Electrochemical Wearable Biosensors and Bioelectronic Devices Based on Hydrogels: Mechanical Properties and Electrochemical Behavior
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials for Electrochemical Wearable Biosensors
2.1. Hydrogels
2.1.1. Conductive Polymer Hydrogels
2.1.2. Ionic Conductive Polymer Hydrogels
2.1.3. Crosslinking Mechanisms
2.2. Hydrogel Composites
2.2.1. Non-Metallic Nanomaterials
2.2.2. Metallic Nanomaterial
2.3. Hydrogel Functionalization
2.3.1. Redox Species
2.3.2. Biomolecule Species
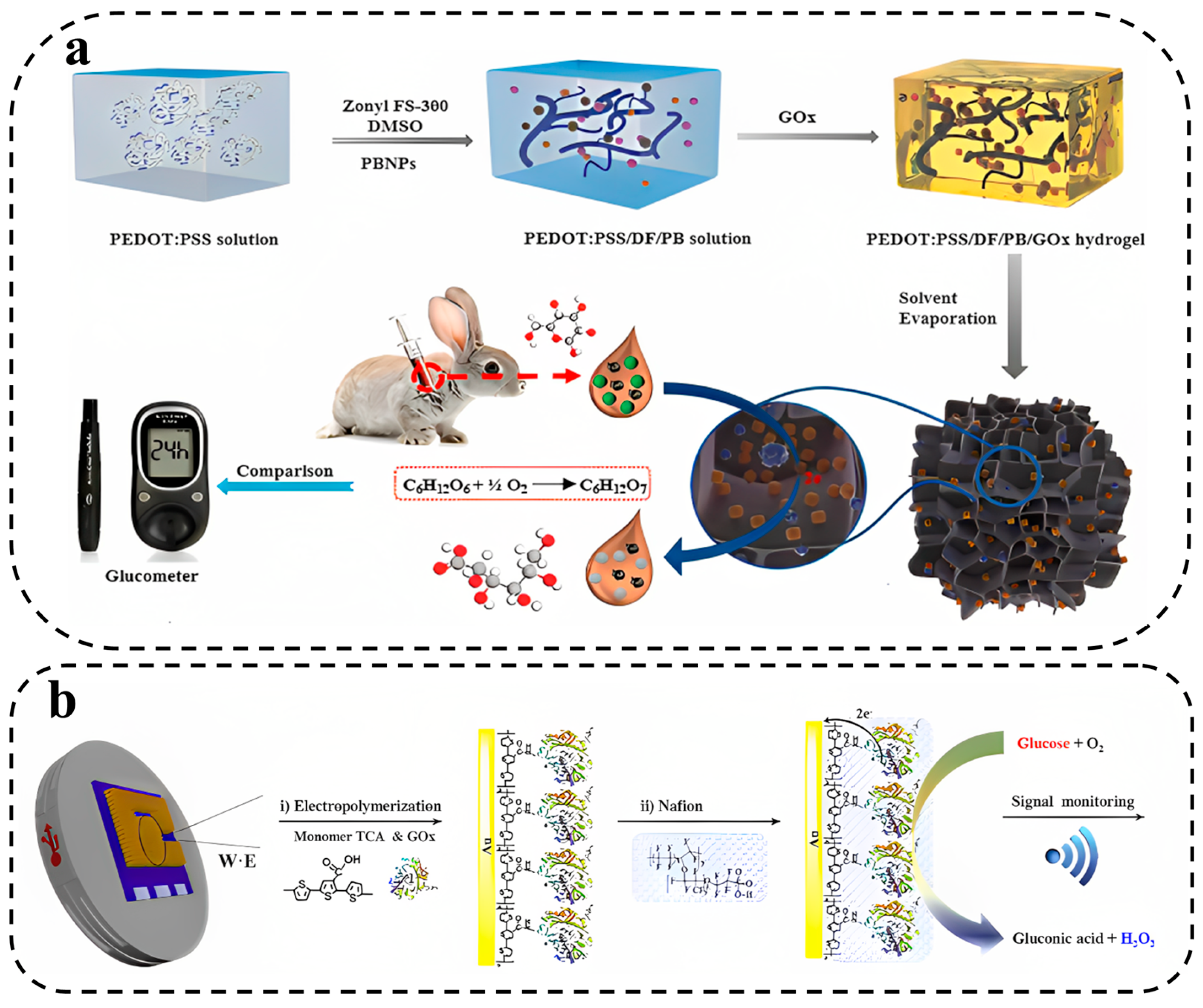
3. HWEB Properties
3.1. Physicochemical Properties
3.1.1. Electrical Conductivity
3.1.2. Diffusibility
3.1.3. Hydrophilicity
3.1.4. Self-Healing Property
3.1.5. Anti-Freezing Property
3.1.6. Adhesion
3.2. Biological Properties
3.2.1. Biocompatibility
3.2.2. Antibacterial Property
3.2.3. Biodegradability
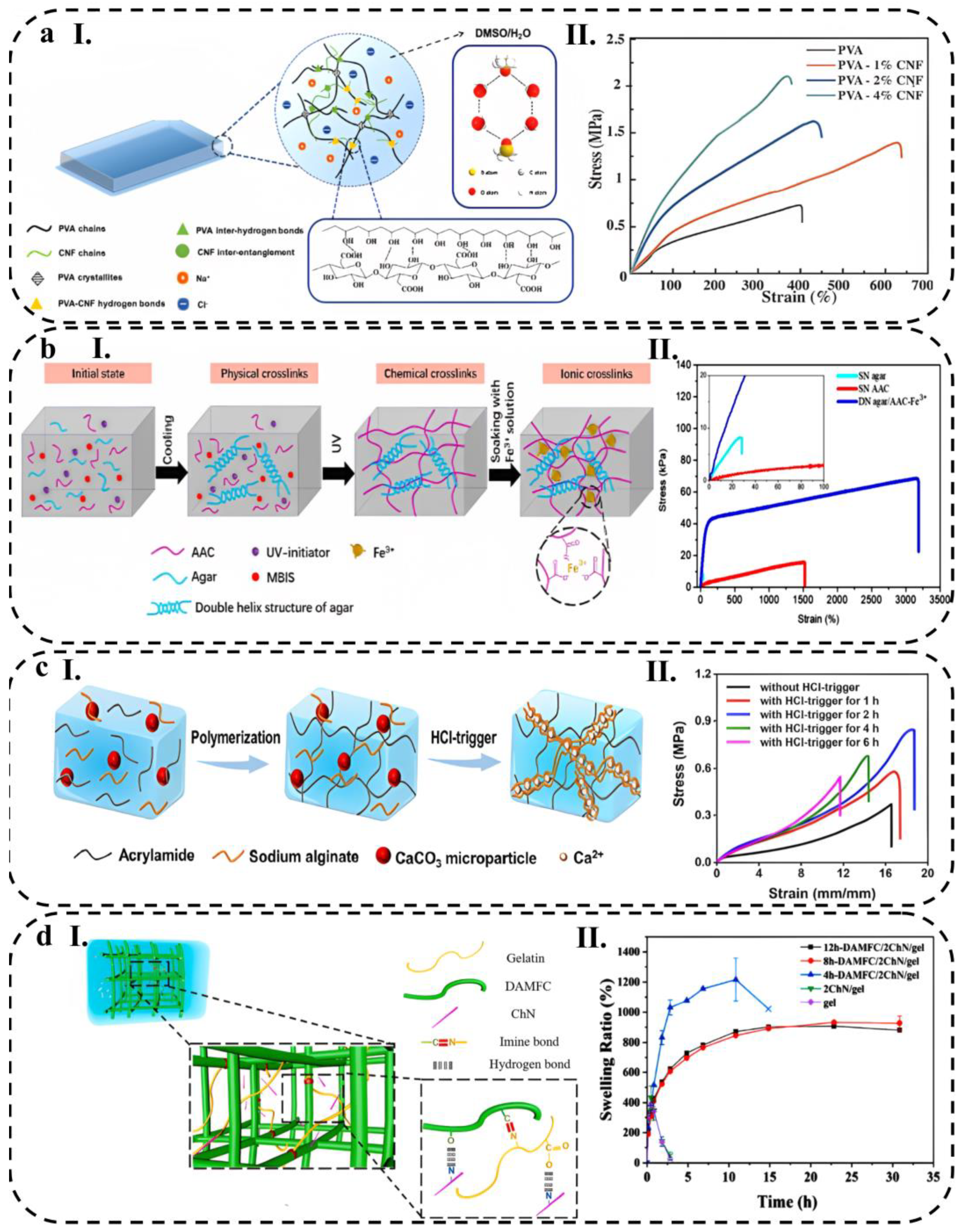
3.3. Rheological and Mechanical Behavior
3.3.1. Stretchability
| Material (s) | Mechanical Performance | Strain Sensing | Features | Ref | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | Stretchability (%) | Toughness (MJ m−3) | Gauge Factor (Strain Range) | Conductivity (S cm−1) | Conductive Type | Repeatability (Cycles) | |||
| PVA/NaCl/Amy (1) | - | 0.184 | 4.96 | 0.034 | Ion | 100 | Biocompatible Anti-swell Anti-fatigue | [205] | |
| PVA/P(AAc- co-AM)/PDA@CNTs (2) | ~1.21 | ~220 | ~1.22 | 1.6 | 3.84 | Electron | - | Fatigue resistant Recoverable | [192] |
| P(AAc-MEA)-Fe3+ (3) | 0.462 | ~1200 | 2.01 | 1.60 (0–100%), 1.97 (100–200%), 2.57 (200–400%) | 0.044 | Ion | - | Anti-swelling Recoverable | [206] |
| CNTs/PVA (4) | - | up to 415 | - | 0.591 (0–150%), 1.165 (150–250%) | 1.11 | Electron | 1000 | Durable | [191] |
| PANi/CBH (5) | 0.8 | ~914 | 4.3 | 0.5 (0–90%), 1.7 (90–600%) | 0.3 | Electron | 300 | Biocompatible Skin mimicking Self-stiffness | [207] |
| PVA-CNF (6) | 1.4 | up to 660 | 5.25 | 1.2 (<150%), 1.5 (>150%) | 3.2 | Ion | 500 | Anti-freeze Long-term solvent retention | [193] |
| PAM/Cu-alg (7) | ~2.25 | 2013 | - | up to 5.1 | 0.408 | Ion | - | - | [200] |
| PATG-B-Fe3+ (8) | 0.203 | 1950 | - | 1.2 (0–400%), 3.3 (400–1200%) 5.2 (1200–1900%) | 0.237 | Ion | 2000 | Self-heal Self-adhesive | [208] |
| MCNH (9) | 0.0145 | up to 2000 | - | 0.83 | 9.43 | Ion | - | Self-healing | [209] |
| PVA/LNP/AlCl3 (10) | 1.241 | 589 | - | 2.08 | 1.35 × 10−2 | Ion | - | Anti-freezing | [190] |
| CNT/TPU (11) | 73.22 | 476 | - | 11.08 | 0.023 | Electron | 1250 | - | [210] |
| PAC-CGO-Na (11) | 1.51 | 1414 | 15.33 | 4.44 (220–1216%) | 4.10 | Ion | 200 | Anti-freezing | [211] |
| PVA/gelatin/EG/TA@CNC–Al3+ (PGETA) (12) | 1.95 | ~520 | - | 4.23 | 0.23 | Ion | 1000 | Self-heal Recyclable | [212] |
| poly(ACMO)/glycerin/PEGDA (13) | 0.18 | ~356 | - | 2.3 | 1.9 × 10−3 | Ion | 700 | Self-adhesive Fatigue resistant | [213] |
| PAAc/glycerin/PVA/PEDOT (14) | 3.6 | 340 | - | 1.18 (0–400%) | ~0.95 | Electron | - | Anti-freeze | [137] |
| PANi/P(AAm-co-HEMA) (15) | 7.27 (72 h oxidation) | 530 | 9.19 | 11 (at low strain) | 8.24 | Electron | 100 | Fatigue resistant | [214] |
| PVA/glycerol/PANi (16) | 0.094 | 472 | - | 2.14 | 0.32 | Electron | 540 | Anti-freeze Remoldable Reusable | [215] |
| SC/PDA/PAAm (17) | 0.170 | over 2100 | 1.1 | - | - | Ion | - | Self-heal Self-adhesive | [216] |
| HP(AAm/AAc)–CS–Fe3+ (18) | 4.05 | - | 23.8 | 3.621 | - | Ion | 300 | Anti-swell Recoverable | [217] |
3.3.2. Swelling Behavior
3.3.3. Cycle Life
3.3.4. Rheological Behavior
3.4. Electrochemical Techniques
3.4.1. Current Response
3.4.2. Potential Response
3.4.3. Conductometry
3.4.4. Impedance Response
3.4.5. Benefits and Drawbacks of Electrochemical Techniques
4. Applications of HWEBs
4.1. HWEB Platforms
4.1.1. Wearable Patches
4.1.2. Epidermal Tattoos
4.1.3. Microfluidic-Based Platforms
4.1.4. Microneedle-Based Platforms
4.1.5. Soft Contact Lens
4.1.6. Paper-Based and Textile-Based Platforms
4.2. Biosensing Applications
4.2.1. Catalytic HWEBs
4.2.2. Bioaffinity HWEBs
5. Challenges and Prospects
5.1. General Considerations
5.2. Electrochemical Aspects
5.3. Mechanical Aspects
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.; Campbell, A.S.; Esteban-Fernández Ávila, B.; Wang, J. Wearable Biosensors for Healthcare Monitoring. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Peng, H.; Rwei, A.Y. Flexible, Wearable Biosensors for Digital Health. Med. Nov. Technol. Devices 2022, 14, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Javaid, M.; Singh, R.P.; Suman, R.; Rab, S. Biosensors Applications in Medical Field: A Brief Review. Sens. Int. 2021, 2, 100100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.U.; Chatterjee, S.; Lone, S.A.; Ho, H.-H.; Kaswan, K.; Peringeth, K.; Khan, A.; Chiang, Y.-W.; Lee, S.; Lin, Z.-H. Advanced Wearable Biosensors for the Detection of Body Fluids and Exhaled Breath by Graphene. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Qi, J.; Fan, S.; Qiao, Z.; Yeo, J.C.; Lim, C.T. Flexible Wearable Sensors for Cardiovascular Health Monitoring. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, L.; Wang, G.; Hu, K.; Qian, C.; Liu, G. Advances in Biosensors for Continuous Glucose Monitoring Towards Wearables. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 733810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Fu, Z.; Qi, L. A Wearable Biosensor Based on Bienzyme Gel-Membrane for Sweat Lactate Monitoring by Mounting on Eyeglasses. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 20, 1495–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpa, E.; Mastronardi, V.M.; Guido, F.; Algieri, L.; Qualtieri, A.; Fiammengo, R.; Rizzi, F.; De Vittorio, M. Wearable Piezoelectric Mass Sensor Based on PH Sensitive Hydrogels for Sweat PH Monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Yi, Q.; Hoang, E.; Esfandyarpour, R. A 3D Printed Wearable Bioelectronic Patch for Multi-sensing and in Situ Sweat Electrolyte Monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2001021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-C.; Saiphoklang, N.; Jung, D.; Gomez, D.; Phillips, J.E.; Dolezal, B.A.; Tashkin, D.P.; Barjaktarevic, I.; Cooper, C.B. Use of a Wearable Biosensor to Study Heart Rate Variability in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Its Relationship to Disease Severity. Sensors 2022, 22, 2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Zhu, M.; He, Y.; Wei, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Pan, H.; Huang, W.; Chen, S. Flexible Non-Contact Electrodes for Wearable Biosensors System on Electrocardiogram Monitoring in Motion. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 900146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.; Li, J.; Kim, Y.; Van Os, J.M.C.; Brounts, S.H.; Choi, C.Y. Using Implantable Biosensors and Wearable Scanners to Monitor Dairy Cattle’s Core Body Temperature in Real-Time. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 174, 105453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K.; Ho, D.T.Y.; Tam, A.R.; Zhou, M.; Lau, Y.M.; Tang, M.O.Y.; Tong, R.C.F.; Rajput, K.S.; Chen, G.; Chan, S.C. Artificial Intelligence Mobile Health Platform for Early Detection of COVID-19 in Quarantine Subjects Using a Wearable Biosensor: Protocol for a Randomised Controlled Trial. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e038555. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pillai, S.; Upadhyay, A.; Sayson, D.; Nguyen, B.H.; Tran, S.D. Advances in Medical Wearable Biosensors: Design, Fabrication and Materials Strategies in Healthcare Monitoring. Molecules 2022, 27, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemčeková, K.; Labuda, J. Advanced Materials-Integrated Electrochemical Sensors as Promising Medical Diagnostics Tools: A Review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 120, 111751. [Google Scholar]
- Zalpour, N.; Roushani, M. Hydrogel-Based Flexible and Wearable Sensors. In Flexible and Wearable Sensors; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; pp. 179–202. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Wu, S.; Zhang, X.; Feng, T.; Wu, L. Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for Bioelectronic Sensing: Recent Advances and Applications in Biomedicine and Food Safety. Biosensors 2023, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- George, S.M.; Tandon, S.; Kandasubramanian, B. Advancements in Hydrogel-Functionalized Immunosensing Platforms. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 2060–2068. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z.; Song, Z.; Cai, H.; Fang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, J. Wearable and Flexible Electrochemical Sensors for Sweat Analysis: A Review. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2023, 9, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, M.; Kim, K.; Shin, J.; Yu, K.J. Ultra-Thin Flexible Encapsulating Materials for Soft Bio-Integrated Electronics. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2202980. [Google Scholar]
- Bashir, S.; Hina, M.; Iqbal, J.; Rajpar, A.H.; Mujtaba, M.A.; Alghamdi, N.A.; Wageh, S.; Ramesh, K.; Ramesh, S. Fundamental Concepts of Hydrogels: Synthesis, Properties, and Their Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Q. Hydrogels-Based Electronic Devices for Biosensing Applications. In Smart Stimuli-Responsive Polymers, Films, and Gels; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 339–373. [Google Scholar]
- Janghorban, M.; Aradanas, I.; Kazemi, S.; Ngaju, P.; Pandey, R. Recent Advances, Opportunities, and Challenges in Developing Nucleic Acid Integrated Wearable Biosensors for Expanding the Capabilities of Wearable Technologies in Health Monitoring. Biosensors 2022, 12, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, M.; Lim, J.; An, J.; Yoon, J.; Choi, J.-W. Nanomaterial-Based Biohybrid Hydrogel in Bioelectronics. Nano Converg. 2023, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purohit, B.; Vernekar, P.R.; Shetti, N.P.; Chandra, P. Biosensor Nanoengineering: Design, Operation, and Implementation for Biomolecular Analysis. Sens. Int. 2020, 1, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Tang, Y. On Mechanical Properties of Nanocomposite Hydrogels: Searching for Superior Properties. Nano Mater. Sci. 2022, 4, 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Ren, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Huang, Q.; He, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, Q. From Design to Applications of Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogel Strain Sensors. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 3171–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Zhao, L.; Ling, Q.; Gu, H. Tough, Self-Adhesive, Antibacterial, and Recyclable Supramolecular Double Network Flexible Hydrogel Sensor Based on PVA/Chitosan/Cyclodextrin. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 3620–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Hong, H.; Ajiteru, O.; Sultan, M.T.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, O.J.; Lee, H.; Park, H.S.; Choi, K.Y. 3D Bioprinted Silk Fibroin Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 5484–5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, Z.; Salman, S.; Khan, S.A.; Amin, A.; Rahman, Z.U.; Al-Ghamdi, Y.O.; Akhtar, K.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Khan, S.B. Versatility of Hydrogels: From Synthetic Strategies, Classification, and Properties to Biomedical Applications. Gels 2022, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wang, R.; Pan, F.; Fu, Z. Polyvinyl Alcohol/Graphene Oxide Conductive Hydrogels via the Synergy of Freezing and Salting out for Strain Sensors. Sensors 2022, 22, 3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pissis, P.; Kyritsis, A. Electrical Conductivity Studies in Hydrogels. Solid State Ion. 1997, 97, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Xu, X.; Hu, L. Highly Strong, Stretchable, and Conductive Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite Hydrogel-Based Sensors for Motoring Strain and Pressure. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 5155–5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sun, S.; Geng, A.; Wang, L.; Song, C.; Xu, L.; Jia, C.; Shi, J.; Gan, L. Using TEMPO-Oxidized-Nanocellulose Stabilized Carbon Nanotubes to Make Pigskin Hydrogel Conductive as Flexible Sensor and Supercapacitor Electrode: Inspired from a Chinese Cuisine. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 196, 108226. [Google Scholar]
- Boularaoui, S.; Shanti, A.; Lanotte, M.; Luo, S.; Bawazir, S.; Lee, S.; Christoforou, N.; Khan, K.A.; Stefanini, C. Nanocomposite Conductive Bioinks Based on Low-Concentration GelMA and MXene Nanosheets/Gold Nanoparticles Providing Enhanced Printability of Functional Skeletal Muscle Tissues. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 5810–5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuman, K.E.; Kenny, A.; Shi, L.; Koppes, A.N.; Koppes, R.A. Complex Material Properties of Gel-Amin: A Transparent and Ionically Conductive Hydrogel for Neural Tissue Engineering. Cells Tissues Organs 2023, 212, 42–60. [Google Scholar]
- Danmatam, N.; Nakburee, W.; Pearce, J.; Pattavarakorn, D. Smart Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Polythiophene Hydrogel for Electrically Driven Soft Actuators: Physical and Thermal Properties and Electroactive Performances. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52904. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayavenkataraman, S.; Vialli, N.; Fuh, J.Y.H.; Lu, W.F. Conductive Collagen/Polypyrrole-b-Polycaprolactone Hydrogel for Bioprinting of Neural Tissue Constructs. Int. J. Bioprinting 2019, 5, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Feng, P.; Chen, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, B. Electrically Conductive Hydrogels for Flexible Energy Storage Systems. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 88, 220–240. [Google Scholar]
- Nezakati, T.; Seifalian, A.; Tan, A.; Seifalian, A.M. Conductive Polymers: Opportunities and Challenges in Biomedical Applications. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 6766–6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Ahmed, S. Recent Advances in Edible Polymer Based Hydrogels as a Sustainable Alternative to Conventional Polymers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 6940–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, A.A.; Dinesan, M.K. Polyaniline—A Novel Polymeric Material. Talanta 1991, 38, 815–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapurina, I.Y.; Shishov, M.A. Oxidative Polymerization of Aniline: Molecular Synthesis of Polyaniline and the Formation of Supramolecular Structures. New Polym. Spec. Appl. 2012, 740, 272. [Google Scholar]
- Aryal, K.P.; Jeong, H.K. Simultaneous Determination of Ascorbic Acid, Dopamine, and Uric Acid with Polyaniline/Hemin/Reduced Graphite Oxide Composite. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2021, 768, 138405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Bing, Y.; Chen, Q.; Pang, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, T. Nonenzymatic Flexible Wearable Biosensors for Vitamin C Monitoring in Sweat. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 19384–19392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalwa, H.S. Handbook of Organic Conductive Molecules and Polymers; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997; ISBN 0471962759. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, R.B.; Ansari, S.; Purty, B. Robust Electrochemical Performance of Polypyrrole (PPy) and Polyindole (PIn) Based Hybrid Electrode Materials for Supercapacitor Application: A Review. J. Energy Storage 2020, 29, 101302. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H.; Huang, C.; Lu, Y.; Cui, H.; Tan, Y. Chitosan-Driven Biocompatible Hydrogel Based on Water-Soluble Polypyrrole for Stable Human-Machine Interfaces. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 295, 119890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenoy, G.E.; Azzaroni, O.; Knoll, W.; Marmisollé, W.A. Functionalization Strategies of PEDOT and PEDOT: PSS Films for Organic Bioelectronics Applications. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Song, J.; Liu, B.; Lv, S.; Gao, F.; Luo, X.; Wang, P. A Conducting Polymer PEDOT:PSS Hydrogel Based Wearable Sensor for Accurate Uric Acid Detection in Human Sweat. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 348, 130674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Jiang, D.; Ge, Y.; Huang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Ren, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. A PEDOT:PSS Conductive Hydrogel Incorporated with Prussian Blue Nanoparticles for Wearable and Noninvasive Monitoring of Glucose. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 134109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, T.; Banerjee, S.; Manna, P.K.; Kar, K.K. Characteristics of Conducting Polymers. In Handbook of Nanocomposite Supercapacitor Materials I; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 247–268. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.-J.; Wu, H.; Hu, Y.; Young, M.; Wang, H.; Lynch, D.; Xu, F.; Cong, H.; Cheng, G. Ionic Conductivity of Polyelectrolyte Hydrogels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5845–5852. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Han, L.; Li, J.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xu, X.; Pan, L.; Xu, M. Super-Stretchable, Elastic and Recoverable Ionic Conductive Hydrogel for Wireless Wearable, Stretchable Sensor. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 10291–10300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadhoseini, M.; Mohamadnia, Z. Alginate-Based Self-Healing Hydrogels Assembled by Dual Cross-Linking Strategy: Fabrication and Evaluation of Mechanical Properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohamadhoseini, M.; Mohamadnia, Z. Supramolecular Self-Healing Materials via Host-Guest Strategy between Cyclodextrin and Specific Types of Guest Molecules. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 432, 213711. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, D.; Guo, N.; Wang, Y.; Ding, T.; Weng, L. A Highly Stretchable, Sensing Durability, Transparent, and Environmentally Stable Ion Conducting Hydrogel Strain Sensor Built by Interpenetrating Ca2+-SA and Glycerol-PVA Double Physically Cross-Linked Networks. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 1712–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.; Chhetry, A.; Kim, D.; Yoon, H.; Park, J.Y. Hysteresis-Free Double-Network Hydrogel-Based Strain Sensor for Wearable Smart Bioelectronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 31363–31372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Peng, Q.; Thundat, T.; Zeng, H. Stretchable, Injectable, and Self-Healing Conductive Hydrogel Enabled by Multiple Hydrogen Bonding toward Wearable Electronics. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 4553–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Liu, T.; Wen, B.; Gong, C.; Wei, G.; Su, Z. Recent Advances in the Construction of Flexible Sensors for Biomedical Applications. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 15, e2000094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimzadeh, Z.; Mahmoudpour, M.; Rahimpour, E.; Jouyban, A. Nanomaterial Based PVA Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Biomedical Sensing: Advances toward Designing the Ideal Flexible/Wearable Nanoprobes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 305, 102705. [Google Scholar]
- Alsharabi, R.M.; Rai, S.; Mohammed, H.Y.; Farea, M.A.; Srinivasan, S.; Saxena, P.S.; Srivastava, A.; Anchal Srivastava, P. A Comprehensive Review on Graphene-Based Materials as Biosensors for Cancer Detection. Oxf. Open Mater. Sci. 2023, 3, itac013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.; Lee, J.-J.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, H.W.; Oh, S.; Lee, J.J.; Heo, K.; Park, J.-H. Recent Progress in Artificial Synapses Based on Two-Dimensional van Der Waals Materials for Brain-Inspired Computing. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2020, 2, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, F.; Liu, G.; Lin, H.; Bao, Y.; Han, D.; Wang, W.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, B.; Niu, L. Superhydrophobic Functionalized Ti3C2T x MXene-Based Skin-Attachable and Wearable Electrochemical PH Sensor for Real-Time Sweat Detection. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 7319–7328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; He, J.; Baeumner, A.J.; Wolfbeis, O.S.; Wang, Z.L.; Salama, K.N.; Alshareef, H.N. A MXene-Based Wearable Biosensor System for High-Performance In Vitro Perspiration Analysis. Small 2019, 15, e1901190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Mckeon, L.; Garcia, J.; Pinilla, S.; Barwich, S.; Möbius, M.; Stamenov, P.; Coleman, J.N.; Nicolosi, V. Additive Manufacturing of Ti3C2 -MXene-Functionalized Conductive Polymer Hydrogels for Electromagnetic- Interference Shielding. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2106253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Chhetry, A.; Zhang, S.; Yoon, H.; Park, C.; Kim, H.; Sharifuzzaman, M.; Hui, X.; Park, J.Y. Hydrogen-Bond-Triggered Hybrid Nanofibrous Membrane-Based Wearable Pressure Sensor with Ultrahigh Sensitivity over a Broad Pressure Range. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 4380–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, G.; Ge, K.; Jiang, L.; Fang, D. Flexible, High-Strength and Multifunctional Polyvinyl Alcohol/MXene/Polyaniline Hydrogel Enhancing Skin Wound Healing. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 3585–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinita; Nirala, N.R.; Prakash, R. One Step Synthesis of AuNPs@MoS2-QDs Composite as a Robust Peroxidase- Mimetic for Instant Unaided Eye Detection of Glucose in Serum, Saliva and Tear. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 263, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Shang, Z.; Su, T.; Zhang, S.; Lu, Q.; Xu, Q.; Hu, X. A Highly Flexible Ni–Co MOF Nanosheet Coated Au/PDMS Film Based Wearable Electrochemical Sensor for Continuous Human Sweat Glucose Monitoring. Analyst 2022, 147, 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.J.; Kim, K.O. Novel Glucose-responsive of the Transparent Nanofiber Hydrogel Patches as a Wearable Biosensor via Electrospinning. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, X.; Bai, H. Novel Carbon Nanomaterials Based Flexible Electrochemical Biosensors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 27504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, X.; Mugo, S.M.; Zhang, Q. A Portable Sweat Sensor Based on Carbon Quantum Dots for Multiplex Detection of Cardiovascular Health Biomarkers. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 12772–12780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yuan, J.; Zha, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Che, J. Soft Conducting Polymer Hydrogels in Situ Doped by Sulfonated Graphene Quantum Dots for Enhanced Electrochemical Activity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 2153–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Ren, X.; Yang, T.; Xu, C.; Ye, Y.; Sun, Z.; Kong, L.; Wang, B.; Luo, Z. Polypyrrole/Sulfonated Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Conductive Hydrogel for Electrochemical Sensing of Living Cells. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 418, 129483. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Xu, X.; Hu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, M.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, P. Rapid Preparation of N-CNTs/P(AA-Co-AM) Composite Hydrogel via Frontal Polymerization and Its Mechanical and Conductive Properties. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 19022–19028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadpour-Haratbar, A.; Boraei, S.B.A.; Zare, Y.; Rhee, K.Y.; Park, S.J. Graphene-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Breast Cancer Detection. Biosensors 2023, 13, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahriri, M.; Del Monico, M.; Moghanian, A.; Tavakkoli Yaraki, M.; Torres, R.; Yadegari, A.; Tayebi, L. Graphene and Its Derivatives: Opportunities and Challenges in Dentistry. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 102, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Ma, Z. Multiple Signal Amplification Strategies for Ultrasensitive Label-Free Electrochemical Immunoassay for Carbohydrate Antigen 24-2 Based on Redox Hydrogel. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Z.; Yu, J.; Li, D.; Nie, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Q. Free-Standing TiO 2–SiO 2/PANI Composite Nanofibers for Ammonia Sensors. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 3576–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, S. One-Pot Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanoparticle-Loaded 3D Porous Graphene Nanocomposites with Enhanced Nanozyme Activity for Glucose Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 7465–7471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, J.F.R.V.; Besse, R.; Da Silva, J.L.F. Stacking Order Effects on the Electronic and Optical Properties of Graphene/Transition Metal Dichalcogenide Van Der Waals Heterostructures. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 3, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavličková, M.; Lorencová, L.; Hatala, M.; Kováč, M.; Tkáč, J.; Gemeiner, P. Facile Fabrication of Screen-Printed MoS2 Electrodes for Electrochemical Sensing of Dopamine. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, D.K.; Lenka, T.R.; Singh, R.; Goyal, V.; Boukortt, N.E.I.; Nguyen, H.P.T. Analytical Modeling of Dielectric Modulated Negative Capacitance MoS2 Field Effect Transistor for Next-generation Label-free Biosensor. Int. J. Numer. Model. Electron. Netw. Devices Fields 2022, 36, e3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parab, A.; Borade, P.A.; Sant, T.; Jejurikar, S.M. Dual Mode Detection of a Glucose Molecule Using MoS2/NiO Electrode. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 37, 102627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, B.; Ahmad, M.W.; Sarkhel, G.; Yang, D.-J.; Choudhury, A. Fabrication of Porous Nickel (II)-Based MOF@ Carbon Nanofiber Hybrid Mat for High-Performance Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensing. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2022, 142, 106500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Ga, L.; Bi, L.; Ai, J. Wearable Electrochemical Sensors Based on Nanomaterials for Healthcare Applications. Electroanalysis 2023, 35, e202200228. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Jiang, X.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Lai, J.; Wang, X. Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 Encapsulating Gold Nanoclusters and Carbon Dots for Ratiometric Fluorescent Detection of Adenosine Triphosphate and Cellular Imaging. Talanta 2023, 255, 124226. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anu Prathap, M.U.; Kaur, B.; Srivastava, R. Electrochemical Sensor Platforms Based on Nanostructured Metal Oxides, and Zeolite-based Materials. Chem. Rec. 2019, 19, 883–907. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kucherenko, I.S.; Soldatkin, O.O.; Dzyadevych, S.V.; Soldatkin, A.P. Application of Zeolites and Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks in the Biosensor Development. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 143, 213180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panic, V.V.; Jovanovic, J.D.; Popovic, I.G.; Savic, S.I.; Markovic, M.D.; Spasojevic, P.M.; Adnadjevic, B.K. The Study of Composition-Properties Relationships for Composite Hydrogels Based on Poly (Methacrylic Acid) and High Concentrations of MFI Zeolite. Polymer 2023, 269, 125750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Deng, Z.; Guo, Y.; Xu, P. Engineering Functional Natural Polymer-Based Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Wound Healing. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 5, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Su, J.; Zeng, D.; Liu, G.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Mi, X. Gold Nano-Flowers (Au NFs) Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode Electrochemical Biosensor for Label-Free and Quantitative Detection of Glycated Hemoglobin. Talanta 2019, 201, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour-Haratbar, A.; Zare, Y.; Rhee, K.Y. Simulation of Electrical Conductivity for Polymer Silver Nanowires Systems. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziai, Y.; Rinoldi, C.; Nakielski, P.; De Sio, L.; Pierini, F. Smart Plasmonic Hydrogels Based on Gold and Silver Nanoparticles for Biosensing Application. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 24, 100413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, Q.; Hu, T.; Tang, L.; Ni, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, H.; Huang, L.; Ding, C. Adhesive, Antibacterial, Conductive, Anti-UV, Self-Healing, and Tough Collagen-Based Hydrogels from a Pyrogallol-Ag Self-Catalysis System. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 8728–8742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Hao, J.; Li, W.; Ma, F.; Ma, T.; Gao, W.; Yu, Y.; Wen, D. Integrating Highly Porous and Flexible Au Hydrogels with Soft-Mems Technologies for High-Performance Wearable Biosensing. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 14068–14075. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shakeri, A.; Salehi, H.; Taghvay Nakhjiri, M.; Shakeri, E.; Khankeshipour, N.; Ghorbani, F. Carboxymethylcellulose-Quaternary Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Polymer Hydrogel as a Biodegradable Draw Agent for Osmotic Water Treatment Process. Cellulose 2019, 26, 1841–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Du, X. Self-Healable and Redox Active Hydrogel Obtained via Incorporation of Ferric Ion for Supercapacitor Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakar, H.; Sebastian, S.M.; Mandal, S.; Pople, A.; Agarwal, G.; Srivastava, A. Biomolecule-Conjugated Macroporous Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 6320–6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kailasa, S.K.; Joshi, D.J.; Kateshiya, M.R.; Koduru, J.R.; Malek, N.I. Review on the Biomedical and Sensing Applications of Nanomaterial-Incorporated Hydrogels. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 23, 100746. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.; Choi, E.J.; Cho, J.H.; Cho, A.-N.; Jin, Y.; Yang, K.; Song, C.; Cho, S.-W. Three-Dimensional Electroconductive Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels Incorporated with Carbon Nanotubes and Polypyrrole by Catechol-Mediated Dispersion Enhance Neurogenesis of Human Neural Stem Cells. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 3060–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Manna, K.; Dey, S.; Pal, S. Chemical Modification of β-Cyclodextrin towards Hydrogel Formation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 306, 120576. [Google Scholar]
- Barhoum, A.; Sadak, O.; Ramirez, I.A.; Iverson, N. Stimuli-Bioresponsive Hydrogels as New Generation Materials for Implantable, Wearable, and Disposable Biosensors for Medical Diagnostics: Principles, Opportunities, and Challenges. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 317, 102920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Lü, H.; Hui, N. Phytic Acid Functionalized Antifouling Conducting Polymer Hydrogel for Electrochemical Detection of MicroRNA. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1124, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, A.; Fau, M.; Karbarz, M.; Donten, M.; Stojek, Z.; Nowicka, A.M. Hydrogel with Chains Functionalized with Carboxyl Groups as Universal 3D Platform in DNA Biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczyk, A.; Wagner, B.; Karbarz, M.; Nowicka, A.M. A Dual DNA Biosensor Based on Two Redox Couples with a Hydrogel Sensing Platform Functionalized with Carboxyl Groups and Gold Nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 208, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutar, R.; Motealleh, A.; Khademhosseini, A.; Kehr, N.S. Functional Nanomaterials on 2D Surfaces and in 3D Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 1904344, 1904344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cheng, W.; Ziemann, E.; Be’er, A.; Lu, X.; Elimelech, M.; Bernstein, R. Functionalization of Ultrafiltration Membrane with Polyampholyte Hydrogel and Graphene Oxide to Achieve Dual Antifouling and Antibacterial Properties. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 565, 293–302. [Google Scholar]
- Shee, M.; Basak, P.; Das, A.K.; Das, N.C. Hydrogel Based Chemical Sensors. In Materials for Chemical Sensors; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; pp. 75–95. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Thomas, B.; Ramírez-Hernández, M.; Mikmeková, E.M.; Asefa, T. Metal-Functionalized Hydrogels as Efficient Oxygen Evolution Electrocatalysts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 20919–20929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, D.; Shuai, T.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Ren, F.; Fang, L.; Wang, K.; Xie, C.; Lu, X. Mussel-Inspired Redox-Active and Hydrophilic Conductive Polymer Nanoparticles for Adhesive Hydrogel Bioelectronics. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 12, 169. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.H.; Ariga, K. Redox-Active Polymers for Energy Storage Nanoarchitectonics. Joule 2017, 1, 739–768. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, M.; Sahin, S.; Cai, R.; Abdellaoui, S.; Hickey, D.P.; Minteer, S.D.; Milton, R.D. Creating a Low-potential Redox Polymer for Efficient Electroenzymatic CO2 Reduction. Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 6692–6696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishat, Z.S.; Hossain, T.; Islam, M.N.; Phan, H.; Wahab, M.A.; Moni, M.A.; Salomon, C.; Amin, M.A.; Sina, A.A.I.; Hossain, M.S.A. Hydrogel Nanoarchitectonics: An Evolving Paradigm for Ultrasensitive Biosensing. Small 2022, 18, 2107571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John-Herpin, A.; Kavungal, D.; von Mücke, L.; Altug, H. Infrared Metasurface Augmented by Deep Learning for Monitoring Dynamics between All Major Classes of Biomolecules. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006054. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, M.; Simões, H.; Pinto, S.N.; Macedo, A.S.; Fonte, P.; Prazeres, D.M.F. Fusions of a Carbohydrate Binding Module with the Small Cationic Hexapeptide RWRWRW Confer Antimicrobial Properties to Cellulose-Based Materials. Acta Biomater. 2022, 143, 216–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, M.; Simões, H.; Prazeres, D.M.F. Functionalization of Cellulose-Based Hydrogels with Bi-Functional Fusion Proteins Containing Carbohydrate-Binding Modules. Materials 2021, 14, 3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilchrist, A.E.; Serrano, J.F.; Ngo, M.T.; Hrnjak, Z.; Kim, S.; Harley, B.A.C. Encapsulation of Murine Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells in a Thiol-Crosslinked Maleimide-Functionalized Gelatin Hydrogel. Acta Biomater. 2021, 131, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gombotz, W.R.; Hoffman, A.S. Immobilization of Biomolecules and Cells on and within Synthetic Polymeric Hydrogels. In Hydrogels in Medicine and Pharmacy; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 95–126. [Google Scholar]
- Alavi, S.K.; Lotz, O.; Akhavan, B.; Yeo, G.; Walia, R.; McKenzie, D.R.; Bilek, M.M. Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet Treatment of Polymers Enables Reagent-Free Covalent Attachment of Biomolecules for Bioprinting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 38730–38743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.B.; Lee, W.C.; Cho, C.H.; Park, D.S.; Cho, S.J.; Shim, Y.B. Continuous Glucose Monitoring Using a Microneedle Array Sensor Coupled with a Wireless Signal Transmitter. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 281, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiseppi-Elie, A. Electroconductive Hydrogels: Synthesis, Characterization and Biomedical Applications. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2701–2716. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Xiang, Z.; Jiang, W.; He, S.; Xiao, H. Conductive Hydrogels Based on Industrial Lignin: Opportunities and Challenges. Polymers 2022, 14, 3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, C.; Li, G.; Yu, D.; Song, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, W. Development of Conductive Hydrogels for Fabricating Flexible Strain Sensors. Small 2022, 18, 2101518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Liu, K.; Wang, M.; Wang, K.; Fang, L.; Chen, H.; Zhou, J.; Lu, X. Mussel-inspired Adhesive and Conductive Hydrogel with Long-lasting Moisture and Extreme Temperature Tolerance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1704195. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Hu, T.; Han, Y.; Guo, B. Mussel-Inspired, Antibacterial, Conductive, Antioxidant, Injectable Composite Hydrogel Wound Dressing to Promote the Regeneration of Infected Skin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 556, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppes, A.N.; Keating, K.W.; McGregor, A.L.; Koppes, R.A.; Kearns, K.R.; Ziemba, A.M.; McKay, C.A.; Zuidema, J.M.; Rivet, C.J.; Gilbert, R.J. Robust Neurite Extension Following Exogenous Electrical Stimulation within Single Walled Carbon Nanotube-Composite Hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2016, 39, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kougkolos, G.; Golzio, M.; Laudebat, L.; Valdez-Nava, Z.; Flahaut, E. Hydrogels with Electrically Conductive Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 2036–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imaninezhad, M.; Pemberton, K.; Xu, F.; Kalinowski, K.; Bera, R.; Zustiak, S.P. Directed and Enhanced Neurite Outgrowth Following Exogenous Electrical Stimulation on Carbon Nanotube-Hydrogel Composites. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 56034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, J.H.; Patel, M.; Koh, W.-G. Incorporation of Conductive Materials into Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, M.; Gu, Q.; Naficy, S.; Farajikhah, S.; Crook, J.M.; Wallace, G.G.; Beirne, S.; Moulton, S.E. Conductive Tough Hydrogel for Bioapplications. Macromol. Biosci. 2018, 18, 1700270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoyama, K.; Ahumada, M.; McTiernan, C.D.; Bejjani, J.; Variola, F.; Ruel, M.; Xu, B.; Liang, W.; Suuronen, E.J.; Alarcon, E.I. Multi-Functional Thermo-Crosslinkable Collagen-Metal Nanoparticle Composites for Tissue Regeneration: Nanosilver vs. Nanogold. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 47704–47708. [Google Scholar]
- Dispenza, C.; Presti, C.L.; Belfiore, C.; Spadaro, G.; Piazza, S. Electrically Conductive Hydrogel Composites Made of Polyaniline Nanoparticles and Poly (N-Vinyl-2-Pyrrolidone). Polymer 2006, 47, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Zhang, S.; Tang, F.; Wang, J.; Li, L. Silver-Hydrogel/PDMS Film with High Mechanical Strength for Anti-Interference Strain Sensor. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 654, 130071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Lin, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Shang, J.; Luo, Z. Biocompatible Conductive Hydrogels: Applications in the Field of Biomedicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Pi, M.; Zhang, X.; Yan, B.; Li, Y.; Shi, L.; Ran, R. High Strength, Antifreeze, and Moisturizing Conductive Hydrogel for Human-motion Detection. Polymer 2020, 196, 122469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gong, M.; Wan, P. MXene Hydrogel for Wearable Electronics. Matter 2021, 4, 2655–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Hu, Y.P.; Liu, K.Y.; Yu, W.; Li, G.X.; Meng, C.Z.; Guo, S.J. Recent Development of Self-Powered Tactile Sensors Based on Ionic Hydrogels. Gels 2023, 9, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Wu, S.; Qu, J.; Gong, L.; Tang, J. A Review of Conductive Hydrogel Used in Flexible Strain Sensor. Materials 2020, 13, 3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Liu, J.; Gao, S.; Pei, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, K.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Zheng, X. Ionically Conductive Gelatin-Based Hybrid Composite Hydrogels with High Mechanical Strength, Self-Healing, and Freezing-Tolerant Properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 172, 111230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Yu, A.; Lai, G. Conductive Hydrogel-Based Electrochemical Sensor: A Soft Platform for Capturing Analyte. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, D.; Karak, N. Highly Sensitive Detection of Antibodies in a Soft Bioactive Three-Dimensional Bioorthogonal Hydrogel. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 242, 3220–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, J.; Ding, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Wu, J. Functionalized Hydrogel-Based Wearable Gas and Humidity Sensors; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; Volume 15, ISBN 0123456789. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; Gu, Z.; Chu, Y.; Lv, J.; Fan, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, F.; Ying, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Magnetically-Oriented Porous Hydrogel Advances Wearable Electrochemical Solidoid Sensing Heavy Metallic Ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Taneichi, T.; Fukuoka, T.; Namura, K. Study on Transport of Molecules in Gel by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Cellulose 2021, 28, 10803–10813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiaratchi, M.H.; Schudel, A.; Rouse, T.; García, A.J.; Thomas, S.N.; Guldberg, R.E.; McDevitt, T.C. A Rapid Method for Determining Protein Diffusion through Hydrogels for Regenerative Medicine Applications. APL Bioeng. 2018, 2, 26110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hansing, J.; Netz, R.R.; Derouchey, J.E. Article Particle Transport through Hydrogels Is Charge Asymmetric. Biophys. J. 2015, 108, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, A.A.; Kristen Means, A.; Clubb, F.J.; Fei, R.; Locke, A.K.; Gacasan, E.G.; Coté, G.L.; Grunlan, M.A. Foreign Body Reaction to a Subcutaneously Implanted Self-Cleaning, Thermoresponsive Hydrogel Membrane for Glucose Biosensors. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 4104–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, N.; Mu, L.; Pan, J.; Lan, X.; Li, H.; Deng, F. Anti-Biofouling Polymers with Special Surface Wettability for Biomedical Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 807357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Cai, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, N.; Xie, M.; Zhou, B.; Wang, H.; Guo, Z. Anti-Liquid-Interfering and Bacterially Antiadhesive Strategy for Highly Stretchable and Ultrasensitive Strain Sensors Based on Cassie-Baxter Wetting State. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Guo, H.; Li, W.-H. Anti-Fouling Performance of Hydrophobic Hydrogels with Unique Surface Hydrophobicity and Nanoarchitectonics. Gels 2022, 8, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahadoran, N.; Tayebeh, B.; Mohammad, B.; Karimi, H. Modelling of Water Absorption Kinetics and Biocompatibility Study of Synthesized Cellulose Nanofiber-Assisted Starch-Graft-Poly (Acrylic Acid) Hydrogel Nanocomposites. Cellulose 2020, 27, 9927–9945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, D.; Karak, N. Double Network Hydrophobic Starch Based Amphoteric Hydrogel as an Effective Adsorbent for Both Cationic and Anionic Dyes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 242, 116320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cos, B.; Buc, S.; Constantin, M. Temperature/PH-Sensitive Double Cross-Linked Hydrogels as Platform for Controlled Delivery of Metoclopramide. Gels 2022, 8, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Wang, H.; Ma, P.X.; Guo, B. Self-Healing Conductive Hydrogels: Preparation, Properties and Applications. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 1224–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Ma, C.; Yang, G. Highly tough, multi-stimuli-responsive, and fast self-healing supramolecular networks toward strain sensor application. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 389, 123468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Ge, X.; Qian, Y.; Wei, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, W.-E.; Ouyang, Y. Advances in Synthesis and Applications of Self-Healing Hydrogels. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 654. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Ren, Z.; Liu, F.; Zhao, L.; Ling, Q.; Gu, H. Multifunctional Self-Healing Dual Network Hydrogels Constructed via Host-Guest Interaction and Dynamic Covalent Bond as Wearable Strain Sensors for Monitoring Human and Organ Motions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 14612–14622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yin, F.; He, W.; Hang, T.; Li, Z.; Zheng, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, S.; Chen, Y. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules Anti-Freezing, Recoverable and Transparent Conductive Hydrogels Co-Reinforced by Ethylene Glycol as Flexible Sensors for Human Motion Monitoring. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Hu, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, M.; Liu, P.; Li, C.; Yu, Y.; Xiao, X.; Feng, Q. Ultra-Stretchable, Adhesive, and Self-Healing MXene/Polyampholytes Hydrogel as Flexible and Wearable Epidermal Sensors. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 645, 128897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Wang, A.; Song, W.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Ren, P.; Hao, L.; Yin, J. Fabrication of Conductive, Adhesive, and Stretchable Agarose- Based Hydrogels for a Wearable Biosensor. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 6148–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wu, H. One-Step Preparation of Highly Viscoelastic, Stretchable, Antibacterial, Biocompatible, Wearable, Conductive Composite Hydrogel with Extensive Adhesion. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2023, 231, 109793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xiang, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Du, X.; Cheng, X.; Du, Z.; Wang, H. Skin-Inspired Nanofibrillated Cellulose-Reinforced Hydrogels with High Mechanical Strength, Long-Term Antibacterial, and Self-Recovery Ability for Wearable Strain/Pressure Sensors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 261, 117894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Guo, H.; Chen, P.; Zhu, Y.; Wen, C.; Gao, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L. Zwitterionic Osmolyte-based Hydrogels with Antifreezing Property, High Conductivity, and Stable Flexibility at Subzero Temperature. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Hedenqvist, M.S.; Chen, C.; Cai, C.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Fu, J. Multifunctional Conductive Hydrogels and Their Applications as Smart Wearable Devices. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 2561–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, X.; Hou, T.; Guo, K.; Yin, J.; Wang, Z.; Shu, L.; He, M.; Yao, J. Inorganic Salts Induce Thermally Reversible and Anti-freezing Cellulose Hydrogels. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7366–7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhao, X.; Wei, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Lu, H.; Jia, P. Ultrastretchable, Tough, Antifreezing, and Conductive Cellulose Hydrogel for Wearable Strain Sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 53247–53256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gun’ko, V.M.; Savina, I.N.; Mikhalovsky, S.V. Properties of Water Bound in Hydrogels. Gels 2017, 3, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmani, P.; Shojaei, A. A Review on the Features, Performance and Potential Applications of Hydrogel-Based Wearable Strain/Pressure Sensors. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 298, 102553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bovone, G.; Dudaryeva, O.Y.; Marco-Dufort, B.; Tibbitt, M.W. Engineering Hydrogel Adhesion for Biomedical Applications via Chemical Design of the Junction. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 4048–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanavicius, S.; Ramanavicius, A. Conducting Polymers in the Design of Biosensors and Biofuel Cells. Polymers 2021, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huzum, B.; Puha, B.; Necoara, R.; Gheorghevici, S.; Puha, G.; Filip, A.; Sirbu, P.; Alexa, O. Biocompatibility Assessment of Biomaterials Used in Orthopedic Devices: An Overview (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Shi, Y.; Sun, Y.; Okeke, S.I.; Yang, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Xiao, L. Recent Implementations of Hydrogel-Based Microbial Electrochemical Technologies (METs) in Sensing Applications. Sensors 2023, 23, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Ma, C.; Chu, X.; Wang, L.; Xu, W. A Review on Recent Advances of Protein-Polymer Hydrogels. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 162, 110881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, K. Preparation Method, Properties and Crosslinking of Hydrogel: A Review. PharmaTutor 2017, 5, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Moutsatsou, P.; Coopman, K.; Georgiadou, S. Biocompatibility Assessment of Conducting PANI/Chitosan Nanofibers for Wound Healing Applications. Polymers 2017, 9, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Zhao, J.; Ma, X.; Li, H.; Fan, D. Antibacterial Dual Network Hydrogels for Sensing and Human Health Monitoring. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, e2101089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; He, Z.; Yin, S.; Xie, X.; Yuan, W. Adhesive, Stretchable and Antibacterial Hydrogel with External/Self-Power for Flexible Sensitive Sensor Used as Human Motion Detection. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 220, 108984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guascito, M.R.; Chirizzi, D.; Malitesta, C.; Giotta, L.; Mastrogiacomo, D.; Valli, L.; Stabili, L. Development and Characterization of a Novel Bioactive Polymer with Antibacterial and Lysozyme-like Activity. Biopolymers 2014, 101, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, W.; Xu, Q.; Zheng, Y. Progress in Antibacterial Hydrogel Dressing. Gels 2022, 8, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorejová, R.; Haverová, L.; Oriňaková, R.; Oriňak, A.; Oriňak, M. Recent Advancements in Fe-Based Biodegradable Materials for Bone Repair. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 1913–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeo, N.; Nishioka, M.; Mukai, T. Fabrication of Biodegradable Materials with High Strength by Grain Refinement of Mg–0.3 at.% Ca Alloys. Mater. Lett. 2018, 223, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Hu, S.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Mo, X.; Gong, X.; Liu, H.; Luo, W.; Dong, W.; Sima, C. A Biodegradable and Recyclable Piezoelectric Sensor Based on a Molecular Ferroelectric Embedded in a Bacterial Cellulose Hydrogel. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 3744–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Hao, J. Antiswelling and Durable Adhesion Biodegradable Hydrogels for Tissue Repairs and Strain Sensors. Langmuir 2020, 36, 10448–10459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Wang, S.; Shan, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Mao, J. Conductive Fibers for Biomedical Applications. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 22, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Yang, J.; Suo, Z. Fatigue of Hydrogels. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids 2019, 74, 337–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.M.V.; Rajendran, V.; Mishra, R.K.; Jayaraman, M. Trends in Analytical Chemistry Recent Advances and Perspectives in Sweat Based Wearable Electrochemical Sensors. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 131, 116024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay Kumar Thakur, M.K.T. Hydrogels: Recent Advancess; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; ISBN 9789811060793. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Q.; Ji, X.; An, X.; Liu, H.; Ni, Y. Nanolignin Filled Conductive Hydrogel with Improved Mechanical, Anti-Freezing, UV-Shielding and Transparent Properties for Strain Sensing Application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 205, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Chang, G.; Pan, X.; Weng, X.; Wang, Y.; Lei, M. A Double-Layer Carbon Nanotubes/Polyvinyl Alcohol Hydrogel with High Stretchability and Compressibility for Human Motion Detection. Eng. Sci. 2022, 17, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Gu, Y.; Yin, X. An Electrically Conductive Polyvinyl Alcohol/Poly (Acrylic Acid-Co-Acrylamide)/Polydopamine-Decorated Carbon Nanotubes Composite Hydrogel with Appropriate Mechanical Properties for Human Movement Monitoring. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 12947–12959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Jiang, F. Cellulose Nanofibrils Enhanced, Strong, Stretchable, Freezing-Tolerant Ionic Conductive Organohydrogel for Multi-Functional Sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2003430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Feng, S.; Deng, Z. The Role of Reduced Graphene Oxide as a “2D Flexible Crosslinking Point” in Composite Hydrogels. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Qin, G.; Chen, Q. Double Network Hydrogels with Controlled Shape Deformation: A Mini Review. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2018, 56, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zheng, H.; Tan, Y.J.; Tor, S.B.; Zhou, K. Development of an Ultrastretchable Double-Network Hydrogel for Flexible Strain Sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 12814–12823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Geng, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Hao, J.; Cui, J. Modulation of Double-Network Hydrogels via Seeding Calcium Carbonate Microparticles for the Engineering of Ultrasensitive Wearable Sensors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 2996–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Wu, T.; Li, T.; Huang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Ma, S.; et al. A Review of Recent Advances in Metal Ion Hydrogels: Mechanism, Properties and Their Biological Applications. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 13838–13855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Kaur, H.; Roy, S. Inducing Differential Self-Assembling Behavior in Ultrashort Peptide Hydrogelators Using Simple Metal Salts. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 2610–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, T.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; Que, X.; Sheng, L. Polyacrylamide/Copper-Alginate Double Network Hydrogel Electrolyte with Excellent Mechanical Properties and Strain-Sensitivity. Macromol. Biosci. 2022, 22, 2100361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, X.; Liu, Y. Stretchable Slide-Ring Supramolecular Hydrogel for Flexible Electronic Devices. Commun. Mater. 2022, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, M.; Zhao, W.; Chen, L.; Liu, H.; Jin, X.; Ma, A.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, D.; Chen, W. Supramolecularly Mediated Robust, Anti-fatigue, and Strain-sensitive Macromolecular Microsphere Composite Hydrogels. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 2000080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Fei, X.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, J.; Xu, L.; Li, Y. Polyionic Liquids Supramolecular Hydrogel with Anti-Swelling Properties for Underwater Sensing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 628, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopa, T. Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels Crosslink Density Equation: A Rheological and LF-NMR Study of Polymer-Polymer Interactions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 277, 118895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xiang, P.; Li, Y.; Gao, G. Amylopectin Based Hydrogel Strain Sensor with Good Biocompatibility, High Toughness and Stable Anti-Swelling in Multiple Liquid Media. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 164, 110981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Qin, X.; Cao, L.; Li, J.; Wei, Y. Chitosan-Enhanced Nonswelling Hydrogel with Stable Mechanical Properties for Long-Lasting Underwater Sensing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 212, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jian, J.; Xie, Y.; Gao, S.; Ling, Z.; Lai, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Chu, F.; Dumont, M.J. Mimicking Skin Cellulose Hydrogels for Sensor Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 130921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dai, T.; Wu, H.; Ye, M.; Yuan, G.; Jia, H. Tannic Acid-Fe3+ Activated Rapid Polymerization of Ionic Conductive Hydrogels with High Mechanical Properties, Self-Healing, and Self-Adhesion for Flexible Wearable Sensors. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 221, 109345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, S.; Jeong, Y.R.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.S.; Keum, K.; Lee, H.; Ha, J.S. Self-Healing Strain-Responsive Electrochromic Display Based on a Multiple Crosslinked Network Hydrogel. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wu, Y.; Ma, S.; Yan, T.; Pan, Z. Flexible Strain Sensor Based on CNT/TPU Composite Nanofiber Yarn for Smart Sports Bandage. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 232, 109605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-N.; He, X.-F.; Zeng, Z.-F.; Jiang, B.; Wu, Q.; Gong, L.-X.; Li, Y.; Bae, J.; Wang, S.; Tang, L.-C. Mechanically Ductile, Ionically Conductive and Low-Temperature Tolerant Hydrogel Enabled by High-Concentration Saline towards Flexible Strain Sensor. Nano Energy 2022, 103, 107789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Lu, C.; Li, C.; Yu, Z.; Shen, C.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y. A UV-Filtering, Environmentally Stable, Healable and Recyclable Ionic Hydrogel towards Multifunctional Flexible Strain Sensor. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 230, 109528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Zhong, Y.; Song, X.; Chen, X.; Zhou, P.; Zhao, F.; Bai, J. 3D Printing of Mechanically Elastic, Self-Adhesive, and Biocompatible Organohydrogels for Wearable and Breathable Strain Sensors. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 8, 2201078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Cong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, T.; Nie, L.; Fu, J. Ultrastretchable Strain Sensors and Arrays with High Sensitivity and Linearity Based on Super Tough Conductive Hydrogels. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 8062–8069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xing, L.; Shi, L.; Ran, R. Stable, Strain-Sensitive Conductive Hydrogel with Antifreezing Capability, Remoldability, and Reusability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 44000–44010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y.; Ren, X.; Gao, G. Ultrastretchable Wearable Strain and Pressure Sensors Based on Adhesive, Tough, and Self-Healing Hydrogels for Human Motion Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 25613–25623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Jin, R.; Ren, X.; Gao, G. Cartilage-Inspired Hydrogel Strain Sensors with Ultrahigh Toughness, Good Self-Recovery and Stable Anti-Swelling Properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 25441–25448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wu, P.; Yu, F.; Ma, J. Double Network Hydrogels for Energy/Environmental Applications: Challenges and Opportunities. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 9215–9247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, M.A.; Fernández-Garibay, X.; Castaño, A.G.; De Chiara, F.; Hernández-Albors, A.; Balaguer-Trias, J.; Ramón-Azcón, J. Muscle-on-a-Chip with an on-Site Multiplexed Biosensing System for in Situ Monitoring of Secreted IL-6 and TNF-α. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 2568–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Huang, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Huang, J.; Liu, H.; Yan, Y. Fabrication of Hydrogels with Adjustable Mechanical Properties through 3D Cell-Laden Printing Technology. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 646, 128980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Tang, J.; Li, H. Bioinspired Swelling Enhanced Hydrogels for Underwater Sensing. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 664, 131197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q. Diesel Engine System Design; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; ISBN 0857090836. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Yuk, H.; Loh, H.; Parada, G.A.; Settens, C.; Song, J.; Masic, A.; Mckinley, G.H.; et al. Anti-Fatigue-Fracture Hydrogels. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau8528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotoodeh, K. Prevention of Valve Fugitive Emissions in the Oil and Gas Industry; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2021; ISBN 0323918638. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, L.; Fu, J. Stretchable, Self-Healing and Tissue-Adhesive Zwitterionic Hydrogels as Strain Sensors for Wireless Monitoring of Organ Motions. Mater. Horiz. 2020, 7, 1872–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, T.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Chu, F.; Wang, C.; Tang, C. A Highly Elastic and Fatigue-resistant Natural Protein-reinforced Hydrogel Electrolyte for Reversible-compressible Quasi-solid-state Supercapacitors. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2000587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, C.; Wu, P.; Guo, J.; Zhao, N.; Ke, C.; Liu, G.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Synergy of Hofmeister Effect and Ligand Crosslinking Enabled the Facile Fabrication of Super-Strong, Pre-Stretching-Enhanced Gelatin-Based Hydrogels. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 8675–8686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Liang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Kang, G.; Kan, Q. Experimental investigation on pure-shear ratcheting behavior of double-network tough hydrogels. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2023, 60, 101984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, W.; et al. Anti-Freezing, Resilient and Tough Hydrogels for Sensitive and Large-Range Strain and Pressure Sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Tian, X.; Liu, S.; Qin, G.; Chen, Q. Robust, Fatigue Resistant, Self-Healing and Antifreeze Ionic Conductive Supramolecular Hydrogels for Wearable Flexible Sensors. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 115, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Q.; Hong, M.; Yang, S.; Fu, H. Highly Elastic Anti-Fatigue and Anti-Freezing Conductive Double Network Hydrogel for Human Body Sensors. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 6162–6172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, S.L.; Bernards, M.T. Polyampholyte Hydrogels in Biomedical Applications. Gels 2017, 3, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.L.; Kurokawa, T.; Kuroda, S.; Ihsan, A.B.; Akasaki, T.; Sato, K.; Haque, M.A.; Nakajima, T.; Gong, J.P. Physical Hydrogels Composed of Polyampholytes Demonstrate High Toughness and Viscoelasticity. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillet, A.M.; Wyatt, N.B.; Gloe, L.M. Polymer Gel Rheology and Adhesion. Rheology 2012, 3, 59–80. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, K. Current Hydrogel Advances in Physicochemical and Biological Response-Driven Biomedical Application Diversity. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baniasadi, M.; Minary-Jolandan, M. Alginate-Collagen Fibril Composite Hydrogel. Materials 2015, 8, 799–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Pochan, D.J. Rheological Properties of Peptide-Based Hydrogels for Biomedical and Other Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3528–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shi, Y.; Pan, L.; Shi, Y.; Yu, G. Rational Design and Applications of Conducting Polymer Hydrogels as Electrochemical Biosensors. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 2920–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, H.; Vries, J.D.; Strauss, J.; Jahromi, A.K.; Siavash, R.; Mahshid, S. Advances in the Translation of Electrochemical Hydrogel-Based Sensors. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 12, 2201501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesewski, E.; Johnson, B.N. Electrochemical Biosensors for Pathogen Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 159, 112214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, W.; Ma, B.; Ju, H. Device Integration of Electrochemical Biosensors. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2023, 1, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, S.; Feng, S.; Huang, L.; Bian, S. Recent Progress in Wearable Biosensors: From Healthcare Monitoring to Sports Analytics. Biosensors 2020, 10, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeidi, M.; Amidian, M.A.; Sheybanikashani, S.; Mahdavi, H.; Omidfar, K.; Simchi, A. Multilayered Mesoporous Composite Nanostructures for Highly Sensitive Label-Free Quantification of Cardiac Troponin-I. Biosensors 2022, 12, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Upadhyay, L.S.B. Polymeric Gels for Biosensing Applications. In Polymeric Gels: Characterization, Properties and Biomedical Applications; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 487–503. ISBN 9780081021798. [Google Scholar]
- Molina, A.; González, J. Pulse Voltammetry in Physical Electrochemistry and Electroanalysis_ Theory and Applications. In Monographs in Electrochemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ivarsson, P.; Holmin, S.; Höjer, N.E.; Krantz-Rülcker, C.; Winquist, F. Discrimination of Tea by Means of a Voltammetric Electronic Tongue and Different Applied Waveforms. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 76, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K. Electrochemical Principles and Characterization of Bioelectrochemical Systems. In Microbial Electrochemical and Fuel Cells; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2016; ISBN 9781782423751. [Google Scholar]
- Galliani, M.; Diacci, C.; Berto, M.; Sensi, M.; Beni, V.; Berggren, M.; Borsari, M.; Simon, D.T.; Biscarini, F.; Bortolotti, C.A. Flexible Printed Organic Electrochemical Transistors for the Detection of Uric Acid in Artificial Wound Exudate. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 2001218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempionatto, J.R.; Mishra, R.K.; Martín, A.; Tang, G.; Nakagawa, T.; Lu, X.; Campbell, A.S.; Lyu, K.M.; Wang, J. Wearable Ring-Based Sensing Platform for Detecting Chemical Threats. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Han, R.; Tang, K.; Zhao, S.; Ding, C.; Luo, X. Biocompatible Peptide Hydrogels with Excellent Antibacterial and Catalytic Properties for Electrochemical Sensing Application. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1154, 338295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, L.; Qu, H.; Zheng, L. Breath Alcohol Sensor Based on Hydrogel-Gated Graphene Field-Effect Transistor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 210, 114319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, D.-C.; Koh, Y.; Cha, J. Hydrogel-Based Electrochemical Sensor for Non-Invasive and Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Int. Conf. Nano-Bio Sens. Imaging Spectrosc. 2017, 10324, 1032405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.H.; Sheu, S.C.; Chen, C.W.; Huang, S.C.; Li, B.R. Wearable Hydrogel Patch with Noninvasive, Electrochemical Glucose Sensor for Natural Sweat Detection. Talanta 2022, 241, 123187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Ding, Q.; Zilberman, M.; Tao, K.; Xie, X.; Wu, J. Self-Healing, Self-Adhesive and Stable Organohydrogel-Based Stretchable Oxygen Sensor with High Performance at Room Temperature. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abellán-Llobregat, A.; Jeerapan, I.; Bandodkar, A.; Vidal, L.; Canals, A.; Wang, J.; Morallón, E. A Stretchable and Screen-Printed Electrochemical Sensor for Glucose Determination in Human Perspiration. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, X.; Yoon, H.S.; Park, J.Y. A Wearable Electrochemical Glucose Sensor Based on Simple and Low-Cost Fabrication Supported Micro-Patterned Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Electrode on Flexible Substrate. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 109, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poletti, F.; Zanfrognini, B.; Favaretto, L.; Quintano, V.; Sun, J.; Treossi, E.; Melucci, M.; Palermo, V.; Zanardi, C. Continuous Capillary-Flow Sensing of Glucose and Lactate in Sweat with an Electrochemical Sensor Based on Functionalized Graphene Oxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 344, 130253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.J. Glucose-Responsive Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/b-Cyclodextrin Hydrogel with Glucose Oxidase Immobilization. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 12806–12817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Choi, T.K.; Lee, Y.B.; Cho, H.R.; Ghaffari, R.; Wang, L.; Choi, H.J.; Chung, T.D.; Lu, N.; Hyeon, T.; et al. A Graphene-Based Electrochemical Device with Thermoresponsive Microneedles for Diabetes Monitoring and Therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Hou, Q.; Ding, C. Denatured Bovine Serum Albumin Hydrogel–Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Detection of IgG. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.-Y.; Cheong, W.H.; Jang, J.; Park, Y.-G.; Na, K.; Kim, Y.-T.; Heo, J.H.; Lee, C.Y. Soft, Smart Contact Lenses with Integrations of Wireless Circuits, Glucose Sensors, and Displays. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaap9841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, M.; Kim, J.; Won, J.; Kang, W.; Park, Y.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Cheon, J.; Lee, H.H.; Park, J. Smart, Soft Contact Lens for Wireless Immunosensing of Cortisol. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Meeseepong, M.; Trung, T.Q.; Kim, B. A Wearable Lab-on-a-Patch Platform with Stretchable Nanostructured Biosensor for Non-Invasive Immunodetection of Biomarker in Sweat. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 156, 112133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nah, J.S.; Barman, S.C.; Zahed, A.; Yoon, H.; Park, C.; Yoon, S.; Zhang, S.; Park, J.Y. A Wearable Microfluidics-Integrated Impedimetric Immunosensor Based on Ti3C2Tx MXene Incorporated Laser-Burned Graphene for Noninvasive Sweat Cortisol Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 329, 129206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Fan, C.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X. Skin-like Hydrogel-Elastomer Based Electrochemical Device for Comfortable Wearable Biofluid Monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 455, 140609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, N.L.; Dick, J.E. Oxidase-Loaded Hydrogels for Versatile Potentiometric Metabolite Sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 178, 112997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Park, W.; Lee, C.H. Electrochemically Active Materials and Wearable Biosensors for the in Situ Analysis of Body Fluids for Human Healthcare. NPG Asia Mater. 2021, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankhala, D.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. A Four-Channel Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy Module for Cortisol Biosensing in Sweat-Based Wearable Applications. SLAS Technol. 2018, 23, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strong, M.E.; Richards, J.R.; Torres, M.; Beck, C.M.; La Belle, J.T. Faradaic Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy for Enhanced Analyte Detection in Diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 177, 112949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raicopol, M.; Prună, A.; Damian, C.; Pilan, L. Functionalized Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes/Polypyrrole Composites for Amperometric Glucose Biosensors. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romani, A.; Minunni, M.; Mulinacci, N.; Pinelli, P.; Vincieri, F.F.; Del Carlo, M.; Mascini, M. Comparison among Differential Pulse Voltammetry, Amperometric Biosensor, and HPLC/DAD Analysis for Polyphenol Determination. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatkin, O.O.; Peshkova, V.M.; Dzyadevych, S.V.; Soldatkin, A.P. Novel Sucrose Three-Enzyme Conductometric Biosensor. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2008, 28, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandodkar, A.J.; Jia, W.; Yardımcı, C.; Wang, X.; Ramirez, J.; Wang, J. Tattoo-Based Noninvasive Glucose Monitoring: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolat, G.; De la Paz, E.; Azeredo, N.F.; Kartolo, M.; Kim, J.; de Loyola e Silva, A.N.; Rueda, R.; Brown, C.; Angnes, L.; Wang, J.; et al. Wearable Soft Electrochemical Microfluidic Device Integrated with Iontophoresis for Sweat Biosensing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 5411–5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehrani, F.; Teymourian, H.; Wuerstle, B.; Kavner, J.; Patel, R.; Furmidge, A.; Aghavali, R.; Hosseini-Toudeshki, H.; Brown, C.; Zhang, F. An Integrated Wearable Microneedle Array for the Continuous Monitoring of Multiple Biomarkers in Interstitial Fluid. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 6, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keum, D.H.; Kim, S.-K.; Koo, J.; Lee, G.-H.; Jeon, C.; Mok, J.W.; Mun, B.H.; Lee, K.J.; Kamrani, E.; Joo, C.-K. Wireless Smart Contact Lens for Diabetic Diagnosis and Therapy. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Liang, B.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xu, S.; Tu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Cai, X.; Ye, X. Biosensors and Bioelectronics An Integrated and Conductive Hydrogel-Paper Patch for Simultaneous Sensing of Chemical–Electrophysiological Signals. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 198, 113855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, D.T.; Nguyen, C.H.; Nguyen, T.D.P.; Tran, L.H.; Park, S.; Choi, J.; Lee, B.I.; Oh, J. A Flexible, Wearable, and Wireless Biosensor Patch with Internet of Medical Things Applications. Biosensors 2022, 12, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Jiang, X.; Fang, X.; Kong, J. Wearable Chem-Biosensing Devices: From Basic Research to Commercial Market. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 4285–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, L.M.; Ismailov, U.; Greco, F.; Ismailova, E. Capacitive Coupling of Conducting Polymer Tattoo Electrodes with the Skin. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2100352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yang, Y.; Gao, W. Skin-Interfaced Sensors in Digital Medicine: From Materials to Applications. Matter 2020, 2, 1414–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Badea, M.; Tiwari, S.; Marty, J.L. Wearable Biosensors: An Alternative and Practical Approach in Healthcare and Disease Monitoring. Molecules 2021, 26, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, M.B.; Ayachit, N.H.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Biosensors and Microfluidic Biosensors: From Fabrication to Application. Biosensors 2022, 12, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, T.; Xu, C. A Skin Patch Integrating Swellable Microneedles and Electrochemical Test Strips for Glucose and Alcohol Measurement in Skin Interstitial Fluid. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2022, e10413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, H.; Phairatana, T.; Jeerapan, I. Tackling the Challenges of Developing Microneedle-Based Electrochemical Sensors. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, M.-N.; Fan, S.-H.; Huang, C.-H.; Wu, C.-C.; Huang, J.-T. Continuous Lactate Monitoring System Based on Percutaneous Microneedle Array. Sensors 2022, 22, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrilla, M.; Vanhooydonck, A.; Johns, M.; Watts, R.; De Wael, K. 3D-Printed Microneedle-Based Potentiometric Sensor for PH Monitoring in Skin Interstitial Fluid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 378, 133159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, G.; Weng, Z.; Sun, H.; Nistala, R.; Zhang, Y. Microneedle-Based Potentiometric Sensing System for Continuous Monitoring of Multiple Electrolytes in Skin Interstitial Fluids. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2181–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Hou, M.; Yang, R.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z.; Kang, Y.; Xue, P. Transdermal Delivery of Therapeutics through Dissolvable Gelatin/Sucrose Films Coated on PEGDA Microneedle Arrays with Improved Skin Permeability. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 7515–7524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, D.M.E.; Cass, A.E.G. A Perspective on Microneedle Sensor Arrays for Continuous Monitoring of the Body’s Chemistry. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2022, 121, 70502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollella, P.; Sharma, S.; Cass, A.E.G.; Tasca, F.; Antiochia, R. Minimally Invasive Glucose Monitoring Using a Highly Porous Gold Microneedles-Based Biosensor: Characterization and Application in Artificial Interstitial Fluid. Catalysts 2019, 9, 580. [Google Scholar]
- Kashaninejad, N.; Munaz, A.; Moghadas, H.; Yadav, S.; Umer, M.; Nguyen, N.-T. Microneedle Arrays for Sampling and Sensing Skin Interstitial Fluid. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Liu, B.; Zhou, W.; Jiang, L. A Mini Review of Microneedle Array Electrode for Bio-Signal Recording: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 20, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Yang, Z.; An, M. Lab on the Eye: A Review of Tear-Based Wearable Devices for Medical Use and Health Management. Biosci. Trends 2019, 13, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naresh, V.; Lee, N. A Review on Biosensors and Recent Development of Nanostructured Materials-Enabled Biosensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzajani, H.; Mirlou, F.; Istif, E.; Singh, R.; Beker, L. Powering Smart Contact Lenses for Continuous Health Monitoring: Recent Advancements and Future Challenges. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 197, 113761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokus, M.A.; Saha, T.; Fang, J.; Dickey, M.D.; Velev, O.D.; Daniele, M.A. Towards Wearable Electrochemical Lactate Sensing Using Osmotic-Capillary Microfluidic Pumping. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE SENSORS, Montreal, QC, Canada, 27–30 October 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Pandey, C.M.; Hatamie, A.; Simchi, A.; Willander, M.; Malhotra, B.D. Nanomaterial-Modified Conducting Paper: Fabrication, Properties, and Emerging Biomedical Applications. Glob. Chall. 2019, 3, 1900041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dkhar, D.S.; Kumari, R.; Mahapatra, S.; Chandra, P. Engineering Design, Implementation, and Sensing Mechanisms of Wearable Bioelectronic Sensors in Clinical Settings. Electroanalysis 2023, 35, e202200154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamie, A.; Angizi, S.; Kumar, S.; Pandey, C.M.; Simchi, A.; Willander, M.; Malhotra, B.D. Review—Textile Based Chemical and Physical Sensors for Healthcare Monitoring. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 037546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.G.; Viltres, H.; Ortega, G.A.; Phung, V.; Grewal, R.; Mozaffari, H.; Ahmed, S.R.; Rajabzadeh, A.R.; Srinivasan, S. Electrochemical Sensing of Analytes in Saliva: Challenges, Progress, and Perspectives. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 160, 116965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevenot, D.R.; Toth, K.; Durst, R.A.; Wilson, G.S. Electrochemical Biosensors: Recommended Definitions and Classification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 121–131. [Google Scholar]
- Dalal, S. Biosensors as Recognition Tool for Bioelements. In Multifaceted Bio-Sensing Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 151–168. [Google Scholar]
- Balkourani, G.; Brouzgou, A.; Archonti, M.; Papandrianos, N.; Song, S.; Tsiakaras, P. Emerging Materials for the Electrochemical Detection of COVID-19. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 893, 115289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez-Redín, G.; Cagnani, G.R.; Gomes, N.O.; Raymundo-Pereira, P.A.; Machado, S.A.S.; Gutierrez, M.A.; Krieger, J.E.; Oliveira, O.N., Jr. Wearable Potentiometric Biosensor for Analysis of Urea in Sweat. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 223, 114994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.; Barbosa, A.I.; Rebelo, R.; Kwon, I.K.; Reis, R.L.; Correlo, V.M. Skin-Integrated Wearable Systems and Implantable Biosensors: A Comprehensive Review. Biosensors 2020, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, I.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, B.R.; Lee, K.; Lee, H. Hydrogel Based Biosensors for In Vitro Diagnostics of Biochemicals, Proteins, and Genes. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Jeerapan, I.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Barfidokht, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Campbell, A.S.; Hubble, L.J.; Wang, J. Wearable Bioelectronics: Enzyme-Based Body-Worn Electronic Devices. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2820–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, B.; Yao, J.; Fan, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, K.; Huang, W. Rapid Advances of Versatile MXenes for Electrochemical Enzyme-Based Biosensors, Immunosensors, and Nucleic Acid-Based Biosensors. ChemElectroChem 2022, 9, e202200103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goran, J.M.; Lyon, J.L.; Stevenson, K.J. Amperometric Detection of L-Lactate Using Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanotubes Modified with Lactate Oxidase. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8123–8129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathee, K.; Dhull, V.; Dhull, R.; Singh, S. Biosensors Based on Electrochemical Lactate Detection: A Comprehensive Review. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2016, 5, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, D.; Guo, X.; Fu, W.; Ding, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Ramakrishna, S.; Qin, X. The Marriage of Biochemistry and Nanotechnology for Non-Invasive Real-Time Health Monitoring. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2022, 149, 100681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska, K.; Sigurdardóttir, S.B.; Zdarta, J.; Pinelo, M. Co-Immobilization and Compartmentalization of Cholesterol Oxidase, Glucose Oxidase and Horseradish Peroxidase for Improved Thermal and H2O2 Stability. J. Memb. Sci. 2022, 662, 121007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Shin, H.; Seo, H.; Park, W.; Joo, B.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, J.; Park, J. Wireless Non-Invasive Monitoring of Cholesterol Using a Smart Contact Lens. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2203597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Abdelsamie Abdelrahim Abdelsamie, A.; Yuan, X.; Fan, X.; Zhang, R.; Chang, H. Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species in Living Cancer Cells Using Monolithic Metallic Foam Electrodes. ChemElectroChem 2020, 7, 2485–2492. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zeng, S.; Ji, W.; Yao, H.; Lin, L.; Cui, H.; Santos, H.A.; Pan, G. Emerging Theranostic Nanomaterials in Diabetes and Its Complications. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2102466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaretta, J.E.; Duan, H.; Farajikhah, S.; Oveissi, F.; Dehghani, F.; Naficy, S. A Highly Flexible, Physically Stable, and Selective Hydrogel-Based Hydrogen Peroxide Sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 371, 132483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, D.P.; Gaffney, E.M.; Minteer, S.D. Electrometabolic Pathways: Recent Developments in Bioelectrocatalytic Cascades. Electrocatalysis 2020, 376, 149–165. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Jeerapan, I.; Imani, S.; Cho, T.N.; Bandodkar, J.; Cinti, S.; Mercier, P.P.; Wang, J. Non-Invasive Alcohol Monitoring Using a Wearable Tattoo-Based Iontophoretic-Biosensing System Non-Invasive Alcohol Monitoring Using a Wearable Tattoo-Based. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Yuan, J. An Electrochemical Paper-Based Hydrogel Immunosensor to Monitor Serum Cytokine for Predicting the Severity of COVID-19 Patients. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 220, 114898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppaiah, G.; Velayutham, J.; Sethy, N.K.; Manickam, P. DNA Aptamer and Gold-Nanofiller Integrated Hybrid Hydrogel Network for Electrochemical Detection of Salivary Cortisol. Mater. Lett. 2023, 342, 134310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Völlmecke, K.; Afroz, R.; Bierbach, S.; Brenker, L.J.; Frücht, S.; Glass, A.; Giebelhaus, R.; Hoppe, A.; Kanemaru, K.; Lazarek, M.; et al. Hydrogel-Based Biosensors. Gels 2022, 8, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orgel, L. A Simpler Nucleic Acid. Science 2000, 290, 1306–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, U. Nucleic Acid Based Biosensors for Clinical Applications. Biosens. J. 2013, 2, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sen, P.; Adhikari, B.R.; Li, Y.; Soleymani, L. Development of Nucleic-Acid-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Clinical Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202212496. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Fang, X.; Kong, J. Engineered Microneedles for Interstitial Fluid Cell-Free DNA Capture and Sensing Using Iontophoretic Dual-Extraction Wearable Patch. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Huang, R.; Xiao, P.; Liu, Y.; Jin, L.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Deng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z. Current Signal Amplification Strategies in Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Biosensor: A Review. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 1593–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. Oligonucleotide Aptamers: Recent Advances in Their Screening, Molecular Conformation and Therapeutic Applications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenblum, G.T.; Pollitzer, I.G.; Radrizzani, M. Challenges in Electrochemical Aptasensors and Current Sensing Architectures Using Flat Gold Surfaces. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Alkhamis, O.; Canoura, J.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Y. Advances and Challenges in Small-Molecule DNA Aptamer Isolation, Characterization, and Sensor Development. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 16800–16823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
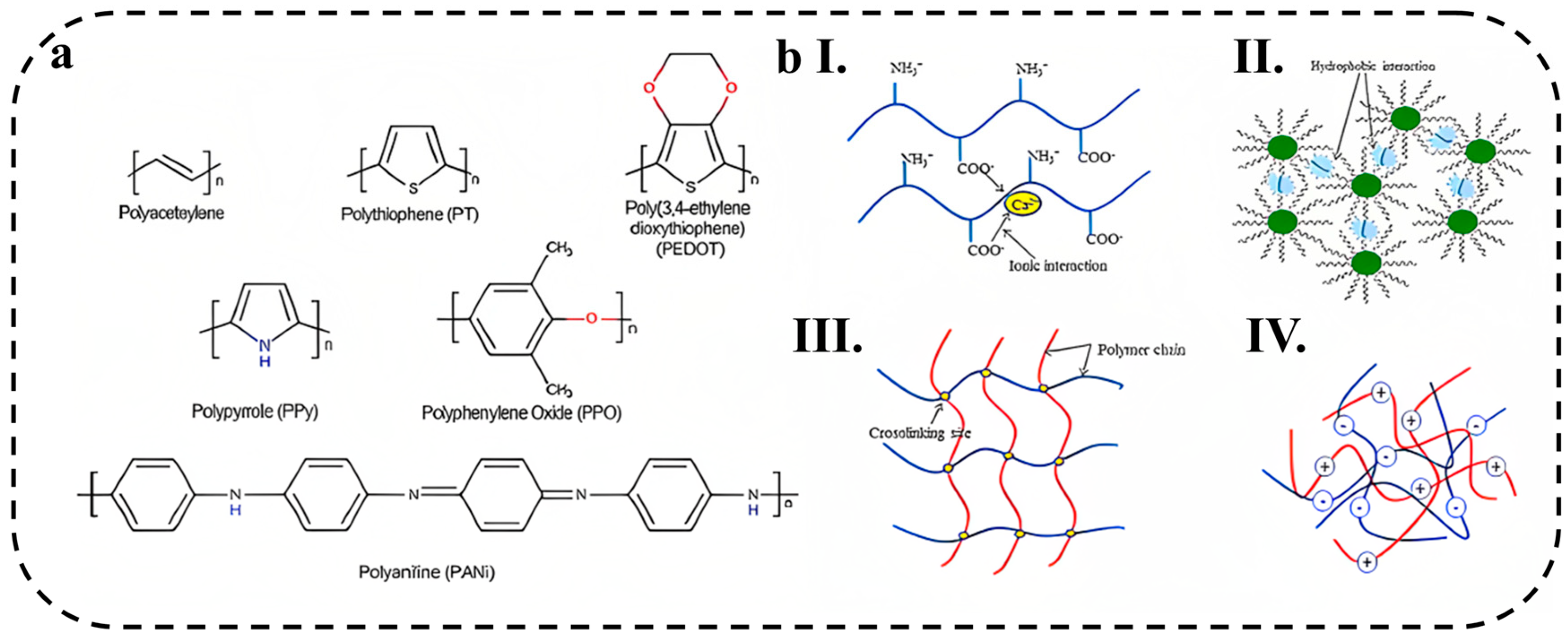
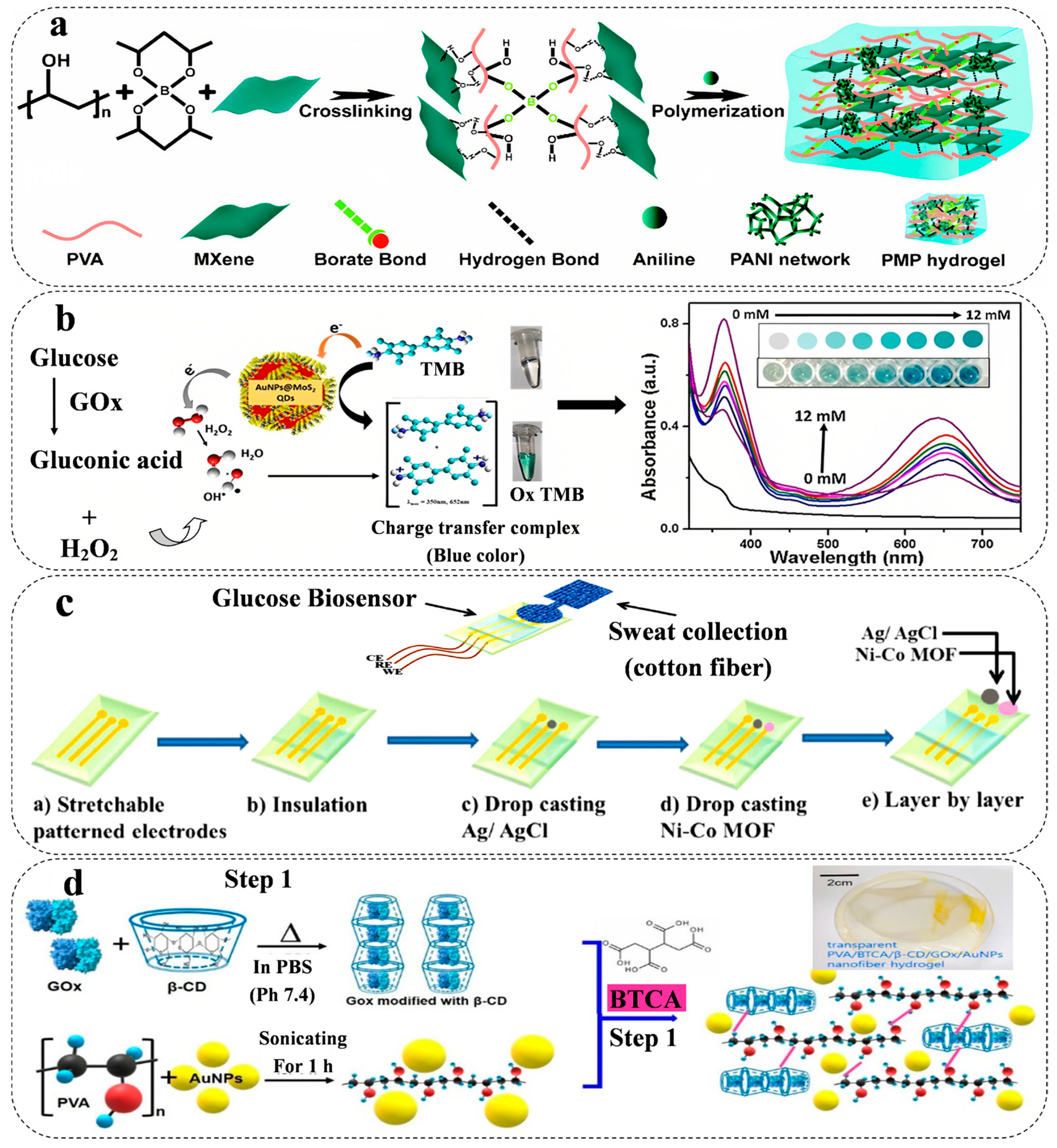

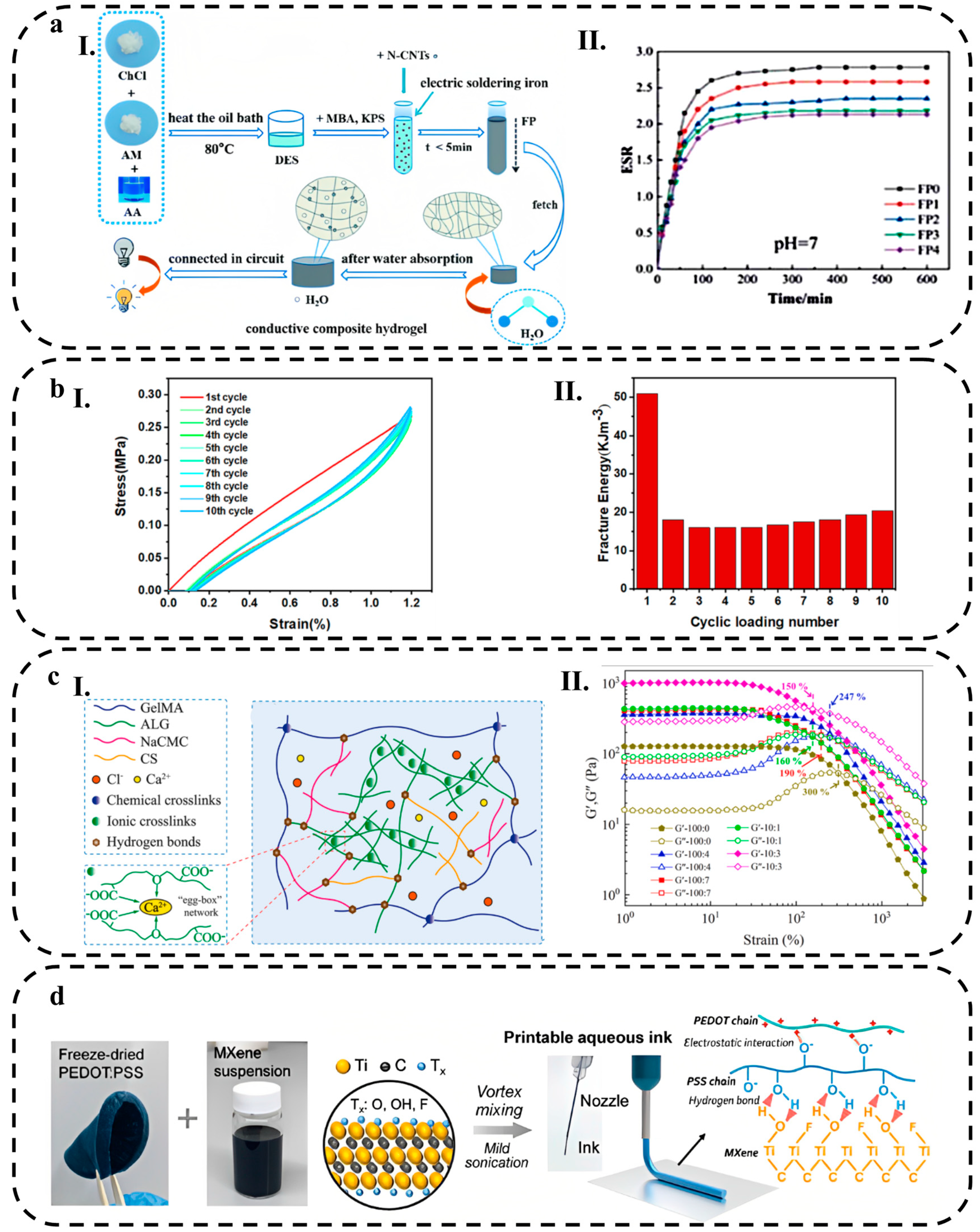
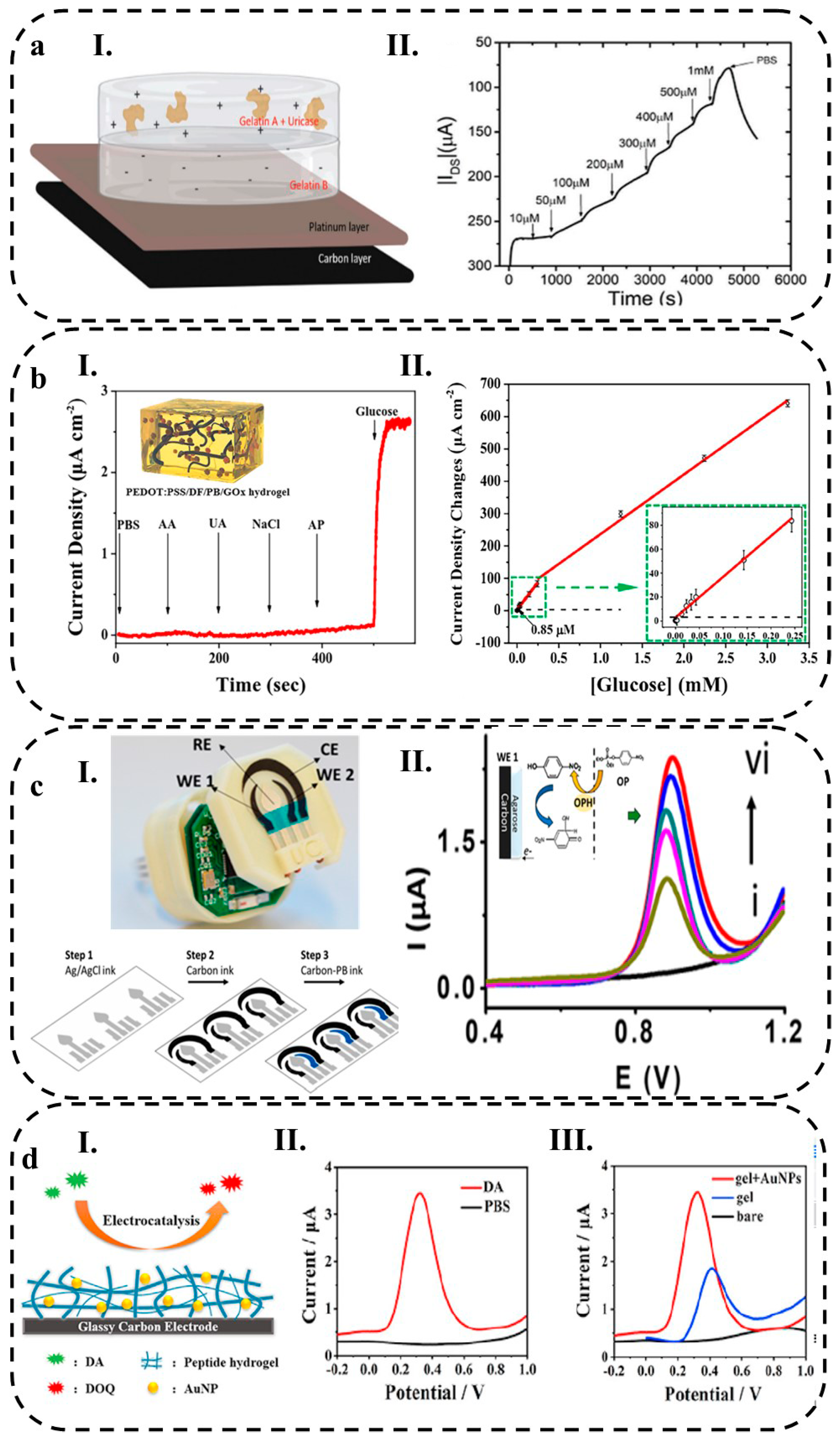
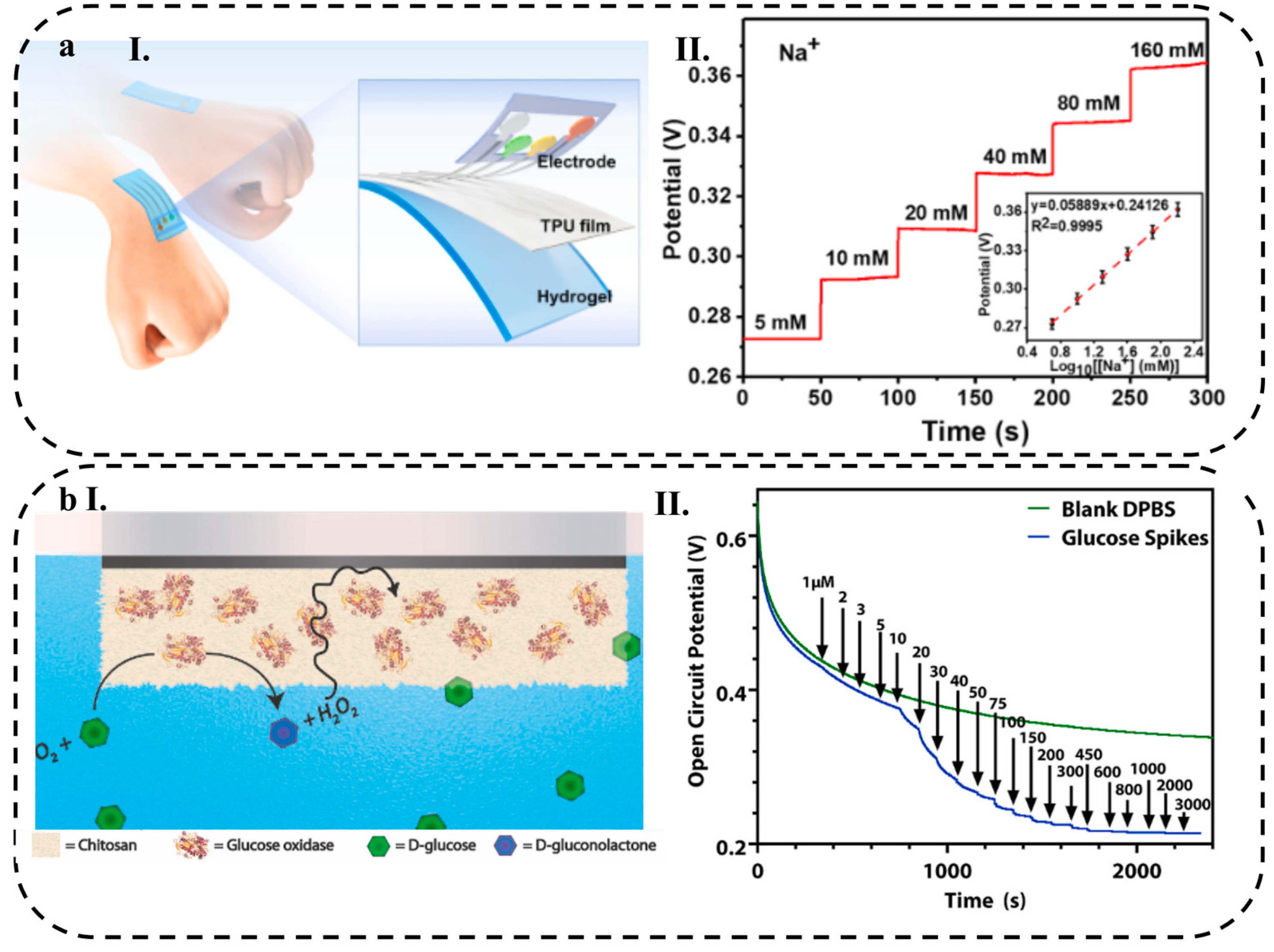
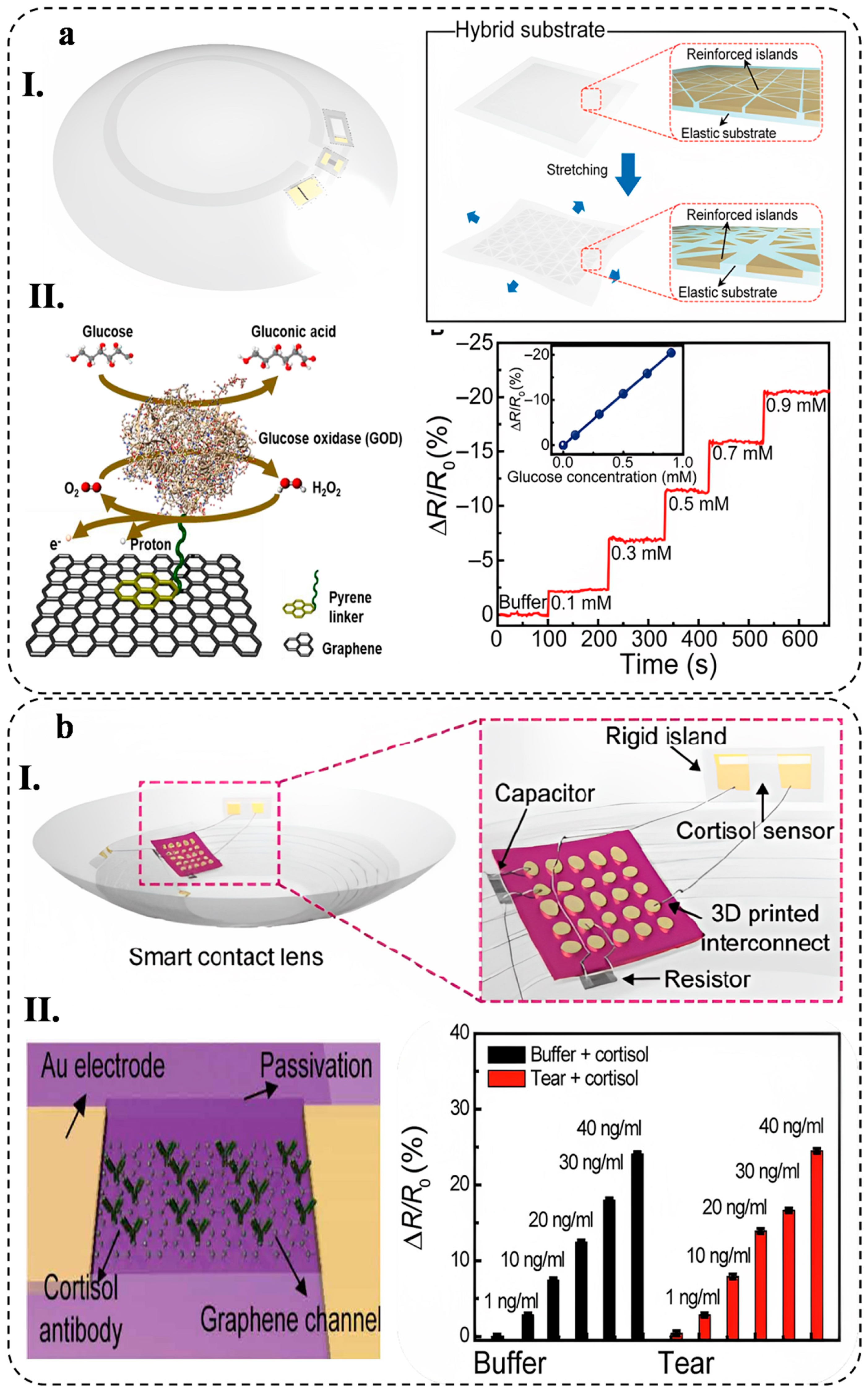

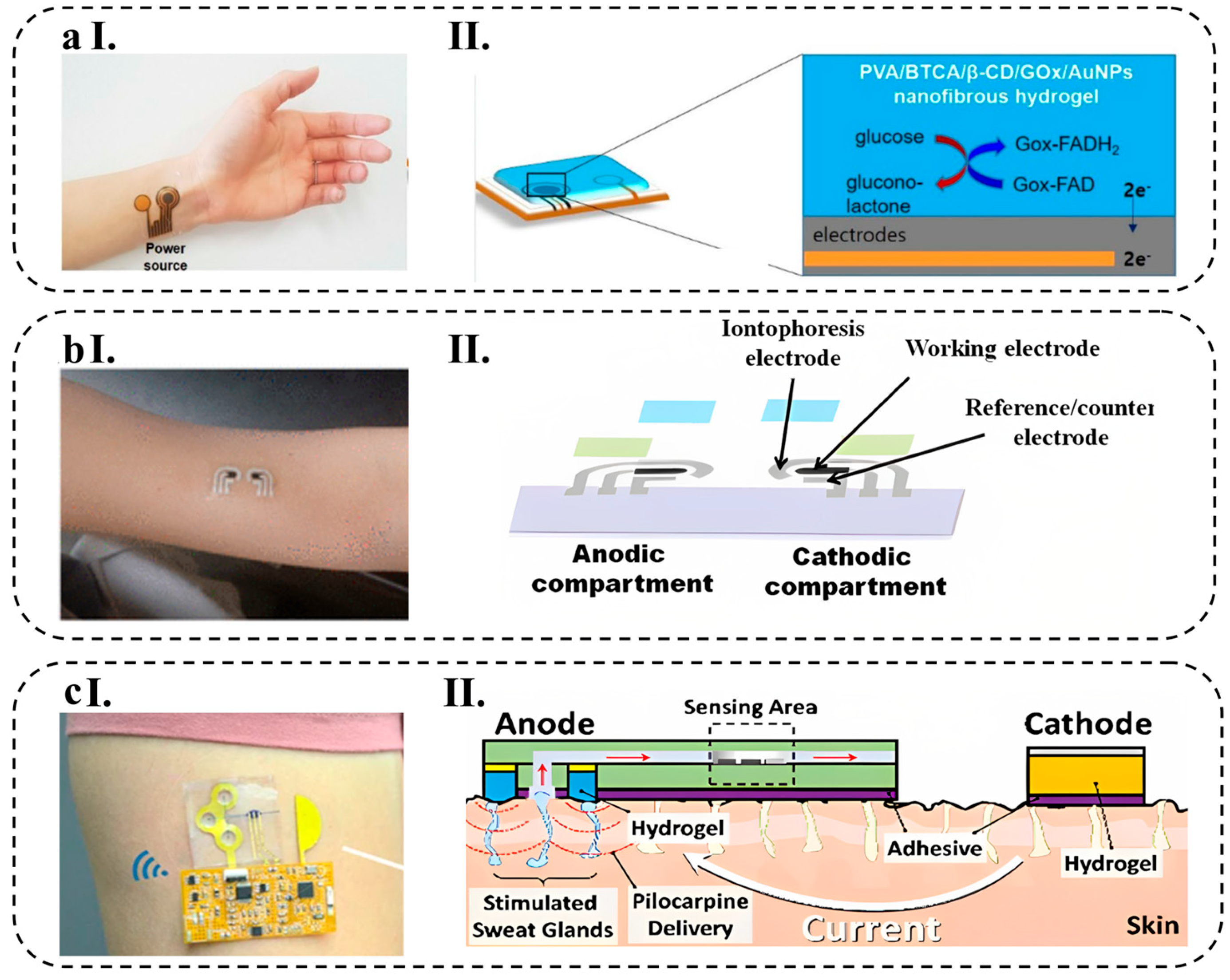
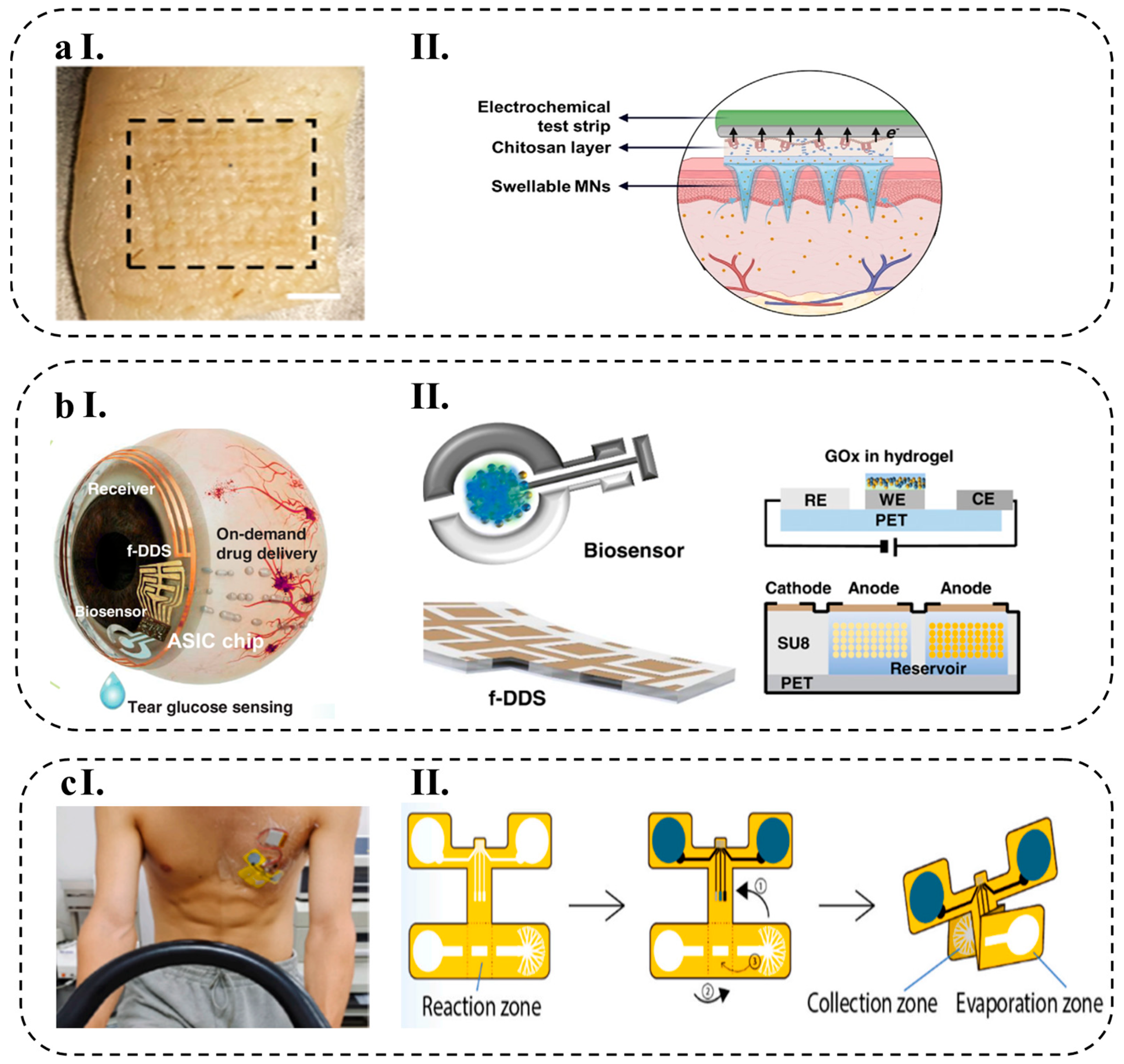
| Materials | Biosensor Properties | Ref. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensing Element @ Hydrogels | Bioreceptor | Substrate | Target | Real Sample | Electrolyte | Measurement Technique | LOD (Unit) | Linear Range (Unit) | Sensitivity (Unit) | |
| CNs 1@ PAM | AOx | Glass | Ethanol | Breath | PBS | Amperometry | 1 (μM) | 10 to 100 (μM) | 12 (mV/decade log(C)) | [251] |
| PB/Carbon @ HEMA | GOx | PTFE coated glass | Glucose | Blood | PBS | 7.9 (μM) | 0 to 210 (μM) | 9.4 (μA/cm2·mM) | [252] | |
| Fe3+/PB @ PEDOT | GOx | SPCE | Glucose | Sweat | PBS | 4 (μM) | 6.25 to 800 (μM) | _ | [253] | |
| PEDOT:PSS | UOx 2 | PET foil | Uric acid | wound | PBS | 4.5 (μM) | 50 to 1000 (μM) | _ | [248] | |
| DF 3/PB@ PEDOT:PSS | GOx | GCE | Glucose | Rabbit serum | PBS | 0.85 (μM) | 1 to 243 (μM) | 340.1 (μA/cm2·mM) | [51] | |
| PAM@CS | _ | _ | O2 | Breath | _ | 5.7 (ppm) | 0–100 (%) | 0.2 (%/ppm) | [254] | |
| Pt/Gr@CS | GOx | PU sheet | Glucose | Sweat | PBS | 10 (μM) | 0 to 900 (μM) | 105 (μA/cm2·mM) | [255] | |
| PtNP/AuNP/rGO/CS | GOx | Polyimide | Glucose | Sweat | PBS | 5 (μM) | 0 to 2400 (μM) | 48 (μA/cm2·mM) | [256] | |
| PB/(GO@CS) | Lox 4 | SPCE | Lactate | Sweat | Artificial sweat | 28 (nM) | 0.068 to 50,000 (μM) | 0.39 (μA/cm2·mM) | [257] | |
| PB/(GO-CS) | GOx | Glucose | 6.7 (nM) | 0.032 to 3800 (μM) | 8.20 (μA/cm2·mM) | |||||
| PVA/β-CD 5 | GOx | SPCE | Glucose | _ | PBS | Cyclic voltammetry | 51 (nM) | 1 to 5 (mM) | 7.58 (μA/mM) | [258] |
| PVA/BTCA 6/β-CD/AuNPs | GOx | SPCE | Glucose | _ | PBS | 10 (μM) | 0.1 to 0.5 (mM) | 47.2 (μA/mM) | [71] | |
| PB/Au@ Graphene | GOx | _ | Glucose | Sweat | _ | 10 (μM) | 10 to 700 (μM) | _ | [259] | |
| AuNPs@Peptide | _ | GCE | S. aureus, E. coli and P. aeruginosa | _ | PBS | DPV | 21 (nM) | 0.1 to 10 (μM) | _ | [250] |
| MXene@BSA 7 | Peptide | GCE | Immunoglobulin G | Serum | PBS | 23 (pg/mL) | 0.0001 to 10 (µg/mL) | _ | [260] | |
| Agarose/Carbon/PB ink | _ | PET | MPOx | _ | PBS | SWV | 200 (μM) | _ | [249] | |
| Graphene/Pyrene | GOx | Si wafer | Glucose | Tears | PBS | Conductometry | 12.57 (μM) | _ | 22.72 (%/mM) | [261] |
| Graphene | Cortisol Mab | SiO2 wafer | Cortisol | Tears | PBS | 10 (pg/mL) | 1 to 40 (ng/mL) | 1.84 (ng/mL. %) | [262] | |
| Au 3D nanostructure | Cortisol Ab | PDMS | Cortisol | Sweat | PBS | EIS | 1 (pg/mL) | _ | 0.25 (Ohm/ng mL) | [263] |
| Ti3C2Tx Mxene/LBG 8 | Cortisol Ab | Polyamide | Cortisol | Sweat | _ | 88 (pM) | 0.001 to 100 (mM) | _ | [264] | |
| PAM/Ca-Alg 9 | _ | Thermoplastic polyurethane | pH | Sweat | _ | Potentiometry | 3.05 | 58.14 mV/pH | [265] | |
| Na+ | 7.94 (μM) | 5 to 160 (mM) | 58.89 mV/decade | |||||||
| K+ | 5.37 (μM) | 1 to 32 (mM) | 59.11 mV/decade | |||||||
| Chitosan/Nafion | GOx | Pt | Glucose | _ | DPBS | _ | 1–10, 10–100, 100–3000 (μM) | 0.5, 0.012, 0.19 (mV/μM) | [266] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saeidi, M.; Chenani, H.; Orouji, M.; Adel Rastkhiz, M.; Bolghanabadi, N.; Vakili, S.; Mohamadnia, Z.; Hatamie, A.; Simchi, A. Electrochemical Wearable Biosensors and Bioelectronic Devices Based on Hydrogels: Mechanical Properties and Electrochemical Behavior. Biosensors 2023, 13, 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13080823
Saeidi M, Chenani H, Orouji M, Adel Rastkhiz M, Bolghanabadi N, Vakili S, Mohamadnia Z, Hatamie A, Simchi A. Electrochemical Wearable Biosensors and Bioelectronic Devices Based on Hydrogels: Mechanical Properties and Electrochemical Behavior. Biosensors. 2023; 13(8):823. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13080823
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaeidi, Mohsen, Hossein Chenani, Mina Orouji, MahsaSadat Adel Rastkhiz, Nafiseh Bolghanabadi, Shaghayegh Vakili, Zahra Mohamadnia, Amir Hatamie, and Abdolreza (Arash) Simchi. 2023. "Electrochemical Wearable Biosensors and Bioelectronic Devices Based on Hydrogels: Mechanical Properties and Electrochemical Behavior" Biosensors 13, no. 8: 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13080823
APA StyleSaeidi, M., Chenani, H., Orouji, M., Adel Rastkhiz, M., Bolghanabadi, N., Vakili, S., Mohamadnia, Z., Hatamie, A., & Simchi, A. (2023). Electrochemical Wearable Biosensors and Bioelectronic Devices Based on Hydrogels: Mechanical Properties and Electrochemical Behavior. Biosensors, 13(8), 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13080823






