Real-Time Ellipsometric Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor Using Polarization Camera May Provide the Ultimate Detection Limit
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
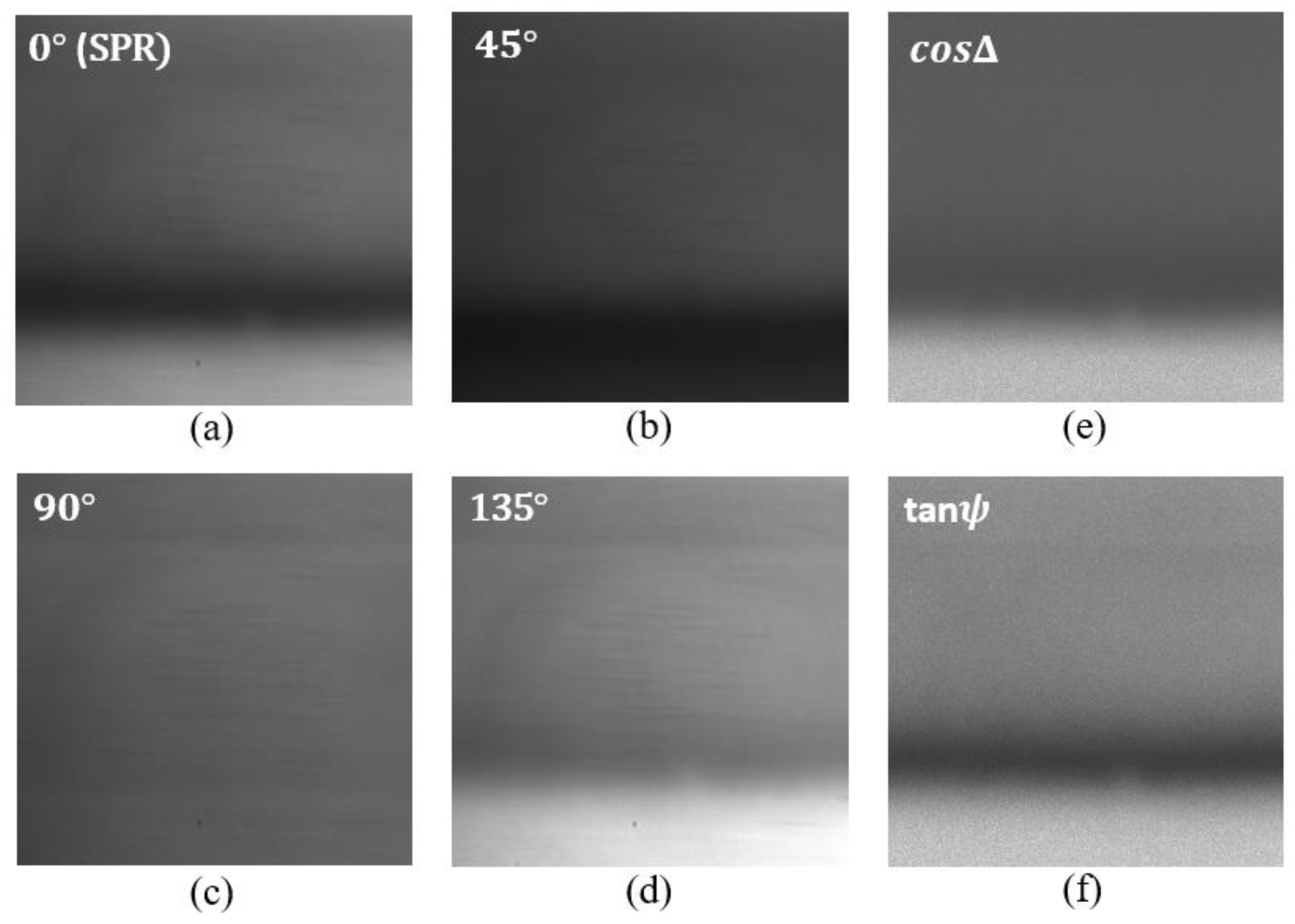
2.1. Phase Extraction Algorithm
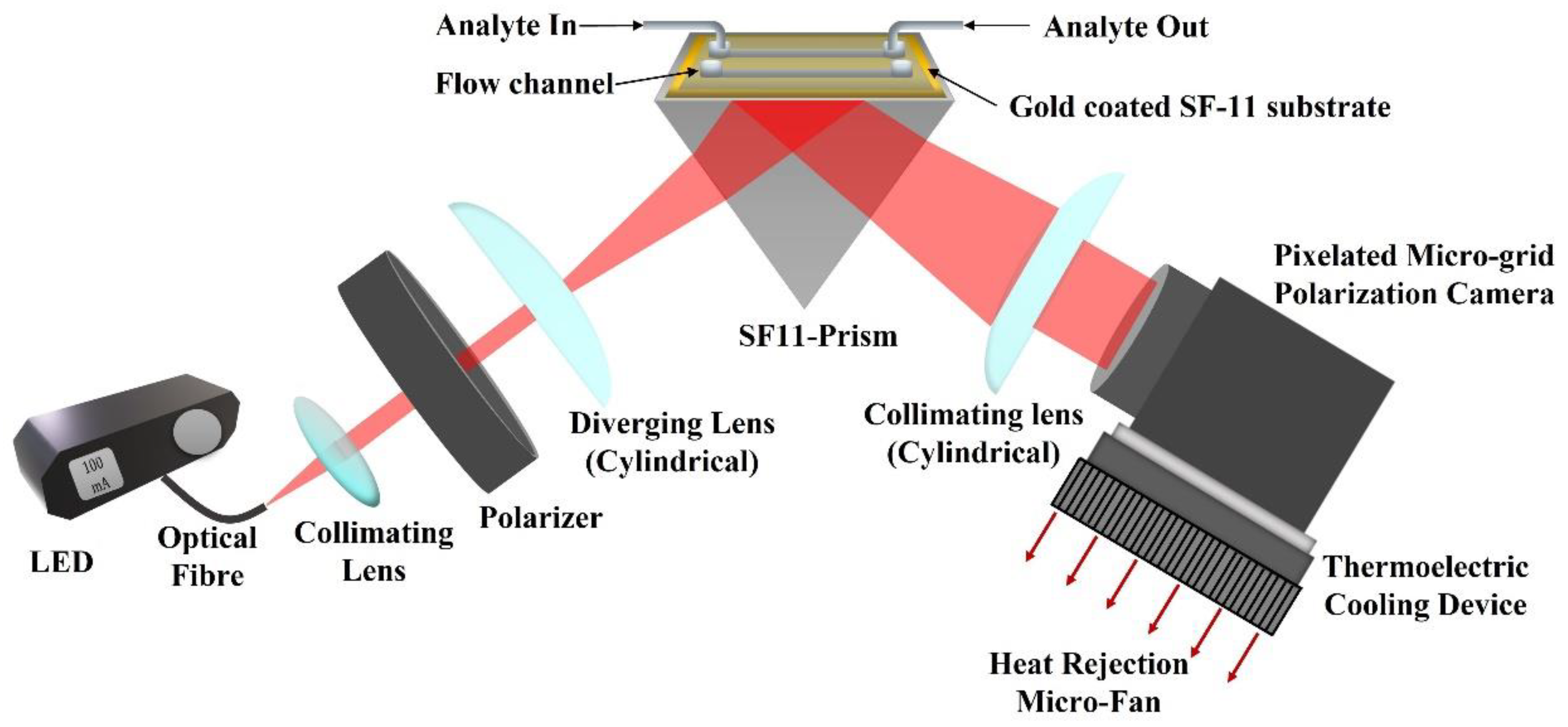
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. BSA Binding Assay-Immunosensing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Refractive Index Measurements and Calibration
3.2. Advantage of Real-Time Ellipsometric SPR Measurement with Fluctuating Light Source Environment
3.3. Dynamical Measurements
3.4. BSA-Binding Assay and Kinetics
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shrivastav, A.M.; Cvelbar, U.; Abdulhalim, I. A comprehensive review on plasmonic-based biosensors used in viral diagnostics. Nat. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 70. [Google Scholar]
- Balbinot, S.; Srivastav, A.M.; Vidic, J.; Abdulhalim, I.; Manzano, M. Plasmonic Sensors for Food Control. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 128–140. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chang, S.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.-H. Surface Plasmonic Sensors: Sensing Mechanism and Recent Applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, N.H.O.; Da Silva, J.P. High Sensitivity Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor Based on a Ge-Doped Defect and D-Shaped Microstructured Optical Fiber. Sensors 2022, 22, 3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastav, A.M.; Satish, L.; Kushmaro, A.; Shvalya, V.; Cvelbar, U.; Abdulhalim, I. Engineering the penetration depth of nearly guided wave surface plasmon resonance towards application in bacterial cells monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 345, 130338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, A.; Hejji, L.; Kim, K.H.; Kukkar, D.; Souhail, B.; Bhardwaj, N.; Brown, R.J.C.; Zhang, W. Advances in surface plasmon resonance-based biosensor technologies for cancer biomarker detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 197, 113767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, T.A.; Kajisa, T.; Ono, M.; Miyasaka, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Saito, A.; Otsuka, K.; Sakane, A.; Sasaki, T.; Yasutomo, K.; et al. Ultrasensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein using large gold nanoparticle-enhanced surface plasmon resonance. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abutoama, M.; Bajaj, A.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Abdulhalim, I. Resonant modes of reflecting gratings engineered for multimodal sensing. APL Photonics 2020, 5, 076108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, L.; He, Y.; Xu, Z.; Ji, Y.; Ma, H. One-dimensional angular surface plasmon resonance imaging based thermometer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 254–261. [Google Scholar]
- Priya, S.; Laha, R.; Datham, V.R. Wavelength-dependent angular shift and figure of merit of silver-based surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 315, 112289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.R.; Akter, S.; Rifat, A.A.; Rana, S.; Ali, S. A Highly Sensitive Gold-Coated Photonic Crystal Fiber Biosensor Based on Surface Plasmon Resonance. Photonics 2017, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Song, W.; Zhang, C.; Fang, H.; Min, C.; Yuan, X. A Phase-Shifted Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor for Simultaneous photoacoustic Volumetric Imaging and Spectroscopic Analysis. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 1840–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, H.; Corn, R.M.; Matthews, B. MicroRNA detection on microsensor arrays by SPR imaging measurements with enzymatic signal enhancement. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-F.; Wang, W.-H.; Hong, Y.-W.; Yuan, R.-Y.; Chen, K.-H.; Huang, Y.-W.; Lu, P.-L.; Chen, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-M.A.; Su, L.-C.; et al. Simple strategy for rapid and sensitive detection of avian influenza A H7N9 virus based on intensity-modulated SPR biosensor and new generated antibody. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh-Asl, S.; Keshtkar, A.; Dolatabadi, J.E.N.; de la Guardia, M. Nanomaterials and phase sensitive based signal enhancement in surface plasmon resonance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 110, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Miyan, R.; Qu, J.; Ho, H.P.; Zhou, K.; Gao, B.Z.; Shao, Y. Phase interrogation SPR sensing based on white light polarized interference for wide dynamic detection range. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 3442–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalabney, A.; Abdulhalim, I. Sensitivity-enhancement methods for surface plasmon sensors. Laser Photon. Rev. 2011, 5, 571–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabowo, B.A.; Purwidyantri, A.; Liu, K.C. Surface Plasmon Resonance Optical Sensor: A Review on Light Source Technology. Biosensors 2018, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ren, Z.H.; Zhao, W.M.; Wang, L.; Yan, X.; Zhu, A.S.; Qiu, F.M.; Zhang, K.K. Research advances on surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 564–591. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, S.; Wang, P.; Yu, X. Phase-Sensitive Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensors: Recent Progress and Future Prospects. Sensors 2017, 17, 2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyan, R.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, Y.; Qu, J.; Ho, H.P.; Zhou, K.; Gao, B.Z.; Chen, J.; Shao, Y. Phase interrogation surface plasmon resonance hyperspectral imaging sensor for multi-channel high-throughput detection. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 31418–31425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, J.; Mandal, S.; Pradhan, M. Polarization-Multiplexed Incoherent Broadband Surface Plasmon Resonance: A New Analytical Strategy for Plasmonic Sensing. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 6689–6694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.Y.; Ho, H.P.; Law, W.C.; Lin, C.; Kong, S.K. Highly sensitive differential phase-sensitive surface plasmon resonance biosensor based on the Mach-Zehnder configuration. Opt. Lett. 2004, 29, 2378–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Ho, H.P.; Wong, C.; Kong, S.K.; Lin, C. Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor Incorporated in a Michelson Interferometer With Enhanced Sensitivity. IEEE Sens. J. 2007, 7, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaňok, R.; Ciprian, D.; Hlubina, P. Surface Plasmon Resonance-Based Sensing Utilizing Spatial Phase Modulation in an Imaging Interferometer. Sensors 2020, 20, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Ho, H.; Wu, S.; Kong, S. Detecting phase shifts in surface plasmon resonance: A review. Adv. Opt. Technol. 2012, 2012, 471957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.-J.; Huang, H.J.; Hsiao, C.-N.; Lin, Y.-W.; Liao, B.-H.; Chou Chau, Y.-F.; Chiang, H.-P. Reusable TiN substrate for surface plasmon resonance heterodyne phase interrogation sensor. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordini, A.; Avino, S.; Malara, P.; Zullo, R.; Natale, P.D.; Mrkova, K.; Homola, J.; Garliardi, G. Surface -plasmon optical -heterodyne clock biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.P.; Law, W.C.; Wu, S.Y.; Liu, X.H.; Wong, S.P.; Lin, C.; Kong, S.K. Phase-sensitive surface plasmon resonance biosensor using the photoelastic modulation technique. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 114, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabashin, A.V.; Patskovsky, S.; Grigorenko, A.N. Phase and amplitude sensitivities in surface plasmon resonance bio and chemical sensing. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 21191–21204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Ho, H.P.; Wu, S.Y.; Kong, S.K.; Wong, W.W.; Shum, P. Phase sensitive SPR sensor for wide dynamic range detection. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 4092–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watad, I.; Abdulhalim, I. Phase-shifted polarimetric surface plasmon resonance sensor using a liquid crystal retarder and a diverging beam. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 1607–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watad, I.; Abdulhalim, I. Spectropolarimetric Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor and the Selection of the Best Polarimetric Function. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2017, 23, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.K. A simple and inexpensive surface plasmon resonance setup for phase detection using rotating analyser ellipsometric method. Laser Phys. 2020, 30, 026202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naraoka, R.; Kajikaw, K. Phase detection of surface plasmon resonance using rotating analyzer method. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 107, 952–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlubina, P.; Duliakova, M.; Kadulova, M.; Ciprian, D. Spectral interferometry-based surface plasmon resonance sensor. Opt. Commun. 2015, 354, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.P.; Loo, F.C.; Wu, S.Y.; Kong, S.K.; Wu, C.M.L.; Ho, H.P. Common-path spectral interferometry with temporal carrier for highly sensitive surface plasmon resonance sensing. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 20268–20273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhalim, I. Optical Sensor Based on Multilayered Plasmonic Structure Comprising a Nanoporos Metallic Layer. PCT/IL2014/050522; WO2015/019341 A1. U.S. Patent # US10048200B2, 8 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulhalim, I. Resonant Periodic Structures and Methods of Using Them as Filters and Sensors. U.S. Patents US10801956 B2, 13 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Watad, I.; Abuleil, M.J.; Abdulhalim, I. Spectro-Ellipsometric Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor Using a Liquid Crystal Achromatic Waveplate. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2020, 32, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safrani, A.; Abdulhalim, I. Real-time phase shift interference microscopy. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 5220–5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizen, A.; Ney, M.; Safrani, A.; Abdulhalim, I. A compact real-time high-speed high-resolution vibrometer, surface profiler and dynamic focus tracker using three wavelengths parallel phase-shift interferometry. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2018, 107, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ney, M.; Safrani, A.; Abdulhalim, I. Three wavelengths parallel phase-shift interferometry for real-time focus tracking and vibration measurement. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazarov, A.; Ney, M.; Abdulhalim, I. Parallel spectroscopic ellipsometry for ultra-fast thin film characterization. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 9288–9309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.C.; Chen, K.R.; Kuo, C.C.; Lin, Y.X.; Su, L.C. A Simple Phase-Sensitive Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor Based on Simultaneous Polarization Measurement Strategy. Sensors 2021, 21, 7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzam, R.M.A.; Bashara, N.M. Elliposmetry and Polarized Light; Paperback, Ed.; North Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 66–148. [Google Scholar]
- RefractiveIndex.INFO. Available online: https://refractiveindex.info/?shelf=glass&book=SF11&page=SCHOTT (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Sony Semiconductor Solutions Group. Available online: https://www.sony-semicon.com/en/products/is/industry/polarization.html (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Lucid Vision Labs. Available online: https://thinklucid.com/tech-briefs/polarization-explained-sony-polarized-sensor/ (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Bajaj, A.; Trimpert, J.; Abdulhalim, I.; Altintas, Z. Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles for SARS-CoV-2 Virus Detection Using Surface Plasmon Resonance. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, B.; Lipson, S.G. Comparison between sensitivities of phase and intensity detection in surface plasmon resonance. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 5641–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umpleby, R.J.; Baxter, S.C.; Chen, Y.; Shah, R.N.; Shimizu, K.D. Characterization of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers with the Langmuir—Freundlich Isotherm. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 4584–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, N.F.; Fan, S.Y.; Yang, C.D.; Huang, T.Y. Carboxyl-Functionalized Graphene Oxide Composites as SPR Biosensors with Enhanced Sensitivity for Immunoaffinity Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Fitting Parameter | Langmuir | Freundlich | Langmuir–Freundlich |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nt | |||
| R2 | |||
| KD |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vashistha, N.; Abuleil, M.J.; Shrivastav, A.M.; Bajaj, A.; Abdulhalim, I. Real-Time Ellipsometric Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor Using Polarization Camera May Provide the Ultimate Detection Limit. Biosensors 2023, 13, 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020173
Vashistha N, Abuleil MJ, Shrivastav AM, Bajaj A, Abdulhalim I. Real-Time Ellipsometric Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor Using Polarization Camera May Provide the Ultimate Detection Limit. Biosensors. 2023; 13(2):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020173
Chicago/Turabian StyleVashistha, Nipun, Marwan J. Abuleil, Anand M. Shrivastav, Aabha Bajaj, and Ibrahim Abdulhalim. 2023. "Real-Time Ellipsometric Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor Using Polarization Camera May Provide the Ultimate Detection Limit" Biosensors 13, no. 2: 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020173
APA StyleVashistha, N., Abuleil, M. J., Shrivastav, A. M., Bajaj, A., & Abdulhalim, I. (2023). Real-Time Ellipsometric Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor Using Polarization Camera May Provide the Ultimate Detection Limit. Biosensors, 13(2), 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020173








