Impedimetric Sensing: An Emerging Tool for Combating the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
1. Introduction
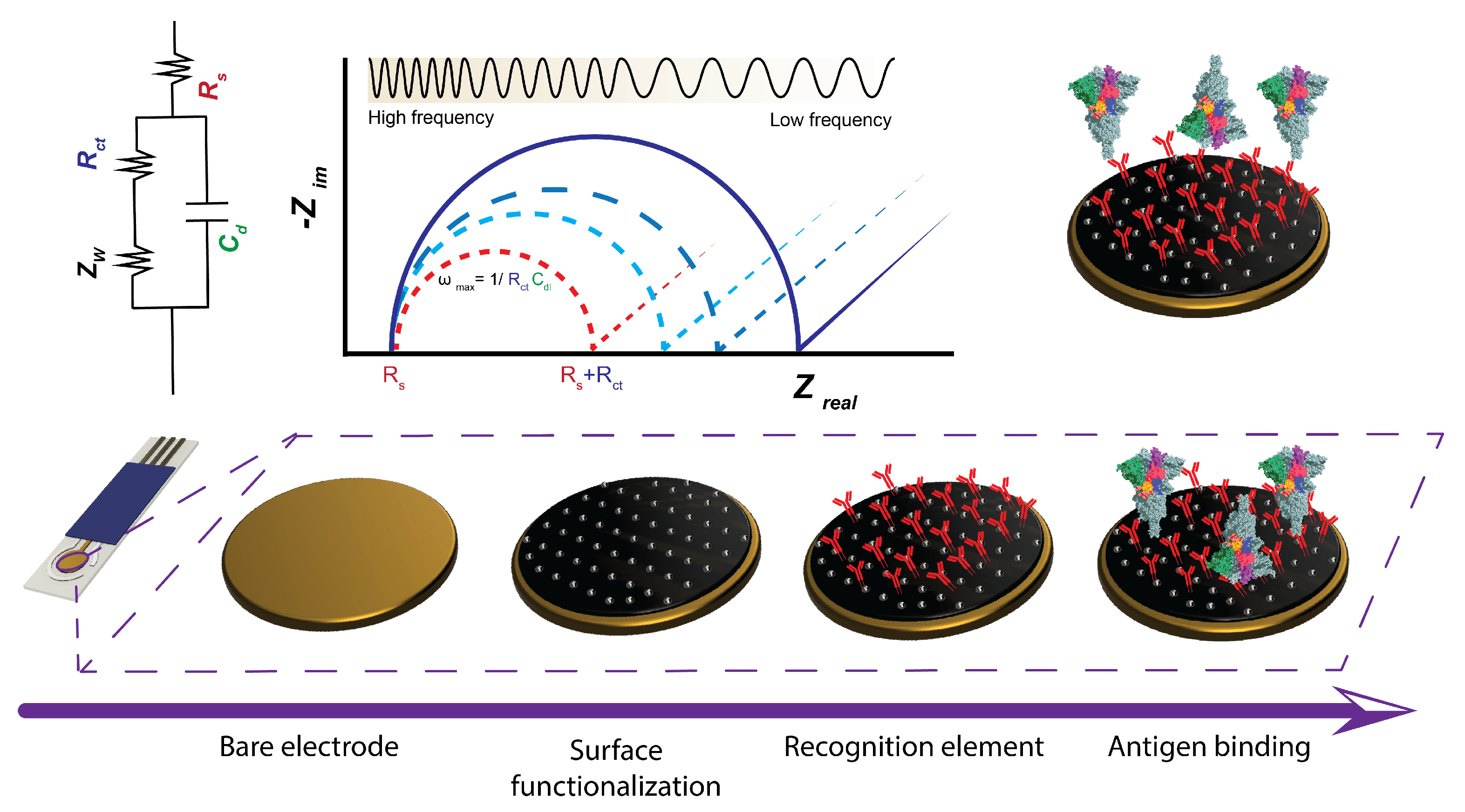
2. Theoretical Considerations in Impedimetric Sensing
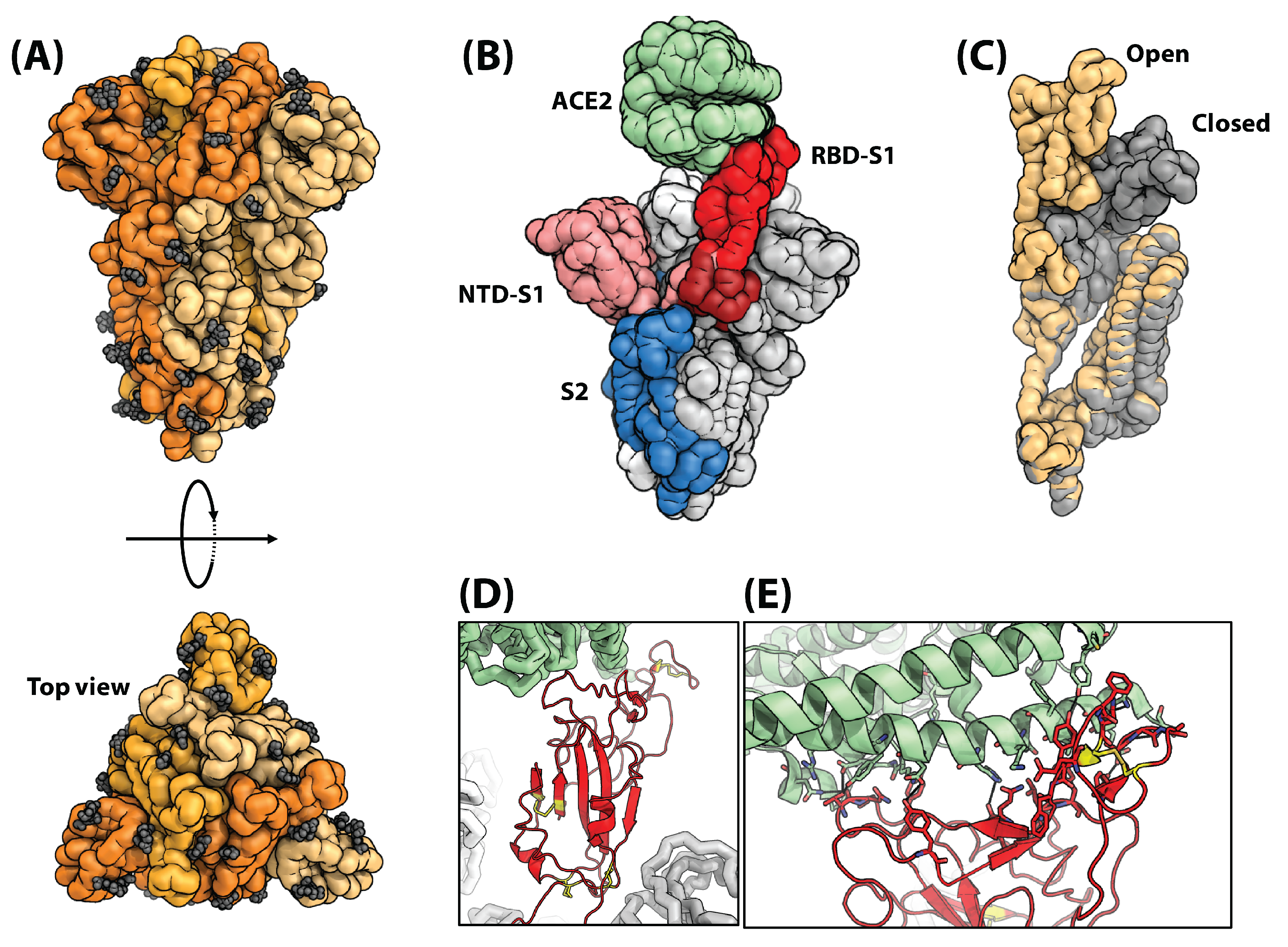
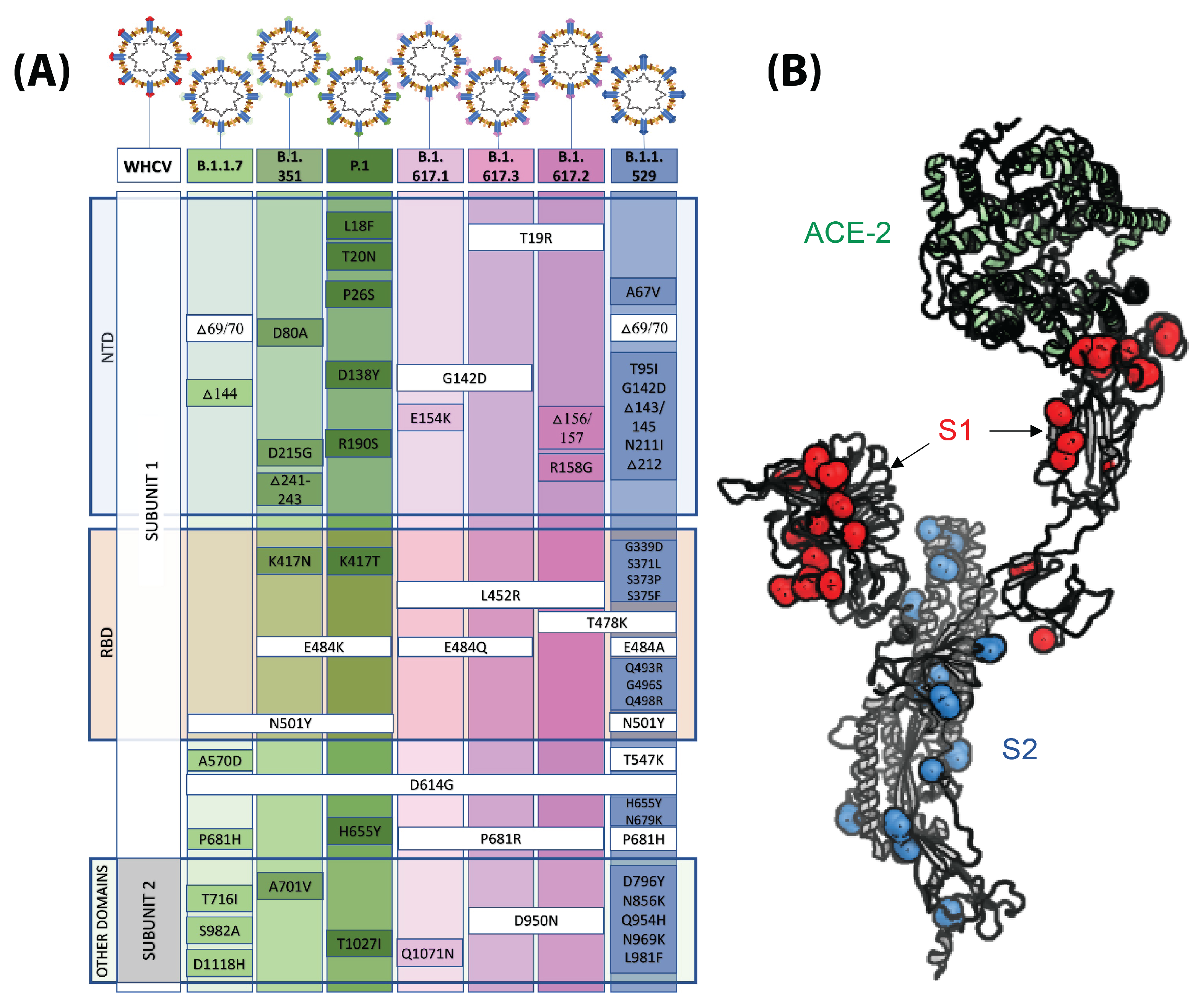
3. SARS-CoV-2 Anatomy
4. Electrode Design
4.1. Electrode Materials
4.2. Electrode Form Factors
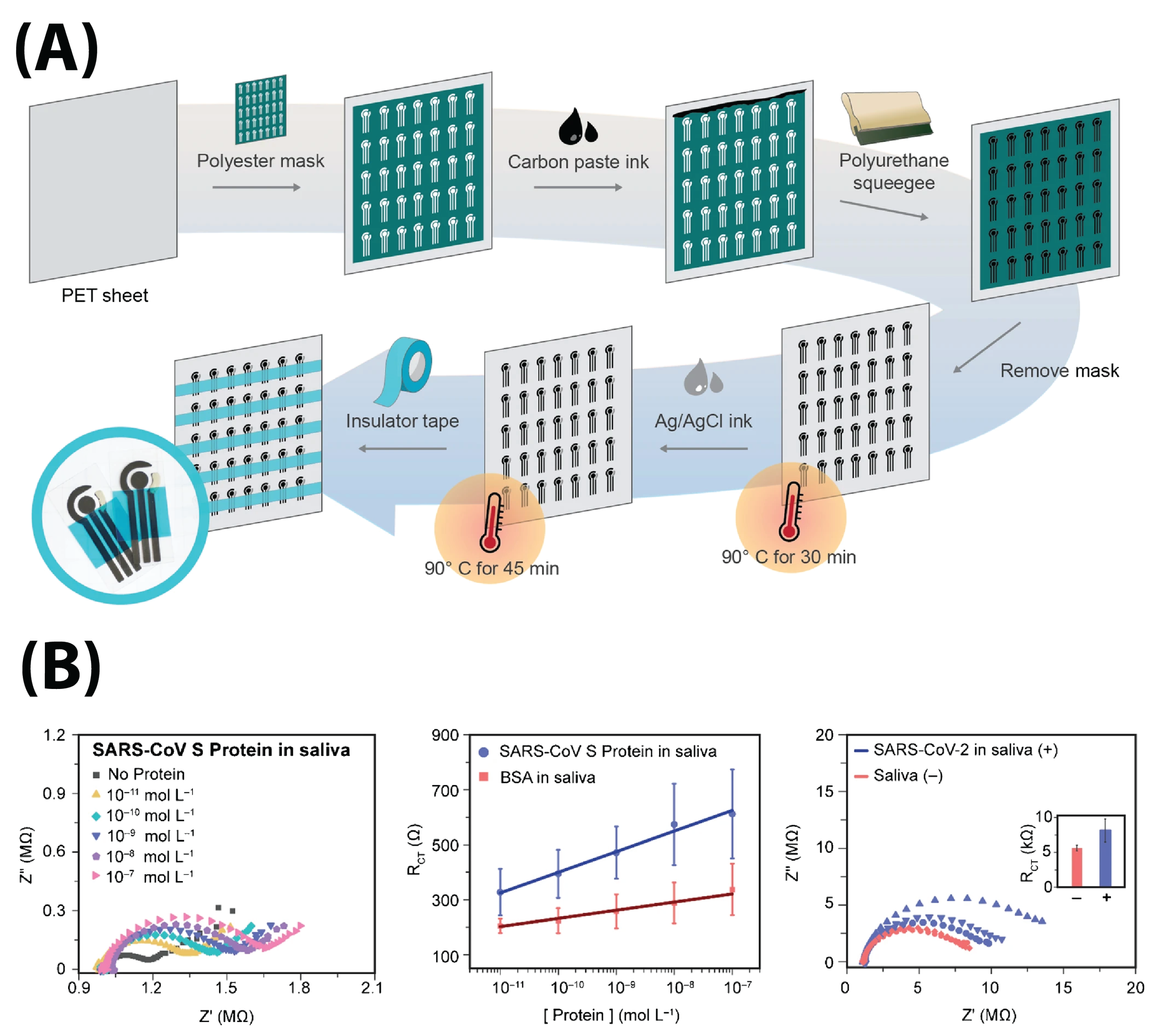
4.2.1. Commercial Screen-Printed Electrodes
4.2.2. Self-Designed Electrodes
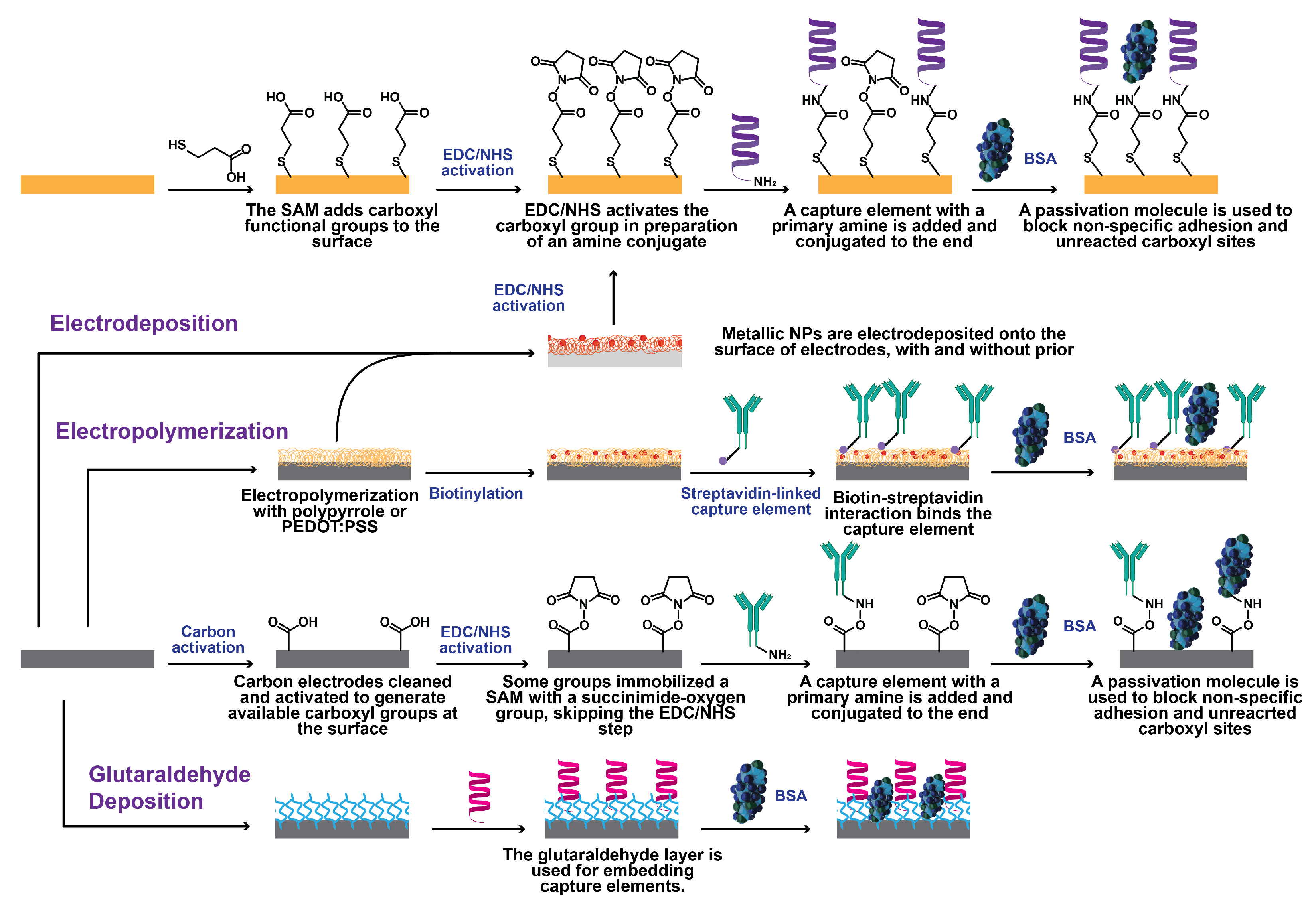
4.3. Immobilization Protocols
4.4. Sample Volume
5. Electrical Detectors and Detection Parameters
6. Analyte Detection
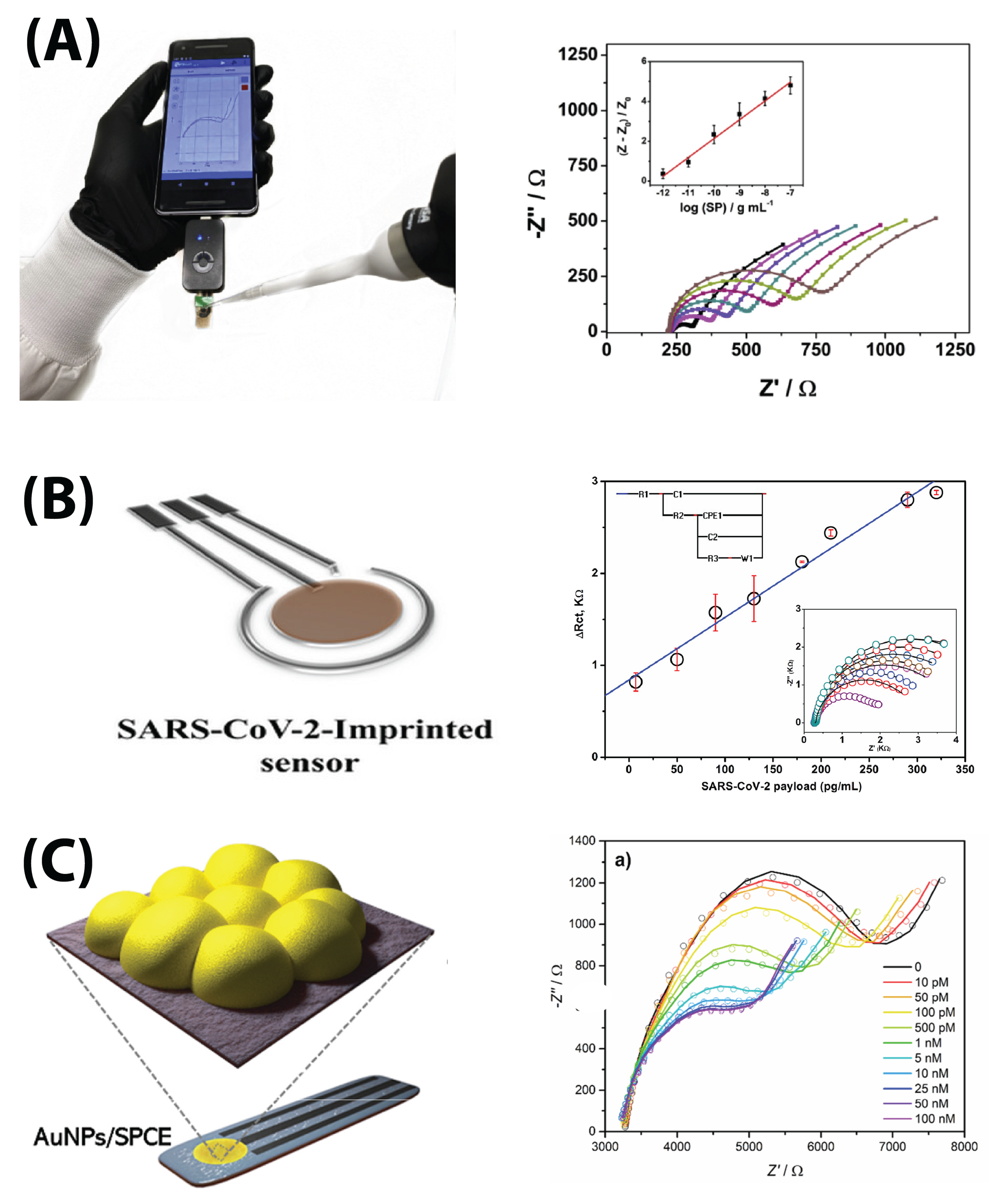
6.1. S Protein Detection
6.2. RBD Detection
6.3. N-Protein Detection
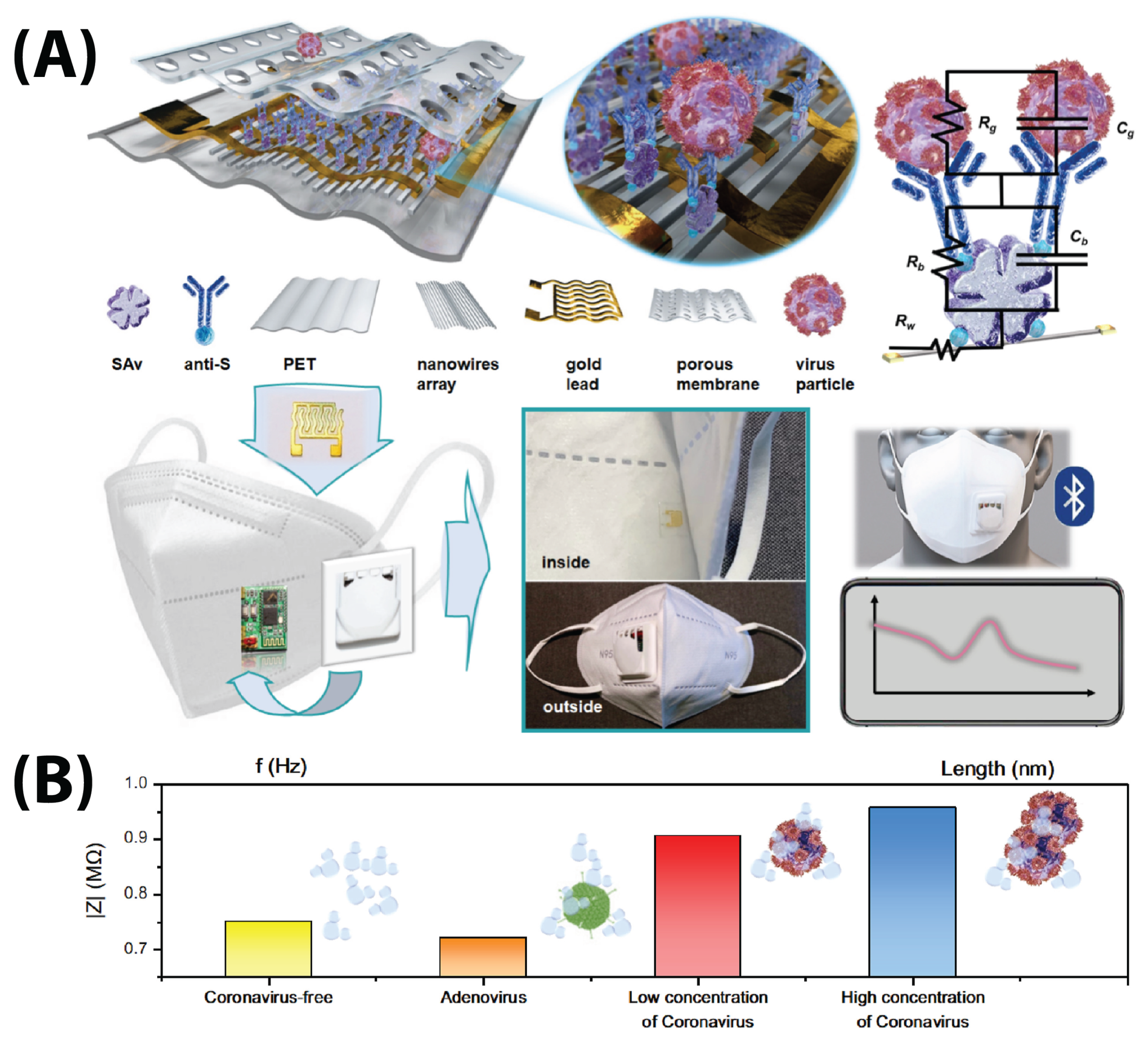
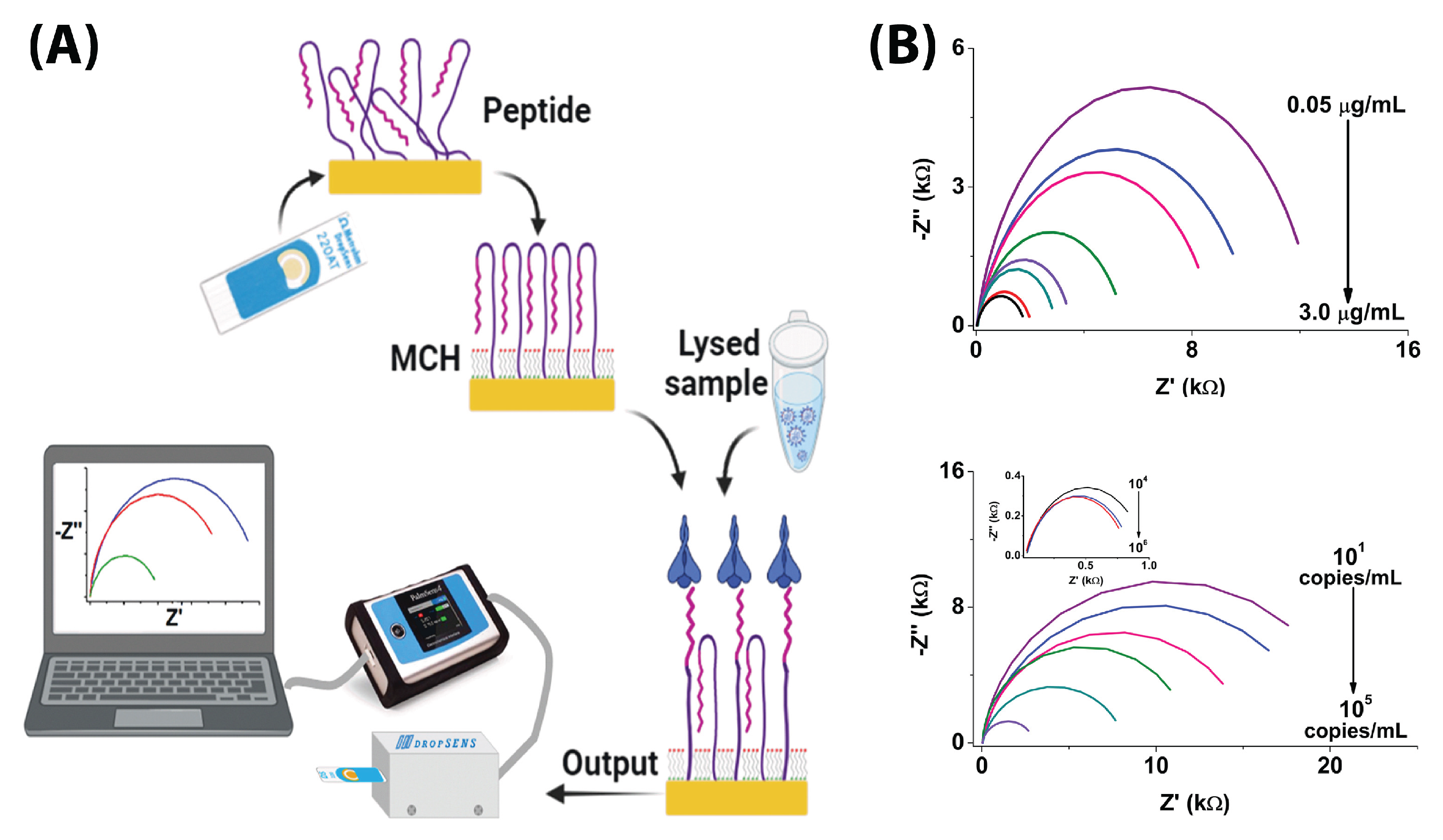
6.4. Whole-Virus Detection
6.5. Antibody Tests
7. Practical Considerations
7.1. Shelf-Life
7.2. Reproducibility
7.3. Measurement Buffer
7.4. Antifouling
8. Summary and Future Perspectives
8.1. Summary
8.2. Standardization
8.3. Novel Form Factors
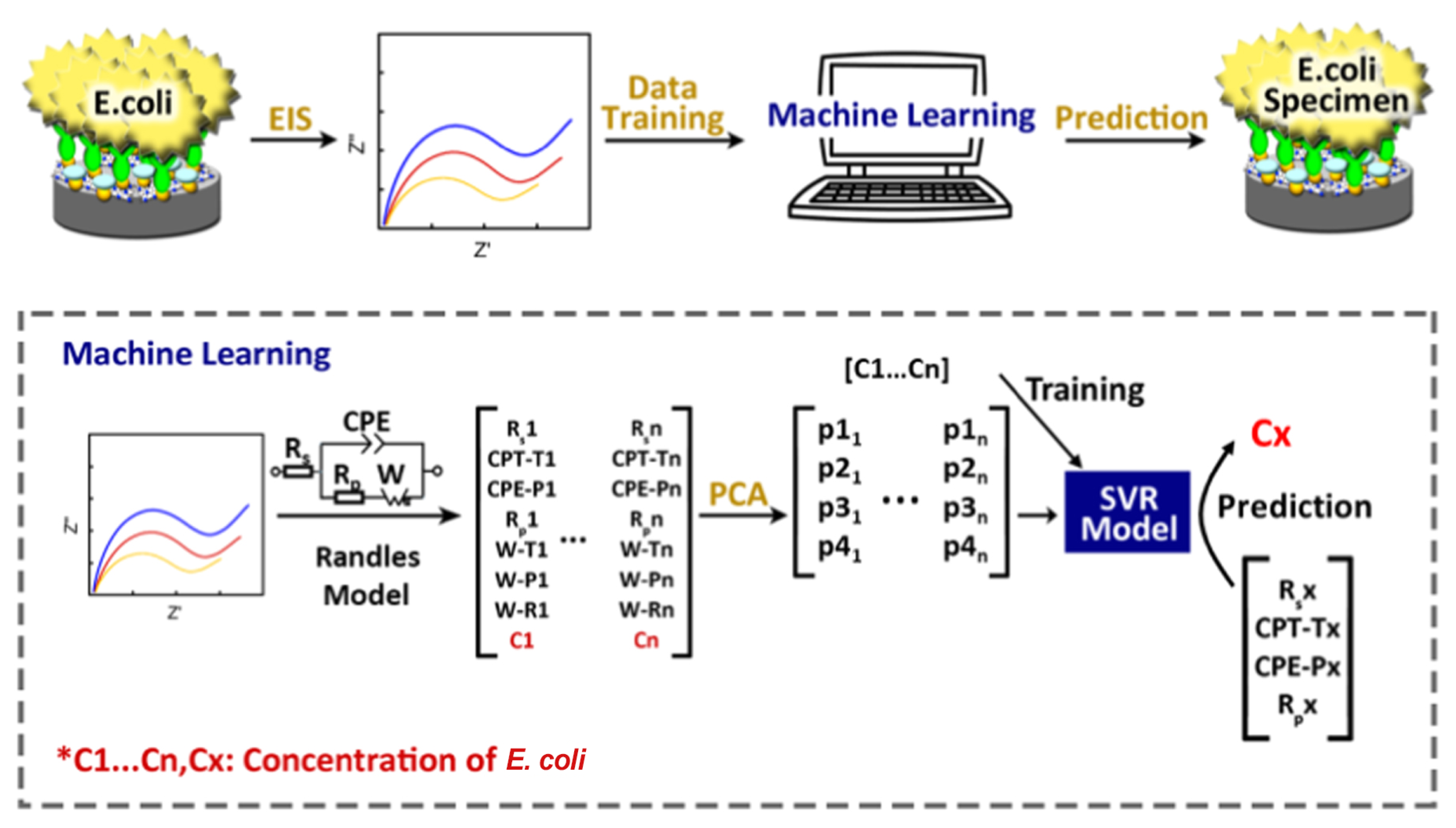
8.4. Novel Data-Analysis Tools
8.5. Novel Capture Probes and Variant Detection
8.6. Final Comments
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muntadas, M.V.; Sunyer, I.A.; Garcia-Navarro, A.A. COVID-19 diagnostic tests: Importance of the clinical context. Med. Clínica 2021, 157, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemon, S.M.; Hamburg, M.A.; Sparling, P.F.; Choffnes, E.R.; Mack, A. Global Infectious Disease Surveillance and Detection: Assessing the Challenges. In Finding Solutions: Workshop Summary; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; p. 285. [Google Scholar]
- Eubank, S.; Guclu, H.; Anil Kumar, V.S.; Marathe, M.V.; Srinivasan, A.; Toroczkai, Z.; Wang, N. Modelling disease outbreaks in realistic urban social networks. Nature 2004, 429, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paltiel, A.D.; Zheng, A.; Walensky, R.P. Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 Screening Strategies to Permit the Safe Reopening of College Campuses in the United States. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2016818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jegerlehner, S.; Suter-Riniker, F.; Jent, P.; Bittel, P.; Nagler, M. Diagnostic accuracy of a SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test in real-life clinical settings. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 109, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordbar, M.M.; Samadinia, H.; Sheini, A.; Aboonajmi, J.; Sharghi, H.; Hashemi, P.; Khoshsafar, H.; Ghanei, M.; Bagheri, H. A colorimetric electronic tongue for point-of-care detection of COVID-19 using salivary metabolites. Talanta 2022, 246, 123537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, B.D.; Cennamo, M.; Minopoli, A.; Campanile, R.; Censi, S.B.; Terracciano, D.; Portella, G.; Velotta, R. Colorimetric Test for Fast Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Nasal and Throat Swabs. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3043–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkourani, G.; Brouzgou, A.; Archonti, M.; Papandrianos, N.; Song, S.; Tsiakaras, P. Emerging materials for the electrochemical detection of COVID-19. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 893, 115289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazaca, L.C.; Imamura, A.H.; Gomes, N.O.; Almeida, M.B.; Scheidt, D.T.; Raymundo-Pereira, P.A.; Oliveira, O.N.; Janegitz, B.C.; Machado, S.A.S.; Carrilho, E. Electrochemical immunosensors using electrodeposited gold nanostructures for detecting the S proteins from SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 5507–5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesewski, E.; Johnson, B.N. Electrochemical biosensors for pathogen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 159, 112214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobysh, M.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Viter, R.; Chen, C.F.; Samukaite-Bubniene, U.; Ratautaite, V.; Ramanavicius, A. Biosensors for the Determination of SARS-CoV-2 Virus and Diagnosis of COVID-19 Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Shetti, N.P.; Jagannath, S.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Electrochemical sensors for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 virus. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limsakul, P.; Charupanit, K.; Moonla, C.; Jeerapan, I. Advances in emergent biological recognition elements and bioelectronics for diagnosing COVID-19. Emergent Mater. 2021, 4, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, T.; Cardoso, A.R.; Sousa, C.E.A.; Marques, A.C.; Tavares, A.P.M.; Matos, A.M.; Cruz, M.T.; Moreira, F.T.C.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E.; et al. Paper-Based Biosensors for COVID-19: A Review of Innovative Tools for Controlling the Pandemic. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 29268–29290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pishva, P.; Yüce, M. Nanomaterials to tackle the COVID-19 pandemic. Emergent Mater. 2021, 4, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, B.A.; Al Mashhadany, Y.; Hafiz Mokhtar, M.H.; Dzulkefly Bin Zan, M.S.; Arsad, N. An Analysis Review of Detection Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Based on Biosensor Application. Sensors 2020, 20, 6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianeselli, L.; Grenci, G.; Callegari, C.; Tormen, M.; Casalis, L. Development of stable and reproducible biosensors based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy: Three-electrode versus two-electrode setup. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 55, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.U.; Chatterjee, S.; Lone, S.A.; Ho, H.H.; Kaswan, K.; Peringeth, K.; Khan, A.; Chiang, Y.W.; Lee, S.; Lin, Z.H. Advanced wearable biosensors for the detection of body fluids and exhaled breath by graphene. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataide, V.N.; Mendes, L.F.; Gama, L.I.L.M.; de Araujo, W.R.; Paixão, T.R.L.C. Electrochemical paper-based analytical devices: Ten years of development. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 1030–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, D.L.; Wilson, W.C.; Nguyen, C.; Yao, Q.W.; Caiazzo, R.J.; Talpasanu, I.; Dow, D.E.; Liu, B.C. Microelectrical sensors as emerging platforms for protein biomarker detection in point-of-care diagnostics. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2009, 9, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Yuan, Y.; Nag, A.; Feng, S.; Afsarimanesh, N.; Han, T.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Organ, D.R. A Review on the Use of Impedimetric Sensors for the Inspection of Food Quality. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbek, O.; Berkel, C. Recent advances in potentiometric analysis: Paper-based devices. Sens. Int. 2022, 3, 100189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naikoo, G.A.; Arshad, F.; Hassan, I.U.; Awan, T.; Salim, H.; Pedram, M.Z.; Ahmed, W.; Patel, V.; Karakoti, A.S.; Vinu, A. Nanomaterials-based sensors for the detection of COVID-19: A review. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2022, 7, e10305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Entesari, M.; Zamani, M.; Heidarizadeh, M.; Moradi, R.; Khakdan, F.; Rafiei, F. An Insight Into Detection Pathways/Biosensors of Highly Infectious Coronaviruses. Mol. Biotechnol. 2022, 64, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotru, S.; Klimuntowski, M.; Ridha, H.; Uddin, Z.; Askhar, A.A.; Singh, G.; Howlader, M.M.R. Electrochemical sensing: A prognostic tool in the fight against COVID-19. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 136, 116198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saatçi, E.; Natarajan, S. State-of-the-art colloidal particles and unique interfaces-based SARS-CoV-2 detection methods and COVID-19 diagnosis. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 55, 101469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Datta, B.; Ashish, A.; Dutta, G. A comprehensive review on current COVID-19 detection methods: From lab care to point of care diagnosis. Sens. Int. 2021, 2, 100119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benda, A.; Zerajic, L.; Ankita, A.; Cleary, E.; Park, Y.; Pandey, S. COVID-19 Testing and Diagnostics: A Review of Commercialized Technologies for Cost, Convenience and Quality of Tests. Sensors 2021, 21, 6581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasri, S.; Wiwanitkit, V. Sustainable materials and COVID-19 detection biosensor: A brief review. Sens. Int. 2022, 3, 100171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, M.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopic Detection of E.coli with Machine Learning. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 047508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagfeldt, A.; Cappel, U.B.; Boschloo, G.; Sun, L.; Kloo, L.; Pettersson, H.; Gibson, E.A. Chapter IE-1—Dye-Sensitized Photoelectrochemical Cells. In Practical Handbook of Photovoltaics, 2nd ed.; McEvoy, A., Markvart, T., Castañer, L., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 479–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orazem, M.E.; Tribollet, B. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald, J.R.; Johnson, W.B. Fundamentals of Impedance Spectroscopy. In Impedance Spectroscopy; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasia, A. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy and Its Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; p. 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randles, J.E.B. Kinetics of rapid electrode reactions. Faraday Discuss. 1947, 1, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randviir, E.P.; Banks, C.E. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy: An overview of bioanalytical applications. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 1098–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Zhao, R.; Gao, L.J.; Gao, X.F.; Wang, D.P.; Cao, J.M. SARS-CoV-2: Structure, Biology, and Structure-Based Therapeutics Development. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 587269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Du, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.Y.; Qu, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Bao, S.; Li, Y.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1663–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubuk, J.; Alston, J.J.; Incicco, J.J.; Singh, S.; Stuchell-Brereton, M.D.; Ward, M.D.; Zimmerman, M.I.; Vithani, N.; Griffith, D.; Wagoner, J.A.; et al. The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein is dynamic, disordered, and phase separates with RNA. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godet, M.; L’Haridon, R.; Vautherot, J.F.; Laude, H. TGEV corona virus ORF4 encodes a membrane protein that is incorporated into virions. Virology 1992, 188, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, R.; Chaudhary, J.K.; Jain, N.; Chaudhary, P.K.; Khanra, S.; Dhamija, P.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, A.; Handu, S. Role of Structural and Non-Structural Proteins and Therapeutic Targets of SARS-CoV-2 for COVID-19. Cells 2021, 10, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeman, D.; Fielding, B.C. Coronavirus envelope protein: Current knowledge. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Q. Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2. Science 2020, 367, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, T.; Lauc, G.; Trbojević-Akmačić, I. The Importance of Glycosylation in COVID-19 Infection. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1325, 239–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liang, Q.; He, X.; Zhao, C.; Ren, W.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ding, Q.; Deng, H.; Wang, T.; et al. Loss of Spike N370 glycosylation as an important evolutionary event for the enhanced infectivity of SARS-CoV-2. Cell Res. 2022, 32, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabara, S.M.; Serdan, T.D.A.; Gorjao, R.; Masi, L.N.; Pithon-Curi, T.C.; Covas, D.T.; Curi, R.; Durigon, E.L. SARS-COV-2 Variants: Differences and Potential of Immune Evasion. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 11, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benton, D.J.; Wrobel, A.G.; Xu, P.; Roustan, C.; Martin, S.R.; Rosenthal, P.B.; Skehel, J.J.; Gamblin, S.J. Receptor binding and priming of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 for membrane fusion. Nature 2020, 588, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrego-Martinez, J.C.; Jafari, M.; Chergui, S.; Pavel, C.; Che, D.; Siaj, M. Aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2: Nanoscale electrode-aptamer-SARS-CoV-2 imaging by photo-induced force microscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 195, 113595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.A.; Hu, C.; Jahan, S.; Yuan, B.; Saleh, M.S.; Ju, E.; Gao, S.J.; Panat, R. Sensing of COVID-19 Antibodies in Seconds via Aerosol Jet Nanoprinted Reduced-Graphene-Oxide-Coated 3D Electrodes. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashur, I.; Alter, J.; Werbner, M.; Ogungbile, A.; Dessau, M.; Gal-Tanamy, M.; Vernick, S. Rapid electrochemical immunodetection of SARS-CoV-2 using a pseudo-typed vesicular stomatitis virus model. Talanta 2022, 239, 123147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avelino, K.Y.; dos Santos, G.S.; Frías, I.A.; Silva-Junior, A.G.; Pereira, M.C.; Pitta, M.G.; de Araújo, B.C.; Errachid, A.; Oliveira, M.D.; Andrade, C.A. Nanostructured sensor platform based on organic polymer conjugated to metallic nanoparticle for the impedimetric detection of SARS-CoV-2 at various stages of viral infection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 206, 114392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsan, M.A.; Khan, S.A.; Rehman, A. Screen-Printed Graphene/Carbon Electrodes on Paper Substrates as Impedance Sensors for Detection of Coronavirus in Nasopharyngeal Fluid Samples. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL Sharif, H.; Dennison, S.; Tully, M.; Crossley, S.; Mwangi, W.; Bailey, D.; Graham, S.; Reddy, S. Evaluation of electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymers (E-MIPs) on disposable electrodes for detection of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1206, 339777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.A.; Kandeil, A.; Gomaa, M.; Mohamed El Nashar, R.; El-Sherbiny, I.M.; Hassan, R.Y.A. SARS-CoV-2-Impedimetric Biosensor: Virus-Imprinted Chips for Early and Rapid Diagnosis. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 4098–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasserre, P.; Balansethupathy, B.; Vezza, V.J.; Butterworth, A.; Macdonald, A.; Blair, E.O.; McAteer, L.; Hannah, S.; Ward, A.C.; Hoskisson, P.A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Aptasensors Based on Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy and Low-Cost Gold Electrode Substrates. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 2126–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qin, Z.; Fu, H.; Li, T.; Peng, R.; Li, Z.; Rini, J.M.; Liu, X. Enhancing the performance of paper-based electrochemical impedance spectroscopy nanobiosensors: An experimental approach. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 177, 112672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzen, A.L.; dos Santos, A.M.; dos Santos, L.P.; da Silva Pinto, L.; Conceição, F.R.; Wolfart, F. PEDOT-AuNPs-based impedimetric immunosensor for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 404, 139757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoliche, C.Y.N.; Pascon, A.M.; Bezerra, Í.R.S.; de Castro, A.C.H.; Martos, G.R.; Bettini, J.; Alves, W.A.; Santhiago, M.; Lima, R.S. In Situ Nanocoating on Porous Pyrolyzed Paper Enables Antibiofouling and Sensitive Electrochemical Analyses in Biological Fluids. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 2522–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdomo, S.A.; Ortega, V.; Jaramillo-Botero, A.; Mancilla, N.; Mosquera-DeLaCruz, J.H.; Valencia, D.P.; Quimbaya, M.; Contreras, J.D.; Velez, G.E.; Loaiza, O.A.; et al. SenSARS: A Low-Cost Portable Electrochemical System for Ultra-Sensitive, Near Real-Time, Diagnostics of SARS-CoV-2 Infections. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pola, C.C.; Rangnekar, S.V.; Sheets, R.; Szydłowska, B.M.; Downing, J.R.; Parate, K.W.; Wallace, S.G.; Tsai, D.; Hersam, M.C.; Gomes, C.L.; et al. Aerosol-jet-printed graphene electrochemical immunosensors for rapid and label-free detection of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva. 2D Mater. 2022, 9, 035016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, D.; Orozco, J. Peptide-based simple detection of SARS-CoV-2 with electrochemical readout. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1205, 339739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepeli Büyüksünetçi, Y.; Çitil, B.E.; Anık, Ü. An impedimetric approach for COVID-19 detection. Analyst 2022, 147, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.D.; de Lima, L.F.; Ferreira, A.L.; de Araujo, W.R.; Callahan, P.; Dávila, A.; Abella, B.S.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 with RAPID: A prospective cohort study. iScience 2022, 25, 104055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.C.; Chiang, Y.H.; Chiang, H.Y. A Label-Free Electrochemical Impedimetric Immunosensor with Biotinylated-Antibody for SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein Detection in Saliva. Biosensors 2022, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccariotto, G.C.; Silva, M.K.L.; Rocha, G.S.; Cesarino, I. A Novel Method for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Based on Graphene-Impedimetric Immunosensor. Materials 2021, 14, 4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.C.; Soares, A.C.; Angelim, M.K.S.; Proença-Modena, J.L.; Moraes-Vieira, P.M.; Mattoso, L.H.; Oliveira Jr, O.N. Diagnostics of SARS-CoV-2 infection using electrical impedance spectroscopy with an immunosensor to detect the spike protein. Talanta 2022, 239, 123076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, S.; Gopinath, S.C.; Ismail, Z.H.; Md Arshad, M.; Poopalan, P. Aptasensing nucleocapsid protein on nanodiamond assembled gold interdigitated electrodes for impedimetric SARS-CoV-2 infectious disease assessment. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 197, 113735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashed, M.Z.; Kopechek, J.A.; Priddy, M.C.; Hamorsky, K.T.; Palmer, K.E.; Mittal, N.; Valdez, J.; Flynn, J.; Williams, S.J. Rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies using electrochemical impedance-based detector. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Q.; Kan, X.; Pan, Z.; Li, Z.; Pan, W.; Zhou, F.; Duan, X. An intelligent face mask integrated with high density conductive nanowire array for directly exhaled coronavirus aerosols screening. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 186, 113286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, M.D.; de Araujo, W.R.; de Lima, L.F.; Ferreira, A.L.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C. Low-cost biosensor for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 at the point of care. Matter 2021, 4, 2403–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahandish, R.; Haghayegh, F.; Ayala-Charca, G.; Hyun, J.E.; Khalghollah, M.; Zare, A.; Far, B.; Berenger, B.M.; Niu, Y.D.; Ghafar-Zadeh, E.; et al. Bi-ECDAQ: An electrochemical dual-immuno-biosensor accompanied by a customized bi-potentiostat for clinical detection of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid proteins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 203, 114018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, L.k.; Kayser, S.v.C.; Strong, S.A.; Lavin, J.M. High Resolution Aerosol Jet Printed Components with Electrodeposition-Enhanced Conductance. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 047001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavanelli, N.; Yeo, W.H. Advances in Screen Printing of Conductive Nanomaterials for Stretchable Electronics. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 9344–9351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, E.; Rathi, R.; Misharwal, J.; Sinhmar, B.; Kumari, S.; Dalal, J.; Kumar, A. Evolution in Lithography Techniques: Microlithography to Nanolithography. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoki, P.N.; Lim, I.I.S.; Mott, D.; Park, H.Y.; Khan, B.; Mishra, S.; Sujakumar, R.; Luo, J.; Zhong, C.J. Size Correlation of Optical and Spectroscopic Properties for Gold Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 14664–14669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, S.M.; Pinzón, E.F.; Meléndez, A.M.; Mendez-Sanchez, S.; Miranda, D.A. Electrode cleaning and reproducibility of electrical impedance measurements of HeLa cells on aqueous solution. Revista de la Academia Colombiana de Ciencias Exactas Físicas y Naturales 2020, 44, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Pradel, A.; Ribes, M.; Record, M.C. A voltammetric study of the underpotential deposition of cobalt and antimony on gold. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 724, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalhal, R.F.; Sanches Freire, R.; Kubota, L.T. Polycrystalline Gold Electrodes: A Comparative Study of Pretreatment Procedures Used for Cleaning and Thiol Self-Assembly Monolayer Formation. Electroanalysis 2005, 17, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, J.H.; Strauss, E.G. The Structure of Viruses. In Viruses and Human Disease; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaz, D.V.; Goldoni, R.; Tartaglia, G.M.; Malitesta, C.; Mazzotta, E. Effect of Recombinant Antibodies and MIP Nanoparticles on the Electrical Behavior of Impedimetric Biorecognition Surfaces for SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein: A Short Report. Electrochem 2022, 3, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.J.; Ferhan, A.R.; Jackman, J.A.; Cho, N.J. Conformational flexibility of fatty acid-free bovine serum albumin proteins enables superior antifouling coatings. Commun. Mater. 2020, 1, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, T.M. Machine Learning; McGraw-hill: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kwekha-Rashid, A.S.; Abduljabbar, H.N.; Alhayani, B. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) cases analysis using machine-learning applications. Appl. Nanosci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Sun, X.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, N.; Sha, J. Equivalent circuit model recognition of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy via machine learning. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 855, 113627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Stimming, U.; Lee, A.A. Identifying degradation patterns of lithium ion batteries from impedance spectroscopy using machine learning. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belayadi, A.; Mougari, A.; Zabat, M. Modeling of electrochemical properties of potential-induced defects in butane-thiol SAMs by using artificial neural network and impedance spectroscopy data. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2019, 23, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjimi, S.; Belayadi, A.; Zabat, M.; Mougari, A.; Khemici, M.W. Impedance Spectroscopy and Neurocomputing Approaches to Investigate the Enhanced Electrical Blocking Properties of CH3(CH2)n–1SH Thin Monolayers Electrodeposited on a Gold Electrode. J. Electron. Mater. 2019, 48, 3908–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, R. Overcoming the Bottleneck in COVID-19 Detection: A Machine-Learning Approach to Improve Accuracy of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) Detection Sensitivity. Open Access J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 2, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalmuanawma, S.; Hussain, J.; Chhakchhuak, L. Applications of machine learning and artificial intelligence for Covid-19 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic: A review. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 139, 110059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynants, L.; Van Calster, B.; Collins, G.S.; Riley, R.D.; Heinze, G.; Schuit, E.; Albu, E.; Arshi, B.; Bellou, V.; Bonten, M.M.J.; et al. Prediction models for diagnosis and prognosis of COVID-19: Systematic review and critical appraisal. BMJ 2020, 369, m1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syeda, H.B.; Syed, M.; Sexton, K.W.; Syed, S.; Begum, S.; Syed, F.; Prior, F.; Yu Jr, F. Role of Machine Learning Techniques to Tackle the COVID-19 Crisis: Systematic Review. JMIR Med. Inform. 2021, 9, e23811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, D.; Agrawal, A.; Maiti, S. Rapid identification and tracking of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Lancet 2021, 397, 1346–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Fabrication Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Aerosol jet printing |
|
|
| Electrodeposition |
|
|
| Electropolymerization |
|
|
| Flatbed microprinter |
|
|
| Hydrothermal wire growth |
|
|
| Pyrolization |
|
|
| Photolithography |
|
|
| Screen Printing |
|
|
| Electrode Type | Working Electrode | Sample Volume | Response Time | Analyte | Capture Element | Linear Range | Detection Limit | Real Sample | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fully integrated | Carbon + AuNP | 5 L | – | RBD protein | Aptamer | 1 × 10–25 × 10 M (5.08 × 10–1.27 × 10 g/mL) | 1.30 × 10 M (66 pg/mL) | – | [48] |
| Fully Integrated | Au + rGO flakes | 30 L | 15 s | S1 protein Ab RBD protein Ab | S1 protein RBD protein | S1: 1 × 10– 30 × 10 M RBD: 1 × 10–20 × 10 M | S1: 2.8 × 10 M RBD: 16.9 × 10 M | – | [49] |
| Fully Integrated | Au | 15 L | 45 min | SARS-CoV-2 pseudo types VSV particle | S1 protein Ab | 10–10 VSV/mL | 15 ng/mL (500 pM) | – | [50] |
| Fully Integrated | Carbon Ink + AuNP | 10 L | 30 min | S protein Ab | S1 protein | 10 × 10 to 10 × 10 | 3.16 pM (83.7 pg/mL) | – | [9] |
| Fully Integrated | Carbon Ink | 0.3 L | 5 min | S protein | S protein mAb | 1–20 fg/mL | 1.065 fg/mL | – | [59] |
| Fully Integrated | Carbon + Graphene + PEDOT:PSS | 50 L | 30 min | N protein | N protein Ab | 1–10,000 pg/mL | 116 fg/mL | Nasopharyngeal swab | [71] |
| Fully Integrated | Carbon Ink | 4 L | 2 min | S protein | ACE2 | 10 fg/mL–100 ng/mL | 2.18 fg/mL | Saliva, Oropharyngeal and Nasopharyngeal swabs | [70] |
| Fully Integrated (Dropsens) | Au | 50 L | 15 min | RBD protein S protein Lysed COVID-19 particles | Targeting peptide | 102–103 copies/mL | 0.01 copies/mL | Nasopharyngeal swabs | [61] |
| Fully Integrated (Dropsens) | Au | 10 L | 45 min | S protein | ACE2 receptor CD147 receptor | ACE2: 700–7000 ng/mL CD147: 500 ng–5000 ng/mL | ACE2: 299.30 ng/mL CD147: 38.99 ng/mL | Oropharyngeal and Nasopharyngeal swabs | [62] |
| Fully Integrated (Dropsens) | Au | 50 L | 2 min | SARS-CoV-2 | Molecularly-imprinted polymer | 3.0–7.0 log10 PFU/mL | 4.9 log10 pfu/mL | Saliva | [53] |
| Fully Integrated (Gamry) | Carbon + CNT + Tungsten Trioxide | 5 L in 2.95 mL PBS | 3 min | Whole Virus - Human-obtained sample, grown in cell line | Virus-imprinted monomer (3-aminophenol) | Up to 320 pg/mL tested | 57 pg/mL | Nasopharyngeal swabs | [54] |
| Fully integrated (Paper, wax printed) | Carbon Graphene ink | 10 L | 5 min | RBD Protein | S1 IgG Ab | 0.25 fg/mL–1 ng/mL | 0.25 fg/mL | Nasopharyngeal swabs | [52] |
| Fully Integrated (Paper) | Carbon + Zinc-Oxide Nanowires | 3 L | 15 min | S1 protein Ab | N protein | Tested: 10 × 10–1 × 10 g/mL | 0.4 pg/mL | Serum | [56] |
| Interdigitated | Au + Carboxylmethylchitosan | Immersion | 10 min | S protein Real samples | anti-S protein Ab | Protein: × 10– × 10 g/mL Real Sample: 7 × 10–7 × 10 PFU/mL | 0.179 fg/mL | Isolated real virus | [66] |
| Interdigitated | PEDOT:PSS | Aerosol | 5 min | S protein | Antibody | – | 7 pfu/mL, 350 pfu/mL (air) | Aerosolized porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus | [69] |
| Interdigitated | Au + diamond nanopowder | 20 L | 5 min | N protein | N protein aptamer | 1 × 10–1 × 10 M | 0.389 fM | – | [67] |
| Single Electrode | Tin-doped indium oxide + polypyrrole + AuNP | 2 L | 15 min | SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Gene | Amino-modified primer | 800–4000 copies/L | 258.01 copies/L | Nasopharyngeal | [51] |
| Working Only | Carbon (Pyrolyzed Graphitic Paper) | 6 L | 30 min | COVID-19 Ab | S protein | – | – | – | [58] |
| Working Only | Carbon + AuNP | 10 L | 40 min | N protein | N protein murine Ab | 0.1–100 ng/mL | 6 pg/mL | Saliva | [64] |
| Working Only | Glassy Carbon + rGO | 10 L | – | RBD protein | S1 protein Ab | 0.16–40 g/mL | 150 ng/mL | Saliva | [65] |
| Working Only | Graphene powder in ethyl cellulose (custom ink) | 15 L | 30 min | RBD protein S1 protein | S protein (Rabbit PAb) | 1–1000 ng/mL | 22.91 ± 4.72 pg/mL (RBD) 110.38 ± 9.00 pg/mL (S1) | – | [60] |
| Working Only | Thin-Film Au Electrode | – | 15 min | S1 protein | Aptamer | Not tested | Positive/negative only (80 ng/mL), n = 8 | Nasopharyngeal and Oropharyngeal swabs | [55] |
| Working Only | Steel Mesh + PEDOT-AuNP | Immersion | 30 min | SARS-CoV-2 Ab | Truncated | 20 × 10–2.5 × 10 dilutions | – | Serum | [57] |
| Well-plate | Au | 50 L | None | SARS-CoV-2 antibody | RBD protein | 0.1, 1.0, 10 mg/mL standards tested | – | – | [68] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ong, V.; Soleimani, A.; Amirghasemi, F.; Khazaee Nejad, S.; Abdelmonem, M.; Razaviyayn, M.; Hosseinzadeh, P.; Comai, L.; Mousavi, M.P.S. Impedimetric Sensing: An Emerging Tool for Combating the COVID-19 Pandemic. Biosensors 2023, 13, 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020204
Ong V, Soleimani A, Amirghasemi F, Khazaee Nejad S, Abdelmonem M, Razaviyayn M, Hosseinzadeh P, Comai L, Mousavi MPS. Impedimetric Sensing: An Emerging Tool for Combating the COVID-19 Pandemic. Biosensors. 2023; 13(2):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020204
Chicago/Turabian StyleOng, Victor, Ali Soleimani, Farbod Amirghasemi, Sina Khazaee Nejad, Mona Abdelmonem, Meisam Razaviyayn, Parisa Hosseinzadeh, Lucio Comai, and Maral P. S. Mousavi. 2023. "Impedimetric Sensing: An Emerging Tool for Combating the COVID-19 Pandemic" Biosensors 13, no. 2: 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020204
APA StyleOng, V., Soleimani, A., Amirghasemi, F., Khazaee Nejad, S., Abdelmonem, M., Razaviyayn, M., Hosseinzadeh, P., Comai, L., & Mousavi, M. P. S. (2023). Impedimetric Sensing: An Emerging Tool for Combating the COVID-19 Pandemic. Biosensors, 13(2), 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020204






