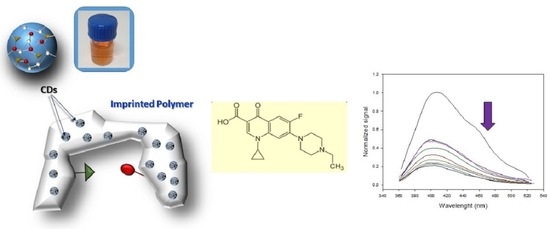
Development of a Screening Method for Fluoroquinolones in Meat Samples Using Molecularly Imprinted Carbon Dots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Synthesis of Carbon Dots (CDs)
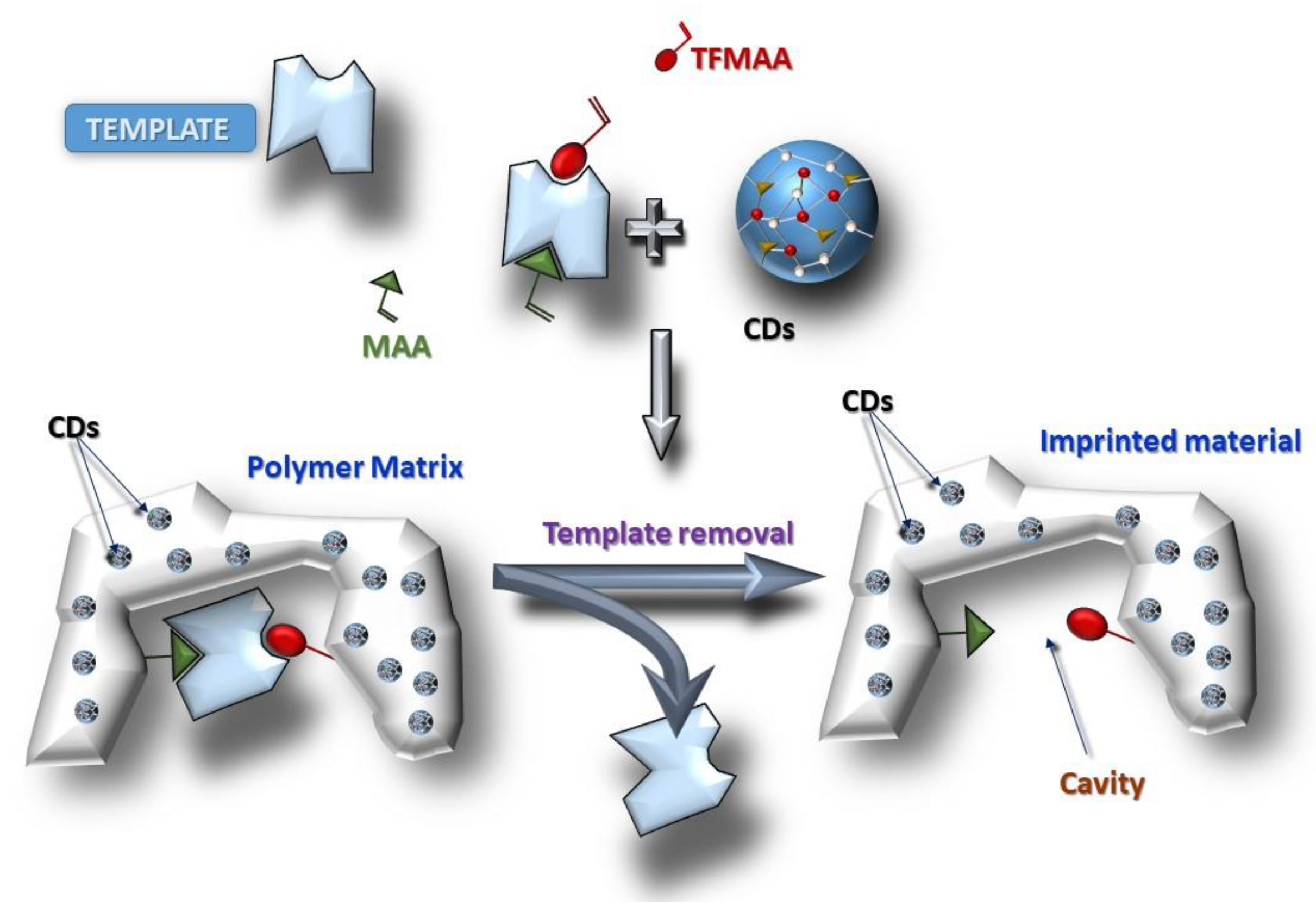
2.4. Synthesis of the Molecularly Imprinted Polymers—Quantum Dots Composites
2.5. Spectrofluorimetric Measurements
2.6. Preparation of Fortified Meat Samples
3. Results and Discussion
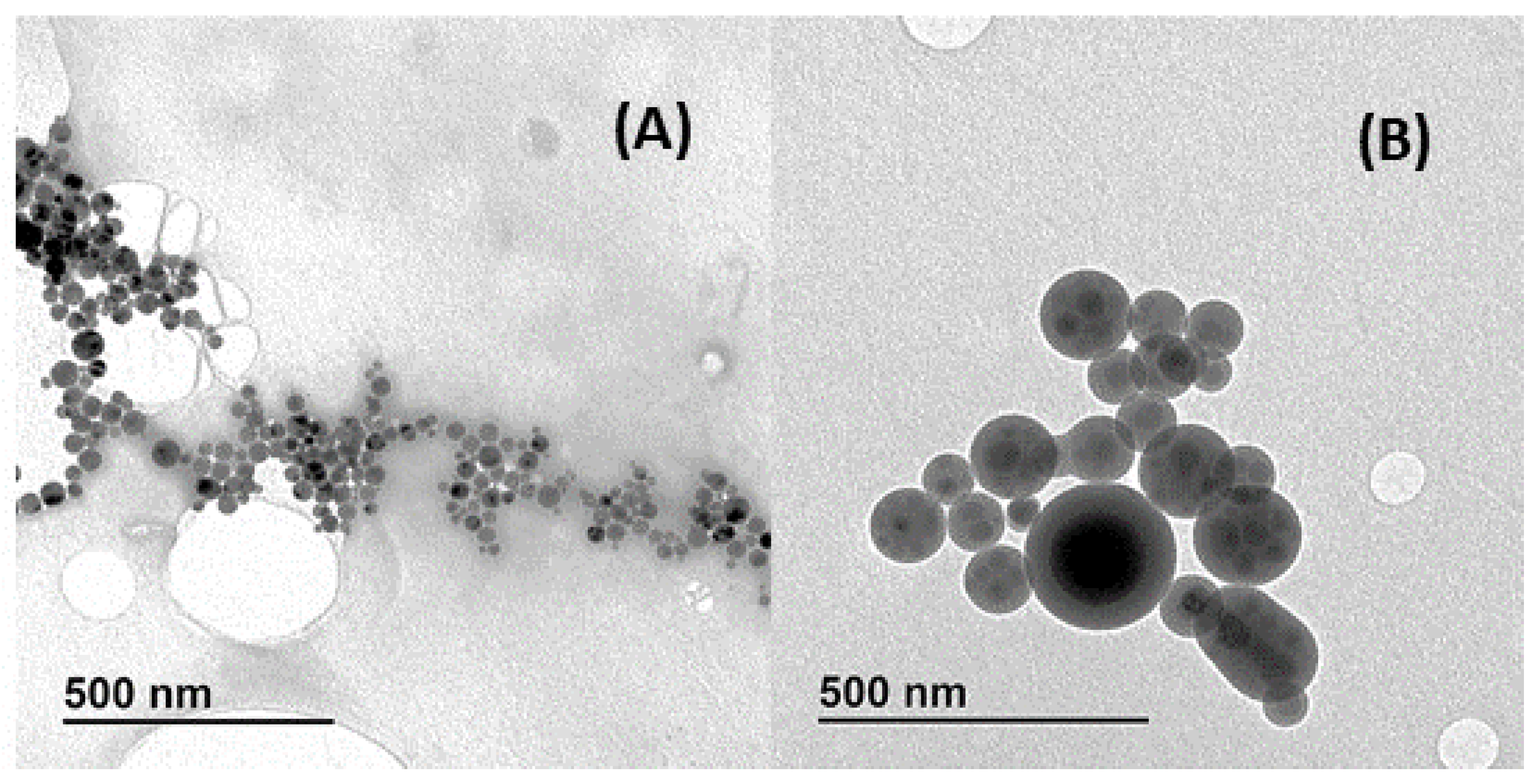
3.1. Synthesis of the CDs and CDs@MIPs
3.2. Characterization of the CDs and CDs@MIPs
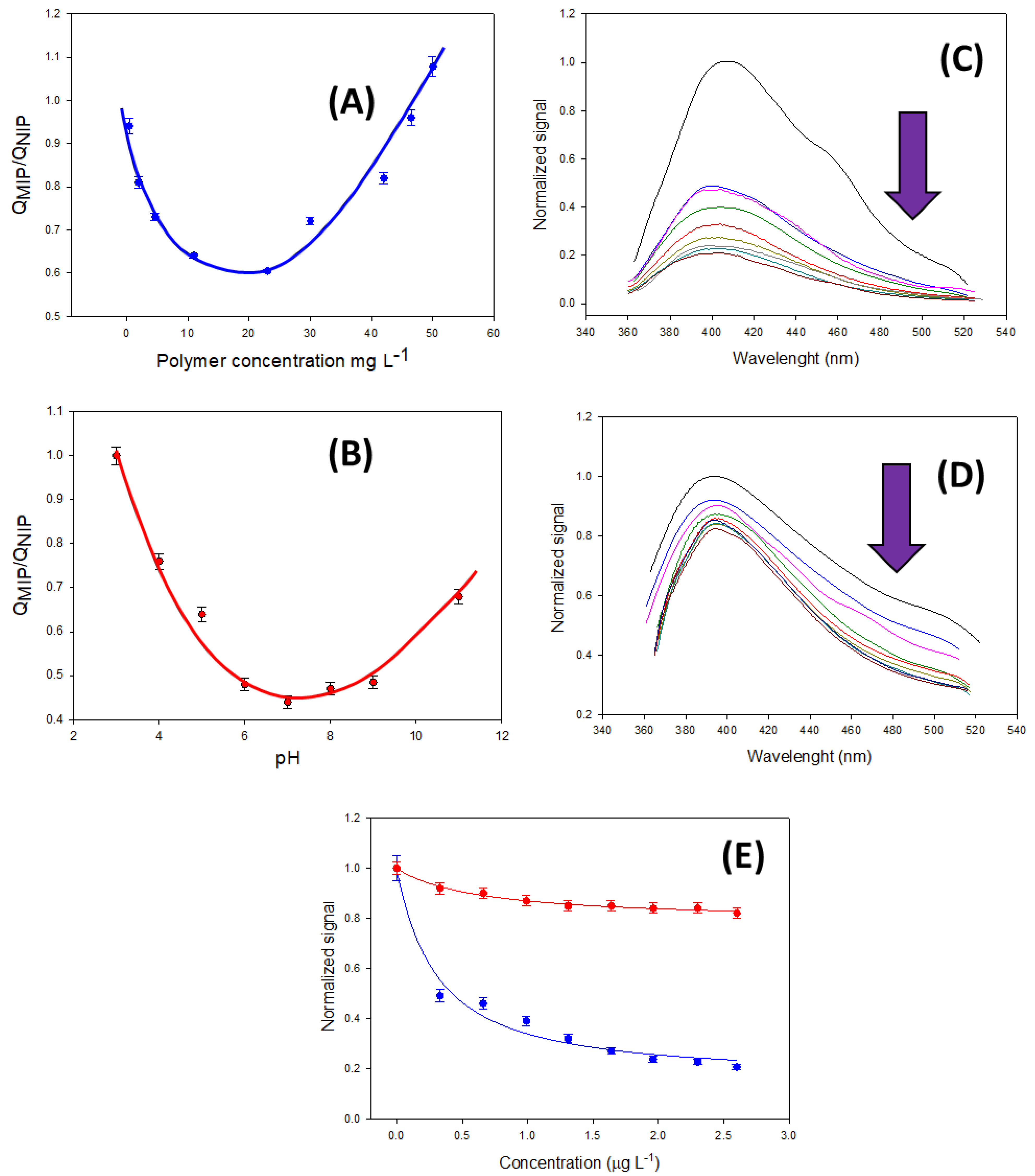
3.3. Optimization of the Assay Conditions
3.4. Assay Analytical Characterization
3.5. Application to Meat Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinez, M.; McDermott, P.; Walker, R. Pharmacology of the fluoroquinolones: A perspective for the use in domestic animals. Vet. J. 2006, 172, 10–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, A.; Andersen, J.S.; Kaewmak, T.; Somsiri, T.; Dalsgaard, A. Impact of integrated fish farming on antimicrobial resistance in a pond environment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 6036–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sáenz, Y.; Zarazaga, M.; Lantero, M.; Gastanares, J.; Baquero, F.; Torres, C. Antibiotic resistance in campylobacter strains isolated from animals, foods, and humans in Spain in 1997–1998. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, M.B.; Zamora, E.; Diaz, P.; Tollefson, L.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J.; Headrick, M.L. Risk factors for fecal quinolone-resistant Escherichia coli in mexican children. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 1999–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendrel, D.; Chalumeau, M.; Moulin, F.; Raymond, J. Fluoroquinolones in paediatrics: A risk for the patient or for the community? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2003, 3, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products. Veterinary Medicine and Inspections. MRL Assessments in the Context of Council Regulation 2377/90, EMEA/CVMP/765/99-Rev 10, 12 July 2002. Available online: http://www.emea.eu.int (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Mayes, A.G.; Mosbach, K. Molecularly imprinted polymers: Useful materials for analytical chemistry? Trends Anal. Chem. 1997, 16, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellergren, B. Noncovalent molecular imprinting: Antibody-like molecular recognition in polymeric network materials. Trends Anal. Chem. 1997, 16, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, T.; Haginaka, J. Separation and sensing based on molecular recognition using molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1999, 728, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, G. Molecular imprinting in cross-linked materials with the aid of molecular templates—A way towards artificial antibodies. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1995, 34, 1812–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito-Peña, E.; Urraca, J.L.; Sellergren, B.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolones from aqueous samples using a water-compatible stochiometrically imprinted polymer. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1208, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Qiao, F. Recognition mechanism of water-compatible molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction and determination of nine quinolones in urine by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1212, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Row, K.H.; Yang, G. Water-compatible molecularly imprinted polymers for selective extraction of ciprofloxacin from human urine. Talanta 2008, 75, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, E.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C.; Marazuela, M.D. Multiresidue determination of fluoroquinolone antimicrobials in baby foods by liquid chromatography. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caro, E.; Marcé, R.M.; Cormack, P.A.G.; Sherrington, D.C.; Borrull, F. Novel enrofloxacin imprinted polymer applied to the solid-phase extraction of fluorinated quinolones from urine and tissue samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 562, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Choo, J.; Chen, L. Molecular imprinting: Green perspectives and strategies. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, M.; Chen, L. Technical challenges of molecular-imprinting-based optical sensors for environmental pollutants. Langmuir 2022, 38, 5963–5967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotta, M.A. Quantum Dots and Their Applications: What Lies Ahead? ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 4920–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, S.; Macairan, J.-R.; Yousefi, N.; Tufenkji, N.; Naccache, R. Green synthesis of carbon dots and their applications. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 25354–25363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuphintharakun, N.; Nurerk, P.; Chullasat, K.; Kanatharana, P.; Davis, F.; Sooksawat, D.; Bunkoed, O. A nanocomposite optosensor containing carboxylic functionalized multiwall carbon nanotubes and quantum dots incorporated into a molecularly imprinted polymer for highly selective and sensitive detection of ciprofloxacin. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 201, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, Y.H.; Cui, P.P.; Feng, X.T.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.Z.; Liu, X.G. Water-soluble, nitrogen-doped fluorescent carbon dots for highly sensitive and selective detection of Hg2+ in aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 40393–40401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urraca, J.L.; Castellari, M.; Barrios, C.A.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Multiresidue analysis of fluoroquinolone antimicrobials in chicken meat by molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1343, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellergren, B.; Shea, K.J. Influence of polymer morphology on the ability of imprinted network polymers to resolve enantiomers. J. Chromatogr. A 1993, 635, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhusban, A.A.; Tarawneh, O.A.; Dawabsheh, S.O.; Alhusban, A.A.; Abumhareb, F.W. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for rapid and selective simultaneous determination of fluoroquinolones level in human aqueous humor. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 97, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, N.; Zhao, M.; Liang, S.; Cao, J.; Wang, C.; Xu, Q.; Li, J. High-throughput and high-efficient micro-solid phase extraction based on sulfonated-polyaniline/polyacrylonitrile nanofiber mats for determination of fluoroquinolones in animal-origin foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 6892–6901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galarini, R.; Fioroni, L.; Angelucci, F.; Tovo, G.R.; Cristofani, E. Simultaneous determination of eleven quinolones in animal feed by liquid chromatography with fluorescence and ultraviolet absorbance detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 8158–8164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Zhang, W.; Yang, L.; Gong, J.; Li, L.; Jin, T.; Li, C. Determination of 11 quinolones in bovine milk using immunoaffinity stir bar sorptive microextraction and liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 1003, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aufartová, J.; Brabcová, I.; Torres-Padrón, M.E.; Solich, P.; Sosa-Ferrera, Z.; Santana-Rodríguez, J.J. Determination of fluoroquinolones in fishes using microwaveassisted extraction combined with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography and fluorescence detection. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 56, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.-Z.; Wu, H.-L.; Fang, H.; Wang, T.; Sun, X.-D.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Ding, Y.-J.; Yu, R.-Q. Rapid and simultaneous determination of three fluoroquinolones in animal-derived foods using excitation-emission matrix fluorescence coupled with second-order calibration method. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 224, 117458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kośka, I.; Kubalczyk, P.; Cichomski, M.; Kisielewska, A. The Use of extraction on C18-silica-modified magnetic nanoparticles for the determination of ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin in meat tissues. Molecules 2023, 28, 6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathai, T.; Pal, T.; Prakash, N.; Mukherji, S. Portable biosensor for the detection of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin antibiotic residues in food, body fluids, environmental and wastewater samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 237, 115478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, X.; Yu, J.; Ye, H.; Zhao, L. A novel carbon dots synthesized based on easily accessible biological matrix for the detection of enrofloxacin residues. Microchem. J. 2023, 190, 108690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, M.; Ara, B.; Ali, F.; Ahmad, I.; Ullah, H. Mn-dopped ZnS quantum dots as sensitive sensor for determination of ciprofloxacin in pharmaceutical and biological samples. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2021, 66, 5130–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Q.; Dong, W.; Hao, A. Fluorescent carbon dots based sensing system for detection of enrofloxacin in water solutions. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 219, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Jiao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Qiao, J.; Mozneb, M.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C.; Li, C.-Z. Bright yellow fluorescent carbon dots as a multifunctional sensing platform for the label-free detection of fluoroquinolones and histidine. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 42915–42924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, Y. Determination of norfloxacin or ciprofloxacin by carbon dots fluorescence enhancement using magnetic nanoparticles as adsorbent. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korah, B.K.; Chacko, A.R.; Mathew, S.; John, B.K.; Abraham, T.; Mathew, B. Biomass-derived carbon dots as a sensitive and selective dual detection platform for fluoroquinolones and tetracyclines. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 4935–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Ding, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, T.; Ding, H.; Chen, Y.; Ding, L. Microwave- assisted synthesis of highly luminescent N- and S-co-doped carbon dots as a ratiometric fluorescent probe for levofloxacin. Michrochim. Acta 2018, 185, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Sun, M.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Li, J. A ratiometric fluorescence platform based on carbon dots for visual and rapid detection of copper(II) and fluoroquinolones. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Zong, B.; Fang, X.; Liu, M.; Li, Z.; Mao, S.; Ostrikov, K. Discriminative and quantitative color-coding analysis of fluoroquinolones with dual-emitting lanthanide metal-organic frameworks. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 373, 132701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derayea, S.M.; Hassan, Y.F.; Hammad, M.A.; Alahmadi, Y.M.; Omar, M.A.; Samir, E. Feasible spectrofluorimetric approach for the ultrasensitive determination of lomefloxacin based on synergistic effects of micellization and metal complexation. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 292, 122399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdinasab, M.; Mitsubayashi, K.; Marty, J.L. Optical and electrochemical sensors and biosensors for the detection of quinolones. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 898–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelin, V.G.; Shogah, Z.A.; Bol’shakov, D.S. Solid-phase-fluorimetric determination of quinolones in medicinal preparations on cellulose paper and in a thin silica layer using a smartphone. J. Anal. Chem. 2021, 76, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
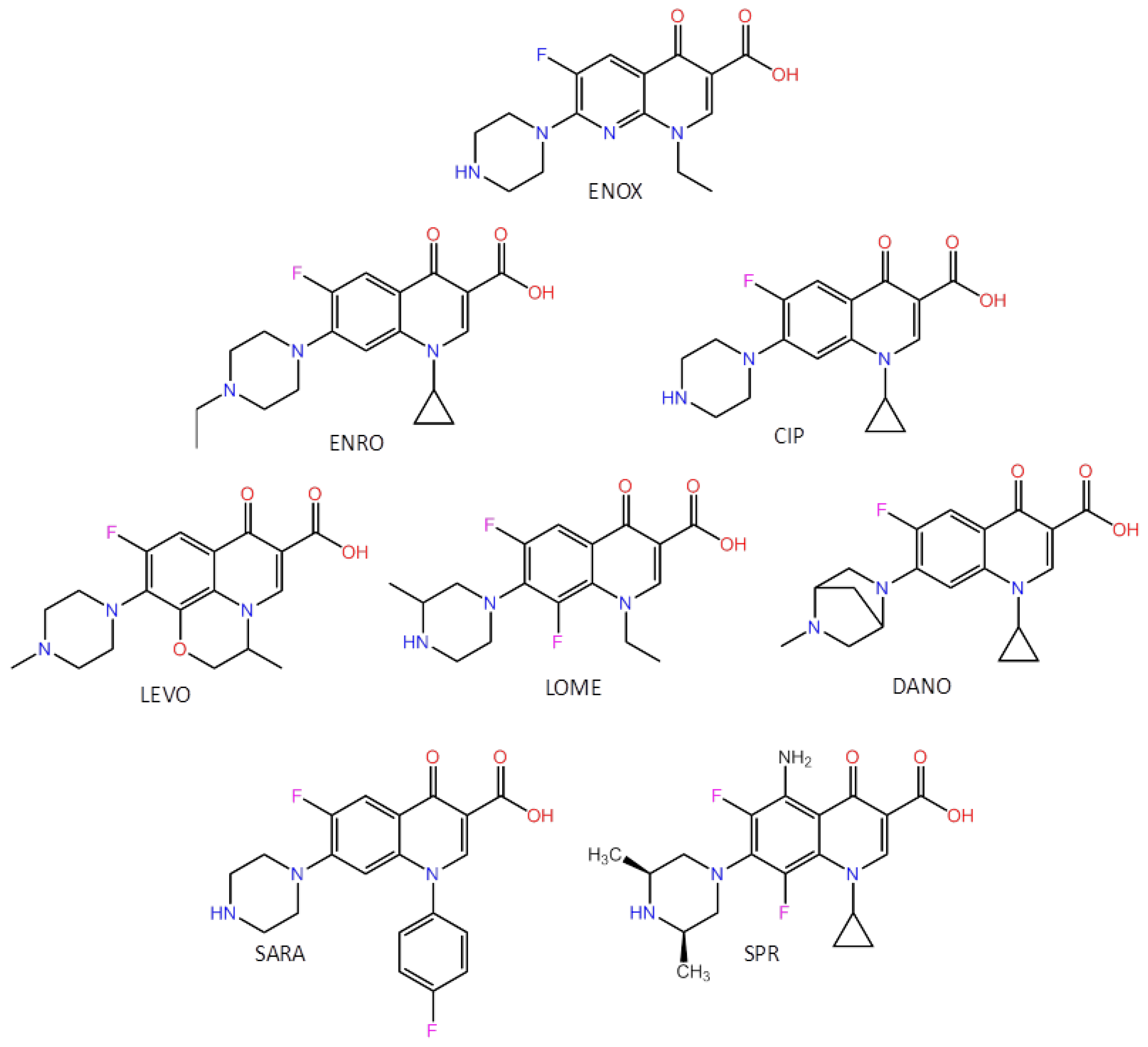
| FQs | LOD (µg mL−1) | LOQ (µg mL−1) | AC50 (µg mL−1) | Reproducibility (%) (n = 3) | Cross-Reactivity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enoxacin | 0.070 | 0.211 | 0.345 | 4.3 | 100.0 |
| Enrofloxacin | 0.067 | 0.221 | 0.331 | 3.7 | 95.9 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 0.062 | 0.186 | 0.371 | 3.8 | 107.5 |
| Levofloxacin | 0.327 | 0.982 | 1.788 | 5.1 | 512.2 |
| Lomefloxacin | 0.072 | 0.220 | 0.420 | 3.6 | 121.7 |
| Danofloxacin | 0.065 | 0.195 | 0.294 | 4.3 | 85.2 |
| Sarafloxacin | 0.188 | 0.564 | 0.814 | 4.2 | 235.9 |
| Sparfloxacin | 0.432 | 1.296 | 0.785 | 4.0 | 227.5 |
| Sample | Spiked Level (ng g−1) (n = 3) | CDs@MIP Assay | HPLC-FLD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beef | 50 | 50 ± 4 | 51 ± 2 |
| 75 | 70 ± 5 | 74 ± 2 | |
| 100 | 83 ± 8 | 90 ± 4 | |
| Pork | 50 | 42 ± 4 | 41 ± 5 |
| 75 | 52 ± 6 | 60 ± 6 | |
| 100 | 75 ± 9 | 80 ± 8 | |
| Chicken | 50 | 48 ± 3 | 50 ± 3 |
| 75 | 75 ± 5 | 76 ± 2 | |
| 100 | 85 ± 7 | 92 ± 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hakiem, A.F.A.; Urriza-Arsuaga, I.; Urraca, J.L. Development of a Screening Method for Fluoroquinolones in Meat Samples Using Molecularly Imprinted Carbon Dots. Biosensors 2023, 13, 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13110972
Hakiem AFA, Urriza-Arsuaga I, Urraca JL. Development of a Screening Method for Fluoroquinolones in Meat Samples Using Molecularly Imprinted Carbon Dots. Biosensors. 2023; 13(11):972. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13110972
Chicago/Turabian StyleHakiem, Ahmed Faried Abdel, Idoia Urriza-Arsuaga, and Javier L. Urraca. 2023. "Development of a Screening Method for Fluoroquinolones in Meat Samples Using Molecularly Imprinted Carbon Dots" Biosensors 13, no. 11: 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13110972
APA StyleHakiem, A. F. A., Urriza-Arsuaga, I., & Urraca, J. L. (2023). Development of a Screening Method for Fluoroquinolones in Meat Samples Using Molecularly Imprinted Carbon Dots. Biosensors, 13(11), 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13110972