On-Field Test of Tuberculosis Diagnosis through Exhaled Breath Analysis with a Gas Sensor Array
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Recruitment
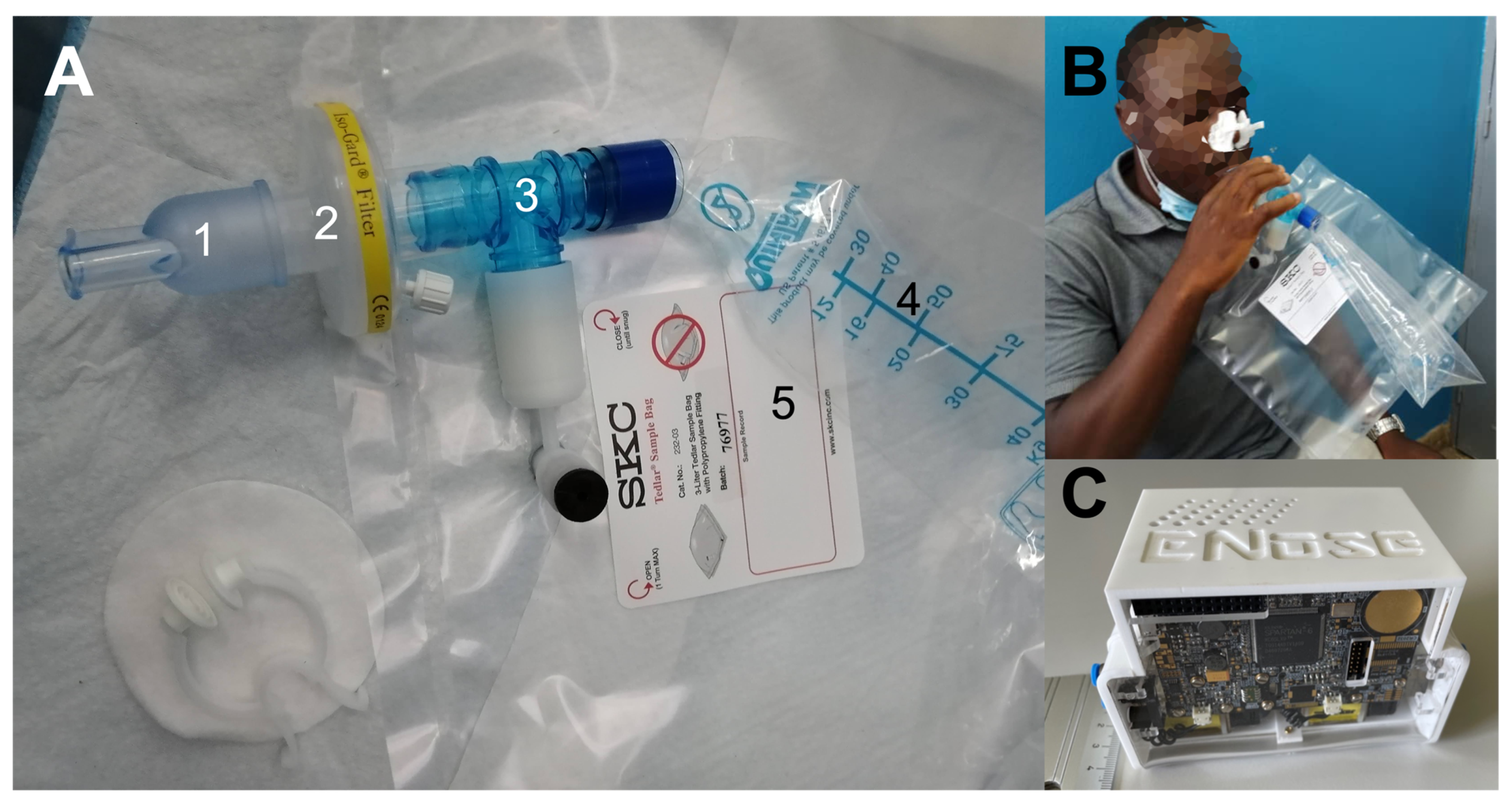
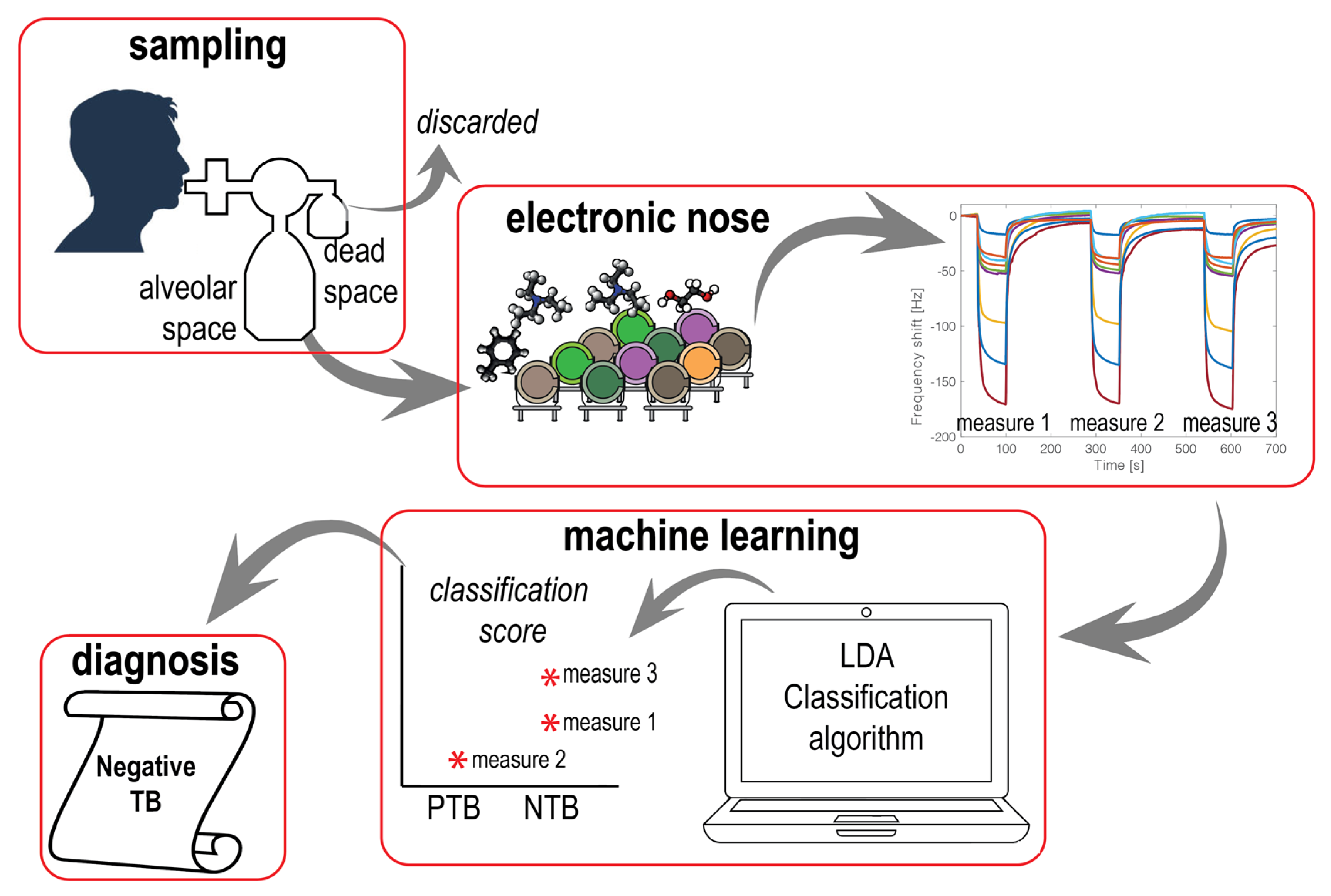
2.2. Breath Sampling and Processing
2.3. Electronic Nose
2.4. Statistical Analysis
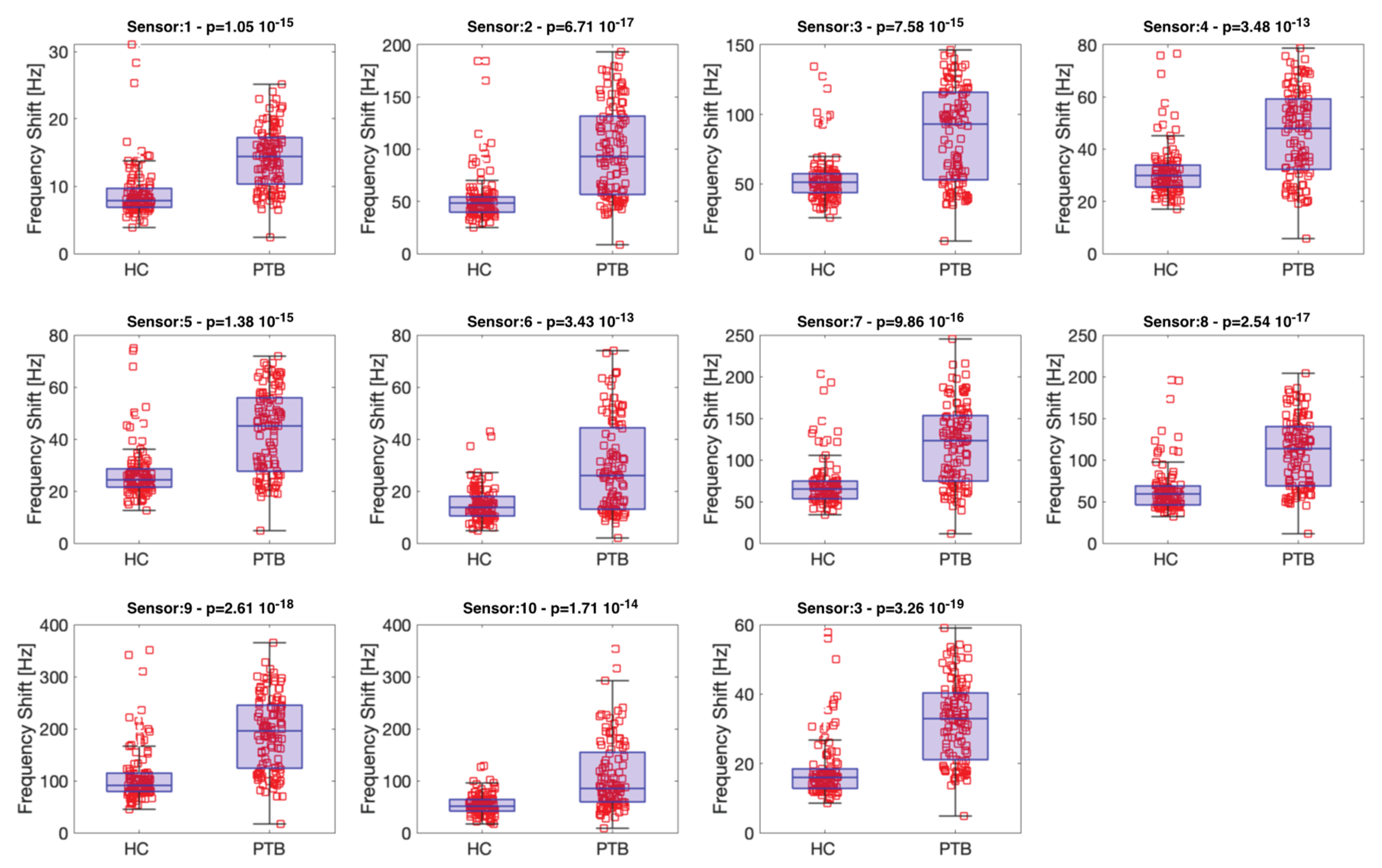
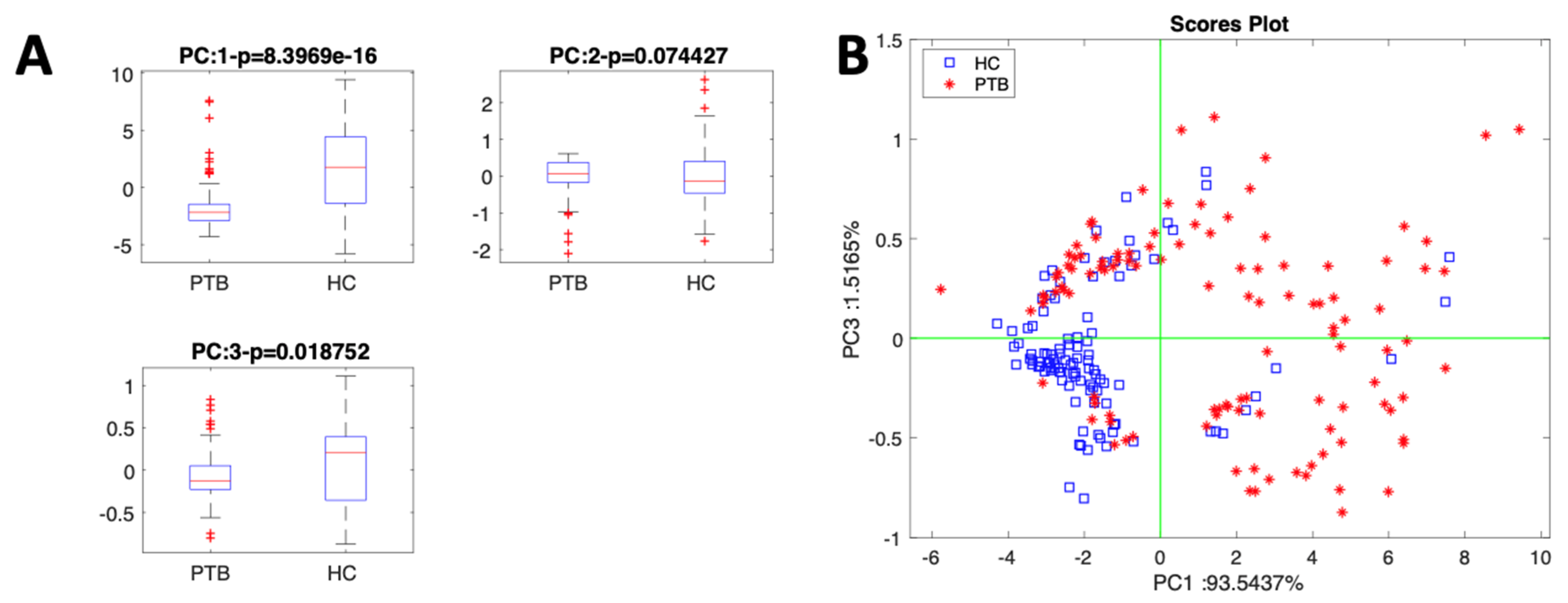
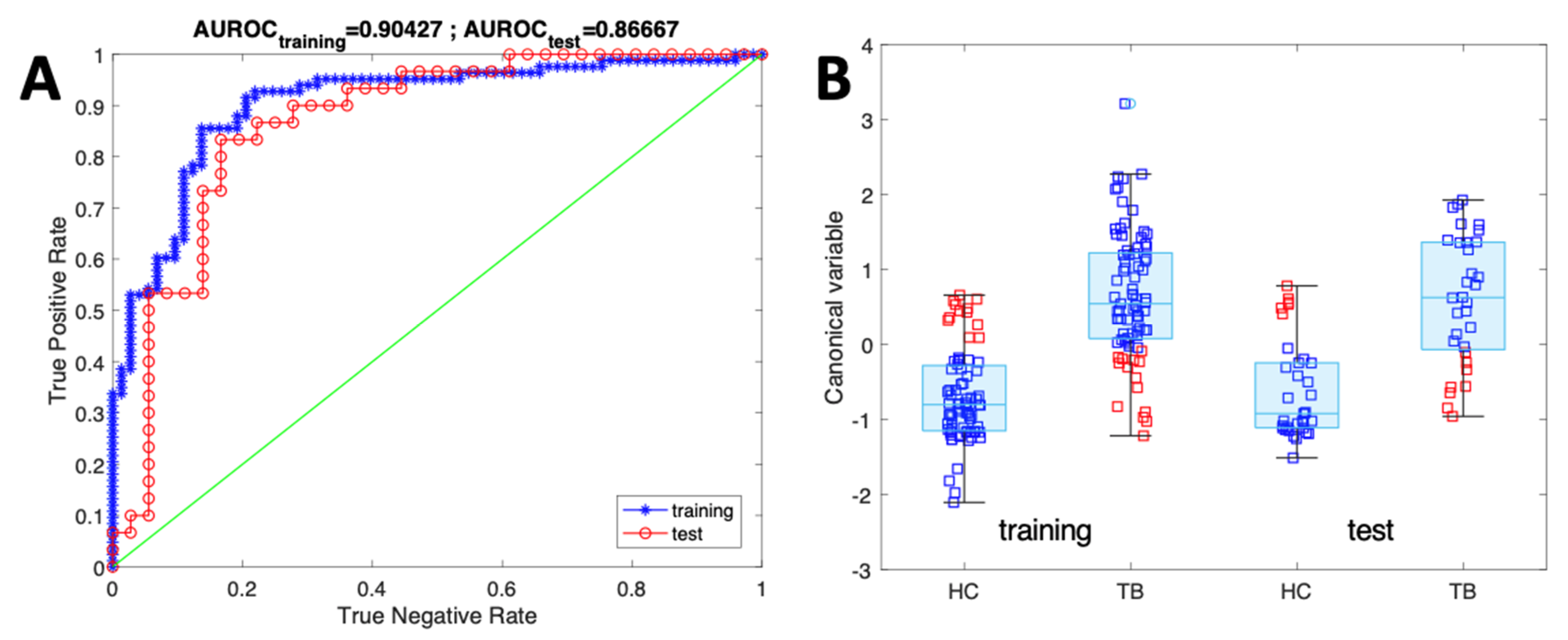
3. Results and Discussion
Sensor Data Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pai, M.; Behr, M.A.; Dowdy, D.; Dheda, K.; Divangahi, M.; Boehme, C.C.; Ginsberg, A.; Swaminathan, S.; Spigelman, M.; Getahun, H.; et al. Tuberculosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 16076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Tuberculosis Report 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240013131 (accessed on 17 May 2023).
- Dye, C.; Lonnroth, K.; Jaramillo, E.; Williams, B.; Raviglione, M. Trends in tuberculosis incidence and their determinants in 134 countries. Bull. World Health Organ. 2009, 87, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steingart, K.R.; Ng, V.; Henry, M.; Hopewell, P.C.; Ramsay, A.; Cunningham, J.; Urbanczik, R.; Perkins, M.D.; Aziz, M.A.; Pai, M. Sputum processing methods to improve the sensitivity of smear microscopy for tuberculosis: A systematic review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqi, K.; Lambert, M.-L.; Walley, J. Clinical diagnosis of smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis in low-income countries: The current evidence. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2003, 3, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, M.; Sharma, S.; Sood, S.; Sharma, V. Diagnostic accuracy of urine based lipoarabinomannan point of care tuberculosis diagnostic test in HIV negative children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 105, 115879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Basteiro, A.L.; DiNardo, A.; Saavedra, B.; Silva, D.R.; Palmero, D.; Gegia, M.; Migliori, G.B.; Duarte, R.; Mambuque, E.; Centis, R.; et al. Point of care diagnostics for tuberculosis. Pulmonology 2018, 24, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. The Use of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (TB-LAMP) for the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis Policy Guidance; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vassall, A.; van Kampen, S.; Sohn, H.; Michael, J.S.; John, K.R.; Boon, S.D.; Davis, J.L.; Whitelaw, A.; Nicol, M.; Gler, M.T.; et al. Rapid Diagnosis of Tuberculosis with the Xpert MTB/RIF Assay in High Burden Countries: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. PLoS Med. 2011, 8, e1001120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dummer, J.; Storer, M.; Swanney, M.; McEwan, M.; Scott-Thomas, A.; Bhandari, S.; Chambers, S.; Dweik, R.; Epton, M. Analysis of biogenic volatile organic compounds in human health and disease. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drabińska, N.; Flynn, C.; Ratcliffe, N.; Belluomo, I.; Myridakis, A.; Gould, O.; Fois, M.; Smart, A.; Devine, T.; Costello, B.P.J.D.L. A literature survey of all volatiles from healthy human breath and bodily fluids: The human volatilome. J. Breath Res. 2021, 15, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.; Pleil, J.; Beauchamp, J. (Eds.) Breathborne Biomarkers and the Human Volatilome, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobak, C.A.; Kang, L.; Workman, L.; Bateman, L.; Khan, M.S.; Prins, M.; May, L.; Franchina, F.A.; Baard, C.; Nicol, M.P.; et al. Breath can discriminate tuberculosis from other lower respiratory illness in children. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.; Basa-Dalay, V.; Bothamley, G.; Cataneo, R.N.; Lam, P.K.; Natividad, M.P.R.; Schmitt, P.; Wai, J. Breath biomarkers of active pulmonary tuberculosis. Tuberculosis 2010, 90, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beccaria, M.; Mellors, T.R.; Petion, J.S.; Rees, C.A.; Nasir, M.; Systrom, H.K.; Sairistil, J.W.; Jean-Juste, M.-A.; Rivera, V.; Lavoile, K.; et al. Preliminary investigation of human exhaled breath for tuberculosis diagnosis by multidimensional gas chromatography–Time of flight mass spectrometry and machine learning. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1074–1075, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saktiawati, A.M.; Putera, D.D.; Setyawan, A.; Mahendradhata, Y.; van der Werf, T.S. Diagnosis of tuberculosis through breath test: A systematic review. Ebiomedicine 2019, 46, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syhre, M.; Manning, L.; Phuanukoonnon, S.; Harino, P.; Chambers, S. The scent of Mycobacterium tuberculosis–Part II breath. Tuberculosis 2009, 89, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milone, A.; Monteduro, A.G.; Rizzato, S.; Leo, A.; Di Natale, C.; Kim, S.S.; Maruccio, G. Advances in Materials and Technologies for Gas Sensing from Environmental and Food Monitoring to Breath Analysis. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2022, 7, 2200083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilewski, T.; Migoń, D.; Gębicki, J.; Kamysz, W. Critical review of electronic nose and tongue instruments prospects in pharmaceutical analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1077, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüffer, D.; Hoehne, F.; Bühler, J. New Digital Metal-Oxide (MOx) Sensor Platform. Sensors 2018, 18, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzini, I.; Schild, D.; Di Natale, C. Principles of odor coding in vertebrates and artificial chemosensory systems. Physiol. Rev. 2022, 102, 61–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güntner, A.T.; Abegg, S.; Königstein, K.; Gerber, P.A.; Schmidt-Trucksäss, A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Breath Sensors for Health Monitoring. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelli, L.; Taverna, G.; Bellini, A.; Eusebio, L.; Buffi, N.; Lazzeri, M.; Guazzoni, G.; Bozzini, G.; Seveso, M.; Mandressi, A.; et al. Application and Uses of Electronic Noses for Clinical Diagnosis on Urine Samples: A Review. Sensors 2016, 16, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarno, R.; Inoue, S.; Ardani, M.S.H.; Purbawa, D.P.; Sabilla, S.I.; Sungkono, K.R.; Fatichah, C.; Sunaryono, D.; Bakhtiar, A.; Prakoeswa, C.R.; et al. Detection of Infectious Respiratory Disease Through Sweat From Axillary Using an E-Nose With Stacked Deep Neural Network. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 51285–51298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Nogal Sánchez, M.; Callejo Gómez, P.Á.; Pérez Pavón, J.L.; Moreno Cordero, B.; Crisolino Pozas, Á.P.; Sánchez Rodríguez, Á. Sensitivity enhancement in the determination of volatile biomarkers in saliva using a mass spectrometry-based electronic nose with a programmed temperature vaporizer. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 7890–7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capuano, R.; Spitalieri, P.; Talarico, R.V.; Domakoski, A.C.; Catini, A.; Paolesse, R.; Martinelli, E.; Novelli, G.; Sangiuolo, F.; Di Natale, C. A preliminary analysis of volatile metabolites of human induced pluripotent stem cells along the in vitro differentiation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruins, M.; Rahim, Z.; Bos, A.; van de Sande, W.W.; Endtz, H.P.; van Belkum, A. Diagnosis of active tuberculosis by e-nose analysis of exhaled air. Tuberculosis 2013, 93, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, R.C.; Rodríguez, M.; de Romero, N.J.; Bruins, M.; Gómez, R.; Yntema, J.B.; Abente, G.C.; Gerritsen, J.W.; Wiegerinck, W.; Bejerano, D.P.; et al. The potential of a portable, point-of-care electronic nose to diagnose tuberculosis. J. Infect. 2017, 75, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakhleh, M.K.; Jeries, R.; Gharra, A.; Binder, A.; Broza, Y.Y.; Pascoe, M.; Dheda, K.; Haick, H. Detecting active pulmonary tuberculosis with a breath test using nanomaterial-based sensors. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 1522–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetola, N.M.; Modongo, C.; Matsiri, O.; Tamuhla, T.; Mbongwe, B.; Matlhagela, K.; Sepako, E.; Catini, A.; Sirugo, G.; Martinelli, E.; et al. Diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis and assessment of treatment response through analyses of volatile compound patterns in exhaled breath samples. J. Infect. 2017, 74, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosack, C.S.; Page, A.-L.; Klatser, P.R. A guide to aid the selection of diagnostic tests. Bull. World Health Organ. 2017, 95, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Tuberculosis Report 2018; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- D’amico, A.; Pennazza, G.; Santonico, M.; Martinelli, E.; Roscioni, C.; Galluccio, G.; Paolesse, R.; Di Natale, C. An investigation on electronic nose diagnosis of lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2010, 68, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprea, U.; Weimar, A. Gas sensors based on mass-sensitive transducers part 1: Transducers and receptors—Basic understanding. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 1761–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolesse, R.; Nardis, S.; Monti, D.; Stefanelli, M.; Di Natale, C. Porphyrinoids for Chemical Sensor Applications. Chem. Rev. 2016, 117, 2517–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Natale, C.; Gros, C.P.; Paolesse, R. Corroles at work: A small macrocycle for great applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 1277–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparri, R.; Santonico, M.; Valentini, C.; Sedda, G.; Borri, A.; Petrella, F.; Maisonneuve, P.; Pennazza, G.; D’amico, A.; Di Natale, C.; et al. Volatile signature for the early diagnosis of lung cancer. J. Breath Res. 2016, 10, 016007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdocca, M.; Torino, F.; Pucci, S.; Costantini, M.; Capuano, R.; Greggi, C.; Polidoro, C.; Somma, G.; Pasqualetti, V.; Mougang, Y.K.; et al. Urine LOX-1 and Volatilome as Promising Tools towards the Early Detection of Renal Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougang, Y.K.; Di Zazzo, L.; Minieri, M.; Capuano, R.; Catini, A.; Legramante, J.M.; Paolesse, R.; Bernardini, S.; Di Natale, C. Sensor array and gas chromatographic detection of the blood serum volatolomic signature of COVID-19. IScience 2021, 24, 102851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Yoo, J.E.; Han, K.; Choi, W.; Rhee, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Shin, D.W. Body Mass Index, Diabetes, and Risk of Tuberculosis: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 739766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catini, A.; Kumar, R.; Capuano, R.; Martinelli, E.; Paolesse, R.; di Natale, C. An Exploration of the Metal Dependent Selectivity of a Metalloporphyrins Coated Quartz Microbalances Array. Sensors 2016, 16, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sensitive Molecule | |
|---|---|
| 1 | 5,10,15,20-tetrakis-(4-butyloxyphenyl)porphyrinCopper |
| 2 | 5,10,15,20-tetrakis-(4-butyloxyphenyl)porphyrinCobalt |
| 3 | 5,10,15,20-tetrakis-(4-butyloxyphenyl)porphyrinZinc |
| 4 | 5,10,15,20-tetrakis-(4-butyloxyphenyl)porphyrinMagnesium |
| 5 | 5,10,15,20-tetrakis-(4-butyloxyphenyl)porphyrinManganeseChloride |
| 6 | 5,10,15,20-tetrakis-(4-butyloxyphenyl)porphyrin-IronChloride |
| 7 | 5,10,15,20-tetrakis-(4-butyloxyphenyl)porphyrin-TinDichloride |
| 8 | 2,3,7,8,12,13,17,18-octabromo-5,10,15,20-tetraphenylporphyrinH2 |
| 9 | 2,3,7,8,12,13,17,18-octabromo-5,10,15,20-tetraphenylporphyrin oxoMolybdenum |
| 10 | 5,10,15-tris(3,5-dimethylphenyl)corroleCopper |
| 11 | 5,10,15-tris(9-phenantryl)corrole |
| Factor | PTB (#46 Subjects) | HC (38 Subjects) | PTBX (6 Subjects) | NTB (10 Subjects) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (M/F) | 30/16 | 23/15 | 4/2 | 6.82E-012/8 |
| Age (mean, SD) | 36.93 (13.96) | 34.03 (9.90) | 43.5(19.18) | 40.3(10.87) |
| BMI (mean, SD) | 19.511(2.86) | 26.3364 (3.98) | 23.68(5.62) | 25.26(6.76) |
| VIH+ | 8 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| X-ray (positive) | 39 | N/A | 6 | 0 |
| SMEAR (positive) | 18/30 | N/A | 0/6 | 0 |
| C-RP (positive) | 08/11 | N/A | 2/3 | 2/6 |
| Fever | 41 | 0 | 4 | 2 |
| Cough (>2 weeks) | 46 | 0 | 5 | 10 |
| Appetite loss | 45 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Weight loss | ||||
| (2–21 kg) | 33 | 0 | 6 | 6 |
| Night sweats | 40 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Smokers | 9 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| Alcohol drinkers | 20 | 28 | 3 | 2 |
| Recovered | 9 | N/A | 1 | 0 |
| TB history | 17 | N/A | 0 | 3 |
| Diabetic | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MDR (Rifampicin) | 1 | N/A | N/A | 0 |
| Hypertension (HTA) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | AUROC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | 89.8% | 92.6 ± 10% | 87.5 ± 11% | 0.90 |
| Test | 88.0% | 90.8 ± 17% | 85.7 ± 18% | 0.88 |
| PTBX | NTB | |
|---|---|---|
| Predicted as PTB | 5 | 2 |
| Predicted as HC | 1 | 8 |
| Sensor Technology | Sensitivity | Specificity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metal oxide semiconductors | 93.5% | 85.3% | [27] |
| Metal oxide semiconductors | 88.0% | 92.0% | [28] |
| Organic capped gold nanoparticles | 85.0% | 89.0% | [29] |
| Porphyrin-coated QMBs | 94.0% | 90.0% | [30] |
| Porphyrin- and corrole-coated QMBs | 90.8% | 85.7% | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ketchanji Mougang, Y.C.; Endale Mangamba, L.-M.; Capuano, R.; Ciccacci, F.; Catini, A.; Paolesse, R.; Mbatchou Ngahane, H.B.; Palombi, L.; Di Natale, C. On-Field Test of Tuberculosis Diagnosis through Exhaled Breath Analysis with a Gas Sensor Array. Biosensors 2023, 13, 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13050570
Ketchanji Mougang YC, Endale Mangamba L-M, Capuano R, Ciccacci F, Catini A, Paolesse R, Mbatchou Ngahane HB, Palombi L, Di Natale C. On-Field Test of Tuberculosis Diagnosis through Exhaled Breath Analysis with a Gas Sensor Array. Biosensors. 2023; 13(5):570. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13050570
Chicago/Turabian StyleKetchanji Mougang, Yolande Christelle, Laurent-Mireille Endale Mangamba, Rosamaria Capuano, Fausto Ciccacci, Alexandro Catini, Roberto Paolesse, Hugo Bertrand Mbatchou Ngahane, Leonardo Palombi, and Corrado Di Natale. 2023. "On-Field Test of Tuberculosis Diagnosis through Exhaled Breath Analysis with a Gas Sensor Array" Biosensors 13, no. 5: 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13050570
APA StyleKetchanji Mougang, Y. C., Endale Mangamba, L.-M., Capuano, R., Ciccacci, F., Catini, A., Paolesse, R., Mbatchou Ngahane, H. B., Palombi, L., & Di Natale, C. (2023). On-Field Test of Tuberculosis Diagnosis through Exhaled Breath Analysis with a Gas Sensor Array. Biosensors, 13(5), 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13050570








