Development of Taste Sensor with Lipid/Polymer Membranes for Detection of Umami Substances Using Surface Modification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
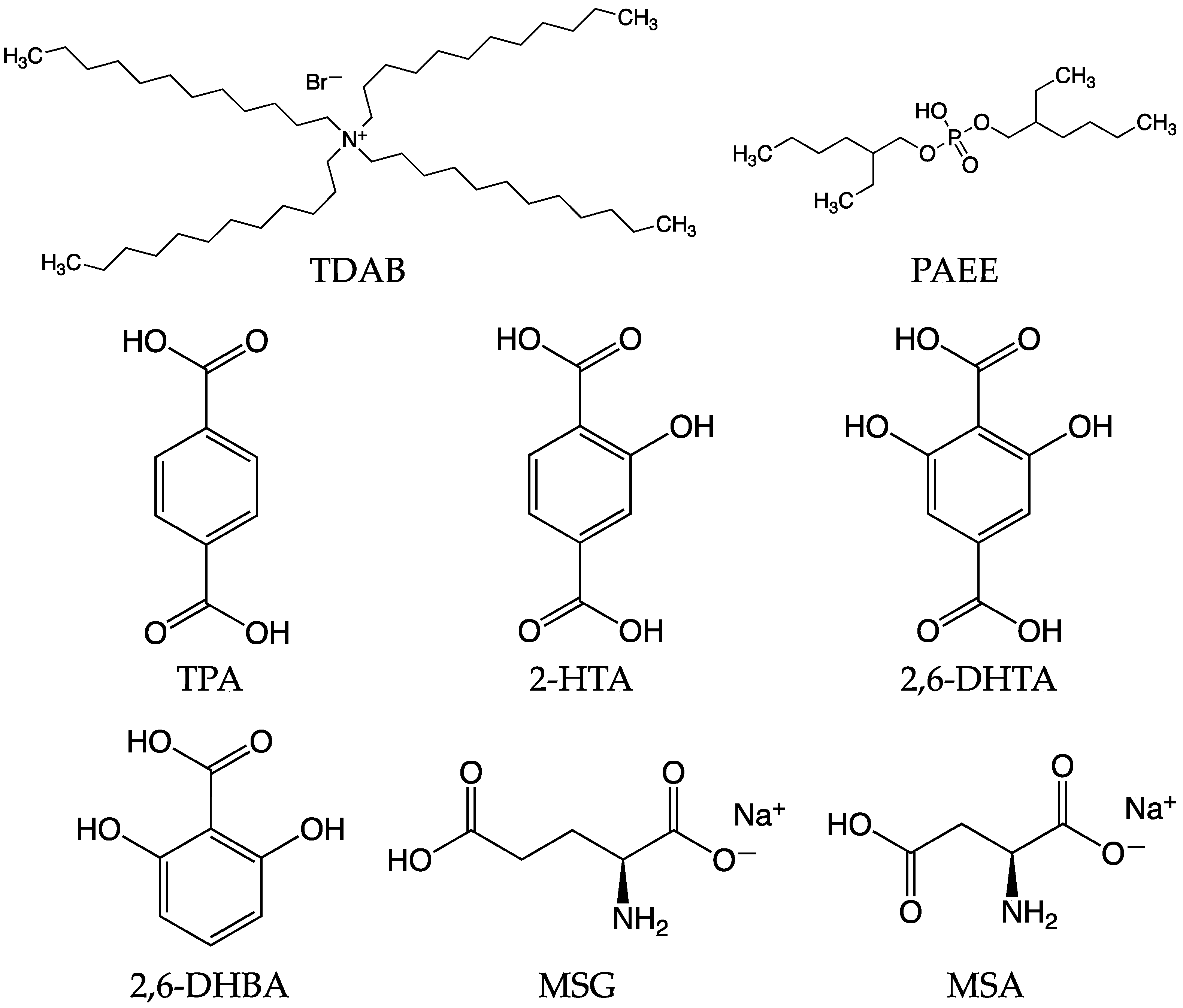
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Fabrication of Lipid/Polymer Membrane and Surface Modification
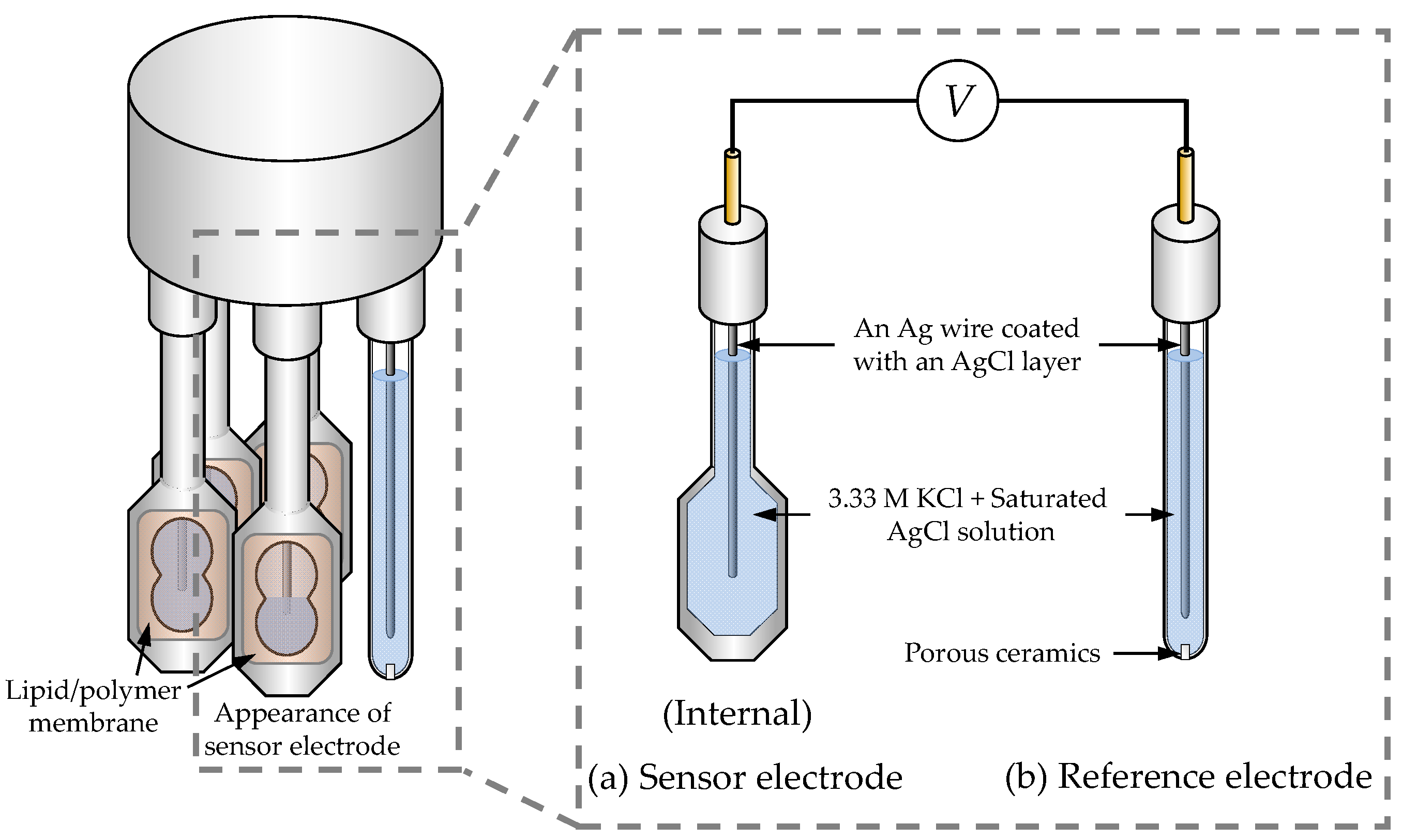
2.3. Procedure of Taste Sensor Measurement
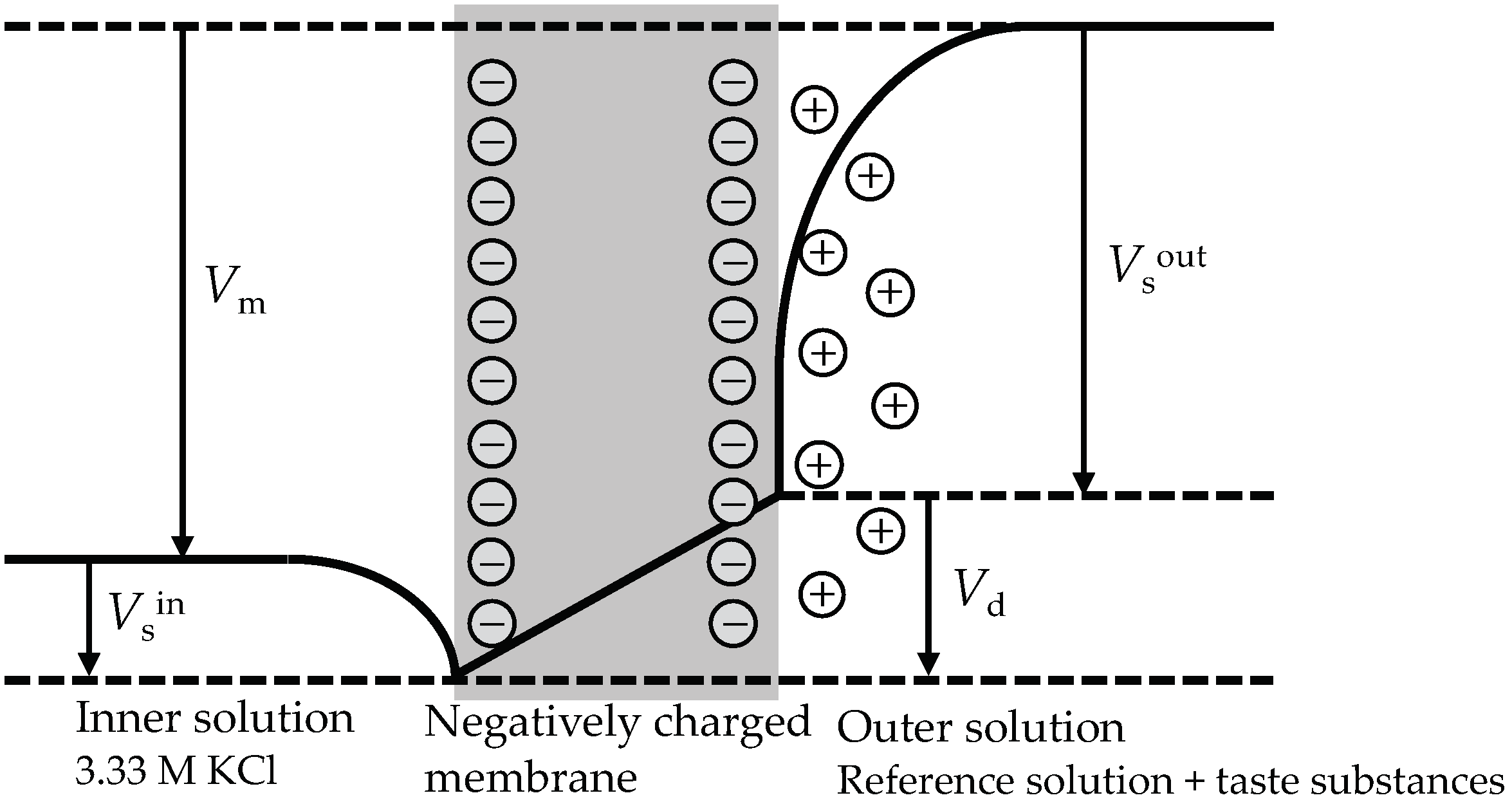
2.4. Response Principle of the Taste Sensor
2.5. Measurement of Taste Samples by Fabricated Taste Sensors
3. Result and Discussion
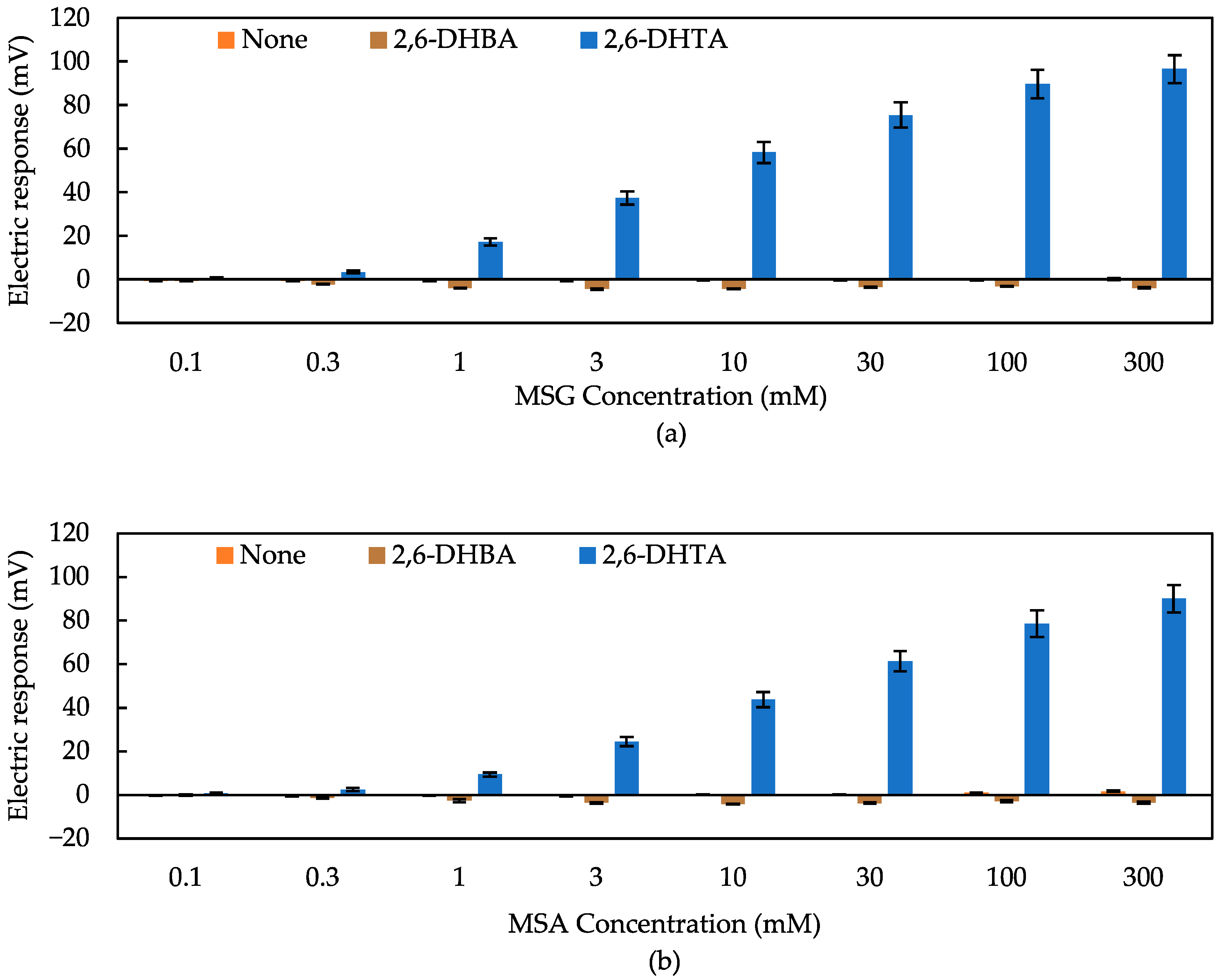
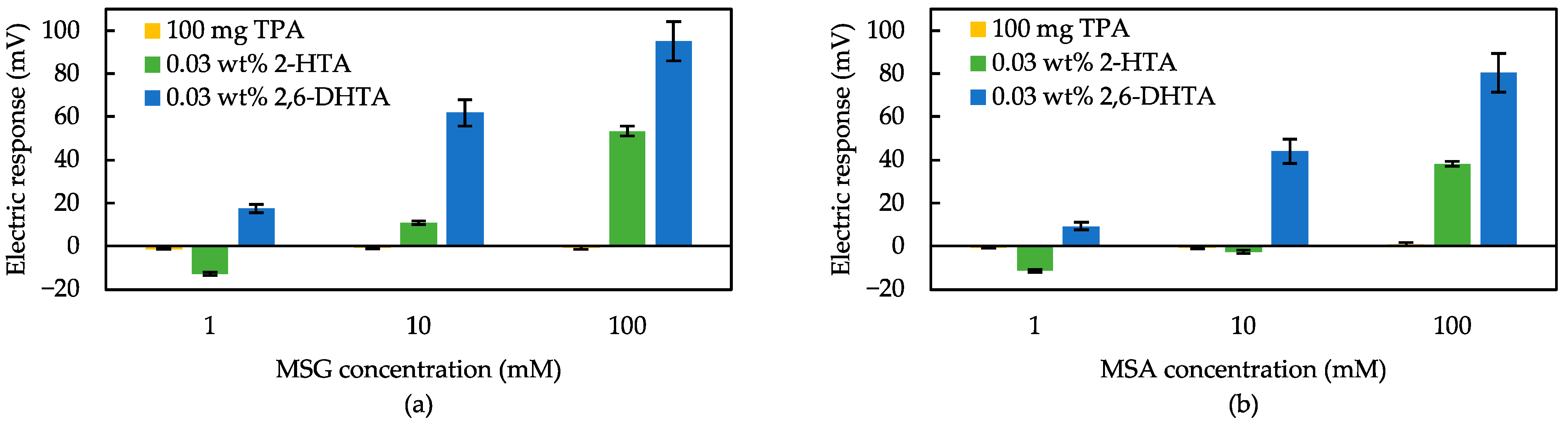
3.1. Detection of Umami Substances Using Taste Sensors Treated with 2,6-DHBA and 2,6-DHTA
3.2. Effect of Intramolecular H-Bonds within Modifier for Umami Substances Detection
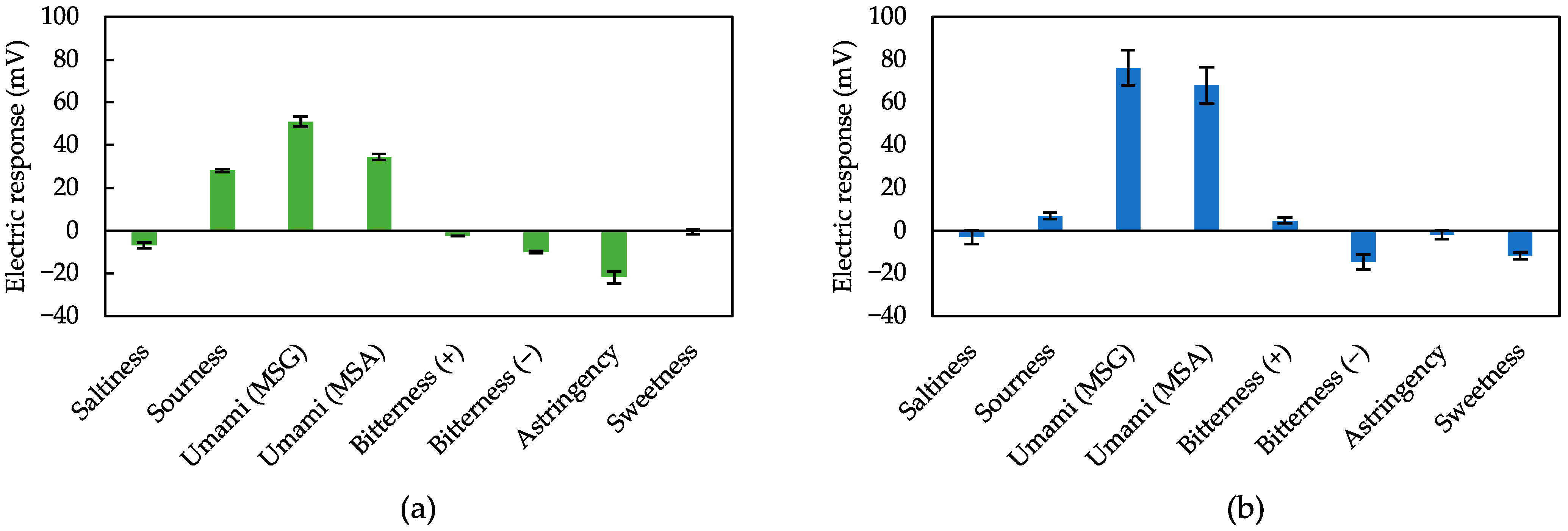
3.3. Measurement of Various Taste Samples Using Sensors Treated with 2,6-DHTA and 2-HTA
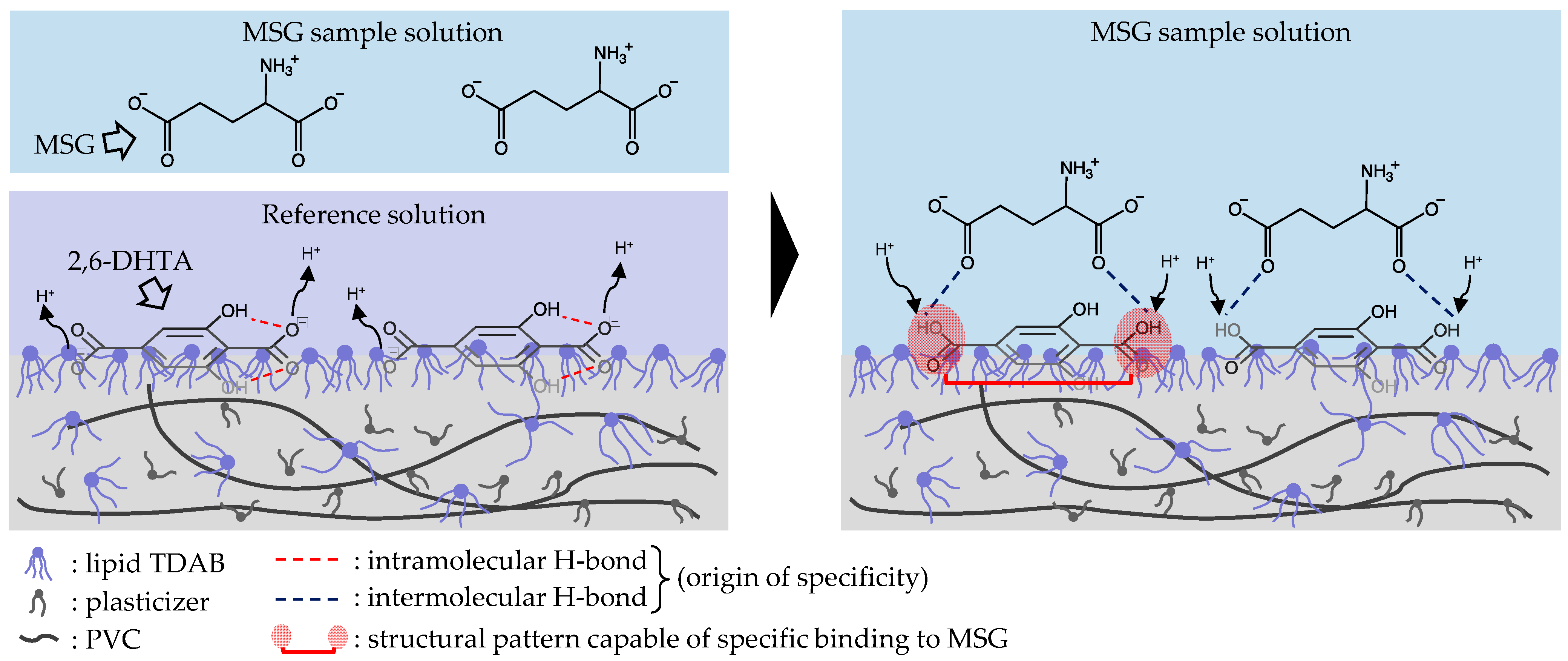
3.4. Mechanism Speculation of Positive Response Value of Taste Sensor Treated with 2,6-DHTA to MSG
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khansili, N.; Rattu, G.; Krishna, P.M. Label-Free Optical Biosensors for Food and Biological Sensor Applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 265, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloso, A.C.A.; Dias, L.G.; Rodrigues, N.; Pereira, J.A.; Peres, A.M. Sensory Intensity Assessment of Olive Oils Using an Electronic Tongue. Talanta 2016, 146, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipos, L.; Kovács, Z.; Sági-Kiss, V.; Csiki, T.; Kókai, Z.; Fekete, A.; Héberger, K. Discrimination of Mineral Waters by Electronic Tongue, Sensory Evaluation and Chemical Analysis. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2947–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, L.A.; Peres, A.M.; Veloso, A.C.A.; Reis, F.S.; Vilas-Boas, M.; Machado, A.A.S.C. An Electronic Tongue Taste Evaluation: Identification of Goat Milk Adulteration with Bovine Milk. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 136, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winquist, F.; Bjorklund, R.; Krantz-Rülcker, C.; Lundström, I.; Östergren, K.; Skoglund, T. An Electronic Tongue in the Dairy Industry. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 111, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Khalaf, N.; Zaid, A.N.; Jaradat, N.; Alkilany, A.; Rumaila, B.A.; Al Ramahi, R.; Shweiki, S.; Nidal, S.; Surakhi, N. The Taste of Commercially Available Clarithromycin Oral Pharmaceutical Suspensions in the Palestinian Market: Electronic Tongue and in Vivo Evaluation. Sensors 2018, 18, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podrazka, M.; Báczyńska, E.; Kundys, M.; Jeleń, P.S.; Nery, E.W. Electronic Tongue-A Tool for All Tastes? Biosensors 2017, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Parmar, D.; Patel, U.; Patel, G.; Daslaniya, D.; Bhimani, B.; Aditi, T.D. Taste Masking: A Novel Approach for Bitter and Obnoxious Drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. Biosci. Res. 2011, 1, 136–142. [Google Scholar]
- Ciosek, P.; Wróblewski, W. Sensor Arrays for Liquid Sensing—Electronic Tongue Systems. Analyst 2007, 132, 963–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.; Sun, Q.; Su, K.; Wan, H.; Li, H.; Xu, N.; Sun, F.; Zhuang, L.; Hu, N.; Wang, P. Recent Achievements in Electronic Tongue and Bioelectronic Tongue as Taste Sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno i Codinachs, L.; Kloock, J.P.; Schöning, M.J.; Baldi, A.; Ipatov, A.; Bratov, A.; Jiménez-Jorquera, C. Electronic Integrated Multisensor Tongue Applied to Grape Juice and Wine Analysis. Analyst 2008, 133, 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polshin, E.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Kirsanov, D.; Legin, A.; Saison, D.; Delvaux, F.; Delvaux, F.R.; Nicolaï, B.M.; Lammertyn, J. Electronic Tongue as a Screening Tool for Rapid Analysis of Beer. Talanta 2010, 81, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudnitskaya, A.; Nieuwoudt, H.H.; Muller, N.; Legin, A.; Du Toit, M.; Bauer, F.F. Instrumental Measurement of Bitter Taste in Red Wine Using an Electronic Tongue. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 3051–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrieta, Á.A.; Rodríguez-Méndez, M.L.; de Saja, J.A.; Blanco, C.A.; Nimubona, D. Prediction of Bitterness and Alcoholic Strength in Beer Using an Electronic Tongue. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.Y.; Deng, S.P.; Chen, Z.X. Multifrequency Large Amplitude Pulse Voltammetry: A Novel Electrochemical Method for Electronic Tongue. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 123, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, I.; Masot, R.; Alcañiz, M.; Gil, L.; Soto, J.; Vivancos, J.L.; García-Breijo, E.; Labrador, R.H.; Barat, J.M.; Martínez-Mañez, R. Accurate Concentration Determination of Anions Nitrate, Nitrite and Chloride in Minced Meat Using a Voltammetric Electronic Tongue. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 149, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivarsson, P.; Holmin, S.; Höjer, N.-E.; Krantz-Rülcker, C.; Winquist, F. Discrimination of Tea by Means of a Voltammetric Electronic Tongue and Different Applied Waveforms. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 76, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, F.P.A.; Bergamo, B.B.; Dantas, C.A.R.; Riul, A.; Giacometti, J.A. Impedance E-Tongue Instrument for Rapid Liquid Assessment. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2009, 80, 026107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, V.; Arrieta, Á.A.; Fernández-Escudero, J.A.; Íñiguez, M.; De Saja, J.A.; Rodríguez-Méndez, M.L. Monitoring of the Ageing of Red Wines in Oak Barrels by Means of an Hybrid Electronic Tongue. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 563, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riul, A., Jr.; Correa, D.S. A First Taste to Electronic Tongues. In Electronic Tongues: Fundamentals and Recent Advances; Shimizu, F.M., Braunger, M.L., Riul, A., Jr., Eds.; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; pp. 1-1–1-4. ISBN 0750336870. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, F.M.; Gaál, G.; Braunger, M.L.; Riul, A., Jr. Recent Developments on Devices Applied to Impedimetric Electronic Tongues. In Electronic Tongues Fundamentals and Recent Advances; Shimizu, F.M., Braunger, M.L., Riul, A., Jr., Eds.; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; pp. 7-1–7-19. ISBN 0750336870. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, P.; Du, L.; Wu, C. Advances in Gustatory Biomimetic Biosensing Technologies: In Vitro and in Vivo Bioelectronic Tongue. TrAC Trends Analyt. Chem. 2022, 157, 116778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Chen, W.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, P.; Wu, C.; Wang, P. A Biomimetic Taste Biosensor Based on Bitter Receptors Synthesized and Purified on Chip from a Cell-Free Expression System. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 312, 127949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sànchez, J.; Del Valle, M. A New Potentiometric Photocurable Membrane Selective to Anionic Surfactants. Electroanalysis 2001, 13, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-M.; Jang, S.-W.; Lee’, S.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Kang, S.-W. Measurement of Basic Taste Substances by a Fiber Optic Taste Sensor Using Evanescent Field Absorption. Sens. Mater. 2002, 4, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda, H.; Watari, J.; Takashio, M.; Okahata, Y. Adsorption and Desorption of Beer and Coffee on a Lipid Membrane as Related to Sensory Bitterness. J. Inst. Brew. 2003, 109, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauliukaite, R.; Zhylyak, G.; Citterio, D.; Spichiger-Keller, U.E. L-Glutamate Biosensor for Estimation of the Taste of Tomato Specimens. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 386, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cetó, X.; Céspedes, F.; Del Valle, M. Assessment of Individual Polyphenol Content in Beer by Means of a Voltammetric BioElectronic Tongue. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumarana, S.K.; Yeea, K.K.; Iwatab, S.; Kothaa, R.; Quezada-Calvillo, R.; Nichols, B.L.; Mohan, S.; Pinto, B.M.; Shigemura, N.; Ninomiya, Y.; et al. Taste Cell-Expressed α-Glucosidase Enzymes Contribute to Gustatory Responses to Disaccharides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 6035–6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toko, K. Taste Sensor with Global Selectivity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 1996, 4, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, I.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Joo, S.-T. Low-Temperature and Long-Time Heating Regimes on Non-Volatile Compound and Taste Traits of Beef Assessed by the Electronic Tongue System. Food Chem. 2020, 320, 126656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bi, J.; Lin, Z.; Yang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Ping, C.; Chen, Z. Mining of Kokumi Peptides in Chicken Broth with Peptidomics. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2023, 32, 100693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikuni, K.; Oe, M.; Sasaki, K.; Shibata, M.; Nakajima, I.; Ojima, K.; Muroya, S. Effects of Muscle Type on Beef Taste-Traits Assessed by an Electric Sensing System. Anim. Sci. J. 2010, 81, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nodake, K.; Numata, M.; Kosai, K.; Kim, Y.J.; Nishiumi, T. Evaluation of Changes in the Taste of Cooked Meat Products during Curing Using an Artificial Taste Sensor. Anim. Sci. J. 2013, 84, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, H.; Narita, Y.; Iwai, K.; Hanzawa, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Kakiuchi, M.; Ariki, S.; Wu, X.; Miyake, K.; Tahara, Y. Bitterness Compounds in Coffee Brew Measured by Analytical Instruments and Taste Sensing System. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zou, G.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Z. Beer Taste Detection Based on Electronic Tongue. Sens. Mater. 2020, 32, 2949–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Miyake, K.; Tahara, Y.; Fujimoto, H.; Iwai, K.; Narita, Y.; Hanzawa, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Kakiuchi, M.; Ariki, S. Quantification of Bitterness of Coffee in the Presence of High-Potency Sweeteners Using Taste Sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 309, 127784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, Y.; Yamashita, M.; Kato, M.; Suzuki, T.; Omori, M.; Chen, R. Evaluation of the Taste of Tea with Different Degrees of Fermentation Using a Taste Sensing System. Sens. Mater. 2011, 23, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.; Dai, L.; Kang, B.; Zhang, L.; Shi, J.; Gui, X.; Liu, P.; Li, X. Traditional Human Taste Panel and Taste Sensors Methods for Bitter Taste Masking Research on Combined Bitterness Suppressants of Berberine Hydrochloride. Sens. Mater. 2017, 29, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnenblust-Woertz, K.; Pein, M.; Breitkreutz, J. Development and Characterization of Medicines for Children. In Biochemical Sensors: Mimicking Gustatory and Olfactory Senses; Kiyoshi, T., Ed.; Pan Stanford Publishing: Singapore, 2013; pp. 185–203. [Google Scholar]
- Uchida, T.; Yoshida, M.; Hazekawa, M.; Haraguchi, T.; Furuno, H.; Teraoka, M.; Ikezaki, H. Evaluation of Palatability of 10 Commercial Amlodipine Orally Disintegrating Tablets by Gustatory Sensation Testing, OD-Mate as a New Disintegration Apparatus and the Artificial Taste Sensor. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 65, 1312–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woertz, K.; Tissen, C.; Kleinebudde, P.; Breitkreutz, J. A Comparative Study on Two Electronic Tongues for Pharmaceutical Formulation Development. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 55, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, H.; Kurihara, T.; Yoshida, M.; Haraguchi, T.; Nishikawa, H.; Ikegami, S.; Okuno, T.; Yamashita, T.; Nishikawa, J.; Tsujino, H.; et al. A New Bitterness Evaluation Index Obtained Using the Taste Sensor for 48 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients of Pediatric Medicines. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 69, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, T.; Uchida, T.; Yoshida, M.; Kojima, H.; Habara, M.; Ikezaki, H. The Utility of the Artificial Taste Sensor in Evaluating the Bitterness of Drugs: Correlation with Responses of Human TASTE2 Receptors (HTAS2Rs) Methods Taste Sensor Measurement The Taste Sensor SA402B (Intelligent Sensor Technol. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 66, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Toko, K. Taste Sensor with Multiarray Lipid/Polymer Membranes. TrAC Trends Analyt. Chem. 2022, 158, 116874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toko, K. Research and Development of Taste Sensors as a Novel Analytical Tool. Proc. Jpn. Acad., Ser. B 2023, 99, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woertz, K.; Tissen, C.; Kleinebudde, P.; Breitkreutz, J. Rational Development of Taste Masked Oral Liquids Guided by an Electronic Tongue. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 400, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tahara, Y.; Yatabe, R.; Toko, K. Taste Sensor: Electronic Tongue with Lipid Membranes. Anal. Sci. 2020, 36, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimatsu, J.; Toko, K.; Tahara, Y.; Ishida, M.; Habara, M.; Ikezaki, H.; Kojima, H.; Ikegami, S.; Yoshida, M.; Uchida, T. Development of Taste Sensor to Detect Non-Charged Bitter Substances. Sensors 2020, 20, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunasekaran, K.; Ma, B.; Nussinov, R. Is Allostery an Intrinsic Property of All Dynamic Proteins? Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 2004, 57, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.Y.M.; Keri, D.; Barth, P. Computational Design of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Allosteric Signal Transductions. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Klebansky, B.; Fine, R.M.; Xu, H.; Pronin, A.; Liu, H.; Tachdjian, C.; Li, X. Molecular Mechanism for the Umami Taste Synergism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20930–20934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Ishida, M.; Onodera, T.; Toko, K. Effect of Hydroxybenzoic Acids on Caffeine Detection Using Taste Sensor with Lipid/Polymer Membranes. Sensors 2022, 22, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, M.; Ide, H.; Arima, K.; Zhao, Z.; Matsui, T.; Toko, K. Identification of the Principle of Taste Sensors to Detect Non-Charged Bitter Substances by 1H-NMR Measurement. Sensors 2022, 22, 2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Kimura, S.; Onodera, T.; Toko, K. Molecular Structure Underlying the Allosteric Mechanism of Caffeine Detection in Taste Sensor. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuy, L.N.; Salanta, L.C.; Tofana, M.; Sicaci, S.A.; Fărcaș, A.C.; Pop, C.R. Mini Review About Monosodium Glutamate. Bull. UASVM Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 77, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cepanec, K.; Vugrinec, S.; Cvetković, T.; Ranilović, J. Potassium Chloride-based Salt Substitutes: A Critical Review with a Focus on the Patent Literature. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 881–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairoli, P.; Pieraccini, S.; Sironi, M.; Morelli, C.F.; Speranza, G.; Manitto, P. Studies on Umami Taste. Synthesis of New Guanosine 5′-Phosphate Derivatives and Their Synergistic Effect with Monosodium Glutamate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, H.; Yang, J.T. Dilatometric and Refractometric Studies of the Helix—Coil Transition of Poly-L-glutamic Acid in Aqueous Solution. Biopolymers 1963, 1, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurko, E.N.; Neueder, R.; Kunz, W. Water Activity and Osmotic Coefficients in Solutions of Glycine, Glutamic Acid, Histidine and Their Salts at 298.15 K and 310.15 K. J. Solution Chem. 2007, 36, 651–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iiyama, S.; Kuga, H.; Ezaki, S.; Hayashi, K.; Toko, K. Peculiar Change in Membrane Potential of Taste Sensor Caused by Umami Substances. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 91, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Habara, M.; Ikezazki, H.; Chen, R.; Naito, Y.; Toko, K. Advanced Taste Sensors Based on Artificial Lipids with Global Selectivity to Basic Taste Qualities and High Correlation to Sensory Scores. Sensors 2010, 10, 3411–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosimbescu, L.; Merkel, D.R.; Darsell, J.; Petrossian, G. Simple but Tricky: Investigations of Terephthalic Acid Purity Obtained from Mixed PET Waste. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 12792–12797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszek, K.; Pankalla, E.; Grymel, A.; Latos, P.; Chrobok, A. Studies on the Solubility of Terephthalic Acid in Ionic Liquids. Molecules 2019, 25, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, F.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Li, K. Influence of Intramolecular Hydrogen Bond of Templates on Molecular Recognition of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 450, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, G.E.; Kung, F. Effect of Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding on Ionization Constants of Substituted Salicylic Acids. Can. J. Chem. 1996, 44, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, P.I. Competing Intramolecular vs. Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonds in Solution. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 19562–19633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijayasekara, K.; Wansapala, J. Uses, Effects and Properties of Monosodium Glutamate (MSG) on Food & Nutrition. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 2, 132–143. [Google Scholar]

| Sample | Composition | Concentration |
|---|---|---|
| Sourness | Tartaric acid | 3 mM |
| Bitterness (+) | Quinine hydrochloride | 0.1 mM |
| Bitterness (−) | Iso-α acid | 0.01 vol% |
| Saltiness | Potassium chloride (KCl) | 300 mM |
| Astringency | Tannic acid | 0.05 wt% |
| Sweetness | Sucrose | 1 M |
| Umami | Monosodium L-glutamate (MSG) | 100 mM |
| Monosodium L-aspartate (MSA) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, W.; Zhao, Z.; Kimura, S.; Toko, K. Development of Taste Sensor with Lipid/Polymer Membranes for Detection of Umami Substances Using Surface Modification. Biosensors 2024, 14, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14020095
Yuan W, Zhao Z, Kimura S, Toko K. Development of Taste Sensor with Lipid/Polymer Membranes for Detection of Umami Substances Using Surface Modification. Biosensors. 2024; 14(2):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14020095
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Wenhao, Zeyu Zhao, Shunsuke Kimura, and Kiyoshi Toko. 2024. "Development of Taste Sensor with Lipid/Polymer Membranes for Detection of Umami Substances Using Surface Modification" Biosensors 14, no. 2: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14020095
APA StyleYuan, W., Zhao, Z., Kimura, S., & Toko, K. (2024). Development of Taste Sensor with Lipid/Polymer Membranes for Detection of Umami Substances Using Surface Modification. Biosensors, 14(2), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14020095






