An All-in-One Platform for On-Site Multiplex Foodborne Pathogen Detection Based on Channel-Digital Hybrid Microfluidics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
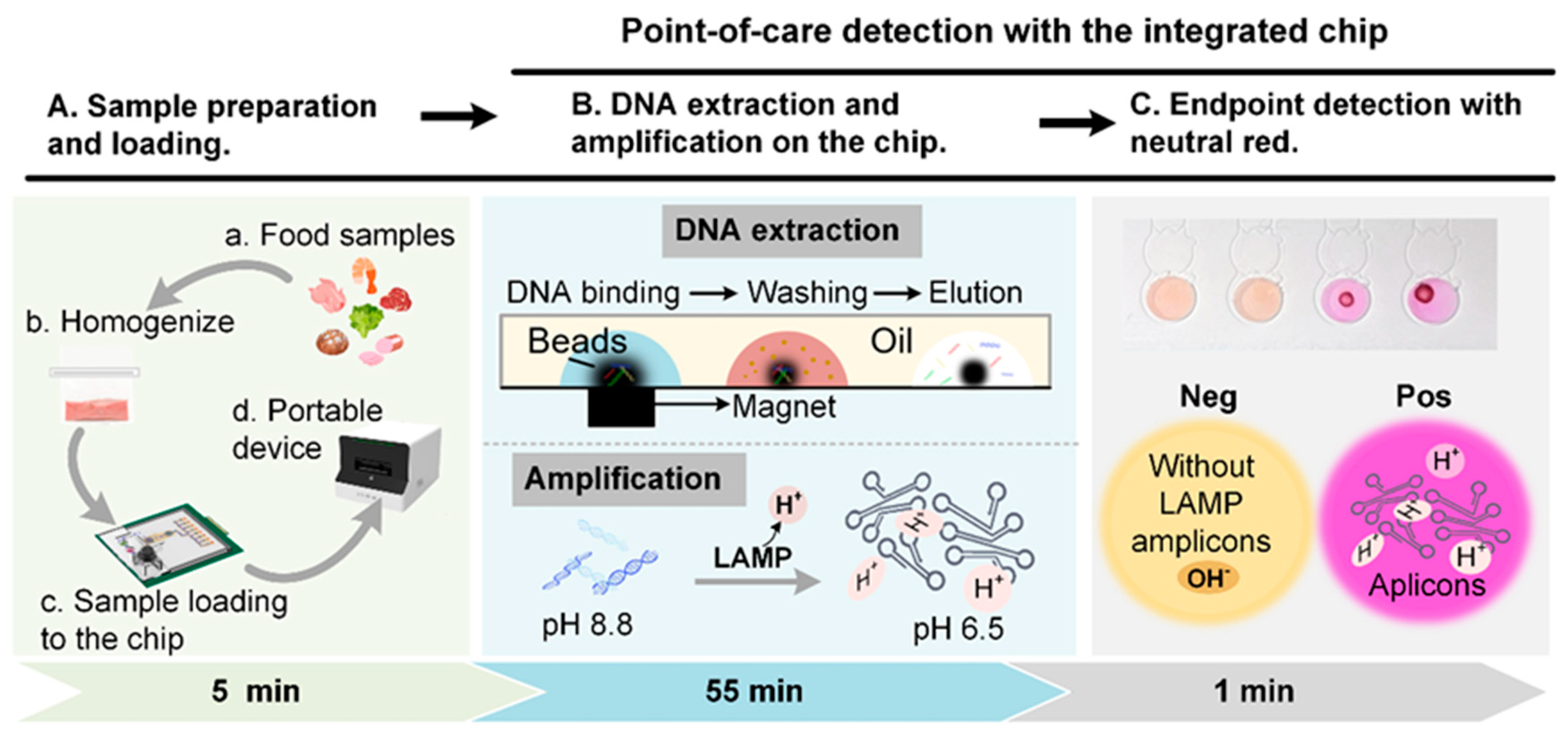
2.2. Platform Overview and Assay Mechanism
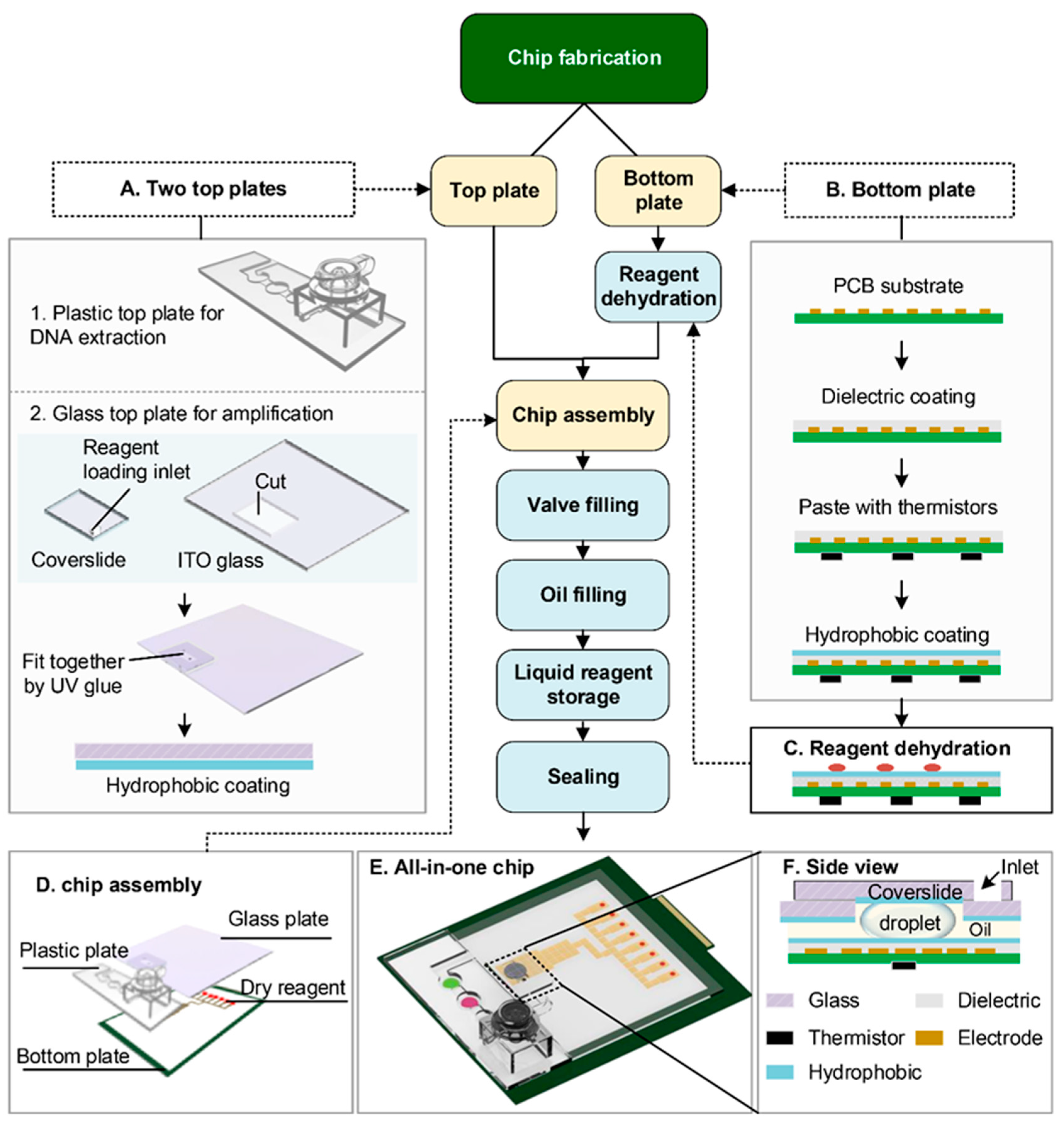
2.3. Design and Fabrication of the Hybrid Chip
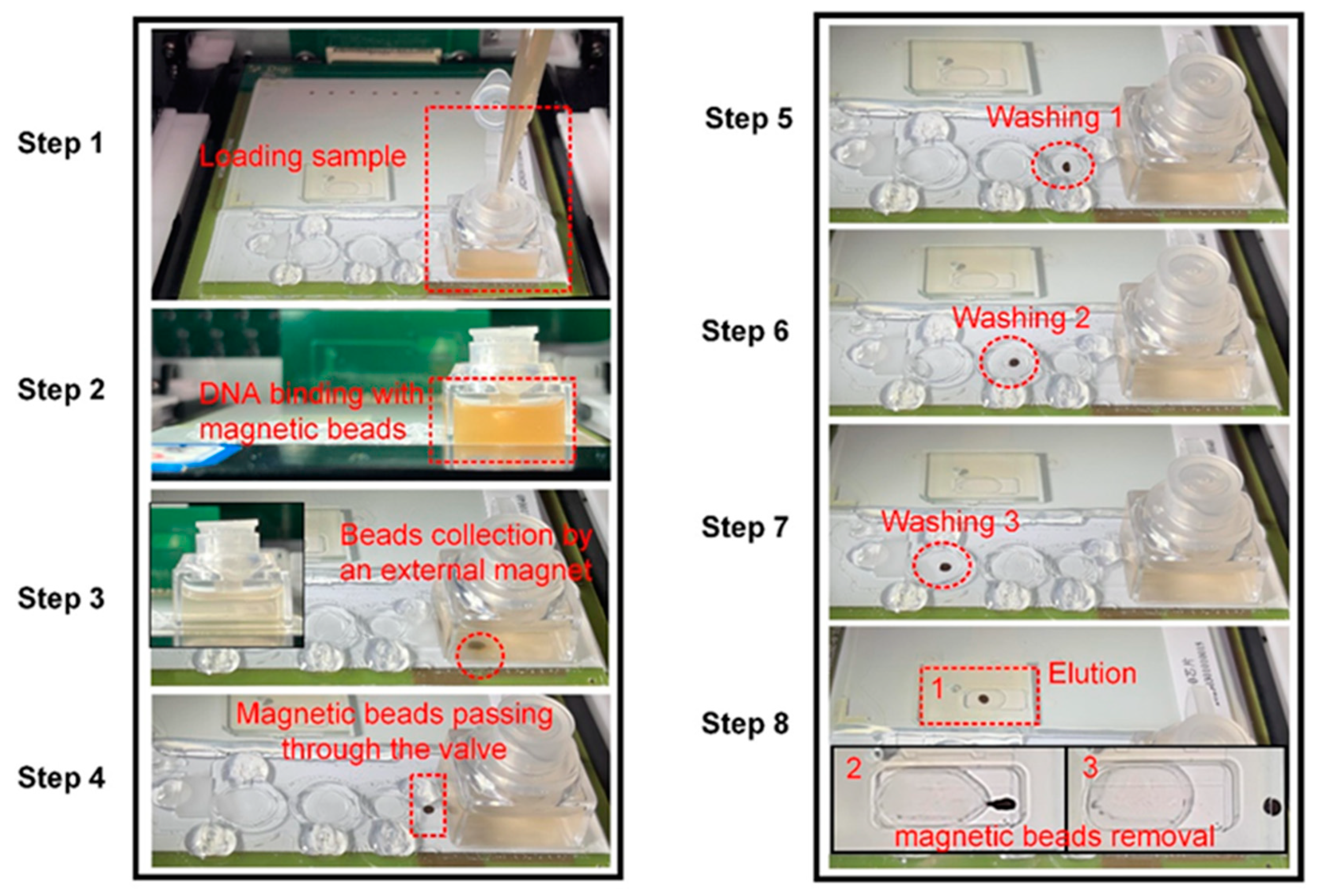
2.4. Overview of the Microfluidic System and Workflow on the Chip
2.5. Regents Dehydration and Colorimetric LAMP
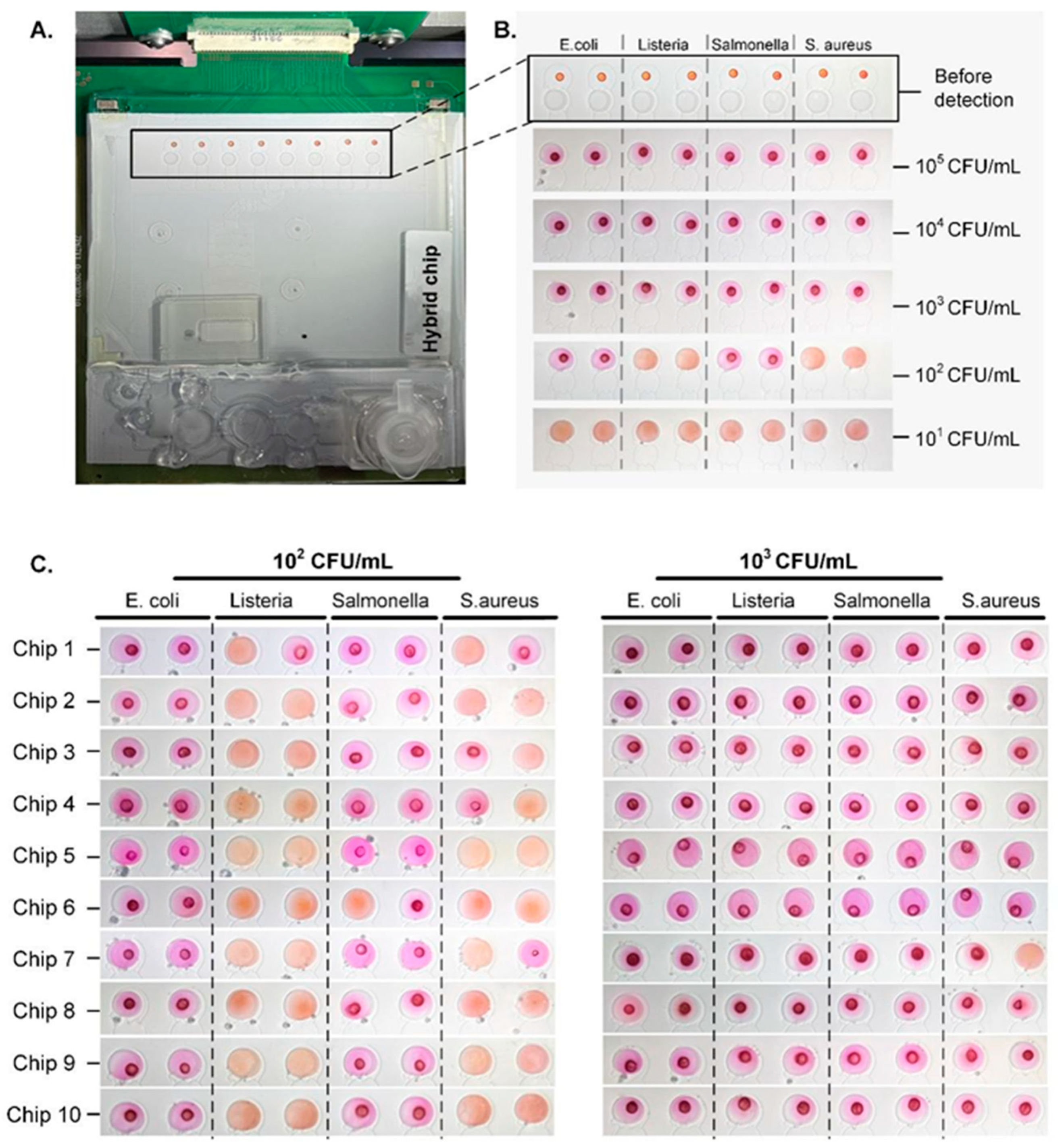
2.6. Evaluation of Sensitivity
2.7. Verification of the All-in-One DMF System by the Detection of Multiple Pathogens in Spiked Food Samples
3. Results and Discussion
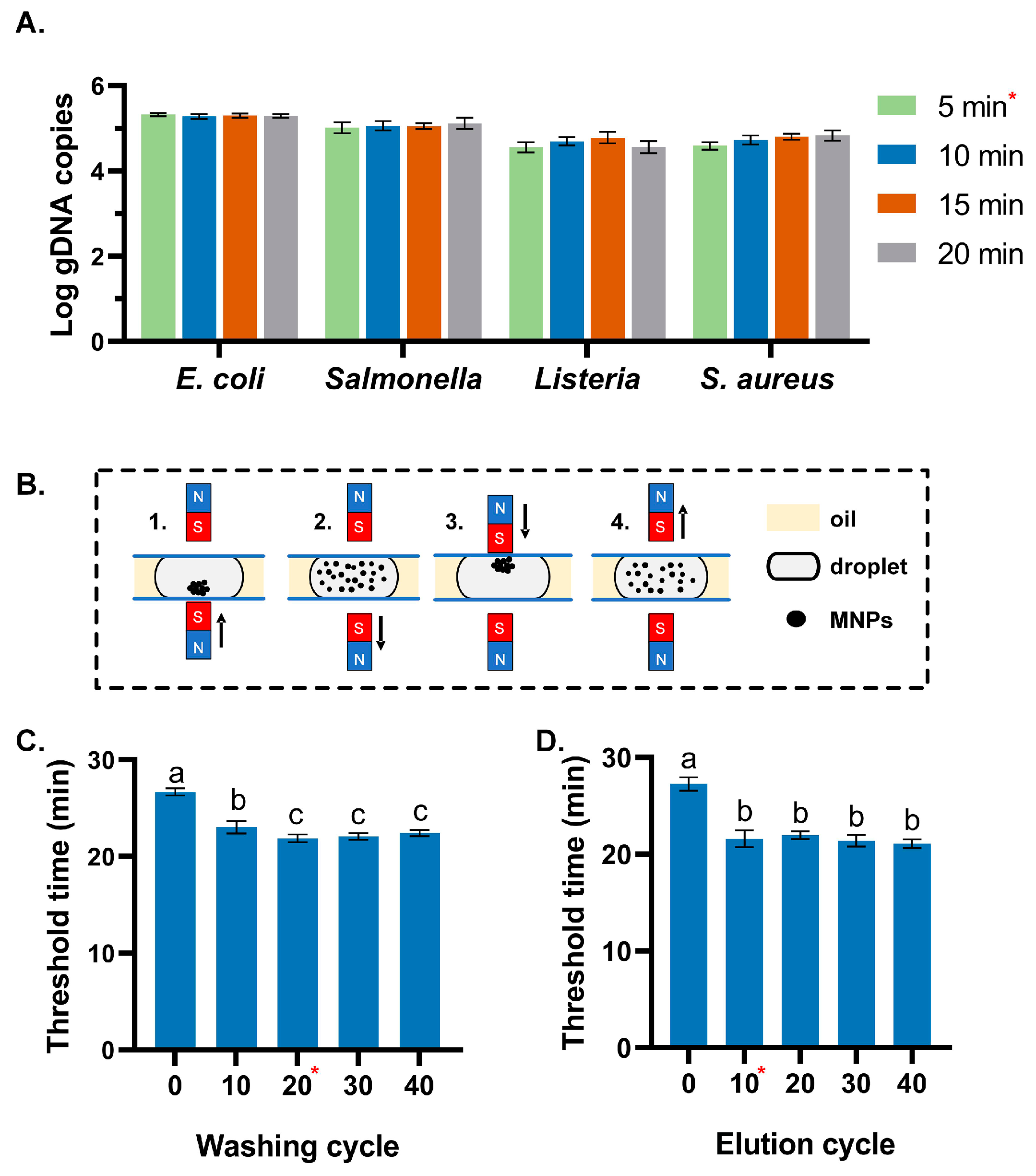
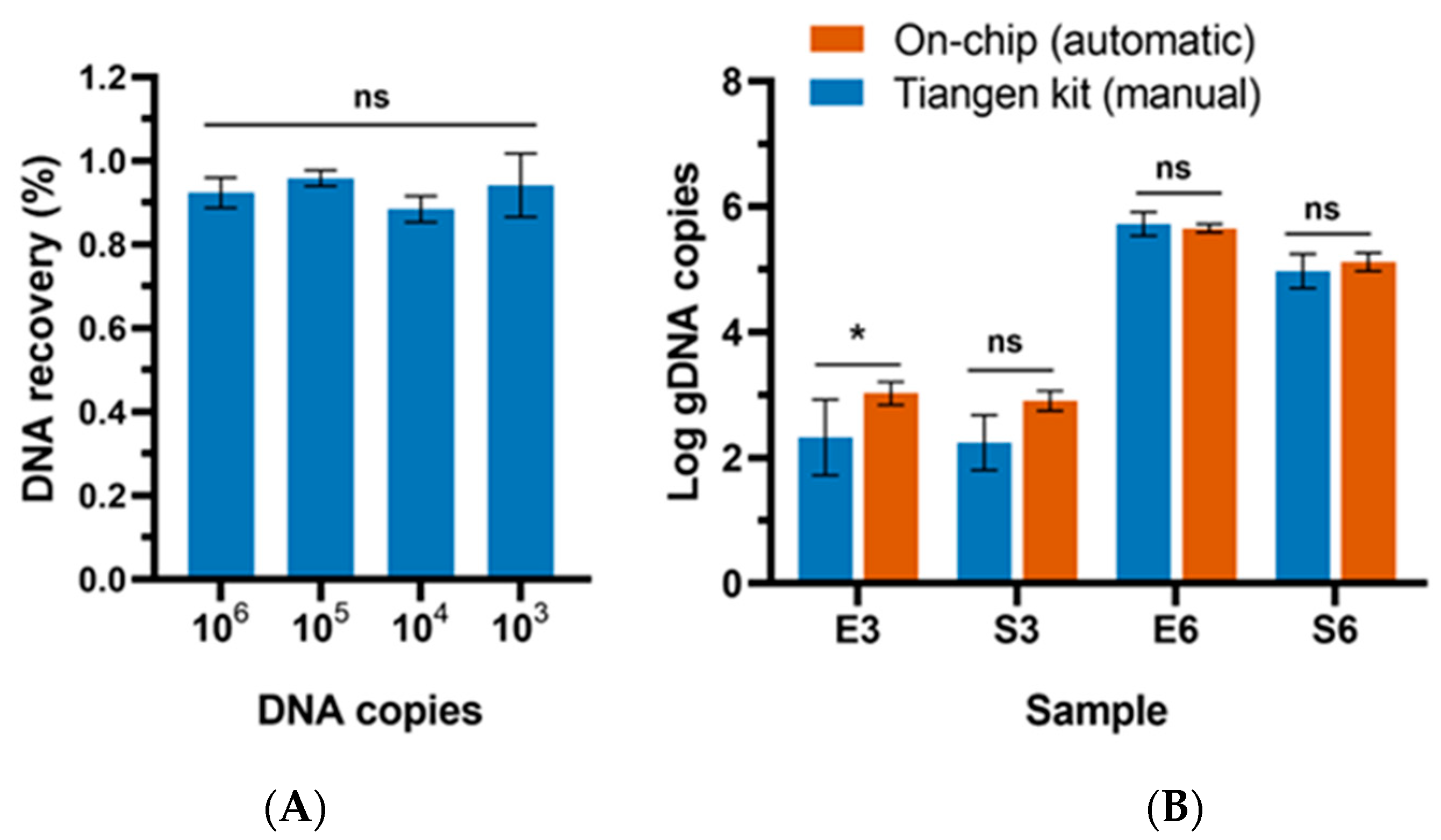
3.1. Optimization of the Extraction Conditions
3.2. Evaluation of the Extraction Efficiency
3.3. Sensitivity of Microfluidic-Based LAMP Detection
3.4. Application of the Integrated Platform for Pathogen Detection in Spiked Meat
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. WHO Estimates of the Global Burden of Foodborne Diseases: Foodborne Disease Burden Epidemiology Reference Group 2007–2015; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- Grace, D. Burden of foodborne disease in low-income and middle-income countries and opportunities for scaling food safety interventions. Food Secur. 2023, 15, 1475–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmy, Y.A.; El-Adawy, H.; Sanad, Y.M.; Ghanem, M. Food safety and public health. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1169139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar, A.; Chiu, P.; Qu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.Q. Integrated Microfluidic-Based Platforms for On-Site Detection and Quantification of Infectious Pathogens: Towards On-Site Medical Translation of SARS-CoV-2 Diagnostic Platforms. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, K.; Huang, M.; Zeng, M.; Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, H.; Li, W.; Chen, Z. Research progress on detection techniques for point-of-care testing of foodborne pathogens. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 958134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Ma, Z.; Jiang, Y. Recent advances in microfluidic devices for foodborne pathogens detection. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 157, 116788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.V.; Nguyen, V.D.; Lee, E.Y.; Seo, T.S. Point-of-care genetic analysis for multiplex pathogenic bacteria on a fully integrated centrifugal microdevice with a large-volume sample. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 136, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, K.T.L.; Stabler, R.A.; Lee, N.Y. Fabrication of a foldable all-in-one point-of-care molecular diagnostic microdevice for the facile identification of multiple pathogens. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 314, 128057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Bai, Y.; You, M.; Hu, J.; Yao, C.; Cao, L.; Xu, F. Fully integrated microfluidic devices for qualitative, quantitative and digital nucleic acids testing at point of care. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 177, 112952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.J.; Seo, T.S. Combination of a centrifugal microfluidic device with a solution-loading cartridge for fully automatic molecular diagnostics. Analyst 2019, 144, 5766–5774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, N.; Zheng, L.; Cai, G.; Lin, J. A lab-on-chip device for the sample-in-result-out detection of viable Salmonella using loop-mediated isothermal amplification and real-time turbidity monitoring. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 2296–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciuto, E.L.; Petralia, S.; Calabrese, G.; Conoci, S. An integrated biosensor platform for extraction and detection of nucleic acids. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 1554–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, G.; Yang, S.; Zhao, F.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X.; He, C.; et al. An integrated dual-layer microfluidic platform for multiple respiratory viruses screening. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1242, 340812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, R.; Yi, S.; Wang, P.; Mak, P.-I.; Martins, R.P.; Jia, Y. Nucleic acid analysis on electrowetting-based digital microfluidics. Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 158, 116826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.H.; Lee, G.B.; Huang, F.C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lin, J.L. Integrated polymerase chain reaction chips utilizing digital microfluidics. Biomed. Microdevices 2006, 8, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, B.J.; Veigas, B.; Aguas, H.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Baptista, P.V.; Igreja, R. A digital microfluidics platform for loop-mediated isothermal amplification detection. Sensors 2017, 17, 2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Rouse, J.L.; Eckhardt, A.E.; Srinivasan, V.; Pamula, V.K.; Schell, W.A.; Benton, J.L.; Mitchell, T.G.; Pollack, M.G. Multiplexed real-time polymerase chain reaction on a digital microfluidic Platform. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulff-Burchfield, E.; Schell, W.A.; Eckhardt, A.E.; Pollack, M.G.; Hua, Z.; Rouse, J.L.; Pamula, V.K.; Srinivasan, V.; Benton, J.L.; Alexander, B.D.; et al. Microfluidic platform versus conventional real-time polymerase chain reaction for the detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in respiratory specimens. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 67, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Chen, T.; Xin, X.; Cai, Z.; Dong, C.; Lei, B. Multiplex detection of foodborne pathogens by real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification on a digital microfluidic chip. Food Control 2022, 136, 108824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Gao, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, H.; Fan, P.; Cui, Y.; Gu, F.; et al. Instrumentation-Compact Digital Microfluidic Reaction Interface-Extended Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification for Sample-to-Answer Testing of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 9728–9736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, N.; Geiss, B.; Field, S.; Demann, A.; Chen, T.W. Design of a Hand-Held and Battery-Operated Digital Microfluidic Device Using EWOD for Lab-on-a-Chip Applications. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, P.-Y.; Chen, A.-T.; Lee, J.-H.; Lu, Y.-W.; Fan, S.-K. Genetic testing on electrowetting-on-dielectric chips for magnetic bead-based DNA extraction. In Proceedings of the 14th IFToMM World Congress, Taipei, Taiwan, 25–30 October 2015; pp. 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, P.-Y.; Jiang, P.-S.; Lee, E.-F.; Fan, S.-K.; Lu, Y.-W. Genomic DNA extraction from whole blood using a digital microfluidic (DMF) platform with magnetic beads. Microsyst. Technol. 2017, 23, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebrail, M.J.; Sinha, A.; Vellucci, S.; Renzi, R.F.; Ambriz, C.; Gondhalekar, C.; Schoeniger, J.S.; Patel, K.D.; Branda, S.S. World-to-digital-microfluidic interface enabling extraction and purification of RNA from human whole blood. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 3856–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sista, R.S.; Eckhardt, A.E.; Srinivasan, V.; Pollack, M.G.; Palanki, S.; Pamula, V.K. Heterogeneous immunoassays using magnetic beads on a digital microfluidic platform. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 2188–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Jie, Y.; Jin, K.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, T.; Huang, Q.; Mei, Q.; Ma, F.; Ma, H. All-in-One Digital Microfluidics System for Molecular Diagnosis with Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification. Biosensors 2022, 12, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Advances in integrated digital microfluidic platforms for point-of-care diagnosis: A review. Sens. Diagn. 2022, 1, 648–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, N.A.; Zhang, Y.; Evans, T.C., Jr. Visual detection of isothermal nucleic acid amplification using pH-sensitive dyes. Biotechniques 2015, 58, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Chen, T.; Cai, Z.; Lei, B.; Dong, C. A digital microfluidic platform coupled with colorimetric loop-mediated isothermal amplification for on-site visual diagnosis of multiple diseases. Lab Chip 2023, 23, 2778–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, V.; Beule, L.; Lehtsaar, E.; Liao, H.-L.; Karlovsky, P. Improved protocol for DNA extraction from subsoils using phosphate lysis buffer. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Duan, N.; Xu, H.; Xie, T.; Xue, Y.-R.; Liu, C.-H.J.M.B. CTAB-PEG DNA extraction from fungi with high contents of polysaccharides. Mol. Biol. 2018, 52, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, N.; Sebuyoya, R.; Moranova, L.; Hrstka, R.; Anton, M.; Bartosik, M. Electrochemical bioassay coupled to LAMP reaction for determination of high-risk HPV infection in crude lysates. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1187, 339145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Mori, Y.; Tomita, N.; KandaNotomi, H. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): Principle, features, and future prospects. J. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadakis, G.; Pantazis, A.K.; Fikas, N.; Chatziioannidou, S.; Tsiakalou, V.; Michaelidou, K.; Pogka, V.; Megariti, M.; Vardaki, M.; Giarentis, K. Portable real-time colorimetric LAMP-device for rapid quantitative detection of nucleic acids in crude samples. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brassard, D.; Geissler, M.; Descarreaux, M.; Tremblay, D.; Daoud, J.; Clime, L.; Mounier, M.; Charlebois, D.; Veres, T. Extraction of nucleic acids from blood: Unveiling the potential of active pneumatic pumping in centrifugal microfluidics for integration and automation of sample preparation processes. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Chen, C.; Su, H.; Zhou, M.; Li, S.; Du, W.; Feng, X.; Liu, B.F. Integrated and finger-actuated microfluidic chip for point-of-care testing of multiple pathogens. Talanta 2021, 224, 121844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsougeni, K.; Kastania, A.S.; Kaprou, G.D.; Eck, M.; Jobst, G.; Petrou, P.S.; Kakabakos, S.E.; Mastellos, D.; Gogolides, E.; Tserepi, A. A modular integrated lab-on-a-chip platform for fast and highly efficient sample preparation for foodborne pathogen screening. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 288, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zou, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, F.; Wang, B.; Lv, S.; Mu, Y. A “sample-in-multiplex-digital-answer-out” chip for fast detection of pathogens. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Wang, C.H.; Hsu, K.F.; Lee, G.B. Integrated Microfluidic System for Cell-Free DNA Extraction from Plasma for Mutant Gene Detection and Quantification. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 4311–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, Z.; Cao, X.; Li, Z.; Stavrakis, S.; Choo, J.; de Mello, A.J.; Howes, P.D.; He, N. A sample-in-digital-answer-out system for rapid detection and quantitation of infectious pathogens in bodily fluids. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 7019–7030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugle, M.; Behrmann, O.; Raum, M.; Hufert, F.T.; Urban, G.A.; Dame, G. A lab-on-a-chip for free-flow electrophoretic preconcentration of viruses and gel electrophoretic DNA extraction. Analyst 2020, 145, 2554–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.; Puertas, G.; Gaspar, J.; Azinheiro, S.; Dieguez, L.; Garrido-Maestu, A.; Vazquez, M.; Barros-Velazquez, J.; Cardoso, S.; Prado, M. Highly efficient DNA extraction and purification from olive oil on a washable and reusable miniaturized device. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1020, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katevatis, C.; Fan, A.; Klapperich, C.M. Low concentration DNA extraction and recovery using a silica solid phase. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martzy, R.; Bica-Schroder, K.; Palvolgyi, A.M.; Kolm, C.; Jakwerth, S.; Kirschner, A.K.T.; Sommer, R.; Krska, R.; Mach, R.L.; Farnleitner, A.H.; et al. Simple lysis of bacterial cells for DNA-based diagnostics using hydrophilic ionic liquids. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalanabis, M.; Al-Muayad, H.; Kulinski, M.D.; Altman, D.; Klapperich, C.M. Cell lysis and DNA extraction of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria from whole blood in a disposable microfluidic chip. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 2811–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Qu, W.; Yao, L.; Yao, B.; Yan, C.; Chen, W. Filtration assisted pretreatment for rapid enrichment and accurate detection of Salmonella in vegetables. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Yang, H.; Gong, Y.; You, M.; Liu, Z.; Choi, J.R.; Wen, T.; Qu, Z.; Mei, Q.; Xu, F. A fully disposable and integrated paper-based device for nucleic acid extraction, amplification and detection. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, Y.; Yan, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Xing, W. Sensitive and rapid detection of pathogenic bacteria from urine samples using multiplex recombinase polymerase amplification. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 2441–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Park, J.; Kim, S.J.; Ko, D.-H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.J.; Park, J.-K.; Lee, M.-K. On-site extraction and purification of bacterial nucleic acids from blood samples using an unpowered microfluidic device. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 320, 128346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Concentration a (CFU/mL) | Result b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | S. typhimurium | L. monocytogenes | S. aureus | |
| 104 | 6/6 | 6/6 | 6/6 | 6/6 |
| 103 | 6/6 | 6/6 | 4/6 | 2/6 |
| 102 | 4/6 | 3/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 |
| 101 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, M.; Chen, T.; Cai, Z.; Lei, B.; Dong, C. An All-in-One Platform for On-Site Multiplex Foodborne Pathogen Detection Based on Channel-Digital Hybrid Microfluidics. Biosensors 2024, 14, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14010050
Xie M, Chen T, Cai Z, Lei B, Dong C. An All-in-One Platform for On-Site Multiplex Foodborne Pathogen Detection Based on Channel-Digital Hybrid Microfluidics. Biosensors. 2024; 14(1):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14010050
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Mei, Tianlan Chen, Zongwei Cai, Bo Lei, and Cheng Dong. 2024. "An All-in-One Platform for On-Site Multiplex Foodborne Pathogen Detection Based on Channel-Digital Hybrid Microfluidics" Biosensors 14, no. 1: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14010050
APA StyleXie, M., Chen, T., Cai, Z., Lei, B., & Dong, C. (2024). An All-in-One Platform for On-Site Multiplex Foodborne Pathogen Detection Based on Channel-Digital Hybrid Microfluidics. Biosensors, 14(1), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14010050





