Biosensing of Alpha-Fetoprotein: A Key Direction toward the Early Detection and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of Biosensing Technology
3. Optical Methods
3.1. Colorimetric Sensing Substrates for Alpha-Fetoprotein Detection
3.2. Fluorescence Sensing Probes for Alpha-Fetoprotein Detection
3.3. Luminescence and Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer-Based Detection of Alpha-Fetoprotein
3.4. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy and SPR-Based Detection of Alpha-Fetoprotein
4. Electrochemical Sensor-Based Detection of Alpha-Fetoprotein
4.1. Electrochemical Aptasensor-Based Detection of Alpha-Fetoprotein
4.2. Electrochemical Immunosensor-Based Detection of Alpha-Fetoprotein
5. Mass-Based Sensor-Based Detection of Alpha-Fetoprotein
5.1. Mass-Based Piezoelectric Sensor-Based Detection of Alpha-Fetoprotein
5.2. Mass-Based Cantilever Sensor-Based Detection of Alpha-Fetoprotein
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2021, 73, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, P.; Silletta, M.; Prinzi, F.L.; Farolfi, T.; Coppola, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Modern Context for an Ancient Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.I.; Khan, M.U.; Kodali, S.; Shetty, A.; Bell, S.M.; Victor, D. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Due to Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Current Concepts and Future Challenges. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2022, 9, 477–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batool, S.; Morton Cuthrell, K.; Tzenios, N.; Shehryar, Z. Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Emerging Burden. Int. Res. J. Oncol. 2022, 6, 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Elderkin, J.; Al Hallak, N.; Azmi, A.S.; Aoun, H.; Critchfield, J.; Tobon, M.; Beal, E.W. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Surveillance, Diagnosis, Evaluation and Management. Cancers 2023, 15, 5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, E.; Singal, A.G. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Surveillance: Evidence-Based Tailored Approach. Surg. Oncol. Clin. 2024, 33, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-M.; Tan, J.-X.; Wang, F.; Dao, F.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Lin, H. Early Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Machine Learning Method. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candita, G.; Rossi, S.; Cwiklinska, K.; Fanni, S.C.; Cioni, D.; Lencioni, R.; Neri, E. Imaging Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A State-of-the-Art Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, M.A.; Omran, M.M.; Farid, K.; Tabll, A.A.; Shahein, Y.E.; Emran, T.M.; Petrovic, A.; Lucic, N.R.; Smolic, R.; Kovac, T. Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From Origin to Clinical Diagnosis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, T.; Wang, K.; Xiang, A.; Guo, J.; Tang, N.; Jin, X.; Lin, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X. Serum Exosome-Derived piRNAs Could Be Promising Biomarkers for HCC Diagnosis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 1989–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, N.D.; Tayob, N.; Singal, A.G. Blood-Based Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Screening: Approaching the End of the Ultrasound Era? J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabri, A.; Khan, J.; Taftafa, B.; Alsharif, M.; Mhannayeh, A.; Chinnappan, R.; Alzhrani, A.; Kazmi, S.; Mir, M.S.; Alsaud, A.W.; et al. Bioengineered Organoids Offer New Possibilities for Liver Cancer Studies: A Review of Key Milestones and Challenges. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, Y.-H.; Kee, K.-M.; Li, W.-F.; Liu, Y.-W.; Wang, C.-C.; Hu, T.-H.; Tsai, M.-C.; Lin, C.-Y. Stationary Trend in Elevated Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein Level in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Cancers 2023, 15, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.-C.; Wei, C.-Y.; Chu, C.-J.; Lee, P.-C.; Huo, T.-I.; Huang, Y.-H.; Chao, Y.; Hou, M.-C.; Wu, J.-C.; Su, C.-W. The Outcomes and Prognostic Factors of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Normal Serum Alpha Fetoprotein Levels. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2023, 122, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galle, P.R.; Foerster, F.; Kudo, M.; Chan, S.L.; Llovet, J.M.; Qin, S.; Schelman, W.R.; Chintharlapalli, S.; Abada, P.B.; Sherman, M. Biology and Significance of Alpha-fetoprotein in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 2214–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Chi, B.; Wu, F.; Ma, S.; Zhan, S.; Yi, M.; Xu, H.; Mao, C. A Sensitive Label-Free Immunosensor for Detection α-Fetoprotein in Whole Blood Based on Anticoagulating Magnetic Nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 95, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhang, L. Serum AFP Levels in Patients Suffering from 47 Different Types of Cancers and Noncancer Diseases. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2019, 162, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carr, B.I.; Akkiz, H.; Üsküdar, O.; Yalçın, K.; Guerra, V.; Kuran, S.; Karaoğullarından, Ü.; Altıntaş, E.; Özakyol, A.; Tokmak, S. HCC with Low-and Normal-Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein Levels. Clin. Pract. 2018, 15, 453. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, G.; He, X.; Zhou, C.; Ya, D.; Feng, J.; Yu, C.; Deng, B. A Novel ECL Sensor Based on a Boronate Affinity Molecular Imprinting Technique and Functionalized SiO2@CQDs/AuNPs/MPBA Nanocomposites for Sensitive Determination of Alpha-Fetoprotein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preechakasedkit, P.; Siangproh, W.; Khongchareonporn, N.; Ngamrojanavanich, N.; Chailapakul, O. Development of an Automated Wax-Printed Paper-Based Lateral Flow Device for Alpha-Fetoprotein Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, D.; Ma, H.; Pang, X.; Fan, D.; Wei, Q.; Du, B. Ultrasensitive Label-Free Electrochemical Immunosensor Based on Multifunctionalized Graphene Nanocomposites for the Detection of Alpha Fetoprotein. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, B.; Xu, H.; Xie, G.; Chen, Q.; Sun, Z.; Cao, H.; Liu, X. Generation of a Nanobody-Alkaline Phosphatase Fusion and Its Application in an Enzyme Cascade-Amplified Immunoassay for Colorimetric Detection of Alpha Fetoprotein in Human Serum. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 262, 120088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Guo, M.; Liu, C.; Pei, M. Fluorescence Sensing Strategy Based on Aptamer Recognition and Mismatched Catalytic Hairpin Assembly for Highly Sensitive Detection of Alpha-Fetoprotein. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1141, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Hou, Y.; Sun, Y.; Fang, F.; Luo, C.; Wang, X. A Chemiluminescence Aptasensor for Sensitive Detection of Alpha-Fetoprotein Based on Hemin@ ZIF-67. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 4757–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Wang, J.; Yu, M.; Zhuang, X. Preparation of Aptamer Responsive DNA Functionalized Hydrogels for the Sensitive Detection of α-Fetoprotein Using SERS Method. Bioconjugate Chem. 2020, 31, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Chen, M.; Liang, J.; Lu, C.; Zhang, M.; Hu, F.; Zhou, Z.; Li, G. Electrochemical Aptasensor for Analyzing Alpha-Fetoprotein Using RGO–CS–Fc Nanocomposites Integrated with Gold–Platinum Nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 4956–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi-Monfared, S.; Krishnamurthy, V.; Cornell, B. A Molecular Machine Biosensor: Construction, Predictive Models and Experimental Studies. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 34, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borisov, S.M.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Optical Biosensors. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 423–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wright, G.; Yang, Y. Materials and Techniques for Electrochemical Biosensor Design and Construction. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2000, 15, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Datta, S.; Prasad, R.; Singh, J. Microbial Biotechnology: Basic Research and Applications. In Environmental and Microbial Biotechnology; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 317–335. [Google Scholar]
- Naseri, M.; Ziora, Z.M.; Simon, G.P.; Batchelor, W. ASSURED-compliant Point-of-care Diagnostics for the Detection of Human Viral Infections. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnappan, R.; Mir, T.A.; Alsalameh, S.; Makhzoum, T.; Adeeb, S.; Al-Kattan, K.; Yaqinuddin, A. Aptasensors Are Conjectured as Promising ALT and AST Diagnostic Tools for the Early Diagnosis of Acute Liver Injury. Life 2023, 13, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnappan, R.; Mir, T.A.; Alsalameh, S.; Makhzoum, T.; Alzhrani, A.; Al-Kattan, K.; Yaqinuddin, A. Low-Cost Point-of-Care Monitoring of ALT and AST Is Promising for Faster Decision Making and Diagnosis of Acute Liver Injury. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsalameh, S.; Alnajjar, K.; Makhzoum, T.; Al Eman, N.; Shakir, I.; Mir, T.A.; Alkattan, K.; Chinnappan, R.; Yaqinuddin, A. Advances in Biosensing Technologies for Diagnosis of COVID-19. Biosensors 2022, 12, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, T.A.; Shinohara, H.; Shimizu, Y. Enzyme-Luminescence Method: Tool for Evaluation of Neuronal Differentiation Based on Real-Time Monitoring of Dopamine Release Response from PC12 Cells. Anal. Methods 2011, 3, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnappan, R.; Mir, T.A.; Alsalameh, S.; Makhzoum, T.; Alzhrani, A.; Alnajjar, K.; Adeeb, S.; Al Eman, N.; Ahmed, Z.; Shakir, I.; et al. Emerging Biosensing Methods to Monitor Lung Cancer Biomarkers in Biological Samples: A Comprehensive Review. Cancers 2023, 15, 3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljohani, M.M.; Cialla-May, D.; Popp, J.; Chinnappan, R.; Al-Kattan, K.; Zourob, M. Aptamers: Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Agents for Blood Diseases. Molecules 2022, 27, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnappan, R.; AlAmer, S.; Eissa, S.; Rahamn, A.A.; Abu Salah, K.M.; Zourob, M. Fluorometric Graphene Oxide-Based Detection of Salmonella Enteritis Using a Truncated DNA Aptamer. Microchim. Acta 2017, 185, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnappan, R.; Ramadan, Q.; Zourob, M. An Integrated Lab-on-a-Chip Platform for Pre-Concentration and Detection of Colorectal Cancer Exosomes Using Anti-CD63 Aptamer as a Recognition Element. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 220, 114856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, T.A.; Shinohara, H. Two-Dimensional Surface Plasmon Resonance Imager: An Approach to Study Neuronal Differentiation. Anal. Biochem. 2013, 443, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, T.A.; Shinohara, H. Label-Free Observation of Three-Dimensional Morphology Change of a Single PC12 Cell by Digital Holographic Microscopy. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 429, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnappan, R.; Al Faraj, A.; Abdel Rahman, A.M.; Abu-Salah, K.M.; Mouffouk, F.; Zourob, M. Anti-VCAM-1 and Anti-IL4Rα Aptamer-Conjugated Super Paramagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Enhanced Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. Molecules 2020, 25, 3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Sun, D.; Gu, T.; Dong, Y.; Wang, G.-L. Photoswitching Enzymatic Activity of Horseradish Peroxidase by Graphene Oxide for Colorimetric Immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 145, 111707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.-J.; Yang, X.-T.; Tang, Y.-Y. Colorimetric and Fluorometric Dual-Channel Detection of α-Fetoprotein Based on the Use of ZnS-CdTe Hierarchical Porous Nanospheres. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xu, J.; Dai, Z.; Guo, J.; Xu, H.; Zhao, J.; Song, Y.-Y.; Gao, Z. Target-Modulated Hydrophobic Precipitation in Photocatalytic Nanochannels for Sensitive Detection of Alpha Fetoprotein. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 11282–11289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celikbas, E.; Ceylan, A.E.; Timur, S. Based Colorimetric Spot Test Utilizing Smartphone Sensing for Detection of Biomarkers. Talanta 2020, 208, 120446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.; Xiong, S.; Li, X.; Zhan, S.; Zeng, L.; Xiong, Y. Dual-Mode Fluorescent and Colorimetric Immunoassay for the Ultrasensitive Detection of Alpha-Fetoprotein in Serum Samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1038, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fan, C.; Liu, M.; Liu, F.; Bian, S.; Du, S.; Zhu, S.; Wang, H. Biominerized Gold-Hemin@ MOF Composites with Peroxidase-like and Gold Catalysis Activities: A High-Throughput Colorimetric Immunoassay for Alpha-Fetoprotein in Blood by ELISA and Gold-Catalytic Silver Staining. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 266, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dong, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Xie, M. Development of Graphite Carbon Nitride Based Fluorescent Immune Sensor for Detection of Alpha Fetoprotein. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 196, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.-C.; Chou, C.-C.; Yang, Y.-Q.; Wei-Kai, T.; Wang, Y.-T.; Chan, Y.-H. Multiplexed Detection of Tumor Markers with Multicolor Polymer Dot-Based Immunochromatography Test Strip. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2134–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Pan, L.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Yao, D.; Wang, C.-Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Chen, L.; Yuan, C. A Biomimetic Fluorescent Nanosensor Based on Imprinted Polymers Modified with Carbon Dots for Sensitive Detection of Alpha-Fetoprotein in Clinical Samples. Analyst 2019, 144, 6760–6772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishige, T.; Takano, E.; Sunayama, H.; Kitayama, Y.; Takeuchi, T. Post-Imprinting-Modified Molecularly Imprinted Nanocavities with Two Synergetic, Orthogonal, Glycoprotein-Binding Sites to Transduce Binding Events into Fluorescence Changes. ChemNanoMat 2019, 5, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapitan, L.D.; Pietrzak, M.; Krawczyk, M.; Malinowska, E. Serum Biomarkers and Ultrasensitive Biosensors for Diagnosis of Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 393, 134209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Zhao, G.; Dong, X.; Li, X.; Miao, J.; Wei, Q.; Cao, W. Ultrasensitive Electrochemiluminescence Immunosensor for the Detection of Amyloid-β Proteins Based on Resonance Energy Transfer between g-C3N4 and Pd NPs Coated NH2-MIL-53. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Ji, F.; Zhang, T.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z.; Jin, X.; Ruan, B. An Fluorescent Aptasensor for Sensitive Detection of Tumor Marker Based on the FRET of a Sandwich Structured QDs-AFP-AuNPs. Talanta 2019, 197, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-F.; Wang, Z.-G.; Sun, X.-Y.; Chen, M.-J.; Lv, Y.-K. An Ultrasensitive Fluorescent Aptasensor for Detection of Cancer Marker Proteins Based on Graphene Oxide–ssDNA. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 41143–41149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintz, K.; Waidely, E.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, Z.; Al-Youbi, A.O.; Bashammakh, A.S.; El-Shahawi, M.S.; Leblanc, R.M. Carbon Dots and Gold Nanoparticles Based Immunoassay for Detection of Alpha-L-Fucosidase. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1041, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Wei, D.; Li, G. A Fluorescence Turn-On Biosensor Based on Gold Nanoclusters and Aptamer for Alpha Fetoprotein Detection; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 218, p. 012106. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, A.; Gao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Au Nanocone Array with 3D Hotspots for Biomarker Chips. CrystEngComm 2020, 22, 5191–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Gao, R.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, A.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y. Facile SERS-Active Chip (PS@ Ag/SiO2/Ag) for the Determination of HCC Biomarker. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 272, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, L.; Petti, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Xie, S.; Chen, J.; Qing, Y. Ultrasensitive SERS-Based Immunoassay of Tumor Marker in Serum Using Au–Ag Alloy Nanoparticles and Ag/AgBr Hybrid Nanostructure. Nano 2018, 13, 1850001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Fu, W.; Yao, C. A SPR Biosensor Based on Signal Amplification Using Antibody-QD Conjugates for Quantitative Determination of Multiple Tumor Markers. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Liang, Q. A Graphene Oxide-Based Label-Free Electrochemical Aptasensor for the Detection of Alpha-Fetoprotein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 112, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, Z.; Roushani, M.; Hosseini, H. Hierarchical Nickel Hydroxide Nanosheets Grown on Hollow Nitrogen Doped Carbon Nanoboxes as a High-Performance Surface Substrate for Alpha-Fetoprotein Cancer Biomarkers Electrochemical Aptasensing. Talanta 2022, 237, 122924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, C.; Wen, K.; Zhu, Y. Bi-Directionally Amplified Ratiometric Electrochemical Aptasensor for the Ultrasensitive Detection of Alpha-Fetoprotein. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 323, 128666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Cui, B.; Ma, Y.; Yan, X.; Xia, L.; Zhou, N.; Wang, M.; He, L.; Zhang, Z. Three-Dimensional Nitrogen-Doped Mesoporous Carbon Nanomaterials Derived from Plant Biomass: Cost-Effective Construction of Label-Free Electrochemical Aptasensor for Sensitively Detecting Alpha-Fetoprotein. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1078, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Zhang, W.; Tan, Q.; Cui, X.; Dai, Z. Electrochemical Assay of the Alpha Fetoprotein-L3 Isoform Ratio to Improve the Diagnostic Accuracy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 13051–13058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Jia, Y.; Ji, P.; Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, G. One-Step Detection of Alpha Fetal Protein Based on Gold Microelectrode through Square Wave Voltammetry. Anal. Biochem. 2022, 658, 114916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upan, J.; Youngvises, N.; Tuantranont, A.; Karuwan, C.; Banet, P.; Aubert, P.-H.; Jakmunee, J. A Simple Label-Free Electrochemical Sensor for Sensitive Detection of Alpha-Fetoprotein Based on Specific Aptamer Immobilized Platinum Nanoparticles/Carboxylated-Graphene Oxide. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liang, D.; Guo, W.; Tang, D.; Zeng, Y. New Insights on Potentiometric Immunosensor at Carbon Fiber Microelectrode for Alpha-Fetoprotein in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Electroanalysis 2022, 34, 976–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Liu, F.; Deng, D.; Zhu, X.; He, H.; Yan, X.; Luo, L. A Sandwich-Type Electrochemical Immunosensor Based on Spherical Nucleic Acids-Templated Ag Nanoclusters for Ultrasensitive Detection of Tumor Biomarker. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 223, 115029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Wang, M.; Lai, W.; Zhang, M.; Ma, C.; Li, P.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Hong, C. Preparation of a pH-Responsive Controlled-Release Electrochemical Immunosensor Based on Polydopamine Encapsulation for Ultrasensitive Detection of Alpha-Fetoprotein. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, S.; Zou, L.; Li, Y.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, H.; Yu, H.; Zhao, F.; Pan, H. An Ultrasensitive Disposable Sandwich-Configuration Electrochemical Immunosensor Based on OMC@ AuNPs Composites and AuPt-MB for Alpha-Fetoprotein Detection. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 141, 107846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, X.; Su, B.; Zhang, H.; Li, R.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Huang, T.; Cao, H. An Innovative Electrochemical Immunosensor Based on Nanobody Heptamer and AuNPs@ ZIF-8 Nanocomposites as Support for the Detection of Alpha Fetoprotein in Serum. Microchem. J. 2022, 179, 107463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-S.; Tan, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Liu, A. A Simple Electrochemical Immunosensor Based on Worm-like Platinum for Highly Sensitive Determination of Alpha-Fetoprotein. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 140, 107804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, D.; Zhang, K.; Lu, Y.; Chen, J.; Wei, Y. Gold Microstructures/Polyaniline/Reduced Graphene Oxide/Prussian Blue Composite as Stable Redox Matrix for Label-Free Electrochemical Immunoassay of α-Fetoprotein. Anal. Sci. 2020, 36, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, P.; Xie, R.; Wang, P.; Lei, Y.; Chen, B.; Li, S.; Wu, Y.; Lin, X.; Yao, H. Non-Covalent Modification of Glassy Carbon Electrode with Isoorientin and Application to Alpha-Fetoprotein Detection by Fabricating an Immunosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 305, 127494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Cao, K.; Ma, C.; Li, W.; Song, Y.; Qiao, X.; Hong, C. Ultrasensitive Immunosensor for AFP Detection Based on Cu2O to Generate Electrical Signals. Micro Nano Lett. 2020, 15, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L. Development of Novel Piezoelectric Biosensor Using PZT Ceramic Resonator for Detection of Cancer Markers. In Biosensors and Biodetection. Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Ma, X.; Guan, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhang, B. Microcantilever Array Biosensor for Simultaneous Detection of Carcinoembryonic Antigens and α-Fetoprotein Based on Real-Time Monitoring of the Profile of Cantilever. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 3034–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Fu, D.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, F. Gold Nanoparticles Amplified Microcantilever Biosensor for Detecting Protein Biomarkers with High Sensitivity. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 321, 112563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.-M.; Xu, B.; Dong, C. Recent Advances in Colorimetric Strategies for Acetylcholinesterase Assay and Their Applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 142, 116320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldewachi, H.; Chalati, T.; Woodroofe, M.; Bricklebank, N.; Sharrack, B.; Gardiner, P. Gold Nanoparticle-Based Colorimetric Biosensors. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, B.P.; Rani, P.; Paul, P.; Bhatia, R. Recent Trends and Impact of Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance (LSPR) and Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) in Modern Analysis. J. Pharm. Anal. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrahari, S.; Kumar Gautam, R.; Kumar Singh, A.; Tiwari, I. Nanoscale Materials-Based Hybrid Frameworks Modified Electrochemical Biosensors for Early Cancer Diagnostics: An Overview of Current Trends and Challenges. Microchem. J. 2022, 172, 106980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
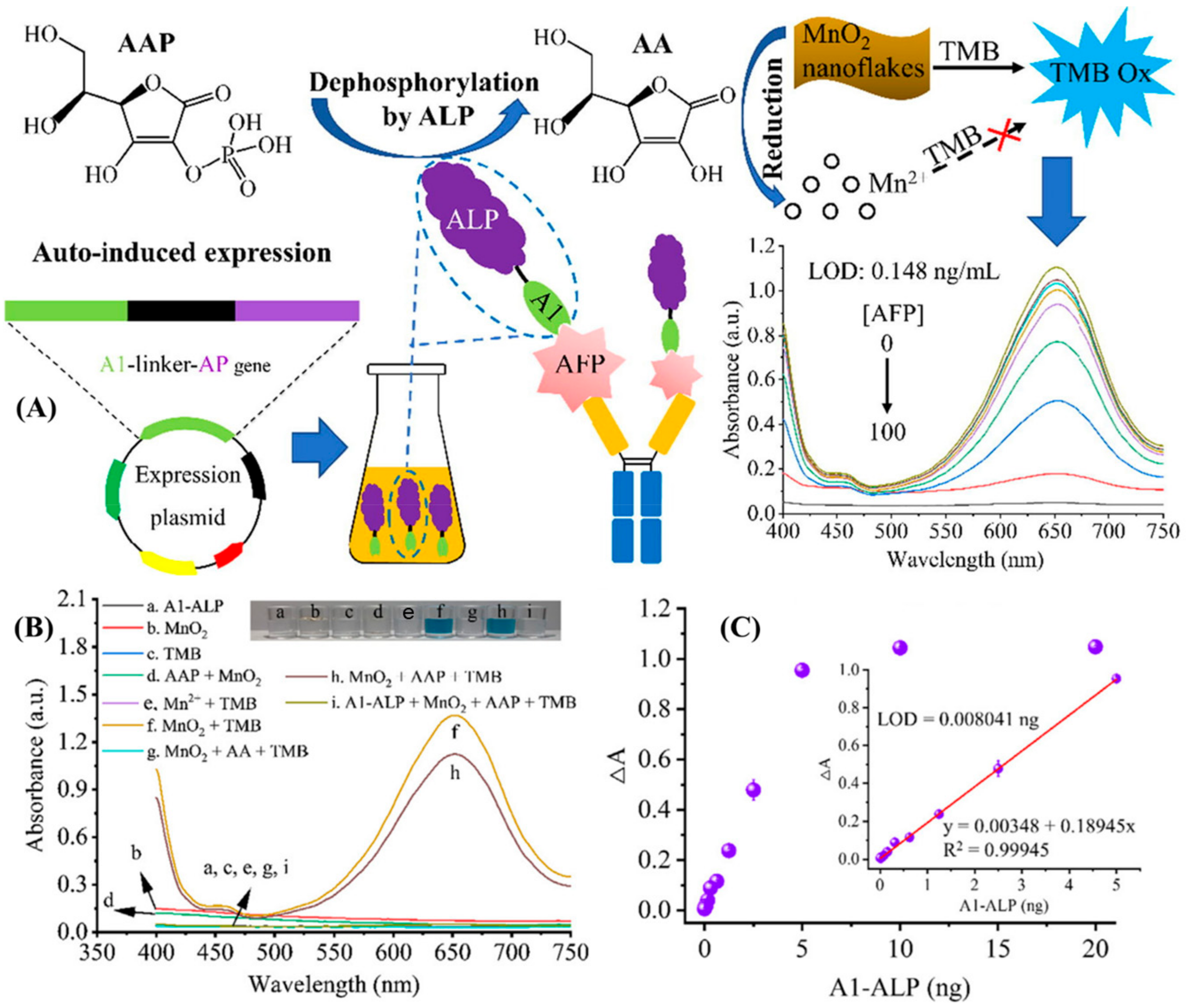
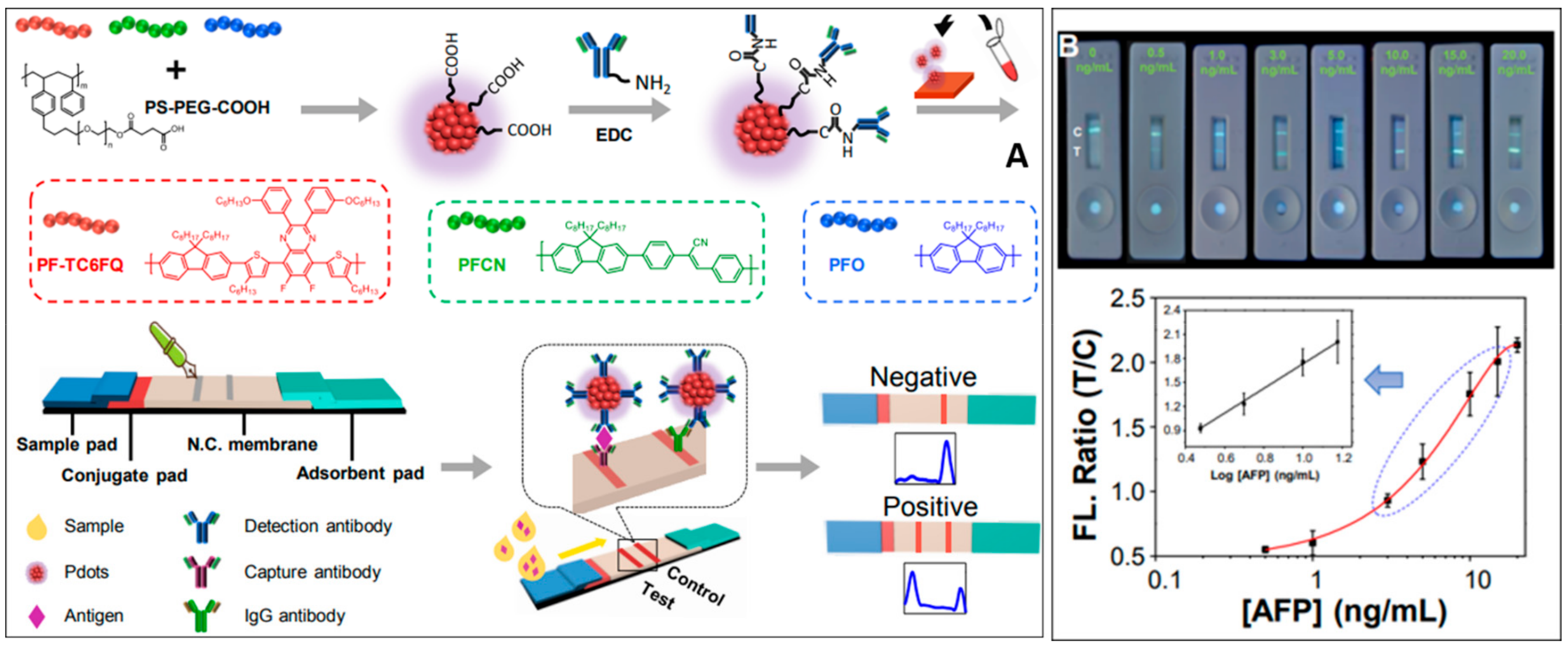

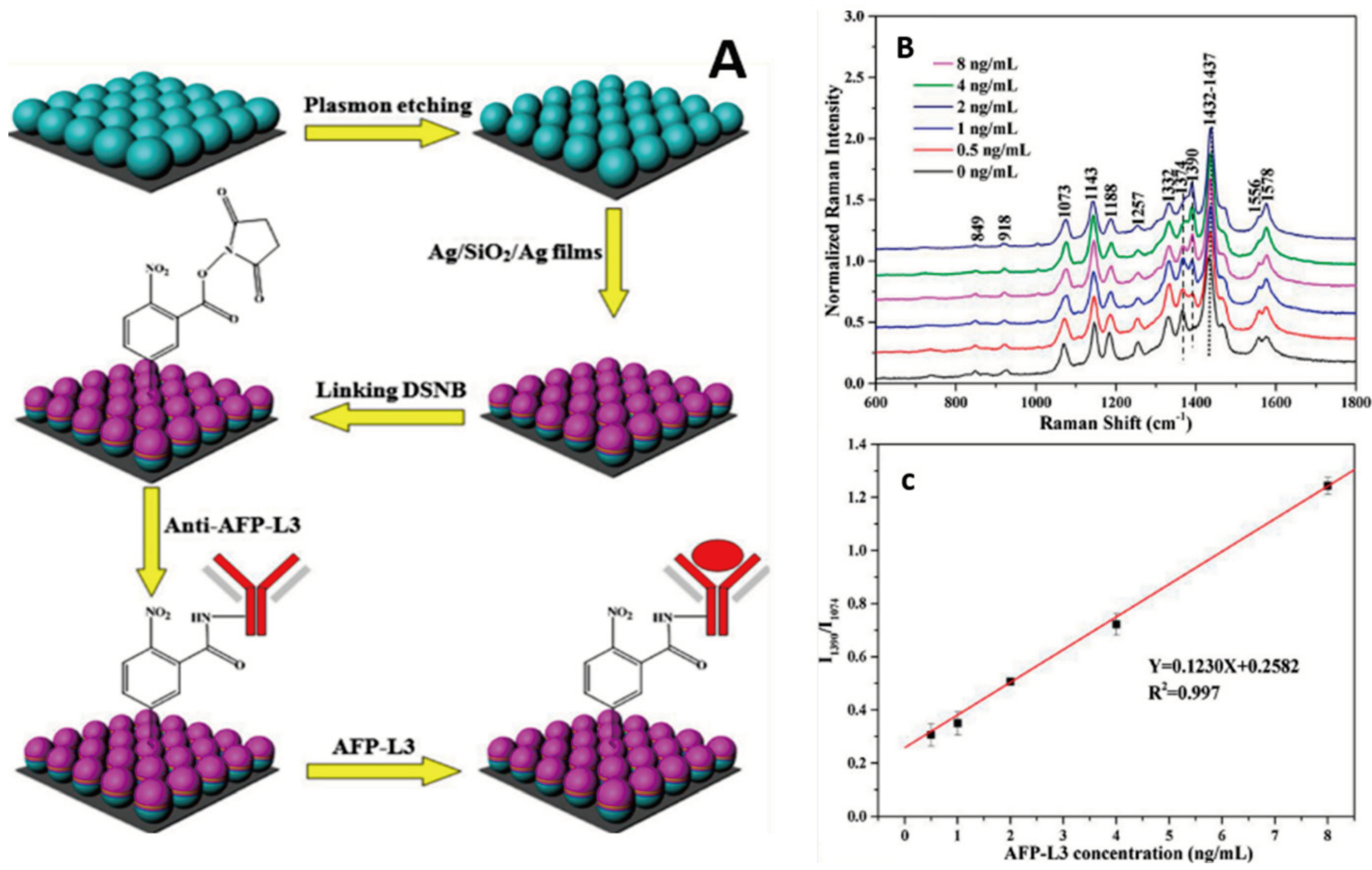

| S. No | Detection Method | LOD | Range | Advantages | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Colorimetric | 0.1 fg/mL | 0.2 fg/mL to 1.0 ng/mL | High catalytic ability, precise time control, and free of harmful reagents | [43] |
| 2 | Colorimetric | 10 pg/mL | 0.05 ng/mL to 12 ng/mL | High accuracy due to the dual-detection feature | [44] |
| 3 | Colorimetric | 2 ng/mL | 2 ng/mL to 10 µg/mL | Capable of detecting other immune targets, increasing usability | [45] |
| 4 | Colorimetric | 1.054 ng/mL | 0.1 ng/mL–100 ng/mL | Capable of detecting MUC-16 biomarker used in ovarian cancer | [46] |
| 5 | Colorimetric/Fluorescence | 29 fg/mL (fluorescence) | 10 fg/mL to 10,000 fg/mL (fluorescence) | It can be used for ultrasensitive detection via the fluorescence mode and standard diagnosis via the colorimetric mode | [47] |
| 17.7 pg/mL (colorimetric) | 5 pg/mL to 5000 pg/mL (colorimetric) | ||||
| 6 | Colorimetric | 0.020 ng/mL | 0.25 to 38 ng/mL | The methodology can be used for the fabrication of other enzymes or enzymatic mimics | [48] |
| 7 | Fluorescence | 0.43 ng/mL | 5 ng/mL to 600 ng/mL | Good sensitivity, excellent selectivity, high biocompatibility, and low cost; the results can be used for further detection of biomarkers in complex matrices | [49] |
| 8 | Fluorescence | 3.30 pg/mL | 3 ng/mL to 15 ng/mL | First polymer dot-based immunochromatography strip capable of multiplex detection | [50] |
| 9 | Fluorescence | 0.474 ng/mL | 10 to 100 ng mL−1 | This method is rapid, convenient, and highly selective | [51] |
| 10 | Fluorescence | 0.27 ng/mL | 0.5 to 100 ng/mL | This technique can be used for ELISA-relevant, antibody-free sensing of glycoproteins | [52] |
| 11 | Luminescence | 3.4 fg/mL | 10 fg/mL to 50 ng/mL | It can be used as a tool for analysis for trace detection of sensitive molecules in clinical analysis | [54] |
| 12 | FRET | 400 pg/mL | 0.5 ng/mL to 45 ng/mL | This method can be modified and used for the testing various biomarkers in POC analysis | [55] |
| 13 | FRET | 0.909 pg/mL | 1 pg/mL to 150 pg/mL | It can be used for serum and cell imaging for the detection of AFP | [56] |
| 14 | FRET | 6.631 ng/mL | 10 ng/mL to 100 ng/mL | The sensor has a simple configuration and can be modified to detect various biomarkers | [58] |
| 15 | SERS | 0.5 ng/mL | 0.5 to 4 ng/mL | Can detect AFP-L3, which is better suited for early diagnosis of HCC | [59] |
| 16 | SERS | 0.078 ng/mL | 0 ng/mL to 8 ng/mL | Can detect AFP-L3, which is better suited for early diagnosis of HCC | [60] |
| 17 | SERS | 1.86 fg/mL | 2 fg/mL to 0.8 μg/mL | The sensor is ultrasensitive and can be used for HCC point-of-care testing | [61] |
| 18 | Aptasensor | 3 pg/mL | 0.01 ng/mL to 100 ng/mL | It is simple to manufacture, cost-effective, and has a wide linear range of detection | [63] |
| 19 | Aptasensor | 0.3 fg/mL | 1 fg/mL to 100 ng/mL | The detection capabilities were tested with real live samples and proved superior and reliable | [64] |
| 20 | Aptasesnsor | 269.4 ag/mL | 0 fg/mL to 1 µg/mL | It has an ultralow detection limit and a wide range of detection of seven orders of magnitude | [65] |
| 21 | Aptasensor | 60.8 fg/m | 0.1 pg/mL to 100 ng/mL | Has high reproducibility and good stability in serum samples of cancer patients | [66] |
| 22 | Aptasensor | 0.01 ng/mL | 0.4 ng/mL to 1000 ng/mL | Can detect AFP-L3, which is better suited for early diagnosis of HCC | [67] |
| 23 | Aptasensor | 2.5 × 10−11 g/mL | 10−10 g/mL to 10−7 g/mL | Real blood samples were used, and they correlated with the results provided by the electrochemiluminescence assay. This one-step assay is perfect for point-of-care diagnostic | [68] |
| 24 | Aptasensor | 1.22 ng/mL | 3 ng/mL to 30 ng/mL | Has high sensitivity to AFP molecules, good stability, and high recovery rates | [69] |
| 25 | Aptasensor | 3.2 pg/mL | 0.1 ng/mL to 100 ng/mL | It has a high sensitivity, good reproducibility, and the results are consistent with ELISA | [70] |
| 26 | Immunosensor | 7.74 fg/mL | 0.001 ng/mL to 100 ng/mL | It is an ultrasensitive sensor with a broad detection range and has excellent reliability and reproducibility | [71] |
| 27 | Immunosensor | 0.254 pg/mL | 1 pg/mL to 100 ng/mL. | The sensor has high levels of stability, repeatability, and selectivity | [72] |
| 28 | Immunosensor | 3.33 fg/mL | 10 fg/mL to 100 ng/mL | The device demonstrated excellent selectivity, high stability, and outstanding reproducibility | [73] |
| 29 | Immunosensor | 0.033 pg/mL | 0.1 to 105 pg/mL | The nanobody multimerization strategy can be used to enhance sensitivity and detection capability in other methods | [74] |
| 30 | Immunosensor | 0.028 pg/mL | 0.0001 ng/mL to 100 ng/mL | The method makes use of chemical etching rather than ultra-high temperatures, thus making it affordable, and has excellent detection capabilities | [75] |
| 31 | Immunosensor | 0.003 ng/mL | 0.01 ng/mL to 30 ng/mL | It can be used with several other antibodies with minor modification, detects AFP well, and can be used for clinical HCC diagnosis | [76] |
| 32 | Immunosensor | 0.0002 ng/mL | 0.001 ng/mL to 10 ng/mL | It has an ultralow limit of detection and a wide linear range | [78] |
| 33 | Immunosensor | 0.33 pg/mL | 0.001 ng/mL to 40 ng/mL | The sensor has been tested with human serum and has demonstrated good reproducibility and excellent long-term stability | [78] |
| 34 | Piezoelectric | 0.25 ng/mL | 2.5 ng/mL to 2.5 × 102 ng/mL | This sensor can be used with different chemical interfaces and can be developed to detect multiple analytes simultaneously | [79] |
| 35 | Microcantilever | 0.6 ng/mL | 1 ng/mL to 900 ng/mL | This biosensor is capable of detecting two biomarkers simultaneously, thus highlighting its potential in detecting other biomarkers simultaneously for early clinical diagnosis | [80] |
| 36 | Microcantilever | 21 pg/mL | 10 ng/mL to 70 ng/mL | This sensor’s gold nanoparticle amplificant method amplified the detection capabilities about 70 times. This can be further worked on and employed in different sensors to establish a lower limit of detection | [81] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramachandran, L.; Abul Rub, F.; Hajja, A.; Alodhaibi, I.; Arai, M.; Alfuwais, M.; Makhzoum, T.; Yaqinuddin, A.; Al-Kattan, K.; Assiri, A.M.; et al. Biosensing of Alpha-Fetoprotein: A Key Direction toward the Early Detection and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biosensors 2024, 14, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14050235
Ramachandran L, Abul Rub F, Hajja A, Alodhaibi I, Arai M, Alfuwais M, Makhzoum T, Yaqinuddin A, Al-Kattan K, Assiri AM, et al. Biosensing of Alpha-Fetoprotein: A Key Direction toward the Early Detection and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biosensors. 2024; 14(5):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14050235
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamachandran, Lohit, Farah Abul Rub, Amro Hajja, Ibrahim Alodhaibi, Momo Arai, Mohammed Alfuwais, Tariq Makhzoum, Ahmed Yaqinuddin, Khaled Al-Kattan, Abdullah M. Assiri, and et al. 2024. "Biosensing of Alpha-Fetoprotein: A Key Direction toward the Early Detection and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Biosensors 14, no. 5: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14050235
APA StyleRamachandran, L., Abul Rub, F., Hajja, A., Alodhaibi, I., Arai, M., Alfuwais, M., Makhzoum, T., Yaqinuddin, A., Al-Kattan, K., Assiri, A. M., Broering, D. C., Chinnappan, R., Mir, T. A., & Mani, N. K. (2024). Biosensing of Alpha-Fetoprotein: A Key Direction toward the Early Detection and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biosensors, 14(5), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14050235






