A Ratiometric Fluorescence Method Based on PCN-224-DABA for the Detection of Se(IV) and Fe(III)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of PCN-224-DABA
2.3. PCN-224-DABA-Based Ratiometric Fluorescence for Se(IV) Detection
2.4. PCN-224-DABA-Based Ratiometric Fluorescence for Fe(III) Detection
2.5. Selectivity and Interference Study
2.6. Real Sample Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
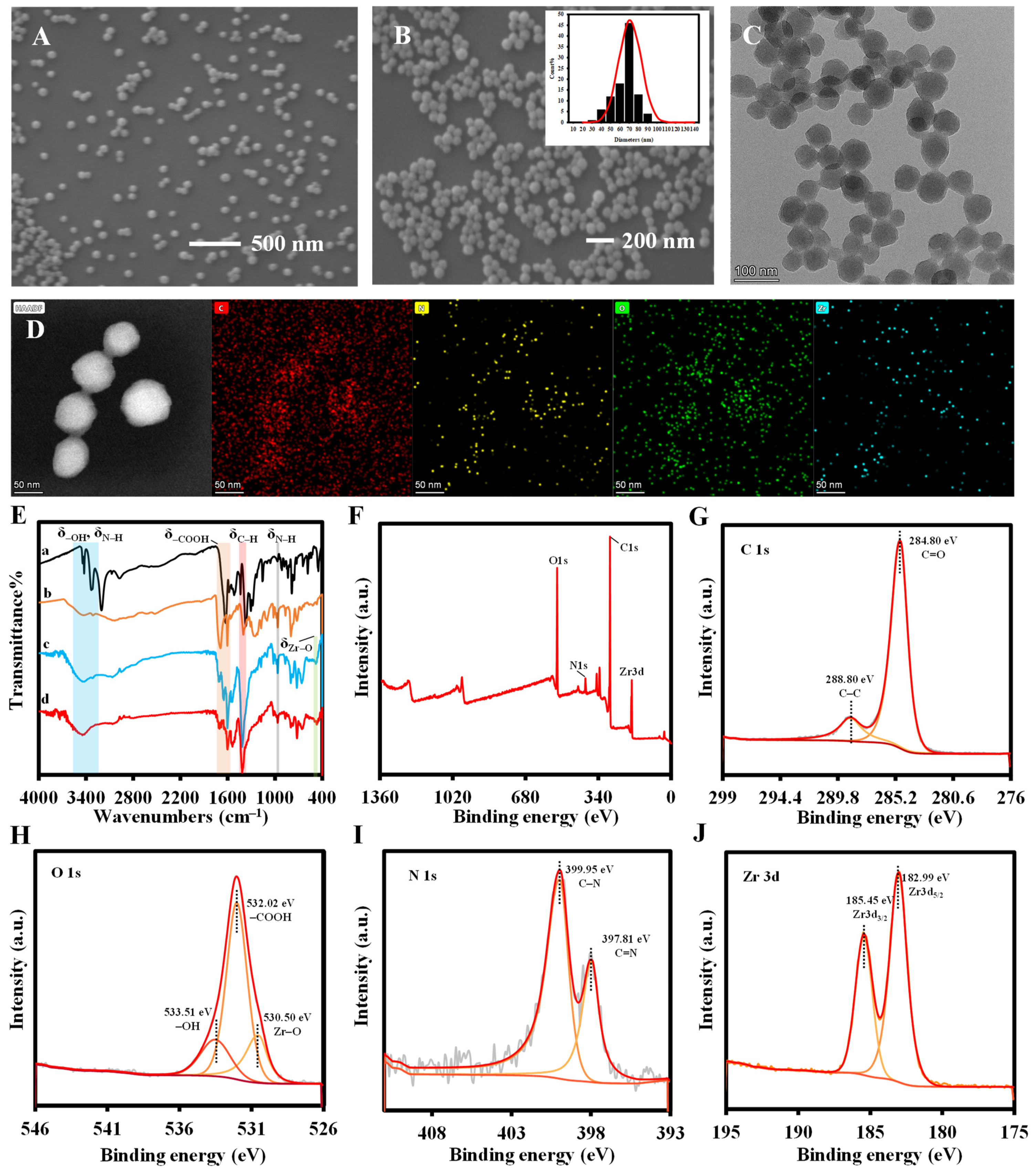
3.1. Characterizations of PCN-224-DABA
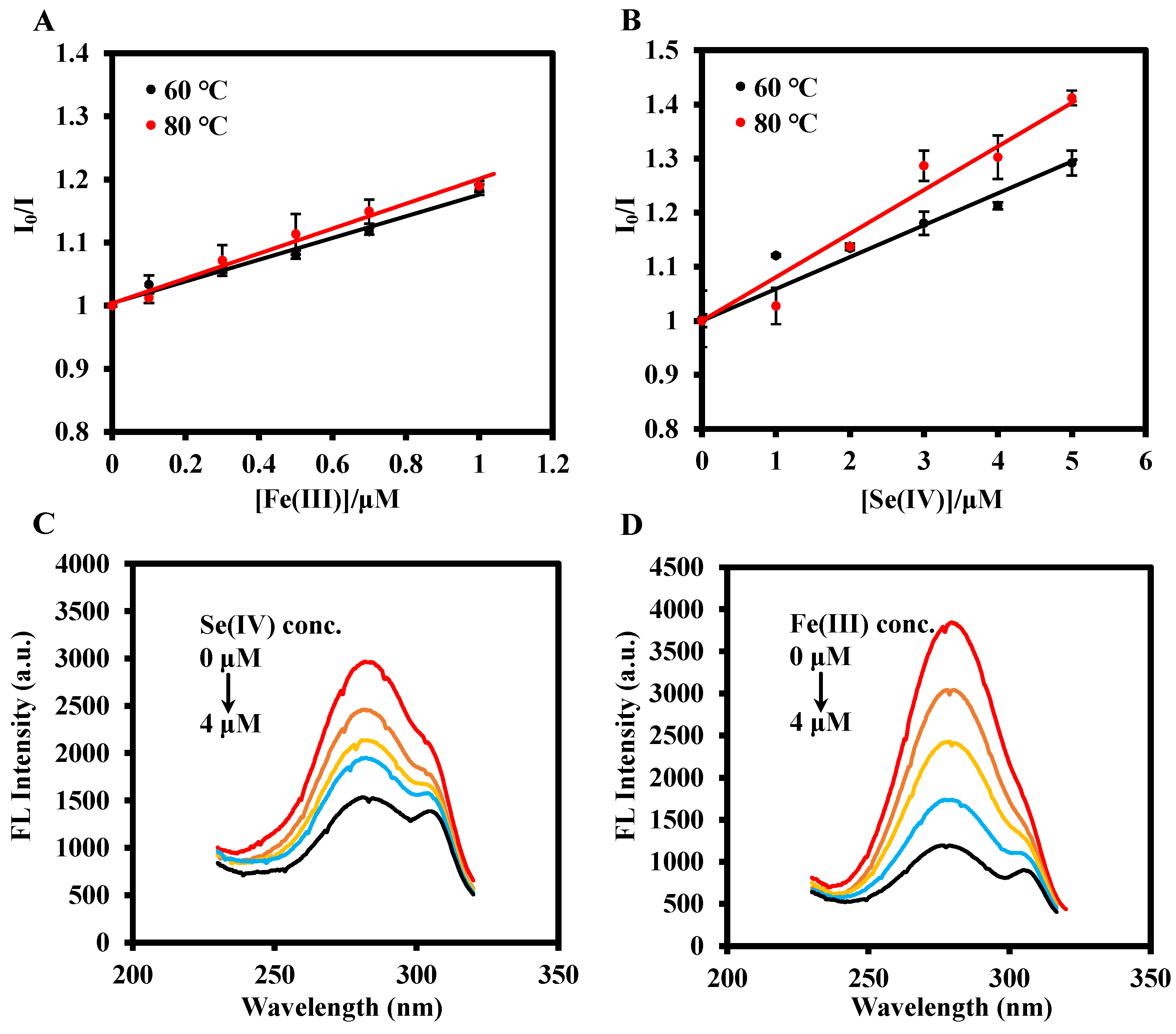
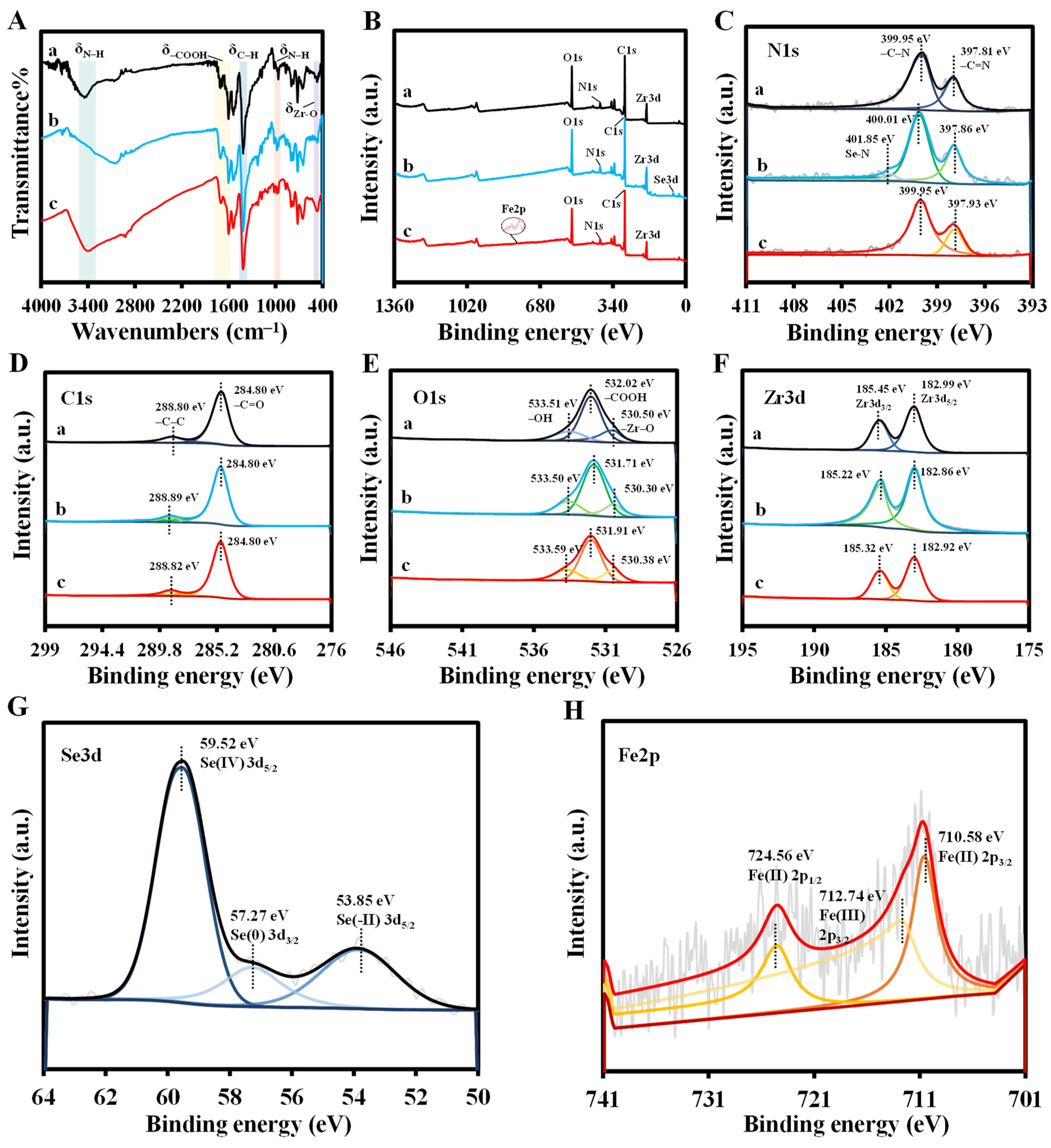
3.2. Feasibility and Detection Mechanism
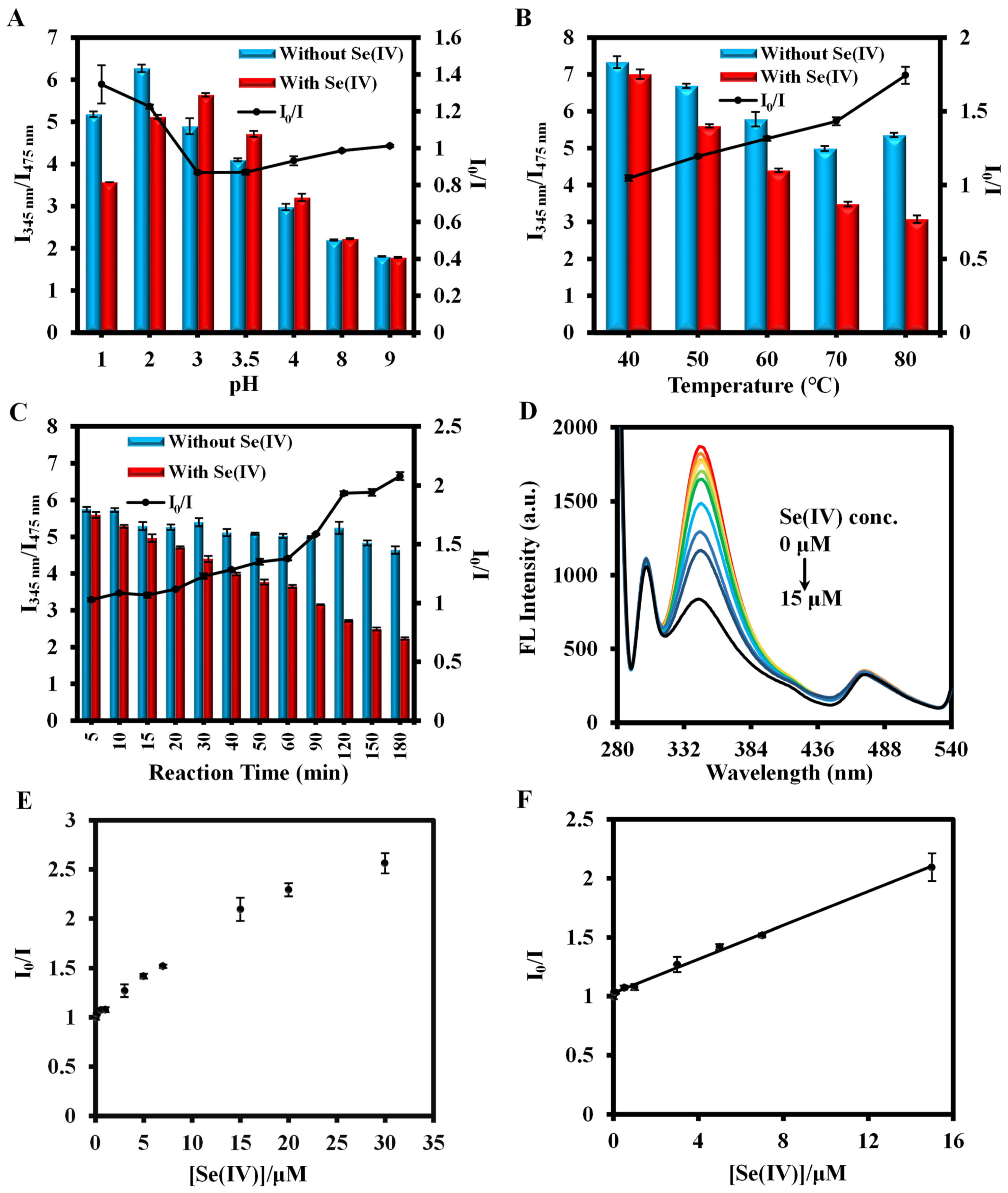
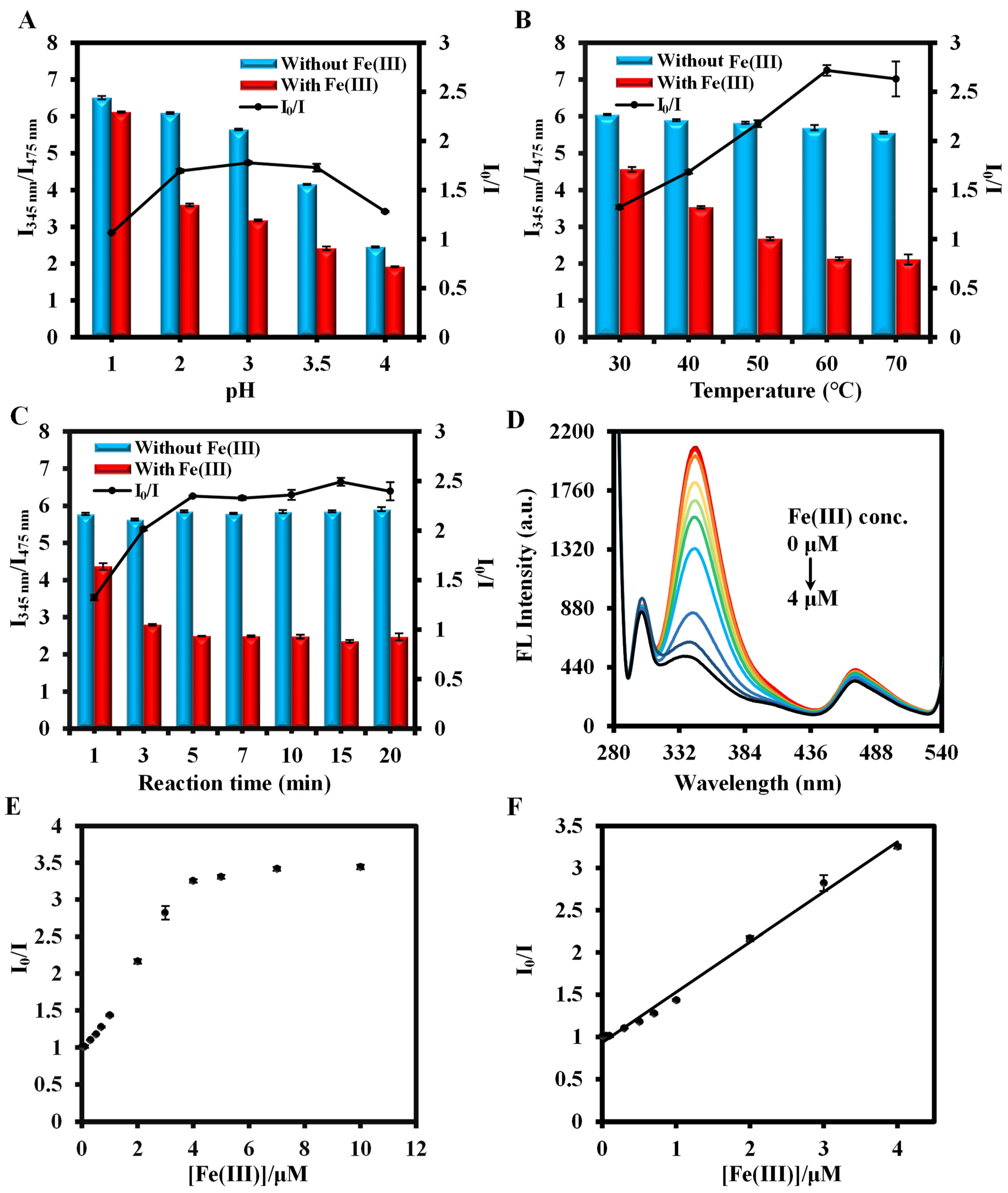
3.3. Optimization of Se(IV) and Fe(III) Detection Conditions
3.4. Detection of Se(IV) and Fe(III) by the Ratiometric Fluorescence Method Based on PCN-224-DABA
3.5. Selectivity and Interference Study
3.6. Real Sample Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gebreeyessus, G.D.; Zewge, F. A review on environmental selenium issues. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, A.; Lombi, E.; Donner, E.; de Jonge, M.D.; Punshon, T.; Jackson, B.P.; Guerinot, M.L.; Price, A.H.; Meharg, A.A. A review of recent developments in the speciation and location of arsenic and selenium in rice grain. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 3275–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadrup, N.; Ravn-Haren, G. Toxicity of repeated oral intake of organic selenium, inorganic selenium, and selenium nanoparticles: A review. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2023, 79, 127235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkel, L.H.; Vriens, B.; Jones, G.D.; Schneider, L.S.; Pilon-Smits, E.; Banuelos, G.S. Selenium cycling across soil-plant-atmosphere interfaces: A critical review. Nutrients 2015, 7, 4199–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.S.; Soyk, A.; Wolf, I.; Peter, M.; Meyer, A.J.; Rausch, T.; Wirtz, M.; Hell, R. Discriminative long-distance transport of selenate and selenite triggers glutathione oxidation in specific subcellular compartments of root and shoot cells in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 894479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinceti, M.; Filippini, T.; Jablonska, E.; Saito, Y.; Wise, L.A. Safety of selenium exposure and limitations of selenoprotein maximization: Molecular and epidemiologic perspectives. Environ. Res. 2022, 211, 113092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brozmanova, J.; Manikova, D.; Vlckova, V.; Chovanec, M. Selenium: A double-edged sword for defense and offence in cancer. Arch. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 919–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; He, C.; Shi, L.; Li, J. Fe(III) concentrations controlled highly soluble carboxylated inulin-Fe toward efficient supplement of iron. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Li, L.; Zhao, R.; Xiang, L.; Gong, X.; Zheng, Z.; Qiao, X. Developing garlic polysaccharide-Fe(III) complexes using garlic pomace to provide enhanced iron-supplementing activity in vivo. Food Chem. 2024, 437, 137819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, A.R.; Nunes, I.S.; Fernandes, J.P.A.; Andrade, S.I.E.; Pessoa, A.G.G.; de Lima, R.A.C. A digital image-based flow-batch analyzer for iron speciation in tomato. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 115, 104998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yu, L.; Liu, Q.; Ma, X.; Zhang, S.; Sun, M.; Wang, S. Multi-dentate chelation induces fluorescence enhancement of pyrene moiety for highly selective detection of Fe(III). Anal. Sci. 2022, 38, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Cui, C.; Luo, Y.; Peng, Z. Sensitive, selective and reliable detection of Fe3+ in lake water via carbon dots-based fluorescence assay. Molecules 2022, 27, 6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altunay, N.; Tuzen, M. A simple and green ultrasound liquid-liquid microextraction method based on low viscous hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent for the preconcentration and separation of selenium in water and food samples prior to HG-AAS detection. Food Chem. 2021, 364, 130371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ul Haq, H.; Elik, A.; Isci, G.; Ekici, M.; Gürsoy, N.; Boczkaj, G.; Altunay, N. Development of a vortex-assisted switchable-hydrophilicity solvent-based liquid phase microextraction for fast and reliable extraction of Zn(II), Fe(II), Pb(II), and Cd(II) from various baby food products. Food Chem. 2024, 447, 139024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelo, J.; Fernandez, C.; Pedras, B.; Santos, P.; Gonzalez, P.; Vaz, C. Trends in selenium determination/speciation by hyphenated techniques based on AAS or AFS. Talanta 2006, 68, 1442–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llaver, M.; Barrionuevo, S.D.; Núñez, J.M.; Chapana, A.L.; Wuilloud, R.G.; Aguirre, M.H.; Ibañez, F.J. Fluorescent graphene quantum dots-enhanced machine learning for the accurate detection and quantification of Hg2+ and Fe3+ in real water samples. Environ. Sci. Nano 2024, 11, 2703–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, R.; Xiao, X.; Liu, J.; Guo, Z.; He, H.; Wang, X.; Wen, X.; Angelo, V.; Han, J. Protective effects of functional nano-selenium supplementation on spleen injury through regulation of p38 MAPK and NF-κB protein expression. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 130, 111574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Huangfu, K.; Zhao, J.; Lei, H.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Gu, X. An efficient and low-cost method for the determination of selenium in selenium-enriched tea by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with 3,3’-diaminobenzidine derivatization. Talanta 2024, 268, 125335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichinoki, S.; Fujita, S.; Fujii, Y. Selective determination of iron ion in tap water by solvent extraction with 3,4-dihydro-3-hydroxy-4-oxo-1,2,3-benzotriazine, followed by reversed phase HPLC. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2010, 32, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, P.; Chetan; Sharma, V.; Malakar, A.; Bhinder, S.S.; Kansal, S.K.; Devi, P. A facile method for detection and speciation of inorganic selenium with ion chromatography. Chromatographia 2022, 85, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, V.V.; Kar, A.S.; Jeyakumar, S.; Saxena, M.K. Simultaneous separation and determination of Ti and Fe in uranium alloy by ion chromatography. Microchem. J. 2024, 196, 109639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomar, T.S.; Habila, M.A.; Almasoud, N.; Alothman, Z.A.; Sheikh, M.; Soylak, M. Biomass-derived adsorbent for dispersive solid-phase extraction of Cr(III), Fe(III), Co(II) and Ni(II) from food samples prior to ICP-MS detection. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, C.; Hu, J.; Hou, X. Ultrasensitive determination of selenium in water and food samples by ICP-MS: UIO-66-NH2 for preconcentration and direct slurry hydride generation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1283, 341901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettine, M.; Mcdonald, T.J.; Sohn, M.; Anquandah, G.A.K.; Zboril, R.; Sharma, V.K. A critical review of selenium analysis in natural water samples. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2015, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, A.O.; Mabuba, N.; Arotiba, O.A. Electroanalysis of selenium in water on an electrodeposited gold-nanoparticle modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 758, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalhori, S.; Ahour, F.; Aurang, P. Determination of trace amount of iron cations using electrochemical methods at N, S doped GQD modified electrode. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rievaj, M.; Culková, E.; Aandorová, D.; Lukáčová-Chomisteková, Z.; Bellová, R.; Durdiak, J.; Tomčík, P. Electroanalytical techniques for the detection of selenium as a biologically and environmentally significant analyte–a short review. Molecules 2021, 26, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, T.; Ke, R.; Lu, M.; An, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, K.; Luo, Y.; Li, J.; Cheng, N. Rapid and user-friendly detection of selenium-rich foods using a THEATER colorimetric device with Pt-Co-N-C as viewing glasses. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 472, 144787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzadi-Ahodashti, M.; Ebrahimzadeh, M.A.; Biparva, P.; Bekhradnia, A.R.; Abedirad, S.M. A highly sensitive and selective quinazoline-based colorimetric probe for naked-eye detection of Fe3+ ions. J. Fluoresc. 2022, 32, 2309–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimaitiniyazi, M.; Muhammad, T.; Yasen, A.; Abula, S.; Dolkun, A.; Tursun, Z. Determination of selenium in selenium-enriched products by specific ratiometric fluorescence. Sensors 2023, 23, 9187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, H.; Bhandary, P.; Thakore, S. Biogenic carbon dot-embedded chitosan hydrogels as a two-stage fluorescence OFF-ON probe for sequential and ratiometric detection of Fe(III) and glutathione. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 16253–16266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdillah, A.; Sonawane, P.M.; Kim, D.; Mametov, D.; Shimodaira, S.; Park, Y.; Churchill, D.G. Discussions of fluorescence in selenium chemistry: Recently reported probes, particles, and a clearer biological knowledge. Molecules 2021, 26, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, P.; Niu, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Lu, X. ”Switch-on” fluorescence detection of glucose with high specificity and sensitivity based on silver nanoparticles supported on porphyrin metal-organic frameworks. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 7980–7986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Sun, Q.; Shen, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Yu, S.; Li, X.; Chen, Y. Emerging tetrapyrrole porous organic polymers for chemosensing applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 482, 215078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Mukherjee, S.; Zahid Hussain, M.; Ye, S.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Cao, R.; Elsner, M.; Fischer, R.A. Porphyrin-based MOFs for sensing environmental pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 492, 152377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ai, J.; Nie, X.; Li, Z.; Xia, X.; Hussain, T.; Wang, Q.; Wei, Q. Photodynamic activity enhanced by in situ biosynthetic BC/CQDs@PCN-224 membranes through FRET strategy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 307, 120623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Chung, W.; Wei, Z.; Gu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Y.; Darensbourg, D.J.; Zhou, H. Construction of ultrastable porphyrin Zr metal-organic frameworks through linker elimination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 17105–17110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Shen, Y.; Gao, S.; Chen, Y.; Cui, Y.; Ning, D.; Ji, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L. The Mn-modified porphyrin metal-organic framework with enhanced oxidase-like activity for sensitively colorimetric detection of glutathione. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 213, 114446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, E.; Rahimi, R.; Farahani, Y.D.; Safarifard, V. Porphyrinic zirconium-based MOF with exposed pyrrole lewis base site as a luminescent sensor for highly selective sensing of Cd2+ and Br− ions and THF small molecule. J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 282, 121103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, P.; Yue, J.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, B. Linker-eliminated nano metal-organic framework fluorescent probe for highly selective and sensitive phosphate ratiometric detection in water and body fluids. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 3722–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Song, Y.; Wang, L. Multi-emission metal-organic framework composites for multicomponent ratiometric fluorescence sensing: Recent developments and future challenges. J. Mat. Chem. B 2020, 8, 3292–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xiao, J.; Zhong, G.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X. Design and application of dual-emission metal-organic framework-based ratiometric fluorescence sensors. Analyst 2024, 149, 1381–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Chen, M. Cerium/polyacrylic acid modified porphyrin metal-organic framework as fluorescence and photothermal sensor for ascorbic acid measurement. Talanta 2023, 252, 123825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yang, J.; Du, X.; Lu, X. Fabrication of octahedral GO/UiO-67@PtNPs nanocomposites as an electrochemical sensor for ultrasensitive recognition of arsenic (III) in Chinese herbal medicine. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2022, 1195, 339451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani Nejad, S.; Rahimi, R.; Najafi, M.; Rostamnia, S. Sustainable gold nanoparticle (AuNP) growth within interspaces of porphyrinic zirconium-based metal-organic frameworks: Green synthesis of PCN-224/AuNPs and its anticancer effect on colorectal cancer cells assay. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2024, 16, 3162–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Hu, P.; Li, J.; Huang, P.; Tong, W.; Gao, C. Enhanced peroxidase-like activity of Fe@PCN-224 nanoparticles and their applications for detection of H2O2 and glucose. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 577, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Li, H.; Meng, Q.; Wu, J.; Hou, H. Efficient and selective visible-light-driven oxidative coupling of amines to imines in air over CdS@Zr-MOFs. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2021, 13, 2779–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Xu, Q.; Lv, T.; Liu, H. Integration of rod-shaped PCN-224(Cu) and BIVO4 to establish S–scheme heterojunction for effective photocatalytic CO2-to-CO transformation. J. Alloy. Compd. 2024, 977, 173342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolmohammad-Zadeh, H.; Zamani-Kalajahi, M. A turn-on/off fluorescent sensor based on nano-structured Mg-Al layered double hydroxide intercalated with salicylic acid for monitoring of ferric ion in human serum samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1061, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boorboor Azimi, E.; Badiei, A.; Jafari, M.; Banitalebi Dehkordi, A.; Ghasemi, J.B.; Mohammadi Ziarani, G. Boron-doped graphitic carbon nitride as a novel fluorescent probe for mercury(II) and iron(III): A circuit logic gate mimic. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 12087–12093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Yu, S.; Ci, S.; Xu, Q.; Wen, Z. Z ZnSe-doped N-C skeleton-driven electrode for enhanced electron transport in microbial fuel cells. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 650, 159207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Chen, D.; Lu, C.; Wang, X. Fluorescence and colorimetric dual-signal determination of Fe3+ and glutathione with MoSe2@Fe nanozyme. Microchem. J. 2022, 177, 107283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Shan, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Lu, X. Dual-emitting fluorescent metal–organic framework nanocomposites as a broad-range pH sensor for fluorescence imaging. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 7056–7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, X.; Guan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S. Ultrasensitive and selective fluorescence recognition of selenite by o-phenylenediamine functionalized carbon quantum dots. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 19712–19721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, J.; Wang, G. Naphthalene-grafted MOF as a unique fluorescent sensor for ”turn-off” detection for Fe3+ and “turn-on” detection for ClO4- in different solvents with high selectivity and sensitivity. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2023, 374, 132837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tian, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, X. A ratiometric fluorescence nanosensor for highly selective and sensitive detection of selenite. Analyst 2016, 141, 4685–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Chen, J.; Pierce, D.T.; Zhao, J.X. A turn-on fluorescent nanoprobe for selective determination of selenium(IV). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 5165–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, G.; Luo, J.; Cui, T.; Zou, J.; Xu, M.; Ma, Y.; Shi, L.; Jia, J.; Ma, C.; Li, H.; et al. Microwave-assisted one-pot synthesis of carbon dots for highly sensitive and selective detection of selenite. Microchem. J. 2022, 179, 107440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves Benzi, L.; Graças Andrade Korn, M.; Melo Magalhães Santana, R. Capped cadmium telluride quantum dots fluorescence enhancement by Se(IV) and its application to dietary supplements analysis. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2021, 771, 138526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Dai, Y.; Jin, H.; Xue, P.; Huan, Y.; Shan, H.; Fei, Q. A highly selective fluorescent probe for the determination of Se(IV) in multivitamin tablets. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2014, 193, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Huan, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Fei, Q.; Fei, Y.; Fan, Q.; Feng, G.; Shan, H. A selective and sensitive fluorescence probe for Se(IV) based on fluorescence quenching of gatifloxacin. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2016, 32, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Xin, F.; Jing, J.; Zhang, X. Ratiometric fluorescence imaging for sodium selenite in living cells. Dyes Pigment. 2019, 164, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Devi, P. A novel fluorescent “turn-off” probe for selenium (IV) detection in water and biological matrix. Trans. Indian Natl. Acad. Eng. 2021, 6, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiamati, E.; Boroujerdi, R. Cd-cysteine nanorods as a fluorescence sensor for determination of Fe(III) in real sample. J. Fluoresc. 2016, 26, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Cai, H.; Sun, J.; Di, J. A turn on fluorescent method for the detection of ferric ions based on the size effect of silver nanoclusters. Spectr. Lett. 2022, 55, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R.; Taghipour, M. Quick speciation of iron(II) and iron(III) in natural samples using a selective fluorescent carbon dot-based probe. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 4064–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Y.; Wang, S.; Yin, Q.; Wen, A.; Peng, X.; Long, Y.; Chen, S. Green synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots using chloroplast dispersions as precursors and application for Fe3+ ion sensing. Luminescence 2020, 35, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Tian, Y.; Wang, X.; Gong, D.; Guo, Y.; Iqbal, K.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; Qin, W. Carbon dots prepared by solid state method via citric acid and 1,10-phenanthroline for selective and sensing detection of Fe2+ and Fe3+. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2016, 237, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Materials | Detection Ion | Liner Range (μM) | LOD (μM) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AM + DAN | Se(IV) | 0.063–15.829 | 2.03 × 10−2 | [30] |
| OPD-CQDs | Se(IV) | 1.000–100.000 | 8.60 × 10−2 | [54] |
| DAB-CdTe@SiO2 QDs | Se(IV) | 0–25.000 | 6.68 × 10−3 | [56] |
| DAB-SiNPs | Se(IV) | 12.660–126.600 | 2.41 × 10−3 | [57] |
| CDs | Se(IV) | 0.013–1.270 | 6.33 | [58] |
| TGA-CdTe | Se(IV) | 2.190–5.700 | 0.77 | [59] |
| ABDO | Se(IV) | 0.010–0.100 | 2.80 × 10−3 | [60] |
| GAT | Se(IV) | 10.000–50.000 50.000–100.000 | 1.70 | [61] |
| HBTN-Se | Se(IV) | 0–25.000 | 0.13 | [62] |
| WHO | Se in water | – | 0.13 | [63] |
| DABA | Se(IV) | 10.000–70.000 1.000–200.000 | 4.12 2.00 | This work |
| PCN-224-DABA | Se(IV) | 0.010–15 | 0.804 |
| Materials | Detection Ion | Liner Range (μM) | LOD (μM) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg-Al-LDH-SA | Fe(III) | 0.07–100.00 | 0.026 | [49] |
| BCN | Fe(III) | 0–3.00 | 0.185 | [50] |
| MoSe2@Fe | Fe(III) | 25.00–300.00 | 0.930 | [52] |
| Cd-Cys NRs | Fe(III) | 0.10–500.00 | 0.269 | [64] |
| AgNCs | Fe(III) | 0.02–50.00 | 0.010 | [65] |
| a CDs | Fe(III) | 0–100.00 | 0.170 | [66] |
| b CDs | Fe(III) | 1.00–100.00 | 0.300 | [67] |
| c CDs | Fe(II) Fe(III) | 0–32.00 0–50.00 | 0.020 0.035 | [68] |
| WHO | Fe(III) | – | 5.36 | [55] |
| EPA | Fe(III) | – | 3.57 | [12] |
| PCN-224-DABA | Fe(III) | 0.01–4 | 0.045 | This work |
| Sample | Analyte | Detected (μM) | Found b (μM) | Spiked (μM) | Found b (μM) | Recovery c (%) | RSD (n = 3) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spinach | Fe(III) | 5.565 ± 0.151 a mg/kg | 4.730 ± 0.040 mg/kg | ||||
| Yun Lake | – d | – | 0.500 | 0.410 | 82.0 | 1.9 | |
| 1.000 | 0.837 | 83.7 | 4.4 | ||||
| 3.000 | 3.277 | 109.2 | 1.9 | ||||
| Jin Lake | – | – | 0.500 | 0.423 | 84.7 | 2.5 | |
| 1.000 | 0.854 | 85.4 | 0.6 | ||||
| 3.000 | 3.352 | 111.8 | 1.6 | ||||
| Selenium-enriched rice | Se(IV) | – | – | 1.000 | 1.160 | 116.0 | 3.0 |
| 5.000 | 4.172 | 83.4 | 2.8 | ||||
| 10.000 | 9.365 | 93.6 | 7.6 | ||||
| Yun Lake | – | – | 1.000 | 1.028 | 102.8 | 7.4 | |
| 5.000 | 5.340 | 106.8 | 6.9 | ||||
| 10.000 | 9.627 | 96.3 | 5.2 | ||||
| Jin Lake | – | – | 1.000 | 1.135 | 113.5 | 3.6 | |
| 5.000 | 5.779 | 115.6 | 5.2 | ||||
| 10.000 | 10.577 | 105.8 | 5.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, M.-L.; Chen, G.-Y.; Li, W.-J.; Li, J.-X.; Chai, T.-Q.; Qian, Z.-M.; Yang, F.-Q. A Ratiometric Fluorescence Method Based on PCN-224-DABA for the Detection of Se(IV) and Fe(III). Biosensors 2024, 14, 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14120626
Luo M-L, Chen G-Y, Li W-J, Li J-X, Chai T-Q, Qian Z-M, Yang F-Q. A Ratiometric Fluorescence Method Based on PCN-224-DABA for the Detection of Se(IV) and Fe(III). Biosensors. 2024; 14(12):626. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14120626
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Mao-Ling, Guo-Ying Chen, Wen-Jia Li, Jia-Xin Li, Tong-Qing Chai, Zheng-Ming Qian, and Feng-Qing Yang. 2024. "A Ratiometric Fluorescence Method Based on PCN-224-DABA for the Detection of Se(IV) and Fe(III)" Biosensors 14, no. 12: 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14120626
APA StyleLuo, M.-L., Chen, G.-Y., Li, W.-J., Li, J.-X., Chai, T.-Q., Qian, Z.-M., & Yang, F.-Q. (2024). A Ratiometric Fluorescence Method Based on PCN-224-DABA for the Detection of Se(IV) and Fe(III). Biosensors, 14(12), 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14120626






