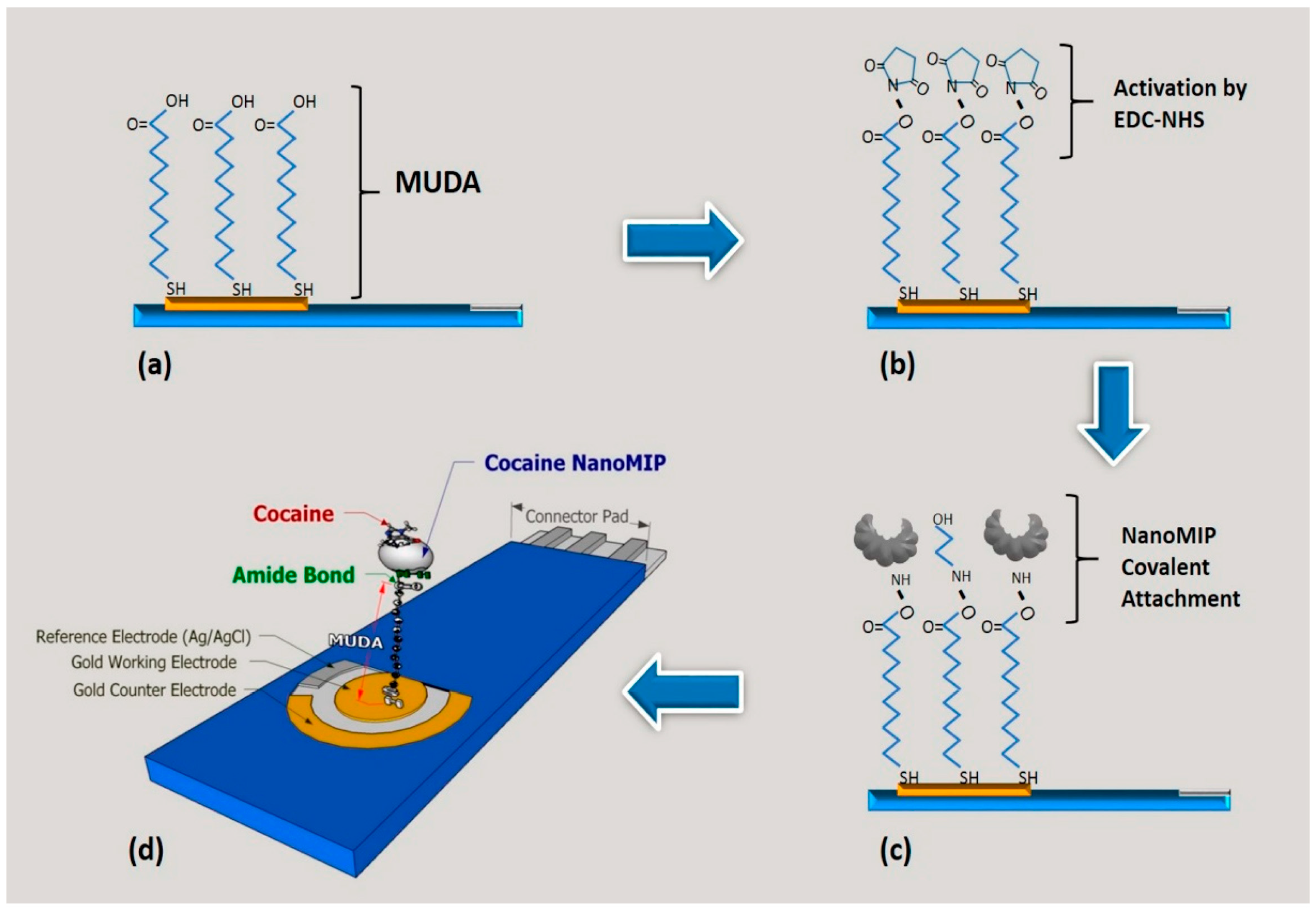
3.1.2. NanoMIPs Anchoring to the Electrode Surface via Coupling Chemistry
3.2. NanoMIPs within the Electrode Material
4. Generation of Electrochemical Signals in NanoMIP-Based Electrochemical Sensors
4.1. Direct Detection of Analytes
4.2. Indirect Detection of Analytes
| Analyte | Detection Technique 1 | NanoMIPs Type 2 | NanoMIPs Synthesis 3 | Electrode Material and NanoMIPs Anchoring | LOD 4 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diazinon | CV SWV | NE | SP | Carbon-paste electrode | 7.9 × 10−10 M | [35] |
| 4EP | CV EIS | NE | SPS | Gold; SAM of MUDA or lipoic acid, EDC/NHS | 0.068 mg/L | [70] |
| Vancomycin | CV | E | SPS | Glassy-carbon electrode; nafion | 83 μM | [90] |
| Morphine | A | NE | PP | Indium-tin oxide glass; electrosynthesis of PEDOT in the presence of nanoMIPs | 0.3 mM | [97] |
| Diphenylamine | DPV | NE | TPE | Gold; electrosynthesis of PEDOT in the presence of nanoMIPs | 5.4 μM | [98] |
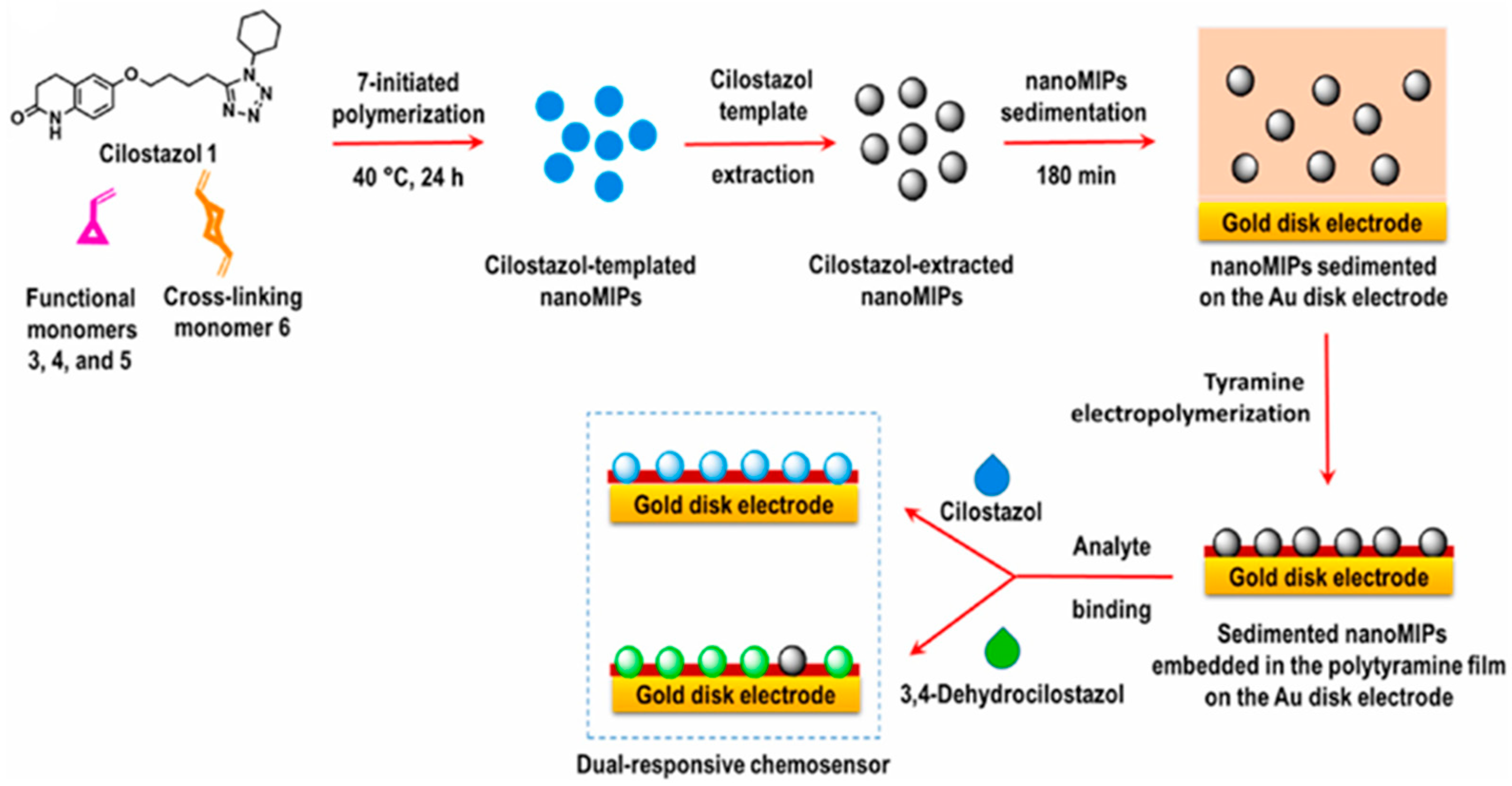
| Cilostazol | DPV EIS | NE | PP | Gold; poly(tyramine) |
93.5 nM (DPV) 86.5 nM (EIS) | [99] |
| Trypsin Glucose Paracetamol C4-HSL THC | DPV | E | SPS | Screen-printed gold electrode; cysteamine, EDC/NHS |
0.2 nM 0.4 nM 50 nM 0.1 nM 82 nM | [102] |
| Trypsin | EIS | NE | LPS; SPS | Screen-printed gold electrode; SAM of lipoic acid | 1.06 ng/mL | [103] |
| Insulin | DPV | E | SPS | Screen-printed platinum electrode; APTES, glutaraldehyde | 26 fM | [105] |
| Trypsin THC | CV C | NE | SPS | Gold; poly(tyramine), glutaraldehyde | 10−14 M 10−14 M | [106] |
| Lysozyme | EIS | NE | SPS | Screen-printed graphite electrode; electrografting of 4-ABA, EDC/NHS | 13 pM | [109] |
| Cocaine | P | NE | SPS | Ion-selective electrode; membrane of PVC, nanoMIPs, NPOE, kTpBCl | nd | [115] |
| Pb2+ | P | NE | PP | (1) IIP-poly(vynil chloride)-coated Pt-wire; (2) IIP-PVC membrane; (3) IIP-PVC-coated graphite electrode; (4) IIP-PVC/polyaniline-coated graphite electrode; (5) IIP-PVC/MWCNTs-coated graphite electrode; (6) IIP-PVC/MWCNTs/PA-coated graphite electrode | 3.4 × 10−10 M | [116] |
| Fluoxetine | DPV EIS | NE | PP | Carbon-paste electrode | 2.8 × 10−9 M | [118] |
| BSA Trypsin | CV EIS | E | SA | Gold; electropolymerization of PAHN | nd | [123] |
| Sitagliptin | DPV | E | SPS | Screen-printed platinum electrode; APTES, EDC/NHS | 0.06 pM | [124] |
| Glyphosate | DPV EIS | E | SPS | Screen-printed platinum electrode; APTES or AAPS, EDC/NHS | 3.7 pM | [125] |
| Nonanal | CR | E | PP | Gold; drop-casting of a conductive composite of nanoMIPs and AuNPs | 4.5 ppm | [126] |
| Sarcosine | CV DPV | NE | SG | Carbon-paste electrode | 0.38 μM | [127] |
| Estriol | CV DPV EIS | NE | MP | Glassy-carbon electrode; drop-casting | 0.16 μM | [128] |
| Metformin | DPV | E | SPS | Screen-printed platinum electrode; APTES, EDC/NHS | 9 pM | [129] |
| Paracetamol | DPV EIS | E | SPS | Screen-printed carbon electrode; APTES, EDC/NHS | 50 μM | [130] |
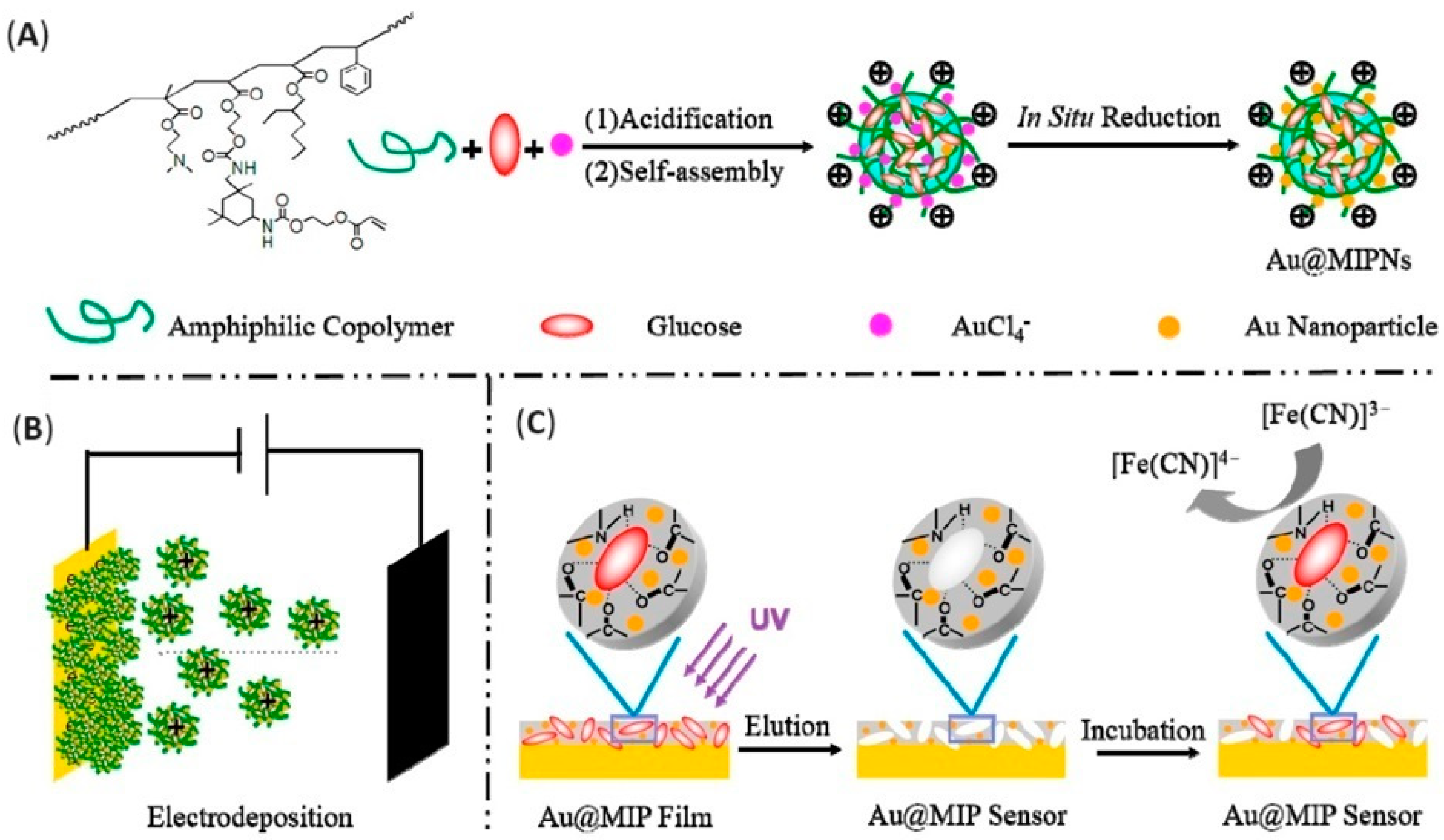
| Glucose | CV | E | MSA | gold; electrodeposition | 3 × 10−2 M | [131] |
| Fumonisin B1 | DPV EIS | NE | SPS | Platinum; electrosynthesis of PPY-(zinc porphyrin), EDC/NHS | 0.03 fM (EIS) 0.7 fM (DPV) | [132] |
| Histamine | P | NE | SPS | Ion-selective electrode; membrane of PVC, nanoMIPs, plasticizer, kTpBCl | 1.12 × 10−6 M | [133] |
| Amphetamine | DPV CV | E | SPS | Graphite; chitosan, or chitosan and graphene oxide | 0.3 nM | [134] |
| MDMA | DPV | E | SPS | Screen-printed graphite electrode; nanoMIPs with chitosan and graphene oxide | 1.6 nM | [135] |
| Pb2+ | DPV | NE | PP | Carbon-paste electrode | 30 pM | [136] |
| Mg2+ | SWV | NE | TPP | Carbon-paste electrode | 0.029 nM | [137] |
| Cd2+ | DPV | NE | BCT | Carbon-paste electrode | 1.94 nM | [138] |
| Cu2+ | DPV | NE | FRP | Screen-printed gold electrode; cysteamine, EDC/NHS | 74 pM | [139] |
| Bisphenol A | P | NE | PP | Paper-based electrode; membrane of nanoMIPs, TDMAC, ETH, PVC, DOP | 0.15 μM | [140] |
| Diazinon | SWV | NE | BP | Carbon-paste electrode | 410 pM | [141] |
4.3. Electroactive Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Target Indirect Detection
5. Applications of NanoMIP-Based Electrochemical Sensors
5.1. Non-Invasive Diagnostics
5.2. Food Analysis
5.3. Water Pollutant Detection
5.4. Drugs for Abuse Testing
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Appadurai, R.; Koneru, J.K.; Bonomi, M.; Robustelli, P.; Srivastava, A. Clustering Heterogeneous Conformational Ensembles of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins with T-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2023, 19, 4711–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsson, B. Artificial Receptors. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2007, 109, 97–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, R.R.; Singamaneni, S. Introduction: Bioinspired and Biomimetic Materials. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 12581–12583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belbruno, J.J. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 94–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemiş, F.; Alkan, P.; Yenigül, B.; Yenigül, M. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers and Their Synthesis by Different Methods. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2013, 21, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasapollo, G.; Del Sole, R.; Mergola, L.; Lazzoi, M.R.; Scardino, A.; Scorrano, S.; Mele, G. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Present and Future Prospective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5908–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canfarotta, F.; Whitcombe, M.J.; Piletsky, S.A. Polymeric Nanoparticles for Optical Sensing. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1585–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moczko, E.; Guerreiro, A.; Piletska, E.; Piletsky, S. PEG-Stabilized Core–Shell Surface-Imprinted Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2013, 29, 9891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moczko, E.; Poma, A.; Guerreiro, A.; Perez De Vargas Sansalvador, I.; Caygill, S.; Canfarotta, F.; Whitcombe, M.J.; Piletsky, S. Surface-Modified Multifunctional MIP Nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3733–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poma, A.; Guerreiro, A.; Whitcombe, M.J.; Piletska, E.V.; Turner, A.P.F.; Piletsky, S.A. Solid-Phase Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles with a Reusable Template—“Plastic Antibodies”. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 2821–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Uddin, K.M.A.; Shen, X.; Jayawardena, S.; Yan, M.; Ye, L. Photoconjugation of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer with Magnetic Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 5208–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berghaus, M.; Mohammadi, R.; Sellergren, B. Productive Encounter: Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles Prepared Using Magnetic Templates. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 8993–8996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamizadeh, K.; Vahedpour, M.; Bozorgi, S. Synthesis, Characterization and Evaluation of Computationally Designed Nanoparticles of Molecular Imprinted Polymers as Drug Delivery Systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 424, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowen, T.; Busato, M.; Karim, K.; Piletsky, T.; Cowen, S.A.; Karim, K.; Piletsky, S.A.; Busato, M. In Silico Synthesis of Synthetic Receptors: A Polymerization Algorithm. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2016, 37, 2011–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowen, T.; Karim, K.; Piletsky, S.A. Solubility and Size of Polymer Nanoparticles. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 4566–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, S.; Piletsky, S.S.; Yesilkaya, H.; Gazioglu, O.; Habtom, M.; Canfarotta, F.; Piletska, E.; Spivey, A.C.; Aboagye, E.O.; Piletsky, S.A. Assessing the In Vivo Biocompatibility of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles. Polymers 2022, 14, 4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 32, 1806328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, K.; Medina Rangel, P.X.; Bui, B.T.S. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Antibody Mimics for Bioimaging and Therapy. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 9554–9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieshaber, D.; MacKenzie, R.; Vörös, J.; Reimhult, E. Electrochemical Biosensors—Sensor Principles and Architectures. Sensors 2008, 8, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monzó, J.; Insua, I.; Fernandez-Trillo, F.; Rodriguez, P. Fundamentals, Achievements and Challenges in the Electrochemical Sensing of Pathogens. Analyst 2015, 140, 7116–7128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhito, I.R.; Koo, K.M.; Kim, T.H. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Sensors for the Detection of Biomolecules and Whole Cells. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wackerlig, J.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles in Chemical Sensing—Synthesis, Characterisation and Application. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 2015, 207, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzi, D.; Saputri, F.A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles (MIP-NPs) Applications in Electrochemical Sensors. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2019, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayerdurai, V.; Cieplak, M.; Kutner, W. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Food Contaminants Determination. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 158, 116830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.I.; Khan, M.S.; Mustafa, G.; Asmatullah; Ullah, I. Sensors as a Modern Tool for the Detection of Cephalosporin Antibiotics in the Environment: A Short Review. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2021, 17, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanoun, O.; Lazarević-Pašti, T.; Pašti, I.; Nasraoui, S.; Talbi, M.; Brahem, A.; Adiraju, A.; Sheremet, E.; Rodriguez, R.D.; Ben Ali, M.; et al. A Review of Nanocomposite-Modified Electrochemical Sensors for Water Quality Monitoring. Sensors 2021, 21, 4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, L.; Dennany, L. Applications of Electrochemical Sensors: Forensic Drug Analysis. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2017, 3, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Choo, J.; Chen, L. Molecular Imprinting: Green Perspectives and Strategies. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Hamielec, A. Polymerization Kinetic Modeling and Macromolecular Reaction Engineering. Polym. Sci. 2012, 4, 779–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Cruz, L.A.; Velazco-Medel, M.A.; Bucio, E. Aqueous Polymerizations; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardeshi, S.; Singh, S.K. Precipitation Polymerization: A Versatile Tool for Preparing Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Beads for Chromatography Applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 23525–23536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfarotta, F.; Poma, A.; Guerreiro, A.; Piletsky, S. Solid-Phase Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samui, A.B. Functionalized Nanomaterials for Environmental Applications. In Functionalized Nanomaterials Based Devices for Environmental Applications, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 303–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asua, J.M. Polymer Reaction Engineering; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motaharian, A.; Motaharian, F.; Abnous, K. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles-Based Electrochemical Sensor for Determination of Diazinon Pesticide in Well Water and Apple Fruit Samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 6769–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, T.; Ganjali, M.R.; Rafiei, F.; Akhoundian, M. Synthesis of Nano-Sized Timolol-Imprinted Polymer via Ultrasonication Assisted Suspension Polymerization in Silicon Oil and Its Use for the Fabrication of Timolol Voltammetric Sensor. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.V.; Fletcher, C.; Armitage, R.; Blackburn, C.; Turner, N.W. A Rapid Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles for the Extraction of Performance Enhancing Drugs (PIEDs). Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 5352–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, S.N.; Nishida, K.; Shiomoto, S.; Tanaka, M. Surfactant-Free Suspension Polymerization of Hydrophilic Monomers with an Oil-in-Water System for the Preparation of Microparticles toward the Selective Isolation of Tumor Cells. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 5043–5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.B.; Pathak, P.K. Development of Surface Imprinted Nanospheres Using the Inverse Suspension Polymerization Method for Electrochemical Ultra Sensing of Dacarbazine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 974, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Włoch, M.; Datta, J. Synthesis and Polymerisation Techniques of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2019, 86, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, P.A.; Schork, F.J. Fundamentals of Emulsion Polymerization. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 4396–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umoren, S.A.; Solomon, M.M.; Saji, V.S. Basic Polymer Concepts I. Polym. Mater. Corros. Inhib. 2022, 3–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capek, I. On Inverse Miniemulsion Polymerization of Conventional Water-Soluble Monomers. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 156, 35–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaneh, S.; Asadi, E.; Abdouss, M.; Barghi-Lish, A.; Azodi-Deilami, S.; Khonakdar, H.A.; Gharghabi, M. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles for Olanzapine Recognition: Application for Solid Phase Extraction and Sustained Release. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 9154–9166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Amaral, M.; Asua, J.M. Synthesis of Large, High-Solid-Content Latexes by Miniemulsion Polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2004, 42, 4222–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, K.; Kawaguchi, H. High-Performance Fluorescent Particles Prepared via Miniemulsion Polymerization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 285, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeng, J.; Dai, C.A.; Chiu, W.Y.; Chern, C.S.; Lin, K.F.; Young, P.Y. Influence of Hexadecane on the Formation of Droplets and Growth of Particles for Methyl Methacrylate Miniemulsion Polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2006, 44, 4603–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J.C.; Herrera-Ordonez, J.; Gonzalez, V.A. Kinetics of Styrene Minisuspension Polymerization Using a Mixture PVA–SDS as Stabilizer. Polymer 2006, 47, 3336–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourfarzib, M.; Shekarchi, M.; Rastegar, H.; Akbari-Adergani, B.; Mehramizi, A.; Dinarvand, R. Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles Prepared by Miniemulsion Polymerization as a Sorbent for Selective Extraction and Purification of Efavirenz from Human Serum and Urine. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 974, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandyari-Manesh, M.; Darvishi, B.; Ishkuh, F.A.; Shahmoradi, E.; Mohammadi, A.; Javanbakht, M.; Dinarvand, R.; Atyabi, F. Paclitaxel Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-PEG-Folate Nanoparticles for Targeting Anticancer Delivery: Characterization and Cellular Cytotoxicity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 62, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozgur, F.O.; Çimen, D.; Denizli, A.; Bereli, N. Surface Plasmon Resonance Based Sensor for Amaranth Detection With Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles. Photonic Sens. 2023, 13, 230201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, P.; Riegger, B.R.; Niedergall, K.; Tovar, G.E.M.; Bach, M.; Gauglitz, G. Nano-MIP Based Sensor for Penicillin G: Sensitive Layer and Analytical Validation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 267, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorakova, G.; Haschick, R.; Chiad, K.; Klapper, M.; Müllen, K.; Biffis, A. Molecularly Imprinted Nanospheres by Nonaqueous Emulsion Polymerization. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 2035–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorakova, G.; Haschick, R.; Klapper, M.; Müllen, K.; Biffis, A. Nonaqueous Emulsion Polymerization: A Practical Synthetic Route for the Production of Molecularly Imprinted Nanospheres. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2013, 51, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackerlig, J.; Schirhagl, R. Applications of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles and Their Advances toward Industrial Use: A Review. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Gao, R.; Gou, Q.; Lai, J.; Li, X. Precipitation Polymerization: A Powerful Tool for Preparation of Uniform Polymer Particles. Polymers 2022, 14, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Weiss, R.; Mosbach, K. Synthesis and Characterization of Molecularly Imprinted Microspheres. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 8239–8245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirhagl, R.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Dickert, F.L. Chemosensors for Viruses Based on Artificial Immunoglobulin Copies. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2078–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adumitrăchioaie, A.; Tertiş, M.; Cernat, A.; Săndulescu, R.; Cristea, C. Electrochemical Methods Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Drug Detection. A Review. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 2556–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contin, M.; Bonelli, P.; Lucangioli, S.; Cukierman, A.; Tripodi, V. Synthesis and Characterization of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles for Coenzyme Q10 Dispersive Micro Solid Phase Extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1456, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosrokhavar, R.; Motaharian, A.; Milani Hosseini, M.R.; Mohammadsadegh, S. Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode (SPCE) Modified by Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIP) Nanoparticles and Graphene Nanosheets for Determination of Sertraline Antidepressant Drug. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebali, A.; Abdouss, M.; Kazemi, Y.; Daneshnia, S. Fabrication and Characterization of PH-Responsive Poly (Methacrylic Acid)-Based Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Nanosphere for Controlled Release of Amitriptyline Hydrochloride. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 4386–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Wu, T.; Liu, Z.; Gao, S.; Hao, J. Application of Molecular Imprinting Technology Based on New Nanomaterials in Adsorption and Detection of Fluoroquinolones. Anal. Methods 2023, 15, 2467–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouk, M.; Hammad, S.F.; Abdella, A.A.; Mansour, F.R. Tipps and Tricks for Successful Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Analytical Applications: A Critical Review. Microchem. J. 2023, 193, 109152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Muhammad, T.; Yakup, B.; Piletsky, S.A. New Immobilisation Protocol for the Template Used in Solid-Phase Synthesis of MIP Nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 406, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poma, A.; Guerreiro, A.; Caygill, S.; Moczko, E.; Piletsky, S. Automatic Reactor for Solid-Phase Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Polymeric Nanoparticles (MIP NPs) in Water. RSC Adv. 2013, 4, 4203–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Yan, Y.J.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K. Thermo-Sensitive Imprinted Polymer Embedded Carbon Dots Using Epitope Approach. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Ambrosini, S.; Tamahkar, E.; Rossi, C.; Haupt, K.; Tse Sum Bui, B. Toward a Universal Method for Preparing Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles with Antibody-like Affinity for Proteins. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, S.P.B.; Reis, R.L.; Peppas, N.A.; Gomes, M.E.; Domingues, R.M.A. Epitope-Imprinted Polymers: Design Principles of Synthetic Binding Partners for Natural Biomacromolecules. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabi9884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Mutio, D.; Gomez-Caballero, A.; Guerreiro, A.; Piletsky, S.; Goicolea, M.A.; Barrio, R.J. Solid-Phase Synthesis of Imprinted Nanoparticles Grafted on Gold Substrates for Voltammetric Sensing of 4-Ethylphenol. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 236, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crapnell, R.D.; Canfarotta, F.; Czulak, J.; Johnson, R.; Betlem, K.; Mecozzi, F.; Down, M.P.; Eersels, K.; Van Grinsven, B.; Cleij, T.J.; et al. Thermal Detection of Cardiac Biomarkers Heart-Fatty Acid Binding Protein and ST2 Using a Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticle-Based Multiplex Sensor Platform. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2838–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalera, S.; Chiarello, M.; Di Nardo, F.; Anfossi, L.; Baggiani, C. Effect of experimental conditions on the binding abilities of ciprofloxacin-imprinted nanoparticles prepared by solid-phase synthesis. Reac. And Func. Pol. 2021, 163, 104893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosini, S.; Beyazit, S.; Haupt, K.; Tse Sum Bui, B. Solid-Phase Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles for Protein Recognition. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6746–6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourão, C.A.; Bokeloh, F.; Xu, J.; Prost, E.; Duma, L.; Merlier, F.; Bueno, S.M.A.; Haupt, K.; Tse Sum Bui, B. Dual-Oriented Solid-Phase Molecular Imprinting: Toward Selective Artificial Receptors for Recognition of Nucleotides in Water. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 7484–7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khumsap, T.; Corpuz, A.; Nguyen, L.T. Epitope-Imprinted Polymers: Applications in Protein Recognition and Separation. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 11403–11414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Tan, T.; Svec, F. Molecular Imprinting of Proteins in Polymers Attached to the Surface of Nanomaterials for Selective Recognition of Biomacromolecules. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1172–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moczko, E.; Guerreiro, A.; Cáceres, C.; Piletska, E.; Sellergren, B.; Piletsky, S.A. Epitope Approach in Molecular Imprinting of Antibodies. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1124, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera León, C.; Kalacas, N.A.; Mier, A.; Sakhaii, P.; Merlier, F.; Prost, E.; Maffucci, I.; Montagna, V.; Mora-Radó, H.; Dhal, P.K.; et al. Synthetic Peptide Antibodies as TNF-α Inhibitors: Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanogels Neutralize the Inflammatory Activity of TNF-α in THP-1 Derived Macrophages. Angew. Chem. 2023, 135, e202306274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina Rangel, P.X.; Laclef, S.; Xu, J.; Panagiotopoulou, M.; Kovensky, J.; Tse Sum Bui, B.; Haupt, K. Solid-Phase Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanolabels: Affinity Tools for Cellular Bioimaging of Glycans. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.J. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Microsphere Prepared by Precipitation Polymerization for Hydroquinone Recognition. Talanta 2008, 75, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Ju, X.; Qiu, S.; Hu, W.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J. Fast and Sensitive Detection of Diisononyl Phthalate in Liquor Sample by Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Electrochemical Sensor. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2018, 54, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriz, D.; Mosbach, K. Competitive Amperometric Morphine Sensor Based on an Agarose Immobilised Molecularly Imprinted Polymer. Anal. Chim. Acta 1995, 300, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ji, X.F.; Cao, W.Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhong, T.L.; Wang, Y. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Sensor Directly Responsive to Attomole Bovine Serum Albumin. Talanta 2019, 196, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Shannon, C. Electrochemical Sensors Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Grafted onto Gold Electrodes Using Click Chemistry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 708, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, F.; del Valle, M. Voltammetric Sensor for Theophylline Using Sol–Gel Immobilized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Particles. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Chacón, A.; Cetó, X.; del Valle, M. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers—Towards Electrochemical Sensors and Electronic Tongues. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 6117–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, J.D.R.M.; Santos, W.D.J.R.; Lima, P.R.; Tanaka, S.M.C.N.; Tanaka, A.A.; Kubota, L.T. A Hemin-Based Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIP) Grafted onto a Glassy Carbon Electrode as a Selective Sensor for 4-Aminophenol Amperometric. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 152, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.; Yang, S.; Tang, W.; Zhang, F.; He, P. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers-Based Electrochemical DNA Biosensor for the Determination of BRCA-1 Amplified by SiO2@Ag. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 112, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zeng, B. A Molecularly Imprinted Copolymer Based Electrochemical Sensor for the Highly Sensitive Detection of L-Tryptophan. Talanta 2020, 206, 120245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotta, E.; Turco, A.; Chianella, I.; Guerreiro, A.; Piletsky, S.A.; Malitesta, C. Solid-Phase Synthesis of Electroactive Nanoparticles of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. A Novel Platform for Indirect Electrochemical Sensing Applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 229, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, T.; Nayeri, S.; Mirzaee, S. A High Performance Potentiometric Sensor for Lactic Acid Determination Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer/MWCNTs/PVC Nanocomposite Film Covered Carbon Rod Electrode. Talanta 2019, 192, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Chacon, A.; González-Calabuig, A.; Campos, I.; del Valle, M. Bioelectronic Tongue Using MIP Sensors for the Resolution of Volatile Phenolic Compounds. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakas, I.; Hayat, A.; Piletsky, S.; Piletska, E.; Chehimi, M.M.; Noguer, T.; Rouillon, R. Electrochemical Impedimetric Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers/Sol-Gel Chemistry for Methidathion Organophosphorous Insecticide Recognition. Talanta 2014, 130, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayanan, V.; Wu, C.T.; Ho, K.C. Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensors. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 1795–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.S.; Iskierko, Z.; Pietrzyk-Le, A.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Bioinspired Intelligent Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Chemosensing: A Mini Review. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 50, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotta, E.; Picca, R.A.; Malitesta, C.; Piletsky, S.A.; Piletska, E.V. Development of a Sensor Prepared by Entrapment of MIP Particles in Electrosynthesised Polymer Films for Electrochemical Detection of Ephedrine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.C.; Yeh, W.M.; Tung, T.S.; Liao, J.Y. Amperometric Detection of Morphine Based on Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene) Immobilized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Particles Prepared by Precipitation Polymerization. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 542, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granado, V.L.V.; Gutiérrez-Capitán, M.; Fernández-Sánchez, C.; Gomes, M.T.S.R.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Jimenez-Jorquera, C. Thin-Film Electrochemical Sensor for Diphenylamine Detection Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 809, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyoti; Gonzato, C.; Żołek, T.; Maciejewska, D.; Kutner, A.; Merlier, F.; Haupt, K.; Sharma, P.S.; Noworyta, K.R.; Kutner, W. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles-Based Electrochemical Chemosensors for Selective Determination of Cilostazol and Its Pharmacologically Active Primary Metabolite in Human Plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 193, 113542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, A.; Srivastava, J.; Singh, A.K.; Anand, R.; Raghuwanshi, R.; Rai, T.; Singh, M. Epitope Imprinting of Mycobacterium Leprae Bacteria via Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles Using Multiple Monomers Approach. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 145, 111698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aurelio, R.; Chianella, I.; Goode, J.A.; Tothill, I.E. Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles Based Sensor for Cocaine Detection. Biosensors 2020, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cruz, A.; Ahmad, O.S.; Alanazi, K.; Piletska, E.; Piletsky, S.A. Generic Sensor Platform Based on Electro-Responsive Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles (e-NanoMIPs). Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Masi, S.; Costa, M.; Canfarotta, F.; Guerreiro, A.; Hartley, A.; Piletsky, S.A.; Malitesta, C. An Impedimetric Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles for the Determination of Trypsin in Artificial Matrices—Towards Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Anal. Methods 2024, 16, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, A.; Trimpert, J.; Abdulhalim, I.; Altintas, Z. Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles for SARS-CoV-2 Virus Detection Using Surface Plasmon Resonance. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cruz, A.; Haq, I.; Cowen, T.; Di Masi, S.; Trivedi, S.; Alanazi, K.; Piletska, E.; Mujahid, A.; Piletsky, S.A. Design and Fabrication of a Smart Sensor Using in Silico Epitope Mapping and Electro-Responsive Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles for Determination of Insulin Levels in Human Plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canfarotta, F.; Czulak, J.; Guerreiro, A.; Cruz, A.G.; Piletsky, S.; Bergdahl, G.E.; Hedström, M.; Mattiasson, B. A Novel Capacitive Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles as Recognition Elements. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 120, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, J.; Seumo Tchekwagep, P.M.; Vilela Strapazon, A.L.; Canfarotta, F.; Thomson, A.; Czulak, J.; Johnson, R.E.; Novakovic, K.; Losada-Pérez, P.; Zaman, A.; et al. Immobilization of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles onto Surfaces Using Different Strategies: Evaluating the Influence of the Functionalized Interface on the Performance of a Thermal Assay for the Detection of the Cardiac Biomarker Troponin I. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 27868–27879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, J.; Bar, L.; Singla, P.; Canfarotta, F.; Thomson, A.; Czulak, J.; Johnson, R.E.; Crapnell, R.D.; Banks, C.E.; Payne, B.; et al. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles Enable Rapid, Reliable, and Robust Point-of-Care Thermal Detection of SARS-CoV-2. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singla, P.; Kaur, S.; Jamieson, O.; Dann, A.; Garg, S.; Mahon, C.; Crapnell, R.D.; Banks, C.E.; Kaur, I.; Peeters, M. Electrochemical and Thermal Detection of Allergenic Substance Lysozyme with Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 4467–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarejousheghani, M.; Rahimi, P.; Borsdorf, H.; Zimmermann, S.; Joseph, Y. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for Priority Pollutants. Sensors 2021, 21, 2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afsharara, H.; Asadian, E.; Mostafiz, B.; Banan, K.; Bigdeli, S.A.; Hatamabadi, D.; Keshavarz, A.; Hussain, C.M.; Keçili, R.; Ghorbani-Bidkorpeh, F. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Modified Carbon Paste Electrodes (MIP-CPE): A Review on Sensitive Electrochemical Sensors for Pharmaceutical Determinations. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 160, 116949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadem, M.; Faridbod, F.; Norouzi, P.; Foroushani, A.R.; Ganjali, M.R.; Shahtaheri, S.J. Biomimetic Electrochemical Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Dicloran Pesticide Determination in Biological and Environmental Samples. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2016, 13, 2077–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholivand, M.B.; Torkashvand, M. A Novel High Selective and Sensitive Metronidazole Voltammetric Sensor Based on a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Carbon Paste Electrode. Talanta 2011, 84, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, T.; Zare, M.; Ganjali, M.R.; Norouzi, P.; Tavana, B. A New Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIP)-Based Electrochemical Sensor for Monitoring 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene (TNT) in Natural Waters and Soil Samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolinska-Kempisty, K.; Ahmad, O.S.; Guerreiro, A.; Karim, K.; Piletska, E.; Piletsky, S. New Potentiometric Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles for Cocaine Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 96, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardalani, M.; Shamsipur, M.; Besharati-seidani, A. A New Generation of Highly Sensitive Potentiometric Sensors Based on Ion Imprinted Polymeric Nanoparticles/Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes/Polyaniline/Graphite Electrode for Sub-Nanomolar Detection of Lead (II) Ions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 879, 114788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotta, E.; Di Giulio, T.; Malitesta, C. Electrochemical Sensing of Macromolecules Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Challenges, Successful Strategies, and Opportunities. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 5165–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, T.; Azizi, S. Graphene/Graphite Paste Electrode Incorporated with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles as a Novel Sensor for Differential Pulse Voltammetry Determination of Fluoxetine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enache, T.A.; Oliveira-Brett, A.M. Phenol and Para-Substituted Phenols Electrochemical Oxidation Pathways. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2011, 655, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.S.; Garcia-Cruz, A.; Cieplak, M.; Noworyta, K.R.; Kutner, W. ‘Gate Effect’ in Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: The Current State of Understanding. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 16, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, Y.; Morali, U.; Erol, S.; Avci, H. Investigation of Electrochemical Behavior of Potassium Ferricyanide/Ferrocyanide Redox Probes on Screen Printed Carbon Electrode through Cyclic Voltammetry and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. Turkish J. Chem. 2021, 45, 1895–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrattenecker, J.D.; Heer, R.; Melnik, E.; Maier, T.; Fafilek, G.; Hainberger, R. Hexaammineruthenium (II)/(III) as Alternative Redox-Probe to Hexacyanoferrat (II)/(III) for Stable Impedimetric Biosensing with Gold Electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 127, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Li, B.; Xu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X. A Fabrication Strategy for Protein Sensors Based on an Electroactive Molecularly Imprinted Polymer: Cases of Bovine Serum Albumin and Trypsin Sensing. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1117, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, I.; Alanazi, K.; Czulak, J.; Di Masi, S.; Piletska, E.; Mujahid, A.; Hussain, T.; Piletsky, S.A.; Garcia-Cruz, A. Determination of Sitagliptin in Human Plasma Using a Smart Electrochemical Sensor Based on Electroactive Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 4276–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lach, P.; Garcia-Cruz, A.; Canfarotta, F.; Groves, A.; Kalecki, J.; Korol, D.; Borowicz, P.; Nikiforow, K.; Cieplak, M.; Kutner, W.; et al. Electroactive Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles for Selective Glyphosate Determination. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 236, 115381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri-Manesh, A.; Mousazadeh, M.; Nikkhah, M.; Abbasian, S.; Moshaii, A.; Masroor, M.J.; Norouzi, P. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Chemiresistive Sensor for Detection of Nonanal as a Cancer Related Biomarker. Microchem. J. 2022, 173, 106988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheydaei, O.; Khajehsharifi, H.; Rajabi, H.R. Rapid and Selective Diagnose of Sarcosine in Urine Samples as Prostate Cancer Biomarker by Mesoporous Imprinted Polymeric Nanobeads Modified Electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 309, 127559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korol, D.; Kisiel, A.; Cieplak, M.; Michalska, A.; Sharma, P.S.; Maksymiuk, K. Synthesis of Conducting Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles for Estriol Chemosensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 382, 133476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, I.; Garcia Cruz, A.; Di Masi, S.; Cowen, T.; Allcock, N.S.; Malitesta, C.; Mujahid, A.; Hussain, T.; Piletska, E.; Piletsky, S.A. Smart Nano-Actuators for Electrochemical Sensing of Metformin in Human Plasma. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 376, 132928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, K.; Garcia Cruz, A.; Di Masi, S.; Voorhaar, A.; Ahmad, O.S.; Cowen, T.; Piletska, E.; Langford, N.; Coats, T.J.; Sims, M.R.; et al. Disposable Paracetamol Sensor Based on Electroactive Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles for Plasma Monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, R.; Xu, S.; Cai, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, W.; Liu, X.; Luo, J. Molecularly Imprinted Polymeric Nanoparticles Decorated with Au NPs for Highly Sensitive and Selective Glucose Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munawar, H.; Garcia-Cruz, A.; Majewska, M.; Karim, K.; Kutner, W.; Piletsky, S.A. Electrochemical Determination of Fumonisin B1 Using a Chemosensor with a Recognition Unit Comprising Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 321, 128552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basozabal, I.; Guerreiro, A.; Gomez-Caballero, A.; Aranzazu Goicolea, M.; Barrio, R.J. Direct Potentiometric Quantification of Histamine Using Solid-Phase Imprinted Nanoparticles as Recognition Elements. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 58, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truta, F.; Garcia Cruz, A.; Tertis, M.; Zaleski, C.; Adamu, G.; Allcock, N.S.; Suciu, M.; Ștefan, M.G.; Kiss, B.; Piletska, E.; et al. NanoMIPs-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Selective Detection of Amphetamine. Microchem. J. 2023, 191, 108821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truta, F.M.; Cruz, A.G.; Dragan, A.M.; Tertis, M.; Cowen, T.; Stefan, M.G.; Topala, T.; Slosse, A.; Piletska, E.; Van Durme, F.; et al. Design of Smart Nanoparticles for the Electrochemical Detection of 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine to Allow in Field Screening by Law Enforcement Officers. Drug Test. Anal. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojdi, K.M.; Hossein, M.; Behbahani, M. Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Novel Lead Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles as a High Selective Electrochemical Sensor for Ultra-Trace Determination of Lead Ions in Complex Matrixes. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 136, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, T.; Hamidi, N.; Ganjali, M.R.; Rafiei, F. Determination of Subnanomolar Levels of Mercury(II) by Using a Graphite Paste Electrode Modified with MWCNTs and Hg(II)-Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles. Microchimica 2018, 185, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samandari, L.; Bahrami, A.; Shamsipur, M.; Farzin, L.; Hashemi, B. Electrochemical Preconcentration of Ultra-Trace Cd2+ from Environmental and Biological Samples Prior to Its Determination Using Carbon Paste Electrode Impregnated with Ion Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 99, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Masi, S.; Garcia Cruz, A.; Canfarotta, F.; Cowen, T.; Marote, P.; Malitesta, C.; Piletsky, S.A. Synthesis and Application of Ion-Imprinted Nanoparticles in Electrochemical Sensors for Copper (II) Determination. ChemNanoMat 2019, 5, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A.H.; Jiang, X.; Li, P.; Liang, R. A Paper-Based Potentiometric Sensing Platform Based on Molecularly Imprinted Nanobeads for Determination of Bisphenol A. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 3890–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadem, M.; Faridbod, F.; Norouzi, P.; Rahimi Foroushani, A.; Ganjali, M.R.; Shahtaheri, S.J.; Yarahmadi, R. Modification of Carbon Paste Electrode Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Electrochemical Determination of Diazinon in Biological and Environmental Samples. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.T.; Figueiredo, R.; Azenha, M.; Jorge, P.A.S.; Pereira, C.M.; Ribeiro, J.A. Imprinted Hydrogel Nanoparticles for Protein Biosensing: A Review. ACS Sens. 2023, 8, 2898–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzone, P.J. Exhaled Breath Volatile Organic Compound Biomarkers in Lung Cancer. J. Breath Res. 2012, 6, 027106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gagliani, F.; Di Giulio, T.; Asif, M.I.; Malitesta, C.; Mazzotta, E. Boosting Electrochemical Sensing Performances Using Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles. Biosensors 2024, 14, 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14070358
Gagliani F, Di Giulio T, Asif MI, Malitesta C, Mazzotta E. Boosting Electrochemical Sensing Performances Using Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles. Biosensors. 2024; 14(7):358. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14070358
Chicago/Turabian StyleGagliani, Francesco, Tiziano Di Giulio, Muhammad Ibrar Asif, Cosimino Malitesta, and Elisabetta Mazzotta. 2024. "Boosting Electrochemical Sensing Performances Using Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles" Biosensors 14, no. 7: 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14070358
APA StyleGagliani, F., Di Giulio, T., Asif, M. I., Malitesta, C., & Mazzotta, E. (2024). Boosting Electrochemical Sensing Performances Using Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles. Biosensors, 14(7), 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14070358






