Bioimpedance Analysis as Early Predictor for Clot Formation Inside a Blood-Perfused Test Chamber: Proof of Concept Using an In Vitro Test-Circuit
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Circuit Design
2.2. Blood Collection from Human Donors and Filling the Circuit
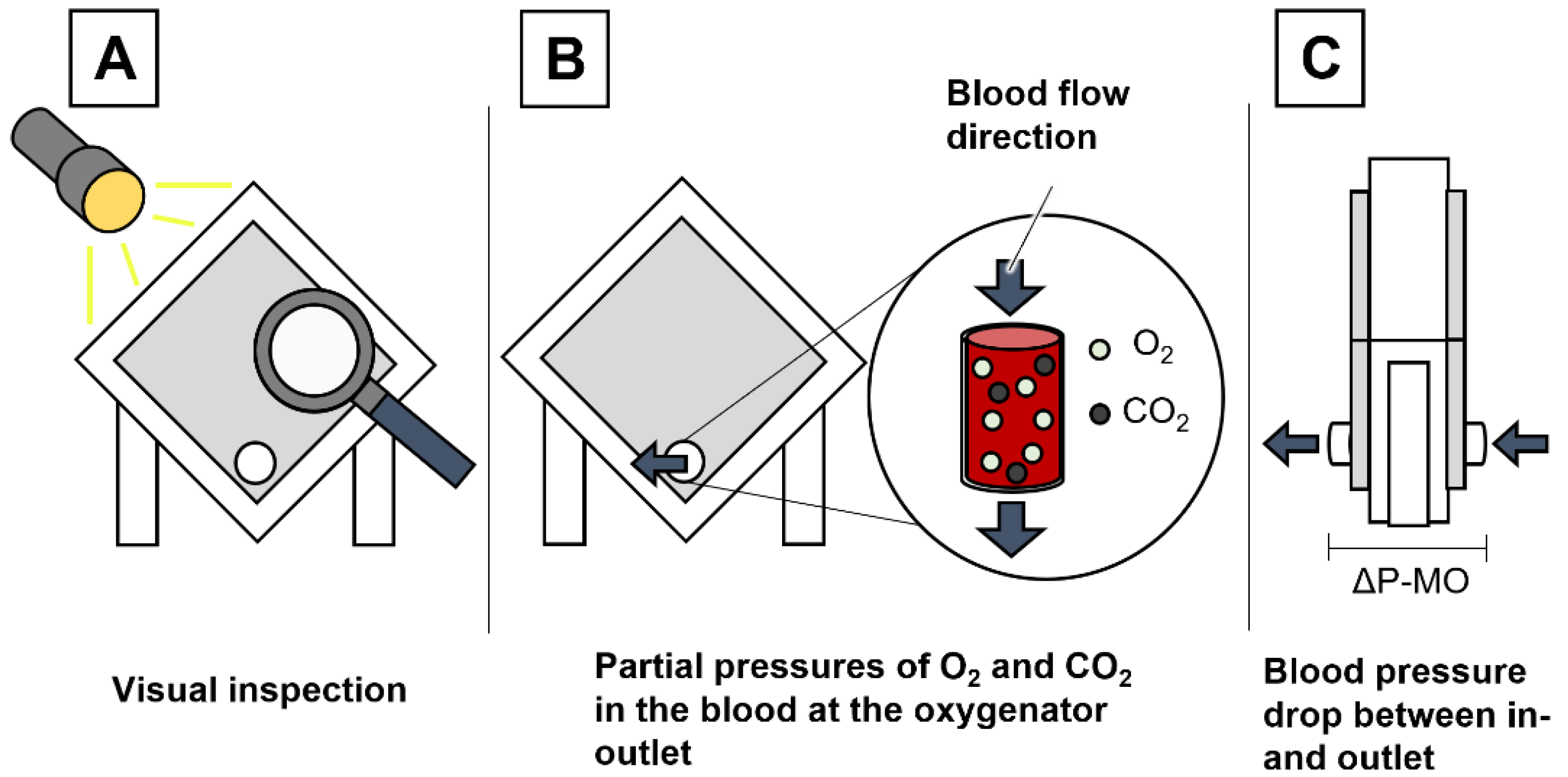
2.3. Pressure Measurement
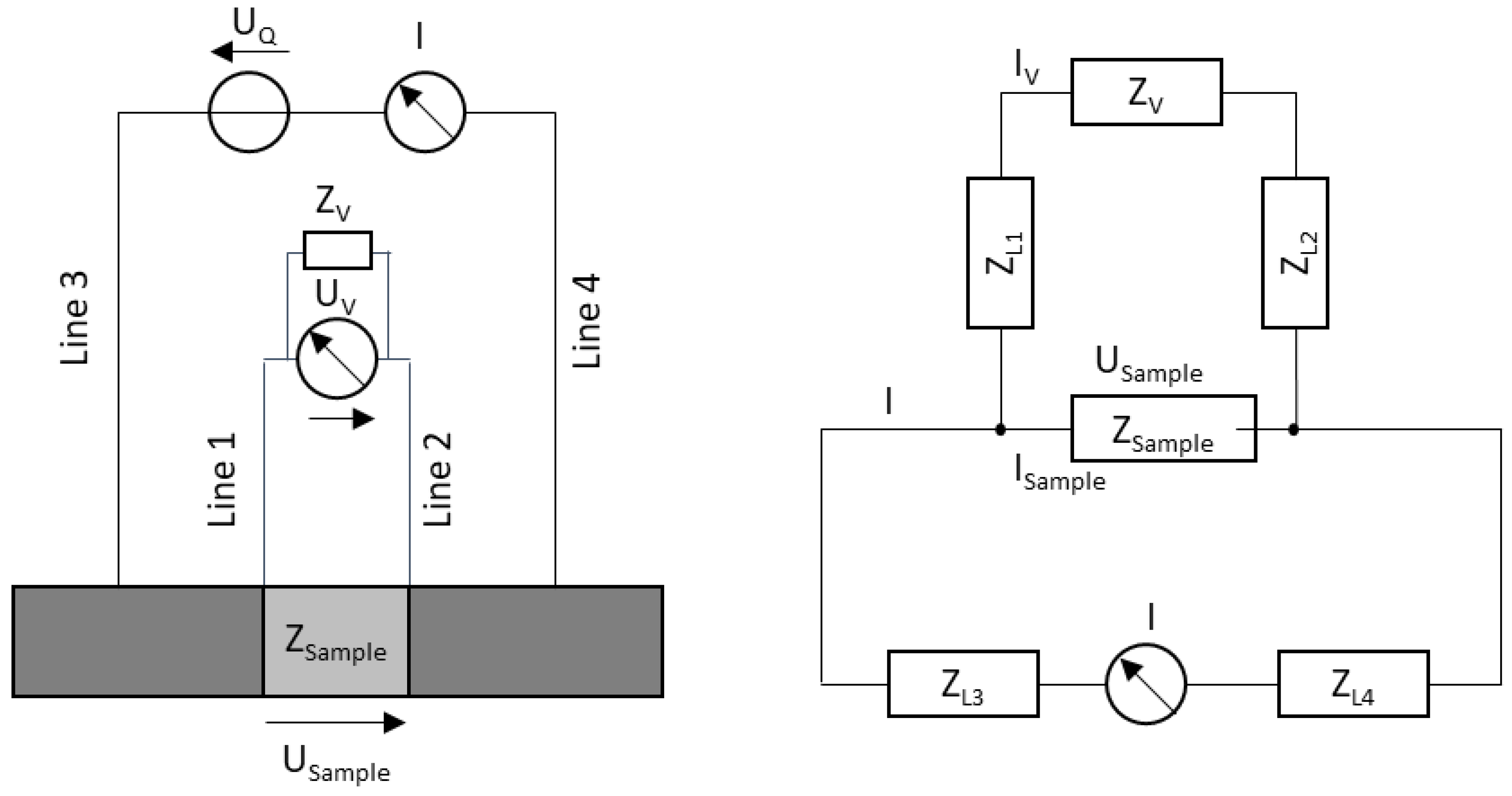
2.4. Fundamentals of Bioimpedance Measurement
2.5. Bioimpedance Measurement
2.6. Experimental Groups
2.7. Experiment Duration and Criteria for Experiment Termination
2.8. Blood Sampling and Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Blood Clot Formation
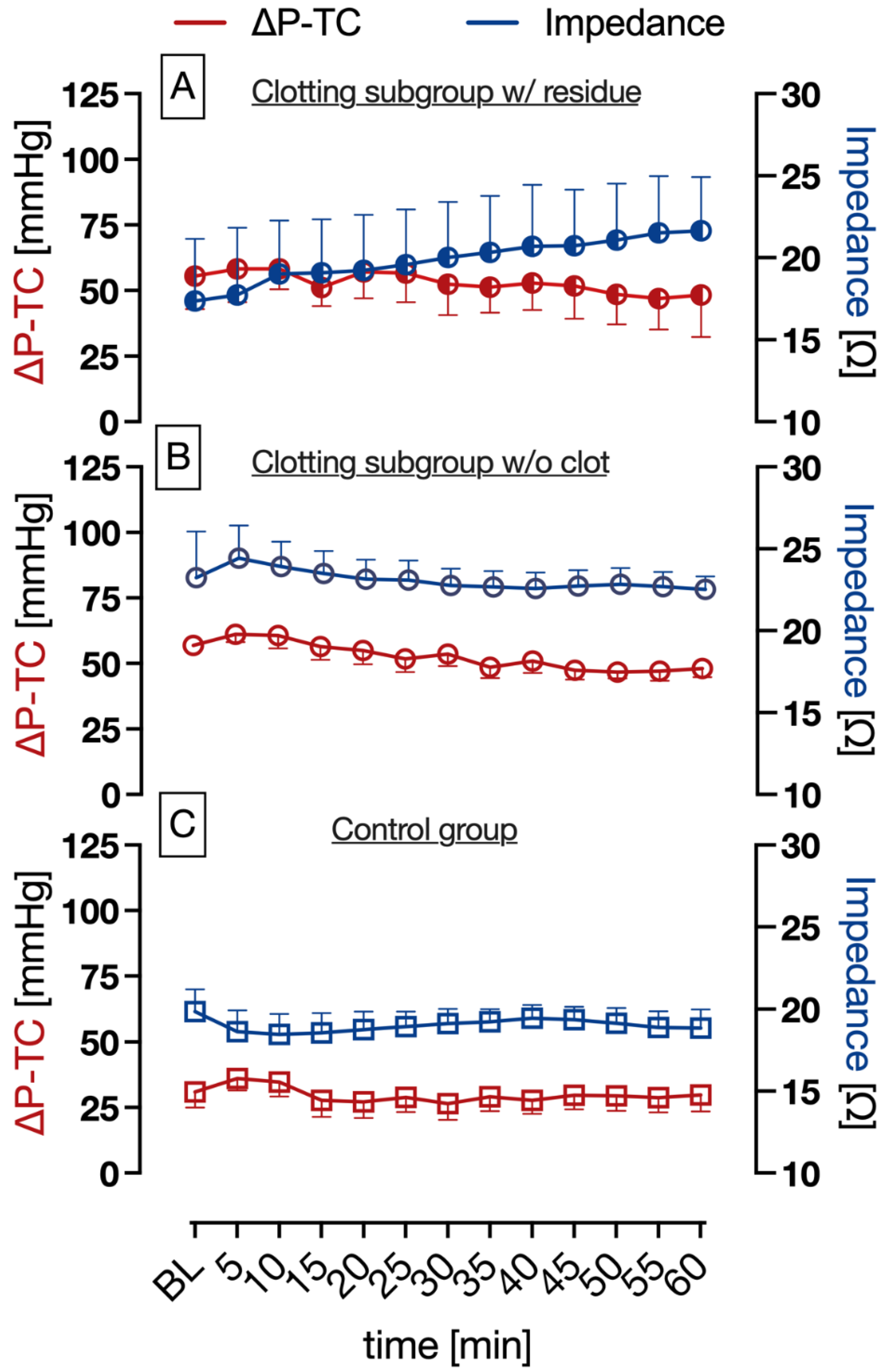
3.2. Pressure and Impedance Measurement
3.3. Platelet Count and β-Thromboglobulin
4. Discussion
4.1. Bioimpedance Analysis and Pressure Difference Measurement (ΔP-TC)
4.2. Coagulation Parameters
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- April, I. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for 2009 Influenza A(H1N1) Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. JAMA 2009, 302, 1888–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaro, R.P.; MacLaren, G.; Boonstra, P.S.; Iwashyna, T.J.; Slutsky, A.S.; Fan, E.; Bartlett, R.H.; Tonna, J.E.; Hyslop, R.; Fanning, J.J.; et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support in COVID-19: An international cohort study of the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization registry. Lancet 2020, 396, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, K.; Shekar, K.; Ling, R.R.; Barbaro, R.P.; Wong, S.N.; Tan, C.S.; Rochwerg, B.; Fernando, S.M.; Takeda, S.; MacLaren, G.; et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnani, I.; Tuazon, D.; Zainab, A.; Uddin, F. The Role and Impact of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Critical Care. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc. J. 2018, 14, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubnow, M.; Philipp, A.; Foltan, M.; Bull Enger, T.; Lunz, D.; Bein, T.; Haneya, A.; Schmid, C.; Riegger, G.; Muller, T.; et al. Technical complications during veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and their relevance predicting a system-exchange--retrospective analysis of 265 cases. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combes, A.; Hajage, D.; Capellier, G.; Demoule, A.; Lavoue, S.; Guervilly, C.; Da Silva, D.; Zafrani, L.; Tirot, P.; Veber, B.; et al. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1965–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, L.; Walkey, A.; Goligher, E.; Pham, T.; Uleryk, E.M.; Fan, E. Venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for acute respiratory distress syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ELSO Live Registry Dashboard of ECMO Patient Data. Available online: https://www.elso.org/registry/elsoliveregistrydashboard.aspx (accessed on 4 March 2023).
- Treml, B.; Breitkopf, R.; Bukumirić, Z.; Bachler, M.; Boesch, J.; Rajsic, S. ECMO Predictors of Mortality: A 10-Year Referral Centre Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaesler, A.; Hesselmann, F.; Zander, M.O.; Schlanstein, P.C.; Wagner, G.; Bruners, P.; Schmitz-Rode, T.; Steinseifer, U.; Arens, J. Technical Indicators to Evaluate the Degree of Large Clot Formation Inside the Membrane Fiber Bundle of an Oxygenator in an In Vitro Setup. Artif. Organs 2019, 43, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domecq, J.P.; Lal, A.; Sheldrick, C.R.; Kumar, V.K.; Boman, K.; Bolesta, S.; Bansal, V.; Harhay, M.O.; Garcia, M.A.; Kaufman, M.; et al. Outcomes of Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 Receiving Organ Support Therapies: The International Viral Infection and Respiratory Illness Universal Study Registry. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp, A.; De Somer, F.; Foltan, M.; Bredthauer, A.; Krenkel, L.; Zeman, F.; Lehle, K. Life span of different extracorporeal membrane systems for severe respiratory failure in the clinical practice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, C.F.; Li, T.; Mishra, V.; Pratt, D.L.; Mohammed, I.S.K.; Kon, Z.N.; Griffith, B.P. Externally visible thrombus partially predicts internal thrombus deposition in extracorporeal membrane oxygenators. Perfusion 2017, 32, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krivitski, N.; Galyanov, G.; Cooper, D.; Said, M.M.; Rivera, O.; Mikesell, G.T.; Rais-Bahrami, K. In vitro and in vivo assessment of oxygenator blood volume for the prediction of clot formation in an ECMO circuit (theory and validation). Perfusion 2018, 33, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaro, R.P.; MacLaren, G.; Boonstra, P.S.; Combes, A.; Agerstrand, C.; Annich, G.; Diaz, R.; Fan, E.; Hryniewicz, K.; Lorusso, R.; et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for COVID-19: Evolving outcomes from the international Extracorporeal Life Support Organization Registry. Lancet 2021, 398, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimnes, S. Bioimpedance and Bioelectricity Basics; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann, S.; Malhotra, A.; Ardelt, G.; Ryschka, M. A high accuracy broadband measurement system for time resolved complex bioimpedance measurements. Physiol. Meas. 2014, 35, 1163–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, Y.; Brun, M.A.; Machida, K.; Nagasawa, M. Principles of dielectric blood coagulometry as a comprehensive coagulation test. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 10072–10079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifuna, M.W.; Koishi, M.; Uemura, T.; Tatekawa, H.; Haneishi, H.; Sapkota, A.; Takei, M. Connector sensors for permittivity-based thrombus monitoring in extracorporeal life support. J. Artif. Organs 2021, 24, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, C.N.; Lima, J.H.C.; Valiev, R.; Meyers, M.A. Biomedical applications of titanium and its alloys. JOM 2008, 60, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidambe, A.T. Biocompatibility of Advanced Manufactured Titanium Implants—A Review. Materials 2014, 7, 8168–8188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, S. Instrumentierung der Bioimpedanzmessung; Springer Vieweg Wiesbaden: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; p. 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlebusch, T. Textilintegrierte Bioimpedanz-Spektroskopie. In Proceedings of the BMT 2010: 44. DGBMT Jahrestagung; 3-Länder-Tagung D-A-CH, Rostock, Germany, 5–8 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Matthie, J.R. Bioimpedance measurements of human body composition: Critical analysis and outlook. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2008, 5, 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfützner, H. Angewandte Biophysik; Springer: Wien, Austria, 2012; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Nacke, T. Messsystem für die impedanzspektroskopische Breitband-Prozessmesstechnik. tm Tech. Mess. 2011, 78, S147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kume, T.; Akasaka, T.; Kawamoto, T.; Ogasawara, Y.; Watanabe, N.; Toyota, E.; Neishi, Y.; Sukmawan, R.; Sadahira, Y.; Yoshida, K. Assessment of coronary arterial thrombus by optical coherence tomography. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 97, 1713–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffer, I.H.; Fredenburgh, J.C.; Hirsh, J.; Weitz, J.I. Medical device-induced thrombosis: What causes it and how can we prevent it? J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13 (Suppl. 1), S72–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annich, G.M. Extracorporeal life support: The precarious balance of hemostasis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13 (Suppl 1), S336–S342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlebowski, M.M.; Baltagi, S.; Carlson, M.; Levy, J.H.; Spinella, P.C. Clinical controversies in anticoagulation monitoring and antithrombin supplementation for ECMO. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, K.L.; Owen, J. Plasma levels of beta-thromboglobulin and platelet factor 4 as indices of platelet activation in vivo. Blood 1981, 57, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidt, J.F.; Allison, P.; Noble, S.; Ashton, J.; Golino, P.; McNatt, J.; Buja, L.M.; Willerson, J.T. Thrombin is an important mediator of platelet aggregation in stenosed canine coronary arteries with endothelial injury. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 84, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrault, C.; Ajzenberg, N.; Legendre, P.; Rastegar-Lari, G.; Meyer, D.; Lopez, J.A.; Baruch, D. Modulation by heparin of the interaction of the A1 domain of Von Willebrand factor with glycoprotein Ib. Blood 1999, 94, 4186–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnersbach, P.; Hosseinnejad, A.; Breuer, T.; Fechter, T.; Jakob, F.; Schwaneberg, U.; Rossaint, R.; Bleilevens, C.; Singh, S. Endogenous Nitric Oxide-Releasing Microgel Coating Prevents Clot Formation on Oxygenator Fibers Exposed to In Vitro Blood Flow. Membranes 2022, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloemen, S.; Hemker, H.C.; Al Dieri, R. Large inter-individual variation of the pharmacodynamic effect of anticoagulant drugs on thrombin generation. Haematologica 2013, 98, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Türkmen, M.; Lauwigi, T.; Fechter, T.; Gries, F.; Fischbach, A.; Gries, T.; Rossaint, R.; Bleilevens, C.; Winnersbach, P. Bioimpedance Analysis as Early Predictor for Clot Formation Inside a Blood-Perfused Test Chamber: Proof of Concept Using an In Vitro Test-Circuit. Biosensors 2023, 13, 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030394
Türkmen M, Lauwigi T, Fechter T, Gries F, Fischbach A, Gries T, Rossaint R, Bleilevens C, Winnersbach P. Bioimpedance Analysis as Early Predictor for Clot Formation Inside a Blood-Perfused Test Chamber: Proof of Concept Using an In Vitro Test-Circuit. Biosensors. 2023; 13(3):394. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030394
Chicago/Turabian StyleTürkmen, Muhammet, Tobias Lauwigi, Tamara Fechter, Fabienne Gries, Anna Fischbach, Thomas Gries, Rolf Rossaint, Christian Bleilevens, and Patrick Winnersbach. 2023. "Bioimpedance Analysis as Early Predictor for Clot Formation Inside a Blood-Perfused Test Chamber: Proof of Concept Using an In Vitro Test-Circuit" Biosensors 13, no. 3: 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030394
APA StyleTürkmen, M., Lauwigi, T., Fechter, T., Gries, F., Fischbach, A., Gries, T., Rossaint, R., Bleilevens, C., & Winnersbach, P. (2023). Bioimpedance Analysis as Early Predictor for Clot Formation Inside a Blood-Perfused Test Chamber: Proof of Concept Using an In Vitro Test-Circuit. Biosensors, 13(3), 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030394






