Characterization of Single-Spheroid Oxygen Consumption Using a Microfluidic Platform and Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
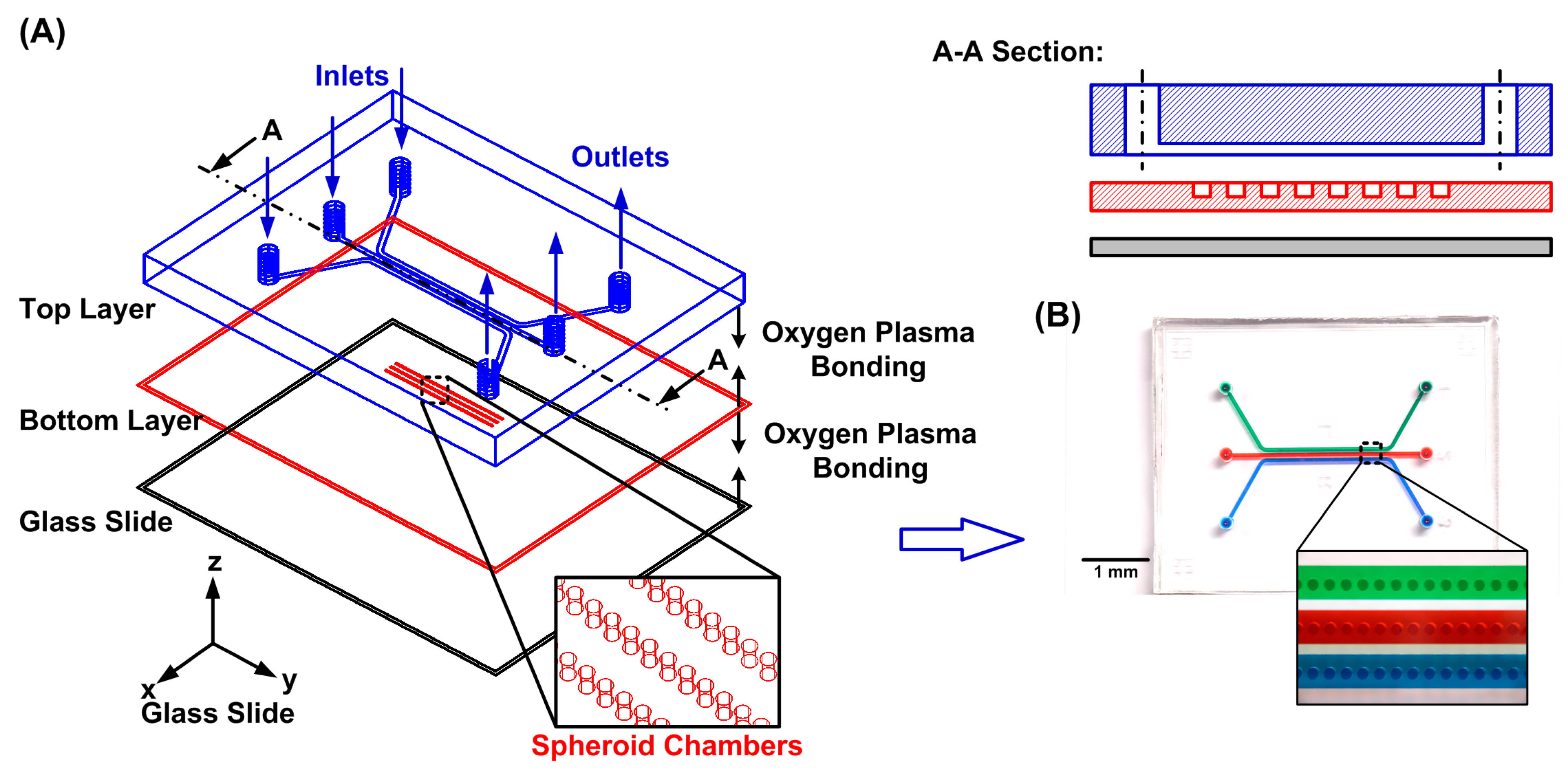
2.1. Microfluidic Device Design and Fabrication
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Tumor Spheroid Formation
2.4. Cell Viability
2.5. Oxygen Tension Measurement
2.6. Drug Treatment
3. Results and Discussion
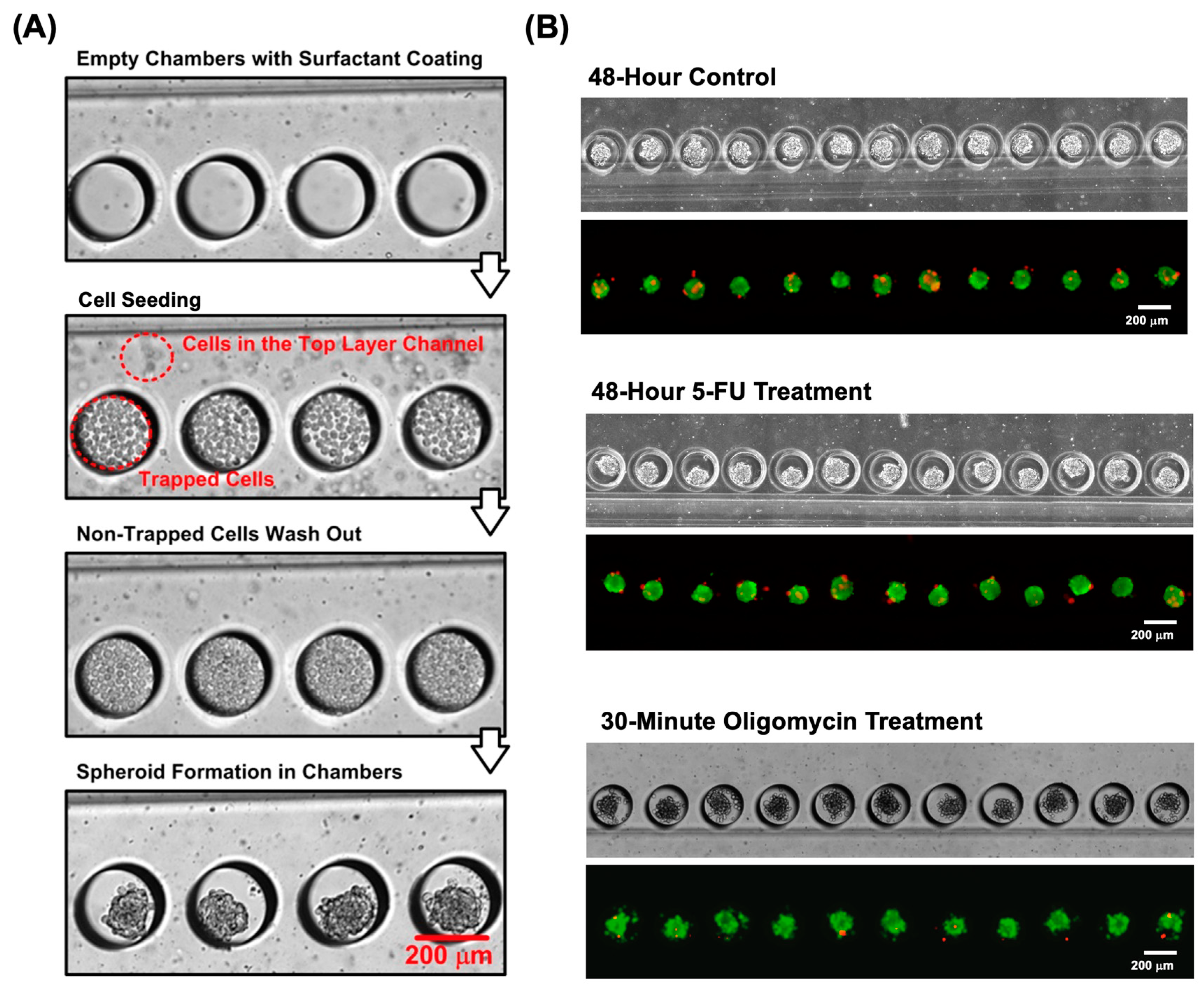
3.1. Formation and Culture of Single Spheroids
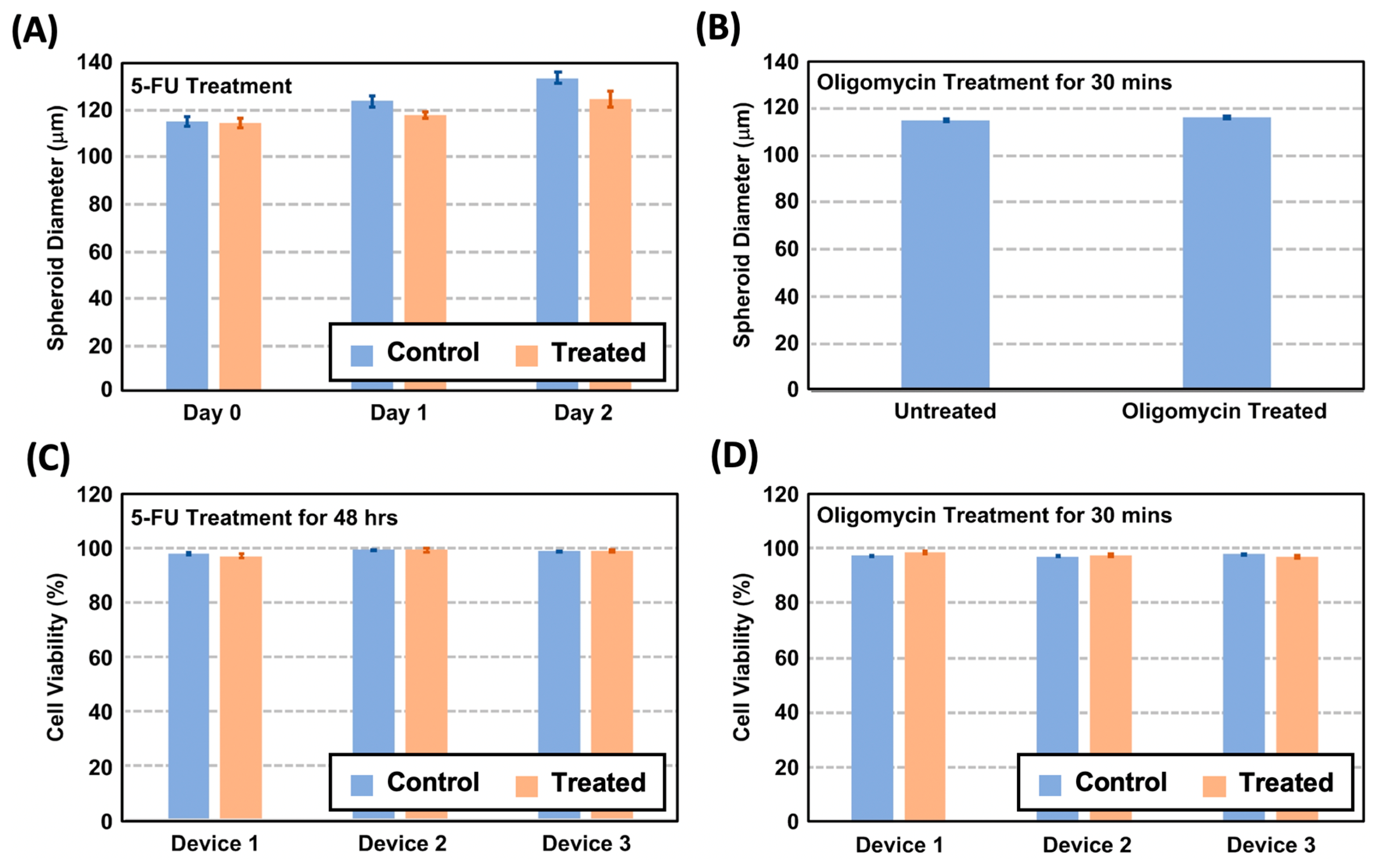
3.2. Cell Viability and Spheroid Growth Analysis
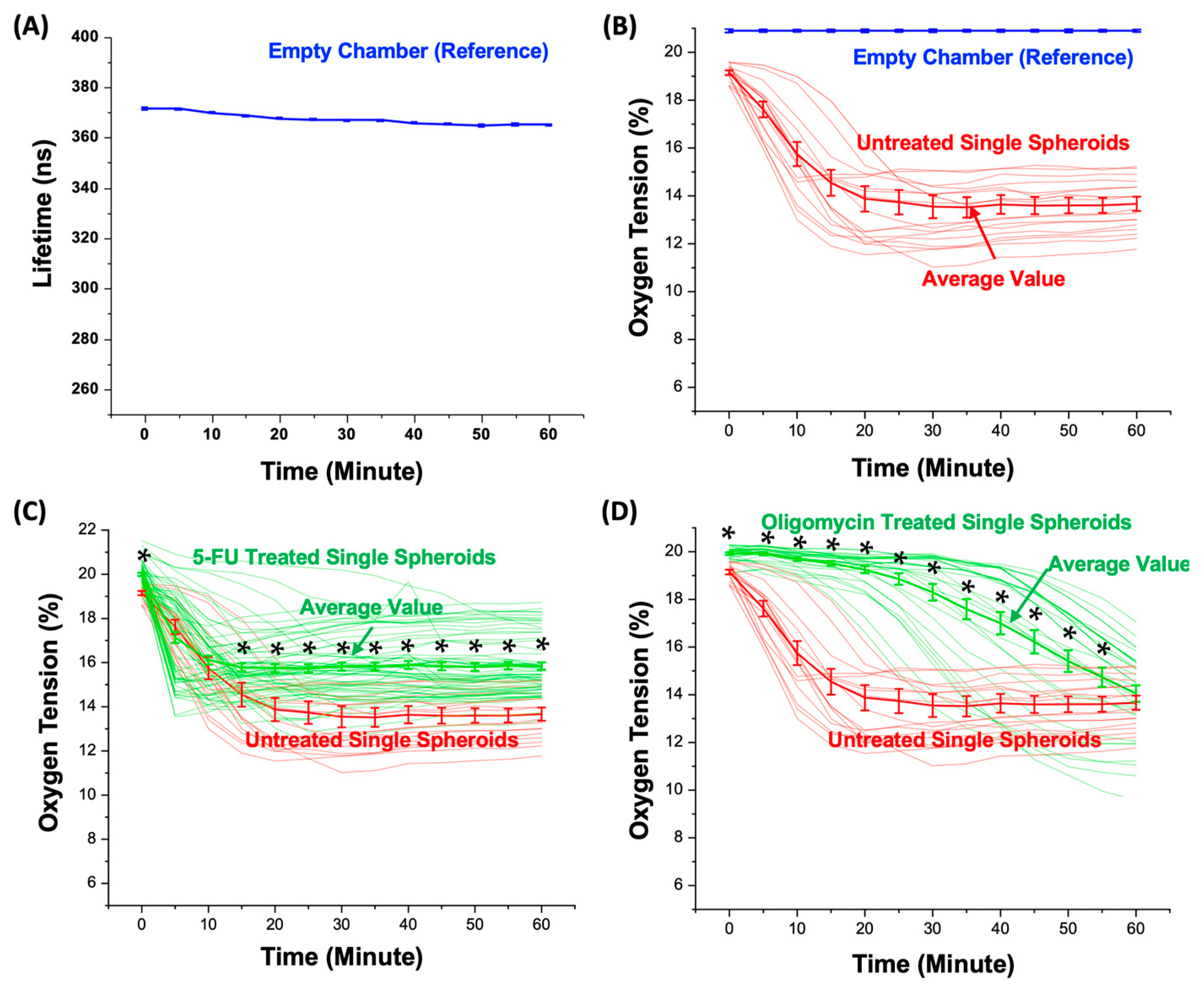
3.3. Oxygen Tension Measurement in the Microfluidic Device
3.4. Oxygen Consumption of the Single Spheroids
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lupoli, F.; Vannocci, T.; Longo, G.; Niccolai, N.; Pastore, A. The role of oxidative stress in Friedreich’s ataxia. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimzadeh, M.; Khashayar, P.; Amereh, M.; Tasnim, N.; Hoorfar, M.; Akbari, M. Microfluidic-Based Oxygen (O2) Sensors for On-Chip Monitoring of Cell, Tissue and Organ Metabolism. Biosensors 2021, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrell, R.A.; Mcgranahan, N.; Bartek, J.; Swanton, C. The causes and consequences of genetic heterogeneity in cancer evolution. Nature 2013, 501, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.; Wojtkowiak, J.; Neilson, A.; Gillies, R.J. Metabolic Profiling of healthy and cancerous tissues in 2D and 3D. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leek, R.; Grimes, D.R.; Harris, A.L.; McIntyre, A. Methods: Using Three-Dimensional Culture (Spheroids) as an In Vitro Model of Tumour Hypoxia. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 899, 167–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, X.; Gao, L.; Dean, D.C.; Liu, Y. Spheroid-induced heterogeneity and plasticity of uveal melanoma cells. Cell. Oncol. 2022, 45, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.Y.; Purdie, T.G.; Stewart, E. CT imaging of angiogenesis. Q. J. Nucl. Med. 2003, 47, 171–187. [Google Scholar]
- Langan, L.M.; Dodd, N.J.; Owen, S.F.; Purcell, W.M.; Jackson, S.K.; Jha, A.N. Direct Measurements of Oxygen Gradients in Spheroid Culture System Using Electron Parametric Resonance Oximetry. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, B.M.; Paoni, S.F.; Lee, J.; Koch, C.J.; Lord, E.M. Quantification of tumour vasculature and hypoxia by immunohistochemical staining and HbO2 saturation measurements. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 79, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Aleksandrova, A.V.; Pulkova, N.P.; Gerasimenko, T.N.; Anisimov, N.Y.; Tonevitskaya, S.A.; Sakharov, D.A. Mathematical and Experimental Model of Oxygen Diffusion for HepaRG Cell Spheroids. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 160, 857–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller-Klieser, W. Method for the determination of oxygen consumption rates and diffusion coefficients in multicellular spheroids. Biophys. J. 1984, 46, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimes, D.R.; Warren, D.R.; Warren, S. Hypoxia imaging and radiotherapy: Bridging the resolution gap. Br. J. Radiol. 2017, 90, 20160939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmitriev, R.I.; Zhdanov, A.V.; Jasionek, G.; Papkovsky, D.B. Assessment of cellular oxygen gradients with a panel of phosphorescent oxygen-sensitive probes. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 2930–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmitriev, R.I.; Papkovsky, D.B. Intracellular probes for imaging oxygen concentration: How good are they? Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2015, 3, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.H.; Huang, K.S.; Yu, C.H.; Gong, H.Y. Metabolic profile analysis of a single developing zebrafish embryo via monitoring of oxygen consumption rates within a microfluidic device. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 64107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-M.; Lee, T.-A.; Ko, P.-L.; Liao, W.-H.; Hsieh, T.-H.; Tung, Y.-C. Widefield frequency domain fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FD-FLIM) for accurate measurement of oxygen gradients within microfluidic devices. Analyst 2019, 144, 3494–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, S.; Ko, P.L.; Wu, H.M.; Tung, Y.C. Efficient single-cell oxygen consumption rate characterization based on frequency domain fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy measurement and microfluidic platform. Biomicrofluidics 2023, 17, 054105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Whitesides, G.M. Soft Lithography. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1998, 37, 550–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, B.; Chen, Y.H.; Peng, C.C.; Lin, S.C.; Lee, C.H.; Tung, Y.C. A microfluidic device for uniform-sized cell spheroids formation, culture, harvesting and flow cytometry analysis. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 54114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdonald, J.C.; Duffy, D.C.; Anderson, J.R.; Chiu, D.T.; Wu, H.; Schueller, O.J.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Fabrication of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Electrophoresis 2000, 21, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.; Lee, E.; Almeida, M.; Kim, S.; Logrande, N.; Goyal, G.; Sesay, A.M.; Breault, D.T.; Prantil-Baun, R.; Ingber, D.E. Establishment of physiologically relevant oxygen gradients in microfluidic organ chips. Lab A Chip 2022, 22, 1584–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadgar, N.; Gonzalez-Suarez, A.M.; Fattahi, P.; Hou, X.; Weroha, J.S.; Gaspar-Maia, A.; Stybayeva, G.; Revzin, A. A microfluidic platform for cultivating ovarian cancer spheroids and testing their responses to chemotherapies. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrucki, J.W. Interaction of oxygen-sensitive luminescent probes Ru(phen)(3)(2+) and Ru(bipy)(3)(2+) with animal and plant cells in vitro—Mechanism of phototoxicity and conditions for non-invasive oxygen measurements. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B-Biol. 2001, 65, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turecka, K.; Chylewska, A.; Dąbrowska, A.M.; Hałasa, R.; Orlewska, C.; Waleron, K. Ru(II) Oxygen Sensors for Co(III) Complexes and Amphotericin B Antifungal Activity Detection by Phosphorescence Optical Respirometry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakowicz, J.R.; Terpetschnig, E.; Murtaza, Z.; Szmacinski, H. Development of long-lifetime metal-ligand probes for biophysics and cellular imaging. J. Fluoresc. 1996, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.M.; Wu, W.H.; Wu, W.T.; Song, P.; Han, K.L.; Wang, Z.G.; Liu, S.S.; Guo, H.M.; Zhao, J.Z. Tuning the luminescence lifetimes of ruthenium(II) polypyridine complexes and its application in luminescent oxygen sensing. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 1953–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Urayama, P.; Mycek, M.A. Imaging fluorescence lifetime modulation of a ruthenium-based dye in living cells: The potential for oxygen sensing. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, 1689–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, H.C.; Lee, T.A.; Wu, H.M.; Ko, P.L.; Liao, W.H.; Tung, Y.C. Microfluidic Collective Cell Migration Assay for Study of Endothelial Cell Proliferation and Migration under Combinations of Oxygen Gradients, Tensions, and Drug Treatments. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigmore, P.M.; Mustafa, S.; El-Beltagy, M.; Lyons, L.; Umka, J.; Bennett, G. Effects of 5-FU. In Chemo Fog; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, G.; Hsiao, A.Y.; Ingram, M.; Luker, G.D.; Takayama, S. Opportunities and challenges for use of tumor spheroids as models to test drug delivery and efficacy. J. Control. Release 2012, 164, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, S.; Jin, S.; Cai, H.; Huang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Lin, K.; et al. The Analysis of Differentially Expressed circRNAs under the Antiproliferative Effect From 5-Fluorouracil on Osteosarcoma Cells. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 153303382096421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruas, J.S.; Siqueira-Santos, E.S.; Rodrigues-Silva, E.; Castilho, R.F. High glycolytic activity of tumor cells leads to underestimation of electron transport system capacity when mitochondrial ATP synthase is inhibited. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kannan, S.; Peng, C.-C.; Wu, H.-M.; Tung, Y.-C. Characterization of Single-Spheroid Oxygen Consumption Using a Microfluidic Platform and Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy. Biosensors 2024, 14, 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14020096
Kannan S, Peng C-C, Wu H-M, Tung Y-C. Characterization of Single-Spheroid Oxygen Consumption Using a Microfluidic Platform and Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy. Biosensors. 2024; 14(2):96. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14020096
Chicago/Turabian StyleKannan, Santhosh, Chien-Chung Peng, Hsiao-Mei Wu, and Yi-Chung Tung. 2024. "Characterization of Single-Spheroid Oxygen Consumption Using a Microfluidic Platform and Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy" Biosensors 14, no. 2: 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14020096
APA StyleKannan, S., Peng, C.-C., Wu, H.-M., & Tung, Y.-C. (2024). Characterization of Single-Spheroid Oxygen Consumption Using a Microfluidic Platform and Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy. Biosensors, 14(2), 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14020096





