Abstract
Cd2+, a major environmental pollutant, is heavily toxic to human health. Many traditional techniques are high-cost and complicated; thus, developing a simple, sensitive, convenient, and cheap monitoring approach is necessary. The aptamer can be obtained from a novel method called SELEX, which is widely used as a DNA biosensor for its easy acquisition and high affinity of the target, especially for heavy metal ions detection, such as Cd2+. In recent years, highly stable Cd2+ aptamer oligonucleotides (CAOs) were observed, and electrochemical, fluorescent, and colorimetric biosensors based on aptamers have been designed to monitor Cd2+. In addition, the monitoring sensitivity of aptamer-based biosensors is improved with signal amplification mechanisms such as hybridization chain reactions and enzyme-free methods. This paper reviews approaches to building biosensors for inspecting Cd2+ by electrochemical, fluorescent, and colorimetric methods. Finally, many practical applications of sensors and their implications for humans and the environment are discussed.
1. Introduction
Cadmium ions (Cd2+) are deadly poisonous and quickly accumulate in organisms via the food chain. It seriously affects the production and development of plants [1], especially causing great harm to human health. Cardiovascular disease [2], Nephropathy, and Alzheimer’s disease [3] are easily caused by the enrichment of Cd2+ in human bodies. Since Cd2+ pollution in life mainly comes from the discharge of wastewater from metal smelters, electroplating plants, and mines [4], it is still a problem to be solved. Considering the potent toxicity of Cd2+, the content of Cd2+ in food and drinking water is strictly regulated. To comply with the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives limits, the Cd2+ level should not exceed 25 mg/kg body weight per month. Additionally, the Codex Alimentarius Commission regulates the maximum content of Cd2+ in polished rice cereals at 0.4 mg/kg [5]. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), 44.5 nmol/L (5.0 μg/L) is the maximum limit for Cd2+ in drinking water [6].
For monitoring and controlling the Cd2+ contamination, analytical methods are necessarily found. A considerable number of traditional methods have been carried out for the measurement of Cd2+, for example, inductively coupled plasma–atomic absorption spectrometry (ICP-AES) [7,8], atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS) [9], and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) [10]. However, these methods can face challenges when analyzing sophisticated samples due to multiple interfering species. The accuracy of Cd2+ detection is easily susceptible to the influence of other metal ion spectra. In the case of monitoring Cd2+ in rice, the presence of other metal cations at much higher concentrations can interfere with the accurate detection of Cd2+ [11]. Additionally, environmental factors, particularly pH, can further complicate the detection process and limit the sensitivity of the methods [12]. Although the above traditional techniques are feasible, their instruments are expensive and inconvenient. They cannot achieve on-site point-of-care detection and require advanced operational skills and long-term pretreatment. It is these shortcomings that limit the convenient on-site real-time detection of Cd2+.
As the unique sequences of DNA can recognize a variety of molecules and ions, DNA is widely used as a biosensor. DNA aptamers are frequently employed to create biosensors to detect a variety of targets, because of their distinctive secondary structures, strong affinity, and selectivity to targets [13]. It provides a means to achieve single-component detection in complex samples. By designing aptamers that specifically recognize the target analyte, biosensors can selectively capture and detect the desired molecule or ion, even in the presence of interfering species. Thus, the construction of electrochemical, fluorescent, and colorimetric biosensors is a quick analytical tool for Cd2+ inspection at the molecular level. It has high selectivity and excellent efficiency. Despite the biosensors can accurately identify the target Cd2+, its sensitivity is looking forward to improving. Therefore, it is always associated with hybridization chain reaction (HCR) [14], rolling circle amplification (RCA) [15], and entropy-driven catalysis [16] to enhance the detected signal to obtain clear and accurate detection results.
This review first presents the DNA aptamers for Cd2+ that are screened by SELEX methods, which obtain high-quality aptamers for relevant targets. Secondly, it summarizes that the DNA biosensors based on aptamers perform a significant role in environmental monitoring, health care, and food inspection. Thirdly, it overviews the application of biosensors for Cd2+ detection using electrochemical, fluorescent, and colorimetric methods.
2. DNA Aptamers for Cd2+
DNA biosensors play an indispensable role in monitoring trace pollutants and studying the interaction between pollutants and DNA, which provides the possible mechanism to explain the toxic action of pollution. Previously, researchers have proposed the use of antibodies [17,18], chelators [19,20,21,22], and DNAzymes [23,24] as recognition factors for Cd2+ detection. However, aptamers play a significant role in biosensor procedures compared with such methods due to their reliability and great affinity [10,25,26,27]. Aptamer is a segment of the oligonucleotide sequence, which is typically obtained by in-vitro screening on an oligonucleotide molecular library. In 1990, the traditional SELEX technique was developed by Szostak and Gold groups [28], consisting of selection, distribution, and amplification. It typically takes a long time to obtain a specific candidate aptamer with low hit rates. An improved SELEX method has been established in recent years to attain highly selective aptamers, which can reduce selection time and improve the hit rate.
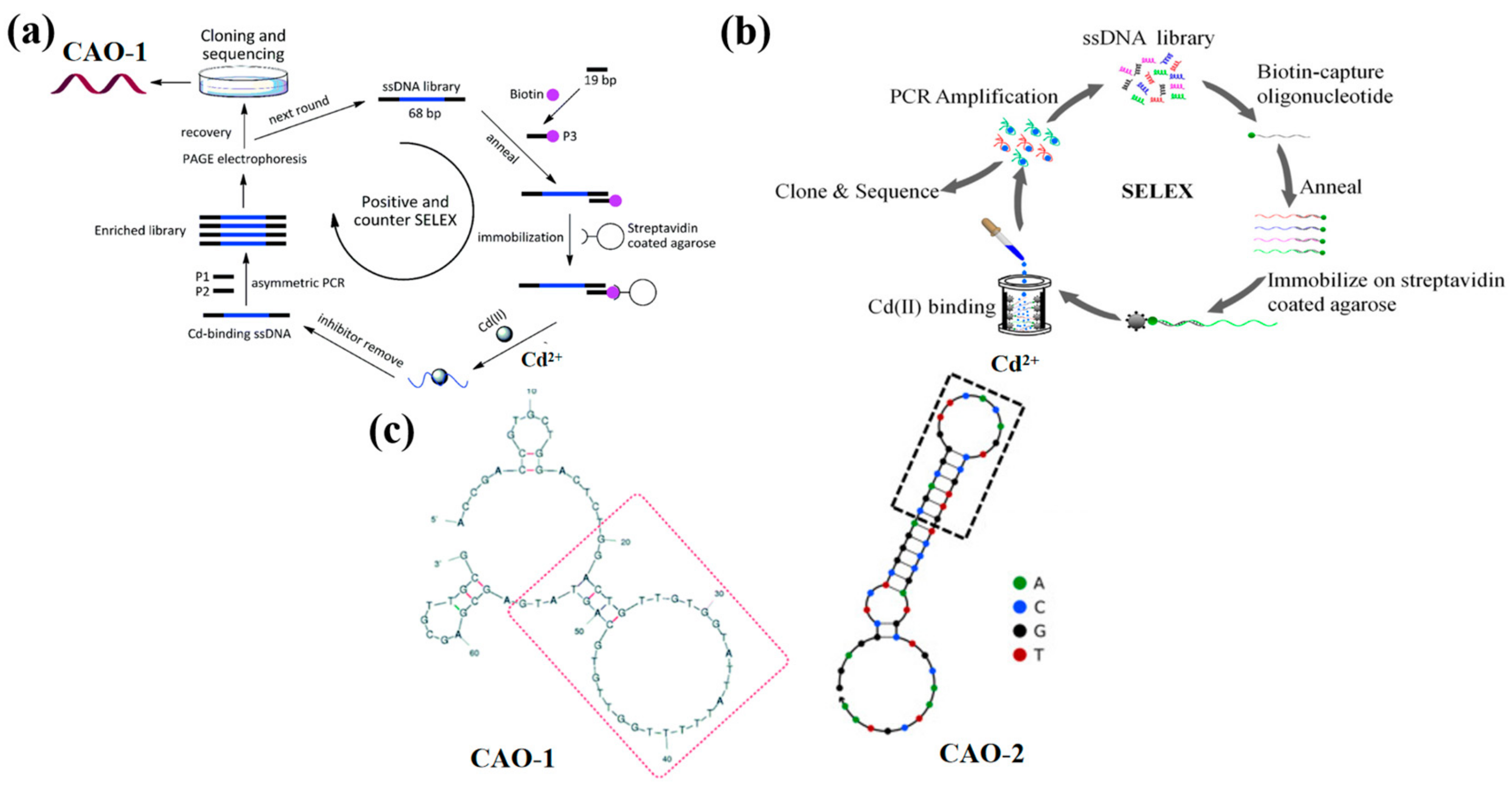
A new SELEX strategy has been preferred to immobilize the ssDNA libraries instead of the target molecule on the matrix to make the Cd2+ aptamer with high affinity (Figure 1a). It received a series of nonrepeat T and G-rich sequences by ten positive tests and one round of adverse selection. Among all sequences, the aptamer CAO-1 (Table 1, Figure 1c) was identified to have the highest binding affinity for Cd2+. Their secondary structure shows that the stem-loop structure is the key to the aptamer binding target, which collapses according to the domain of 30 random chains [29]. The dissociation constant (Kd) was used to estimate the aptamer with the highest affinity for Cd(II), which was determined by the relationship between the fluorescence intensity and the concentration of the aptamer using SigmaPlot software with the one-site saturation equation: Y = BmaxX/(Kd + X), where Y represents the fluorescence intensity of Cd2+ binding, Bmax is the maximum Cd2+ binding capacity, X is the concentration of the aptamer. The Kd of CAO-1 was calculated to be 34.5 nM. This plan could effectively improve the SELEX process, especially for small molecules such as Cd2+, deficient enough sites for immobilization. It will make a potential difference in Cd2+ detection and other applications similar to the recovery of contaminated Cd2+.
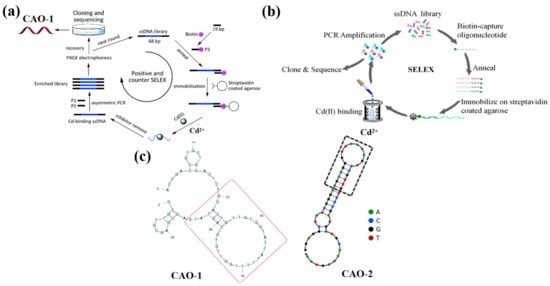
Figure 1.
(a) The schematic strategy for Cd2+ aptamers selection by Wu et al., CAO-1 was obtained [29]; (b) The selection protocol of Cd2+ aptamers designed by Wang et al., CAO-2 was selected [26]; (c) The second structure of CAO-1 and CAO-2.

Table 1.
DNA sequences of the mentioned probe, and the Cd2+ aptamer sequences are underlined.
Compared with the above method, an improved SELEX in-vitro selection technique was developed to address the degradability and high cost caused by the long sequences of DNA aptamers, which were designed by the biotin and streptavidin interplay [30,31]. After experimental studies, a shortened aptamer, CAO-2 (Table 1, Figure 1c), was folded into a specific structure to combine Cd2+ with high selectivity [26]. As a result, the DNA sequences were released from the ssDNA library, which was captured on the streptavidin column by the target-triggered method (Figure 1b). Also, it efficiently select Cd2+ aptamers when the metal ions were free in a liquid solution. The approach revealed that the aptamer could be further curtailed and directly applied as a probe to develop biosensors.
Moreover, an approach selects aptamers as capture probes to identify Cd2+ and describes a modified SELEX founded on fixing ssDNA libraries on streptavidin magnetic beads. After nine rounds of screening, four DNA sequences of Cd2+ aptamers with the maximum enrichment were obtained. The CAO-3 (Table 1) had the highest affinity for Cd2+, with the Kd value being 81.39 μM. The dissociation constant Kd of CAO-3 for Cd2+ was calculated the same as CAO-1. Since Cd2+ is present in the free state, the strategy can isolate the aptamers more efficiently. The improved SELEX process solves the target selection problem with fewer sites and expands the probe range for Cd2+ [32]. To evaluate the specificity of Cd2+ aptamers, including CAO-1, the various metal ions, such as Ag+, Hg2+, Ni2+, Ba2+, Ca2+, Co2+, Mn2+, Pb2+, Zn2+, Cu2+, and Al3+ were tested. The fluorescence response was observed in the presence of Cd2+. The sensor system exhibited enhanced selectivity by differentiating Cd2+ from other interfering metal ions. Additionally, the fluorescence intensity increased upon the binding of Cd2+ to the aptamer, further confirming its selectivity and sensitivity as a sensor for Cd2+.
These three SELEX techniques have been successfully used in screening the Cd2+ aptamers. Based on DNA aptamers, the sensitive and efficient detection approaches of Cd2+ are designed for electrochemical, fluorescent, and colorimetric biosensors.
3. Electrochemical Biosensors
Standard electrochemical detection techniques for Cd2+ detection include inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) [33], inductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopy [34], and electrochemical anodic stripping voltammetry (ASV) [35]. However, their bulky instruments, complex preprocessing, and precise operation often restrict the considerable detection limits and selectivity. Therefore, for the past few years, different nanomaterials have gotten significant attention and have been extensively used in electrochemical biosensors due to their successful synthesis. Owing to their distinctive chemical and physical characteristics, the electrochemical biosensors can detect Cd2+ as low as fM. Sensing platforms utilize immobilized Cd2+ aptamers on nanomaterial surfaces via catalyzing chemical reactions or intermolecular forces in biosensors to increase electrical signals as sensitizers. This technique enhances biosensor sensitivity [36].
3.1. Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs)
In 2017, Liu et al. developed an ultra-sensitive biosensor for detecting Cd2+ by modifying glass carbon electrodes (GCE) with AuNPs (gold nanoparticles) and CS (chitosan). The Cd2+ aptamer, CAO-4 (Table 1), was neutralized using PDDA (poly- (diallyl dimethyl ammonium chloride)) via electrostatic interactions. Upon the presence of Cd2+, the conformation of CAO-4 was altered, resulting in more absorption of [Ru(NH3)6]3+, the electrochemical signal indicator, by the Cd/CAO-4 complex than by PDDA. Differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) revealed an increased peak with increasing Cd2+ concentrations. The GCE biosensor demonstrated that it is a promising candidate for monitoring Cd2+ levels. It has been successfully applied in tap water samples (Table 2) for Cd2+ detection [37].
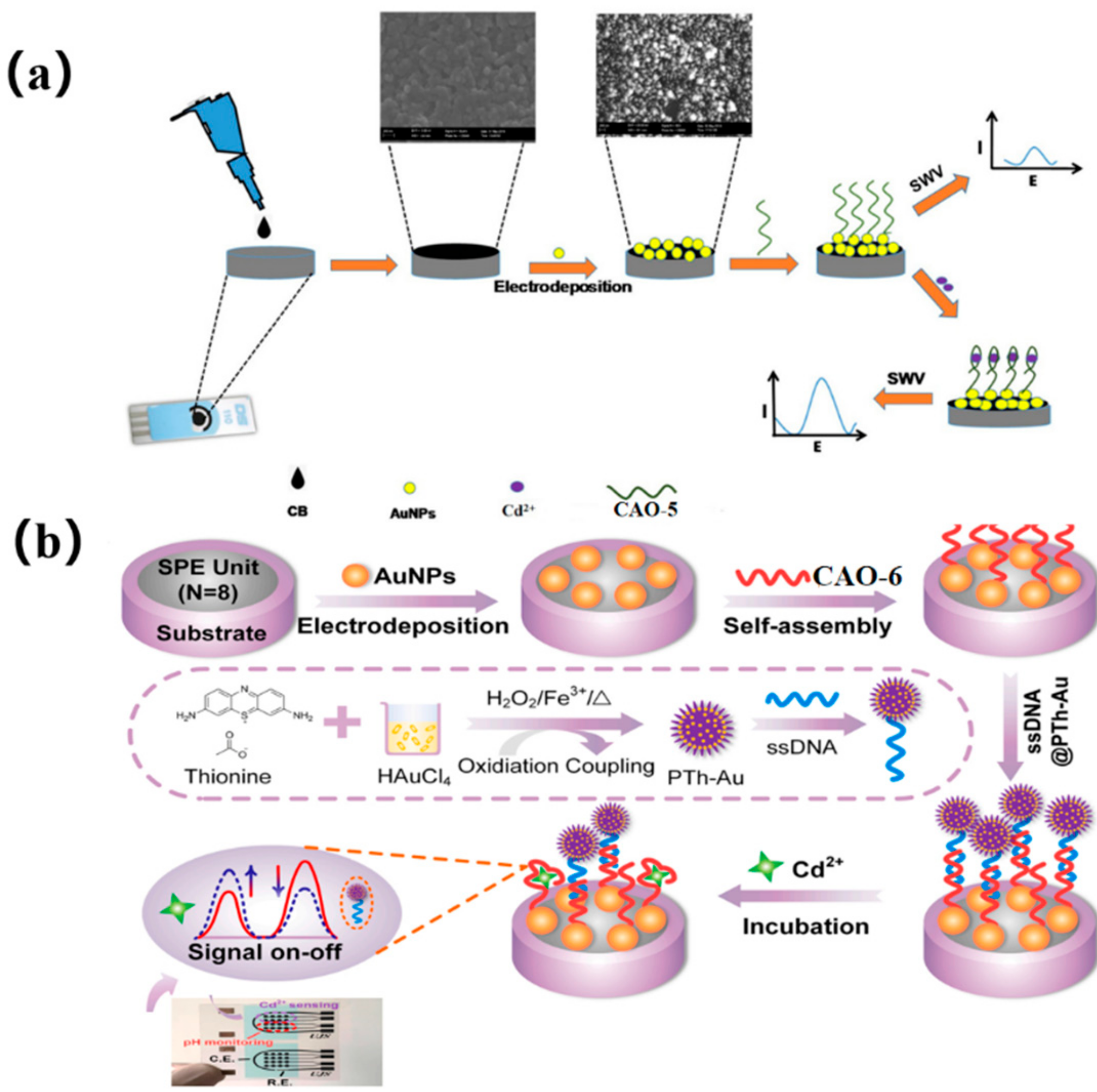
An alternative approach to the previous method was explored using screen-printed carbon electrodes (SPCEs) for manufacturing electrochemical biosensors for Cd2+. The SPCEs were shaped using AuNPs and carbon black (CB) (Figure 2a), and a nano-platform was constructed by electrodepositing AuNPs and drop-casting CB via potential cycling from −400 mV to 1100 mV under the scanning rate of 50 mVs−1. In the presence of Cd2+, CAO-5 (Table 1) immobilized the SPCE-CB-AuNPs, and the conformational change influenced the electrochemical current response. The biosensor exhibited better reproducibility, excellent selectivity (Table 2), and good stability towards Cd2+, which had been effectively used to analyze actual water samples [38].
Dual-signal sensing using ratio strategies typically employs either signal-on/off mode or signal-switched mode, with the distinct responses of target analytes depending on their electrochemical properties [39]. The reference signal is kept nearly constant in the signal-switching mode. Thus, Chen et al. also utilized a multipurpose screen-printed electrode (SPE) in synergy with an aptamer couple, creatively using a signal-switching ratio strategy. Onto the SPE, the electrodeposited gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) provided combining points for CAO-6 (Table 1) through Au-S binding, shaping Apt/AuNPs/SPE. In the sensing system, the single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) was designed as a semi-complementary strand of CAO-6, which was bound by polythionate-Au (PTh-Au). This resulted in the formation of ssDNA@PTh-Au, which can self-assemble with Apt/AuNPs/SPE via hybridization. However, ssDNA@PTh-Au was quickly instead of Cd2+. Hence, the reference signal (PTh-Au) and the target signal (Cd2+) nicely form a radiometric sensing system (Figure 2b) [40]. Compared to the previous two methods, which only showed one signal, the signal-switching mode utilizes both signals to alternate between the target and reference signals. As a result, analytical data, ultimate sensitivity, and accurate reliability can be obtained simultaneously. The biosensor has been successfully used to determine Cd2+ in complex biological samples such as clams and mussels, with the low detection limit being 0.006 μgL−1 [41].
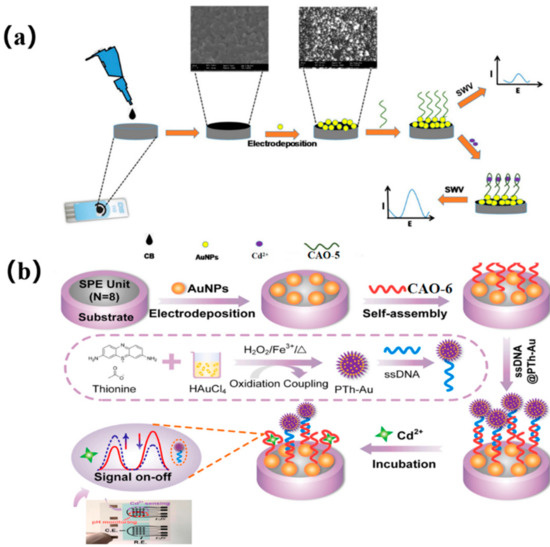
Figure 2.
(a) diagram of the technical procedure and detection mechanism of the Cd2+ biosensor [38]. (b) The CAO-6 probes are labeled with 5’−FAM and 3’−Dactyl, designed by Chen et al. [40].
Figure 2.
(a) diagram of the technical procedure and detection mechanism of the Cd2+ biosensor [38]. (b) The CAO-6 probes are labeled with 5’−FAM and 3’−Dactyl, designed by Chen et al. [40].
3.2. ZnO Nanocomposites
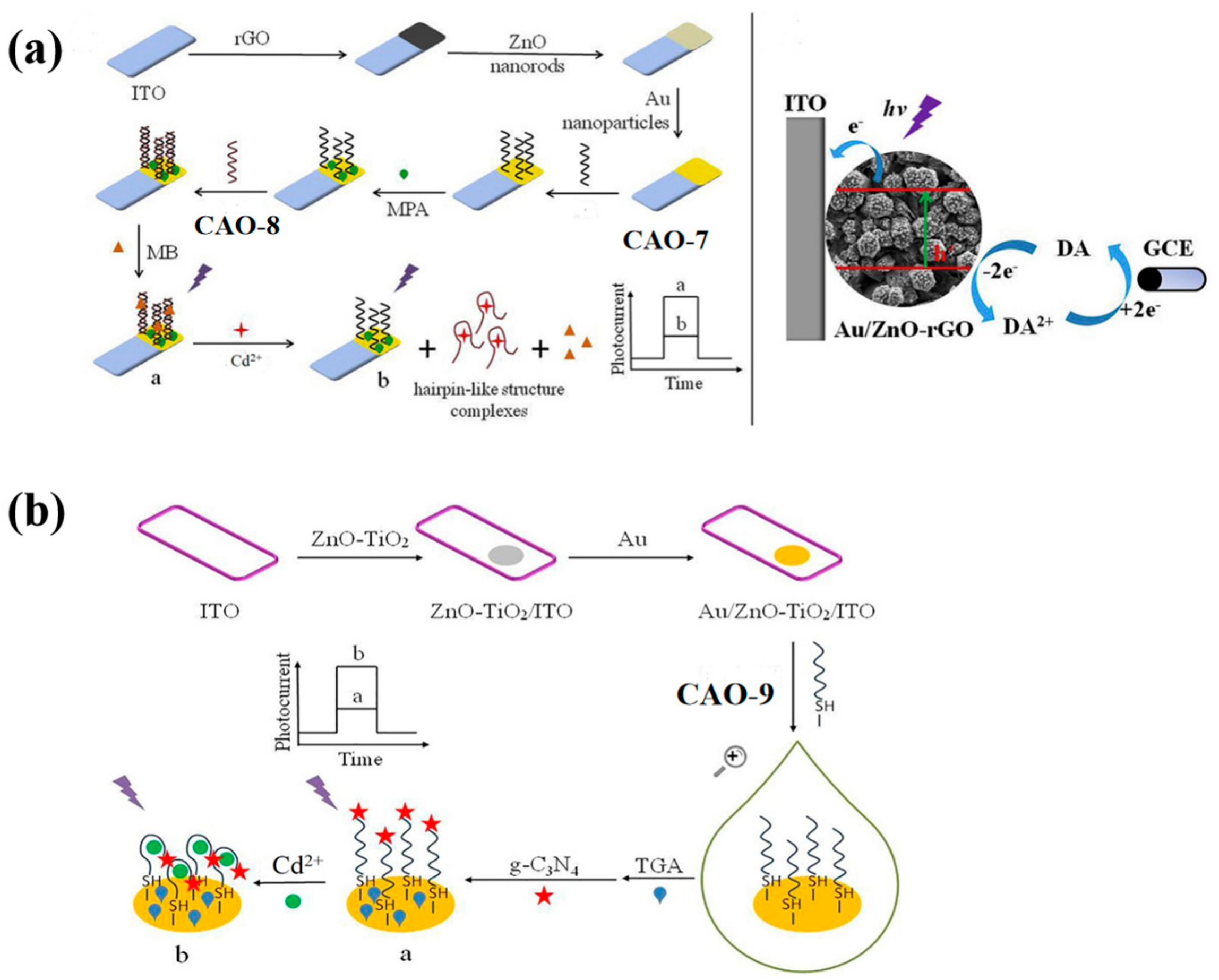
ZnO-rGO nanocomposite was used as the photoactive material to prepare a PEC biosensor. It can specifically recognize the target Cd2+ and undergo conformational changes upon identification (Table 2), as illustrated in Figure 3a. Subsequently, AuNPs were incorporated into the ZnO-rGO nanocomposite due to their excellent conductivity and localized surface plasmon resonance. It can enhance the photocurrent signal. CAO-8 (Table 1) will fold into a firm hairpin-like structure because the O and N elements in the G and T bases provide specific sites for Cd2+ recognition [29]. To immobilize the SH-shaped aptamer CAO-7, AuNPs acted as anchors. The complementary double-stranded DNA CAO-7 (Table 1) was then modified onto the electrode exterior, pairing with CAO-8. The assembly of methylene blue [42] as a sensitizer in the dsDNA structure enhanced the photocurrent response. To detect the photocurrent, a dual-working electrode system was applied, with the modified electrode and glassy carbon electrode (GCE) as the working electrodes. A cyclic reaction occurred by adding dopamine (DA) to the electrolyte as an electron donor. On the first electrode, DA could be oxidized. On the GCE, it could be reduced. This process enhanced the photocurrent response and improved photocurrent stability, enabling efficient and precise detection of Cd2+ [43]. The biosensor had already been utilized for monitoring the water samples and yielding credible results successfully.
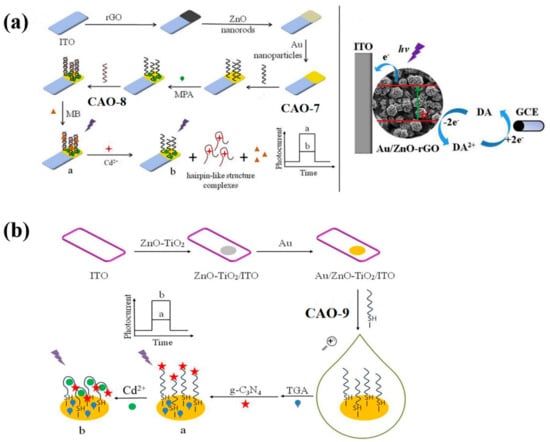
Figure 3.
(a) Diagram showing PEC’s Cd2+ detection strategy and its construction; An electron donor system using four electrodes and DA as the electron donor [43]. (b) Detailed schematic of a PEC-adapted sensor for detecting Cd2+ [44].
In order to simplify the operation, photoelectrochemical (PEC) biosensors have been developed by constructing various sensing interfaces based on the unique identity between the aptamer and target Cd2+ [25]. The photosensitive substrates were prepared by modifying electrodes with Au nano-chains (Au NCs) and ZnO-TiO2 nanocomposites. The free end of CAO-9 (Table 1) was covalently bonded to g-C3N4 (graphite-like carbon nitride) to amplify the detection signal. The specific photoelectric property of g-C3N4 was exhibited with visible light and ultraviolet irradiation (Figure 3b) [44]. Compared to the previous method, this approach produced more sensitive and linear photocurrent signals proportional to the Cd2+ concentration for precise quantitative analysis of the target. The signal amplification strategy employed in this method is more straightforward, yet it still achieves high sensitivity and selectivity (Table 2).
3.3. Other Materials
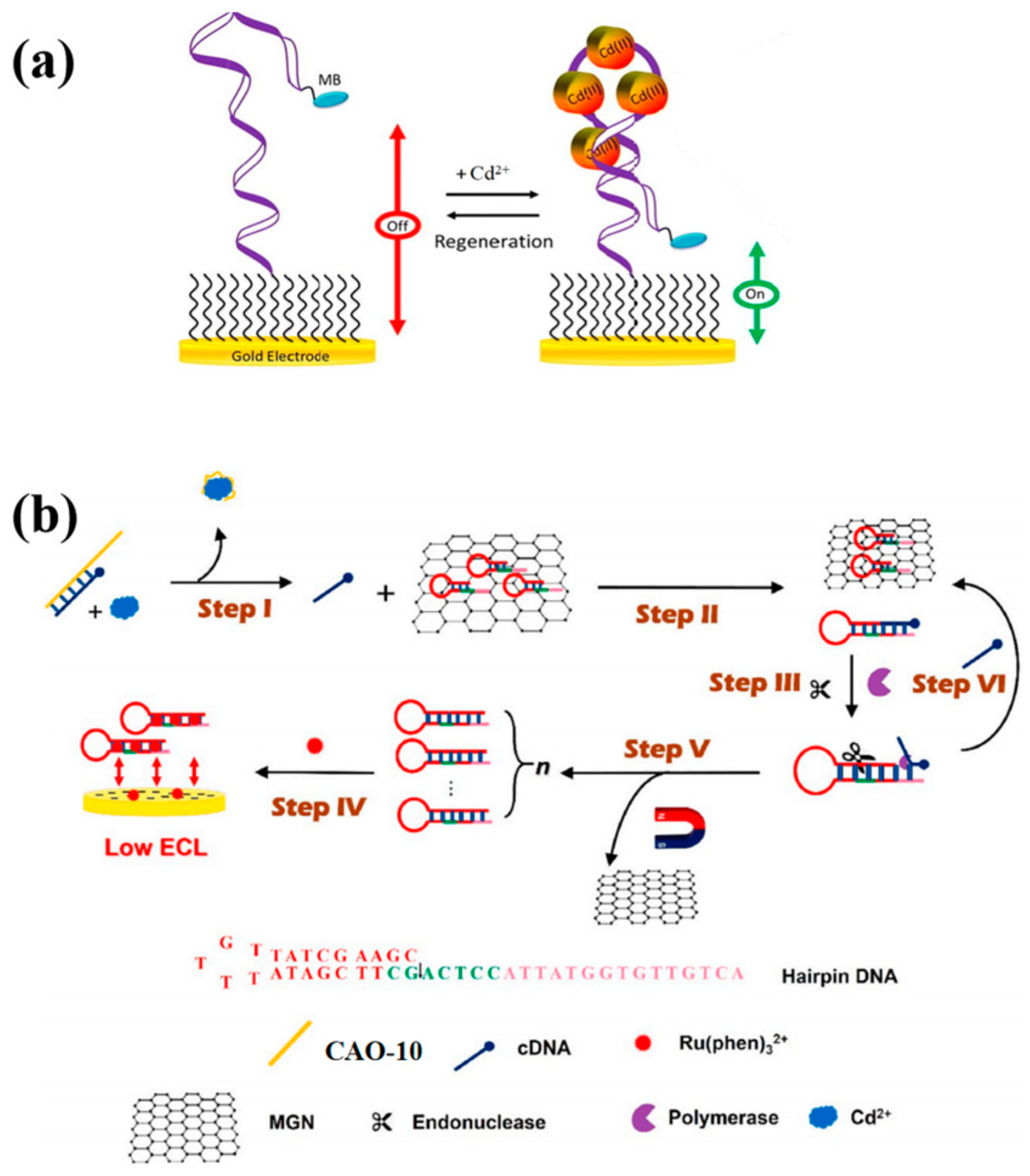
This study implemented the use of the same aptamer CAO-5 mentioned in the previous method to develop a reagent-free and reusable electrochemical biosensor. An E-AB (electrochemical aptamer-based) biosensor was used to detect Cd2+. CAO-5 was labeled with methylene blue [42]. When Cd2+ is absent, the superficial immobilized aptamer probe was locally folded (Figure 4a). Upon binding to Cd2+, the probe CAO-5 changed its confirmation and adaptability, increasing the MB signal [25]. The “signal-on” strategy was used, which is generally more advantageous than “signal-off” in developing biosensors. Parameters that influence the monitoring of Cd2+ were systematically optimized in this reagent-free and reusable electrochemical biosensor. Such biosensors have shown high selectivity in complex samples and can be applied directly. Furthermore, immediate results can be obtained through this method, which is also renewable and reusable. It is possible to use it in the measurement of Cd2+ in biological and environmental materials in the future with additional improvements.
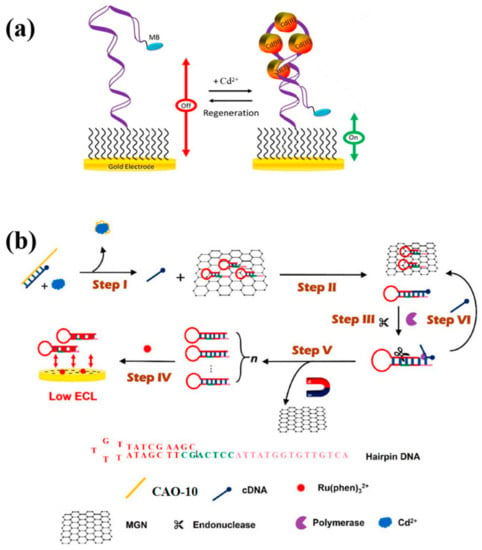
Figure 4.
(a) The diagram illustrates the construction of “signal-on” E-AB biosensors that are utilized for monitoring Cd2+ [25]; (b) The schematic diagram was developed for Cd2+ detection by Xu et al. [45].
Recently, researchers carefully created a hairpin DNA that was used in strand displacement amplification (SDA) and structured an electronic biosensor based on magnetic graphene oxide nanosheets (MGN) (Figure 4b). The MGN restricted previously designed hairpin DNA because of the lack of Cd2+. It releases cDNA via combination with CAO-10 (Table 1), removing the hairpin DNA on MGN surfaces in the presence of Cd2+. In the solution, the electrochemiluminescence (ECL) probe Ru(phen)32+ readily diffuses and efficiently reaches the electrode surface, causing an enhanced ECL signal. In this case, SDA amplification is induced to excite and generate a large amount of dsDNA, trapping Ru(phen)32+ in its groove. The implanted ECL probe connecting the electrode surface cannot produce an ECL signal. Consequently, the concentration of Cd2+ could be detected based on the decay of the detection signal [45]. This technique greatly simplifies the performance procedure. Furthermore, it is appropriate to be utilized in the complicated matrix.
4. Fluorescent Biosensors
Traditional methods for detecting Cd2+ using fluorescence include a Cyclen-based Fluorescent Chemosensor [46] and a radiometric fluorescent peptide sensor [47]. However, these techniques have drawbacks such as complicated operation, low monitoring sensitivity, and consuming time [48,49,50]. In contrast, fluorescent biosensors based on aptamers offer high sensitivity, precision, and a low detection limit. Whether using label-free/labeled methods or signal amplification strategies, fluorescent biosensors have the potential to replace traditional methods for Cd2+ detection [51,52].
4.1. Label-Free
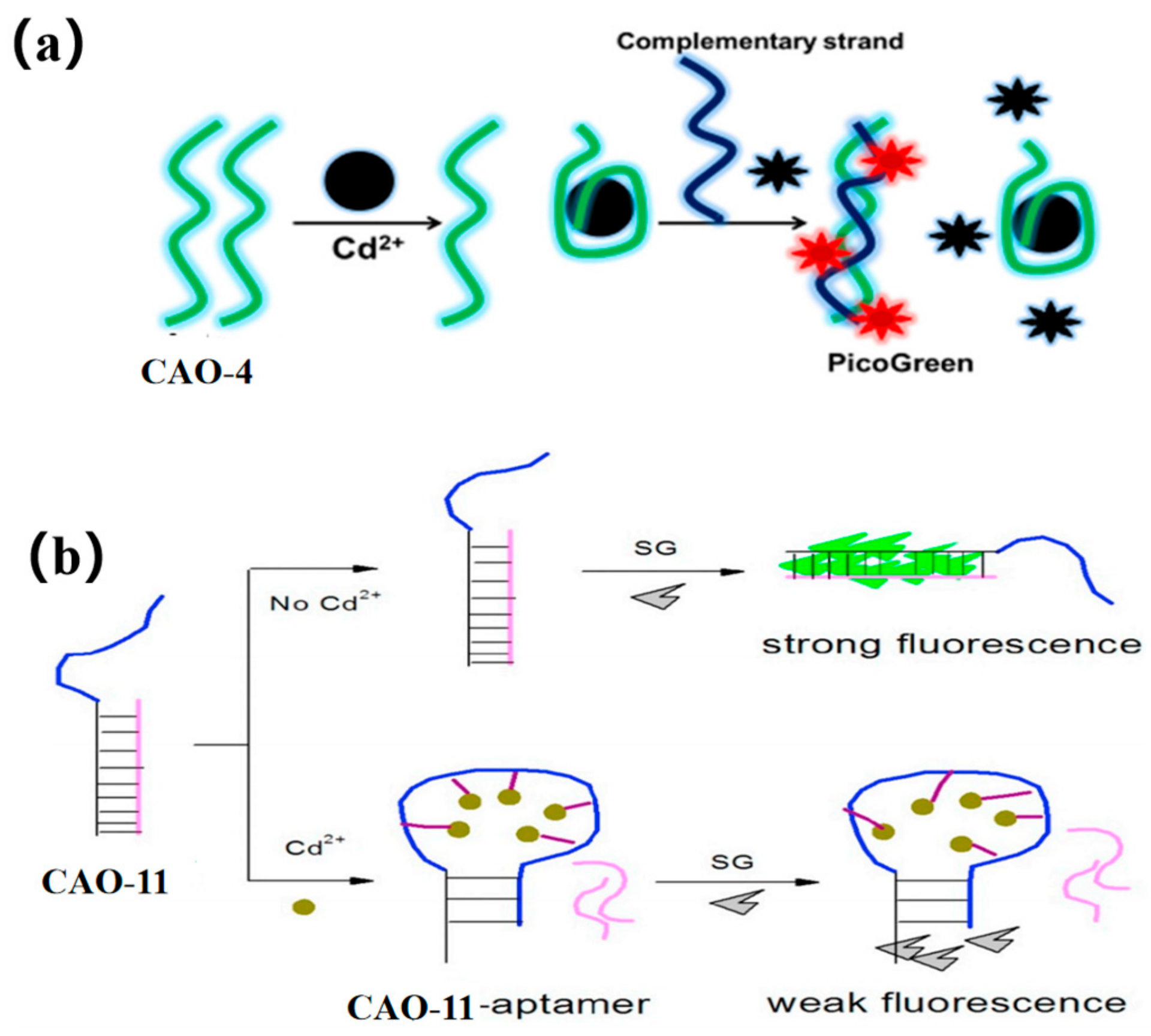
PicoGreen (PG) is an asymmetric anthocyanin dye, which cannot fluoresce freely. However, when it is bound to CAO-4 (Table 1) by hybridization with its complementary strand, its fluorescence is increased by more than 1000-fold (Figure 5a). Additionally, it does not exhibit fluorescence when bound to CAO-4 as single-stranded DNA [15]. Thus, PG can be used as a dye that enhances fluorescence based on such a mechanism. By combining an aptamer sensor with this dye [42], an easy, sensitive, and versatile fluorescence sensing plan for Cd2+ detection can be developed [53]. This method demonstrated greater sensitivity to the matrix effect when compared to atomic absorption spectrometry [54].
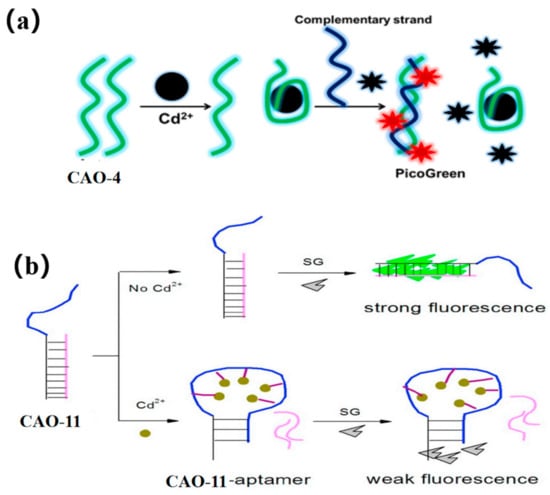
Figure 5.
(a) PicoGreen (PG) used for Cd2+ detection [53]; (b) SYBR green applied for the Cd2+ determination [55].
SYBR green is an intercalator dye, which can combine with the minor groove of double-stranded DNA. CAO-11 (Table 1) can hybridize to form a DNA duplex with its complementary strand. After adding SG, the intensity of the fluorescence signal increases (Figure 5b). When Cd2+ is present, CAO-11 can bind to it, and DNA hybridization is disrupted [55]. The fluorescent biosensor does not require target preconcentration or sample treatment and exhibits a higher degree of selectivity.
4.2. Labeled Method
In 2017, a susceptible and selective Cd2+ detection strategy was designed by Zhu et al. The strategy involved the utilization of a multifunctional probe, which was individually labeled and consisted of a specific Cd2+ aptamer, CAO-12 (Table 1). The aptamer was responsible for recognizing Cd2+ and acted as a signal reporter. Upon interaction with Cd2+, the CAO-12 underwent a conformational transition from a free sequence to a hairpin structure. Due to photoinduced electron transfer, the conformational change caused fluorescence quenching. As the concentration of Cd2+ increased, the fluorescence response was enhanced, leading to the successful employment of a novel fluorescence approach for monitoring Cd2+ [27]. Compared to traditional techniques such as inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry [56], this biosensor only required the utilization of the aptamer probe. The strategy did not require complex processes or sophisticated apparatus. However, further improvements are still needed to enhance its detection limit.
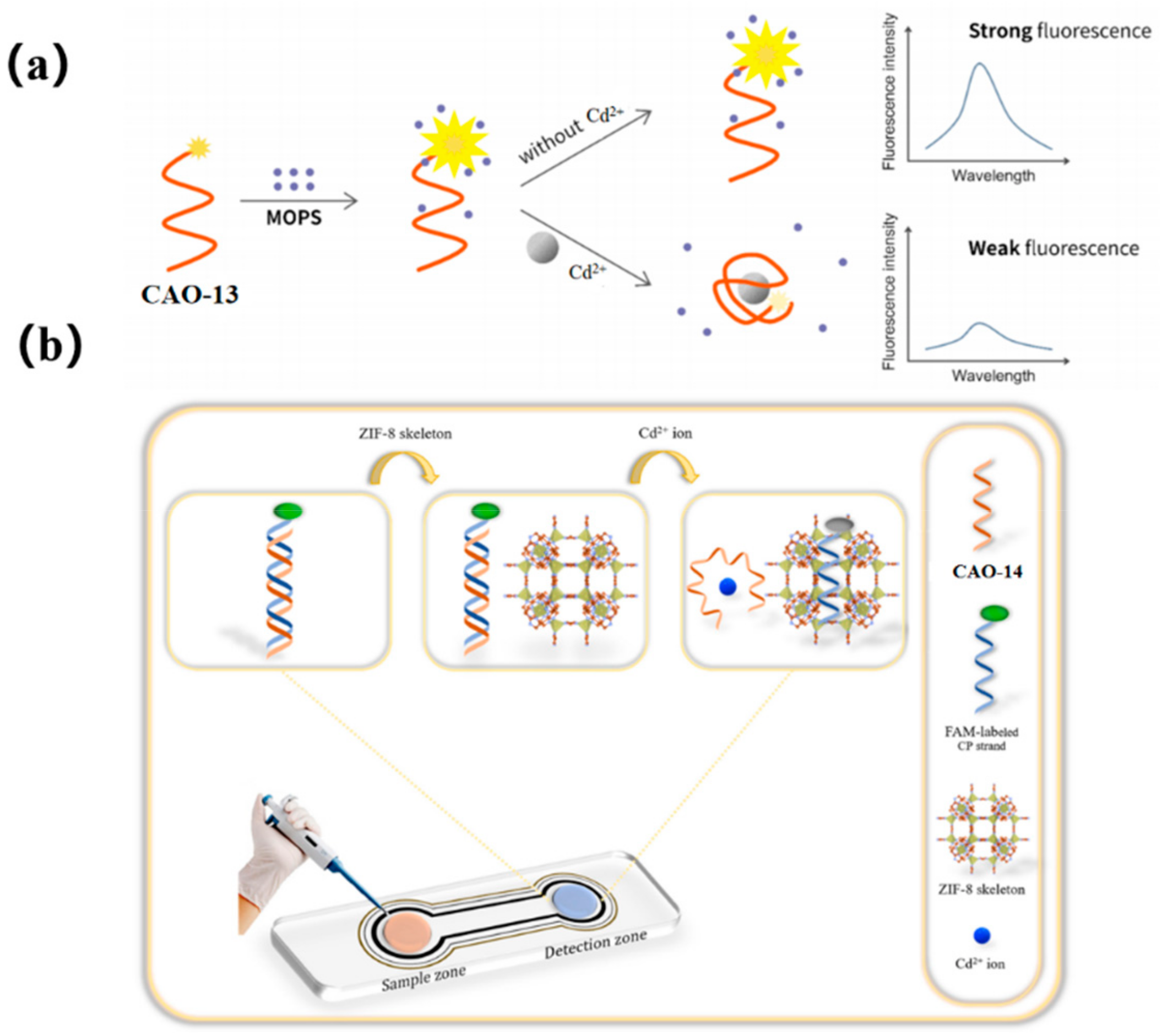
To achieve more accurate and efficient detection of Cd2+, a later study found that 3−(N-morpholino) propane sulfonic acid (MOPS), a widely used buffer, could significantly enhance the fluorescent intensity of FAM-labeled CAO-13. Upon adding Cd2+, the fluorescence changes and remains stable for at least an hour before decreasing proportionally with the increasing concentration of Cd2+. This development led to the creation of a simple adaptive sensor for the instantaneous determination of Cd2+, as illustrated in Figure 6a [57]. MOPS was found to possess fluorescence amplification properties with the FAM-aptamer CAO-13, which is uncommon among other commonly used buffers. Despite being sensitive to pH, MOPS could still be practically applied for real-time monitoring of Cd2+ due to its easy handling, high performance, and exceptional efficiency as a biosensor.
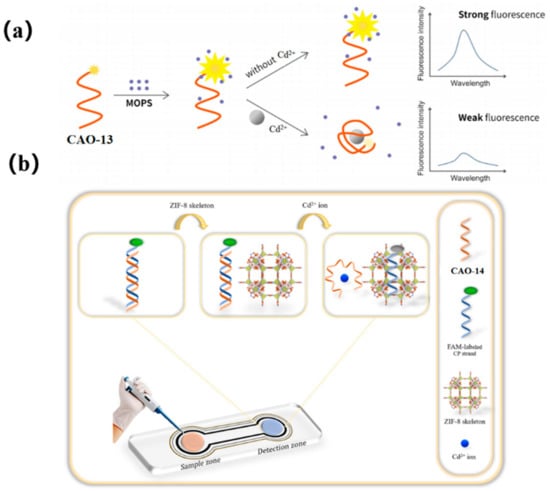
Figure 6.
(a) A schematic illustrating a simple and ultra-efficient sensor for measuring Cd2+, which was developed by Liu et al. [57]; (b) Schematic representation of the project biosensor for sensitive detecting of Cd2+ [6].
The latest report introduces an innovative monitoring array for detecting ultra-low levels of Cd2+ by utilizing the excellent selectivity and sensitivity of aptamers as sensing probes and the ability of ZIF-8 (zeolitic imidazolate framework-8) to quench fluorescence. To develop a portable spot monitoring technique, the biosensor was prepared utilizing a paper-supported substrate, as shown in Figure 6b. The detection strategy exploited the specific combination of CAO-14 (Table 1) with Cd2+ and the distinct affinities between single and double DNA chains for sorption on the ZIF-8 framework. When Cd2+ was absent, a CP-CAO-14 rigid duplex was formed through the hybridization between CAO-14 and its complementary (CP) strand, which was labeled with FAM. Adding the CP-CAO-14 complex onto the monitoring area resulted in a negligible trend for sorption by the exterior of the quencher ZIF-8, which led to a notable fluorescence signal. Upon forming the CAO-14-Cd2+ complex, the cross of the CP strand and the CAO-14 would be obstructed. Consequently, the ZIF-8 appearance adsorbed the CP strand, quenching the FAM fluorescence. Compared to previous studies on fluorescence biosensors, this approach designed a paper-supported sensing array, which was successfully applied in real complex food samples, including water, rice, and potatoes [6].
4.3. Signal Amplification
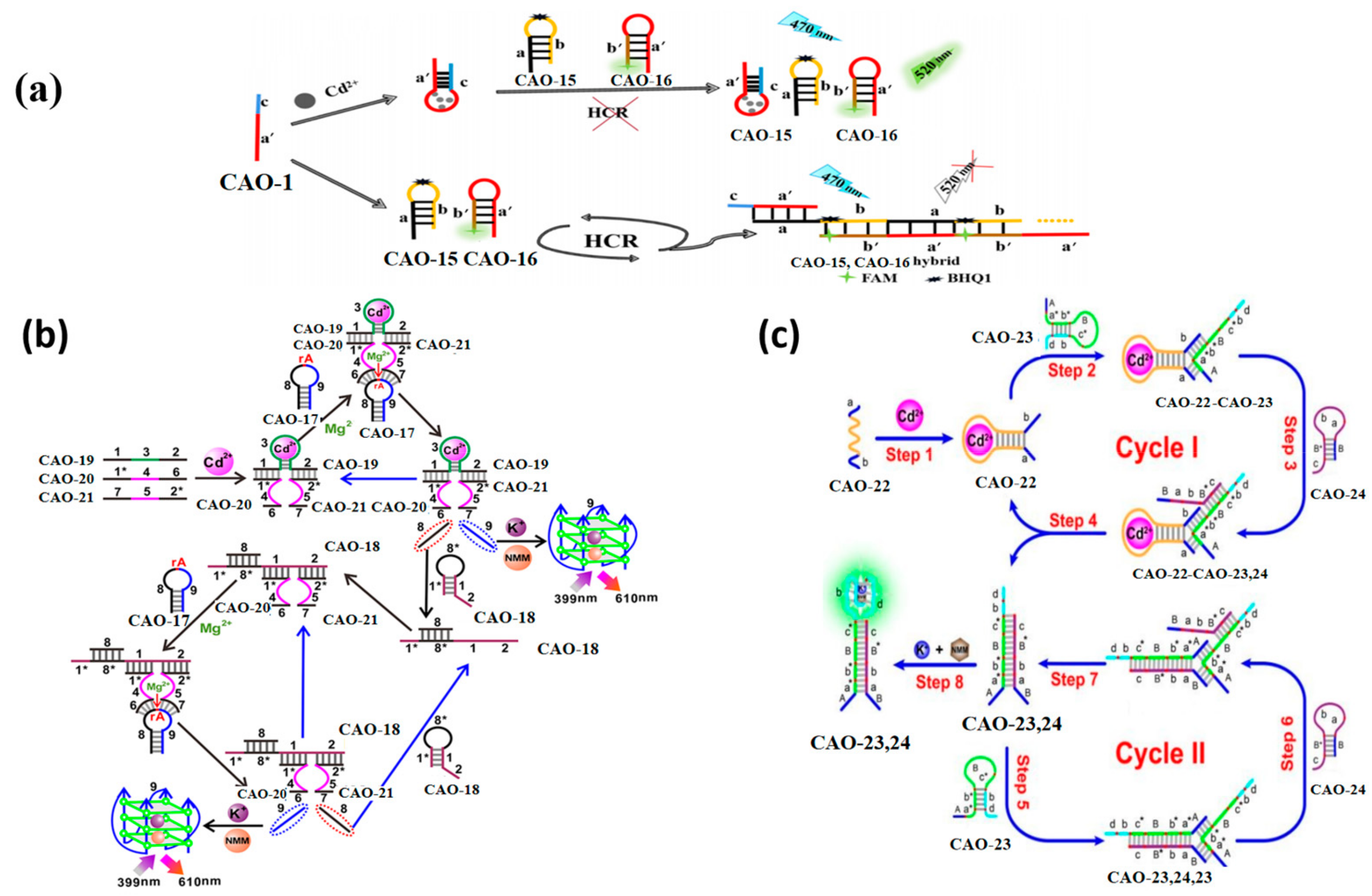
A biosensor for Cd2+ detection was designed using Cd2+ aptamers and a hybridization chain reaction (HCR). The operational principles of the biosensor are illustrated in Figure 7a. The biosensor was based on three oligonucleotide probes, namely CAO-1, CAO-15, and CAO-16 (Table 1). CAO-1 was utilized as a promoter for HCR and a Cd2+−specific aptamer, while CAO-15 and CAO-16 were subjected to heating and cooling to form a hairpin structure, respectively. BHQ1 was used to label CAO-15, whereas 5-carboxyfluorescein (FAM), which can emit fluorescence, was used to label CAO-16 [58]. In the absence of Cd2+, a pulse on the HCR by CAO-1 will form long-nicked dsDNA structures. However, fluorescence quenching is achieved by binding Cd2+ to CAO-1, which prevents HCR from regaining fluorescence. The limit of detection is 0.36 nM, so this can further improve sensitivity in Cd2+ detection (Table 2).
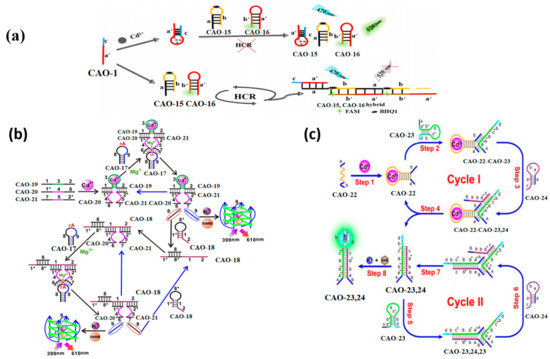
Figure 7.
(a) Principles of the biosensor detection of Cd2+ [58]; (b) Illustration of a Cd2+ biosensor based on DNAzyme-dependent Mg2+ [59]. (c) Diagrammatic sketch of monitoring Cd2+ by toehold combination and branch migration. [60]. *: was used to distinguish the different domain of each DNA sequence.
This approach utilizes toehold-mediated strand displacement with the aid of Mg2+−dependent DNAzyme to develop a versatile Cd2+ sensor, as demonstrated in Figure 7b. Domain 3 of CAO-19 (Table 1) is a specific aptamer sequence that can combine with Cd2. The split sequences of the DNAzyme consist of domain 4 of CAO-20 (Table 1) and domain 5 of CAO-21 (Table 1). With Cd2+, domains 1 and 2 were led to be short enough distance via the interplay between CAO-19 and Cd2+ and DNA. Then field 1* of CAO-20 and field 2* of CAO-21 could be hybridized, respectively. CAO-19-CAO-20-CAO-21, a synergistically stabilized construction, produced an active Mg2+−dependent DNAzyme that leads the hairpin substrate strand (CAO-17) (Table 1) to be catalyzed to make the cleavage reaction. The trigger in CAO-17 can turn on CAO-18, another hairpin probe enabling the cyclic signal intensification procedure to be activated [59]. The fluorochrome produces many G-quadruplex DNAzyme structures, creating a highly fluorescent response upon incubation with N-methyl mesoporphyrin IX (NMM). The experiment utilizes OR logic gates, allowing the logic system to conduct the function commendably, even with the complicated specimens. This approach is simple to operate, enzyme and label-free, and capable of amplifying universal signals.
Pan et al. designed a more sensitive approach for detecting Cd2+ utilizing an enzyme-free DNA circuit according to branch migration and hairpin probe-mediated toehold binding. The identity probe in the DNA circuit is CAO-22 (Table 1), and the reporter gene is a G-quadruplex, making it more convenient to achieve the goal. Figure 7c illustrates the biosensor’s principle for enzyme-free monitoring of Cd2+. When Cd2+ is present, the structural domains a and b within CAO-22 are nearby, allowing the fragment of CAO-22 to be used as a trigger fragment for subsequent strand substitution reactions with CAO-23 and CAO-24. It forms a G-quadruplex, producing a highly fluorescent response upon incubation with NMM. This method is more sensitive to detecting Cd2+ at ultra-low concentrations (Table 2) [60].
5. Colorimetric Biosensors
Recently, colorimetric biosensors based on metallic nanoparticle (NP) assays have garnered increasing interest owing to their interparticle distance-dependent optical properties and partial solid surface plasmon resonance absorption [61,62,63,64]. Colorimetric biosensors offer several advantages, including easy measurement, rapidity, high sensitivity, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness [65,66].
5.1. Gold Nanoparticles
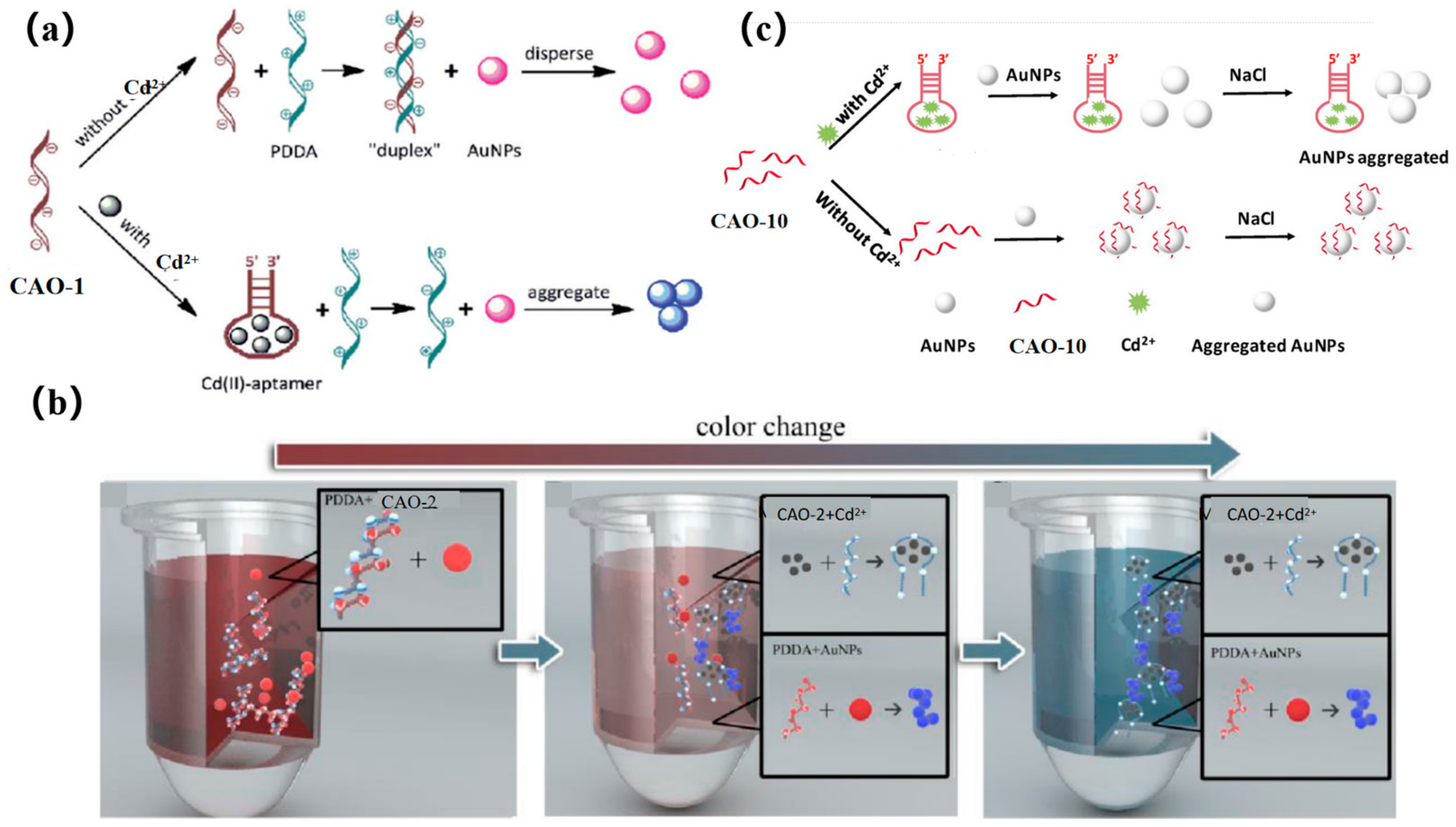
The accumulation of AuNPs is mediated via a cationic polymer to produce a colorimetric signal. In early research, CAO-1 (Table 1) was considered the Cd2+−based recognition element for cationic polymer (AuNPs) aggregation for colorimetric detection (Figure 8a) [29]. In the absence of Cd2+, the CAO-1 is free and can form a “duplex” structure by hybridizing with PDDA, which prevents AuNPs from aggregating due to the lack of PDDA. In the presence of Cd2+, CAO-1 is consumed, leading to a significant color change from red to blue due to the accumulation between PDDA and AuNPs. This method can accurately detect Cd2+ in an aqueous solution. If CAO-1′s selectivity can be improved, the method will be valuable in applications such as Cd2+ detection or remediation of contaminated Cd2+.
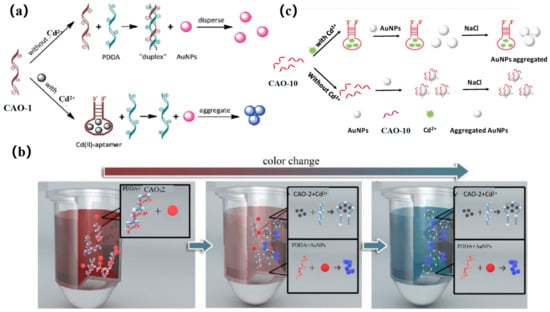
Figure 8.
(a) A diagram of the colorimetric detection of Cd2+ using AuNP aggregation mediated by cationic polymers using CAO-1 aptamers for recognition [29]; (b) Colorimetric method illustrated for Cd2+ detection [67]; (c) Colorimetric principle was designed for Cd2+ detection based on the functional AuNPs [10].
A more recent and innovative approach for testing Cd2+ involves a simple combination of CAO-2 and AuNPs by a colorimetric mobile phone readout. The technique utilizes a competitive binding assay between CAO-2, PDDA, and Cd2+. AuNPs act as signal reporters, and the color changes from red to blue, increasing the Cd2+ concentration, and resulting in free PDDA availability. Additionally, mobile phones equipped with ColorAssist applications can capture the detection results (Figure 8b). The detector can observe the image’s red (R) values with different signal intensities in response to different concentrations of Cd2+. This technique has already been employed for detecting and quantifying Cd2+ in rice and drinking water. As a result, low-cost and convenient colorimetry demonstrates its potential for practical use in quantitative and visual monitoring with a mobile phone [67].
Recently, a colorimetric approach for monitoring Cd2+ based on CAO-10 (Table 1) and the functionalized AuNPs has been developed for unique recognition, and it is more efficient in terms of colorimetric smartphone readings. In high-salt solutions, AuNPs tend to aggregate due to the screening of electrostatic repulsion. However, CAO-10 can prevent aggregation and enhance the stability of AuNPs. When Cd2+ exists, CAO-10could react with Cd2+, which results in a reduction of the free CAO-10. It leads to a color alternation of the solution and decreased stability of AuNPs (Figure 8c) [10]. The detection limit is 1.12 g/L, less than the USEPA’s permitted level for drinking water (5 μg/L) [68]. Compared to the previously mentioned method using a smartphone, this colorimetric system can be analyzed and captured by a smartphone within 10 min, and it can also achieve quantitative and in-situ monitoring of Cd2+ (Table 2).
5.2. Other Nanoparticles
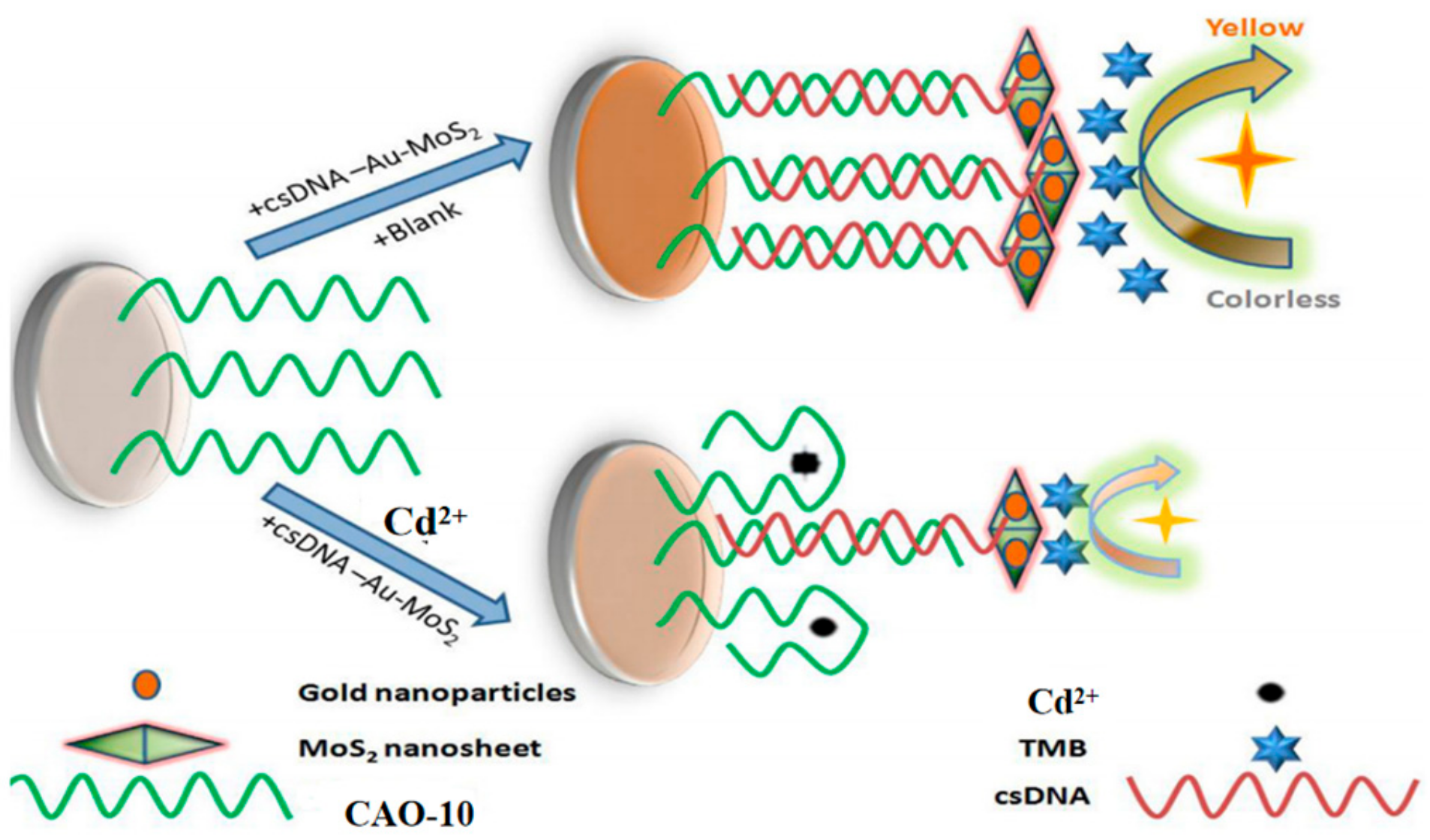
A new approach based on gold nanoparticle-modified molybdenum disulfide nanocomposites has been developed for monitor Cd2+. In this approach, the biotinylated Cd2+ aptamer CAO-10 (Table 1) is immobilized on a microplate through biotin-affinity binding. Additionally, a signal probe called csDNA-Au-MoS2 is made up of complementary strands of CAO-10 adsorbed onto the gold nanoparticle-modified molybdenum disulfide composite. When target Cd2+ competes with the csDNA-Au-MoS2 for binding to CAO-10, a color change is observed upon the addition of a chromogenic substrate (Figure 9) [69]. It was applied for Cd2+ detection in white wine samples, demonstrating its practical applicability. This approach is relatively complex to operate but has relatively high sensitivity (Table 2).
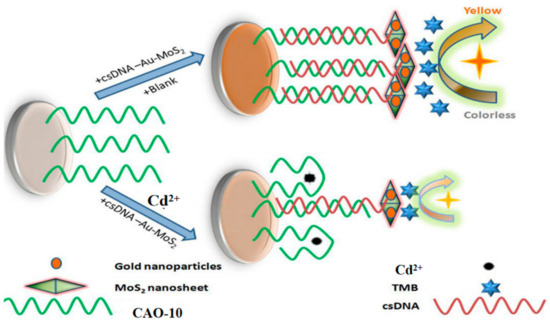
Figure 9.
The principle of Cd2+ detection by this assay [69].
This colorimetric method for determining Cd2+ employed Mn3O4 nanoparticles (NPs) with oxidase-mimicking function, which could be regulated by oligonucleotides. The chromogenic agent tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) can be oxidated by the catalyst of Mn3O4 NPs, resulting in a yellow product in acidic solutions. When CAO-25 (Table 1) is absorbed onto the surface of Mn3O4 NPs, TMB is temporarily inhibited from oxidizing, and the solution appears light green due to decreased absorbance. However, when Cd2+ is present, the inhibition is canceled, and thymine bases in CAO-25 bind to Cd2+, changing the solution’s color from light green to yellow. This method provides a more rapid and accurate determination of Cd2+, and it is a simple, evident, and selective process [70].
5.3. G-4/Hemin-Assisted Method
This assay exploited a label-free aptamer biosensor for Cd2+ determination using an aptamer specific to G-quadruplex-Cd2+ (GCDSA). GCDSA was designed by combining a G-rich sequence and an essential structural domain of CAO-26 (Table 1) to recognize Cd2+ and act as a signal DNAzyme specifically. When no Cd2+ exists, GCDSA remains mostly a random coil sequence. However, upon adding Cd2+, G-quadruplex formation can be induced in GCDSA, which can combine with hemin to act as peroxidase-like DNAzymes. It increases the signal of the sensing design, and the Cd2+ concentration can be determined by observing the absorbance. This method avoids using labeled oligonucleotides, makes the experimental procedure simple and convenient, allows for direct quantitative sample analysis, and has an excellent dynamic range. It displays two segments with a broad linear range, allowing Cd2+ to be detected at concentrations as low as 0.15 nM [71].
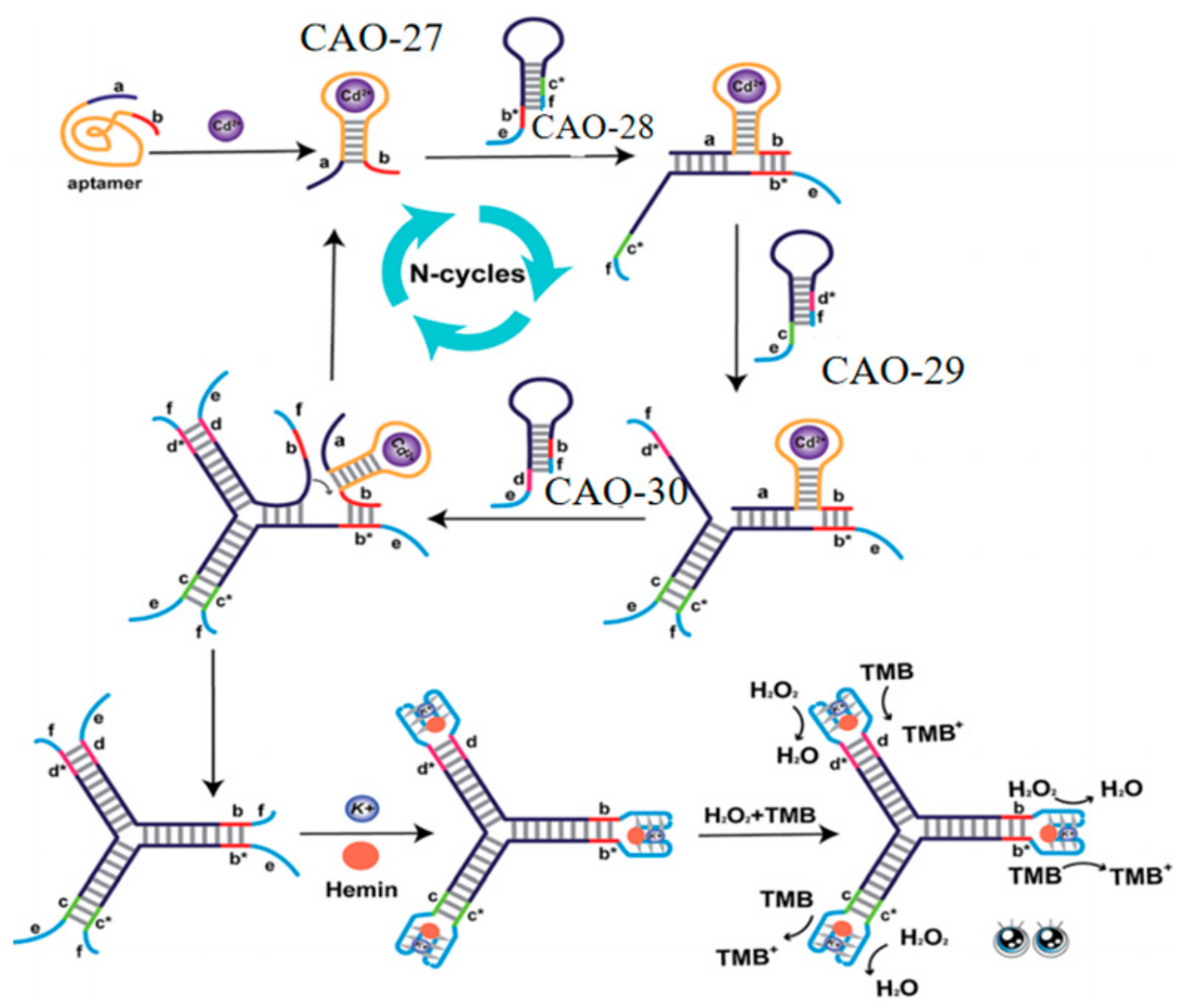
Lastly, to further improve sensitivity and convenience, a label-free and enzyme-free three-way ligation sensing system was proposed for Cd2+ detection by G-quadruplex/heme DNAzyme. Three hairpin structures (CAO-28, CAO-29, CAO-30) (Table 1) were designed to build three-way G-quadruplex linkages as the building blocks. When Cd2+ is present, the binding of Cd2+ to CAO-27 (Table 1) results in the branching migration of the hairpin and the formation of an unstable complex. The Cd2+−CAO-27 separates from the complex and becomes a catalyst that allows additional branching connections to be hybridized. It leads to the formation of G-quadruplexes. Upon adding heme, many intact G-quadruplex/heme DNAzymes can be produced, enhancing the color changes observable to the naked eye (Figure 10). This biosensor has excellent selectivity and sensitivity for Cd2+ monitoring. It is also simple to operate without washing, modifying, or labeling. It is practical for the routine detection of Cd2+ [72].
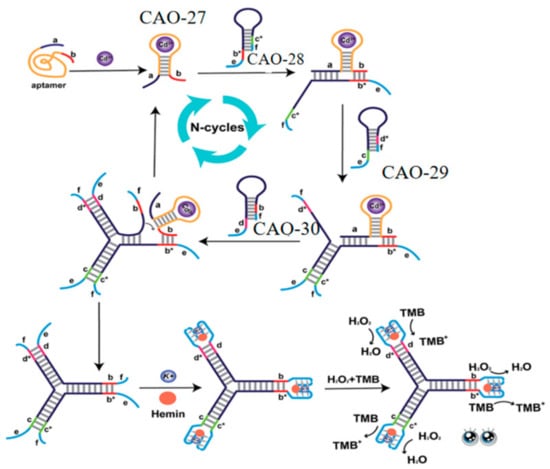
Figure 10.
DNA Y junctions containing the G-quadruplex act as the label-free signal reporters to monitor Cd2+ [72].

Table 2.
Comparison of the biosensors for Cd2+ monitoring based on electrochemical, fluorescent, and colorimetric methods in sensitivity and detection range.
Table 2.
Comparison of the biosensors for Cd2+ monitoring based on electrochemical, fluorescent, and colorimetric methods in sensitivity and detection range.
| Method | No. | LOD | Detection Range | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical detection | CAO-4 | 0.04995 pM | 0.001~100 nM | Tap water | [37] |
| CAO-5 | 0.14 ppb | 1~50 ppb | Drinking water | [38] | |
| CAO-6 | 7 × 10−4 mg/L | 2 × 10−3~8 × 10−1 mg/L | Genuine mussels | [40] | |
| CAO-7 | 1.8 × 10−12 mol/L | 5.0 × 10−12~2.0 × 10−8 mol/L | Lake water | [43] | |
| CAO-9 | 1.1 × 10−11 mol/L | 3.0 × 10−11~4.0 × 10−8 mol/L | Lake water | [44] | |
| CAO-5 | 92 nM | 250~1 μM | Tap water | [25] | |
| CAO-10 | 1.1 × 10−4 ppb | 3.0 × 10−2~4.0 × 105 ppb | Traditional medicine | [45] | |
| Fluorescence detection | CAO-4 | 0.038 ng/mL | 0.10~100 µg/mL | Drinking water | [53] |
| CAO-11 | 0.34 μg/L | 1.12~224.82 μg/L | Drinking water | [55] | |
| CAO-12 | 2.15 nM | 7.19 nM~5.0 μM | Drinking water | [27] | |
| CAO-13 | 1.92 ng/mL | 5~140 ng/mL | Drinking water | [57] | |
| CAO-14 | 0.076 pM | 0.1~120 pM | Milk, coffee, and human blood serum | [6] | |
| CAO-1 | 0.36 nM | 0~10 nM | Pond water | [58] | |
| CAO-17 | 2.5 pM | 0~10 μM | Rice | [59] | |
| CAO-22 | 5 pM | 10 pM~100 μM | Human urine | [60] | |
| Naked eye observation | CAO-1 | 4.6 nM | 1~50 nM | Drinking water | [29] |
| CAO-2 | 1 ng/mL | 1~400 ng/mL | Rice and drinking water | [67] | |
| CAO-10 | 1.12 μg/L | 2~20 μg/L | Tap and drinking water | [10] | |
| CAO-10 | 0.7 ng/mL | 1~500 ng/mL | White wine | [69] | |
| CAO-25 | 2.4 μg/L | 5~100 μg/mL | Tap, river, lake, wastewater | [70] | |
| CAO-26 | 0.15 nM | 33.72~112.41 μg/L | Tap and pond water | [71] | |
| CAO-27 | 10 pM | 10 pM~1 μM | Tap, river, lake, wastewater | [72] |
6. Conclusions
This article provides an overview of SELEX, a new technology used to extract DNA aptamers that can be utilized as electrochemical, fluorescent, and colorimetric biosensors. These biosensors have the potential to detect harmful pollutants in water and food, particularly Cd2+. DNA biosensors offer several advantages over traditional methods, such as inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry and atomic absorption spectrometry. One of the main advantages is their simpler pre-preparation and operation. DNA biosensors involve the design and synthesis of specific DNA probes, which can be easily prepared in the laboratory setting. Additionally, the detection process in DNA biosensors is relatively straightforward and does not require complex sample preparation steps. However, traditional methods often rely on expensive and bulky equipment, such as ICP-AES or AAS instruments, which may not be easily accessible or affordable for every laboratory or field application. In contrast, DNA biosensors can be designed to work with more straightforward and compact instrumentation, making them more cost-effective and portable.
The biosensors designed using specific and high-affinity Cd2+ aptamers have demonstrated excellent sensor behavior, surpassing other methods regarding detection limits and detection range comparisons. These biosensors exhibit exceptional selectivity and sensitivity due to efficient signal amplification strategies employed in their design. However, biosensors based on the Cd2+ aptamer design are still at an early stage of development. The specificity and productivity of the SELEX approach for Cd2+ aptamers can be challenging, as it is a time-consuming process that may yield a limited number of aptamers. This limitation can hinder aptamer-based biosensors’ affinity and binding efficiency, ultimately impacting their sensitivity. Moreover, when applying these biosensors to natural samples, additional factors must be considered. Environmental factors, such as proteins, DNA sequences, and enzymes in the sample, can interact and bind to Cd2+ aptamers, leading to interference and potentially restricting the detection of Cd2+. These factors can affect the accuracy and reliability of biosensor results obtained from laboratory experiments. Therefore, further research and development efforts are necessary to overcome these challenges and achieve practical monitoring of Cd2+ using biosensors.
DNA aptamers offer a promising approach for detecting Cd2+ in the environment and ensuring food safety. Nonetheless, more work is required to overcome the current challenges and optimize the potential of these biosensors. Indeed, real-time detection is a valuable function increasingly achieved by biosensors based on aptamers. These biosensors offer advantages such as high sensitivity, selectivity, and the ability to recognize specific targets. It is anticipated that aptamer-based biosensors will continue to evolve and enable real-time monitoring and in vivo detection with high sensitivity. Overall, the future of aptamer-based biosensors looks promising, and their continued development and application will likely pave the way for real-time monitoring and in vivo detection with high sensitivity across various fields and applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.X. and X.L.; validation, Y.X. and X.L.; formal analysis, X.L.; investigation, Z.G.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.G.; writing—review and editing, Z.G. and Y.W.; visualization, H.W.; supervision, J.Q.; funding acquisition, J.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Zhejiang Sci-Tech University grant number 16042017-Y.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Das, P.; Samantaray, S.; Rout, G.R. Studies on cadmium toxicity in plants: A review. Environ. Pollut. 1997, 98, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellez-Plaza, M.; Guallar, E.; Howard, B.V.; Umans, J.G.; Francesconi, K.A.; Goessler, W.; Silbergeld, E.K.; Devereux, R.B.; Navas-Acien, A. Cadmium Exposure and Incident Cardiovascular Disease. Epidemiology 2013, 24, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiguchi, H.; Aoshima, K.; Oguma, E.; Sasaki, S.; Miyamoto, K.; Hosoi, Y.; Katoh, T.; Kayama, F. Latest status of cadmium accumulation and its effects on kidneys, bone, and erythropoiesis in inhabitants of the formerly cadmium-polluted Jinzu River Basin in Toyama, Japan, after restoration of rice paddies. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2010, 83, 953–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irfan, M.; Liu, X.H.; Hussain, K.; Mushtaq, S.; Cabrera, J.; Zhang, P.P. The global research trend on cadmium in freshwater: A bibliometric review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, T.; Nakamura, K.; Katou, H.; Ishikawa, S.; Ito, M.; Honma, T.; Miyazaki, N.; Takehisa, K.; Sano, S.; Matsumoto, S.; et al. Simultaneous decrease of arsenic and cadmium in rice (Oryza sativa L.) plants cultivated under submerged field conditions by the application of iron-bearing materials. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2016, 62, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshbin, Z.; Moeenfard, M.; Zahraee, H.; Davoodian, N. A fluorescence imaging-supported aptasensor for sensitive monitoring of cadmium pollutant in diverse samples: A critical role of metal organic frameworks. Talanta 2022, 246, 123514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titov, V.I.; Goundobin, N.V.; Kotikov, V.N. Determination of Ruthenium in Heat-Resistant Nickel Alloys by Atomic Emission Spectrometry with Inductively Coupled Plasma. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2013, 80, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Rizwani, H.M.; Yousef, A.F.; Zhi, C.; Chen, F.X. Analysis of toxic elements in leaves and fruits of loquat by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2021, 20, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ran, G.; Lu, G.; Ni, X.; Liu, D.; Sun, J.; Xie, C.; Yao, D.; Bai, W. Highly Sensitive Label-Free Electrochemical Aptasensor Based on Screen-Printed Electrode for Detection of Cadmium (II) Ions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, B449–B455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Liang, T.; Hu, Q.; Zhong, L.; Wang, X.; Wan, H.; Wang, P. In-situ detection of cadmium with aptamer functionalized gold nanoparticles based on smartphone-based colorimetric system. Talanta 2020, 208, 120231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Niu, L.Y.; Yang, Q.Z.; Guan, Y.F.; Feng, L. An SPE-assisted BODIPY fluorometric paper sensor for the highly selective and sensitive determination of Cd2+ in complex sample: Rice. Analyst 2014, 139, 3146–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.E.; Wu, X.X.; Ren, X.F.; Xue, B.; Qiu, W.J.; Nong, D.H.; Yang, T.; Xu, F. Mechanism of pH influence on aptamer binding with Cd2+ revealed by molecular dynamics simulation. New J. Chem. 2023, 47, 9239–9249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yan, M.X.; Huang, J.S.; Yang, X.R. Label-Free and Regenerable Aptasensor for Real-Time Detection of Cadmium(II) by Dual Polarization Interferometry. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10007–10015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.R.; Park, S.J.; Lee, W.G.; Hwang, B.H. Biosensors Using Hybridization Chain Reaction—Design and Signal Amplification Strategies of Hybridization Chain Reaction. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2018, 23, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragan, A.I.; Casas-Finet, J.R.; Bishop, E.S.; Strouse, R.J.; Schenerman, M.A.; Geddes, C.D. Characterization of PicoGreen interaction with dsDNA and the origin of its fluorescence enhancement upon binding. Biophys. J. 2010, 99, 3010–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, E.; Zhen, D.; Jiang, L. Homogeneous enzyme-free and entropy-driven isothermal fluorescent assay for nucleic acids based on a dual-signal output amplification strategy. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 12594–12597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Marzo, A.M.; Pons, J.; Blake, D.A.; Merkoçi, A. All-integrated and highly sensitive paper based device with sample treatment platform for Cd2+ immunodetection in drinking/tap waters. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3532–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López_Marzo, A.M.; Pons, J.; Blake, D.A.; Merkoçi, A. High sensitive gold-nanoparticle based lateral flow Immunodevice for Cd2+ detection in drinking waters. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 47, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X. Label-Free Colorimetric Detection of Cadmium Ions in Rice Samples Using Gold Nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8530–8534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, F.; Yuan, D.; Lv, G.; Liang, L.; Liu, L.; Hong, M. A regenerative metal–organic framework for reversible uptake of Cd(ii): From effective adsorption to in situ detection. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 5983–5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, A.S.; Zhou, E.Y.; Francis, M.B. Development of peptoid-based ligands for the removal of cadmium from biological media. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 4042–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Mao, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, S.; Nie, Z.; Lu, X. Ultratrace and robust visual sensor of Cd2+ ions based on the size-dependent optical properties of Au@g-CNQDs nanoparticles in mice models. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 103, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprowicz, A.; Stokowa-Sołtys, K.; Wrzesiński, J.; Jeżowska-Bojczuk, M.; Ciesiołka, J. In vitro selection of deoxyribozymes active with Cd(2+) ions resulting in variants of DNAzyme 8-17. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 8138–8149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.J.; Liu, J. Rational evolution of Cd2+−specific DNAzymes with phosphorothioate modified cleavage junction and Cd2+ sensing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 6125–6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhad, H.; Torres, Y.M.R.; Lai, R.Y. A reagentless and reusable electrochemical aptamer-based sensor for rapid detection of Cd(II). J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 803, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Cheng, H.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.J.; Chen, H.X.; Pei, R.J. Selection and characterization of DNA aptamers for the development of light-up biosensor to detect Cd(II). Talanta 2016, 154, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Wang, Y.S.; Zhou, B.; Yu, J.H.; Peng, L.L.; Huang, Y.Q.; Li, X.J.; Chen, S.H.; Tang, X.; Wang, X.F. A multifunctional fluorescent aptamer probe for highly sensitive and selective detection of cadmium(II). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 4951–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Z.; Yu, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Lu, A.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, B. Recent Advances in SELEX Technology and Aptamer Applications in Biomedicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.G.; Zhan, S.S.; Wang, L.M.; Zhou, P. Selection of a DNA aptamer for cadmium detection based on cationic polymer mediated aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Analyst 2014, 139, 1550–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Wang, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhang, F.; He, P. Internal Calibration Potentiometric Aptasensors for Simultaneous Detection of Hg2+, Cd2+, and As3+ Based on a Screen-Printed Carbon Electrodes Array. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8337–8344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutiu, R.; Li, Y. In vitro selection of structure-switching signaling aptamers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2005, 44, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.J.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, S.; He, N.Y. Selection of a High-Affinity DNA Aptamer for the Recognition of Cadmium Ions. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2021, 17, 2240–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Deng, B.; Yan, L.; Huang, H. An environmentally-friendly, highly efficient, gas pressure-assisted sample introduction system for ICP-MS and its application to detection of cadmium and lead in human plasma. Talanta 2017, 167, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwashita, A.; Nakajima, T.; Takanashi, H.; Ohki, A.; Fujita, Y.; Yamashita, T. Determination of trace elements in coal and coal fly ash by joint-use of ICP-AES and atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 2007, 71, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.N.; Yang, X.J.; Cui, Z.D.; Zhu, S.L.; Li, Z.Y.; Liang, Y.Q. Detection of Cd2+ by Square Wave Anodic Stripping Voltammetry Using an Activated Bismuth-film Electrodes. J. Inorg. Mater. 2019, 34, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, N.; Song, Y.; Fu, Q.; Du, D.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; Lin, Y. Aptasensor based on fluorophore-quencher nano-pair and smartphone spectrum reader for on-site quantification of multi-pesticides. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lai, Y.X.; Yang, G.J.; Tang, C.L.; Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.L. Cd-Aptamer Electrochemical Biosensor Based on AuNPs/CS Modified Glass Carbon Electrode. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2017, 13, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakude, C.T.; Arotiba, O.A.; Mabuba, N. Electrochemical aptasensing of cadmium (II) on a carbon black-gold nano-platform. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 858, 113796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Gui, R.; Yu, J.; Lv, W.; Wang, Z. Fabrication strategies, sensing modes and analytical applications of ratiometric electrochemical biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Liu, C.; Su, X.Y.; Zhang, W.; Zou, X.B. Signal on-off ratiometric electrochemical sensor based on semi-complementary aptamer couple for sensitive cadmium detection in mussel. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 346, 130506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, K.K.; Bhand, S. A colorimetric paper-based ATONP-ALP nanobiosensor for selective detection of Cd2+ ions in clams and mussels. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 1715–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.; Soo Oh, S.; Nie, J.; Stewart, R.; Eisenstein, M.; Chambers, J.; Marth, J.D.; Walker, F.; Thomson, J.A.; Soh, H.T. Quantitative selection and parallel characterization of aptamers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18460–18465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.Y.; Xie, H.; Luo, G.L.; Zhuang, Y.J.; Wu, X.Q.; Li, G.J.; Sun, W. ZnO-reduced graphene oxide composite based photoelectrochemical aptasensor for sensitive Cd(II) detection with methylene blue as sensitizer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1118, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.X.; Zhang, X.P.; Xie, H.; Luo, G.L.; Sun, W. Target-enhanced photoelectrochemical aptasensor for Cd(II) detection using graphite-like carbon nitride as sensitizer with high sensitivity. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.F.; Zhang, S.Q.; Zhang, T.; Huang, W.H.; Dai, Y.T.; Zheng, R.X.; Wu, G.W. An electrochemiluminescence biosensor for cadmium ion based on target-induced strand displacement amplification and magnetic Fe3O4−GO nanosheets. Talanta 2022, 237, 122967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.; Tae, J. Rhodamine Cyclen-based Fluorescent Chemosensor for the Detection of Cd2+. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, 32, 2928–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.Z.; Pu, X.W.; Ma, G.L.; Wang, E.Q.; Kong, J.M.; Liu, Z.P.; Liu, Y.Z. Synthesis of a ratiometric fluorescent peptide sensor for the highly selective detection of Cd2+. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 4014–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cui, S.Q.; Qiu, S.Y.; Pu, S.Z. A novel fluorescent sensor based on a diarylethene containing a hydrazinylpyridine unit for Cd2+ and Zn(2+)with high selectivity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2018, 367, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, R.; Caruso, U.; Concilio, S.; Piotto, S.; Tuzi, A.; Panunzi, B. A real-time tripodal colorimetric/fluorescence sensor for multiple target metal ions. Dyes Pigment. 2018, 155, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cui, S.; Shi, F.; Pu, S. A diarylethene based multi-functional sensor for fluorescent detection of Cd2+ and colorimetric detection of Cu2+. Dyes Pigment. 2019, 161, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Chen, X.Z.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.J.; Gao, G.; Zhang, X.Y.; Sun, R.Z.; Hou, S.C.; Wang, H.M.; et al. A highly sensitive multifunctional sensor based on phenylene-acetylene for colorimetric detection of Fe2+ and ratiometric fluorescent detection of Cd2+ and Zn2+. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Cui, S.; Qiu, S.; Pu, S. A new fluorescence probe based on diarylethene with a benzothiazine unit for selective detection of Cd2+. Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 7431–7437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.; Lu, A.; Chen, J.; Fu, H.; Xu, L. A Label-Free Aptamer-Based Fluorescent Assay for Cadmium Detection. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.; Dahiya, D.; Sharma, V.; Khan, N.; Chaurasia, D.; Nadda, A.K.; Varjani, S.; Pandey, A.; Bhargava, P.C. Advances from conventional to real time detection of heavy metal(loid)s for water monitoring: An overview of biosensing applications. Chemosphere 2022, 307 Pt 4, 136124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Yang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Yi, J.C.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.T.; Hu, X.J.; Suo, Q.L. Label-free fluorescent aptasensor of Cd2+ detection based on the conformational switching of aptamer probe and SYBR green I. Microchem. J. 2019, 144, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoudi, A.S.; Hassani, S.; Mirnia, K.; Abdollahi, M. Recent Advances in Nanotechnology-Based Biosensors Development for Detection of Arsenic, Lead, Mercury, and Cadmium. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 803–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.W.; Ding, J.N.; Hayat, K.; Yang, X.J.; Zhan, X.J.; Zhang, D.; Lu, Y.T.; Zhou, P. A Facile Aptasensor for Instantaneous Determination of Cadmium Ions Based on Fluorescence Amplification Effect of MOPS on FAM-Labeled Aptamer. Biosensors 2021, 11, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.M.; Peng, Y.; Yang, H.L.; Zhou, Y. Highly sensitive biosensor based on aptamer and hybridization chain reaction for detection of cadmium ions. Luminescence 2022, 37, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Pan, J.F.; Liu, C.S. Versatile Sensing Platform for Cd2+ Detection in Rice Samples and Its Applications in Logic Gate Computation. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 6173–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.F.; Zeng, L.W.; Chen, J.H. An enzyme-free DNA circuit for the amplified detection of Cd2+ based on hairpin probe-mediated toehold binding and branch migration. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 11932–11935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Y.; Daniel, W.L.; Wei, W.; Mirkin, C.A. Colorimetric Cu2+ Detection Using DNA-Modified Gold-Nanoparticle Aggregates as Probes and Click Chemistry. Small 2010, 6, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.S.; Liu, Y.Y.; Liu, D.B.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, X.Y. Copper-Mediated Amplification Allows Readout of Immunoassays by the Naked Eye. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3442–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.K.; Cheng, C.L.; Geng, H.; Wang, C.; Hu, W.P.; Xu, W.; Shuai, Z.G.; Zhu, D.B. Efficient ambipolar transport properties in alternate stacking donor-acceptor complexes: From experiment to theory. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 14094–14103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.Y.; Miao, Y.Q.; Zhan, X.J.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhao, X.J. Colorimetric determination of cysteine by a paper-based assay system using aspartic acid modified gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.L.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z.B. Colorimetric detection of DNA at the nanomolar level based on enzyme-induced gold nanoparticle de-aggregation. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Chen, P.P.; Xu, Z.; Chen, M.M.; Ding, Y.A.; Yue, K.; Xu, J. A facile strategy to prepare porphyrin functionalized ZnS nanoparticles and their peroxidase-like catalytic activity for colorimetric sensor of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2017, 251, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liang, J.; Wang, Y.H.; Ren, S.Y.; Wu, J.; Zhou, H.Y.; Gao, Z.X. Highly Selective, Aptamer-Based, Ultrasensitive Nanogold Colorimetric Smartphone Readout for Detection of Cd(II). Molecules 2019, 24, 2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafe Dilebo, W.; Desta Anchiso, M.; Tereke Kidane, T.; Eskezia Ayalew, M. Assessment of Selected Heavy Metals Concentration Level of Drinking Water in Gazer Town and Selected Kebele, South Ari District, Southern Ethiopia. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2023, 2023, 1524850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Wei, L.; Wu, S.; Duan, N.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. A colorimetric aptamer-based method for detection of cadmium using the enhanced peroxidase-like activity of Au-MoS(2) nanocomposites. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 608, 113844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Wang, J.L.; Zhou, P.; Tao, H.; Wang, X.L.; Wu, Y.G. Oligonucleotide-induced regulation of the oxidase-mimicking activity of octahedral Mn3O4 nanoparticles for colorimetric detection of heavy metals. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Chen, Y.T.; Yang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Hu, X.J.; Suo, Q.L. An Ultrasensitive Colorimetric Strategy for Detection of Cadmium Based on the Peroxidase-like Activity of G-Quadruplex-Cd(II) Specific Aptamer. Anal. Sci. Int. J. Jpn. Soc. Anal. Chem. 2019, 35, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.H.; Wu, W.; Li, Q.; Pan, J.F.; Chen, J.H. A label-free and enzyme-free aptasensor for visual Cd2+ detection based on split DNAzyme fragments. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 3546–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).