Development of a Tetherless Bioimpedance Device That Uses Morphologic Changes to Predict Blood Flow Restrictions Mimicking Peripheral Artery Disease Progression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
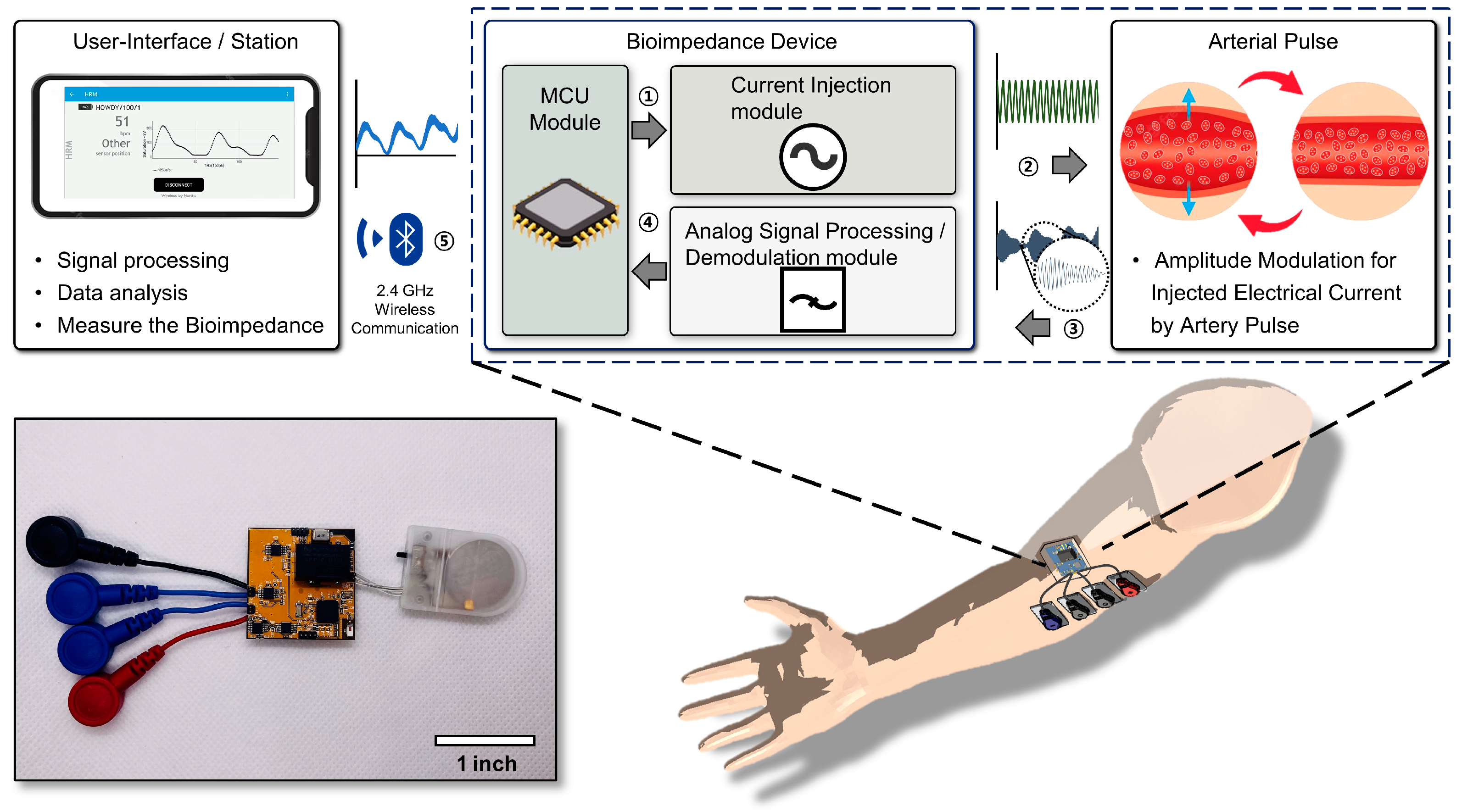
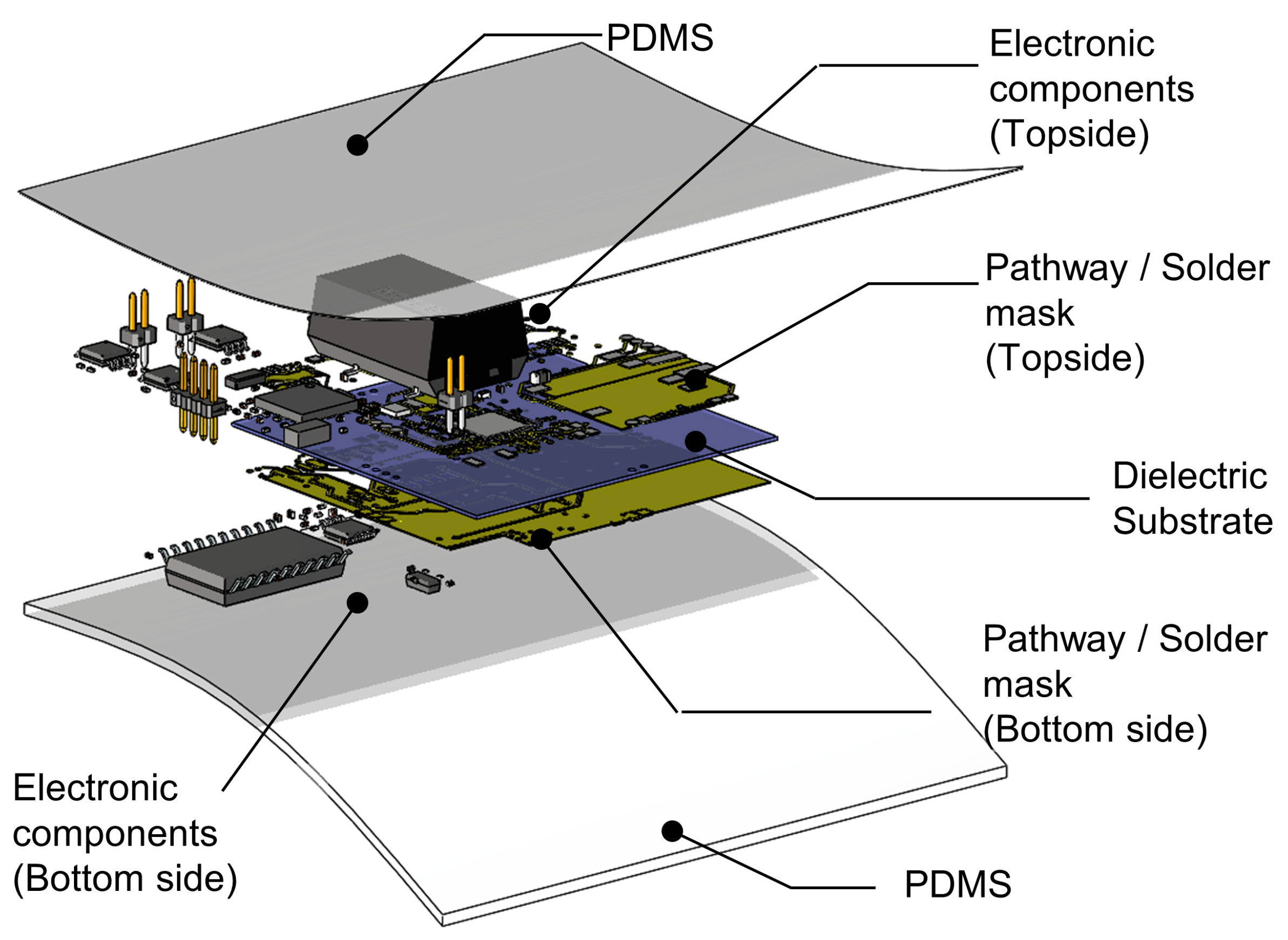
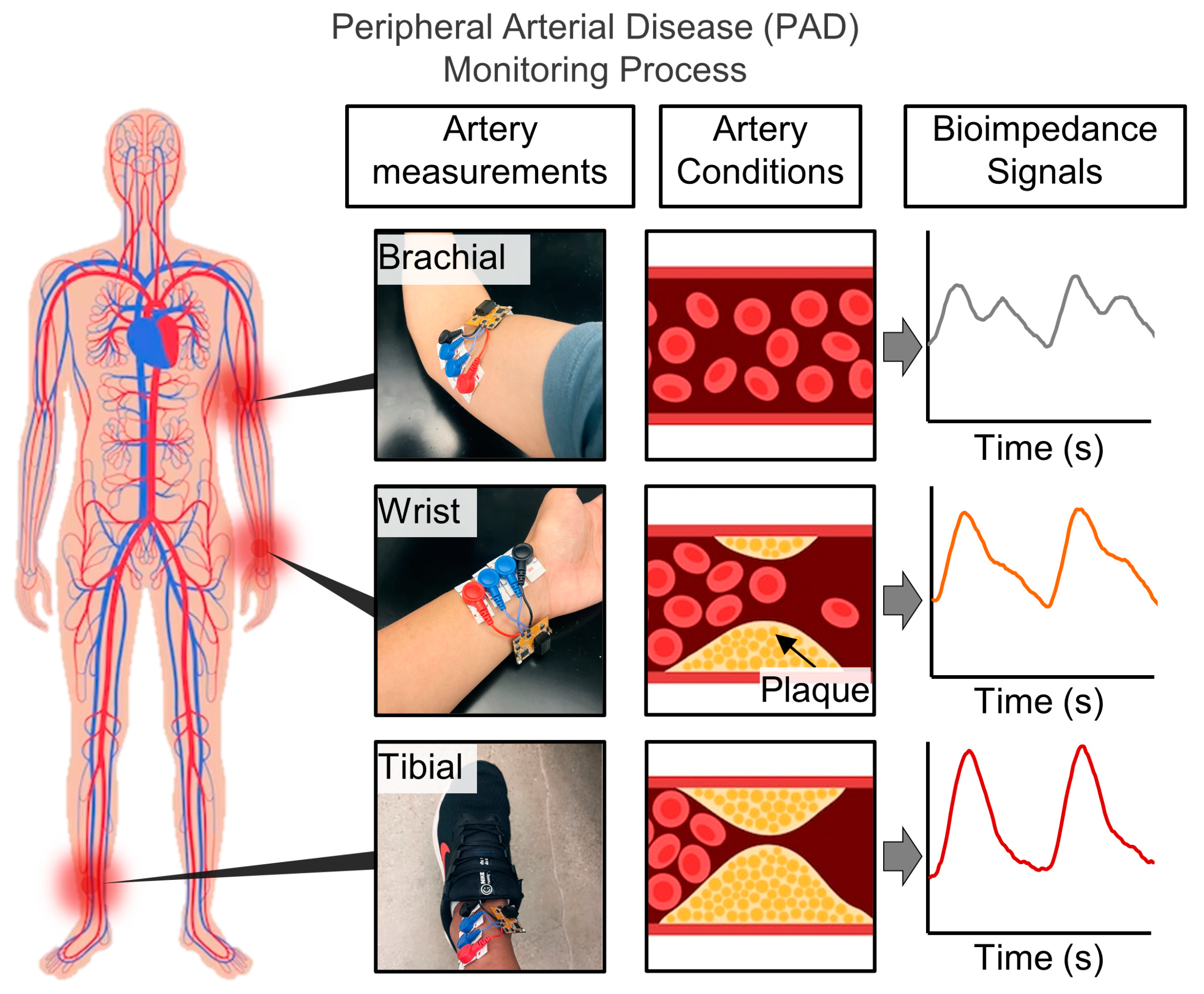
2.1. System Illustration and Target Locations on the Body
2.2. Bioimpedance Circuit and Node-by-Node Signal Examples
3. Results
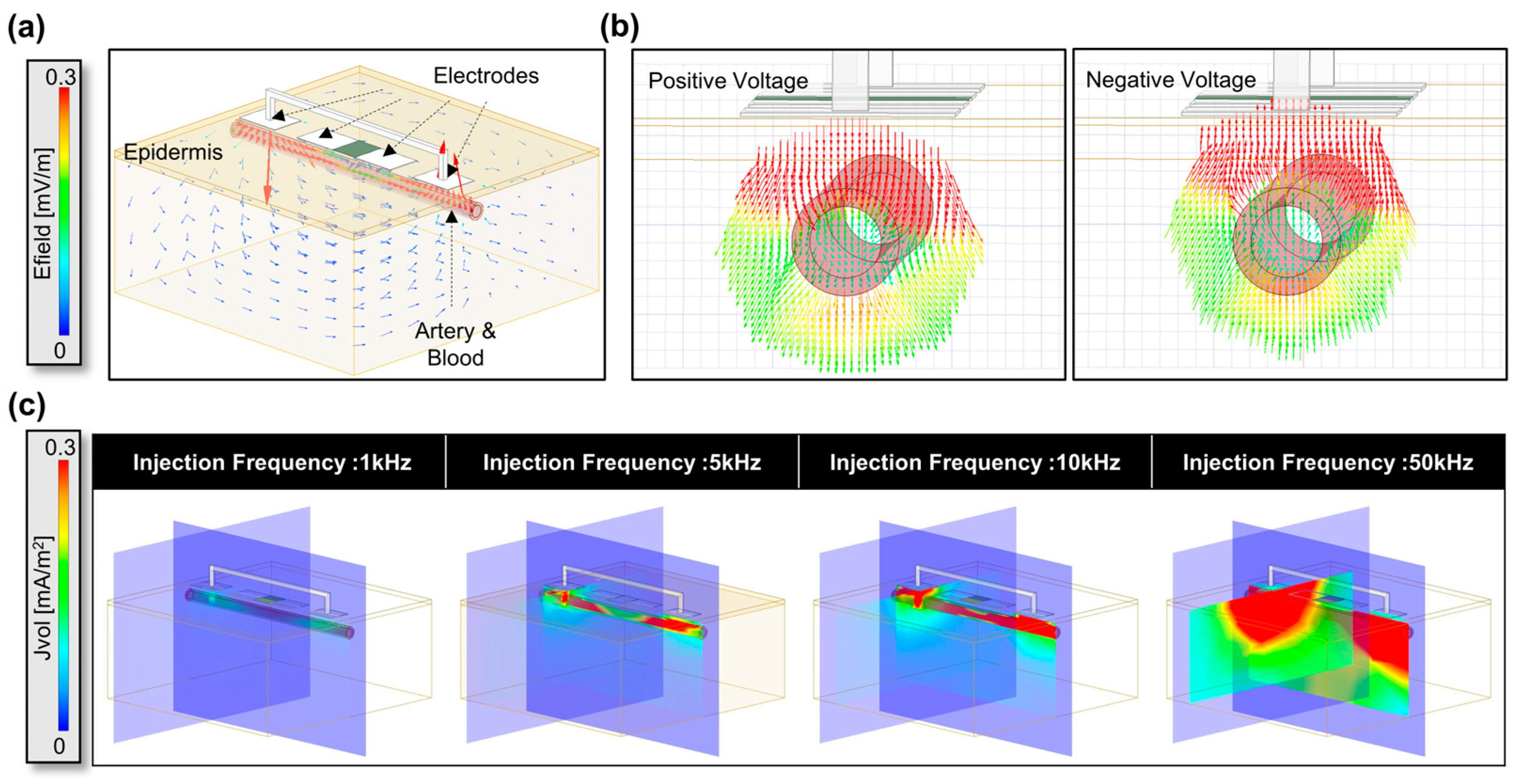
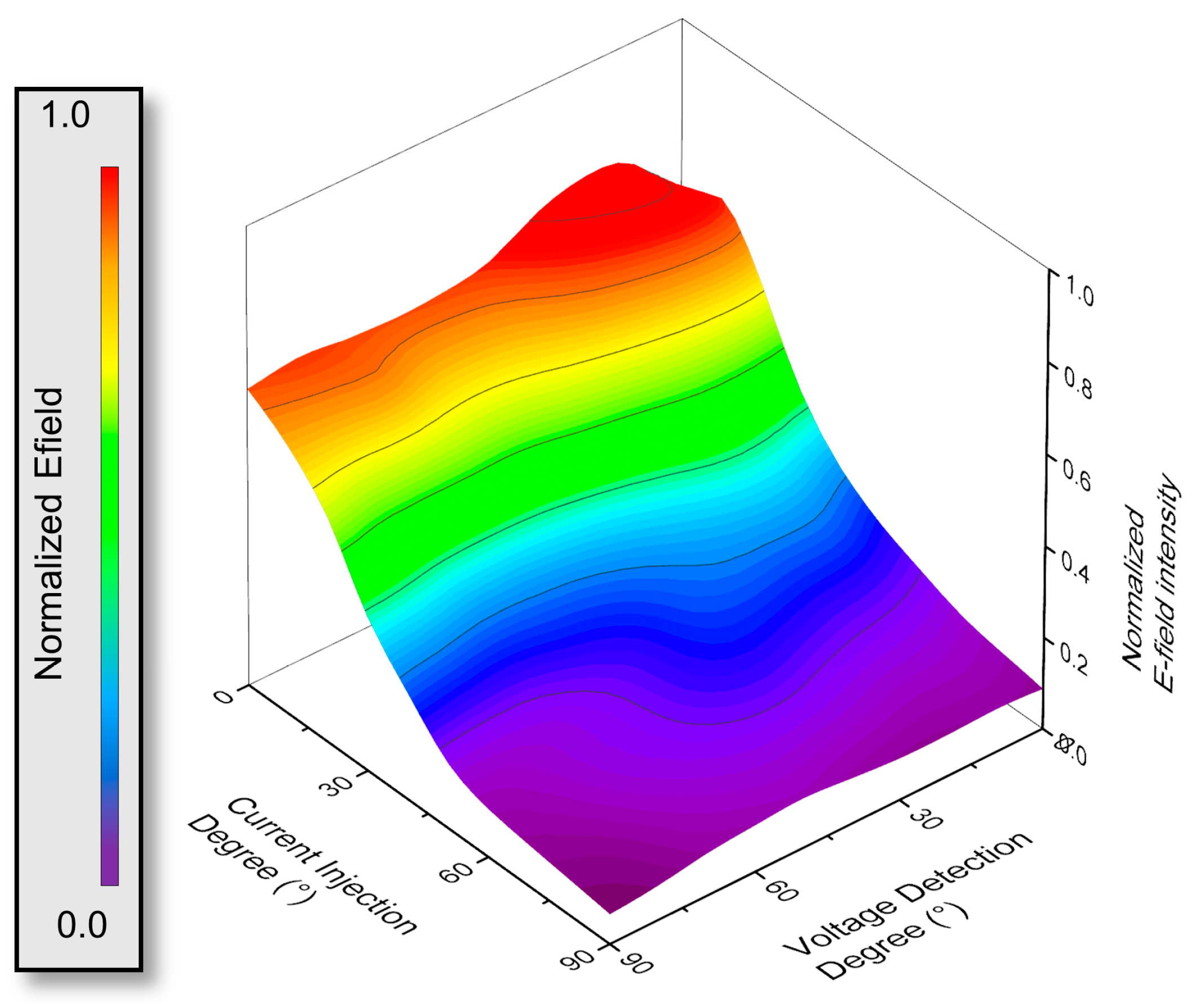
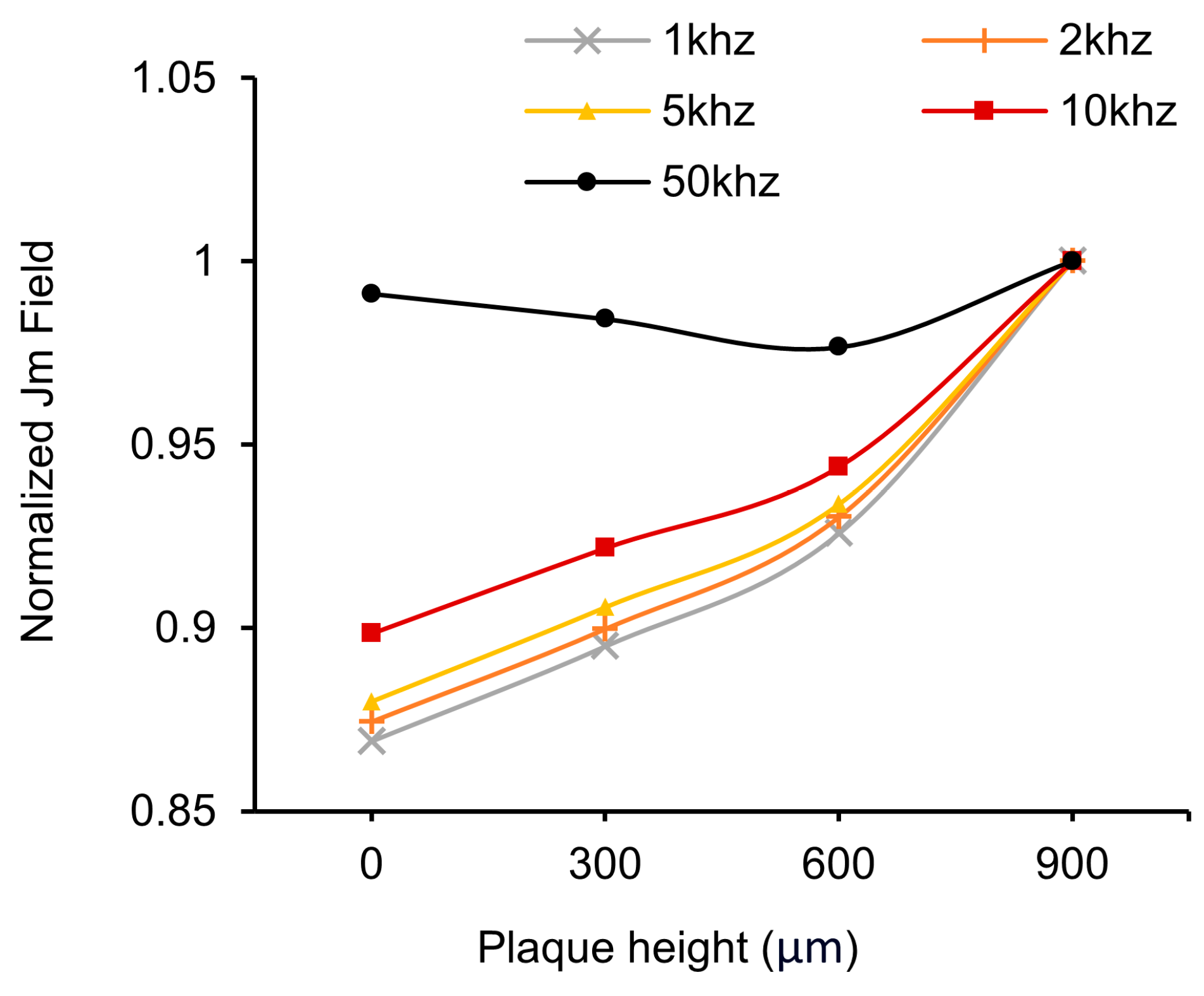
3.1. HFSS Simulation for Optimization
3.2. System Illustration and Target Locations on the Body
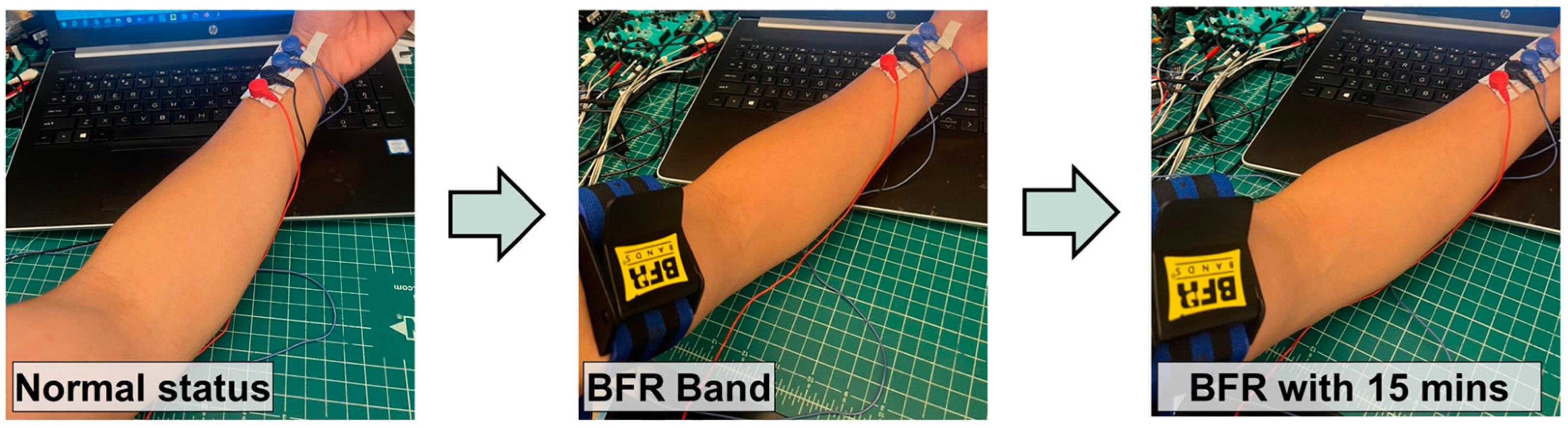
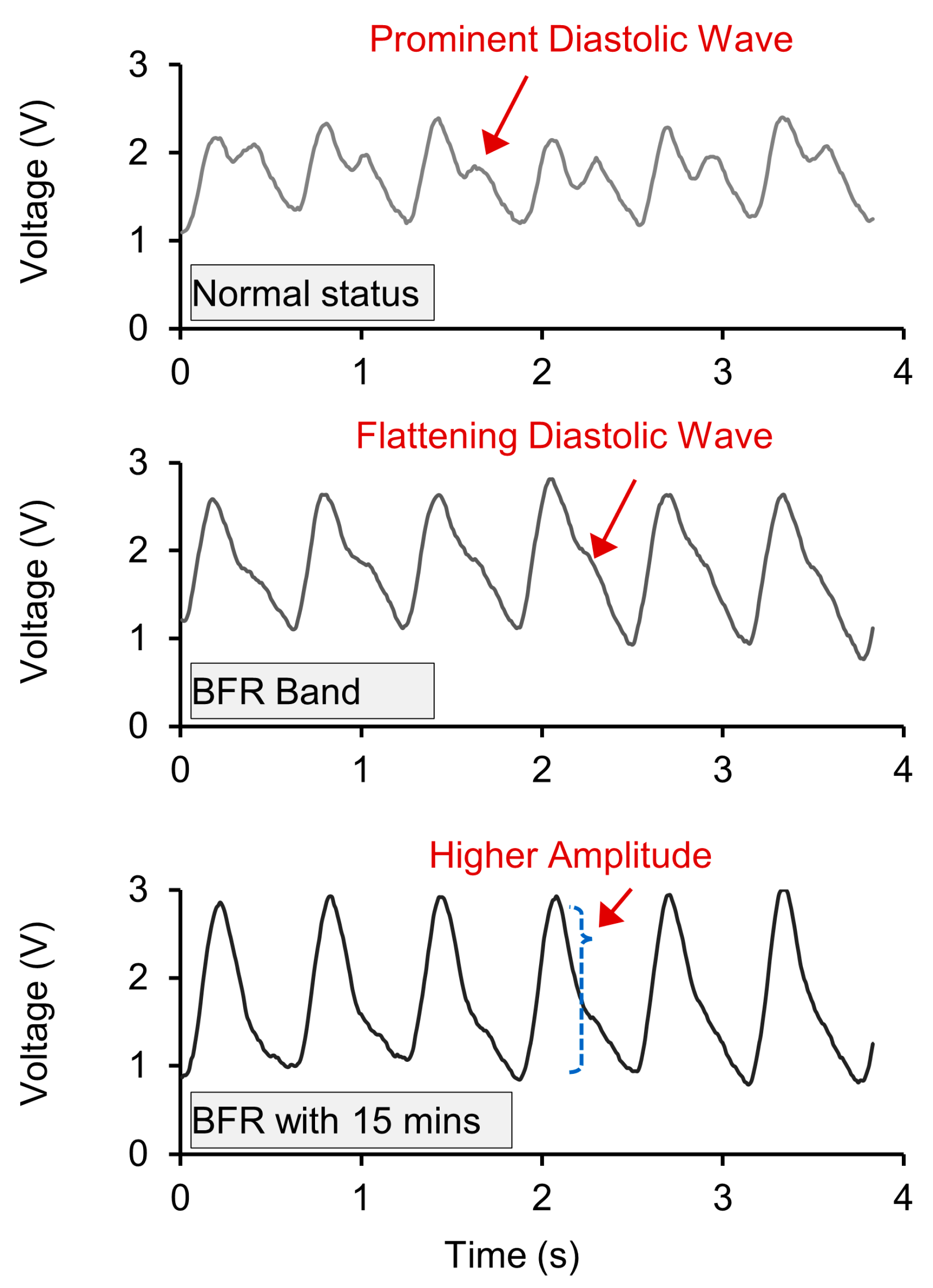
3.3. Bioimpedance Circuit and Node-by-Node Signal Examples
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hiatt, W.R.; Goldstone, J.; Smith Jr, S.C.; McDermott, M.; Moneta, G.; Oka, R.; Newman, A.B.; Pearce, W.H.; American Heart Association Writing Group 1. Atherosclerotic peripheral vascular disease symposium II: Nomenclature for vascular diseases. Circulation 2008, 118, 2826–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soor, G.S.; Vukin, I.; Leong, S.W.; Oreopoulos, G.; Butany, J. Peripheral vascular disease: Who gets it and why? A histomorphological analysis of 261 arterial segments from 58 cases. Pathology 2008, 40, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, N.; Li, Z.; Xu, S. Burden of peripheral artery disease and its attributable risk factors in 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 868370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammoud, A.; Tikhomirov, A.; Myasishcheva, G.; Shaheen, Z.; Volkov, A.; Briko, A.; Shchukin, S. Multi-channel bioimpedance system for detecting vascular tone in human limbs: An approach. Sensors 2021, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, S. Determination of Arterial Compliance Using Electrical Peripheral Bioimpedance. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2023, 18, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm, D.; Fukaya, E.; Leeper, N.J.; Ingelsson, E. Bioimpedance and New-Onset Heart Failure: A Longitudinal Study of >500 000 Individuals From the General Population. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e008970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, T.H.; Jafari, R.; Chung, W.-Y. A Robust Bioimpedance Structure for Smartwatch-Based Blood Pressure Monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shash, Y.H.; Eldosoky, M.A.A.; Elwakad, M.T. The effect of vascular diseases on bioimpedance measurements: Mathematical modeling. Biomed. Res. Ther. 2018, 5, 2414–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metshein, M.; Abdullayev, A.; Gautier, A.; Larras, B.; Frappe, A.; Cardiff, B.; Annus, P.; Land, R.; Märtens, O. Sensor-Location-Specific Joint Acquisition of Peripheral Artery Bioimpedance and Photoplethysmogram for Wearable Applications. Sensors 2023, 23, 7111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouwendijk, R.; de Vries, M.; Pattynama, P.M.T.; van Sambeek, M.R.H.M.; de Haan, M.W.; Stijnen, T.; van Engelshoven, J.M.A.; Hunink, M.G.M. Imaging peripheral arterial disease: A randomized controlled trial comparing contrast-enhanced MR angiography and multi–detector row CT angiography. Radiology 2005, 236, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, J.P.; Wilson, A.M. Biomarkers of peripheral arterial disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 2017–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwers, J.J.W.M.; Willems, S.A.; Goncalves, L.N.; Hamming, J.F.; Schepers, A. Reliability of Bedside Tests for Diagnosing Peripheral Arterial Disease in Patients Prone to Medial Arterial Calcification: A Systematic Review. EClinicalMedicine 2022, 50, 101532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wald, L.L.; McDaniel, P.C.; Witzel, T.; Stockmann, J.P.; Cooley, C.Z. Low-cost and portable MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 52, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, R.; Samian, S.; Mazli, M.Z.; Amrizal, M.N.; Aljunid, S.M. Cost of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scan in UKMMC. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2012, 12, P11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLane, H.C.; Berkowitz, A.L.; Patenaude, B.N.; McKenzie, E.D.; Wolper, E.; Wahlster, S.; Fink, G.; Mateen, F.J. Availability, accessibility, and affordability of neurodiagnostic tests in 37 countries. Neurology 2015, 85, 1614–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenemeyer, D.H.W.; Seibel, R.M.M. Interventional CT and MRI: A challenge for safety and cost reduction in the health care system. In Proceedings of the Health Care Technology Policy II: The Role of Technology in the Cost of Health Care: Providing the Solutions, Arlington, VA, USA, 10–12 May 1995; Volume 2499, pp. 132–148. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, L. Radiation exposure and diagnostic imaging. J. Am. Acad. Nurse Pract. 2010, 22, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semelka, R.C.; Armao, D.M.; Elias, J.; Huda, W. Imaging strategies to reduce the risk of radiation in CT studies, including selective substitution with MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2007, 25, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herfarth, H.; Palmer, L. Risk of radiation and choice of imaging. Dig. Dis. 2009, 27, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachopoulos, C.; Georgakopoulos, C.; Koutagiar, I.; Tousoulis, D. Diagnostic modalities in peripheral artery disease. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2018, 39, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criqui, M.H.; Matsushita, K.; Aboyans, V.; Hess, C.N.; Hicks, C.W.; Kwan, T.W.; McDermott, M.M.; Misra, S.; Ujueta, F. Lower extremity peripheral artery disease: Contemporary epidemiology, management gaps, and future directions: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 144, e171–e191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivunen, V.; Juonala, M.; Venermo, M.; Laivuori, M.; Jalkanen, J.M.; Hakovirta, H.H. Toe pressure and toe brachial index are predictive of cardiovascular mortality regardless of the most diseased arterial segment in symptomatic lower-extremity artery disease—A retrospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, Y.; Masaki, H.; Kojima, K.; Tanemoto, K. Toe-brachial index in the second toe: Substitutability to toe-brachial index in the great toe and ankle-brachial index. Ann. Vasc. Dis. 2016, 9, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, T.P.; Prasad, R.; Allison, M.A.; Criqui, M.C.; Ix, J.H.; Rifkin, D.E.; Garimella, P.S. Association of Ankle-Brachial and toe-Brachial Indexes with Mortality in patients with CKD. Kidney Med. 2020, 2, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Rourke, M.F.; Seward, J.B. Central arterial pressure and arterial pressure pulse: New views entering the second century after Korotkov. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2006, 81, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arain, F.A.; Cooper, L.T., Jr. Peripheral arterial disease: Diagnosis and management. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davila, M.I.; Lewis, G.F.; Porges, S.W. The Physiocam: A novel non-contact sensor to Measure heart rate Variability in clinical and Field applications. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedayatipour, A.; Aslanzadeh, S.; Hesari, S.H.; Haque, M.A.; McFarlane, N. A wearable CMOS impedance to frequency sensing system for non-invasive impedance measurements. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2020, 14, 1108–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweon, S.-J.; Rafi, A.K.; Cheon, S.-I.; Je, M.; Ha, S. On-chip sinusoidal signal generators for electrical impedance spectroscopy: Methodological review. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2022, 16, 337–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Coté, G. Arterial Pulse Wave Velocity Signal Reconstruction Using Low Sampling Rates. Biosensors 2024, 14, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sel, K.; Osman, D.; Jafari, R. Non-Invasive Cardiac and Respiratory Activity Assessment from Various Human Body Locations Using Bioimpedance. IEEE Open J. Eng. Med. Biol. 2021, 2, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaumann, R.; Xiao, H.; Mac, V.V. Design of Analog Filters, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press, Inc.: Oxford, UK, 2009; ISBN 0195373944. [Google Scholar]
- Cornish, B.H.; Ward, L.C.; Thomas, B.J.; Jebb, S.A.; Elia, M. Evaluation of Multiple Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance and Cole-Cole Analysis for the Assessment of Body Water Volumes in Healthy Humans. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 50, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.; Freeborn, T.J. Cole-impedance parameters representing biceps tissue bioimpedance in healthy adults and their alterations following eccentric exercise. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 25, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.-W.; Chen, W.-X.; Chu, H.-W.; Lin, S.-F. Single-channel bioimpedance measurement for wearable continuous blood pressure monitoring. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 70, 4001909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, C. Compilation of the Dielectric Properties of Body Tissues at RF and Microwave Frequencies; Defense Technical Information Center: Fort Belvoir, VA, USA, 1996.
- Vogel, J.; Niederer, D.; Engeroff, T.; Vogt, L.; Troidl, C.; Schmitz-Rixen, T.; Banzer, W.; Troidl, K. Effects on the Profile of Circulating miRNAs after Single Bouts of Resistance Training with and without Blood Flow Restriction—A Three-Arm, Randomized Crossover Trial. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, J.; Niederer, D.; Jung, G.; Troidl, K. Exercise-Induced Vascular Adaptations under Artificially Versus Pathologically Reduced Blood Flow: A Focus Review with Special Emphasis on Arteriogenesis. Cells 2020, 9, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernando, F.J.S.; Conejero, A.M. Peripheral artery disease: Pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2007, 60, 969. [Google Scholar]
- Gamero, M.; Kim, W.S.; Hong, S.; Vorobiev, D.; Morgan, C.D.; Park, S. Il Multimodal sensing capabilities for the detection of shunt failure. Sensors 2021, 21, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maundy, B.J.; Elwakil, A.S.; Gift, S.J.G. Enhancing the improved Howland circuit. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2019, 47, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallas-Areny, R.; Webster, J.G. AC instrumentation amplifier for bioimpedance measurements. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1993, 40, 830–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, M.; Parve, T.; Ronk, A.; Annus, P.; Paavle, T. Synchronous sampling and demodulation in an instrument for multifrequency bioimpedance measurement. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2007, 56, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, I.; González-Landaeta, R.; Simini, F. Pressure sensors used as bioimpedance plantar electrodes: A feasibility study. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Lausanne, Switzerland, 23–25 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H.; Moon, J.-H.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, S.M.; Lee, S.-H. Flexible, stretchable and implantable PDMS encapsulated cable for implantable medical device. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2011, 1, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Kim, W.S.; Han, Y.; Cherukuri, R.; Jung, H.; Campos, C.; Wu, Q.; Park, S. Il Optogenetic Targeting of Mouse Vagal Afferents Using an Organ-specific, Scalable, Wireless Optoelectronic Device. Bio-Protocol 2022, 12, e4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, M.; Annus, P.; Kõiv, H.; Krivošei, A.; Uuetoa, T.; Lamp, J. Bioimpedance sensing—A viable alternative for tonometry in non-invasive assessment of central aortic pressure. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Rochester, MN, USA, 7–10 May 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 373–378. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Zou, L.; Xing, Y.; Hou, L.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, Y.; Hu, D.; Xu, Y.; Li, J. Diagnostic value of ankle-brachial index in peripheral arterial disease: A meta-analysis. Can. J. Cardiol. 2013, 29, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Showkat, I.; Khanday, F.A.; Beigh, M.R. A review of bio-impedance devices. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2023, 61, 927–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutt, A.G.; Verling, M.; Karlen, W. Wearable bioimpedance for continuous and context-aware clinical monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 3985–3988. [Google Scholar]
- Farre Romera, M.D. Design, Implementation and Test of a Low-Cost Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy System Based on an AD5940. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Scagliusi, S.F.; Pérez, P.; Martín, D.; Huertas, G.; Olmo, A.; Yúfera, A.; Delano, M. Enhancing the Precision of AD5940 Segmental Bioimpedance Measurements through Self-Calibration. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE BioSensors Conference (BioSensors), London, UK, 30 July–1 August 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Critcher, S.; Freeborn, T.J. Residual Impedance Impact on MAX30001 Accuracy for Bioimpedance Applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 12th Latin America Symposium on Circuits and System (LASCAS), Arequipa, Peru, 21–24 February 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Crandall, H.; Burt, A.; Sanchez, B. Characterization of the Analog Device Inc (ADI) MAX30009 Bioimpedance Analog Front End Chip. In Proceedings of the 2022 44th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Glasgow, UK, 11–15 July 2022; pp. 2502–2505. [Google Scholar]
- Kassanos, P. Bioimpedance Sensors: A Tutorial. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 22190–22219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykin, S.; Van Veen, B. Signals and Systems; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; ISBN 8126512652. [Google Scholar]
- Razavi, B.; Behzad, R. RF Microelectronics; Prentice Hall: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Razavi, B. Fundamentals of Microelectronics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; ISBN 1119695147. [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal, B. Design of a Sine Wave Inverter Using Arm LPC1768 Controller. Ph.D. Thesis, Maulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology, West Bengal, India, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Carlosena, A.; Martinez, P.; Porta, S. Wein-bridge oscillators with opamp independent oscillation frequency. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1991, 40, 644–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qiao, X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, G.; Lin, L. The differential Howland current source with high signal to noise ratio for bioimpedance measurement system. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 85, 055111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrouzirad, A.; Sugrue, P.; Todorovic, M.; McCarthy, K.G.; Galvin, P. Analysis and Application of a Buffered Feedback Path Improved Howland Current Source in BioImpedance Measurements. In Proceedings of the 2021 32nd Irish Signals and Systems Conference (ISSC), Athlone, Ireland, 10–11 June 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mahnam, A.; Yazdanian, H.; Mosayebi Samani, M. Comprehensive study of Howland circuit with non-ideal components to design high performance current pumps. Measurement 2016, 82, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedotov, A.A. Baseline drift filtering for an arterial pulse signal. Meas. Tech. 2014, 57, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, T.K. Bioelectrical impedance methods for noninvasive health monitoring: A review. J. Med. Eng. 2014, 2014, 381251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Wu, L.; Mao, K.; Feng, Y.; Li, J.; Ning, L.; Chen, J. Bioimpedance measurement of knee injuries using bipolar electrode configuration. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2022, 16, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nøvik, S.; Drageseth, M.F.; Grøndalen, M.B.; Nilsen, O.; Krauss, S.J.K.; Martinsen, Ø.G.; Häfliger, P.D. A CMOS Multi-Electrode Array for Four-Electrode Bioimpedance Measurements. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2022, 16, 1276–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, K.S. Electric impedance of suspensions of spheres. J. Gen. Physiol. 1928, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Kim, W.; Park, S. Design of an inductive spiral-loop loaded unit cell in a mushroom-shaped high impedance surface for sub-ghz applications. Prog. Electromagn. Res. M 2021, 100, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harosh, M.; Yangirov, M.; Kolesnikov, D.; Shchukin, S. Bio-impedance sensor for real-time artery diameter waveform assessment. Sensors 2021, 21, 8438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyashita, H. Clinical assessment of central blood pressure. Curr. Hypertens. Rev. 2012, 8, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vlachopoulos, C.; O’Rourke, M.; Nichols, W.W. McDonald’s Blood Flow in Arteries: Theoretical, Experimental and Clinical Principles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; ISBN 1444128787. [Google Scholar]
- Bereza, T.; Skrzat, J.; Mróz, I.; Pasternak, A.; Tomaszewski, K.; Mizia, E.; Kielczewski, S.; Pawlicki, D.; Kurzydło, W.; Bachul, P. Blood vessels of the shin—Anterior tibial artery—Anatomy and embryology—Own studies and review of the literature. Folia Med. Cracov. 2016, 56, 33–47. [Google Scholar]
- Paarmann, L.D. Design and Analysis of Analog Filters: A Signal Processing Perspective; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 617, ISBN 0306480123. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, A.B. Analog Filter and Circuit Design Handbook; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2014; ISBN 0071816712. [Google Scholar]
- de la O Serna, J.A. Taylor–Fourier analysis of blood pressure oscillometric waveforms. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2013, 62, 2511–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Water, J.M.; Dove, G.B.; Mount, B.E.; Linton, L.A. Application of bioelectric impedance to the measurement of arterial flow. J. Surg. Res. 1973, 15, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Method | Objective Measurements | Cost Efficiency | Portable for POC | Ionizing Radiation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X-rays | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| MRI | Yes | No | No | No |
| CT | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Blood test | Yes | No | No | No |
| Ankle-brachial index | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Toe-branchial index | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Toe pressure | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Our Technology | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Method | BIOPAC | MAX30009 EVKIT | Suggested Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Injection Frequency | 12.5 kHz | 9.984 kHz | 10 kHz |
| Injection Current amount | 400 μA | 96 μA | 84.7 μA |
| Digital Filter Type | Low Pass Filter | Low Pass Filter | N/A |
| Cutoff Frequency | 10 Hz | 6.24 Hz | N/A |
| Measurement Time | 30 s | 30 s | 30 s |
| 1st Harmonic | 2nd Harmonic | Harmonic Ratio (2nd/1st) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 24.73 dB (±1.36 dB) | 17.43 dB (±2.53 dB) | 0.43 (±0.06) |
| BFR | 30.03 dB (±0.83 dB) | 19.43 dB (±2.53 dB) | 0.30 (±0.05) |
| BFR 15 mins | 30.03 dB (±0.83 dB) | 17.17 dB (±3.36 dB) | 0.23 (±0.06) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, S.; Coté, G. Development of a Tetherless Bioimpedance Device That Uses Morphologic Changes to Predict Blood Flow Restrictions Mimicking Peripheral Artery Disease Progression. Biosensors 2024, 14, 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14060286
Hong S, Coté G. Development of a Tetherless Bioimpedance Device That Uses Morphologic Changes to Predict Blood Flow Restrictions Mimicking Peripheral Artery Disease Progression. Biosensors. 2024; 14(6):286. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14060286
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Sungcheol, and Gerard Coté. 2024. "Development of a Tetherless Bioimpedance Device That Uses Morphologic Changes to Predict Blood Flow Restrictions Mimicking Peripheral Artery Disease Progression" Biosensors 14, no. 6: 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14060286
APA StyleHong, S., & Coté, G. (2024). Development of a Tetherless Bioimpedance Device That Uses Morphologic Changes to Predict Blood Flow Restrictions Mimicking Peripheral Artery Disease Progression. Biosensors, 14(6), 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14060286





